Fuyo General Lease Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Fuyo General Lease Bundle
Fuyo General Lease operates within an industry shaped by significant buyer power and the constant threat of substitutes, impacting their pricing strategies and market share. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this competitive landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Fuyo General Lease’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fuyo General Lease, a broad leasing entity, depends on a range of capital providers, including banks and bond markets. The ability of these financial suppliers to influence terms, particularly during periods of rising interest rates or restricted credit availability, can significantly affect Fuyo's cost of funding. For instance, in early 2024, global central banks continued to navigate inflationary pressures, leading to elevated borrowing costs across many markets, which would directly impact Fuyo's capital expenses.
Fuyo General Lease procures a vast range of assets, from IT hardware to large-scale industrial machinery and transportation vehicles like aircraft and ships. The bargaining power of these asset manufacturers and vendors is influenced by factors such as the uniqueness of their products, the strength of their brand reputation, and crucially, the ease with which Fuyo can source similar assets from alternative suppliers. For instance, in the specialized aircraft leasing sector, a limited number of manufacturers hold significant sway due to the high barriers to entry and proprietary technology.
Technology and software providers are increasingly vital for Fuyo General Lease, impacting everything from operational efficiency to digital customer experiences. In 2024, the financial services sector saw a significant uptick in spending on cloud computing and AI-driven solutions, reflecting the growing reliance on advanced software. Companies like Microsoft and Oracle, with their deeply integrated enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, hold considerable sway. These providers can dictate terms and pricing, especially when their software is critical for Fuyo's core leasing operations and data analytics.
Human Capital and Specialized Expertise
The availability of skilled professionals in areas like financial analysis and risk management is a significant factor for Fuyo General Lease. When there's a scarcity of these specialized talents, especially in niche leasing sectors such as aircraft or real estate finance, employees gain more leverage. This can translate directly into increased labor costs for the company, impacting its operational expenses.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for experienced financial analysts in Japan remained robust, with reports indicating a shortage of candidates possessing advanced data analytics skills. This tight labor market for specialized financial expertise can empower employees, potentially driving up salary expectations and benefits packages for Fuyo General Lease to attract and retain top talent.
- Shortage of specialized financial talent can increase labor costs.
- Demand for financial analysts with advanced data skills remained high in 2024.
- Niche leasing segments like aircraft finance require highly specialized expertise.
- Employee bargaining power rises with high demand for unique skills.
Information and Data Service Providers
Information and data service providers hold moderate bargaining power over Fuyo General Lease. Access to reliable market data, credit rating services, and industry insights is crucial for Fuyo General Lease to effectively assess risks and identify investment opportunities. For instance, a significant portion of financial institutions, including leasing companies, rely on data from providers like Bloomberg and Refinitiv. In 2024, the global financial data market was valued at approximately $30 billion, indicating the substantial investment in such services.
The power of these suppliers is amplified when their data is unique, comprehensive, or has become an industry standard, making it difficult for Fuyo General Lease to switch providers without incurring significant costs or data gaps.
- Data Uniqueness and Comprehensiveness: Suppliers with proprietary or highly detailed datasets can command higher prices.
- Industry Standards: If a data provider's services are widely adopted as the benchmark, their bargaining power increases.
- Switching Costs: The effort and expense involved in migrating data and retraining staff can deter Fuyo General Lease from changing suppliers.
- Market Concentration: A limited number of high-quality data providers in specific niches can consolidate their influence.
Suppliers of capital, such as banks and bond markets, hold significant bargaining power over Fuyo General Lease, particularly when credit conditions tighten. In early 2024, persistent inflation led to higher global interest rates, directly increasing Fuyo's cost of borrowing. This financial leverage allows capital providers to influence loan terms and pricing, impacting Fuyo's funding expenses.
Asset manufacturers and vendors also possess considerable sway, especially for specialized equipment like aircraft, where few suppliers exist. Fuyo's reliance on these unique products, coupled with high switching costs, strengthens supplier negotiation power. For instance, the limited number of major aircraft manufacturers means they can dictate terms to leasing companies.
Technology and software providers, such as those offering cloud or AI solutions, wield substantial influence due to the critical nature of their services for Fuyo's operations. In 2024, the financial sector's increased investment in these areas, estimated to be in the billions globally, highlights the dependence on key tech vendors. Companies with deeply integrated systems can set pricing and terms, making it difficult for Fuyo to negotiate.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Fuyo General Lease | 2024 Context/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Providers (Banks, Bond Markets) | Interest rate environment, credit availability, Fuyo's creditworthiness | Increased borrowing costs, stricter loan covenants | Global interest rates remained elevated in early 2024 due to inflation concerns. |
| Asset Manufacturers/Vendors | Product uniqueness, brand reputation, availability of alternatives, switching costs | Higher asset acquisition costs, limited negotiation flexibility | High barriers to entry in specialized sectors like aircraft manufacturing limit supplier options. |
| Technology/Software Providers | Criticality of software, integration level, switching costs, vendor market share | Potential for price increases, dependence on vendor updates and support | Financial services spending on cloud and AI solutions saw significant growth in 2024. |
What is included in the product
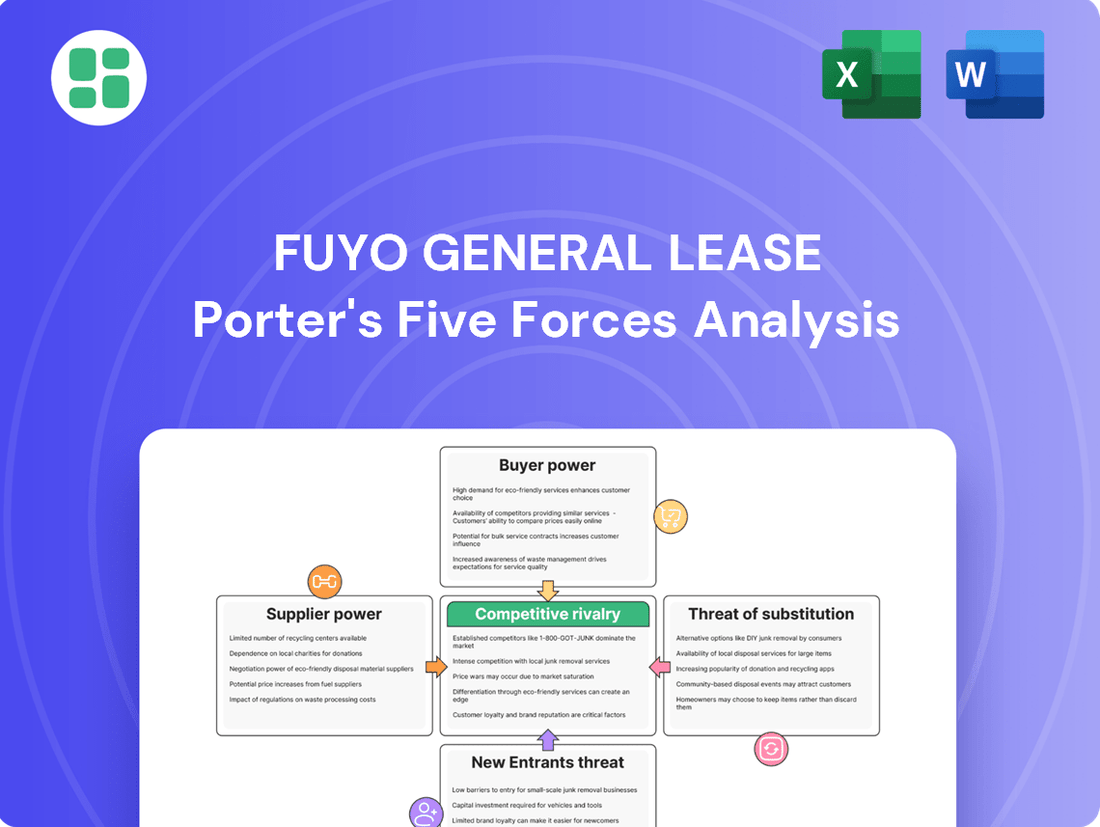
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Fuyo General Lease, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the presence of substitutes within the leasing industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visually mapping Fuyo General Lease's Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Fuyo General Lease's diverse customer base, spanning sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and real estate, inherently limits the bargaining power of any single customer. This broad reach means the company is not overly reliant on any one industry segment.
While individual small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) might possess limited negotiation leverage, Fuyo General Lease's larger corporate clients, particularly those in highly competitive industries, can indeed negotiate more favorable lease terms. For instance, a major manufacturing firm leasing a significant volume of equipment might secure better pricing or more flexible contract durations.
Customers can explore options beyond leasing, such as outright asset purchase or securing traditional bank loans and other debt financing. This availability of alternatives directly impacts Fuyo General Lease's leverage.
The accessibility and attractiveness of these alternative financing methods, especially from competitive banks and financial institutions, significantly bolster customers' ability to negotiate better terms or seek providers offering more favorable conditions, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Customer switching costs in the leasing industry, particularly for Fuyo General Lease, are often quite low. While there's some paperwork involved, the direct financial outlay to change leasing providers for standard equipment or simple contracts is minimal. This ease of transition means customers can readily explore and move to competitors offering more attractive terms or better service.
Price Sensitivity and Transparency
In Japan's mature leasing market, customers, particularly for standard assets, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are highly attuned to the cost of leasing and will actively seek out the best deals. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of small and medium-sized enterprises in Japan consider price the primary factor when selecting a leasing provider.
The growing availability of digital comparison tools has dramatically increased price transparency. This empowers customers by allowing them to easily benchmark offerings from various leasing companies. Consequently, customers are better equipped to negotiate for more competitive rates and favorable terms, directly impacting the bargaining power they hold.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in mature leasing markets like Japan are highly sensitive to pricing, especially for non-specialized assets.
- Transparency Boost: Digital comparison tools enhance price transparency, enabling customers to easily compare leasing options.
- Negotiating Power: Increased transparency allows customers to demand competitive rates and terms from leasing providers.
- Market Impact: This dynamic can lead to pressure on leasing companies to offer more attractive pricing to retain and attract clients.
Customization and Tailored Solutions
Fuyo General Lease's ability to offer highly customized solutions is a key factor in managing customer bargaining power. By developing unique, tailored offerings, the company aims to foster strong customer loyalty and create value propositions that are difficult for competitors to match, thereby reducing the likelihood of customers switching. For instance, in 2024, Fuyo General Lease reported a significant portion of its revenue derived from long-term, customized leasing agreements, indicating a successful strategy in locking in clients.
However, the effectiveness of this strategy hinges on the ease with which competitors can replicate these tailored solutions. If the customization process is easily imitable or if alternative providers can quickly develop comparable offerings, the bargaining power of customers can increase. This is particularly relevant in sectors where technological advancements allow for rapid product development and adaptation, potentially diminishing the stickiness of Fuyo General Lease's customized services.
- Customization as a Barrier: Fuyo General Lease leverages tailored solutions to build strong customer relationships, making it harder for clients to switch.
- Competitive Replication Risk: If competitors can easily copy these customized offerings, customer bargaining power might rise.
- 2024 Impact: The company's 2024 performance data suggests a positive correlation between customized solutions and client retention.
Customers' bargaining power is influenced by their ability to switch providers and the availability of alternatives. In 2024, the leasing market saw increased price sensitivity among Japanese SMEs, with over 60% prioritizing cost. Digital comparison tools have further empowered customers by enhancing price transparency, allowing them to negotiate more effectively for competitive rates and terms.
| Factor | Impact on Fuyo General Lease | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High for standard assets, pressures pricing | >60% of Japanese SMEs prioritize price |
| Availability of Alternatives | Asset purchase, bank loans offer competition | Competitive financing options readily available |
| Switching Costs | Generally low for standard leases | Minimal financial outlay for switching providers |
| Information Transparency | Digital tools increase, aiding negotiation | Growing use of comparison platforms |
What You See Is What You Get
Fuyo General Lease Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Fuyo General Lease Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive instantly upon purchase, ready for immediate use and strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Japanese leasing market is highly competitive, characterized by the presence of numerous large, diversified domestic players. These include the leasing subsidiaries of major Japanese banks, such as Mitsubishi HC Capital, and other established independent leasing firms. This mature market environment fosters intense rivalry as these companies vie for market share, particularly in core leasing services.
The Japanese leasing market, while generally mature, exhibits pockets of significant growth. For instance, the real estate leasing segment saw a steady increase in demand in 2024, driven by urban development projects and a recovery in commercial property values. Similarly, the energy and environment sector is experiencing a surge in leasing activity for renewable energy equipment, reflecting Japan's commitment to decarbonization goals.
This segmentation means that while overall market saturation can intensify rivalry, companies like Fuyo General Lease can still find substantial growth opportunities. For example, in 2023, the global equipment leasing market was valued at approximately $340 billion, with Asia-Pacific showing robust expansion, indicating potential for international growth strategies to offset domestic saturation.
Fuyo General Lease stands out by offering a broad spectrum of financial services, extending well beyond its core leasing operations to encompass credit cards, real estate ventures, and specialized asset finance. This diversification allows the company to create unique value propositions for its clients.
The company’s strategy hinges on differentiating itself through highly specialized solutions and the provision of value-added services, alongside the development of innovative financial products. This approach is crucial for Fuyo General Lease to effectively counter intense competition that often centers on price alone.
Aggressive Investment and Expansion Strategies
Competitors in the leasing sector, including those directly challenging Fuyo General Lease, are increasingly investing in digital transformation and AI-driven solutions to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. For instance, in 2024, many leasing firms reported significant capital allocation towards cloud infrastructure and data analytics platforms. This aggressive push forces Fuyo General Lease to similarly prioritize innovation to avoid falling behind in service quality and cost-effectiveness.
Expansion into burgeoning markets and high-growth sectors, such as renewable energy equipment leasing and electric vehicle financing, is another key competitive tactic. Companies are actively seeking to diversify their portfolios and tap into new revenue streams. Fuyo General Lease must therefore continuously assess and adapt its strategic focus to remain competitive in these evolving landscapes.
- Technological Investment: Competitors are channeling substantial funds into AI, IoT, and blockchain for asset tracking and predictive maintenance.
- Market Expansion: Focus on emerging economies and sectors like sustainable infrastructure and digital services.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships with tech firms and financial institutions to offer integrated solutions.
- Product Innovation: Development of flexible leasing models and value-added services to attract and retain clients.
Regulatory Environment and Consolidation
The regulatory environment in Japan significantly shapes competitive rivalry within the leasing sector. Stricter regulations, such as those introduced in recent years concerning consumer protection and data privacy, can increase operational costs and compliance burdens, potentially leading to industry consolidation as smaller players struggle to adapt. For instance, the Financial Services Agency's ongoing efforts to enhance financial market stability can indirectly influence leasing company strategies and market entry.
New regulations or amendments can also create new competitive avenues or act as barriers to entry. Companies that proactively adapt to evolving compliance requirements, such as those related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting, may gain a competitive advantage. The Japanese government's focus on digital transformation and green initiatives, for example, could spur demand for specialized leasing services, altering the competitive landscape.
- Regulatory Impact: Japanese financial regulations can lead to consolidation by increasing compliance costs for smaller leasing firms.
- Market Structure: New rules might create barriers for new entrants or open up niche markets for specialized leasing services.
- ESG Focus: The push for ESG compliance is influencing leasing product development and competitive positioning.
- Digital Transformation: Government initiatives promoting digitalization are creating new opportunities in IT and digital asset leasing.
Competitive rivalry in the Japanese leasing market is intense, driven by a large number of established players, including bank-affiliated leasing companies and independent firms. This maturity means companies like Fuyo General Lease must differentiate through specialized services and innovation to avoid competing solely on price.
Competitors are heavily investing in digital transformation, with significant capital allocated to AI and data analytics in 2024. This necessitates Fuyo General Lease to keep pace with technological advancements to maintain service quality and cost-effectiveness.
Expansion into high-growth sectors like renewable energy and electric vehicle financing is a key competitive strategy, requiring Fuyo General Lease to continuously adapt its focus to new revenue streams.
| Key Competitor Actions in Japanese Leasing (2024) | Focus Area | Impact on Fuyo General Lease |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Transformation Investment | AI, Cloud, Data Analytics | Necessitates similar investment to maintain competitiveness. |
| Market Expansion | Renewable Energy, EV Financing | Requires strategic adaptation to capture new growth segments. |
| Product Innovation | Flexible Leasing Models, Value-Added Services | Drives need for unique value propositions beyond core leasing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Businesses can bypass leasing altogether by directly purchasing the assets they need. This is particularly feasible for companies with strong cash reserves or those prioritizing long-term asset ownership for strategic advantage. For instance, in 2024, many companies with robust balance sheets explored outright purchases of IT equipment and vehicles to avoid ongoing lease payments and gain full control.
Traditional bank loans and debt financing present a significant threat of substitution for leasing. Companies can opt to borrow directly from financial institutions or issue corporate bonds to fund their capital expenditures, bypassing the need for a lease agreement. For instance, in 2024, corporate bond issuance by non-financial companies globally reached substantial figures, indicating a robust alternative for accessing capital.
The appeal of these debt-based substitutes hinges on several factors. When interest rates are low and credit markets are readily accessible, bank loans and bonds become more attractive options. Furthermore, a company's strong credit rating can unlock more favorable terms for debt financing compared to leasing, making it a compelling alternative for well-established businesses.
Cloud-based services and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) present a significant threat to Fuyo General Lease's IT equipment leasing business. These models allow companies to access IT resources and software without purchasing or leasing physical hardware, thereby bypassing the need for traditional leasing arrangements. This shift directly impacts Fuyo's revenue streams in this segment.
The appeal of cloud and SaaS lies in their ability to reduce upfront capital expenditure and offer greater flexibility, making them attractive alternatives to leasing. For instance, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, demonstrating the substantial shift towards these service-based models.
Rental Services and Short-Term Usage Models
The rise of rental services and pay-per-use models presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional asset ownership, particularly in sectors where flexibility is paramount. For instance, the burgeoning car-sharing market, with companies like Zipcar and Turo, offers consumers an alternative to outright vehicle purchase, impacting the automotive leasing sector. In 2024, the global car-sharing market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion, with projections indicating continued growth, underscoring the increasing appeal of these flexible usage models.
These alternative models cater to businesses and individuals who require temporary access to assets without the burden of long-term ownership, maintenance, or depreciation. Equipment rental services, for example, allow construction firms to access specialized machinery on a project-by-project basis, avoiding the substantial capital outlay associated with purchasing such assets. This trend is amplified by the digital economy, where platforms facilitate easy access to a wide array of rental options.
- Car-sharing services offer a direct substitute for personal vehicle ownership and leasing.
- Equipment rental businesses provide flexible access to machinery, reducing the need for capital investment in owned assets.
- The global car-sharing market's valuation in 2024 reached around $10.5 billion, highlighting the scale of this substitution threat.
- Short-term usage models appeal to businesses seeking operational flexibility and cost-efficiency over asset ownership.
Internal Financing and Self-Funding
Large corporations with robust balance sheets often opt for internal financing and self-funding for their capital expenditures. This capability directly substitutes the need for external leasing or financing services. For instance, in 2024, many technology giants continued to leverage their substantial cash reserves, with Apple reporting over $168 billion in cash and marketable securities by the end of Q1 2024, allowing for significant self-funded projects.
This internal funding reduces the demand for leasing and financing, impacting companies like Fuyo General Lease. Companies that can self-fund avoid the costs and contractual obligations associated with leasing agreements. In 2023, the S&P 500 companies collectively held over $2.5 trillion in cash and equivalents, illustrating the widespread availability of internal capital for investment.
The threat of substitutes from self-funding is particularly potent when interest rates rise, making external financing more expensive. Businesses with ample liquidity can bypass these costs entirely. This trend was evident in early 2024 as companies prioritized efficient capital allocation, with many choosing to deploy existing cash rather than taking on new debt or lease obligations.
- Reduced Reliance: Strong balance sheets allow major corporations to bypass external financing, diminishing the need for leasing services.
- Cost Avoidance: Self-funding eliminates interest expenses and lease fees, offering a more economical route for capital investment.
- Financial Flexibility: Companies with substantial cash reserves gain greater control over project timelines and investment decisions.
- Market Conditions: In environments with higher interest rates, the appeal of self-funding as a substitute for leasing intensifies.
The threat of substitutes for Fuyo General Lease is significant, stemming from direct asset purchase, alternative financing, and evolving service models. Companies can bypass leasing by buying assets outright, especially if they have strong cash reserves. For example, in 2024, many firms with healthy balance sheets opted for direct IT equipment and vehicle purchases to avoid ongoing lease payments.
Traditional debt financing, such as bank loans and corporate bonds, also serves as a potent substitute. When interest rates are favorable, these options become more attractive than leasing. In 2024, global corporate bond issuance by non-financial companies remained robust, indicating a strong alternative for capital access.
Furthermore, the rise of cloud computing and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) directly challenges Fuyo's IT leasing business. These models allow users to access IT resources without leasing hardware, significantly impacting revenue. The global cloud computing market was projected to exceed $1.3 trillion in 2024, showcasing this shift.
Pay-per-use and rental services, like car-sharing, also offer viable alternatives to leasing. The car-sharing market, valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2024, demonstrates the growing appeal of flexible usage models over ownership or leasing.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Purchase | Companies buying assets instead of leasing. | Feasible for firms with strong cash reserves; many explored outright purchases of IT and vehicles. |
| Debt Financing | Bank loans and corporate bonds. | Global corporate bond issuance remained substantial; attractive when interest rates are low. |
| Cloud/SaaS | Accessing IT resources without physical hardware. | Global cloud computing market projected over $1.3 trillion; bypasses IT equipment leasing. |
| Rental/Pay-per-use | Flexible, short-term asset access. | Global car-sharing market valued at ~$10.5 billion, indicating growing preference for usage over ownership. |
Entrants Threaten
The leasing and diversified financial services sector, particularly for major players like Fuyo General Lease, necessitates significant upfront investment. These capital demands cover acquiring a substantial asset portfolio, securing robust funding lines, and establishing extensive operational networks, effectively creating a high barrier to entry.
The financial services sector in Japan, where Fuyo General Lease operates, is characterized by extensive regulatory oversight. Obtaining the necessary licenses and adhering to strict compliance rules, including robust risk management, presents a significant challenge for potential new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) continued to emphasize capital adequacy and consumer protection, making the initial investment and operational setup for new leasing companies particularly demanding.
Established players like Fuyo General Lease benefit from deeply ingrained customer relationships, a strong brand reputation built over years, and a proven track record of reliability in the leasing sector. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating this trust and market acceptance.
For instance, in 2024, Fuyo General Lease likely continued to leverage its extensive network and customer loyalty programs, making it challenging for new entrants to gain immediate traction. Building equivalent brand equity and customer loyalty requires substantial investment and time, often exceeding the initial capital outlay for simply entering the market.
Economies of Scale and Scope
The threat of new entrants for a company like Fuyo General Lease is significantly impacted by economies of scale and scope. Established, large leasing companies benefit from substantial cost advantages. For instance, their sheer volume allows for more favorable terms on funding, efficient asset management, and streamlined operational processes. In 2023, major leasing players often reported operating margins that reflected these efficiencies, with some achieving net profit margins in the 5-10% range, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
New companies entering the leasing market would find it incredibly challenging to compete on price without first achieving comparable volumes. Building a broad and diverse service offering, known as economies of scope, is also a major hurdle. This requires significant capital investment and considerable time to develop the expertise and infrastructure needed to offer a comprehensive suite of leasing solutions, from equipment to real estate.
- Economies of Scale: Large leasing firms leverage bulk purchasing power for assets and secure lower borrowing costs.
- Operational Efficiency: High volumes enable specialized technology and process optimization, reducing per-unit costs.
- Economies of Scope: Diversified service offerings create cross-selling opportunities and customer loyalty, which are costly to build from scratch.
- Capital Intensity: New entrants need substantial upfront capital to match the scale and scope of incumbents.
Specialized Expertise and Niche Market Saturation
While new entrants might aim for specialized niches, Fuyo General Lease has a well-established presence in diverse sectors, including aircraft leasing, real estate financing, and healthcare equipment. This broad operational scope means newcomers face the hurdle of acquiring similar specialized knowledge and competing in markets where Fuyo already possesses significant experience and infrastructure.
The challenge for potential new entrants is amplified by the existing saturation within many of these specialized segments. For instance, in the aircraft leasing market, established players like Fuyo General Lease have long-standing relationships with airlines and extensive fleets, making it difficult for new companies to gain traction. Similarly, the real estate finance sector is highly competitive, requiring substantial capital and deep market understanding.
- Niche Market Penetration: New entrants often target niche markets, but Fuyo General Lease already operates across multiple specialized segments.
- Expertise Barrier: Building the specialized expertise required for sectors like aircraft or healthcare leasing presents a significant challenge for newcomers.
- Market Saturation: Many of Fuyo's operational niches are already well-developed and competitive, making entry difficult.
- Capital Requirements: Entering specialized leasing markets demands considerable capital investment, which can be a deterrent for new firms.
The threat of new entrants for Fuyo General Lease is considerably low due to the immense capital requirements and regulatory hurdles inherent in the leasing and diversified financial services sector. Established players benefit from strong brand loyalty and economies of scale, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. For instance, in 2024, the stringent capital adequacy requirements enforced by Japan's Financial Services Agency continue to act as a significant barrier.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Fuyo General Lease Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment needed for asset acquisition and funding. | Established funding lines and substantial asset portfolio. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict licensing and adherence to financial regulations. | Proven track record of compliance and operational licenses. |
| Brand Reputation & Customer Loyalty | Difficulty in building trust and customer relationships. | Deeply ingrained customer relationships and a reliable brand. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Inability to match cost advantages and diversified offerings. | Significant cost efficiencies and broad service portfolio. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Fuyo General Lease leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key competitors, and publicly available company filings. We also incorporate insights from economic indicators and trade association publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.