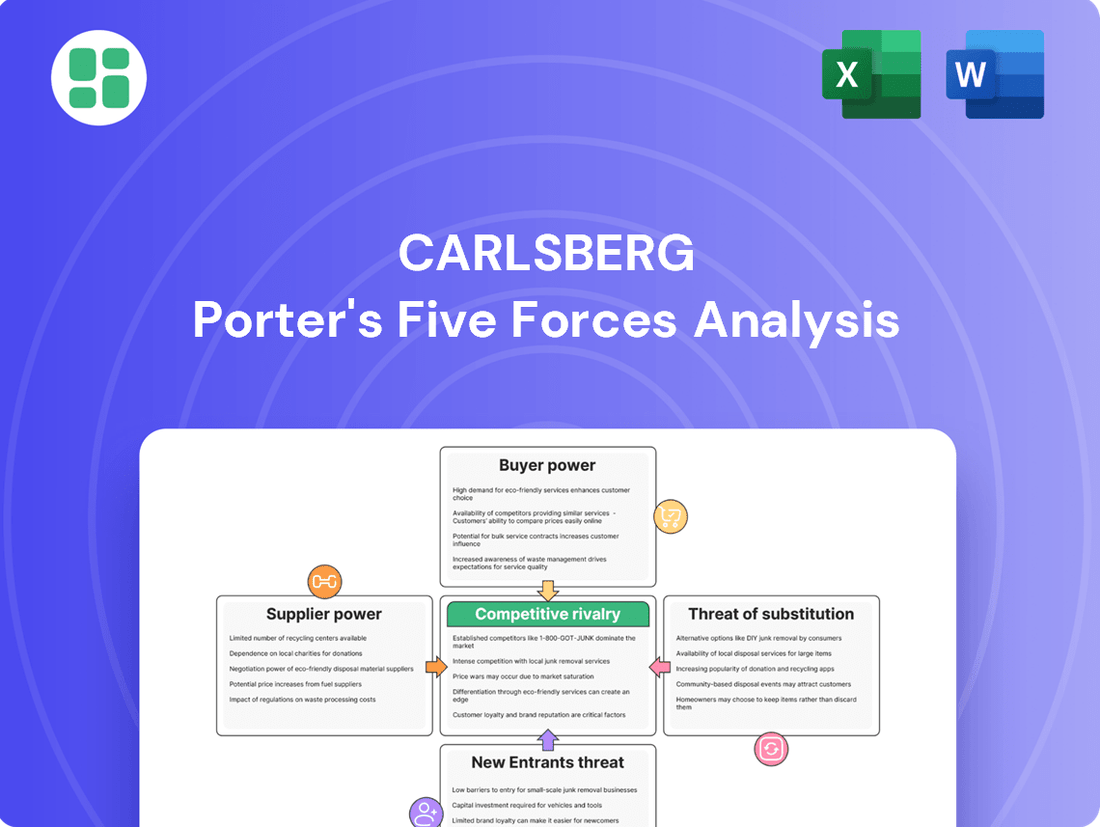
Carlsberg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Carlsberg Bundle
Carlsberg navigates a complex beer market, facing intense rivalry from global and local players, while also contending with the growing influence of powerful buyers and the constant threat of substitutes like wine and spirits. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Carlsberg’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The brewing industry's dependence on essential inputs like malted barley, hops, yeast, and water, alongside packaging materials such as cans and glass, highlights potential supplier influence. While water is often a local commodity, the global concentration of hop and specialty malt markets can grant suppliers considerable bargaining power.
However, Carlsberg's substantial global presence and sophisticated supply chain management are instrumental in mitigating this. By centralizing procurement for critical categories, the company can leverage its scale to negotiate more favorable terms and conditions, thereby reducing the impact of concentrated supplier markets.
Switching costs for Carlsberg's suppliers can be moderate to high, particularly concerning specialized ingredients or proprietary brewing equipment. Establishing new supplier relationships, ensuring consistent quality, and adapting production processes all represent significant investments in both time and capital for Carlsberg.
For instance, if a key supplier of a unique yeast strain or a specialized bottling line component were to change terms, Carlsberg would face the challenge of finding an equivalent, testing it rigorously, and potentially retooling production. This process is not only costly but also time-consuming, potentially disrupting supply chains.
Carlsberg's strategy of cultivating long-term, stable relationships with its suppliers is crucial in managing these switching costs. These established partnerships often involve volume commitments and collaborative forecasting, which can lead to more favorable terms and a greater willingness from suppliers to invest in meeting Carlsberg's specific needs, thereby reducing the perceived threat of supplier power.
The availability of substitute inputs for Carlsberg's core brewing ingredients, like malt, hops, and yeast, is somewhat limited, meaning suppliers of these essential components hold considerable sway. While there's some variation possible in the specific types of malt or hops used, finding readily available, equally suitable alternatives for the foundational elements of beer production is challenging. This constraint empowers suppliers, as Carlsberg relies on them for consistent quality and supply.
Supplier's Ability for Forward Integration
The likelihood of raw material suppliers integrating forward into brewing is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment, intricate distribution channels, and strong brand recognition inherent in the brewing sector. Suppliers typically lack the extensive infrastructure and established market presence needed to effectively challenge major breweries like Carlsberg.
For instance, the global brewing industry, valued at over $700 billion in 2023, demands significant upfront investment in production facilities, marketing, and distribution networks. Suppliers of ingredients such as barley or hops, while crucial, usually do not possess the scale or expertise to navigate these complexities and compete directly with established players. Their core competencies lie in agricultural production or ingredient processing, not in large-scale beverage manufacturing and consumer brand building.
- Low Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers of raw materials like barley, hops, and packaging materials face significant barriers to entry in the brewing industry.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing breweries requires massive capital outlays for plant, equipment, and distribution infrastructure, which most suppliers cannot afford.
- Brand Loyalty and Distribution: Established brewers like Carlsberg benefit from decades of brand building and extensive, efficient distribution networks, difficult for new entrants to replicate.
- Lack of Expertise: Suppliers' expertise typically lies in sourcing and processing raw materials, not in the complex operations of brewing, marketing, and sales of finished beer products.
Impact of Raw Material Price Fluctuations
Fluctuating raw material prices, such as barley and hops, present a significant challenge for Carlsberg, directly impacting its cost of goods sold and overall profitability. For instance, a notable increase in grain prices in 2024 could squeeze margins if not managed effectively.
Carlsberg's strategy to mitigate these price swings involves a dual approach: increasing revenue per hectoliter and maintaining stringent cost control measures across its operations. This focus aims to absorb higher input costs and protect earnings.
- Raw Material Volatility: Carlsberg is exposed to price volatility in key inputs like barley and hops.
- Cost Management: The company actively pursues cost efficiencies to offset rising raw material expenses.
- Revenue Enhancement: Strategies to increase revenue per hectoliter are employed to bolster profitability amidst cost pressures.
- 2024 Outlook: Carlsberg's 2024 financial projections indicate an awareness of these cost pressures and a plan to manage them.
Suppliers of key brewing ingredients like malted barley and hops can exert significant influence due to market concentration and the limited availability of suitable substitutes. For example, in 2023, global hop prices saw fluctuations impacting input costs for brewers.
Carlsberg's large scale and strategic procurement help to counter this power, allowing for better negotiation leverage. The company's efforts to manage raw material price volatility, as seen in its 2024 financial strategies, are crucial for maintaining profitability.
Switching costs for Carlsberg's suppliers are moderate to high, particularly for specialized ingredients, creating a degree of supplier dependence. This dependence is balanced by Carlsberg's long-term supplier relationships, which foster stability and mutual investment.
| Factor | Impact on Carlsberg | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Hops, Specialty Malts) | Potential for higher prices and supply disruptions. | Leveraging global scale for procurement, diversifying supplier base where possible. |
| Limited Substitutes for Core Ingredients | Increased reliance on existing suppliers for consistent quality. | Cultivating long-term relationships, collaborative forecasting. |
| Raw Material Price Volatility (e.g., Barley) | Direct impact on Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and profit margins. | Increasing revenue per hectoliter, stringent cost control measures. |
| Forward Integration by Suppliers | Low likelihood due to high capital and brand barriers in brewing. | Focus on core competencies in brewing and distribution. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Carlsberg's position in the global beer market.
Instantly identify key competitive pressures with a visually intuitive Porter's Five Forces dashboard, streamlining strategic analysis for Carlsberg's Porter.
Customers Bargaining Power
Carlsberg's customer base, encompassing major retailers, distributors, and individual beer drinkers, shows a spectrum of price sensitivity. In tougher economic periods, like the stagnant Chinese beer market or shrinking segments in France and the UK, price becomes a more significant driver of purchasing decisions, directly influencing sales volumes and market standing.
While individual beer drinkers buy in small quantities, large supermarket chains and distributors represent massive purchasing volumes. This concentration of demand in the hands of a few major buyers significantly amplifies their bargaining power with Carlsberg. For instance, in 2023, the top five global retail chains accounted for over 40% of all off-premise alcohol sales, a trend that continues to grow.
Carlsberg's strategy of maintaining strong market positions across diverse geographies, including significant shares in markets like Western China, Scandinavia, Laos, Nepal, and Malaysia, helps to mitigate this customer concentration. This global diversification means that while a single distributor might hold sway in one region, Carlsberg's overall scale and market presence provide a degree of leverage across its entire customer base.
Customers have a vast selection of alternatives to Carlsberg's beer offerings. This includes a multitude of other domestic and international beer brands, as well as a wide spectrum of alcoholic beverages like wine, spirits, and ready-to-drink (RTD) cocktails. Furthermore, the market is seeing a significant rise in non-alcoholic beverage options, providing yet another avenue for consumers to explore.
This extensive availability of substitutes directly amplifies customer bargaining power. Consumers can readily switch to a competitor's beer if Carlsberg's pricing or product features are not to their liking, or opt for an entirely different beverage category altogether. For instance, the global RTD market alone was projected to reach over $70 billion by 2024, indicating a strong consumer shift towards diverse alcoholic options.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today are incredibly well-informed. With the internet and readily available media, they can easily research product ingredients, compare prices across different brands, and check a company's reputation. This level of transparency significantly boosts their bargaining power.
This increased knowledge, especially concerning health trends and the growing demand for low or no-alcohol beverages, allows consumers to be more discerning. They can actively seek out products that align with their preferences and expect better value for their money, putting pressure on companies like Carlsberg to innovate and offer competitive products.
- Informed Consumers: Access to online reviews, ingredient lists, and pricing data empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Health & Wellness Trends: A growing preference for healthier options and a focus on ingredients gives consumers leverage to demand better product formulations. For example, the global low-alcohol and no-alcohol beer market was valued at approximately USD 23.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly.
- Price Sensitivity: Easy comparison of prices across various brands and retailers means consumers can readily switch to competitors offering better deals.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by Carlsberg's customers, like major supermarket chains or pub groups, is typically low. These entities would face significant hurdles in replicating Carlsberg's intricate brewing processes, establishing a strong brand identity, and managing a vast distribution infrastructure. For instance, the capital expenditure required for a large-scale brewery alone can run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a substantial barrier for most retailers.
Consider the example of a large supermarket chain. While they possess significant purchasing power, the technical expertise and investment needed to produce beer that meets consumer expectations and regulatory standards are immense. They would need to invest in malting, brewing, fermentation, bottling, and packaging facilities, alongside securing specialized talent. In 2024, the global beer market is characterized by established players with decades of experience and brand loyalty, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction.
- High Capital Investment: Building a brewery comparable to Carlsberg's scale would require hundreds of millions in capital, a prohibitive cost for most potential integrating customers.
- Technical Expertise Required: Brewing involves complex processes and quality control, demanding specialized knowledge that retailers typically lack.
- Brand Building Challenges: Creating a recognized and trusted beer brand takes significant time, marketing investment, and consistent product quality.
- Distribution Network Complexity: Establishing and managing a nationwide or international distribution network is a logistical challenge that most customers are not equipped to handle.
The bargaining power of Carlsberg's customers is moderate, influenced by factors like buyer concentration, product differentiation, and switching costs. While individual consumers have little power, large retailers and distributors wield significant influence due to their volume purchases. For instance, in 2023, major grocery chains continued to consolidate their market share, giving them greater leverage in price negotiations with brewers.
The availability of numerous substitutes, including other beer brands and alternative alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages, further empowers customers. The global ready-to-drink (RTD) market, projected to exceed $70 billion by 2024, exemplifies the breadth of choices available. This abundance of alternatives means customers can easily switch if Carlsberg's pricing or product offerings are not competitive.
Customers are also increasingly informed, utilizing online resources to compare prices and product attributes. The growing demand for low- and no-alcohol options, a market valued at approximately $23.3 billion in 2023, highlights how consumer preferences for healthier or specific product types can shift demand and increase their bargaining leverage.
The threat of backward integration by customers is low due to the high capital investment and technical expertise required to establish large-scale brewing operations. Building a brewery comparable to Carlsberg’s requires hundreds of millions of dollars and specialized knowledge in brewing, distribution, and brand building, barriers that most retailers cannot overcome.
| Factor | Impact on Carlsberg | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Concentration | Moderate to High | Top 5 global retail chains account for over 40% of off-premise alcohol sales. |
| Product Differentiation | Moderate | While Carlsberg has established brands, the beer market is crowded with many similar offerings. |
| Switching Costs | Low for Consumers, Moderate for Distributors | Consumers can easily switch brands; distributors face some integration costs but can shift orders. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Global RTD market projected over $70 billion by 2024; significant growth in low/no-alcohol beer (valued at $23.3 billion in 2023). |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low | High capital costs ($100M+ for a large brewery) and technical expertise needed. |
Same Document Delivered
Carlsberg Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, professionally written Carlsberg Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the brewing industry. This preview accurately reflects the comprehensive insights and formatting you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing information. You're looking at the actual document, ready for download and immediate use, providing a thorough understanding of the strategic landscape Carlsberg operates within.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global brewing landscape is intensely competitive, with giants like AB InBev and Heineken holding significant market share. Carlsberg also contends with major regional players such as China Resources Snow Breweries. This crowded field means Carlsberg must constantly innovate and adapt to stay ahead.
The global beer market experienced a slight dip in 2024, with some key markets like China showing flat or even declining volumes. This slowdown naturally heats up rivalry as companies fight harder for their existing share.
However, this challenge also sparks innovation. Growth areas such as premium beers and alcohol-free alternatives are becoming battlegrounds, pushing major players like Carlsberg to strategically invest and compete in these evolving segments.
Carlsberg actively differentiates its offerings through a diverse portfolio, encompassing globally recognized brands like Carlsberg and Tuborg, alongside a growing selection of local and craft beers. This strategy extends to a deliberate emphasis on premium products and the expanding market for alcohol-free beverages, catering to evolving consumer preferences.
The company cultivates strong brand loyalty, a vital asset in the highly competitive beer market. This loyalty is fostered through consistent marketing efforts and ongoing product innovation. For example, Carlsberg reported a 7% increase in its premium beer sales in 2023, highlighting the success of this differentiation strategy.
High Exit Barriers
The brewing industry, including major players like Carlsberg, faces significant competitive rivalry stemming from high exit barriers. These barriers are largely a consequence of substantial capital investments required for breweries, specialized equipment, and extensive distribution networks. For instance, establishing a modern brewery can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, making it difficult to recoup such investments if a company decides to leave the market.
These substantial fixed costs, coupled with long-term contracts with suppliers and distributors, and commitments to a skilled workforce, create a strong incentive for companies to remain operational even when profitability is low. This situation can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition as firms strive to maintain market share and cover their fixed expenses.
High exit barriers contribute to a more concentrated industry structure where established players are reluctant to divest, thereby intensifying the rivalry among existing competitors. This dynamic can manifest in aggressive pricing strategies and increased marketing efforts as companies fight to retain their positions.
- Capital Investment: Establishing a new brewery can cost upwards of $200 million, a significant barrier to entry and exit.
- Distribution Networks: Building and maintaining a nationwide distribution system is costly and time-consuming, locking companies into their existing markets.
- Long-Term Contracts: Agreements with suppliers for raw materials like barley and hops, as well as distribution agreements, can extend for years, making it difficult to disengage.
- Brand Loyalty and Market Share: Companies invest heavily in building brand equity and market share, which are difficult to abandon or transfer.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Carlsberg's competitive rivalry is intensified by its proactive strategy of pursuing strategic acquisitions and forming key partnerships. A prime example is their recent acquisition of Britvic plc, a significant move to broaden their beverage offerings beyond beer into the growing soft drinks market. This acquisition, which was announced in early 2024, underscores Carlsberg's commitment to diversification and market share expansion.
These strategic maneuvers, including buyouts of partners in emerging markets like India and Nepal, are designed to consolidate their market position and enhance their distribution networks. For instance, in 2023, Carlsberg completed the acquisition of its partner's stake in Nepal, strengthening its control and operational efficiency in that region.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Carlsberg's purchase of Britvic plc in 2024 significantly expands its soft drinks segment.
- Market Consolidation: Buyouts of partners, such as the completed acquisition in Nepal in 2023, bolster market control.
- Diversification: These actions aim to diversify product portfolios and strengthen route-to-market capabilities.
- Competitive Landscape: Such strategic moves directly reshape the competitive dynamics within the beverage industry.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of Carlsberg's operating environment. The global brewing market is saturated with major international players like AB InBev and Heineken, alongside strong regional competitors. This intense competition forces Carlsberg to continuously innovate and differentiate its product offerings, particularly in growth segments like premium beers and alcohol-free options, to maintain and expand its market share.
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial capital investments in breweries and distribution networks, keep existing players locked in, further intensifying rivalry. Carlsberg's strategic acquisitions, such as the 2024 purchase of Britvic plc, demonstrate a proactive approach to consolidating market position and diversifying its portfolio in response to this competitive pressure.
| Competitor | Market Share (approx. 2024) | Key Brands |
|---|---|---|
| AB InBev | ~25% | Budweiser, Corona, Stella Artois |
| Heineken | ~15% | Heineken, Tiger, Amstel |
| China Resources Snow Breweries | ~10% | Snow |
| Carlsberg | ~5% | Carlsberg, Tuborg, Grimbergen |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Carlsberg's beer products is significant, given the wide array of alcoholic beverages available. Consumers can easily switch to wine, spirits, or the increasingly popular ready-to-drink (RTD) segment, which includes hard seltzers and canned cocktails.
In 2024, the global RTD market continued its strong growth trajectory, with some analysts projecting it to reach over $60 billion by 2027, demonstrating a clear shift in consumer preference towards convenient and flavored alcoholic options. This diversification of choice directly siphons potential demand away from traditional beer.
The non-alcoholic beverage market is a growing threat, with non-alcoholic beer sales surging 22.2% year-to-date in 2025, making up 87% of US non-alc sales. This indicates a strong shift in consumer preference towards healthier or moderation-focused options.
Beyond non-alcoholic beer, a wide array of other beverages like soft drinks, energy drinks, and functional beverages also represent viable substitutes. These alternatives appeal to consumers prioritizing health, wellness, or simply seeking variety, further intensifying competitive pressure.
The growing consumer emphasis on health and wellness presents a significant threat of substitutes for Carlsberg. Trends like the popular 'Dry January' initiative and a broader societal move towards moderation in alcohol consumption directly divert demand away from traditional beer products.
This shift encourages consumers to explore and adopt non-alcoholic beer alternatives or entirely different beverage categories that align better with their healthier lifestyles. For instance, the global low- and no-alcohol (LNA) beer market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear substitution trend.
Cannabis-Infused and Other Novel Drinks
Cannabis-infused beverages represent a growing threat of substitution for traditional alcoholic drinks like Carlsberg's beer, especially in regions where cannabis is legalized. These novel drinks offer consumers a different recreational experience, potentially drawing them away from beer consumption.
In 2024, the global cannabis beverage market is experiencing significant growth. For instance, the market size was estimated to be around $1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $3.5 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of over 18%. This expansion indicates a tangible shift in consumer preferences and spending, directly impacting the market share of established beverage categories.
- Growing Market: The global cannabis beverage market is expanding rapidly, projected to exceed $3.5 billion by 2028.
- Alternative Experience: These drinks provide a distinct recreational alternative to traditional beer.
- Legalization Impact: Increased legalization in various markets directly fuels the substitution threat.
- Consumer Diversion: A portion of consumers may shift their spending from beer to cannabis-infused options.
Entertainment and Socializing Alternatives
Beyond direct beverage substitutes, other forms of entertainment and social activities that do not involve alcohol also pose an indirect threat to Carlsberg. Consumers might opt for activities like sports, gaming, or dining experiences where non-alcoholic options or different forms of leisure are preferred, potentially reducing overall beer consumption occasions.
For instance, the global esports market was projected to reach over $1.5 billion in 2024, indicating a significant shift in entertainment spending towards digital and interactive experiences. Similarly, the rise of streaming services and home entertainment continues to offer compelling alternatives to traditional social outings, which may have previously included beer consumption.
- Increased spending on digital entertainment: In 2023, global spending on video games alone surpassed $180 billion, diverting disposable income from other leisure activities.
- Growth of non-alcoholic beverage market: The non-alcoholic beer segment is experiencing robust growth, with projections suggesting it could reach over $30 billion globally by 2025, directly competing for consumer beverage choice.
- Popularity of experience-based spending: Consumers are increasingly prioritizing spending on experiences over material goods, with activities like travel and culinary exploration offering alternatives to traditional social drinking occasions.
The threat of substitutes for Carlsberg is substantial, encompassing a wide range of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. The burgeoning ready-to-drink (RTD) market, projected to exceed $60 billion by 2027, offers convenient and flavored alternatives. Furthermore, the non-alcoholic beer segment saw a remarkable 22.2% year-to-date growth in 2025, capturing a significant portion of the US non-alc market.
Beyond beverages, alternative leisure activities also divert consumer spending and attention. The global esports market, estimated to reach over $1.5 billion in 2024, and the massive video game spending exceeding $180 billion in 2023, illustrate a shift in entertainment preferences away from traditional social drinking occasions.
| Substitute Category | 2024/2025 Data Point | Projected Future Value | Impact on Carlsberg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ready-to-Drink (RTD) | Continued strong growth in 2024 | >$60 billion by 2027 | Siphons demand from traditional beer |
| Non-Alcoholic Beer | +22.2% year-to-date growth (2025) | >$30 billion globally by 2025 | Direct competition for beverage choice |
| Cannabis Beverages | ~$1.5 billion market (2023) | >$3.5 billion by 2028 | Offers alternative recreational experience |
| Esports/Gaming | >$1.5 billion market (2024 projection) | N/A | Diverts entertainment spending |
| Video Games Spending | >$180 billion (2023) | N/A | Reduces disposable income for other leisure |
Entrants Threaten
The brewing industry, particularly for major players like Carlsberg, necessitates enormous capital outlays. Building and equipping large-scale breweries, along with establishing robust production and distribution infrastructure, requires significant financial commitment. For instance, major brewery expansions or new plant constructions can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to compete.
Established distribution channels represent a significant barrier for new entrants in the beer industry. Major players like Carlsberg have cultivated deep, long-standing relationships with distributors, retailers, and on-trade establishments, creating highly efficient routes to market. For instance, in 2024, Carlsberg's extensive network ensured its products were readily available across a vast number of points of sale throughout its key operating regions.
Newcomers face considerable challenges in replicating this market access. Securing prime shelf space in supermarkets, gaining placement in popular taprooms, and establishing efficient logistics for widespread distribution are critical hurdles. Without this established infrastructure, new entrants struggle to reach a broad customer base, limiting their potential for growth and market penetration.
Incumbent brewers, including Carlsberg, have cultivated strong brand loyalty over decades, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction. Established brands like Carlsberg and Tuborg benefit from deep consumer trust and ingrained purchasing habits. For instance, in 2023, Carlsberg's brand value was estimated at over $5 billion, reflecting this deep-seated loyalty.
New companies entering the beer market must invest heavily in marketing and innovative strategies to challenge these established giants. Building brand recognition and capturing consumer mindshare requires significant financial resources, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars annually for major campaigns. This high barrier to entry, driven by the need for substantial marketing spend to overcome existing brand loyalty, significantly dampens the threat of new entrants.
Economies of Scale in Production and Procurement
Economies of scale in production and procurement present a significant barrier for new entrants into the brewing industry. Established players like Carlsberg leverage their massive production volumes to secure lower per-unit costs for raw materials, such as barley and hops, and also benefit from optimized logistics and distribution networks. For instance, in 2023, major global brewers reported production volumes in the tens of millions of hectoliters, allowing them to negotiate bulk discounts that smaller competitors simply cannot access.
This cost advantage makes it incredibly challenging for new breweries to compete on price. A new entrant, operating at a fraction of the scale, will inherently have higher production costs per liter. This disparity means they would need to charge a premium for their products, potentially alienating price-sensitive consumers and limiting their market penetration against well-established brands with strong brand loyalty and efficient cost structures.
- Production Scale: Major brewers operate vast, highly automated facilities, reducing labor and overhead costs per hectoliter.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing of key ingredients like malt and hops provides significant cost savings.
- Logistical Efficiency: Extensive distribution networks and optimized supply chains further lower per-unit delivery costs.
- Capital Investment: The immense capital required to build comparable production and distribution infrastructure acts as a substantial deterrent.
Regulatory Hurdles and Licensing
The alcoholic beverage sector faces a labyrinth of regulations. These include stringent licensing requirements, varying tax structures across jurisdictions, and significant restrictions on advertising and product promotion. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a liquor license in many US states can stretch from several months to over a year, involving extensive paperwork and fees.
These regulatory complexities create a substantial barrier for potential new entrants. The cost and time investment required to understand and comply with these diverse rules, from production standards to distribution laws, can be prohibitive. Companies must also adhere to strict health and safety regulations, adding further layers of compliance and expense.
- Licensing: Obtaining and maintaining necessary federal, state, and local licenses is a complex and costly process.
- Taxation: Excise taxes on alcoholic beverages can significantly impact pricing and profitability, requiring careful financial planning.
- Advertising Restrictions: Limitations on marketing channels and content can hinder brand building and customer acquisition for new players.
- Health Standards: Compliance with evolving health and safety regulations necessitates ongoing investment in product development and quality control.
The threat of new entrants for Carlsberg is generally low due to substantial barriers. The immense capital required for brewery construction and distribution networks, coupled with established brand loyalty, makes it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold. Furthermore, complex regulatory landscapes and the significant economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like Carlsberg further deter potential entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building breweries and distribution infrastructure requires hundreds of millions of dollars. | Very High | New brewery construction costs often exceed $100 million. |
| Brand Loyalty | Established brands have deep consumer trust and purchasing habits. | High | Carlsberg's brand value estimated over $5 billion in 2023. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to retailers and on-trade establishments is crucial and hard to replicate. | High | Carlsberg's extensive network ensures widespread product availability. |
| Economies of Scale | Large production volumes lead to lower per-unit costs for raw materials and logistics. | High | Major brewers produced tens of millions of hectoliters in 2023, securing bulk discounts. |
| Regulations | Licensing, taxes, and advertising restrictions add complexity and cost. | Medium | Liquor license acquisition can take over a year and involve significant fees. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Carlsberg leverages data from Carlsberg's official annual reports and investor relations materials, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like Euromonitor and IBISWorld.