Eldorado Gold Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Eldorado Gold Bundle
Eldorado Gold operates in a sector where supplier power can be significant due to specialized equipment and raw material dependencies. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles create barriers, but innovative technologies could disrupt the landscape. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Eldorado Gold’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
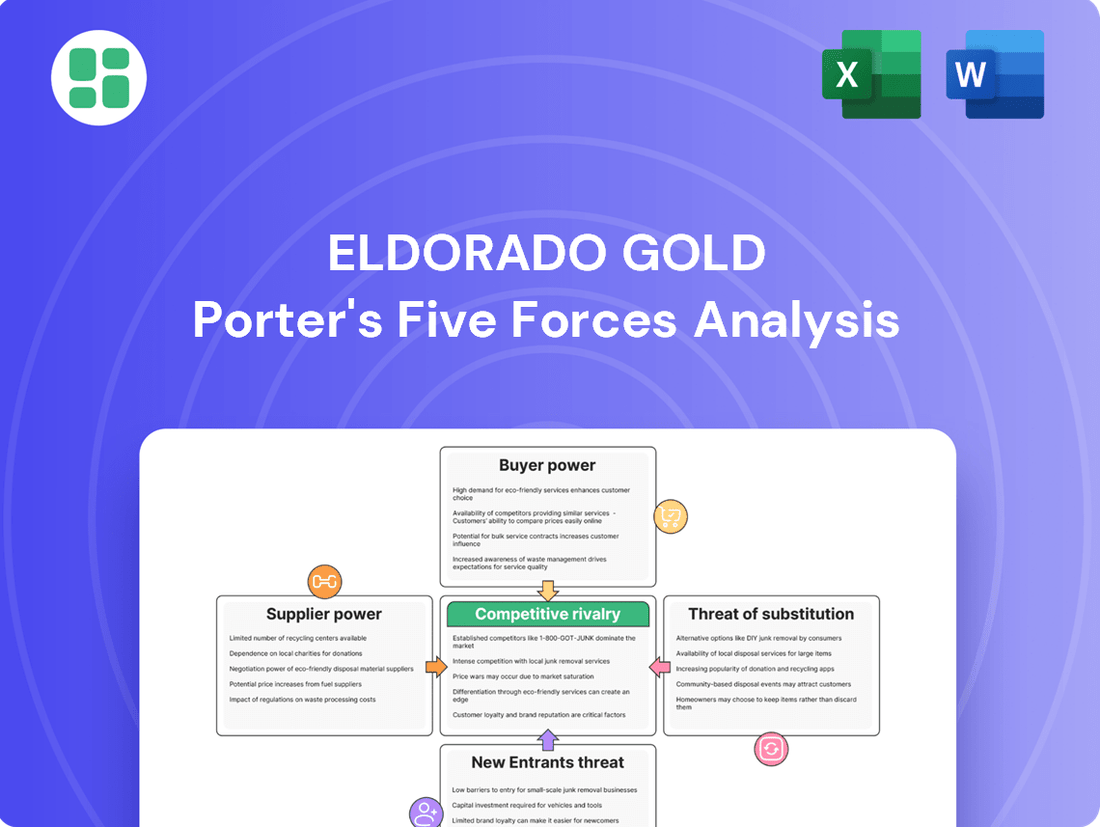
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The mining sector, including companies like Eldorado Gold, often depends on a limited number of specialized suppliers for crucial components such as heavy machinery, advanced processing chemicals, and sophisticated mining software. When few suppliers dominate these markets, their ability to dictate terms and prices to Eldorado Gold is significantly amplified. For instance, in 2024, the market for certain rare earth elements essential for advanced mining equipment saw consolidation, with a few key producers holding substantial market share, thereby increasing their leverage.
Switching suppliers for essential mining components or services presents significant hurdles for Eldorado Gold, directly impacting the bargaining power of its suppliers. The process of re-qualifying new vendors, adapting existing infrastructure, or retraining staff incurs substantial time and financial investment, thereby strengthening the leverage of current providers.
Eldorado Gold's commitment to optimizing operational efficiency further complicates supplier transitions. Any disruption, even minor, can lead to production delays and increased costs, making the company more amenable to maintaining existing supplier relationships, even if terms are less favorable.
Suppliers providing highly specialized or proprietary technologies, unique geological consulting services, or critical components with few alternatives wield significant bargaining power. For Eldorado Gold, this could mean dependence on specific equipment for advanced mineral processing or patented environmental solutions, directly impacting operational costs and flexibility.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into gold production, thereby becoming direct competitors to Eldorado Gold, is generally low. This is primarily due to the immense capital requirements and the complex, specialized knowledge needed for successful gold mining operations. For instance, establishing a new gold mine can cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, a significant barrier for most suppliers of equipment or services to the mining industry.
While a supplier could theoretically attempt forward integration, the practical challenges are substantial. These include navigating stringent environmental regulations, securing mining rights, and developing the technical expertise for exploration, extraction, and processing. The capital expenditure for a single mine, like Eldorado Gold's Kisladag mine in Turkey which has seen significant investment, far exceeds the typical investment capacity of a supplier in the mining value chain.
- High Capital Barrier: Gold mining requires substantial upfront investment, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, making it difficult for suppliers to enter the production phase.
- Regulatory Complexity: Obtaining mining permits and adhering to environmental and safety regulations is a complex and time-consuming process that most suppliers are not equipped to handle.
- Specialized Expertise: Successful gold production demands deep technical knowledge in geology, metallurgy, and mine engineering, which is a core competency for mining companies like Eldorado Gold, not typically found among its suppliers.
Labor Union Strength
The bargaining power of labor unions is a critical factor for Eldorado Gold, particularly given its operations in regions with established labor movements like Turkey, Canada, and Greece. Strong unions can significantly influence labor costs through wage negotiations and benefit demands. For instance, in 2023, the average wage in the Canadian mining sector, where Eldorado Gold has significant interests, saw continued upward pressure due to inflation and skilled labor shortages, impacting operational expenses.
The potential for work stoppages or strikes, often wielded by powerful unions, represents a direct threat to operational continuity and production schedules. Such actions can lead to substantial financial losses and delays in project development. For Eldorado Gold, disruptions in its key operating regions could directly impact its ability to meet production targets and manage costs effectively.
- Labor Cost Influence: Unions in Turkey, Canada, and Greece can negotiate for higher wages and improved benefits, directly increasing Eldorado Gold's operational expenditures.
- Operational Stability: The threat of strikes or work stoppages by organized labor can disrupt production and project timelines, impacting revenue and profitability.
- Industry Wage Trends: In 2023, the Canadian mining sector, a key operational area for Eldorado Gold, experienced wage growth driven by inflation and labor scarcity, setting a benchmark for negotiations.
Eldorado Gold faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the specialized nature of mining inputs and the limited number of providers. This leverage is amplified when few suppliers control essential components like advanced processing chemicals or heavy machinery, enabling them to dictate terms. For example, in 2024, consolidation in the market for rare earth elements used in mining equipment increased the market share of a few key producers, bolstering their negotiating strength.
What is included in the product
This analysis of Eldorado Gold's competitive environment reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats posed by new entrants and substitutes. It provides strategic insights into Eldorado Gold's market position and potential vulnerabilities.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis for Eldorado Gold, highlighting key threats and opportunities to inform strategic decisions.
Customers Bargaining Power
Eldorado Gold's primary product, gold, is sold into a vast and diverse global market. This market includes central banks, institutional investors, jewelry makers, and various technology firms, creating a broad and fragmented customer base.
The significant demand for gold, particularly from central banks and investors throughout 2024, further strengthens this fragmentation. This widespread demand means no single customer holds substantial sway, thereby limiting the bargaining power of any individual buyer.
Gold's multifaceted role as a safe-haven asset, a store of value, and an essential element in luxury goods and advanced electronics significantly limits customer bargaining power. These critical functions mean that for many applications, particularly in investment and high-tech manufacturing, there are few readily available substitutes for gold's unique properties.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for gold as an investment remained robust, driven by geopolitical uncertainties and inflation concerns, as evidenced by central bank purchases continuing at a strong pace. This persistent demand for gold's core attributes inherently reduces the ability of individual customers or even large groups to exert significant downward pressure on prices.
The price sensitivity of customers for gold varies significantly. While institutional buyers and central banks might prioritize gold's stability and store of value over minor price shifts, segments like jewelry consumers and industrial users are more attuned to price changes.
In 2024, the impact of elevated gold prices was evident, with a notable 11% drop in jewelry demand volume globally. This decline directly illustrates the price sensitivity within a key customer segment, showing that as prices rise, demand can contract considerably.
Availability of Substitutes for Customers
The availability of substitutes for gold significantly influences its bargaining power. While gold holds a unique status as a store of value and a hedge against inflation, investors and industrial users do have alternatives.
For investment purposes, customers can turn to other precious metals like silver and platinum, or explore financial instruments such as bonds, real estate, or even cryptocurrencies for diversification. In industrial applications, particularly in electronics, companies might seek out alternative conductive materials if gold prices become prohibitive. For instance, in 2023, the price of gold averaged around $1,970 per ounce, while silver hovered near $23 per ounce, presenting a substantial cost difference that could drive some substitution.
- Limited Direct Substitutes for Store of Value: Despite alternatives, gold's historical role as a reliable store of value and a safe-haven asset is not easily replicated, giving it a degree of pricing power.
- Price Sensitivity Drives Substitution: Significant price discrepancies between gold and its substitutes, like silver, can encourage a shift in demand, particularly in industrial sectors.
- Diversification Motivates Alternatives: Investors seeking broad diversification may allocate capital to a range of assets beyond precious metals, reducing reliance solely on gold.
- Technological Advancements Impact Industrial Use: Ongoing research into alternative materials for electronics could further diminish gold's necessity in certain high-tech applications.
Customer Information and Transparency
The global gold market's inherent transparency, with readily available spot prices, significantly empowers customers. This widespread access to real-time pricing information means buyers are well-informed about prevailing market rates, directly impacting Eldorado Gold's pricing flexibility. Consequently, Eldorado Gold faces limitations in its ability to charge prices substantially above the market average, although robust overall demand can still provide a supportive pricing environment.
This transparency translates into tangible advantages for customers:
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Buyers can easily compare Eldorado Gold's offerings against global benchmarks, ensuring they are getting competitive pricing.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Unlike less transparent markets, gold buyers have access to the same price data as sellers, leveling the playing field.
- Price Sensitivity: The readily available data makes customers more sensitive to price fluctuations and less likely to accept premium pricing without justification.
Eldorado Gold faces limited customer bargaining power due to the fragmented nature of the global gold market, where demand from central banks, investors, and industrial users outstrips any single buyer's influence. While some customer segments, like jewelry consumers, show price sensitivity, as evidenced by an 11% drop in global jewelry demand volume in 2024 due to higher prices, gold's unique properties as a store of value and its essential role in technology create few direct substitutes.
The transparency of the gold market, with readily available spot prices, further empowers customers by enabling informed purchasing decisions and reducing Eldorado Gold's pricing flexibility. For instance, the average gold price in 2023 was around $1,970 per ounce, while silver traded near $23 per ounce, highlighting potential substitution opportunities for price-sensitive industrial buyers.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Central Banks & Institutional Investors | Low (focus on stability/store of value) | Low |
| Jewelry Consumers | High (responsive to price fluctuations) | Moderate |
| Industrial Users (Electronics) | Moderate to High (potential for substitution) | Moderate |
What You See Is What You Get
Eldorado Gold Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Eldorado Gold, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic factors impacting the company. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Eldorado Gold operates in a global gold mining sector populated by giants like Newmont and Barrick Gold, who command substantial market share. These larger entities possess greater financial resources and economies of scale, presenting a significant competitive hurdle. For instance, in 2023, Newmont reported gold sales of approximately 6.9 million ounces, dwarfing Eldorado Gold's production.
While global gold production saw a 1% increase in 2024, reaching a new record high, the industry's overall growth rate remains moderate. Forecasts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 0.9% through 2030, indicating a mature market.
This moderate expansion intensifies competitive rivalry among gold mining companies. As the pie grows slowly, firms must actively vie for existing market share, leading to increased competition for resources, talent, and favorable mining concessions.
Gold is primarily a commodity, making it difficult to differentiate products based on physical attributes. This means competition in the gold mining sector, including for Eldorado Gold, often centers on factors like cost-effectiveness, production scale, and increasingly, on the ethical sourcing and sustainability of operations. Eldorado Gold highlighted its commitment to these areas in its 2024 Sustainability Report, aiming to build a competitive edge beyond the raw metal itself.
Exit Barriers
The gold mining industry, including companies like Eldorado Gold, faces substantial exit barriers. These are the significant costs and complexities involved in leaving the market, which can trap companies in operations even when profitability wanes. Think about the sheer amount of money tied up in a mine. For Eldorado Gold, this includes the ongoing costs of developing and maintaining extraction infrastructure.
These barriers keep companies competing, even in tough times. For instance, environmental rehabilitation is a huge factor. Mines require extensive, long-term cleanup after operations cease, a commitment that can span decades and cost millions.
- Capital Investment: Developing a gold mine requires billions in upfront capital for exploration, equipment, and infrastructure. For example, the Kisladag mine in Turkey, operated by Eldorado Gold, represents a significant long-term investment.
- Environmental Obligations: Post-closure rehabilitation and environmental monitoring are legally mandated and financially burdensome, often running into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars per mine.
- Specialized Workforce and Assets: The specialized nature of mining equipment and the skilled labor force are difficult and costly to redeploy or sell, further discouraging quick exits.
Cost Structure and Capacity Utilization
Gold mining is inherently capital-intensive, burdened by substantial fixed costs associated with exploration, mine development, and processing equipment. This high cost base necessitates that companies like Eldorado Gold strive for maximum capacity utilization to effectively spread these expenses and drive down the per-ounce production cost.
Eldorado Gold's commitment to operational enhancements and rigorous cost management, as highlighted in its 2024 guidance, directly addresses this competitive pressure. By optimizing production processes and controlling expenditures, the company aims to maintain a competitive cost structure in a market where efficiency is paramount.
- High Fixed Costs: Exploration, development, and equipment represent significant upfront investments in gold mining.
- Capacity Utilization: Maximizing output from existing infrastructure is key to lowering per-unit production costs.
- Eldorado's 2024 Focus: Operational improvements and cost control are central to Eldorado Gold's strategy for competitive advantage.
Competitive rivalry within the gold mining sector is intense, driven by a mature market with moderate growth and high exit barriers. Companies like Eldorado Gold compete on cost efficiency, scale, and increasingly, on sustainability. The commodity nature of gold means differentiation is challenging, forcing firms to focus on operational excellence and resource acquisition.
SSubstitutes Threaten
For investors considering Eldorado Gold, the threat of substitutes is significant. Gold directly competes with a wide array of alternative investment vehicles, including stocks, bonds, and real estate. These substitutes can offer different risk-return profiles and may become more attractive depending on prevailing economic conditions and market sentiment.
The appeal of these alternatives directly impacts gold's investment demand. For instance, rising interest rates can make bonds more appealing, drawing capital away from non-yielding assets like gold. Similarly, strong equity market performance might divert investor focus from precious metals, particularly in periods of economic growth and stability.
In 2024, while inflation concerns have supported gold prices, other assets have also seen robust performance. The S&P 500, for example, reached new highs, demonstrating the competitive landscape for investor capital. This dynamic highlights how shifts in economic indicators and market performance directly influence the attractiveness of gold relative to its substitutes.
Gold's unique position as a safe-haven asset, especially during economic turmoil, inflation, or geopolitical crises, sets it apart from many other investments. This intrinsic quality significantly diminishes the threat of substitutes for a substantial part of gold's demand. For instance, central banks and investors alike showed strong interest, with record buying observed in 2024, underscoring gold's enduring appeal when other assets falter.
While gold possesses unique properties, technological advancements are creating potential substitutes in industrial sectors like electronics and dentistry. However, gold's exceptional conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and malleability continue to make it indispensable in many high-performance applications. In 2024, demand for gold in the technology sector saw a notable 7% increase, largely fueled by the burgeoning fields of artificial intelligence and advanced electronics.
Consumer Preferences for Jewelry
Consumer preferences for jewelry present a significant threat of substitutes for Eldorado Gold. While gold jewelry is a dominant segment, shifts in consumer tastes towards alternative materials, such as platinum or even lab-grown diamonds, can impact demand. Furthermore, consumers may opt for other luxury goods, like high-end electronics or experiences, diverting spending away from traditional jewelry.
The price sensitivity of the jewelry market is evident. For instance, in 2024, the elevated price of gold contributed to an 11% decrease in jewelry volume sold. Despite this volume drop, the overall value of jewelry sales saw an increase, suggesting a trend towards purchasing fewer, but more valuable, gold pieces. This dynamic highlights how substitutes or changes in spending priorities can directly affect demand for gold jewelry.
- Shifting Material Preferences: Consumers may move towards platinum, silver, or other precious metals.
- Rise of Lab-Grown Diamonds: These offer a more affordable alternative to mined diamonds, impacting the broader luxury jewelry market.
- Competition from Other Luxury Goods: Spending on travel, technology, or fashion can divert consumers from jewelry purchases.
- Price Elasticity: A significant price increase, like that seen in 2024, can reduce the volume of gold jewelry sold, even if total sales value rises.
Recycled Gold as a Supply Source
Recycled gold presents a significant substitute for newly mined gold, influencing Eldorado Gold's supply dynamics. In 2024, the supply from recycled gold saw a notable increase of 11%, contributing to the overall gold market availability.
This increased recycling activity can directly impact the demand for primary mine production. When gold prices are high, it becomes more economically viable to recover gold from existing sources, effectively substituting new mine output.
- Recycled Gold's Growing Contribution: In 2024, recycled gold supply increased by 11%, directly impacting the total available gold supply.
- Price Sensitivity: Higher gold prices incentivize greater recycling efforts, making recovered gold a more attractive alternative to newly mined gold.
- Supply Chain Substitution: Increased recycling acts as a form of substitution within the gold supply chain, potentially reducing reliance on Eldorado Gold's mine production.
The threat of substitutes for Eldorado Gold is multifaceted, encompassing both investment alternatives and material replacements. In the investment realm, assets like stocks and bonds compete for capital, their appeal waxing and waning with economic conditions. For instance, the S&P 500's strong performance in 2024 highlighted the competitive draw of equity markets. However, gold's safe-haven status, particularly during inflationary periods or geopolitical uncertainty, remains a powerful counter-argument to substitutes, as evidenced by record central bank buying in 2024.
Industrially, while technological advancements are exploring alternatives, gold's unique properties like conductivity and malleability ensure its continued demand, with tech sector demand rising 7% in 2024. Consumer preferences for jewelry also present a substitution threat, with shifts towards platinum or lab-grown diamonds, and a general diversion of luxury spending to experiences or technology. The jewelry market's price sensitivity was apparent in 2024, with an 11% drop in jewelry volume sold despite rising gold prices.
| Substitute Category | Key Factors | 2024 Impact/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Alternatives | Stocks, Bonds, Real Estate, Interest Rates, Equity Performance | S&P 500 reached new highs; rising rates boost bond appeal. |
| Industrial Materials | Technological Advancements, Conductivity, Corrosion Resistance | 7% increase in tech sector demand for gold. |
| Jewelry & Luxury Goods | Alternative Metals (Platinum, Silver), Lab-Grown Diamonds, Consumer Preferences, Other Luxury Spending | 11% decrease in jewelry volume sold; shift towards higher-value pieces. |
| Recycled Gold | Price Sensitivity, Recycling Economics | 11% increase in recycled gold supply, impacting primary mine demand. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new gold mine is incredibly capital-intensive. Think about the costs involved: finding the gold through exploration, building the actual mine, setting up all the necessary infrastructure like roads and power, and then having the equipment to process the ore. These upfront expenses are enormous.
Eldorado Gold’s Skouries project highlights this perfectly. In 2024, the company continued to pour significant capital into this development, underscoring the massive financial commitment required. These substantial capital requirements act as a major hurdle, making it very difficult for new companies to enter the gold mining industry and compete.
The gold mining sector is heavily regulated, with extensive environmental, social, and operational permitting requirements. These complex and often lengthy approval processes act as a significant barrier, deterring potential new entrants by increasing upfront costs and project timelines. For instance, obtaining all necessary permits for a new mine can take several years, as seen in projects requiring extensive environmental impact assessments and community consultations.
The threat of new entrants to the gold mining sector, particularly concerning access to scarce resources, is significantly constrained. High-quality gold deposits are finite and becoming increasingly challenging to locate, meaning fewer prime opportunities exist for newcomers. For instance, by the end of 2023, global gold reserves, while substantial, are concentrated in known, often already exploited, or difficult-to-access areas.
Established companies like Eldorado Gold have a distinct advantage as they already control significant reserves and possess the expertise and capital to operate in challenging environments. This existing control makes it difficult for new players to secure economically viable deposits and compete for the most promising mining concessions, thereby limiting new entry.
Technological Expertise and Operational Know-how
The threat of new entrants in the gold mining sector, particularly concerning technological expertise and operational know-how, is significantly mitigated by the industry's inherent complexities. Success hinges on deep understanding across geology, metallurgy, and engineering, alongside highly efficient operational management. New players often struggle to acquire this critical, accumulated knowledge, facing a steep learning curve and substantial operational risks.
This knowledge gap translates into tangible barriers. For instance, in 2024, the average capital expenditure for developing a new underground gold mine can range from $300 million to over $1 billion, reflecting the sophisticated technology and infrastructure required. Without proven experience, new entrants are less likely to secure financing or efficiently manage these vast investments.
- High Capital Investment: Developing a new gold mine demands hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Specialized Skills: Expertise in geology, metallurgy, and engineering is crucial and difficult to replicate quickly.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined operations are key to profitability; new entrants often lack the established processes and experienced personnel to achieve this.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex environmental and mining regulations requires significant experience and resources.
Social License to Operate
The mining sector's reliance on a social license to operate presents a formidable barrier for new entrants. Securing community and stakeholder approval is paramount, and without it, projects can face severe disruptions. This often translates into significant delays and increased costs, as new companies struggle to build the necessary trust and acceptance.
For instance, the mining industry regularly grapples with community opposition, which can manifest as protests and legal challenges. These hurdles can add years to project development timelines and inflate capital expenditures, making it difficult for newcomers to compete with established players who already possess this crucial social capital. In 2024, several high-profile mining projects globally experienced significant delays attributed to community relations issues, underscoring the persistent nature of this threat.
- Community Acceptance is Key: New mining companies must invest heavily in building relationships and demonstrating tangible benefits to local populations to gain trust.
- Risk of Delays and Cost Overruns: Failure to secure a social license can lead to protests, legal battles, and operational shutdowns, significantly impacting project economics.
- Established Players' Advantage: Existing mining firms often have long-standing relationships with communities, giving them a distinct advantage over new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the gold mining industry is generally low due to the immense capital required to start operations. For example, developing a new gold mine can easily cost hundreds of millions to over a billion dollars, a figure that deters most potential newcomers. This high barrier to entry is further amplified by the need for specialized technical expertise and navigating complex regulatory landscapes, which established players like Eldorado Gold have already mastered.
Furthermore, securing access to viable gold deposits is increasingly challenging, with prime locations often already controlled by existing companies. This scarcity of resources, coupled with the significant investment in exploration and development, means that new entrants face an uphill battle from the outset. In 2024, the continued high costs associated with exploration and permitting underscore these persistent entry barriers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Enormous upfront costs for exploration, mine development, and infrastructure. | Developing a new underground gold mine can cost $300 million to over $1 billion (as of 2024). |
| Technical Expertise | Requires deep knowledge in geology, metallurgy, and engineering. | New entrants often lack the accumulated operational know-how, leading to higher risks and inefficiencies. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex and lengthy permitting processes for environmental and operational approvals. | Obtaining permits can take several years, increasing project timelines and costs. |
| Resource Access | Limited availability of high-quality, economically viable gold deposits. | Established firms control many known reserves, making it difficult for newcomers to secure promising concessions. |
| Social License to Operate | Gaining community and stakeholder acceptance is crucial for project viability. | Failure to secure this can lead to significant delays and cost overruns, as seen in projects facing community opposition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Eldorado Gold leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings to understand the company's operational landscape and competitive positioning.
We also incorporate insights from industry research reports, commodity price databases, and news articles to assess market trends, threat of new entrants, and the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.