Dolby Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dolby Bundle
Dolby's position in the audio and visual technology market is shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power from device manufacturers, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder in the tech industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dolby’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Dolby's proprietary technology and significant R&D investment are key in mitigating supplier power. The company's core business is built on internally developed, patented technologies, meaning it doesn't heavily depend on external suppliers for its fundamental intellectual property. This strong internal innovation engine, fueled by continuous R&D, ensures that outside technology providers have minimal leverage over Dolby.
Dolby's strategic acquisition of patent portfolios significantly bolsters its bargaining power against suppliers. For instance, the 2024 acquisition of GE Licensing, which included over 5,000 patents, particularly in video compression, diversifies Dolby's technological foundation. This reduces reliance on any single external technology provider, thereby strengthening Dolby's position in negotiations.
While not traditional material suppliers, highly specialized engineers and researchers are crucial for Dolby's innovation. The availability of such talent, especially in niche audio and imaging fields, could exert some power. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning specialists, often crucial for audio processing advancements, remained exceptionally high across the tech sector.
Dolby's established reputation as a leader in audio technology likely attracts top-tier professionals, mitigating the risk of supplier power from talent scarcity. The company's robust internal processes for innovation disclosure and patent filing further ensure that valuable contributions from its workforce are captured and leveraged, strengthening its competitive position.
Limited Raw Material Dependence
Dolby's position as a technology licensor significantly insulates it from the traditional pressures of raw material suppliers. Unlike manufacturers that rely on physical inputs, Dolby's business model is asset-light, meaning its core operations aren't directly tied to the availability or cost of raw materials. This lack of dependence fundamentally limits the bargaining power of potential suppliers in this specific area.
This characteristic is a key differentiator. For instance, in 2023, Dolby's revenue was derived primarily from licensing fees and royalties, not from the sale of manufactured goods. This means that fluctuations in commodity prices or supply chain disruptions affecting physical materials have a minimal direct impact on Dolby's cost structure or operational capacity, a stark contrast to companies in sectors like automotive or consumer electronics.
- Reduced Input Cost Volatility: Dolby's reliance on intellectual property rather than physical components shields it from the price volatility often seen in raw material markets, a significant advantage in 2024.
- Asset-Light Business Model: The company’s operational structure minimizes the need for extensive physical inventory or direct sourcing of raw materials, thereby curtailing supplier leverage.
- Focus on Technology and IP: Dolby's core value proposition stems from its patented audio and imaging technologies, shifting the power dynamic away from traditional material suppliers.
Patent Pool Participation
Dolby's participation in patent pools, such as those for audio codecs, significantly influences the bargaining power of other patent holders. By joining these collaborative licensing arrangements, Dolby effectively shares the licensing burden and reduces the individual leverage of any single patent owner. This structure tends to equalize bargaining power among pool members, as it standardizes terms and promotes broader adoption of the underlying technologies.
This collaborative approach can mitigate the risk of individual suppliers wielding excessive power. For instance, in the realm of audio compression, where Dolby holds significant patents, its involvement in pools means that other patent holders must negotiate within the pool's framework. This often leads to more predictable and manageable licensing costs for Dolby and its customers, rather than facing uncoordinated demands from numerous individual patent holders.
The strategic advantage of patent pool participation for Dolby is evident in its ability to offer integrated solutions. By licensing a bundle of essential patents through a pool, Dolby can present a more comprehensive and cost-effective offering to device manufacturers. This reduces the complexity and potential for hold-up by individual patent owners, thereby diminishing their individual bargaining power.
- Patent Pools as a Mitigator: Dolby's involvement in patent pools for technologies like audio coding reduces the bargaining power of individual patent holders by creating a collective licensing framework.
- Streamlined Licensing: Participation in these pools simplifies the licensing process and lowers transaction costs, indicating a more balanced negotiation environment for Dolby.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: By contributing to and benefiting from patent pools, Dolby lessens the ability of any single patent owner to exert significant individual leverage or demand exorbitant royalties.
- Competitive Advantage: This strategy allows Dolby to offer more predictable and competitive licensing terms to its customers, enhancing its market position against competitors who may not have access to similar pooled intellectual property.
Dolby's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly influenced by its reliance on intellectual property rather than physical components. This asset-light model, where revenue stems from licensing fees as seen in 2023, shields the company from raw material cost volatility and supply chain disruptions, thereby limiting traditional supplier leverage.
Furthermore, Dolby's strategic acquisitions, such as the 2024 purchase of GE Licensing's patent portfolio, diversify its technological base. This reduces dependence on any single external technology provider, strengthening Dolby's negotiating position and diminishing the bargaining power of potential technology suppliers.
Dolby's participation in patent pools, which standardize licensing terms for technologies like audio codecs, also acts as a significant mitigator of supplier power. This collaborative approach equalizes leverage among patent holders, leading to more predictable licensing costs and reducing the ability of individual patent owners to exert undue influence.
| Factor | Dolby's Position | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Reliance on IP vs. Physical Inputs | High (Revenue from licensing) | Low |
| Strategic Acquisitions (e.g., GE Licensing 2024) | Diversified technology base | Low |
| Patent Pool Participation | Collaborative licensing framework | Low |
| Talent Acquisition (AI/ML Specialists 2024 demand) | Strong brand reputation | Low to Moderate |
What is included in the product
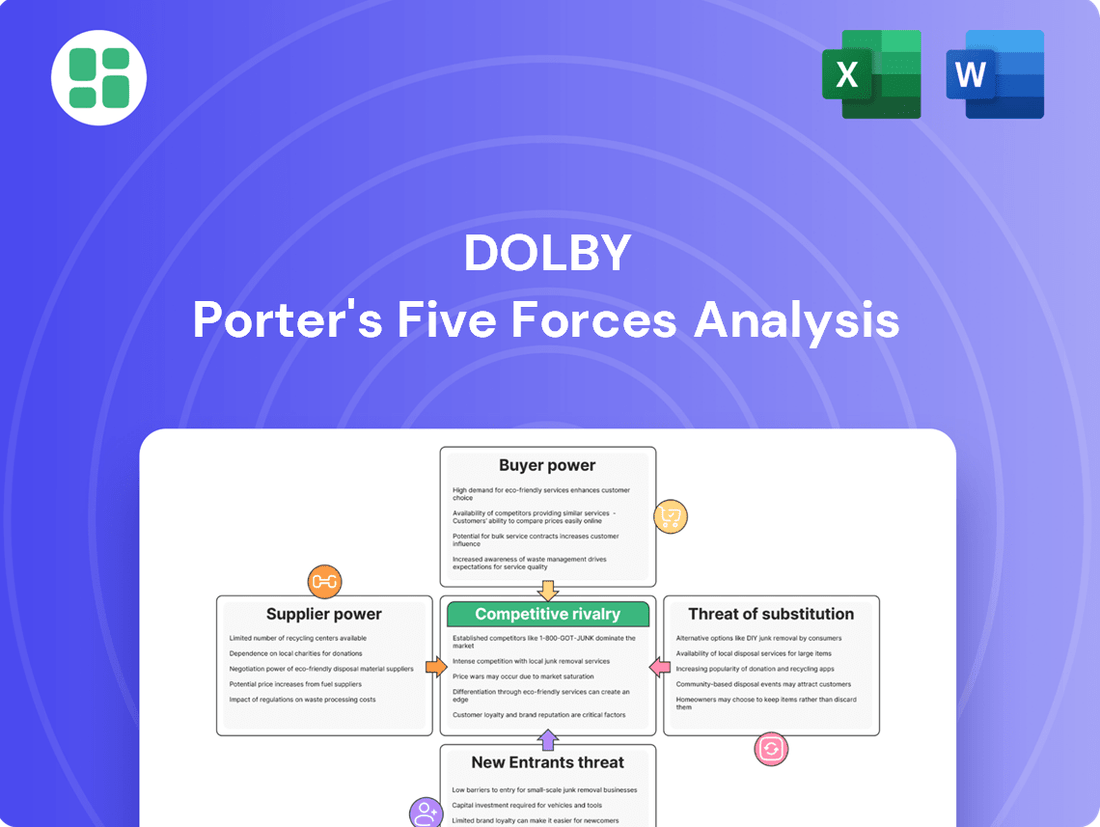
Analyzes the intensity of rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes specifically for Dolby's business.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with pre-built templates for each Porter's force.
Customers Bargaining Power
Dolby's customer base is remarkably concentrated among a few very large and influential entities. These include global electronics giants like Samsung, LG, and Audi, as well as major content producers such as Hollywood studios and leading streaming platforms like HBO Max. This concentration means these customers wield considerable power.
The sheer scale of these customers allows them to negotiate favorable licensing terms due to the high volume of Dolby-enabled devices or content they produce. For instance, a single major smartphone manufacturer licensing Dolby Atmos could represent a significant portion of Dolby's revenue, giving them leverage in price and contract negotiations. Their ability to influence market standards further amplifies their bargaining power.
The decisions made by these key players significantly shape the market. If a large manufacturer like Samsung decides to integrate Dolby's technologies across its extensive product lines, it can drive widespread adoption and set a de facto standard. Conversely, a refusal or a demand for less favorable terms from such a customer can create substantial headwinds for Dolby's growth and market penetration.
When manufacturers embed Dolby's advanced technologies, such as Dolby Atmos for immersive sound and Dolby Vision for enhanced picture quality, into their products, the cost and complexity of switching to competing standards become substantial. This integration represents a significant investment for companies like Apple, Samsung, and Sony, often involving extensive research, development, and manufacturing adjustments.
The high switching costs associated with these integrated technologies effectively lock in customers. For instance, a smartphone manufacturer that has optimized its hardware and software for Dolby Atmos will face considerable expenses in redesigning and retooling if they decide to adopt a different audio codec. This creates a strong incentive to remain with Dolby, thereby diminishing the immediate bargaining power of these manufacturers as customers.
Consumers are increasingly looking for more than just basic functionality; they want immersive and high-quality audio and visual experiences. This trend directly benefits Dolby, as its technologies are synonymous with premium sound and picture. For instance, in 2024, the global market for immersive audio technologies, including Dolby Atmos, saw significant growth, driven by consumer demand for home theater and premium mobile audio. This appetite for better experiences gives customers more leverage to demand products featuring Dolby's innovations.
This strong consumer pull for premium experiences translates into increased bargaining power for customers. Manufacturers recognize that integrating Dolby's branded technologies is a key differentiator in a crowded market. By offering Dolby Vision and Dolby Atmos, companies can attract discerning consumers willing to pay more for superior entertainment. This allows customers, in a way, to dictate terms by choosing products that meet their desire for enhanced sensory engagement, thereby strengthening their position in negotiations with device makers.
Potential for In-house Development or Open-Source Alternatives
Large customers, especially tech giants like Samsung and Google, possess the financial muscle to develop their own competing immersive audio and video technologies. For instance, Samsung has been actively investing in its own audio solutions, and Google's recent advancements in spatial audio demonstrate this trend. This potential for in-house development significantly bolsters their bargaining power with Dolby.
The increasing availability of open-source alternatives presents another avenue for customers to exert pressure. As these alternatives mature, they offer viable, often lower-cost, options, particularly for less premium applications. This diversification of technological choices directly enhances customer leverage in negotiations.
- In-house Development: Major tech companies can allocate significant R&D budgets to create proprietary audio and video solutions, reducing reliance on external providers.
- Open-Source Adoption: The growing maturity of open-source audio codecs and processing frameworks provides cost-effective alternatives for developers and manufacturers.
- Competitive Landscape: The emergence of new technologies, like Eclipsa Audio, creates a more competitive environment, forcing existing players to offer more attractive terms.
- Customer Leverage: The ability to switch to or develop alternatives empowers customers, especially large-volume buyers, to negotiate better pricing and licensing agreements with Dolby.
Tiered Licensing and Volume-Based Pricing
Dolby's tiered licensing and volume-based pricing strategies directly impact customer bargaining power. Larger clients, by committing to higher volumes of Dolby's audio and visual technologies, can negotiate more favorable per-unit royalty rates. This creates a dynamic where significant adoption of Dolby's products by major players can lead to reduced costs for those specific customers.
- Volume Discounts: Dolby's pricing structure often includes discounts that increase with the volume of licensed units, empowering large manufacturers to negotiate lower per-unit costs.
- Negotiated Terms: Major customers with substantial market share can leverage their potential volume to negotiate bespoke licensing terms, further enhancing their bargaining position.
- Competitive Pressure: The existence of alternative audio and visual technologies, though perhaps less dominant, can also provide customers with leverage, especially when negotiating with Dolby for large-scale deployments.
Dolby's bargaining power with its customers is significantly influenced by the concentration of its client base among a few large, powerful entities like Samsung, LG, and major Hollywood studios. These major players can negotiate favorable licensing terms due to the sheer volume of Dolby-enabled products or content they produce, directly impacting Dolby's revenue and market strategy.
The high switching costs associated with integrating Dolby's advanced technologies, such as Dolby Atmos and Dolby Vision, into hardware and software create a lock-in effect for customers. For instance, companies like Apple and Sony invest heavily in optimizing their devices for these Dolby features, making a transition to alternative solutions costly and complex, thereby reducing their immediate bargaining power.
Consumer demand for premium audio-visual experiences, exemplified by the growth in immersive audio technologies in 2024, empowers customers. Manufacturers leverage this demand by integrating Dolby's branded features, which can then be used to negotiate better terms with Dolby, as these technologies become a key market differentiator.
The potential for large customers, such as Samsung and Google, to develop their own competing technologies, alongside the increasing availability of open-source alternatives, further amplifies their bargaining power. This diversification of options allows them to exert pressure on Dolby for more competitive pricing and licensing agreements.
| Customer Type | Key Negotiation Lever | Impact on Dolby |
|---|---|---|
| Major Electronics Manufacturers (e.g., Samsung, LG) | High volume commitments, potential for in-house development | Ability to negotiate lower per-unit royalties, influence technology adoption |
| Content Producers (e.g., Hollywood Studios) | Volume of content produced, market influence | Negotiate favorable licensing for content distribution, shape content standards |
| Streaming Platforms (e.g., Netflix, Disney+) | Subscriber base, platform reach | Influence licensing terms for streaming services, drive adoption of Dolby features for user experience |
Preview Before You Purchase
Dolby Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Dolby Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of competitive rivalry within the audio technology industry. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You can confidently assess the depth and quality of this strategic tool, knowing it represents the exact deliverable you will receive upon purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Dolby's commanding market leadership and deep brand recognition, particularly for Dolby Atmos and Dolby Vision, significantly intensifies competitive rivalry. This established presence acts as a formidable barrier to entry, allowing Dolby to command premium pricing and maintain healthy gross margins, thereby influencing how other players in the audio and imaging technology space must strategize.
Dolby faces direct competition from companies like Xperi, which owns the DTS brand, and chip manufacturers such as Cirrus Logic and Analog Devices. These firms also provide audio and signal-processing technologies, directly challenging Dolby's market presence in various audio solutions.
Xperi, particularly with its DTS technologies, competes in home theater, automotive audio, and mobile devices, offering alternative immersive sound experiences. For instance, DTS:X is a direct competitor to Dolby Atmos in the premium audio space.
Cirrus Logic and Analog Devices, while often supplying components, also offer sophisticated audio processing solutions that can be integrated into products, sometimes bypassing the need for Dolby's licensing or offering alternative functionalities, impacting Dolby's reach in the semiconductor supply chain.
The audio technology sector thrives on constant innovation, fueling intense competition. Companies like Dolby invest heavily in research and development, securing patents to protect their advancements. This patent strength becomes a crucial differentiator in the market.
Dolby's strategic acquisition of GE Licensing in 2015, for instance, significantly expanded its intellectual property portfolio. This move underscored the importance of patents in maintaining a competitive edge and defending market share against rivals who might seek to leverage similar technologies.
Integrated System Solutions from Rivals
Dolby faces intense competition from rivals offering integrated system solutions that bundle various entertainment technologies. These competitors can sometimes present compelling alternatives at a lower overall cost, putting pressure on Dolby to underscore the unique value and sophisticated integration of its own offerings.
For instance, in 2024, the consumer electronics market saw a significant trend towards bundled smart home and entertainment packages. Companies like Apple, with its ecosystem of devices and services, and Samsung, with its broad range of connected TVs and audio products, provide integrated experiences that can be perceived as a more cohesive, all-in-one solution by consumers.
- Integrated Offerings: Competitors bundle audio, video, and connectivity technologies, creating a single-point solution for consumers.
- Price Sensitivity: Bundled solutions can be priced attractively, forcing Dolby to justify its premium for specialized, high-quality audio and imaging.
- Value Proposition: Dolby must continuously highlight the superior performance, immersive experience, and brand reputation of its technologies to counter integrated, potentially lower-cost alternatives.
Strategic Partnerships and Ecosystem Lock-in
Dolby's competitive strength is significantly boosted by its strategic partnerships with major device manufacturers like Apple, Xiaomi, Audi, Lenovo, and HP. These collaborations ensure widespread integration of Dolby technologies across a vast array of consumer electronics. For instance, in 2024, Dolby Atmos was featured in over 100 new smartphone models and numerous premium automotive sound systems, solidifying its presence in key product categories.
This deep integration fosters an ecosystem lock-in effect, making it challenging for competitors to penetrate established markets. When consumers consistently experience Dolby's audio and video enhancements on their preferred devices, it creates a strong preference and loyalty. This makes it difficult for alternative technologies to gain significant market share, as the cost and effort to switch ecosystems can be prohibitive for both manufacturers and end-users.
- Key Partnerships: Collaborations with Apple, Xiaomi, Audi, Lenovo, HP, and other leading brands.
- Market Penetration: Dolby technologies integrated into a wide range of smartphones, laptops, TVs, and automotive systems.
- Ecosystem Advantage: Creates strong consumer preference and loyalty, hindering rival technology adoption.
- 2024 Impact: Over 100 new smartphone models and numerous automotive sound systems featured Dolby Atmos, underscoring ongoing integration.
The competitive rivalry in the audio and imaging technology sector is robust, with Dolby facing direct challenges from established players and emerging innovators. Companies like Xperi, through its DTS brand, offer competing immersive audio solutions across home theater, automotive, and mobile segments, directly vying with Dolby Atmos. Furthermore, chip manufacturers such as Cirrus Logic and Analog Devices provide advanced audio processing capabilities that can serve as alternatives or complements to Dolby's licensing model, impacting Dolby's position within the semiconductor supply chain.
Innovation is a constant driver of competition, pushing companies like Dolby to invest heavily in research and development to secure patents and maintain a technological edge. This focus on intellectual property, exemplified by Dolby's 2015 acquisition of GE Licensing to bolster its patent portfolio, is crucial for defending market share. The sector also sees competition from integrated system solutions that bundle various entertainment technologies, potentially offering consumers a more cohesive and cost-effective package, thereby pressuring Dolby to continually emphasize the superior performance and brand value of its specialized offerings.
Dolby's extensive partnerships with major device manufacturers, including Apple, Xiaomi, Audi, Lenovo, and HP, are key to its market penetration. In 2024, Dolby Atmos was integrated into over 100 new smartphone models and a significant number of premium automotive sound systems, reinforcing its widespread adoption. This deep integration creates an ecosystem advantage, fostering consumer loyalty and making it difficult for competing technologies to gain traction due to the inherent costs and complexities of switching ecosystems for both manufacturers and end-users.
| Competitor | Key Technologies | Market Segments | Competitive Impact |
| Xperi (DTS) | DTS:X, DTS Virtual:X | Home Theater, Automotive, Mobile | Directly competes with Dolby Atmos for immersive audio experiences. |
| Cirrus Logic | Audio processing ICs, DSPs | Consumer Electronics, Mobile | Offers integrated audio solutions that can reduce reliance on Dolby licensing. |
| Analog Devices | Audio DSPs, converters | Professional Audio, Consumer Electronics | Provides high-performance audio processing components, enabling alternative audio solutions. |
| Apple | Spatial Audio, Ecosystem Integration | Smartphones, Laptops, Audio Devices | Bundles audio with its hardware and software ecosystem, creating a strong integrated offering. |
| Samsung | Q-Symphony, Smart TV Audio | TVs, Soundbars, Home Entertainment | Offers integrated audio solutions within its broad consumer electronics ecosystem. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Dolby's audio and video codec technologies is significant, primarily stemming from generic, lower-cost, or open-source alternatives. These substitutes can offer core functionality without the associated licensing fees that Dolby typically charges.
A notable example is Samsung and Google's Eclipsa Audio, an open-source codec designed as an alternative to Dolby Atmos. While its initial adoption is limited to Samsung devices, its existence highlights the growing availability of functional, fee-free options in the market.
For consumers and manufacturers where cost is a primary driver, lower-quality, cheaper audio and imaging solutions can function as viable substitutes for Dolby's premium offerings. This is especially true in budget-conscious market segments, where the incremental benefit of Dolby's advanced technology may not justify the added expense.
In 2024, the market for affordable audio equipment, including unbranded speakers and headphones, continued to grow, with many consumers opting for functional over feature-rich solutions. For instance, the global market for consumer electronics saw a significant portion of sales attributed to entry-level products, indicating a strong demand for cost-effective alternatives across various categories.
Major technology firms, many of whom are also Dolby's clients, possess the resources and motivation to create their own unique audio and imaging solutions. This capability directly lessens their dependence on outside technology providers like Dolby for essential functionalities.
For instance, companies like Apple and Google have invested billions in research and development, with a significant portion allocated to enhancing their hardware and software capabilities, including audio processing. This internal development can offer a competitive edge and reduce licensing fees, directly impacting Dolby's market share.
Evolution of Content Delivery and Consumption
The rise of diverse digital entertainment, such as podcasts and audiobooks, presents a significant threat of substitutes for premium audio experiences. These alternatives offer accessible audio content that bypasses the need for high-fidelity, immersive technologies, thereby broadening the competitive landscape. For instance, the global podcasting market was valued at approximately $12.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer preference for easily consumable audio formats.
User-generated content platforms also contribute to this threat. These platforms allow for a vast array of audio creation and distribution, often at little to no cost, providing consumers with an almost limitless supply of audio entertainment. This accessibility means consumers can find substitutes for premium audio by simply searching for content on platforms they already use, potentially diverting attention and spending away from Dolby's core offerings.
The expanding availability of these alternative audio experiences challenges the necessity of investing in advanced audio technologies like Dolby Atmos for many consumers. As digital content continues to diversify, the perceived value of high-fidelity audio may diminish for a segment of the market, leading them to opt for more readily available and often free or low-cost substitutes.
Key substitute trends include:
- Growth of the audiobook market: The global audiobook market size was valued at USD 4.22 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.5% from 2024 to 2030.
- Podcast listener engagement: In 2024, it's estimated that over 170 million people in the US will listen to podcasts, highlighting a significant audience shift towards this medium.
- User-generated audio content: Platforms like TikTok and YouTube increasingly feature audio-centric content, offering a vast, free alternative to professionally produced audio.
- Streaming service audio tiers: Some music streaming services offer lower-fidelity audio options as standard, catering to a price-sensitive segment of the market.
Emerging Technologies and AI in Media
Advances in artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies present a significant threat of substitutes for Dolby's core business. These innovations can create novel methods for delivering enhanced audio and visual experiences, potentially circumventing traditional licensing agreements. For instance, AI-powered content creation tools could generate immersive audio or visual effects without requiring Dolby's proprietary technologies.
While Dolby is actively investing in AI research and development, these same technological leaps can also foster new avenues for substitution. Companies or creators might develop alternative, open-source, or AI-driven solutions that offer comparable or even superior quality at a lower cost, directly challenging Dolby's market position. The rapid evolution of AI in media production and distribution means that solutions once exclusive to companies like Dolby could become democratized.
- AI-driven audio synthesis: Generative AI models are increasingly capable of creating realistic and complex soundscapes, potentially reducing reliance on licensed audio technologies.
- Real-time rendering engines: Advancements in real-time graphics and audio rendering, often powered by AI, can offer immersive experiences without needing specialized hardware or licensing.
- Open-source codecs and standards: The development and adoption of open-source alternatives for audio and video processing could offer cost-effective substitutes to Dolby's patented solutions.
- Decentralized content platforms: Emerging platforms that leverage blockchain or peer-to-peer networks might enable new distribution models that bypass traditional licensing gatekeepers.
The threat of substitutes for Dolby's technologies is substantial, driven by the increasing availability of cost-effective and open-source alternatives. These substitutes can deliver core audio and video functionalities, often without the licensing fees associated with Dolby's premium offerings.
For instance, the growth of user-generated content on platforms like TikTok and YouTube provides consumers with a vast, free alternative to professionally produced audio experiences. In 2024, over 170 million people in the US were projected to listen to podcasts, indicating a significant shift towards accessible audio content that bypasses the need for high-fidelity technologies.
Furthermore, advancements in AI are enabling the creation of sophisticated audio synthesis and real-time rendering engines, potentially offering comparable or superior quality at a lower cost. This democratization of immersive audio experiences directly challenges Dolby's market position.
The global audiobook market, valued at USD 4.22 billion in 2023, is also expanding, further diversifying accessible audio content and presenting an alternative to premium audio solutions.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples/Trends | Market Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Source Codecs | Eclipsa Audio (Samsung/Google) | Offers fee-free functionality, reducing reliance on licensed tech. |
| User-Generated Content | TikTok, YouTube audio | Vast, free audio entertainment, diverting attention from premium offerings. |
| Digital Audio Content | Podcasts, Audiobooks | Podcasting market valued at $12.25 billion in 2023; Audiobook market expected 10.5% CAGR (2024-2030). |
| AI-Driven Solutions | AI audio synthesis, real-time rendering | Potential for comparable quality at lower cost, democratizing immersive audio. |
Entrants Threaten
Dolby faces a significant threat from new entrants due to the high costs associated with research and development (R&D) and robust intellectual property (IP) protections. Developing cutting-edge audio and imaging technologies demands continuous, substantial investment. For instance, Dolby's commitment to innovation is reflected in its significant R&D spending, which is crucial for maintaining its technological edge.
The creation and ongoing maintenance of extensive patent portfolios act as a formidable financial and intellectual barrier. These patents protect Dolby's proprietary technologies, making it extremely difficult and expensive for newcomers to replicate their offerings or operate without infringing on existing IP. This IP moat is a key reason why new entrants struggle to gain traction in the premium audio and cinema technology space.
Established industry standards and ecosystems present a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to compete with Dolby. Dolby's technologies are deeply integrated into the fabric of the audio-visual world, permeating everything from cinema projection systems to the smartphones in our pockets. For instance, Dolby Atmos is a standard feature on millions of devices, and its presence in over 20,000 cinemas globally by late 2023 highlights its widespread adoption.
The challenge for newcomers lies in achieving this level of interoperability and widespread acceptance. Breaking into these entrenched networks requires substantial investment and time to gain the trust and integration necessary for broad market penetration. Without compatibility with existing hardware and content, new audio technologies struggle to find a foothold, making Dolby's established position a formidable hurdle.
Dolby's decades of deep-rooted relationships with major electronics manufacturers and content creators create a significant barrier to entry. These established partnerships, built on trust and proven performance, mean new entrants would struggle to gain similar access and distribution channels.
Furthermore, Dolby's strong brand recognition among consumers is a powerful deterrent. In 2024, consumer awareness of Dolby technologies, such as Dolby Atmos and Dolby Vision, remains exceptionally high, signifying a substantial competitive advantage that new players would find challenging and costly to replicate.
Regulatory and Certification Hurdles
New audio and imaging technologies, like those Dolby develops, often face significant regulatory and certification hurdles. These can include adherence to complex industry standards, such as those set by bodies like the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) or international standardization organizations. For instance, Dolby Vision HDR certification involves rigorous testing and compliance with specific technical requirements, adding a substantial layer of complexity and cost for any potential new entrant aiming for widespread market adoption.
These processes can significantly deter new entrants by increasing the upfront investment and time required to bring a product to market. For example, the development and validation of new audio codecs or imaging processing algorithms must align with established interoperability protocols and performance benchmarks. Failure to meet these stringent requirements can prevent a new technology from being integrated into consumer electronics devices, a crucial step for market penetration.
The financial implications are substantial; achieving compliance can cost hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars in testing, legal fees, and engineering resources. This creates a high barrier to entry, favoring established players with existing relationships and resources to navigate these complex landscapes. In 2024, the continued evolution of digital broadcasting standards and the increasing demand for immersive experiences further underscore the need for rigorous, but costly, certification processes.
- Industry Standards: New technologies must comply with established technical specifications for compatibility and performance.
- Certification Processes: Rigorous testing and validation are required for market acceptance, adding significant cost and time.
- Financial Investment: Compliance can demand substantial capital for testing, legal, and engineering efforts, deterring smaller players.
- Market Access: Meeting these requirements is essential for integration into consumer electronics and achieving broad adoption.
Economies of Scale in Licensing
Dolby's licensing model creates substantial economies of scale. This allows them to offer attractive terms to major manufacturers, ensuring their technology is widely adopted, while still preserving robust gross margins. For instance, in 2023, Dolby's gross profit margin was approximately 83%, a testament to the efficiency of their licensing structure.
New companies entering the audio licensing space would face significant hurdles in matching Dolby's cost efficiencies. Building a comparable licensing infrastructure and achieving the same volume of agreements takes considerable time and investment, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price or breadth of offering.
- Economies of Scale: Dolby leverages its established licensing network to achieve cost advantages unavailable to new entrants.
- Margin Preservation: High licensing volumes enable Dolby to maintain strong gross margins, reinvesting in R&D and further solidifying its market position.
- Barriers to Entry: The capital and time required to replicate Dolby's licensing scale present a significant threat to potential new competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Dolby is generally low, largely due to the substantial barriers to entry already established. These include significant R&D investment, extensive patent portfolios, and deeply integrated industry standards. For instance, Dolby's commitment to innovation is ongoing, with R&D expenses consistently high to maintain its technological lead. By late 2023, Dolby Atmos was featured in over 20,000 cinemas worldwide, illustrating the depth of its ecosystem integration.
Newcomers face immense challenges in replicating Dolby's established relationships with manufacturers and content creators, as well as its strong brand recognition. The cost and time required to build similar trust and market presence are prohibitive. For example, Dolby Vision HDR certification involves rigorous testing and compliance, adding significant cost and complexity, estimated to be hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars in 2024, deterring smaller players.
Dolby's licensing model also creates significant economies of scale, allowing them to offer competitive terms while maintaining strong margins. In 2023, Dolby reported a gross profit margin of approximately 83%, highlighting the efficiency of its established licensing network. Replicating this scale and cost efficiency presents a formidable hurdle for any new entrant in the audio licensing space.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Dolby Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Dolby's official investor relations reports, SEC filings, and detailed market research from firms specializing in the audio and entertainment technology sectors. We also incorporate industry-specific trade publications and analyst reports to gauge competitive intensity and emerging threats.