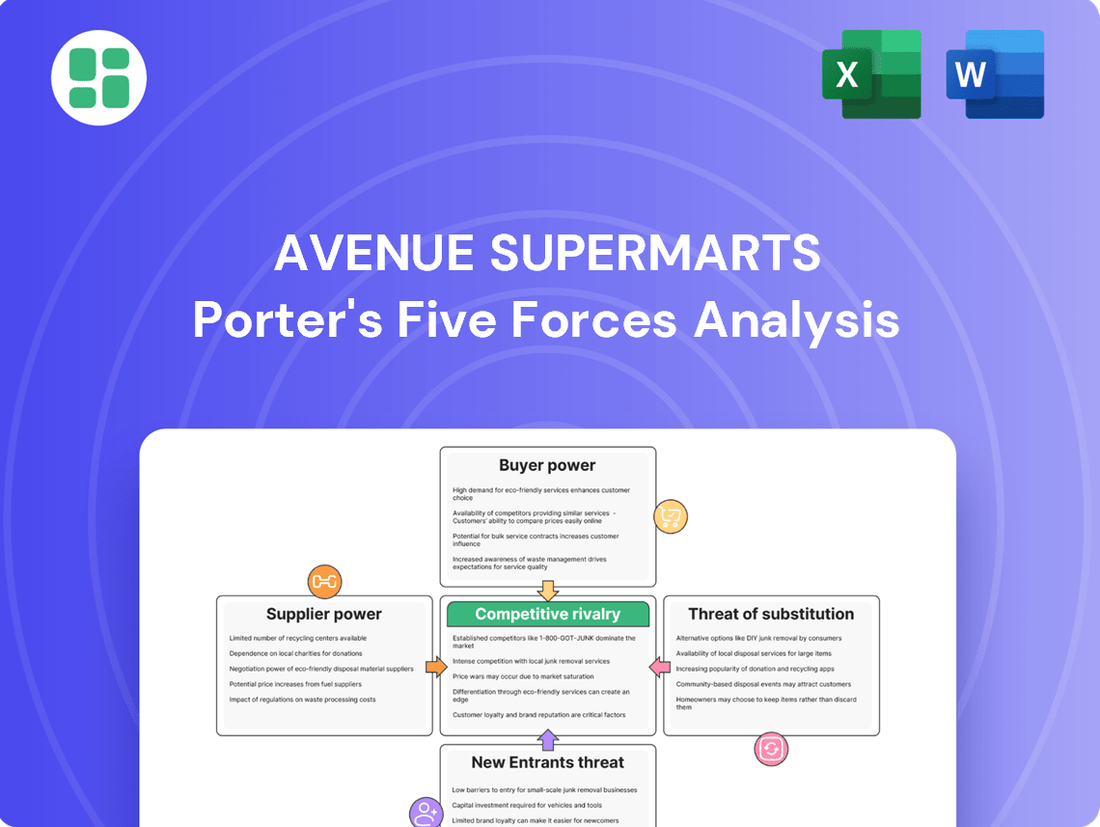
Avenue Supermarts Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Avenue Supermarts Bundle
Avenue Supermarts, operating in the highly competitive Indian retail sector, faces significant buyer power due to price-sensitive consumers and the availability of numerous alternatives. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as establishing a strong supply chain and brand loyalty requires substantial capital and time.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Avenue Supermarts’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
DMart's strategy of high-volume purchasing directly from manufacturers significantly bolsters its bargaining power with suppliers. By consolidating its purchasing power, DMart can negotiate more favorable terms and prices, as evidenced by its consistent ability to offer competitive pricing. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, DMart's revenue grew by 18.4% to INR 45,800 crore, demonstrating the scale of its operations and its capacity to leverage bulk buying.
DMart's efficient payment terms, often settling with suppliers within a week, significantly bolster its bargaining power. This rapid payment cycle is a strong incentive for suppliers, making DMart a preferred customer. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 2024, DMart maintained robust supplier relationships, a testament to its operational efficiency.
Avenue Supermarts, operating as DMart, cultivates robust, enduring partnerships with its suppliers. These relationships are built on mutual benefit, ensuring a commercially rewarding and profitable ecosystem for all involved.
These deep-rooted connections are instrumental in guaranteeing a steady and dependable supply of merchandise. This reliability significantly mitigates supply chain risks, thereby fortifying DMart's overall market standing and operational resilience.
Focus on Fast-Moving Goods
Avenue Supermarts, operating as DMart, strategically concentrates on fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG). This focus ensures rapid inventory turnover, which is a significant advantage for suppliers. By guaranteeing quick sales volumes, DMart becomes a highly attractive partner for FMCG manufacturers.
This approach translates into consistent demand and rapid stock movement for suppliers. For instance, DMart's high sales velocity means that products are often sold within days, reducing holding costs and inventory risk for its suppliers.
- High Inventory Turnover: DMart's focus on essential FMCG leads to an average inventory turnover ratio that is often significantly higher than industry averages, benefiting suppliers with faster cash conversion cycles.
- Consistent Demand: The curated product selection creates predictable demand patterns, allowing suppliers to better manage their production and supply chains.
- Preferred Partner Status: Suppliers are incentivized to partner with DMart due to the guaranteed sales volume and reduced risk associated with their products.
Private Label Products
Avenue Supermarts, operating DMart, significantly mitigates supplier bargaining power through its extensive development of private label products. This strategy allows DMart to offer its own branded alternatives across numerous categories, directly reducing its dependence on external manufacturers.
By controlling the production and branding of these private label goods, DMart not only enhances its profit margins but also gains substantial leverage over product quality and pricing. This internal sourcing capability directly diminishes the influence that external suppliers can exert on DMart's operations.
- Private Label Dominance: DMart's private label penetration is a key factor in weakening supplier power.
- Margin Enhancement: In FY23, DMart reported a revenue of ₹42,840 crore, with private labels contributing to improved gross margins.
- Quality and Price Control: The ability to dictate quality and pricing for its own brands directly counters supplier demands.
- Reduced Reliance: By offering alternatives, DMart lessens the impact of any single supplier's market power.
DMart’s considerable bargaining power with suppliers stems from its massive scale and efficient operations. By consolidating purchasing, DMart secures favorable terms, as seen in its FY24 revenue of INR 45,800 crore, indicating significant volume leverage.
The company's rapid payment cycles, often within a week, make it a highly attractive customer, reinforcing its negotiating position. This operational efficiency, evident throughout fiscal year 2024, ensures strong supplier relationships and preferential treatment.
Furthermore, DMart's strategic emphasis on fast-moving consumer goods ensures rapid inventory turnover, benefiting suppliers with quicker cash conversion and reduced holding costs.
DMart's development of private label products significantly diminishes supplier power by offering in-house alternatives, enhancing control over quality and pricing. This strategy directly reduces reliance on external manufacturers.
| Factor | DMart's Position | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Purchasing Volume | High, due to scale and revenue growth (FY24: INR 45,800 crore) | Lowers supplier power |
| Payment Terms | Rapid settlement (within a week) | Lowers supplier power |
| Product Focus | Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) | Lowers supplier power |
| Private Labels | Significant development and penetration | Lowers supplier power |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape for Avenue Supermarts, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly assess Avenue Supermarts' competitive landscape, alleviating the pain of complex market analysis with a clear, actionable framework.
Streamline strategic planning by simplifying the intricate dynamics of supplier power, buyer bargaining, threat of new entrants, substitutes, and rivalry for Avenue Supermarts.
Customers Bargaining Power
DMart's Everyday Low Pricing (EDLP) strategy directly leverages customer bargaining power by making price the primary driver of purchase decisions. This relentless focus on affordability, often selling below Maximum Retail Price, attracts a vast, price-sensitive customer base, particularly middle-income households. For instance, in FY24, DMart reported a revenue of ₹44,393 crore, a testament to the volume driven by their EDLP approach.
Customers in the grocery retail sector, like those shopping at Avenue Supermarts (DMart), generally face low switching costs. This means it’s quite easy for shoppers to move from one supermarket to another if they find a better deal or a more convenient location.
This ease of switching significantly empowers customers. For instance, in 2023, the Indian retail market saw numerous promotional offers and loyalty programs introduced by various players, directly responding to customer price sensitivity and their ability to switch. This competitive landscape means customers have a wide array of choices for their daily needs.
The Indian retail landscape is incredibly varied, presenting consumers with numerous choices. Beyond Avenue Supermarts' own hypermarkets and supermarkets, customers can readily access goods from traditional kirana stores and an expanding online grocery sector. This wide availability of shopping channels significantly bolsters customer bargaining power.
Customers can easily compare prices, product assortments, and service quality across these diverse retail formats. For instance, the Indian online grocery market alone saw significant growth, with reports indicating it reached over $10 billion in 2023 and is projected to continue its upward trajectory, offering consumers competitive pricing and convenience that puts pressure on physical retailers.
Value-Driven Consumer Behavior
Indian consumers, especially the middle class that Avenue Supermarts (DMart) serves, are highly focused on getting the most value for their money. This trend has only strengthened, with many actively seeking out the best deals and discounts. DMart's core strategy of offering consistently low prices directly taps into this, but it also makes its customer base very sensitive to price shifts and competitor promotions.
This heightened price sensitivity means customers have significant bargaining power. They can easily switch to a competitor if a better price or offer is available. In 2024, with inflation remaining a concern for many households, this value-driven behavior is even more pronounced.
- Value Consciousness: Indian consumers, particularly in the middle-income bracket, prioritize affordability and seek maximum value in their purchases.
- Price Sensitivity: DMart's success is built on low prices, but this also means customers are quick to respond to price changes and competitor offers.
- Switching Behavior: The ease of switching between retailers based on price gives consumers considerable leverage.
- Impact of Inflation: Persistent inflation in 2024 reinforces the consumer focus on cost-saving, amplifying their bargaining power.
Information Accessibility
Information accessibility significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. As digital penetration grows, consumers can effortlessly compare prices, promotions, and stock levels from various retailers. This transparency forces businesses like Avenue Supermarts (DMart) to remain highly competitive on pricing to attract and retain shoppers.
In 2024, with e-commerce and online price comparison tools becoming even more ubiquitous, customers are better informed than ever. This readily available data means that a retailer's pricing strategy is under constant scrutiny. DMart, known for its value proposition, must continuously monitor competitor pricing to avoid losing market share to those offering perceived better deals.
- Increased Digital Penetration: Customers can easily access price and product information online.
- Price Transparency: This allows for quick comparisons across multiple retailers.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Customers are empowered to seek out the best value.
- Competitive Pressure: Retailers like DMart face pressure to maintain competitive pricing.
The bargaining power of customers for Avenue Supermarts (DMart) is substantial, driven by a highly price-sensitive Indian consumer base and low switching costs. With DMart's Everyday Low Pricing (EDLP) strategy, customers are conditioned to expect value, making them susceptible to competitor promotions and price changes. The continued rise of online retail and readily available price comparison tools in 2024 further amplifies this power, forcing DMart to maintain its competitive edge.
| Factor | Description | Impact on DMart |
| Price Sensitivity | Indian consumers, especially the middle class, prioritize affordability and seek maximum value. | Customers readily switch to competitors offering lower prices or better deals. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs to switch between grocery retailers. | Customers can easily move to other supermarkets, kirana stores, or online platforms. |
| Information Accessibility | Growing digital penetration allows easy price and promotion comparison. | DMart faces constant pressure to match or beat competitor pricing to retain customers. |
| Competitive Landscape | Numerous retail formats (physical and online) offer diverse choices. | Customers have a wide array of options, increasing their leverage. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Avenue Supermarts Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Avenue Supermarts Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape with insights into buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. The document you see here is precisely what you’ll receive immediately after purchase, offering a professionally formatted and ready-to-use strategic assessment. No mockups, no samples – what you're previewing is the exact, fully comprehensive analysis available for download.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian retail sector is a battleground dominated by formidable players like Reliance Retail and More Retail. These giants are rapidly expanding both their physical stores and online presence, intensifying competition. In 2024, Reliance Retail alone operates over 18,000 stores across various formats, showcasing their significant scale.
This aggressive expansion translates into fierce price wars and aggressive promotional campaigns. Such tactics directly impact DMart, as these large, well-funded competitors can absorb lower margins to capture market share, thereby increasing the competitive pressure.
The competitive rivalry in the retail sector is intensifying due to the rapid growth of quick commerce and online grocery platforms. Companies like Blinkit, Swiggy Instamart, and Zepto are capturing market share by offering unparalleled convenience and speed, directly challenging traditional brick-and-mortar retailers such as DMart.
This shift forces established players to enhance their digital capabilities. For instance, DMart has responded by expanding its own online grocery service, DMart Ready, to compete with these agile online-first businesses. The online grocery market in India saw significant growth, with reports indicating a valuation of over $3 billion in 2023, underscoring the intense competition DMart faces.
Avenue Supermarts faces heightened competitive rivalry due to aggressive store expansion by rivals. Many competitors are actively opening new outlets in both major cities and emerging Tier-2 and Tier-3 markets, increasing retail density. For instance, More Retail has been pursuing significant expansion, aiming to bolster its presence across India.
Product and Price Competition
Competitive rivalry within the Indian retail sector, particularly for Avenue Supermarts (DMart), is intense, especially in fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG). This fierce competition directly impacts profit margins as retailers frequently engage in price wars and offer discounts to attract and retain customers. For instance, in 2024, the grocery retail market saw aggressive promotional activities from both organized and unorganized players, forcing even efficient operators like DMart to maintain competitive pricing to protect market share.
Retailers continuously battle for market share through strategic pricing, aggressive discounts, and the implementation of loyalty programs. This constant pressure makes it difficult for any single player to sustain high profit margins without exceptional operational efficiency and stringent cost management. DMart's business model, focused on everyday low prices, relies heavily on volume and cost control to navigate this competitive landscape effectively.
- Intense FMCG Competition: The fast-moving consumer goods segment is a key battleground, characterized by frequent price adjustments and promotional offers from numerous players.
- Margin Pressures: Aggressive pricing strategies by competitors directly squeeze profit margins for all retailers, necessitating strong cost control measures.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Retailers utilize loyalty schemes and discounts as primary tools to capture and retain customer attention in a highly fragmented market.
- Operational Efficiency is Key: Maintaining profitability in this environment hinges on superior supply chain management and cost-effective operations.
Fragmented Unorganized Sector
Despite the significant expansion of organized retail in India, the unorganized sector, primarily composed of local kirana stores, continues to command a substantial portion of the market. This fragmented landscape, while often lacking advanced technology, remains a persistent competitive force. These neighborhood stores leverage their deep customer relationships, offering credit and personalized service that organized players find challenging to replicate.
The sheer density of these smaller outlets means they are often the most accessible option for consumers. For instance, in 2024, it's estimated that kirana stores still account for over 80% of grocery sales in many Indian cities, underscoring their enduring market presence. This proximity and convenience, coupled with their ability to offer small credit lines, creates a formidable barrier for larger retailers to fully displace them.
- Kirana Store Dominance: Unorganized retail, particularly kirana stores, still holds a majority market share in India's grocery sector as of 2024.
- Competitive Advantages: Proximity, personalized customer service, and the provision of credit are key strengths of the unorganized sector.
- Accessibility Factor: The widespread network of small, local stores ensures high accessibility for a large segment of the population.
- Persistent Threat: These factors make the unorganized sector a continuous competitive challenge for organized retail players like Avenue Supermarts.
Competitive rivalry for Avenue Supermarts is exceptionally high, driven by both large organized players and the persistent unorganized sector. Major retailers like Reliance Retail and More Retail are aggressively expanding their store networks and online presence, leading to intense price competition and promotional activities. This necessitates strong operational efficiency for DMart to maintain its everyday low-price strategy.
The rise of quick commerce platforms, such as Blinkit and Zepto, further intensifies this rivalry by offering speed and convenience, forcing traditional retailers to bolster their digital offerings. For instance, DMart Ready has been expanded to counter this trend. While organized retail grows, kirana stores continue to hold a significant market share, estimated at over 80% of grocery sales in many Indian cities in 2024, due to their proximity and customer relationships.
| Competitor | Store Count (Approx. 2024) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Reliance Retail | 18,000+ | Omnichannel expansion, diverse formats |
| More Retail | Expanding aggressively | Physical store growth across India |
| Quick Commerce (Blinkit, Zepto) | Rapidly growing | Speed and convenience, online focus |
| Unorganized Kirana Stores | Millions | Proximity, credit, personalized service |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Local kirana stores and traditional markets represent a significant threat of substitutes for Avenue Supermarts (DMart). These unorganized retail outlets cater to immediate needs and smaller purchase quantities, often providing a personalized touch and credit options that larger organized retailers may not. For instance, in 2024, the Indian retail sector still saw a substantial portion of its revenue coming from these traditional channels, highlighting their persistent relevance.
The rise of online grocery and quick commerce platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional hypermarkets like DMart. These digital players, exemplified by services promising delivery within minutes, cater to a growing consumer preference for convenience and speed. For instance, the quick commerce market in India saw substantial growth, with platforms like Zepto and Blinkit expanding their reach and customer base, particularly in urban centers where DMart also operates.
For specific product categories like apparel, electronics, or gourmet foods, customers can easily turn to specialty stores or niche retailers. These alternatives often boast a wider selection or superior quality, directly challenging the broad appeal of hypermarkets.
This trend unbundles the convenience of a one-stop shop, as shoppers can fulfill particular needs elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, the online apparel market continued its robust growth, with platforms like Myntra and Ajio offering extensive curated collections that directly compete with the apparel sections of larger retailers.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Brands
The increasing prevalence of direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands presents a significant threat of substitutes for Avenue Supermarts (DMart). These D2C brands, especially in sectors like personal care, food, and apparel, enable consumers to buy directly from manufacturers, circumventing traditional retail. This shift offers consumers unique or personalized products that can serve as alternatives to the general merchandise typically available at DMart.
For instance, in 2024, the global D2C e-commerce market continued its robust growth, with many emerging brands focusing on niche categories that directly compete with DMart's product assortment. Consumers are increasingly drawn to the perceived authenticity, specialized offerings, and often more direct engagement provided by these D2C players, potentially diverting sales from brick-and-mortar retailers like DMart.
- D2C Growth: The D2C model bypasses traditional retail, offering specialized products.
- Category Competition: D2C brands are strong in personal care, food, and apparel, areas where DMart operates.
- Consumer Appeal: D2C offers unique products and personalized experiences, attracting consumers away from general retailers.
- Market Impact: This trend can reduce DMart's market share by providing viable alternatives for consumer spending.
Home Delivery Services from Other Retailers
Many traditional and online retailers now offer robust home delivery services, presenting a direct substitute for visiting Avenue Supermarts DMart's physical locations. These services often include scheduled deliveries, catering to consumer demand for convenience. For instance, by the end of 2023, India's e-commerce market was valued at approximately USD 83.4 billion, with online grocery delivery being a significant segment, indicating a strong consumer shift towards delivered goods.
This increasing availability of convenient alternatives directly impacts DMart's in-store shopping model. Consumers can readily access groceries and household essentials through platforms that bring products directly to their doorstep, reducing the perceived necessity of a physical store visit. The growing preference for such services, especially in urban areas, heightens the threat of substitutes.
- Convenience Factor: Home delivery services by competitors offer a significant convenience advantage, directly challenging DMart's in-store model.
- Market Growth: The Indian e-commerce market, including online grocery delivery, experienced substantial growth in 2023, showcasing a clear consumer preference for delivered goods.
- Increased Substitutability: The proliferation of these delivery options makes it easier for consumers to switch away from DMart's physical stores.
The threat of substitutes for Avenue Supermarts (DMart) is multifaceted, encompassing traditional retail, online platforms, and direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands. Local kirana stores and traditional markets continue to serve immediate needs and smaller purchases, often with a personal touch. In 2024, these unorganized retail channels still accounted for a considerable portion of India's retail revenue, underscoring their enduring relevance.
Quick commerce and online grocery platforms pose a significant challenge by offering unparalleled convenience and speed, catering to evolving consumer preferences. For example, by the close of 2023, India's e-commerce market was valued at approximately USD 83.4 billion, with online grocery delivery being a key growth driver.
D2C brands, particularly in personal care, food, and apparel, provide specialized and often personalized alternatives, directly competing with DMart's product assortment. The global D2C e-commerce market saw robust growth in 2024, with many niche brands attracting consumers seeking unique offerings and direct engagement.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | DMart's Vulnerability | 2024 Market Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kirana Stores/Traditional Markets | Personalized service, small quantities, credit options | Caters to immediate needs, loyalty in specific segments | Still a significant revenue contributor in Indian retail |
| Online Grocery/Quick Commerce | Convenience, speed, home delivery | Challenges in-store footfall, preference for delivered goods | Indian e-commerce market valued at ~$83.4 billion in 2023; strong growth in online grocery |
| Specialty/Niche Retailers | Wider selection, perceived higher quality in specific categories | Reduces one-stop-shop appeal for certain product needs | Online apparel market continues robust growth |
| Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Brands | Unique products, personalized experience, direct engagement | Offers specialized alternatives, diverts spending from general retailers | Global D2C e-commerce market showed robust growth in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a hypermarket chain, especially one prioritizing owned physical stores like Avenue Supermarts (DMart), demands immense capital. For instance, in 2024, the cost of acquiring and developing prime retail real estate, coupled with inventory and operational setup, easily runs into hundreds of millions of dollars per large format store. This substantial financial outlay creates a significant barrier for potential new entrants looking to replicate DMart's brick-and-mortar success.
Avenue Supermarts, operating as DMart, leverages substantial economies of scale in procurement and operations. This allows them to negotiate better prices through bulk purchasing, optimize their supply chain for cost efficiency, and streamline store management. For instance, DMart's revenue per square foot was approximately ₹28,000 in FY2024, indicating highly efficient space utilization and sales volume that smaller competitors cannot easily match.
These scale advantages translate directly into DMart's 'Everyday Low Prices' strategy, a significant barrier for potential new entrants. A new player would find it extremely difficult to achieve comparable cost efficiencies in purchasing and operations from the outset, immediately placing them at a competitive price disadvantage against DMart's established infrastructure and purchasing power.
DMart's established brand recognition and deep customer loyalty, particularly among price-conscious middle-income households, present a significant barrier. This loyalty is built on years of consistent delivery of value. For instance, DMart's revenue grew by 30.5% to ₹46,300 crore in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, showcasing its strong market presence.
New competitors entering the market would face the daunting task of not only matching DMart's pricing strategy but also replicating the trust and familiarity it has cultivated. This requires substantial investment in marketing and a clear differentiation strategy to even begin chipping away at DMart's entrenched customer base.
Complex Supply Chain and Distribution Network
The intricate supply chain and distribution network developed by Avenue Supermarts, or DMart, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Building a similar infrastructure across numerous states demands substantial upfront investment, meticulous planning, and deep operational know-how. For instance, DMart's strategy of owning most of its store properties and managing its own logistics significantly reduces operating costs and ensures product availability, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly or affordably.
Replicating DMart's complex logistical framework to guarantee timely and cost-effective product availability across diverse regions is a formidable challenge. New players would need to invest heavily in warehousing, transportation fleets, and technology to achieve comparable efficiency. In the fiscal year 2024, DMart reported a robust revenue growth, underscoring the effectiveness of its operational model, which is built on this very logistical strength.
- Logistical Expertise: DMart's success is underpinned by its highly efficient supply chain, which minimizes costs and ensures product freshness, a critical factor in the grocery retail sector.
- Infrastructure Investment: Establishing a comparable network of distribution centers and transportation requires billions in capital expenditure, a significant hurdle for potential new entrants.
- Operational Scale: Achieving the scale necessary to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers and manage inventory effectively is a long-term process that new entrants would struggle to match.
- Cost Advantage: DMart's integrated model, from sourcing to delivery, provides a substantial cost advantage that new competitors would find difficult to overcome in the short to medium term.
Regulatory and Real Estate Challenges
New entrants to the Indian retail market face substantial regulatory hurdles and difficulties in securing prime real estate. Navigating the country's complex and varied regulatory landscape, from obtaining licenses to adhering to specific state-level compliance, demands significant time and resources. For instance, in 2024, the process for obtaining retail licenses can still vary considerably across different Indian states, adding layers of complexity for any new player looking to scale operations efficiently.
The acquisition of suitable real estate, particularly for large-format stores like those operated by Avenue Supermarts, presents another formidable barrier. Zoning laws, building permits, and the sheer cost of property, especially in densely populated urban centers, can be prohibitive. In major metropolitan areas like Mumbai or Delhi, the cost per square foot for commercial retail space can easily run into thousands of Indian Rupees, making it challenging for newcomers to compete with established players who have already secured favorable locations.
- Regulatory Complexity: Diverse state-specific regulations and licensing requirements in India increase operational setup costs and time for new entrants.
- Real Estate Acquisition Costs: High property prices and limited availability of large, well-located retail spaces in prime Indian urban areas act as a significant barrier.
- Zoning and Permitting: Stringent zoning laws and the lengthy process of obtaining building permits further delay market entry and inflate initial investment.
The threat of new entrants for Avenue Supermarts (DMart) is generally considered low due to several significant barriers. The immense capital required to establish a similar retail footprint, coupled with the need for extensive supply chain and logistical infrastructure, makes market entry highly challenging for newcomers.
DMart's established economies of scale, cost leadership through efficient operations, and strong brand loyalty further solidify its position. For instance, DMart's revenue growth of 30.5% to ₹46,300 crore in FY2024 demonstrates its market dominance, making it difficult for new players to compete on price and value.
Additionally, navigating India's complex regulatory environment and securing prime real estate are substantial hurdles. These factors combined create a formidable barrier, effectively limiting the likelihood of new, significant competitors emerging to challenge DMart's market share.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | DMart's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of real estate, inventory, and operations. | Prohibitive for most potential entrants. | Established financial strength and access to capital. |
| Economies of Scale | Bulk purchasing, efficient supply chain, optimized operations. | Inability to match DMart's cost efficiencies and pricing. | Lower cost of goods sold, enabling EDLP strategy. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Years of consistent value delivery and customer recognition. | Difficulty in attracting price-sensitive customers. | Strong customer base and repeat purchases. |
| Logistical & Supply Chain | Integrated, efficient network for product availability and cost control. | Significant investment and time needed to build comparable infrastructure. | Reduced operating costs, better inventory management. |
| Regulatory & Real Estate | Complex licensing, zoning laws, and high property costs. | Delays market entry, increases setup costs. | Existing prime locations and established regulatory compliance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Avenue Supermarts is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms.
We also incorporate data from regulatory filings, news articles, and competitor announcements to capture a comprehensive view of the retail landscape and Avenue Supermarts' competitive position.