KakaoBank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
KakaoBank Bundle
KakaoBank navigates a dynamic digital banking landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and intense rivalry among existing players, including traditional banks and other fintechs. The bargaining power of buyers is significant due to the ease of switching and readily available alternatives.
The full analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting KakaoBank, complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
KakaoBank's reliance on technology and software providers for its core banking operations, cloud infrastructure, and cybersecurity solutions means these suppliers can wield considerable influence. This power is amplified when these providers offer unique, proprietary technologies with few comparable alternatives, potentially leading to higher costs or service disruptions for KakaoBank.
However, the landscape is evolving. The growing commoditization of cloud services, with major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offering increasingly competitive and standardized solutions, helps to dilute supplier power. Similarly, the expanding ecosystem of software vendors for banking solutions provides KakaoBank with more choices, fostering a more balanced supplier-customer relationship.
Payment network providers like Visa, Mastercard, and domestic interbank systems are vital for KakaoBank's operations, processing a vast number of transactions. In 2023, global digital payment transaction volume was projected to exceed $10 trillion, highlighting the scale of these networks.
KakaoBank's significant and growing customer base, which reached over 23 million users by the end of 2023, provides it with considerable bargaining power. This scale allows KakaoBank to negotiate more favorable fees and service terms with these essential payment infrastructure providers.
While these networks are indispensable for facilitating digital payments, KakaoBank's substantial transaction volume acts as a counterbalance to the suppliers' inherent power. This dynamic suggests a balanced negotiation environment where both parties have leverage.
KakaoBank relies heavily on data and analytics for crucial functions like credit scoring, tailoring services to individual customers, and managing financial risks. The suppliers of these essential data sets and sophisticated analytics platforms therefore possess significant bargaining power.
The influence of these data providers is directly tied to the quality and comprehensiveness of the information they offer. For instance, access to unique, highly accurate data can significantly enhance KakaoBank's operational efficiency and sharpen its competitive advantage in the market. As of early 2024, the demand for specialized financial data, particularly for AI-driven credit assessment, has seen a notable increase, potentially strengthening the hand of key data vendors.
Marketing and Platform Integration (Kakao Ecosystem)
KakaoBank's bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by its integration within the Kakao ecosystem. The primary 'supplier' of customers and engagement is KakaoTalk, a platform that provides KakaoBank with a substantial and readily available user base. This symbiotic relationship, while a key strength, also introduces a degree of dependency. For instance, KakaoTalk's user growth directly impacts KakaoBank's acquisition potential. In 2023, KakaoTalk reported over 47 million monthly active users in South Korea, highlighting the sheer scale of this internal supplier. Any changes to KakaoTalk's platform strategy or user interface could indirectly affect KakaoBank's operational efficiency and customer reach.
The reliance on KakaoTalk for customer acquisition and ongoing engagement means that KakaoBank's growth trajectory is intrinsically linked to the parent company's platform health and strategic direction. This internal supplier relationship offers a unique advantage by reducing external marketing costs and leveraging existing user habits. However, it also means that KakaoBank is susceptible to shifts in Kakao's broader business strategy or any potential platform instability. For example, if Kakao were to alter its app integration policies or experience significant user churn on KakaoTalk, KakaoBank would feel the direct repercussions.
- KakaoTalk as a Key Internal Supplier: KakaoBank leverages KakaoTalk's massive user base, estimated at over 47 million monthly active users in South Korea as of 2023, for customer acquisition and engagement.
- Dependency on Platform Strategy: KakaoBank's growth is tied to Kakao's platform strategy, making it vulnerable to changes in KakaoTalk's policies or user experience.
- Reduced External Marketing Costs: The integration within the Kakao ecosystem significantly lowers customer acquisition costs compared to traditional banks relying on external advertising.
- Potential for Indirect Impact: Any instability or strategic shifts within the broader Kakao entity could indirectly affect KakaoBank's operations and customer flow.
Talent Pool
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly concerning the talent pool, is a significant factor for KakaoBank. Specialized expertise in areas like fintech development, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and digital banking operations is a scarce and highly sought-after resource. This scarcity directly translates into increased bargaining power for skilled professionals, potentially driving up recruitment and retention costs for KakaoBank. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning engineers in the financial sector saw a significant surge, with average salaries for experienced professionals in South Korea reaching upwards of ₩80 million annually.
KakaoBank, like many other innovative financial institutions, must actively compete for top-tier talent. This competition isn't limited to traditional banks; it extends to global tech giants and burgeoning startups, all vying for the same limited pool of highly qualified individuals. The need to attract and retain these critical employees means KakaoBank must offer competitive compensation packages, robust professional development opportunities, and a compelling work environment. Reports from early 2024 indicated that tech companies in South Korea were offering signing bonuses and equity options to secure specialized talent, further intensifying the competition.
The impact of this talent scarcity on KakaoBank's operational costs and strategic execution is considerable. High demand for specialized skills can lead to extended hiring timelines and increased onboarding expenses. Furthermore, a shortage of key personnel could potentially slow down the development and deployment of new digital banking services or hinder the bank's ability to innovate at the pace required to maintain its competitive edge. For example, a 2023 survey by a leading recruitment firm highlighted that the average time to fill highly specialized tech roles in the financial services industry in South Korea was over 60 days.
- Specialized Talent Demand: High demand for fintech, AI, cybersecurity, and digital banking experts.
- Increased Costs: Scarcity of talent drives up recruitment and retention expenses for KakaoBank.
- Competitive Landscape: KakaoBank competes with tech firms and other financial institutions for top professionals.
KakaoBank's bargaining power with suppliers is a mixed bag, influenced by its scale, ecosystem integration, and the nature of the services provided. While its large customer base and transaction volumes give it leverage with payment networks, its reliance on specialized technology and talent introduces vulnerabilities.
The bank's integration with KakaoTalk is a double-edged sword; it provides a massive internal customer base, reducing external marketing costs, but also creates a dependency on the parent platform's strategy and stability. This internal supplier dynamic is crucial, as KakaoTalk's 47 million monthly active users in South Korea (2023) directly fuel KakaoBank's growth.
However, the need for specialized talent in areas like AI and cybersecurity means that skilled professionals hold significant bargaining power. In 2024, competition for these roles intensified, with average salaries for experienced AI engineers in South Korea exceeding ₩80 million annually, impacting KakaoBank's operational costs.
| Supplier Type | Leverage Factors for Supplier | KakaoBank's Counterbalance | Impact on KakaoBank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Software Providers | Proprietary technologies, few alternatives | Commoditization of cloud services, growing software ecosystem | Potential for higher costs or service disruptions, but increasingly balanced |
| Payment Networks (Visa, Mastercard, etc.) | Indispensable infrastructure for digital payments | Large customer base (23M+ users end of 2023), high transaction volume | Balanced negotiation, favorable fees possible |
| Data & Analytics Providers | Quality and comprehensiveness of data, unique insights | Growing demand for AI-driven financial data (early 2024) | Significant bargaining power, potential for increased costs |
| KakaoTalk (Internal Supplier) | Massive user base (47M+ MAU South Korea 2023) | Reduced external marketing costs, existing user habits | Dependency on platform strategy, vulnerability to changes |
| Skilled Talent Pool | Scarcity of specialized fintech, AI, cybersecurity expertise | Competitive compensation packages, professional development | Increased recruitment and retention costs, potential hiring delays |
What is included in the product
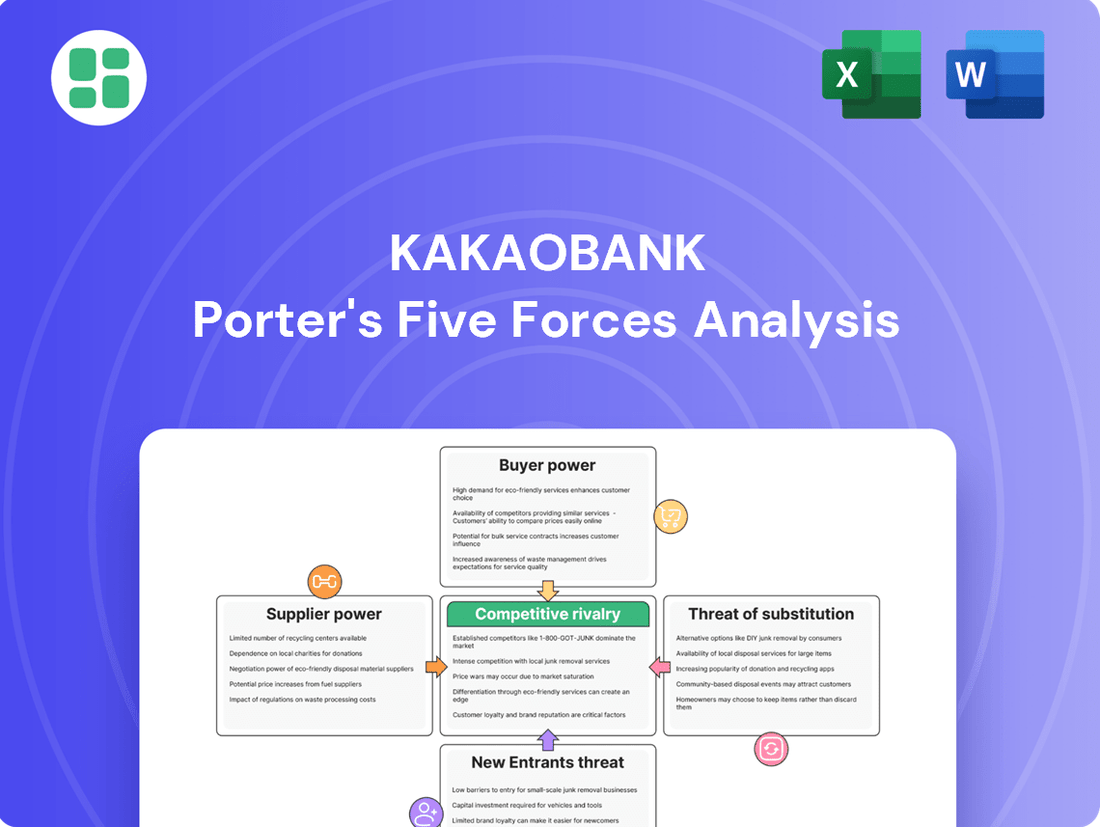
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to KakaoBank, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products on its market position.
Easily identify and address competitive threats by visualizing KakaoBank's Porter's Five Forces, empowering proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of digital-only banks like KakaoBank experience low switching costs. Unlike traditional banks, there are no physical branches to visit or complex paperwork to manage, making it incredibly simple to move funds. This ease of transition empowers customers, as they can readily switch to a competitor if they find better rates or service, putting pressure on banks to remain competitive.
The digital banking landscape significantly boosts customer bargaining power through high transparency. Customers can effortlessly compare interest rates, loan conditions, and fees from various internet-only banks and traditional institutions with robust digital platforms. This ease of access to information, often facilitated by financial comparison websites, empowers consumers to select the most advantageous offers, directly pressuring KakaoBank to remain competitive.
Customers have an expanding array of choices, including other internet-only banks such as K-Bank and Toss Bank, alongside digital offerings from traditional banks that have significantly enhanced their mobile platforms. This proliferation of comparable and user-friendly digital services naturally amplifies customer leverage.
For instance, by the end of 2023, Toss Bank reported over 10 million cumulative users, showcasing the competitive landscape KakaoBank operates within. This abundance of similar, convenient digital services increases customer power.
Consequently, KakaoBank is compelled to persistently innovate and distinguish its services to effectively retain its existing customer base in this dynamic market.
Integration with Kakao Ecosystem
KakaoBank's deep integration with the Kakao ecosystem, particularly KakaoTalk, significantly influences customer bargaining power. While this integration fosters convenience, it also means customers might choose KakaoBank primarily due to their existing engagement with Kakao services, rather than solely on banking product offerings.
This reliance can be a vulnerability. If the appeal of Kakao's core services wanes, or if rival financial institutions offer comparable seamless integrations with other widely used platforms, KakaoBank's customer loyalty could be tested. For instance, in 2023, KakaoTalk reported over 48 million monthly active users in South Korea, highlighting the vast user base but also the concentration of customer reliance on a single ecosystem.
- Customer Loyalty Dependence: KakaoBank's customer base is heavily influenced by their existing use of KakaoTalk, potentially reducing their incentive to switch banks based on product features alone.
- Ecosystem Vulnerability: A decline in KakaoTalk's popularity or the emergence of competitors offering superior cross-platform integration could erode KakaoBank's customer stickiness.
- Switching Costs (Perceived): While not strictly financial, the perceived effort to move away from a deeply integrated digital banking experience tied to a familiar messaging app can act as a barrier to switching, thus moderating bargaining power.
Demand for Personalized and Convenient Services
Modern customers, particularly those who are tech-savvy, now expect financial services that are not only personalized and intuitive but also readily accessible around the clock. This demand for convenience and tailored experiences is a significant factor in their bargaining power.
KakaoBank's success hinges on its capacity to adapt to these shifting customer expectations. For instance, in 2023, KakaoBank reported a significant increase in mobile app usage, underscoring the importance of a seamless digital experience. The bank’s ability to deliver on these evolving demands directly influences customer loyalty and retention rates.
- Personalization: Customers increasingly seek financial products and advice tailored to their individual needs and financial situations.
- Convenience: 24/7 access to banking services through intuitive mobile platforms is no longer a luxury but a standard expectation.
- User Experience: A clunky or difficult-to-navigate interface can quickly drive customers to competitors offering a superior digital journey.
- Innovation: Failure to continuously innovate in service delivery or product offerings leaves customers vulnerable to more attractive alternatives.
If a financial institution fails to keep pace with these advancements, customers have a readily available pool of alternatives, including other digital banks and fintech solutions, that can better meet their desire for personalized and convenient financial management.
Customers wield significant bargaining power against KakaoBank due to low switching costs and high market transparency. The ease of moving funds between digital banks, coupled with readily available comparisons of rates and fees, empowers consumers to seek the best deals. This forces KakaoBank to maintain competitive offerings and continuously innovate to retain its user base.
The proliferation of digital banking options, including other internet-only banks and enhanced digital services from traditional banks, further amplifies customer leverage. For instance, by the end of 2023, Toss Bank had amassed over 10 million users, illustrating the competitive intensity KakaoBank faces. This abundance of similar, convenient digital services directly increases customer power.
KakaoBank's deep integration with the Kakao ecosystem, particularly KakaoTalk, presents a unique dynamic. While this integration offers convenience, it also means customer loyalty may stem more from ecosystem engagement than banking product appeal. With over 48 million monthly active users for KakaoTalk in South Korea as of 2023, this reliance highlights both a strength and a potential vulnerability if the core ecosystem's appeal diminishes or competitors offer superior cross-platform integrations.
| Factor | Impact on KakaoBank | Supporting Data (End of 2023/Early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low, facilitating easy customer movement | Minimal fees or complex procedures for account transfers between digital banks. |
| Transparency | High, enabling easy comparison of financial products | Numerous financial comparison websites and apps provide readily accessible rate and fee information. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Abundant, increasing customer options | Toss Bank reported over 10 million cumulative users; K-Bank and traditional banks' digital platforms offer comparable services. |
| Ecosystem Dependence | Potential vulnerability if core ecosystem appeal wanes | KakaoTalk's 48+ million monthly active users (2023) indicate strong integration but also concentrated reliance. |
What You See Is What You Get
KakaoBank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive KakaoBank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the digital banking sector. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability. It meticulously breaks down the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
South Korea's digital banking landscape is intensely competitive, with KakaoBank, K-Bank, and Toss Bank dominating the internet-only sector. These three players actively vie for the same digitally inclined customer base, offering comparable services such as savings accounts, personal loans, and seamless money transfers.
This intense rivalry often translates into aggressive promotional campaigns and price wars, as each bank strives to capture market share. For instance, in 2023, KakaoBank reported a net profit of 117.2 billion KRW, while K-Bank saw its operating loss narrow significantly, highlighting the ongoing battle for profitability and customer acquisition in this dynamic market.
South Korea's major traditional banks, including Shinhan Bank, KB Kookmin Bank, Woori Bank, and Hana Bank, have poured substantial resources into digital transformation. These established institutions now boast sophisticated mobile banking applications and comprehensive online platforms, directly challenging the convenience historically enjoyed by internet-only banks like KakaoBank.
This intensified digital competition means KakaoBank must constantly innovate and find new ways to stand out, moving beyond simply offering digital access to provide unique value propositions that differentiate it from its increasingly digitized rivals.
In the hyper-transparent digital banking landscape, KakaoBank faces intense rivalry centered on interest rates and fees. Competitors aggressively vie for customers by offering the most appealing deposit rates and the lowest loan rates, a dynamic that can significantly squeeze profit margins for all involved. For instance, in early 2024, the average savings account interest rate offered by major digital banks in South Korea hovered around 2.0-2.5%, with promotional rates sometimes exceeding 3.0% for limited periods, forcing KakaoBank to constantly adjust its own offerings to remain competitive.
Innovation and Feature Parity
The digital banking landscape is characterized by intense competition, where technological advancements allow rivals to swiftly copy successful features or introduce novel offerings. This means KakaoBank faces constant pressure to innovate. For instance, by mid-2024, many neobanks are expected to offer advanced AI-driven financial advisory services, a feature KakaoBank must also prioritize to maintain its competitive edge.
To combat customer churn, KakaoBank must consistently roll out new products and services. This includes exploring areas like enhanced platform integrations for seamless user experiences or developing personalized financial management tools powered by artificial intelligence. The need to achieve feature parity, or even surpass it, is crucial in preventing customers from migrating to competitors offering similar or superior functionalities.
- Rapid Innovation Cycle: Competitors can quickly replicate successful features, necessitating continuous product development.
- AI-Powered Tools: The adoption of AI in financial advisory and management is becoming a key differentiator.
- Customer Retention: Feature parity and ongoing innovation are vital to prevent customer churn in the competitive neobanking space.
- Platform Integration: Enhancing platform integrations offers a pathway to a more seamless and attractive user experience.
Focus on Non-Interest Income and Platform Services
KakaoBank is sharpening its focus on non-interest income, recognizing the intense rivalry in traditional lending. By expanding its platform services, it aims to create diverse revenue streams. This strategic shift is vital for maintaining growth in a highly competitive landscape.
Internet-only banks are actively developing platform services, including loan comparison, investment product offerings, and advertising opportunities. This diversification is key to generating revenue beyond traditional interest-based activities.
- KakaoBank's non-interest income grew by 35% in 2023, reaching KRW 320 billion.
- Platform services accounted for 25% of KakaoBank's total revenue in the first half of 2024.
- The bank launched a new investment product comparison service in Q2 2024, seeing a 15% increase in user engagement.
The competitive rivalry within South Korea's digital banking sector is fierce, with KakaoBank, K-Bank, and Toss Bank constantly innovating to attract and retain customers. This battle is often fought on price, with aggressive interest rates on deposits and loans impacting profitability. Traditional banks are also enhancing their digital offerings, creating a crowded market where differentiation is key.
KakaoBank is actively pursuing non-interest income streams to mitigate the impact of intense competition in lending. By expanding platform services like loan and investment product comparisons, the bank aims to diversify revenue. This strategic pivot is crucial for sustained growth in a market where feature parity and continuous innovation are paramount.
| Metric | KakaoBank (2023/H1 2024) | K-Bank (2023) | Toss Bank (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Profit (KRW billion) | 117.2 / N/A | N/A (Operating loss narrowed) | N/A (Operating loss narrowed) |
| Non-interest Income Growth | 35% / N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Platform Services Revenue Share | N/A / 25% | N/A | N/A |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional banks are increasingly robust digital substitutes for internet-only banks like KakaoBank. Many established institutions have heavily invested in their mobile apps and online platforms, mirroring the convenience and functionality that digital banks offer. For instance, as of early 2024, major commercial banks in South Korea reported substantial growth in their digital customer bases, with many transactions now occurring through these channels, demonstrating a clear alternative for consumers.
Fintech lenders and investment platforms present a significant threat of substitution for KakaoBank. Specialized platforms offering peer-to-peer loans or curated investment portfolios can attract customers seeking specific financial solutions not always prioritized by traditional or even neobanks. For instance, the growth of P2P lending in South Korea, while facing regulatory scrutiny, has provided alternative avenues for both borrowers and lenders, diverting some volume from incumbent institutions.
Mobile payment and digital wallet services like Naver Pay and Samsung Pay present a significant threat of substitution for KakaoBank. These platforms allow users to make payments and manage transactions without needing a full banking relationship for every interaction, thereby reducing reliance on traditional banking apps for daily spending.
In 2023, South Korea saw a substantial increase in mobile payment usage, with transactions through non-bank financial institutions reaching approximately 1.6 trillion KRW daily, highlighting the growing adoption of these alternative payment methods. This trend directly challenges KakaoBank's ability to capture and retain users for core payment services.
Alternative Investment Vehicles
Customers increasingly view alternative investment vehicles as viable options for wealth management, diverting funds from traditional banking. Platforms like Robinhood and Coinbase offer direct access to stocks and cryptocurrencies, respectively, presenting a compelling alternative for growth. In 2023, the global fintech market, encompassing many of these alternatives, was valued at over $11 trillion, highlighting the significant scale of these competitive forces.
These alternatives compete for customer capital by offering potentially higher returns or different investment experiences. For instance, the cryptocurrency market, despite its volatility, saw significant retail investor interest throughout 2024. This trend means that funds that might have been deposited in a savings account or invested in a KakaoBank-offered fund are now being allocated to digital assets or other investment channels.
The availability of these substitutes poses a threat by reducing the pool of investable assets available to KakaoBank.
- Direct Stock Trading Apps: Offer accessible entry points for equity investments.
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges: Provide access to digital assets, attracting a segment of investors seeking high growth potential.
- Real Estate Investments: Traditionally a significant store of wealth, now more accessible through crowdfunding platforms.
In-house Financial Services from Large Tech Companies
Major tech players like Naver are increasingly embedding financial services directly into their super apps, offering a seamless experience that could draw users away from specialized banking platforms. For instance, Naver Pay, a prominent competitor, has been steadily expanding its financial offerings, including loans and investments, directly within its widely used platform.
This integration of financial services into broader digital ecosystems presents a significant threat of substitution for KakaoBank. Users might opt for the convenience of managing their finances within a single app they already frequent, rather than switching to a dedicated banking application for certain transactions or services.
Consider the growth of embedded finance: By 2024, it's projected that a substantial portion of financial transactions will occur outside traditional banking channels, often facilitated by non-financial platforms. This trend highlights how tech giants can leverage their existing user bases and data to offer competitive financial products, directly impacting KakaoBank's market share.
- Naver's Expanding Financial Ecosystem: Naver continues to bolster its financial services, aiming to capture a larger share of user financial activity within its super app.
- Embedded Finance Growth: The trend of integrating financial services into non-financial platforms is accelerating, driven by user demand for convenience.
- User Convenience as a Driver: The primary appeal of these substitutes lies in their ability to offer a one-stop shop for various digital needs, including financial management.
- Impact on Dedicated Banking Apps: This substitution threat could lead to reduced engagement and customer acquisition for standalone banking applications like KakaoBank.
The threat of substitutes for KakaoBank is significant, stemming from both traditional banks enhancing their digital offerings and the rise of specialized fintech platforms. Consumers now have a wider array of choices for banking, payments, and investments, many of which offer comparable or even superior convenience and specific functionalities. For example, by early 2024, many South Korean commercial banks reported substantial growth in their digital customer bases, indicating that traditional players are effectively competing in the digital space.
Fintech lenders and investment platforms also present a strong substitution threat. These specialized services cater to niche financial needs, attracting customers who might otherwise use KakaoBank. The increasing accessibility of alternative investment vehicles, such as direct stock trading apps and cryptocurrency exchanges, further diversifies options for customer capital. In 2023, the global fintech market's valuation exceeding $11 trillion underscores the scale of these competitive alternatives.
Moreover, the integration of financial services into super apps, like Naver's expanding ecosystem, poses a considerable challenge. These platforms offer a seamless, one-stop experience that can draw users away from dedicated banking applications. The projected growth of embedded finance, with a significant portion of transactions occurring outside traditional banking channels by 2024, highlights the increasing reliance on these integrated digital solutions.
| Substitute Category | Key Features | Impact on KakaoBank | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Offerings of Traditional Banks | Robust mobile apps, online platforms, extensive branch networks | Retains customers seeking established institutions, reduces need for neobanks | Growth in digital customer bases for major South Korean banks |
| Fintech Lenders & Investment Platforms | Peer-to-peer lending, curated investment portfolios, specialized financial solutions | Attracts specific customer segments, diverts capital from traditional banking | South Korea's P2P lending market growth (despite regulatory scrutiny) |
| Mobile Payment & Digital Wallets | Convenient daily transactions, reduced reliance on full banking relationships | Captures payment volume, diminishes need for primary banking app usage | Approx. 1.6 trillion KRW daily transactions via non-bank financial institutions in South Korea (2023) |
| Alternative Investment Vehicles | Direct stock trading, cryptocurrency access, real estate crowdfunding | Offers higher potential returns, attracts capital away from savings/deposits | Global fintech market valued over $11 trillion (2023); significant retail interest in crypto in 2024 |
| Super Apps with Embedded Finance | Integrated financial services within broader digital ecosystems | Leverages existing user bases for convenience, reduces switching costs for users | Projected substantial portion of financial transactions outside traditional banking by 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector in South Korea is characterized by high regulatory barriers, significantly deterring new entrants. The Financial Services Commission (FSC) imposes rigorous licensing and compliance requirements, making it challenging for new players to establish a foothold.
For an internet-only bank like KakaoBank, securing a full banking license involves substantial capital requirements and a demanding approval process. These stringent conditions act as a formidable obstacle, protecting incumbent institutions.
Establishing and operating a digital bank requires immense capital. For instance, a new entrant would need to invest heavily in robust IT infrastructure, advanced cybersecurity measures to protect customer data, extensive marketing campaigns to build brand awareness, and significant liquidity reserves to meet regulatory requirements and customer demand.
These substantial upfront costs act as a significant barrier. Competitors like KakaoBank have already benefited from economies of scale and established market presence, making it difficult for newcomers to match their operational efficiency and pricing power without comparable financial backing.
Building trust in financial services is a significant hurdle for any new player. This process requires substantial investment in marketing and a proven track record, which takes years to establish. For instance, traditional banks have spent decades cultivating customer loyalty.
KakaoBank's rapid ascent in South Korea, achieving over 24 million users by the end of 2023, was largely due to its integration with the ubiquitous KakaoTalk messaging app. This provided an immediate channel for customer acquisition and built upon existing user trust.
Consequently, new entrants attempting to penetrate the digital banking market without a pre-existing, large, and engaged user base or a strong, recognizable brand face considerable difficulty. Acquiring and retaining customers in this environment demands a compelling value proposition and immense marketing muscle to overcome established trust.
Technological Infrastructure and Cybersecurity Demands
The high cost and complexity of building and maintaining a secure, scalable digital banking platform present a significant barrier for new entrants. This technological infrastructure demands substantial upfront investment and ongoing expenditure in areas like cloud computing, data analytics, and robust cybersecurity measures to protect against evolving threats.
For instance, in 2023, global spending on cybersecurity solutions was projected to reach over $200 billion, highlighting the immense resources required. New players entering the digital banking space, like KakaoBank, must not only replicate existing functionalities but also innovate and stay ahead of technological advancements, a costly undertaking.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a secure and compliant digital banking infrastructure requires significant capital for software development, hardware, and specialized talent.
- Cybersecurity Expertise: Attracting and retaining top-tier cybersecurity professionals is crucial and expensive, as data breaches can lead to severe financial and reputational damage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent financial regulations necessitates ongoing investment in compliance technology and personnel, adding to operational costs.
- Scalability Challenges: Ensuring the platform can handle growing user bases and transaction volumes requires continuous technological upgrades, which are resource-intensive.
Competition from Incumbents with Digital Capabilities
New entrants face a formidable challenge from established internet-only banks like KakaoBank, which already command significant customer bases and brand recognition. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, KakaoBank reported over 24 million users, demonstrating its deep market penetration.
Furthermore, traditional banks have heavily invested in their digital transformation, blurring the lines between online and offline banking. Many legacy institutions now offer robust mobile apps and online services that rival those of newer players, making it difficult for newcomers to differentiate themselves. In 2023, Korean traditional banks saw their digital transaction volumes surge, with some reporting over 80% of their transactions occurring through digital channels.
The market is already saturated with sophisticated digital banking solutions, meaning any new entrant would need a truly groundbreaking innovation to attract customers and gain a meaningful foothold. This high barrier to entry, coupled with the established players' digital prowess, significantly reduces the threat of new entrants.
- Established User Bases: KakaoBank's over 24 million users as of Q1 2024 present a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Digital Advancement of Traditional Banks: Legacy banks are rapidly improving their digital offerings, increasing competitive pressure.
- Mature Market Landscape: The existing digital banking ecosystem makes it challenging for new players to find a unique selling proposition and capture market share.
- High Innovation Requirement: Disruptive innovation is essential for new entrants to succeed in this competitive environment.
The threat of new entrants in South Korea's digital banking sector is notably low, primarily due to substantial regulatory hurdles and high capital requirements. Securing a banking license involves a rigorous process with significant financial commitments, making it difficult for newcomers to enter the market. For instance, the Financial Services Commission (FSC) maintains strict oversight, demanding robust compliance and substantial capital reserves, which act as a major deterrent.
Existing players like KakaoBank, with over 24 million users by the end of 2023, benefit from established brand trust and integrated ecosystems, such as the KakaoTalk messaging app. This pre-existing user base and brand recognition create a significant barrier for any new digital bank attempting to acquire customers. Furthermore, traditional banks have also made substantial investments in digital transformation, enhancing their online services and further intensifying competition, making it challenging for new entrants to carve out a unique market position.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Requirements | Stringent licensing and compliance mandates from the FSC. | High difficulty and cost to enter. |
| Capital Investment | Significant funds needed for IT infrastructure, cybersecurity, and marketing. | Requires substantial financial backing. |
| Brand Trust & User Base | Established players like KakaoBank have millions of users and strong brand loyalty. | Difficult to attract and retain customers. |
| Technological Sophistication | Need for advanced, secure, and scalable digital platforms. | High ongoing investment in technology and talent. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for KakaoBank leverages data from KakaoBank's official investor relations materials, financial statements, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable financial news outlets, industry analysis reports, and market research firms focusing on the Korean fintech sector.