CK Hutchison Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CK Hutchison Bundle
CK Hutchison operates in a dynamic telecom and infrastructure landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is paramount. Our analysis reveals how buyer power, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry significantly shape its market position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore CK Hutchison’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CK Hutchison's extensive global operations, spanning ports, retail, infrastructure, energy, and telecommunications, mean it interacts with a vast and varied array of suppliers worldwide. This sheer diversity in its supplier network inherently dilutes the individual bargaining power of any single supplier. For instance, in 2023, CK Hutchison's procurement likely involved thousands of vendors across numerous categories, from raw materials for infrastructure projects to advanced technology for its telecom divisions.
The company's capacity to source goods and services from a global pool of providers grants it significant flexibility and leverage during negotiations. If one supplier's terms become unfavorable, CK Hutchison can readily explore alternatives from different regions, thereby mitigating the risk of over-reliance and strengthening its position at the bargaining table.
In critical infrastructure and specialized component sectors, such as those CK Hutchison operates within, the bargaining power of suppliers can be significantly amplified. This is particularly true when the number of qualified or specialized suppliers for essential equipment, like advanced telecommunications network components, is limited. For instance, a supplier holding a patent for a crucial 5G network element might command substantial leverage.
Geopolitical shifts are increasingly impacting supplier bargaining power. For example, heightened tensions in regions vital for global trade routes can lead to supply chain vulnerabilities. This was evident in 2024 as several nations implemented new trade restrictions, directly affecting the cost and availability of key components for multinational corporations.
The strategic importance of certain suppliers, often amplified by political considerations, can significantly enhance their leverage. The 2024 acquisition of critical infrastructure assets by politically aligned entities demonstrated how national interests can reshape supplier dynamics, potentially dictating terms and increasing costs for businesses reliant on those resources.
Energy Sector Specifics
Within CK Hutchison's diverse operations, the energy sector presents a distinct challenge regarding supplier bargaining power. Suppliers of essential raw materials like oil and gas often wield significant influence. This is largely due to the finite nature of national reserves and the complex dynamics of global commodity markets. CK Hutchison's operations, particularly those with energy dependencies, are therefore vulnerable to price volatility and potential supply disruptions stemming from decisions made by major resource-producing countries or cartels.
This elevated supplier power in energy contrasts sharply with segments where suppliers are more numerous and fragmented, leading to a more balanced negotiation landscape. For instance, in 2024, oil prices experienced notable fluctuations, with Brent crude averaging around $83 per barrel for the year, impacting the cost base for energy-intensive operations within CK Hutchison. This highlights the direct financial implications of strong supplier leverage.
- High Supplier Power: In energy, suppliers of oil and gas have substantial bargaining power due to limited reserves and global market control.
- Price Volatility Impact: CK Hutchison faces risks from fluctuating energy prices, directly affecting operational costs and profitability.
- Geopolitical Influence: Decisions by major oil and gas producing nations or cartels can dictate supply and pricing for the company.
- Contrast with Other Segments: Supplier power in energy is notably higher than in sectors with more fragmented supply chains.
Telecommunications Network Dependencies
CK Hutchison's telecommunications operations are significantly influenced by its suppliers for critical network infrastructure, spectrum licenses, and essential software. The ongoing investment in 5G deployment and network upgrades means reliance on a potentially concentrated market of advanced telecom equipment manufacturers, such as Ericsson and Nokia, which can wield substantial bargaining power due to limited competition in specialized areas. For instance, in 2024, the global 5G infrastructure market was dominated by a few key players, with vendors like Huawei, Ericsson, and Nokia capturing a significant share, potentially limiting CK Hutchison's negotiation leverage on pricing and terms.
Furthermore, governments act as powerful suppliers through the allocation and regulation of spectrum licenses, a fundamental component for any mobile network operator. The terms and conditions associated with these licenses, including fees and coverage obligations, directly impact CK Hutchison's operational costs and strategic flexibility. In 2024, spectrum auctions continued globally, with countries like Germany seeing substantial bids, underscoring the high cost and government control over this vital resource.
- Network Infrastructure Dependence: CK Hutchison relies on a limited number of major global vendors for advanced 5G equipment, creating supplier leverage.
- Spectrum Licensing Power: Governments control crucial spectrum licenses, dictating terms and costs for telecommunications operations.
- Software Solutions: The need for specialized network management and operational software further concentrates supplier power.
CK Hutchison's diverse operations mean supplier bargaining power varies significantly across its business segments. In sectors like energy, suppliers of raw materials can exert considerable influence due to market concentration and geopolitical factors, as seen with oil price fluctuations in 2024. Conversely, in telecommunications, while key equipment manufacturers hold leverage due to limited competition in advanced technologies, governments acting as spectrum license suppliers also play a critical role in shaping terms and costs.
| Segment | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor | Example/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | High (Market Concentration, Geopolitics) | Oil and gas suppliers; 2024 Brent crude average ~$83/barrel impacting costs. |
| Telecommunications | Moderate to High (Technology Specialization, Government Regulation) | 5G equipment vendors (e.g., Ericsson, Nokia); Government spectrum licenses (e.g., high auction costs in Germany 2024). |
| Ports & Logistics | Low to Moderate (Fragmented Supply Base) | Suppliers of port equipment, IT services; Large volume can drive down prices. |
What is included in the product
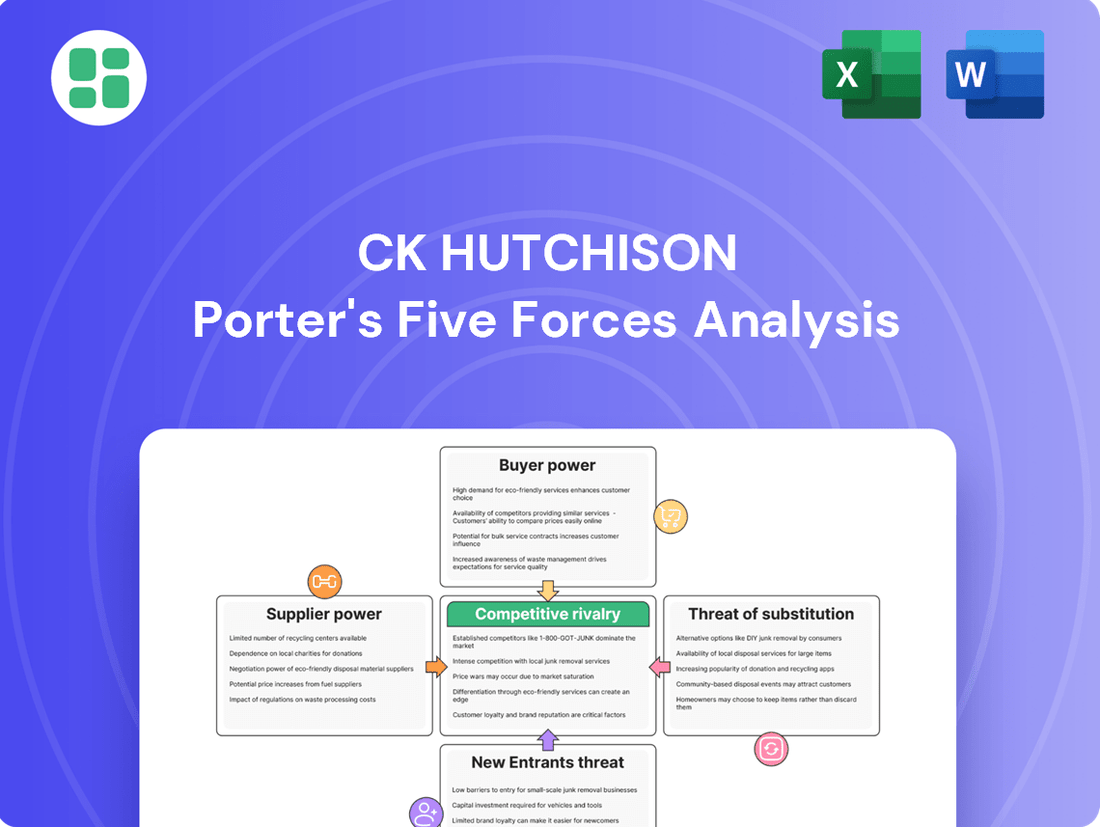
Tailored exclusively for CK Hutchison, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes across its diverse business segments.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape for CK Hutchison's diverse portfolio, highlighting key threats and opportunities across its telecom, infrastructure, and retail operations.
Customers Bargaining Power
CK Hutchison's retail arm, AS Watson Group, boasts an immense global presence with over 16,900 stores, serving a remarkably fragmented customer base. This wide dispersion of individual shoppers means each customer, on their own, wields very little direct bargaining power.
However, the sheer volume of choices available to consumers in the competitive retail landscape significantly amplifies their collective influence. This forces CK Hutchison to remain highly attentive to pricing and service standards to retain its customer base.
To counter this diffuse yet potent customer pressure, AS Watson strategically deploys loyalty programs and a broad product assortment. These initiatives aim to foster customer stickiness and differentiate its offerings, thereby mitigating the inherent bargaining power of a fragmented market.
In the competitive telecommunications landscape, customers often wield considerable bargaining power. This is largely due to the presence of numerous providers and, in many regions, the ease with which consumers can switch between them. For instance, in 2023, the European telecommunications market saw intense competition, with average monthly mobile plan costs varying significantly across countries, reflecting customer price sensitivity.
CK Hutchison's 3 Group Europe actively works to solidify its contract customer base by offering adaptable pricing structures. This strategy acknowledges the significant influence customers have, particularly concerning their willingness to remain with a provider. High customer churn rates, a common challenge in the sector, directly demonstrate this customer power and the imperative for companies to offer compelling value.
CK Hutchison's port operations serve major global shipping lines and logistics firms, who are significant customers. These entities, by virtue of the substantial cargo volumes they manage, possess considerable leverage. This allows them to negotiate favorable terms on port fees and service agreements, directly impacting CK Hutchison's revenue streams.
In 2024, the global shipping industry continued to see consolidation. For instance, Maersk and MSC, two of the world's largest container shipping companies, maintained their dominant positions, handling millions of TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) annually. This scale empowers them to demand competitive pricing from port operators like CK Hutchison, as switching costs, while present, are manageable for such large players.
The ongoing trend of vertical integration within the shipping sector further amplifies customer bargaining power. Shipping lines are increasingly investing in their own logistics networks and, in some cases, port infrastructure. This strategic move grants them greater control over their supply chains and strengthens their negotiating stance with third-party port service providers, including CK Hutchison.
Infrastructure Project Clients
In the infrastructure sector, clients are often government entities, municipalities, or major industrial firms undertaking substantial, long-term projects. This concentration of large buyers grants them considerable bargaining power.
These clients wield significant leverage due to the immense scale of their investments, the extended duration of infrastructure contracts, and the highly competitive, often rigorous, tender processes. For instance, major public infrastructure projects frequently involve multi-billion dollar budgets, allowing clients to dictate terms.
- High Value, Long-Term Commitments: Clients in infrastructure projects, such as those for national transportation networks or energy grids, commit vast sums over many years, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms.
- Rigorous Bidding Processes: Government tenders and large corporate procurement processes are designed to elicit the lowest possible prices and best terms, intensifying client bargaining power.
- Project-Specific Negotiations: The unique nature of each infrastructure project allows clients to negotiate terms and conditions tailored to their specific needs, further enhancing their influence.
- Potential for Switching: While switching costs can be high for clients once a project is underway, the initial bidding phase offers ample opportunity to compare and select providers based on price and contractual flexibility.
Diversified Customer Segments
CK Hutchison's diverse business portfolio means customer bargaining power isn't uniform. In its retail and telecommunications arms, where competition is often fierce, individual and collective customer power can be more pronounced. For instance, mobile service providers often face intense competition, leading to price sensitivity among subscribers.
However, in segments like ports and infrastructure, customer relationships tend to be more balanced. Long-term contracts and the strategic nature of these services often create a more stable, less price-volatile dynamic. CK Hutchison's global footprint also helps to mitigate the impact of concentrated customer power in any single region.
- Retail and Telecom: High competition often grants customers significant leverage due to readily available alternatives.
- Ports and Infrastructure: Long-term contracts and the specialized nature of services can reduce customer bargaining power, fostering more stable relationships.
- Global Diversification: CK Hutchison's international operations allow it to balance regional customer dynamics and reduce reliance on any single market's customer base.
In CK Hutchison's retail operations, the sheer number of consumers means individual bargaining power is minimal. However, the collective purchasing power of millions of shoppers, especially in price-sensitive markets, forces the company to maintain competitive pricing and service levels to retain loyalty.
For its telecommunications segment, CK Hutchison's 3 Group faces customers who can easily switch providers, especially in competitive European markets where average monthly mobile plan costs can vary significantly. This necessitates flexible pricing and strong customer retention strategies.
CK Hutchison's port operations deal with large shipping lines, such as Maersk and MSC, which handle millions of TEUs annually. These major clients possess substantial leverage, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms on port fees due to their significant cargo volumes and the manageable switching costs for their scale of operations.
In infrastructure, CK Hutchison's clients are typically large government entities or industrial firms undertaking massive, long-term projects. The immense scale of these investments and the rigorous tender processes grant these clients significant bargaining power, allowing them to dictate terms and secure the most competitive pricing.
| Segment | Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on CK Hutchison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail (AS Watson) | Individual Consumers | High volume, price sensitivity, brand switching | Pressure on pricing, need for loyalty programs |
| Telecommunications (3 Group) | Mobile/Broadband Subscribers | Ease of switching, competitive market, contract flexibility | Need for competitive plans, focus on churn reduction |
| Ports | Major Shipping Lines (e.g., Maersk, MSC) | High cargo volume, strategic importance, manageable switching costs | Negotiation on fees, service level agreements |
| Infrastructure | Government, Large Industrial Firms | Large project scale, long-term contracts, competitive bidding | Influence on contract terms, pricing |
Same Document Delivered
CK Hutchison Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CK Hutchison Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a detailed examination of the competitive landscape for the company. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally written and formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
CK Hutchison faces fierce competition across its varied global operations. In the telecommunications sector, for instance, it contends with established players like Vodafone and Deutsche Telekom in Europe, alongside nimble regional operators. Its retail arm, including brands like Watsons, battles intense rivalry from global giants such as Walmart and Amazon, as well as specialized beauty and health retailers.
The infrastructure and energy segments also see significant competition. In ports, CK Hutchison competes with major operators like DP World and Maersk's APM Terminals, which manage extensive global networks. In 2024, the global container port market continues to see consolidation and strategic alliances, intensifying the pressure on individual operators to innovate and optimize efficiency.
The European telecommunications sector, a key battleground for CK Hutchison's 3 Group Europe, is highly fragmented. This fragmentation means there are many players vying for customers, leading to aggressive price wars. For instance, in 2023, many European mobile operators reported declining average revenue per user (ARPU) as they competed on price to attract and retain subscribers.
This intense rivalry forces companies like 3 Group Europe to constantly invest in new technologies, such as 5G, to differentiate themselves and avoid becoming commodities. The pressure to upgrade networks while facing shrinking ARPU highlights the challenging competitive dynamics within the European market.
CK Hutchison faces intense competition from other global port operators, many of whom are also investing heavily in expanding their networks and modernizing facilities. For instance, DP World, a major competitor, reported handling 73.1 million TEUs across its global terminals in 2023, highlighting the scale of operations and the competitive landscape.
The trend of vertical integration by large shipping lines, such as MSC and Maersk, further intensifies rivalry. These lines are increasingly acquiring or partnering with port facilities to secure their supply chains, directly challenging traditional port operators for market share and operational control.
Geopolitical considerations, particularly around strategically vital trade routes like the Panama Canal, add another layer of complexity. Fluctuations in trade volumes and potential shifts in control or investment in such key infrastructure can significantly alter competitive dynamics and influence asset valuations for operators like CK Hutchison.
High Competition in Retail
The retail landscape, especially within health and beauty where AS Watson Group thrives, is intensely competitive. This sector is populated by a multitude of local and global brands, further intensified by the rapid expansion of e-commerce. CK Hutchison leverages its vast store footprint and varied brand offerings as significant strengths. However, to stay ahead, continuous investment in new product development, sharp pricing tactics, and superior customer engagement are crucial for retaining market dominance.
The intensity of this rivalry is evident in market share shifts. For instance, in 2024, the global beauty market was projected to reach over $500 billion, showcasing the sheer scale and attractiveness of the sector, but also the fierce battle for consumer spending. AS Watson's ability to adapt to evolving consumer preferences, such as the increasing demand for sustainable and personalized products, directly impacts its competitive standing.
- Intense Competition: The health and beauty retail sector is crowded with both established chains and nimble online retailers.
- E-commerce Impact: Online channels are increasingly capturing market share, forcing traditional retailers to enhance their digital presence.
- AS Watson's Strengths: A broad store network and diverse brand portfolio provide a solid foundation against rivals.
- Need for Innovation: Constant adaptation in product offerings, pricing, and customer experience is vital for sustained market share.
Infrastructure Investment Landscape
The infrastructure sector, despite its capital-intensive nature and lengthy project cycles, experiences robust competition for significant undertakings. CK Hutchison, via its subsidiary CK Infrastructure Holdings, contends with numerous global infrastructure funds and major construction firms for lucrative contracts.
CK Infrastructure Holdings’ broad asset base, spanning utilities, transport, and telecommunications, offers a distinct advantage. However, the pursuit and acquisition of new infrastructure projects remain a highly competitive arena, demanding continuous strategic positioning and financial strength.
- Global Competition: CK Infrastructure Holdings competes with entities like Brookfield Asset Management, Macquarie Group, and Vinci SA, all of which manage substantial infrastructure portfolios and actively bid on large-scale projects worldwide.
- Project Bidding: In 2023, major infrastructure tenders, such as those for offshore wind farm development in Europe or new airport expansions in Asia, attracted bids from multiple consortia, highlighting the intense rivalry for these capital-intensive opportunities.
- Diversification as an Edge: CK Infrastructure Holdings' presence in diverse infrastructure segments, including ports, energy, and water, allows it to leverage expertise across different project types, potentially offering more integrated solutions than less diversified competitors.
CK Hutchison faces intense rivalry across its diverse business segments, particularly in telecommunications where its 3 Group Europe contends with numerous established operators. This competition often leads to price wars, as seen in 2023 when many European mobile providers reported declining average revenue per user due to aggressive pricing strategies to retain subscribers.
In the ports sector, CK Hutchison's operations are challenged by global giants like DP World and APM Terminals. DP World, for instance, handled 73.1 million TEUs in 2023, underscoring the scale of competition. Furthermore, shipping lines are increasingly integrating vertically, acquiring port facilities which directly intensifies rivalry for market share.
The retail arm, AS Watson Group, operates in the highly competitive health and beauty market, a sector projected to exceed $500 billion globally in 2024. Success hinges on continuous innovation in product offerings, pricing, and customer engagement to counter the growing influence of e-commerce and numerous local and international brands.
CK Infrastructure Holdings navigates a competitive landscape for major infrastructure projects, bidding against global funds and construction firms. For example, significant infrastructure tenders in 2023, such as offshore wind farms, attracted multiple consortia, demonstrating the fierce competition for capital-intensive opportunities.
| Segment | Key Competitors | 2023/2024 Data Point | Competitive Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications (Europe) | Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom | Declining Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) reported by many operators in 2023 | High (Price wars, need for 5G investment) |
| Ports | DP World, APM Terminals | DP World handled 73.1 million TEUs in 2023 | High (Vertical integration by shipping lines, global expansion) |
| Retail (Health & Beauty) | Walmart, Amazon, local brands | Global beauty market projected >$500 billion in 2024 | Very High (E-commerce growth, intense product/pricing competition) |
| Infrastructure | Brookfield Asset Management, Macquarie Group, Vinci SA | Multiple consortia bidding on major tenders in 2023 | High (Capital intensity, global competition for projects) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Digital and over-the-top (OTT) services present a substantial threat to traditional telecommunications. Applications like WhatsApp and Telegram offer messaging and voice calls, directly competing with SMS and mobile voice services, which historically contributed significantly to Average Revenue Per User (ARPU). Furthermore, streaming platforms are increasingly replacing linear television, impacting pay-TV revenues for telecom providers.
The rise of Voice-over-IP (VoIP) technology, integrated into many OTT platforms, directly substitutes traditional circuit-switched voice calls. This shift erodes revenue streams for mobile and fixed-line operators. For instance, global mobile ARPU has seen pressure due to the widespread adoption of these free or low-cost digital alternatives.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) is also emerging as a potent substitute for traditional fixed broadband. As FWA technology improves and becomes more accessible, it offers an alternative to fiber or DSL connections, particularly in areas where fixed infrastructure deployment is costly or slow. This can limit the growth and pricing power of incumbent fixed broadband providers.
The rise of e-commerce presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional brick-and-mortar retailers like AS Watson Group, a key part of CK Hutchison. Consumers are increasingly drawn to online platforms for their convenience, vast product selections, and often more competitive pricing. This shift directly challenges the established retail models, forcing companies to re-evaluate their strategies.
In 2024, global e-commerce sales were projected to reach approximately $6.3 trillion, underscoring the substantial market share captured by online channels. This growth indicates a clear consumer preference for digital shopping experiences, making it imperative for CK Hutchison's retail operations to bolster their omnichannel capabilities to remain competitive.
For port services, direct substitutes for ocean freight are scarce, especially for bulk cargo. However, air freight serves as a substitute for high-value or time-sensitive goods, offering faster transit but at a significantly higher cost. In 2024, air cargo rates have seen fluctuations, with some routes experiencing increased demand, making it a viable, albeit premium, alternative for specific cargo types.
Enhanced rail and road networks also act as partial substitutes, particularly for inland distribution and last-mile delivery. These alternatives become more attractive when port congestion or delays occur, as seen during periods of supply chain strain. For instance, in early 2024, several major ports experienced congestion, leading some businesses to reroute cargo via extensive rail networks to bypass maritime bottlenecks.
Global logistics solutions are also influenced by disruptions. Events like the Panama Canal drought in late 2023 and early 2024 forced shippers to consider longer, alternative sea routes or even a combination of sea and land transport, highlighting the limited but impactful nature of substitutes when primary routes are compromised.
Renewable Energy Alternatives
The accelerating global shift towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional energy infrastructure. By the end of 2023, renewable energy capacity additions reached a record 510 gigawatts globally, a 50% increase from 2022, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This rapid expansion directly challenges the long-term viability of fossil fuel-dependent assets.
CK Hutchison's infrastructure portfolio, while diversified, still includes significant investments in traditional energy. As renewables become more cost-competitive and government policies increasingly favor clean energy, the demand for and profitability of these legacy assets could diminish. For instance, the levelized cost of electricity for utility-scale solar PV fell by 89% between 2010 and 2022.
- Accelerating Global Adoption: Renewable energy capacity saw a 50% surge in additions in 2023 compared to 2022, reaching 510 GW.
- Cost Competitiveness: The cost of solar PV has decreased by nearly 90% since 2010, making it a more attractive alternative.
- Policy Support: Government incentives and mandates worldwide are increasingly favoring renewable energy deployment.
- Infrastructure Transition: The growing prevalence of renewables necessitates adaptation or replacement of existing traditional energy infrastructure.
Emerging Technologies as Substitutes
Emerging technologies pose a significant threat of substitution across many industries. For example, in telecommunications, satellite internet services such as Starlink are increasingly offering an alternative to traditional mobile and fixed broadband, particularly in underserved regions. This trend could reduce demand for conventional infrastructure.
Furthermore, advancements in automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to replace certain human-led services and established operational processes. Companies must continually adapt and adopt new technologies to remain competitive and avoid being disrupted by these evolving substitutes.
- Satellite Internet Growth: Starlink, by SpaceX, aims to provide global broadband coverage, with over 2.7 million subscribers as of early 2024, directly challenging traditional providers in some markets.
- AI in Services: The global AI market was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a substantial shift towards AI-powered solutions that can substitute human labor in various service sectors.
- Automation Impact: Industrial automation is expected to save businesses billions annually, with estimates suggesting that by 2025, AI could be responsible for automating tasks that currently occupy 30% of workers' time.
The threat of substitutes for CK Hutchison is multifaceted, impacting its diverse business segments. In telecommunications, digital and over-the-top (OTT) services like WhatsApp directly compete with traditional messaging and voice calls, eroding ARPU. Similarly, e-commerce platforms present a significant substitute for AS Watson's brick-and-mortar retail operations, with global e-commerce sales projected to reach $6.3 trillion in 2024.
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are increasingly substituting traditional energy infrastructure, evidenced by a 50% surge in renewable capacity additions in 2023 and an 89% fall in solar PV costs since 2010. Emerging technologies, such as satellite internet and AI, also pose substitution threats, with Starlink serving over 2.7 million subscribers by early 2024 and AI projected to automate tasks for 30% of workers by 2025.
| Business Segment | Key Substitutes | Impact/Data Point (2024 unless specified) |
|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | OTT Messaging & Voice (WhatsApp, Telegram) | Erosion of ARPU from traditional SMS/voice services. |
| Retail (AS Watson) | E-commerce Platforms | Global e-commerce sales projected at $6.3 trillion. |
| Infrastructure (Energy) | Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind) | 510 GW of renewable capacity added globally in 2023; Solar PV costs down 89% since 2010. |
| Technology/Services | Satellite Internet (Starlink), AI/Automation | Starlink subscribers > 2.7 million (early 2024); AI to automate 30% of worker tasks by 2025. |
Entrants Threaten
CK Hutchison's core operations, including ports, telecommunications, and infrastructure, demand massive upfront capital. For instance, building a new 5G network can cost billions of dollars in spectrum licenses and infrastructure deployment, effectively deterring smaller players from entering the market.
The telecommunications sector, a core area for CK Hutchison, presents substantial regulatory complexities. For instance, securing spectrum licenses, essential for mobile network operation, involves costly and lengthy auction processes. In 2024, spectrum auctions in various European markets continued to demand billions of euros, creating a significant barrier to entry for smaller, less capitalized firms.
CK Hutchison's vast economies of scale and scope present a significant barrier to new entrants. For instance, in 2023, the company's telecommunications segment, Hutchison Telecommunications Hong Kong Holdings, reported revenue of HK$12.3 billion, demonstrating the sheer volume of its operations. This scale allows for substantial cost advantages in areas like network infrastructure investment and spectrum acquisition, making it incredibly challenging for newcomers to compete on price or service breadth.
The integrated nature of CK Hutchison's diverse businesses, from ports and infrastructure to retail and telecommunications, further amplifies this advantage. New entrants would find it difficult to replicate the synergistic benefits and cross-promotional opportunities that CK Hutchison leverages across its global portfolio. This complexity and reach create a formidable hurdle for any aspiring competitor aiming to gain market traction quickly.
Established Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
CK Hutchison benefits from deeply entrenched brand recognition, particularly in its retail and telecommunications sectors. Brands like Watsons and 3 have cultivated significant customer loyalty over years of operation. This loyalty creates a substantial barrier for any new company attempting to enter these markets.
New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and promotional activities to even begin to chip away at the existing brand equity. For instance, Watsons, a leading health and beauty retailer, boasts a vast store network and a well-established online presence, making it difficult for newcomers to match its reach and customer familiarity. In 2023, Watsons continued its expansion, opening new stores across various markets, reinforcing its market position.
- Brand Strength: CK Hutchison’s brands, such as Watsons and 3, possess high levels of consumer trust and recognition.
- Customer Loyalty: A substantial existing customer base is less likely to switch to new, unproven competitors.
- Marketing Barriers: New entrants face high customer acquisition costs due to the need to build brand awareness and overcome established loyalty.
- Market Penetration: The sheer number of existing touchpoints for brands like Watsons (e.g., over 1,600 stores in Hong Kong and Macau as of recent reports) makes it challenging for new players to achieve similar market penetration quickly.
Network Effects and Existing Infrastructure
The threat of new entrants for CK Hutchison, particularly in sectors like telecommunications and ports, is significantly mitigated by powerful network effects and established infrastructure. The more users a telecommunications network has, the more valuable it becomes to each individual user, creating a strong barrier for newcomers trying to gain traction. Similarly, port operations benefit from established logistical chains and customer relationships built over time.
CK Hutchison leverages its existing, extensive networks and infrastructure, which represent substantial upfront investments. For instance, in the UK, its Three network has been a significant player, and building a comparable mobile network from the ground up requires billions in capital expenditure and years to achieve the same coverage and capacity. This existing footprint makes it incredibly challenging and costly for a new competitor to build a competitive alternative and attract a critical mass of users or clients.
- Network Effects: In telecommunications, the value of a network grows exponentially with each additional user, a phenomenon well-documented in the industry.
- Infrastructure Investment: Building a new mobile network comparable to existing ones can cost tens of billions of dollars, as seen in recent 5G spectrum auctions. For example, UK operators spent billions acquiring 5G spectrum licenses in 2022.
- Customer Loyalty: Established providers benefit from customer inertia and switching costs, making it harder for new entrants to poach subscribers.
- Economies of Scale: Existing operators enjoy lower per-unit costs due to their scale, further disadvantaging smaller, new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for CK Hutchison is generally low due to the immense capital requirements and established infrastructure across its key sectors like ports and telecommunications. Building a new port facility or a nationwide 5G network demands billions in investment and years of development, creating significant hurdles for potential competitors.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments, particularly in telecommunications, with costly spectrum auctions and licensing processes, act as powerful deterrents. For instance, in 2024, European countries continued to see spectrum bids reaching billions of euros, a sum often beyond the reach of new, smaller entities.
CK Hutchison's established brand loyalty, particularly in retail and mobile services, and its extensive economies of scale further solidify its market position. For example, Watsons, a flagship retail brand, operated over 1,600 stores in Hong Kong and Macau by recent reports, a scale difficult for newcomers to match quickly.
The synergistic advantages derived from its diversified business portfolio also present a formidable challenge for any new entrant seeking to replicate its integrated operational model.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for CK Hutchison is built upon a robust foundation of data, including their annual reports, investor presentations, and financial filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms and market intelligence platforms to capture competitive dynamics.