Assured Guaranty Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Assured Guaranty Bundle
Assured Guaranty operates in a unique financial services landscape where the threat of new entrants is moderate, but the bargaining power of buyers, particularly sophisticated institutional investors, can be significant. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic assessment.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Assured Guaranty’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Assured Guaranty's access to capital is a critical factor, directly affecting its capacity to underwrite new financial guaranty insurance policies. In 2024, the cost and availability of both equity and debt financing remain paramount. The reinsurance market also plays a significant role; if reinsurance capacity tightens or prices increase, it can limit Assured Guaranty's ability to offload risk, thereby impacting its profitability and overall risk appetite.
The availability of highly specialized talent, such as experienced public finance underwriters and structured finance risk managers, is a critical factor. The pool of professionals possessing these niche skills is notably constrained, impacting Assured Guaranty's ability to secure and retain top talent.
This scarcity directly translates into increased bargaining power for these specialized individuals. They can command higher compensation packages, posing a challenge for Assured Guaranty in managing its human capital costs and ensuring a stable, expert workforce. The intricate nature of assessing complex debt instruments further elevates the value of this unique expertise.
Assured Guaranty's reliance on specialized data and analytics providers for credit risk assessment and policy pricing means these suppliers can wield considerable influence. Companies offering unique datasets or proprietary analytical models are particularly well-positioned to exert this power. For instance, the market for sophisticated financial data services, crucial for evaluating complex debt instruments, is often concentrated among a few key players, potentially limiting Assured Guaranty's negotiation leverage.
Regulatory and Legal Services
Assured Guaranty, as a heavily regulated financial entity, relies on specialized legal and compliance professionals to navigate the intricate web of regulations across different operating regions. The highly specific nature of financial services law and the critical need for unwavering compliance can grant these expert service providers significant leverage. This influence is amplified for legal firms possessing profound knowledge in insurance sector regulations and the dynamics of financial markets.
The bargaining power of these regulatory and legal service providers is a key consideration for Assured Guaranty. For instance, the sheer volume of regulatory changes impacting the financial services industry in 2024 necessitates constant adaptation and expert guidance. The cost of engaging top-tier legal counsel specializing in financial regulation can be substantial, reflecting the demand for their niche expertise.
- Specialized Expertise: Legal firms with deep knowledge of insurance and financial market regulations hold significant sway.
- Regulatory Complexity: The ever-evolving regulatory landscape in 2024 demands constant legal and compliance oversight.
- High Demand for Niche Skills: The scarcity of professionals with proven expertise in financial regulatory law increases their bargaining power.
Technology and Infrastructure Providers
Assured Guaranty's reliance on sophisticated technology and infrastructure means that providers of specialized financial software, cybersecurity, and cloud services hold considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true when these solutions are critical to operations and difficult to replace. For instance, a significant portion of the financial services industry in 2024 continues to depend on established cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, whose scale and specialized offerings create high switching costs.
The ability of these technology suppliers to dictate terms is amplified if their platforms represent industry standards or if Assured Guaranty is dependent on a limited number of vendors for essential functions. This dependence can translate into pricing leverage for the suppliers, impacting Assured Guaranty’s operational costs. The ongoing digital transformation across the financial sector, with increased investment in AI and advanced analytics throughout 2024, further solidifies the importance of these technology partners.
- High Switching Costs: Migrating critical financial systems and data to new providers is complex, time-consuming, and expensive, giving established technology vendors significant leverage.
- Industry Standardization: When specific software or infrastructure becomes an industry standard, suppliers face less competition, allowing them to command higher prices.
- Concentration of Key Vendors: A limited number of providers offering essential services, such as specialized financial modeling software or robust cybersecurity platforms, can concentrate power in their hands.
- Essential Operational Dependence: Assured Guaranty's operational efficiency and analytical capabilities are directly tied to the performance and availability of these technology solutions, making them indispensable.
Suppliers of specialized data and analytics, crucial for Assured Guaranty's risk assessment and pricing, hold significant bargaining power. This is particularly true for providers of unique datasets or proprietary models in the complex debt instrument market, which is often concentrated among a few key players, limiting Assured Guaranty's negotiation leverage.
The bargaining power of technology suppliers, including those for financial software and cybersecurity, is substantial due to high switching costs and industry dependence. For instance, major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are critical for financial services, with their scale and specialized offerings making migration difficult and expensive for companies like Assured Guaranty.
Providers of specialized legal and compliance services also exert considerable influence, especially given the intricate and constantly evolving regulatory landscape impacting financial entities. The demand for niche expertise in financial services law in 2024 means these providers can command substantial fees, directly affecting Assured Guaranty's operational costs.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Assured Guaranty | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data & Analytics Providers | Uniqueness of data, proprietary models, market concentration | Higher costs, potential limitations in risk assessment tools | Crucial for evaluating complex financial instruments |
| Technology Vendors (Cloud, Software, Cybersecurity) | High switching costs, industry standardization, vendor concentration | Increased operational expenses, dependence on vendor performance | Essential for digital transformation and operational efficiency |
| Legal & Compliance Services | Specialized regulatory knowledge, high demand for niche skills | Substantial fees for expert guidance, need for continuous adaptation | Navigating complex and changing financial regulations |
What is included in the product
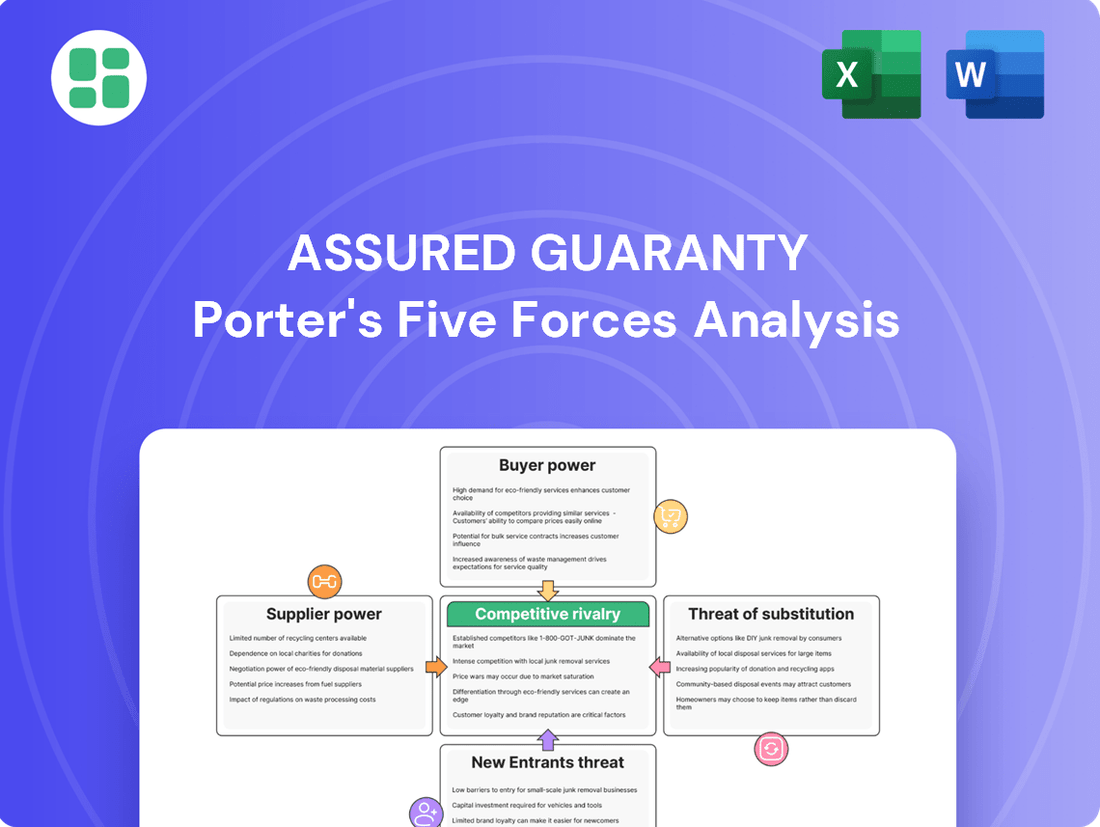
This analysis reveals the competitive forces impacting Assured Guaranty, examining the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier power, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the financial guarantee sector.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces.
Gain immediate clarity on industry power dynamics and pinpoint key areas for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of bond issuers, Assured Guaranty's customers, is directly tied to their own creditworthiness. Issuers with strong credit ratings, like AAA-rated municipalities, often have a lower perceived need for financial guaranty insurance. This can lead them to negotiate lower premiums or opt out of insurance altogether, leveraging their financial stability.
Conversely, issuers with weaker credit profiles, such as those rated below investment grade, typically possess less bargaining power. Their inherent credit risk makes them more reliant on Assured Guaranty's credit enhancement to access capital markets or achieve favorable borrowing terms. This greater need for insurance strengthens Assured Guaranty's position in pricing and terms.
For example, in 2024, the municipal bond market saw continued demand for insured bonds, particularly from lower-rated issuers seeking to improve their market access and reduce borrowing costs. Assured Guaranty's ability to offer competitive pricing to these issuers, while still maintaining profitability, highlights the nuanced interplay between issuer credit quality and bargaining power.
Customers can explore alternatives to financial guaranty insurance to bolster their creditworthiness or lower borrowing expenses. For instance, they might utilize bank-issued letters of credit, opt for self-insurance, or benefit from market conditions that grant direct, low-cost capital access.
The availability of these substitutes directly impacts Assured Guaranty's pricing leverage. If customers find readily accessible and economical alternatives, they are empowered to negotiate more favorable terms and pricing from Assured Guaranty.
Large-volume issuers, such as major municipalities or significant corporate entities, wield considerable bargaining power with Assured Guaranty. These clients represent substantial revenue streams, potentially worth millions in premiums for a single large debt issuance. For instance, a single large municipal bond issuance, exceeding $1 billion, offers a significant financial commitment that Assured Guaranty would seek to secure.
The ability to negotiate more favorable terms, including pricing and contract conditions, stems directly from the sheer size of these transactions. Assured Guaranty, like any business, is incentivized to retain and attract high-value clients, making them more amenable to concessions for these substantial deals. This can translate into lower fees or customized policy features to win and maintain such business.
Price Sensitivity and Market Transparency
Customers, especially large institutional investors and issuers, are very sensitive to price. They have access to clear information about insurance costs and other ways to finance projects, allowing them to negotiate for better rates. This transparency means they can easily shop around for the best deals.
The market for financial guarantees is often characterized by a high degree of transparency. For instance, in 2024, the average yield on municipal bonds, a key market for Assured Guaranty, saw fluctuations influenced by interest rate changes, directly impacting the cost of alternative financing options for issuers. This makes it easier for customers to benchmark insurance premiums.
- Price Sensitivity: Sophisticated buyers can readily compare Assured Guaranty's premiums against the cost of alternative credit enhancements or the unenhanced yield of a security.
- Market Transparency: Information on bond yields, credit default swap rates, and other financial instruments is widely available, enabling informed price comparisons.
- Comparison Shopping: The ability for customers to solicit and compare quotes from multiple financial guarantors, where applicable, directly increases their bargaining power.
- Cost of Alternatives: The pricing of alternative risk mitigation strategies, such as collateralization or higher yields on unenhanced bonds, sets a ceiling on what customers are willing to pay for financial guarantees.
Long-Term Relationships and Switching Costs
While Assured Guaranty's financial guaranty policies are long-term commitments, issuers do retain some bargaining power. The process of switching insurers for future issuances, though not costless, involves due diligence and building new relationships. If potential benefits like lower premiums or superior service from a competitor are significant enough, issuers can exert pressure.
The critical nature of selecting an insurer for the life of a bond means issuers weigh this decision carefully. For instance, in 2023, the municipal bond market saw continued demand for financial guarantees, with Assured Guaranty playing a significant role. However, the competitive landscape means issuers can shop around, influencing pricing and terms.
- Switching Costs: While not prohibitive, issuers face costs in vetting and onboarding a new financial guarantor.
- Perceived Benefits: If a competitor offers demonstrably better pricing or service, this can drive switching behavior.
- Issuer Choice: The long-term nature of insured debt means issuers are judicious in their selection of a guarantor.
The bargaining power of Assured Guaranty's customers, primarily bond issuers, is influenced by their credit quality and the availability of alternatives. Stronger issuers can negotiate better terms, while weaker ones are more reliant on Assured Guaranty's services.
In 2024, the municipal bond market demonstrated this dynamic, with lower-rated issuers actively seeking insured bonds to improve market access. This reliance strengthens Assured Guaranty's pricing power with these specific clients.
Customers can also explore options like letters of credit or self-insurance, which can reduce their dependence on financial guaranty insurance and increase their leverage in negotiations.
Large issuers, representing substantial premium volumes, possess significant bargaining power due to the value of their business. For example, a $1 billion municipal bond issuance represents a considerable revenue opportunity.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer Creditworthiness | Higher credit quality = Lower bargaining power | Demand for insured bonds from lower-rated issuers in 2024 |
| Availability of Alternatives | More alternatives = Higher bargaining power | Interest rate environment in 2024 influenced cost of alternatives |
| Transaction Size | Larger issuances = Higher bargaining power | Significant revenue potential from large municipal deals |
| Market Transparency | Greater transparency = Higher bargaining power | Easy comparison of yields and insurance costs |
Full Version Awaits
Assured Guaranty Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Assured Guaranty Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive document details the competitive landscape for Assured Guaranty, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic positioning and potential challenges facing the company.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The financial guaranty insurance market has seen considerable consolidation, leaving Assured Guaranty with a select group of direct competitors. This has historically led to less aggressive price wars, fostering a more predictable pricing environment. For instance, in 2023, the total market for financial guaranty insurance, while niche, saw a concentration of business among a few key players, with Assured Guaranty maintaining a significant share.
While consolidation dampens direct price competition, rivalry persists for securing market share and winning mandates, especially from highly-rated issuers seeking the most favorable terms. This competition can manifest in innovative product offerings or superior service levels rather than solely on price, particularly as the market matures and regulatory landscapes evolve.
Assured Guaranty faces competition not just from direct rivals but also from specialization within specific financial sectors. For instance, in 2024, firms focusing exclusively on public finance or infrastructure projects might offer tailored solutions that indirectly challenge Assured Guaranty's broader offerings.
This niche focus allows competitors to cultivate deep expertise and cultivate strong relationships within their chosen segments. Such specialization can lead to intense competition for the most lucrative deals, even if the overall number of direct competitors remains limited.
While Assured Guaranty operates across various markets, a competitor deeply entrenched in, say, U.S. municipal bond insurance could command a significant market share within that specific niche, creating a form of indirect rivalry.
The competitive landscape for Assured Guaranty, like other financial guarantors, is significantly shaped by capital strength and financial ratings. These are not just metrics; they are the bedrock of trust and perceived security in the industry. Insurers with top-tier ratings, such as Assured Guaranty's A rating from S&P, are viewed as more reliable partners, attracting more business.
Rivalry, therefore, often boils down to a continuous effort to bolster and maintain these crucial financial indicators. Companies actively manage their capital reserves and seek to improve their credit ratings to gain an advantage. For instance, Assured Guaranty's focus on maintaining strong capital levels directly influences its ability to win bids for insuring municipal bonds and other debt instruments.
In 2024, the emphasis on financial stability remains paramount. Assured Guaranty's robust capital position, with reported total claims paying resources exceeding $50 billion as of the first quarter of 2024, underscores its competitive strength. This financial muscle allows them to underwrite larger transactions and weather potential economic downturns more effectively than less capitalized competitors.
Reputation and Track Record
Assured Guaranty's reputation and track record are paramount in the financial guarantor industry, a sector heavily reliant on trust and demonstrable reliability. In 2024, the company continued to leverage its long history of fulfilling its obligations, a critical differentiator when competing for business with issuers and investors.
A strong track record directly translates into competitive advantage. Assured Guaranty's ability to consistently honor its commitments builds confidence, making it a preferred counterparty even when pricing might be comparable to competitors. This is particularly vital in the municipal finance sector, where long-term stability is a key consideration.
- Financial Strength Ratings: Assured Guaranty maintains strong financial strength ratings from agencies like S&P and Moody's, reflecting its robust capital position and operational stability. For instance, as of mid-2024, Assured Guaranty Ltd. (AGO) held ratings that positioned it favorably among peers.
- Claims Paying History: The company's history of successfully navigating economic downturns and paying claims without interruption is a significant competitive asset, underscoring its reliability.
- Market Perception: A positive market perception, built over years of dependable service, allows Assured Guaranty to attract and retain clients who prioritize security and certainty in their financial guarantees.
Product Differentiation and Value-Added Services
While Assured Guaranty's core product, credit enhancement for municipal and infrastructure finance, is largely standardized, the company actively competes by offering significant value-added services. These services go beyond the basic guarantee, aiming to build deeper client relationships and provide more comprehensive solutions.
Differentiation strategies include offering enhanced analytical support, such as detailed credit analysis and stress testing, alongside streamlined underwriting processes that expedite deal execution. Furthermore, specialized market insights and advisory services help clients navigate complex financial landscapes.
- Value-Added Services: Assured Guaranty provides enhanced analytical support, streamlined underwriting, and specialized market insights to differentiate itself.
- Client Relationship Building: These services foster stronger ties with clients by offering comprehensive solutions beyond the core credit guarantee.
- Reduced Price Competition: By focusing on service quality and expertise, Assured Guaranty aims to lessen reliance on pure price-based competition in the market.
While the financial guaranty market has fewer direct players, rivalry remains intense for securing mandates, particularly from high-quality issuers. Assured Guaranty competes not just on price but also on specialized expertise and service quality, especially in niche segments like public finance. In 2024, the company's strong capital position, with over $50 billion in claims paying resources by Q1, and its established reputation for reliability were key competitive advantages, allowing it to underwrite larger deals and attract clients prioritizing security.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | 2024 Competitive Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Competitors | Capital strength, financial ratings, claims paying history, market perception | Maintaining strong capital, enhancing credit ratings, leveraging track record |
| Niche Specialists | Deep expertise in specific sectors (e.g., municipal finance) | Tailored solutions, specialized market insights, client relationship building |
| Internal Capabilities | Value-added services (analytical support, streamlined underwriting) | Offering comprehensive solutions beyond the guarantee, reducing price-based competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Commercial banks offer letters of credit (LOCs) as a competing form of credit enhancement, essentially a bank’s promise to pay a debt if the borrower defaults. For many corporate debt issuances and shorter-term financing needs, these LOCs can directly substitute for the protection provided by financial guaranty insurance. The appeal of LOCs hinges on the issuing bank's financial strength, the cost of obtaining the LOC, and whether it meets the specific needs of the debt issuer.
In 2024, the market for standby letters of credit remained robust, with many corporations leveraging them for supply chain finance and project guarantees. While specific aggregate data for LOCs as substitutes for financial guaranty insurance is not readily available, it's understood that banks with strong credit ratings, such as JPMorgan Chase or Bank of America, are preferred issuers, making their LOCs competitive alternatives to insurance for certain issuers seeking credit enhancement.
Highly creditworthy municipalities, state agencies, or large corporations can opt to self-insure their debt. This means they leverage their own robust financial health to secure favorable borrowing terms, effectively bypassing the need for traditional credit enhancement from entities like Assured Guaranty.
This strategy acts as a direct substitute because these issuers rely on their strong balance sheets and established market reputations, rather than external financial guaranties, to access capital markets. For instance, in 2023, the municipal bond market saw a significant volume of uninsured debt issued by highly-rated entities, demonstrating the viability of this self-insurance approach.
Government guarantees or programs can act as a significant substitute for Assured Guaranty's services, particularly in public infrastructure financing. For instance, the U.S. Department of Transportation's Transportation Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act (TIFIA) program offers direct loans and credit assistance, reducing reliance on traditional bond insurance for eligible projects. In 2024, TIFIA continued to support major infrastructure development, providing a direct alternative for credit enhancement.
Market Conditions and Investor Appetite
Favorable market conditions significantly influence the threat of substitutes for Assured Guaranty. For instance, in 2024, a persistent low-interest rate environment, even if gradually rising, could make unenhanced bonds more attractive to investors seeking yield. This reduces the perceived necessity of credit enhancement, as market acceptance of riskier, unrated, or lower-rated debt increases.
Investor appetite for specific asset classes also plays a crucial role. When there's high demand for certain types of bonds, perhaps due to perceived safety or attractive yields relative to other investments, issuers might find they can issue debt without financial guaranty insurance. This market acceptance acts as a direct substitute for Assured Guaranty's services. For example, in periods of strong economic growth, investors might be more willing to absorb credit risk directly.
- Low Interest Rates: In 2024, while rates have seen increases, the lingering effects of prolonged low-rate periods can still encourage investors to accept lower yields on unenhanced bonds, diminishing the need for insurance.
- Investor Demand: High investor demand for specific sectors, like infrastructure or renewable energy projects in 2024, can allow issuers in those areas to secure financing more easily without credit enhancement.
- Market Sentiment: Positive market sentiment and a general belief in the stability of certain issuers or asset classes can lead investors to bypass credit enhancement, viewing it as an unnecessary cost.
- Yield Compression: When yields on unenhanced bonds become sufficiently attractive compared to insured bonds, the cost-benefit analysis for issuers shifts, favoring the substitute of market acceptance over insurance premiums.
Alternative Financing Structures
Issuers are increasingly exploring alternative financing structures that can reduce their need for third-party risk mitigation, thereby acting as a substitute for financial guaranty insurance. These alternatives aim to lower borrowing costs or inherently reduce risk without requiring insurance.
Direct lending from financial institutions, for instance, bypasses the need for bond insurers. Private placements, where securities are sold directly to a limited number of sophisticated investors, also offer a way to raise capital without the involvement of public markets and the associated need for insurance. Furthermore, the choice between different bond structures, such as revenue bonds versus general obligation bonds, can influence investor perception of risk and, consequently, the demand for insurance.
- Direct Lending Growth: In 2023, the direct lending market saw substantial growth, with reports indicating over $1.7 trillion in assets under management, showcasing a significant alternative to traditional capital markets that often involve insurance.
- Private Placement Activity: Private placements for U.S. corporations in 2023 reached an estimated $1.3 trillion, demonstrating a robust alternative for companies seeking to raise capital without the full public offering process.
- Municipal Bond Structures: The municipal market continues to see a mix of revenue bonds and general obligation bonds, with investor appetite for lower-risk structures like GO bonds sometimes reducing the perceived necessity of insurance for certain issuers.
Commercial banks' letters of credit (LOCs) serve as a direct substitute for Assured Guaranty's financial guaranty insurance, particularly for corporate debt and short-term financing. The attractiveness of LOCs depends on the issuing bank's financial strength and cost. In 2024, banks like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America continued to offer robust LOCs, competing effectively for credit enhancement needs.
Highly creditworthy entities can self-insure, leveraging their strong balance sheets to secure favorable borrowing terms, thereby bypassing the need for external financial guaranties. This approach was evident in 2023 with significant volumes of uninsured municipal debt issued by highly-rated entities.
Government programs, such as the U.S. DOT's TIFIA, offer direct credit assistance for infrastructure projects, acting as a substitute for traditional bond insurance. In 2024, TIFIA remained a key financing tool for major infrastructure development.
Favorable market conditions, including investor appetite for yield in a gradually rising rate environment in 2024, can make unenhanced bonds more appealing. This reduces the perceived need for credit enhancement, as seen with strong investor demand for sectors like renewable energy projects.
| Substitute | Mechanism | 2023/2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Letters of Credit (LOCs) | Bank promise to pay debt if borrower defaults | Robust market for LOCs in 2024; strong banks like JPMorgan Chase are key issuers. |
| Self-Insurance | Issuer uses own financial strength | Significant volume of uninsured municipal debt in 2023 by highly-rated entities. |
| Government Programs (e.g., TIFIA) | Direct loans and credit assistance | TIFIA continued to support infrastructure in 2024, offering alternative credit enhancement. |
| Market Acceptance/Investor Demand | Investor willingness to accept risk on unenhanced bonds | Investor appetite for yield in 2024 can reduce perceived need for insurance, especially for sectors like renewable energy. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the financial guaranty insurance market demands substantial capital. Assured Guaranty, for instance, operates with a robust capital base to meet stringent regulatory solvency requirements and to absorb potential losses from guaranteed debt. This high capital intensity, requiring significant financial backing, acts as a major deterrent for new competitors.
The financial guaranty industry faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory requirements. New entrants must navigate complex licensing procedures and adhere to strict solvency rules, demanding substantial investment in specialized legal and compliance expertise. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing scrutiny of financial institutions by bodies like the SEC and state insurance departments means that obtaining the necessary approvals can be a lengthy and resource-intensive process, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
The need for an established reputation and trust presents a significant barrier for new entrants in the financial guarantee sector. Assured Guaranty, for instance, has cultivated decades of trust by consistently fulfilling its obligations. In 2023, the company reported a strong financial position, underscoring its reliability, which new, unproven competitors cannot easily replicate.
Specialized Underwriting Expertise and Risk Management
The threat of new entrants in the financial guaranty sector, particularly concerning specialized underwriting expertise and risk management, is significantly mitigated by the inherent barriers to entry. Assured Guaranty, like other established players, relies on a deep well of institutional knowledge and a proven track record in evaluating complex public finance, infrastructure, and structured finance deals. This isn't something easily replicated.
Newcomers face a steep learning curve and substantial capital requirements to build the necessary underwriting capabilities and risk management infrastructure. For instance, the complexity of assessing municipal bond risks, where Assured Guaranty has a strong presence, requires specialized legal, financial, and analytical skills developed over years of operation. A misstep in underwriting can lead to severe financial repercussions, deterring less experienced entities.
- Specialized Knowledge: Underwriting public finance and structured finance requires highly specific expertise, a significant hurdle for new firms.
- Risk Management Sophistication: Developing robust risk management systems comparable to established players is resource-intensive and time-consuming.
- Cost of Errors: The financial penalties for poor underwriting in this sector can be crippling, acting as a strong deterrent to new entrants.
- Reputation and Trust: Building the trust and reputation necessary to attract business in the financial guaranty market takes considerable time and consistent performance.
Limited Market Growth and Historical Challenges
The financial guaranty market has weathered significant storms, notably the 2008 financial crisis. This period triggered industry consolidation and fostered a more risk-averse stance among investors and regulators alike. Such a history, combined with the relatively subdued growth observed in the municipal bond sector, diminishes the industry's allure for new capital focused on substantial returns. Established entities benefit from entrenched relationships and substantial market share, presenting formidable barriers for any new entrants attempting to establish a foothold.
The threat of new entrants in the financial guaranty market, particularly concerning Assured Guaranty, is currently assessed as low. This is largely due to the industry's inherent complexities and the lingering impact of past crises.
- Historical Volatility: The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the sector's vulnerability, leading to increased regulatory scrutiny and a more cautious investor sentiment, making entry less appealing.
- Market Maturity: The municipal bond market, a core area for financial guarantors, exhibits slow growth, limiting the potential for rapid expansion by new players.
- Barriers to Entry: Established players like Assured Guaranty possess deep industry expertise, strong client relationships, and significant capital reserves, creating substantial hurdles for newcomers.
- Regulatory Landscape: Stringent capital requirements and compliance demands further complicate market entry, favoring well-capitalized and experienced participants.
The threat of new entrants into the financial guaranty market remains low, primarily due to significant capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles. Assured Guaranty's substantial capital base, exceeding $30 billion in total equity as of Q1 2024, demonstrates the financial muscle needed to operate in this space and absorb potential market shocks. This high capital intensity, coupled with the need for specialized underwriting expertise and a proven track record, acts as a formidable barrier.
The industry's demanding regulatory environment, including strict solvency rules and licensing procedures, further deters potential newcomers. For instance, in 2024, ongoing regulatory oversight by bodies like the SEC and state insurance departments means obtaining approvals is a lengthy and costly process. This complexity favors established players like Assured Guaranty, which have already navigated these challenges and built robust compliance infrastructures.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Requires substantial financial backing to meet solvency requirements. | High barrier; deters undercapitalized firms. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Complex licensing, compliance, and solvency rules. | Significant hurdle; time-consuming and resource-intensive. |
| Specialized Expertise | Deep knowledge in public finance, infrastructure, and structured finance underwriting. | Steep learning curve; costly to develop. |
| Reputation and Trust | Decades of consistent performance and fulfillment of obligations. | Difficult to replicate; essential for client acquisition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Assured Guaranty leverages data from financial filings, industry-specific research reports, and credit rating agency assessments. This comprehensive approach ensures a robust understanding of market dynamics.