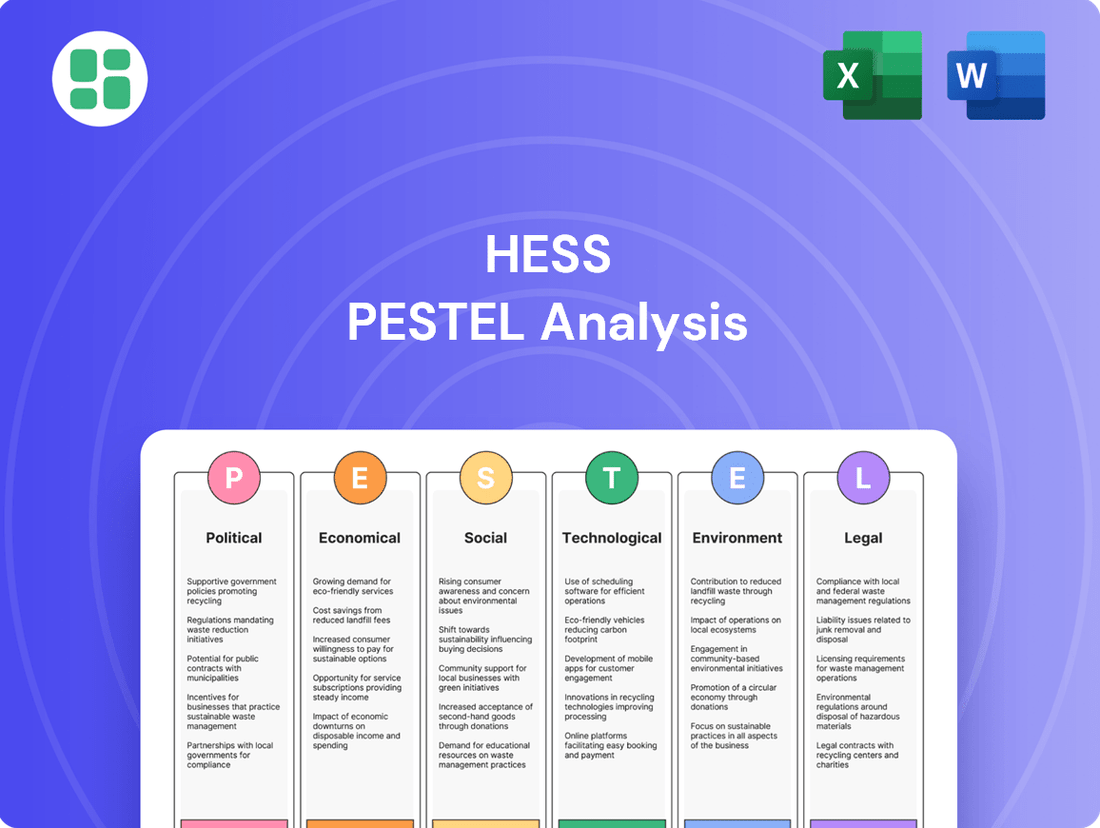
Hess PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hess Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping Hess's strategic landscape. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides actionable insights into these external forces, empowering you to anticipate challenges and capitalize on opportunities. Gain a competitive edge by understanding the full picture—download the complete report now and make informed decisions.
Political factors
Hess Corporation's substantial investments in Guyana's Stabroek Block, a key growth driver, hinge on the region's geopolitical stability. While historical border disputes with Venezuela exist, Hess leadership, including CEO John Hess, has voiced strong confidence in Guyana's political climate, highlighting cross-party support for the ExxonMobil-led joint venture. This confidence is bolstered by the U.S. government's active role in deterring potential escalations, leading to a favorable assessment of political risk for investors.
Changes in government regulations and energy policies significantly shape Hess's operational landscape, especially within the United States and Guyana. A potential shift in U.S. administration could influence climate and environmental policies, potentially opening doors for increased oil and gas development on public lands and offshore, and impacting regulations such as methane fees.
In Guyana, the introduction of legislation like the Oil Pollution Prevention, Preparedness, Response and Responsibility Bill 2025 is a key development. This bill is designed to bolster national preparedness for oil spills and ensure operators are held accountable, reflecting a move towards aligning with global best practices in environmental stewardship.
International climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, and national emissions targets directly shape the operational landscape and future investment strategies for oil and gas firms like Hess. These global commitments are driving a transition, pushing the sector to align with net-zero objectives even as oil and gas remain critical energy sources for the foreseeable future.
Evolving regulations are increasingly incorporating Scope 3 emissions into environmental impact assessments. These indirect emissions, stemming from the use of sold products, represent the largest portion of climate impact for fossil fuel companies, leading to more rigorous scrutiny of new projects and existing operations.
Local Content Requirements
Guyana's Local Content Act is a significant political factor for Hess, mandating increased participation of Guyanese businesses and individuals in the oil and gas sector. This legislation requires Hess and its joint venture partners to prioritize local suppliers and workforce development, aiming to build domestic capacity. For instance, the Act specifies targets for local content across various operational areas, with an initial focus on services like transportation and catering. Failure to comply can impact Hess's operational approvals and community relations.
Hess's commitment to local content in Guyana is demonstrated through various initiatives. By the end of 2023, Hess reported that local content in its operations in Guyana had reached approximately 50% for certain categories of goods and services, a figure expected to grow. The company actively invests in training and development programs for Guyanese citizens, aiming to equip them with the skills needed for the oil and gas industry. These efforts are crucial for maintaining a positive relationship with the Guyanese government and its people, ensuring a continued license to operate.
Key aspects of Guyana's Local Content Act impacting Hess include:
- Mandated procurement targets: The Act sets specific percentages for the procurement of goods and services from Guyanese companies.
- Workforce development: Requirements for training, hiring, and promoting Guyanese nationals in the oil and gas sector.
- Reporting obligations: Hess must regularly report on its local content performance to the relevant Guyanese authorities.
- Capacity building support: Encouragement and potential requirements for companies to support the development of local suppliers.
Regulatory Approval for Mergers and Acquisitions
The proposed acquisition of Hess Corporation by Chevron faces significant political hurdles, primarily revolving around regulatory approvals, particularly anti-trust reviews. These governmental assessments are crucial as they determine the competitive landscape post-merger. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) played a pivotal role, and their decision to lift a prior restriction on July 17, 2025, marked a substantial step forward, signaling a potential green light for the transaction to move towards completion.
Such regulatory processes are not mere formalities; they represent critical political considerations that directly influence a company's future. The outcome can reshape Hess’s corporate structure, dictate its strategic direction, and fundamentally alter its position within the market. For instance, if regulators impose specific conditions, such as divestitures of certain assets, it could significantly impact the combined entity's operational scope and market share.
- Anti-trust Review: The primary political factor is the scrutiny from competition authorities like the FTC to prevent market monopolization.
- FTC Clearance: The FTC's decision on July 17, 2025, to remove its earlier hold was a key political development, indicating a positive regulatory outlook for the merger.
- Impact on Market Position: Regulatory outcomes directly affect Hess's ability to operate and compete after integration with Chevron.
- Strategic Adjustments: Potential regulatory conditions may force strategic adjustments in asset ownership or operational focus for the merged entity.
Political stability in Guyana is paramount for Hess's significant investments in the Stabroek Block, with leadership expressing confidence despite historical border issues with Venezuela. U.S. government engagement actively mitigates escalation risks, creating a favorable political risk profile for Hess.
Shifting U.S. energy policies and environmental regulations, potentially influenced by a change in administration, could impact Hess's domestic operations, including development on public lands and offshore, and influence factors like methane fees.
Guyana's proactive legislation, such as the Oil Pollution Prevention, Preparedness, Response and Responsibility Bill 2025, aims to enhance oil spill readiness and operator accountability, aligning with international environmental standards and affecting Hess's operational requirements.
The Guyana Local Content Act significantly influences Hess by mandating increased participation of local businesses and workforce development, with Hess reporting approximately 50% local content in certain areas by the end of 2023, a figure expected to rise.
What is included in the product
The Hess PESTLE Analysis systematically examines the external macro-environmental factors impacting Hess across Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
This comprehensive evaluation provides actionable insights for strategic decision-making by identifying key opportunities and threats within Hess's operating landscape.
Offers a structured framework to identify and mitigate potential external threats, transforming uncertainty into actionable strategies.
Economic factors
Fluctuations in global crude oil and natural gas prices significantly impact Hess Corporation's revenue and profitability. For instance, Brent crude oil prices averaged around $82.50 per barrel in the first half of 2024, a notable decrease from the $88.00 average seen in the first half of 2023, directly affecting Hess's top-line performance.
While Guyana's oil production is expected to grow, with Hess's share of production projected to increase to approximately 200,000 barrels per day by the end of 2025, the government anticipates lower average oil prices. This forecast suggests a potential slight reduction in overall earnings and government revenue derived from oil sales and royalties, despite increased volumes.
Guyana's economy is on an unprecedented growth trajectory, primarily fueled by its burgeoning oil sector. This boom translates into a highly favorable operating environment for companies like Hess.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) highlighted Guyana's exceptional performance, stating it achieved the world's highest real GDP growth rate, averaging an astonishing 47% annually since 2022. Projections indicate this strong growth is set to continue.
While this rapid expansion presents significant opportunities for Hess, it also necessitates careful management of potential economic challenges, such as inflationary pressures that often accompany such robust growth.
Hess Corporation prioritizes long-term value creation by maintaining strict capital allocation and focusing investments on opportunities with high expected returns. This disciplined approach is evident in their commitment to major projects, such as the substantial $12.7 billion Whiptail development in offshore Guyana, showcasing a significant capital expenditure strategy.
Effective management of this capital is paramount, especially when navigating the inherent volatility of energy markets and the substantial financial commitments required for large-scale offshore developments. The company's ability to allocate resources efficiently directly impacts its profitability and shareholder returns.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation in Guyana is expected to remain manageable, with projections indicating around 3% by the end of 2024 and a slight increase to approximately 4% by the end of 2025. This inflation outlook, coupled with global interest rate movements, directly impacts Hess's operational expenses and the cost of financing its projects.
These economic factors can significantly alter the profitability and feasibility of Hess's ventures. For instance, higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, making it more expensive to fund new developments or expansions.
- Inflationary Pressure: Guyana's inflation projected at 3% (end-2024) to 4% (end-2025) can increase operational costs for Hess.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Global interest rate trends affect Hess's financing expenses and overall project economics.
- Policy Considerations: The IMF's suggestion for proactive monetary or fiscal policies highlights the need for Hess to monitor and adapt to potential economic overheating.
Impact of Chevron Acquisition on Financials
Chevron's acquisition of Hess is poised to reshape Hess's financial landscape. The deal, valued at approximately $53 billion, is anticipated to boost Hess's cash flow per share starting in 2025. This uplift is contingent on realizing projected synergies and the successful deployment of Hess's fourth floating production storage and offloading vessel in Guyana.
Chevron has set an ambitious target of achieving $1 billion in annual run-rate cost synergies by the close of 2025. These cost savings are expected to translate into enhanced returns for shareholders. The strategic integration aims to streamline operations and capitalize on efficiencies across both entities.
- Accretive Cash Flow: Expected to be accretive to cash flow per share in 2025.
- Synergy Target: Aiming for $1 billion in annual run-rate cost synergies by end of 2025.
- Guyana Operations: Start-up of the fourth FPSO vessel in Guyana is a key driver for financial uplift.
- Shareholder Returns: Synergies are intended to drive higher returns for shareholders.
Guyana's remarkable economic growth, averaging an estimated 47% annually since 2022 according to the IMF, creates a highly favorable environment for Hess. However, this rapid expansion also brings inflationary pressures, with Guyana's inflation projected at 3% for end-2024 and 4% for end-2025, potentially increasing Hess's operational costs.
Global oil price volatility remains a key economic factor, with Brent crude averaging around $82.50 per barrel in H1 2024, down from $88.00 in H1 2023, impacting Hess's revenue. Despite this, Hess's share of production in Guyana is expected to rise to about 200,000 barrels per day by end-2025, although the government anticipates lower average oil prices.
Hess's capital allocation strategy, including the $12.7 billion Whiptail development in Guyana, is sensitive to global interest rates, which influence financing costs. The potential acquisition by Chevron, valued at approximately $53 billion, aims for $1 billion in annual run-rate cost synergies by end-2025, which is expected to be accretive to Hess's cash flow per share starting in 2025.
| Economic Factor | Hess Impact | 2024-2025 Data/Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Global Oil Prices | Revenue and profitability | Brent Crude Avg. H1 2024: ~$82.50/bbl (vs. H1 2023: ~$88.00/bbl) |
| Guyana GDP Growth | Operating environment | Avg. ~47% annually since 2022 (IMF) |
| Guyana Inflation | Operational costs | Proj. 3% (end-2024), 4% (end-2025) |
| Interest Rates | Financing costs, project economics | Global trend monitoring required |
| Chevron Acquisition Synergies | Cash flow, shareholder returns | $1bn annual run-rate cost synergies by end-2025; Accretive to cash flow per share from 2025 |
What You See Is What You Get
Hess PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use.
This Hess PESTLE Analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the external factors impacting the company.
You'll gain insights into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental influences relevant to Hess.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises.
Sociological factors
Societal expectations are increasingly pushing energy firms like Hess to focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics. This shift is driven by growing public awareness and concern over climate change and corporate responsibility.
Hess Corporation actively communicates its dedication to sustainability and open reporting, understanding that public opinion significantly influences its reputation and operational license. In 2023, Hess reported a 12% reduction in Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions intensity compared to its 2017 baseline, demonstrating tangible progress.
The company's strategy incorporates sustainable practices to solidify its position as a leader in ESG performance and transparency within the energy sector.
Hess Corporation demonstrates a commitment to community engagement through significant social investments, particularly in North Dakota, a key operational area. These initiatives are designed to build strong, positive relationships with local populations.
In 2023, Hess continued its focus on education and community support, including the provision of scholarships aimed at students pursuing careers in the oil and gas sector or vital community roles. They also donated toy trucks integrated with STEM curriculum, fostering early interest in science and technology, and supported adaptive sports programs to enhance inclusivity.
Hess Corporation's operations are a significant engine for workforce development, notably in its key operational areas. In Guyana, for instance, the company's substantial investments in the offshore Stabroek Block are creating thousands of direct and indirect jobs, fostering a new generation of skilled energy professionals. This focus on local employment is crucial for economic upliftment in the region.
Beyond direct job creation, Hess actively invests in educational and vocational training initiatives. Through scholarships and partnerships with local institutions, the company aims to equip individuals with the skills needed for careers in the energy sector and beyond. This commitment to education directly contributes to enhancing the overall quality of life and economic resilience within the communities where Hess operates, with a notable impact seen in regions like North Dakota where Hess has a strong presence.
Health and Safety Standards
Hess Corporation places significant emphasis on ensuring the health and safety of its workforce and the communities where it operates, viewing it as a core social responsibility. This commitment is regularly detailed in their sustainability reports, outlining their strategies for managing key environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues, with health and safety being a prominent focus.
The evolving regulatory landscape in Guyana, specifically the development of Health and Safety Regulations for the petroleum sector, is expected to further solidify and enhance these standards for Hess's operations there. For instance, in 2024, Guyana's Ministry of Natural Resources continued to advance regulations aimed at improving occupational safety and environmental protection within its burgeoning oil and gas industry, directly impacting companies like Hess.
- Employee Safety Metrics: Hess aims for zero harm, with their 2023 sustainability report highlighting a Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) of 0.25 per 200,000 hours worked.
- Community Engagement: The company actively engages with local stakeholders to address health and safety concerns related to its operations, particularly in its offshore Guyana activities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Hess is committed to adhering to and exceeding all applicable health and safety regulations, including those being developed for the Guyanese petroleum sector.
- Emergency Preparedness: Robust emergency response plans are in place to mitigate risks and ensure the well-being of employees and the public in the event of incidents.
Indigenous Rights and Land Use Concerns
Hess Corporation's operations, particularly in regions with significant indigenous populations like Guyana, face scrutiny regarding land use and resource extraction impacts. Addressing concerns about traditional livelihoods and environmental stewardship is crucial for maintaining a strong social license to operate. For instance, in 2023, Hess's commitment to community engagement in Guyana included investments in local development projects aimed at fostering shared prosperity and mitigating potential negative impacts of oil and gas activities.
Effective stakeholder engagement, involving governments, NGOs, and local communities, is paramount for Hess to navigate these complex sociological dynamics. This collaborative approach helps build trust and ensures that development aligns with community expectations and rights. Hess's 2024 sustainability reports highlight ongoing dialogues with indigenous groups to incorporate their perspectives into operational planning and benefit-sharing mechanisms.
- Indigenous Rights: Hess must continuously engage with indigenous communities to respect their land rights and cultural heritage in operational areas.
- Land Use Conflicts: Potential conflicts over land use for resource extraction versus traditional practices require proactive management and transparent communication.
- Community Impact: Assessing and mitigating the socio-economic and environmental impacts on indigenous livelihoods is a core component of Hess's social responsibility.
- Stakeholder Dialogue: Strengthening relationships through consistent engagement with governments, NGOs, and communities is vital for long-term operational stability.
Societal expectations continue to shape Hess's approach, with a strong emphasis on ESG performance and community well-being. The company's commitment to transparency and sustainability is evident in its ongoing efforts to reduce emissions and invest in local development. For example, Hess's 2023 sustainability report detailed a 12% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions intensity compared to a 2017 baseline, underscoring tangible progress in environmental stewardship.
Hess Corporation's workforce development and community engagement strategies are critical for its social license to operate. In Guyana, the Stabroek Block development is a significant job creator, fostering local expertise. Hess also prioritizes education and vocational training, with scholarships and partnerships aimed at building a skilled workforce. In 2023, the company continued its support for STEM education through initiatives like donating toy trucks integrated with curriculum, aiming to inspire future generations.
| Sociological Factor | Hess's Approach | Key Data/Initiatives (2023-2024) |
| ESG Expectations | Focus on environmental, social, and governance metrics. | 12% reduction in Scope 1 & 2 GHG emissions intensity (vs. 2017 baseline) in 2023. |
| Community Engagement | Investment in local development, education, and social programs. | Scholarships for students, STEM curriculum support, adaptive sports programs. |
| Workforce Development | Job creation and skills training, particularly in operational areas. | Thousands of direct/indirect jobs created in Guyana; vocational training partnerships. |
| Indigenous Rights & Land Use | Respect for cultural heritage and proactive stakeholder dialogue. | Ongoing dialogues with indigenous groups to incorporate perspectives into planning. |
Technological factors
Hess Corporation is actively employing cutting-edge technologies to boost its exploration and production (E&P) operations, especially in demanding regions like the Bakken Shale and offshore Guyana. This focus on technological innovation is crucial for maximizing resource recovery and operational efficiency.
A prime example of Hess's technological prowess is their successful drilling of the first 4-mile lateral wells in North Dakota. This feat significantly extends the reach of wells within the Bakken formation, allowing for greater contact with the reservoir rock. Such advancements translate into improved production rates and potentially lower per-barrel costs, a key driver for profitability in the oil and gas sector.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies are rapidly evolving, becoming a cornerstone for decarbonizing the energy sector. This technological advancement is critical for companies like Hess aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
The global CCUS market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating significant expansion. For instance, the market was valued at approximately $2.7 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around $11.1 billion by 2030, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of over 22%. This surge is fueled by stringent emission reduction targets and increasing government incentives worldwide.
Hess, alongside other major players in the oil and gas industry, is actively investing in and piloting CCUS projects. These initiatives are designed to capture CO2 emissions directly from operational facilities, thereby lowering their overall carbon footprint and aligning with global climate goals.
Digitalization and data analytics are transforming the oil and gas sector, enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Hess, like its peers, is likely leveraging these technologies for better reservoir management and predictive maintenance, aiming to optimize production and reduce downtime.
The industry's investment in digital solutions is substantial, with companies reporting significant cost savings and improved decision-making capabilities. For instance, advancements in AI and machine learning are enabling more accurate production forecasts and proactive identification of potential equipment failures, crucial for a company like Hess operating complex infrastructure.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Techniques
Technological advancements in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) are significantly impacting oil production. CO2 EOR, in particular, is seeing increased adoption as a method to boost output from mature fields. This trend is also a key driver for the growing carbon capture and storage (CCS) market, creating a dual benefit of increased production and emissions management.
These EOR techniques are crucial for maximizing hydrocarbon recovery, thereby extending the operational life of existing oil assets and ensuring more efficient resource utilization. For instance, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) reported that in 2023, CO2 EOR projects accounted for a significant portion of domestic oil production, demonstrating its growing importance.
- CO2 EOR Growth: The demand for CO2 EOR is projected to rise, supporting the expansion of CCS infrastructure.
- Extended Asset Life: EOR methods allow for the extraction of previously uneconomical reserves, prolonging the viability of oil fields.
- Resource Maximization: These technologies improve the overall recovery factor of hydrocarbon reservoirs.
- Market Impact: The success of EOR is directly linked to advancements in drilling, injection, and monitoring technologies.
Floating Production, Storage, and Offloading (FPSO) Vessels
Technological advancements in Floating Production, Storage, and Offloading (FPSO) vessels are paramount for Hess's offshore operations, particularly in Guyana. These sophisticated units are essential for the efficient processing, storage, and transfer of crude oil from subsea wells. The successful deployment of FPSOs directly impacts Hess's ability to bring its significant discoveries online.
Hess's key projects in Guyana, including Yellowtail and Whiptail, are heavily reliant on FPSO technology. These vessels represent a significant capital investment and a critical component of the production infrastructure. The performance and availability of these FPSOs directly influence Hess's production volumes and revenue generation.
A notable example is the ONE GUYANA FPSO, destined for the Yellowtail project. This vessel, with its substantial capacity, signifies a leap in the scale and complexity of offshore production Hess is undertaking. Such technological milestones are crucial for meeting production targets and realizing the full potential of the Stabroek Block.
- FPSO Capacity: The ONE GUYANA FPSO for Yellowtail is designed to produce up to 250,000 barrels of oil per day and store approximately 2 million barrels of crude oil.
- Project Timeline Impact: The timely arrival and commissioning of FPSOs are critical for meeting Hess's projected production ramp-up in Guyana, with Yellowtail expected to commence production in 2025.
- Technological Sophistication: Modern FPSOs incorporate advanced subsea processing, digital monitoring, and environmental control systems, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
Hess is leveraging advanced drilling techniques, such as the 4-mile lateral wells in the Bakken, to enhance resource extraction efficiency. This focus on technological innovation is key to optimizing production and managing costs in its operational areas.
The company is also positioned to benefit from the growth in Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies, a sector projected to grow significantly. This aligns with industry-wide efforts to decarbonize operations and meet environmental targets.
Digitalization and data analytics are increasingly vital for Hess, enabling better reservoir management and predictive maintenance, which are crucial for maximizing uptime and operational performance in complex environments.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) methods, particularly CO2 EOR, are gaining traction, offering a dual benefit of increased production from mature fields and supporting carbon management initiatives. The U.S. EIA noted CO2 EOR's significant contribution to domestic oil production in 2023.
Legal factors
Hess Corporation's significant operations, especially in Guyana's prolific Stabroek Block, are meticulously shaped by Production Sharing Agreements (PSAs) and licensing regimes. These legal frameworks dictate crucial aspects like Hess's 30% stake and include provisions for relinquishing undeveloped areas, ensuring resource optimization and incentivizing timely development.
The Stabroek Block PSA, for example, is a cornerstone of Hess's strategy, outlining the rights and responsibilities for oil and gas exploration and production. Navigating these intricate legal structures, including compliance with local and international regulations, is paramount for maintaining operational continuity and future growth prospects.
Hess Corporation's operations are significantly shaped by stringent environmental regulations and the complex permitting processes required for exploration and production. These rules are designed to minimize the ecological footprint of oil and gas activities.
In Guyana, a key operational area for Hess, the Environmental Protection Agency plays a crucial role. This agency is tasked with reviewing and approving Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) and issuing necessary permits, ensuring that Hess's projects adhere to established environmental standards. For instance, the Stabroek Block development, a major asset for Hess, requires ongoing environmental approvals and monitoring.
Furthermore, evolving legislation is increasingly focused on operator accountability for environmental incidents. New laws are being implemented to hold companies like Hess liable for the costs and remediation efforts associated with oil spills and other environmental damages, adding another layer of risk and compliance to their operations.
Guyana's Local Content Act mandates that oil and gas companies like Hess must prioritize local suppliers and workforce. This legislation, enacted in 2021, aims to ensure a significant portion of the value chain benefits Guyanese citizens and businesses.
For Hess, this translates into specific procurement targets and employment quotas. For instance, the Act requires companies to submit annual local content plans detailing how they will meet these requirements, impacting Hess's operational and strategic planning in Guyana.
The success of this framework is evident in the increasing participation of Guyanese companies in the oil and gas sector. As of early 2024, reports indicate that over 2,000 Guyanese businesses are now registered suppliers to the sector, a testament to the Act's influence on Hess's partnership and supply chain decisions.
Arbitration and Legal Disputes
Hess Corporation has faced significant legal challenges, including arbitration related to its Stabroek Block interests offshore Guyana. A key dispute involved differing interpretations of a right-of-first-refusal clause concerning Chevron's proposed acquisition of Hess. These legal entanglements highlight the critical role of contractual interpretations in major energy asset transactions.
The outcomes of such legal disputes can have a substantial impact on Hess's financial standing and strategic direction. For instance, the ongoing arbitration could affect the valuation and completion of the Chevron deal, which was valued at approximately $53 billion as of early 2024. Successful resolution of these matters is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and facilitating future growth opportunities.
- Stabroek Block Arbitration: Hess is engaged in arbitration concerning a right-of-first-refusal provision related to Chevron's acquisition.
- Chevron Acquisition Impact: The arbitration's outcome could significantly influence the $53 billion Chevron deal, impacting Hess's asset portfolio.
- Contractual Interpretation Risks: Disputes underscore the financial and strategic risks associated with differing interpretations of key contractual clauses in large-scale transactions.
- Future Transactional Certainty: Resolution of legal disputes is vital for ensuring certainty in Hess's future strategic moves and asset valuations.
Taxation and Fiscal Regimes
Hess Corporation's financial performance is significantly influenced by the tax and fiscal policies of the countries where it operates. For instance, in Guyana, where Hess has substantial interests, the upstream oil and gas sector is governed by The Income Tax Act and The Corporation Tax Act. These regulations directly impact profitability and investment viability.
Changes in Guyana's fiscal regime, including modifications to production sharing agreements or tax rates, can alter Hess's net revenue and cash flow. Furthermore, the management and operational framework of the Natural Resource Fund (NRF) in Guyana, established to manage oil revenues, plays a crucial role. The NRF’s policies and how its resources are allocated can affect the overall investment climate and the economic returns for companies like Hess. For example, as of early 2024, discussions around the NRF’s governance and potential adjustments to fiscal terms are ongoing, underscoring the dynamic nature of these legal factors.
- Taxation Impact: Direct application of The Income Tax Act and The Corporation Tax Act in Guyana affects Hess's upstream oil and gas profitability.
- Fiscal Regime Changes: Potential adjustments to production sharing agreements or tax rates in Guyana could alter Hess's net revenue and cash flow projections.
- Natural Resource Fund Management: The governance and operational policies of Guyana's Natural Resource Fund influence the economic returns and investment decisions for Hess.
- 2024/2025 Outlook: Ongoing discussions regarding NRF governance and potential fiscal term adjustments in Guyana present a key area of focus for Hess in the 2024-2025 period.
Hess's operations are significantly influenced by the legal and regulatory frameworks of its operating regions, particularly in Guyana. The country's Local Content Act of 2021 mandates prioritizing local suppliers and workforce, impacting Hess's procurement and employment strategies. As of early 2024, over 2,000 Guyanese businesses are registered suppliers, demonstrating the Act's influence on Hess's supply chain decisions.
The legal landscape also includes critical contractual agreements like Production Sharing Agreements (PSAs), which define Hess's stake and development responsibilities, such as its 30% interest in the Stabroek Block. Navigating these, alongside environmental regulations and permitting processes overseen by bodies like Guyana's Environmental Protection Agency, is vital for operational continuity.
Legal disputes, such as the ongoing arbitration concerning a right-of-first-refusal clause related to Chevron's proposed $53 billion acquisition of Hess, highlight the risks associated with contractual interpretation. The resolution of these matters is crucial for Hess's strategic direction and future asset valuations.
Fiscal policies, including Guyana's Income Tax Act and Corporation Tax Act, directly affect Hess's profitability. The management of its Natural Resource Fund also plays a role, with ongoing discussions in early 2024 about governance and potential fiscal adjustments presenting a key focus for Hess in the 2024-2025 period.
Environmental factors
Hess Corporation is actively addressing climate change, setting ambitious goals for 2025. These include a significant 50% reduction in operated Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas and methane emissions intensities compared to 2017 levels. Furthermore, the company aims to eliminate routine flaring by the close of 2025, a crucial step in reducing environmental impact.
Looking further ahead, Hess has committed to achieving net-zero Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions on an equity basis by 2050. This long-term vision demonstrates a strategic approach to decarbonization, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change.
The potential for oil spills from offshore operations is a significant environmental concern for Guyana. New legislation, the Oil Pollution Prevention, Preparedness, Response and Responsibility Bill 2025, aims to bolster national capabilities and ensure operators bear full responsibility for environmental protection and spill compensation.
Hess Corporation's operations, particularly its significant offshore activities in Guyana, place a strong emphasis on biodiversity and ecosystem protection. These sensitive marine environments require stringent protocols to minimize any potential negative impacts.
As a legal and operational necessity, Hess conducts comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) for its projects. These EIAs are crucial for identifying and evaluating potential risks to marine life and coastal habitats, ensuring that effective mitigation strategies are developed and implemented.
In 2023, Hess continued to invest in environmental stewardship, with a focus on biodiversity. While specific figures for biodiversity protection investments are often integrated into broader environmental expenditure, the company's commitment is underscored by its adherence to international best practices and regulatory requirements in regions like Guyana, where conservation is a key consideration.
Waste Management and Pollution Control
Effective waste management and pollution control are paramount for Hess, particularly concerning its significant operations in the Bakken Shale and offshore Guyana. This involves meticulous handling of drilling waste, produced water, and a concerted effort to minimize air emissions across all facets of its energy production.
Regulatory landscapes are continuously shifting, with an increasing focus on incorporating downstream emissions into environmental impact assessments. This trend necessitates more robust and comprehensive pollution control strategies from companies like Hess to ensure compliance and environmental stewardship.
For instance, in 2023, Hess reported that its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions intensity for its Bakken operations was approximately 18 kg CO2e/boe. The company is investing in technologies and practices to further reduce these emissions, including advanced water treatment and flaring reduction initiatives.
- Bakken Operations: Focus on managing drilling muds, cuttings, and produced water, with investments in recycling and beneficial reuse programs to minimize landfill disposal.
- Offshore Guyana: Emphasis on managing produced water discharge and minimizing flaring, with advanced technologies deployed to capture and reinject associated gas.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adapting to evolving regulations that may extend environmental scrutiny to broader value chains, requiring proactive emissions management.
- Investment in Technology: Allocating capital towards innovative solutions for waste reduction, water treatment, and air quality improvement to meet stringent environmental standards.
Water Usage and Management
Hess Corporation's operations, particularly in water-intensive regions like the Bakken shale, necessitate robust water usage and management strategies. Hydraulic fracturing, a key component of oil and gas extraction, demands substantial volumes of water, placing a premium on efficient resource utilization and responsible stewardship.
Adherence to stringent environmental regulations is paramount for Hess. These regulations govern the sourcing of water, mandating the use of recycled or non-potable sources where feasible, and dictate protocols for the treatment and disposal of produced water. For instance, in 2023, the oil and gas industry in the US utilized an estimated 1.5 million acre-feet of water for fracking, with recycling rates varying significantly by basin. Hess must navigate these requirements to mitigate its environmental footprint, especially in areas facing water scarcity.
Sustainable water management practices are crucial for Hess's long-term operational viability and social license to operate. This includes investing in advanced water treatment technologies to maximize recycling rates and minimize freshwater withdrawal.
- Water Sourcing: Hess prioritizes using recycled produced water and non-potable sources to reduce reliance on freshwater supplies.
- Water Recycling: Investments in advanced treatment technologies aim to increase the percentage of water recycled for reuse in hydraulic fracturing operations.
- Disposal Management: Strict adherence to regulations for the safe and environmentally sound disposal of wastewater is a core operational principle.
- Regulatory Compliance: Hess actively monitors and complies with evolving federal, state, and local regulations pertaining to water usage and environmental protection.
Hess is actively reducing its environmental impact, targeting a 50% decrease in Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas and methane emissions intensities by 2025, compared to 2017. The company also plans to eliminate routine flaring by the end of 2025, a significant step in its decarbonization strategy.
The company's commitment extends to net-zero Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions on an equity basis by 2050, aligning with global climate goals. In 2023, Hess reported its Bakken operations' Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions intensity at approximately 18 kg CO2e/boe, with ongoing investments in technologies to further reduce this figure.
Environmental concerns, particularly regarding potential oil spills in Guyana, are addressed through new legislation like the Oil Pollution Prevention, Preparedness, Response and Responsibility Bill 2025, which aims to enhance national capabilities and ensure operator accountability. Hess also prioritizes biodiversity protection in its operations, especially in sensitive marine environments.
Water management is critical, with Hess focusing on using recycled produced water and non-potable sources to minimize freshwater withdrawal, especially in water-intensive regions like the Bakken. The company adheres to strict regulations for water sourcing, treatment, and disposal, with advanced treatment technologies being implemented to boost recycling rates.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis is built on a robust foundation of publicly available data from government agencies, international organizations like the IMF and World Bank, and leading market research firms. We meticulously gather information on political stability, economic indicators, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and social trends to ensure a comprehensive and accurate assessment.