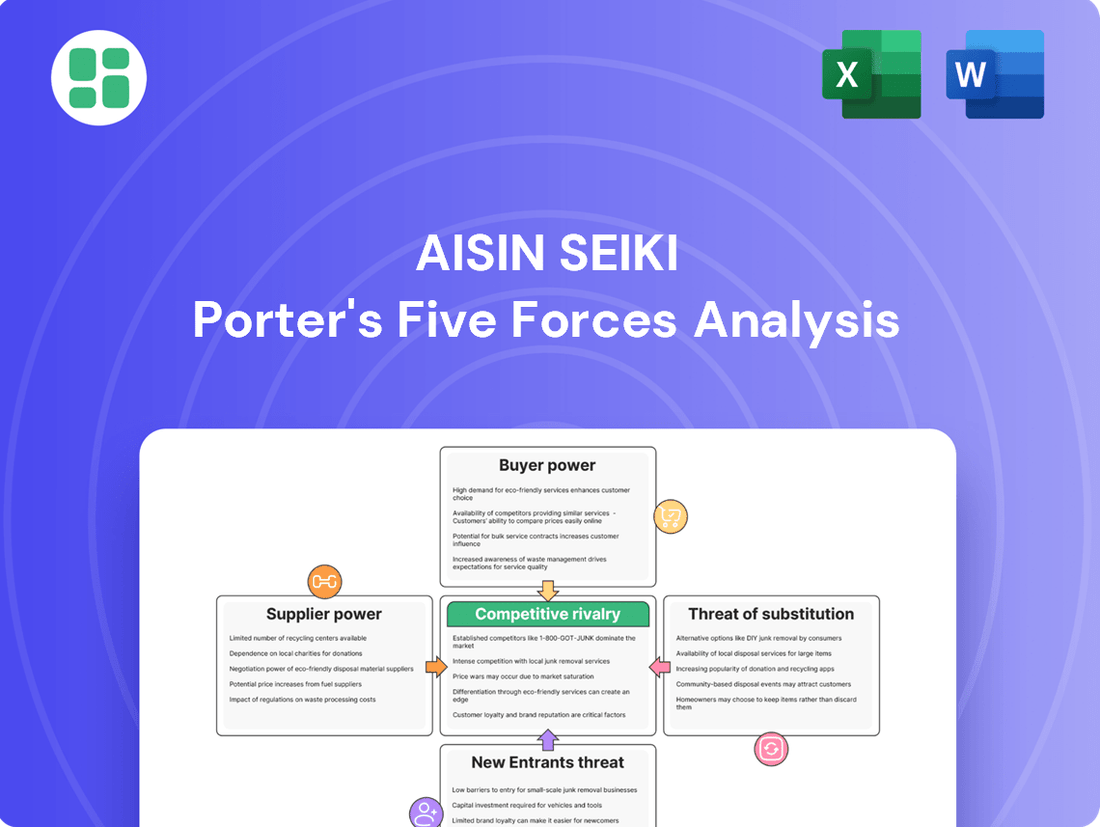
Aisin Seiki Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Aisin Seiki Bundle
Aisin Seiki operates within a dynamic automotive supply chain, facing moderate buyer power from major car manufacturers and significant bargaining power from its own suppliers of raw materials and specialized components. The threat of new entrants is tempered by high capital requirements and established relationships, while the threat of substitutes for its core powertrain and chassis technologies is relatively low, though evolving with electrification. The intensity of rivalry among existing automotive suppliers is a key factor influencing Aisin Seiki's market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Aisin Seiki’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Aisin Seiki's dependence on a select few suppliers for critical components like specialized automotive steel and high-performance plastics significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. For example, the global market for certain advanced polymers used in automotive interiors is highly concentrated, with only a handful of producers capable of meeting the stringent quality and volume requirements. This limited supplier pool means Aisin has fewer options for sourcing, potentially leading to less favorable pricing and contract terms.
Aisin Seiki's reliance on specialized automotive parts, often produced through complex manufacturing, significantly boosts supplier bargaining power. These unique components are typically sourced from a select group of highly skilled suppliers.
This dependence on niche parts means suppliers offering these specialized components hold considerable sway. For instance, automotive components represented a substantial 75% of Aisin's revenue in fiscal year 2022, highlighting this critical supplier relationship.
Switching costs for Aisin are substantial, encompassing expenses like re-tooling production lines, re-certifying new components, and rebuilding established supply chain relationships. These hurdles make it difficult and costly for Aisin to change suppliers, thereby strengthening supplier bargaining power.
A significant factor is Aisin's reliance on long-term contracts, which cover roughly 40% of its supplier agreements. These agreements lock Aisin into existing relationships, reducing its ability to quickly pivot to alternative suppliers even if better terms or quality become available elsewhere.
Threat of forward integration by suppliers
Suppliers possessing proprietary technologies or supplying absolutely essential components may consider forward integration, essentially starting to manufacture the very parts or sub-assemblies that Aisin currently produces. This looming possibility acts as a significant pressure point, potentially compelling Aisin to acquiesce to supplier demands to sidestep direct competition or the risk of losing critical supply chains.
For instance, if a key supplier of advanced sensor technology decided to produce finished automotive modules instead of just the sensors, Aisin would face direct competition. Such a move could significantly impact Aisin's market share and pricing power.
To proactively manage this threat, Aisin actively cultivates robust supplier relationships and explores strategic alliances. Their partnership with Manufacture 2030, focused on decarbonizing the supply chain, is a prime example of strengthening these ties and mitigating the risk of suppliers leveraging their position through forward integration.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers with unique technologies might start producing finished goods, directly competing with Aisin.
- Competitive Pressure: This threat can force Aisin to accept less favorable terms from suppliers to avoid losing essential components.
- Strategic Mitigation: Aisin's focus on strong supplier partnerships, like those aimed at supply chain decarbonization, helps reduce this risk.
- Supplier Leverage: The potential for suppliers to move up the value chain is a constant consideration in Aisin's supply chain strategy.
Supplier's product differentiation
When suppliers offer highly differentiated or proprietary products that are critical to Aisin's innovative automotive solutions, their bargaining power increases. This is particularly true for advanced materials or cutting-edge electronic components vital for modern vehicle systems.
Aisin's focus on electric vehicle (EV) components, like eAxles, means reliance on suppliers of advanced EV-specific materials and technologies. For example, suppliers of specialized rare-earth magnets for EV motors or advanced battery management system (BMS) chips can command higher prices if these components are not readily available from multiple sources. In 2024, the demand for these specialized components is projected to surge, further strengthening the position of key suppliers.
- Supplier Differentiation: Aisin's reliance on unique or proprietary components, such as advanced sensor technology for autonomous driving systems, grants suppliers significant leverage.
- Criticality of Inputs: If a supplier provides a component that is absolutely essential for Aisin's production and cannot be easily substituted, their bargaining power is amplified.
- EV Component Dependence: The automotive industry's shift towards EVs means Aisin depends on specialized suppliers for components like high-performance battery cells or advanced thermal management systems, increasing supplier influence.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers holding patents or unique manufacturing processes for critical automotive parts, like advanced semiconductor chips for infotainment systems, can dictate terms.
Aisin Seiki faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly those providing specialized components crucial for its automotive products. This is exacerbated by the high switching costs involved in changing suppliers, which include re-tooling and re-certification processes. The company's reliance on long-term contracts, covering approximately 40% of its supplier agreements, further solidifies these relationships and limits flexibility.
The growing demand for electric vehicle (EV) components, such as advanced battery management system chips and specialized rare-earth magnets for EV motors, is a key factor in 2024. Suppliers of these critical, often proprietary, technologies are in a strong position to dictate terms due to limited alternative sources and the surge in demand.
Suppliers with unique technologies or those providing absolutely essential components can also exert influence through the threat of forward integration, potentially becoming direct competitors to Aisin. Aisin's strategic partnerships and efforts to strengthen supplier relationships, like those focused on supply chain decarbonization, are vital for mitigating this risk.
| Factor | Impact on Aisin Seiki | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High bargaining power for a few key suppliers. | Global market for certain advanced polymers is highly concentrated. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces Aisin's flexibility and strengthens supplier position. | Includes re-tooling, re-certification, and relationship rebuilding. |
| Long-Term Contracts | Locks Aisin into existing supplier relationships. | Approximately 40% of supplier agreements are long-term. |
| Proprietary/Differentiated Products | Increases supplier leverage for critical components. | Advanced sensor technology for autonomous driving systems. |
| EV Component Demand (2024) | Strengthens suppliers of specialized EV parts. | Demand for advanced BMS chips and rare-earth magnets is surging. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Aisin Seiki, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the automotive parts industry.
Instantly visualize Aisin Seiki's competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing a clear, actionable overview for strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Aisin Seiki's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by customer concentration and the volume of their purchases. Major automotive manufacturers such as Toyota, Honda, and Ford represent a substantial portion of Aisin's clientele.
Toyota, in particular, was a dominant customer, accounting for roughly 32% of Aisin's total sales in 2022. This reliance on a few key automotive giants means these Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) wield considerable power.
Their ability to purchase in massive quantities grants them considerable leverage in negotiating prices and contractual terms with Aisin. The concentration of sales among these few large buyers directly amplifies their bargaining strength.
Large automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) have the financial muscle and technical know-how to potentially produce certain components themselves. This capability means they could bring some manufacturing processes in-house, lessening their dependence on suppliers like Aisin Seiki. For instance, in 2024, major automakers continued to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing technologies, signaling a growing capacity for vertical integration.
This threat of backward integration significantly boosts customer bargaining power. Aisin Seiki must consistently offer competitive pricing and high-quality products to secure and maintain business from these powerful OEMs. The mere possibility of an OEM choosing to manufacture a component internally acts as a strong check against Aisin implementing price increases.
Automotive manufacturers, facing intense competition and slim profit margins, are acutely sensitive to the cost of their components. This means Aisin Seiki must offer competitive pricing for its parts, which can put a strain on Aisin's own profitability. For instance, in 2024, the automotive sector continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions and fluctuating demand, leading many major manufacturers to scrutinize every cost, including those for critical components like those supplied by Aisin.
Availability of alternative suppliers
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers. Aisin Seiki operates within the automotive component industry, a sector populated by numerous strong competitors. Companies like Bosch, Denso, and Magna International are major players, offering comparable product lines and technological capabilities. This robust competition means automotive manufacturers, Aisin's primary customers, have a wide array of choices when sourcing parts.
When multiple credible suppliers can meet demand for similar components, customers gain leverage. If Aisin's pricing is perceived as too high, or if its quality standards falter, automotive manufacturers can readily switch to another supplier. This ability to easily substitute suppliers intensifies competitive pressure and empowers customers by giving them more options and greater negotiation strength.
- Competitive Landscape: Aisin Seiki faces intense competition from global automotive suppliers such as Bosch, Denso, and Magna.
- Customer Options: The presence of these alternatives provides automotive manufacturers with multiple sourcing options for critical components.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can leverage the availability of alternatives to negotiate better prices or secure more favorable terms from Aisin.
- Quality Benchmarking: The ability to compare and switch suppliers allows customers to demand higher quality standards, impacting Aisin's performance.
Product standardization vs. differentiation
The bargaining power of customers for Aisin Seiki is influenced by the balance between product standardization and differentiation. While Aisin strives for technological advancement and unique solutions, certain components might be more commoditized, potentially increasing customer leverage to seek alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to see intense competition in areas like basic transmission parts, where standardization can be higher.
Aisin's strategic focus on developing integrated electric drive units and sophisticated safety systems is a direct response to mitigate this customer power. By offering these highly differentiated and technologically superior products, Aisin aims to create unique value propositions that are harder for customers to replicate or substitute. This strategy is crucial as the automotive sector rapidly shifts towards electrification and advanced driver-assistance systems, where innovation is a key differentiator.
- Product Standardization: Some Aisin components, particularly those in less technologically advanced segments, may be subject to standardization, allowing customers more choice.
- Product Differentiation: Aisin's investment in integrated electric drive units and advanced safety systems aims to create unique, high-value offerings.
- Customer Switching Costs: Differentiation efforts are designed to increase switching costs for customers by embedding proprietary technology and integrated solutions.
- Market Trends: The ongoing electrification and automation in the automotive sector (e.g., a projected 35% increase in EV sales globally by end of 2024) highlight the importance of Aisin's differentiation strategy to maintain competitive advantage and customer loyalty.
The bargaining power of Aisin Seiki's customers is substantial, driven by customer concentration and the sheer volume of their purchases. Major automotive manufacturers, including giants like Toyota, Honda, and Ford, represent a significant portion of Aisin's sales, with Toyota alone accounting for approximately 32% of Aisin's total revenue in 2022. This concentration means these Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) wield considerable leverage in price and contract negotiations.
Furthermore, the potential for these large OEMs to bring certain component manufacturing in-house, a trend reinforced by continued investment in advanced manufacturing technologies in 2024, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This threat of backward integration compels Aisin to maintain competitive pricing and high quality to retain these crucial relationships. The automotive sector's continued sensitivity to costs, exacerbated by supply chain disruptions in 2024, means Aisin must remain highly competitive on pricing.
The availability of numerous strong competitors like Bosch, Denso, and Magna International also empowers customers. These alternatives allow OEMs to easily switch suppliers if Aisin's pricing or quality falters, increasing competitive pressure. Aisin's strategy to counter this involves differentiating its products, particularly in areas like integrated electric drive units and advanced safety systems, to create unique value and higher switching costs for customers, a critical approach given the automotive industry's rapid shift towards electrification, with global EV sales projected to increase by 35% by the end of 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Aisin's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High | Toyota represented ~32% of Aisin's sales in 2022. |
| Purchase Volume | High | Large OEMs buy in massive quantities, granting negotiation leverage. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | High | OEMs invest in advanced manufacturing, enabling potential in-house production (ongoing in 2024). |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Automotive sector's focus on cost reduction, intensified by 2024 supply chain issues. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Strong competitors (Bosch, Denso, Magna) offer comparable products. |
| Product Differentiation | Moderate (Mitigated by Aisin's efforts) | Aisin focuses on integrated electric drive units and safety systems to counter commoditization. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Aisin Seiki Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Aisin Seiki Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. You're viewing the exact document that will be delivered to you instantly upon purchase, ensuring you receive a professionally formatted and ready-to-use strategic assessment. There are no placeholders or samples; what you see is precisely the comprehensive analysis you will gain immediate access to.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The automotive components industry is crowded with major global players, including Bosch, Denso, Continental AG, and ZF Friedrichshafen AG, all competing directly with Aisin. This intense rivalry stems from the sheer number of companies and their varied specializations and regional dominance, creating a dynamic battle for market share.
The automotive industry, especially for traditional internal combustion engine parts, is largely mature. This maturity means slower growth and a fierce battle for existing market share among established players like Aisin Seiki.
While the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) market presents significant growth opportunities, it also reshapes the competitive landscape. Companies must invest heavily in new electrification technologies to remain relevant, creating a dynamic environment where innovation is paramount.
Competitors in the automotive supply sector frequently distinguish themselves through continuous innovation, superior quality, and cutting-edge technological developments. This is particularly evident in rapidly evolving areas such as vehicle electrification and the broader field of intelligent mobility. For instance, in 2024, many suppliers are investing heavily in R&D for advanced battery management systems and autonomous driving sensors.
Aisin's strategic emphasis on developing sophisticated electric vehicle components, including its advanced eAxles and integrated electric drive units, is paramount for preserving its competitive standing. This focus on electrification, coupled with advancements in smart mobility solutions, directly addresses the industry's shift towards sustainable and connected transportation, a trend that saw significant investment and product launches throughout 2024.
Exit barriers for competitors
High fixed costs, such as those associated with advanced manufacturing facilities and research and development, coupled with specialized assets like proprietary tooling and integrated supply chains, significantly raise the cost for competitors to exit the automotive component market. For instance, in 2024, the average capital expenditure for a new automotive component plant can range from $100 million to over $500 million, making it a substantial commitment that is difficult to recoup if a company decides to leave.
Long-term contracts with major automakers, often spanning multiple years and model cycles, further lock competitors into the industry. These agreements provide stability but also create dependencies, making it challenging to divest assets or reallocate resources if market conditions deteriorate. In 2024, these contracts can represent 70-80% of a component supplier's revenue, illustrating the difficulty of an abrupt departure.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investment in specialized machinery and R&D creates a financial hurdle for exiting players.
- Specialized Assets: Proprietary technology and unique production lines are not easily transferable or sold, increasing exit costs.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to major automotive manufacturers bind companies to the industry, limiting flexibility.
- Sustained Rivalry: These barriers contribute to persistent intense competition, potentially leading to price wars and overcapacity as firms struggle to leave.
Strategic alliances and joint ventures
Strategic alliances and joint ventures significantly influence the competitive dynamics within the automotive parts industry. These collaborations can consolidate market power, leading to more formidable competitors, or spur innovation by creating new product offerings and market access. Aisin Seiki actively participates in these arrangements, demonstrating their strategic importance.
For instance, Aisin's joint venture with Minth Group, focused on electric vehicle (EV) parts manufacturing in North America, exemplifies this trend. This partnership aims to strengthen Aisin's presence in the burgeoning EV market, potentially enhancing its competitive advantage. However, such consolidations can also intensify the competitive pressure on other players who may not have similar strategic backing or market reach.
- Aisin's joint venture with Minth Group targets EV parts production in North America.
- These alliances can either bolster a company's market position or create new competitive threats.
- The automotive supply chain is increasingly characterized by strategic partnerships aimed at shared development and market access.
Competitive rivalry within the automotive components sector is exceptionally high, driven by a mature market and a substantial number of global players like Bosch and Denso vying for market share. This intense competition is further amplified by the industry's shift towards electrification, where companies like Aisin Seiki must continually innovate to stay relevant.
The battle for market dominance is fierce, with competitors differentiating themselves through technological advancements, particularly in areas like electric vehicle (EV) components and autonomous driving. For example, in 2024, R&D spending by major automotive suppliers focused heavily on advanced battery management systems and sensor technology, indicating a significant investment in future growth areas.
Barriers to exit, such as high fixed costs for specialized manufacturing facilities and long-term contracts with automakers, lock companies into the industry. These factors contribute to sustained rivalry, potentially leading to price pressures as firms find it difficult to disengage from the market.
| Competitor | Key Product Focus | 2024 Estimated R&D Investment (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|
| Bosch | Powertrain, ADAS, Mobility Solutions | ~7.0 |
| Denso | Electrification, Thermal Systems, ADAS | ~4.5 |
| Continental AG | Tires, Automotive Technologies, Powertrain | ~4.0 |
| ZF Friedrichshafen AG | Drivetrain, Chassis Technology, ADAS | ~3.5 |
| Aisin Seiki | Drivetrain, Body, Electronics, Powertrain | ~2.0 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for Aisin Seiki stems from the accelerating adoption of alternative vehicle technologies. Electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are rapidly gaining market share, as evidenced by the projected global EV sales to reach over 20 million units in 2024. These advanced powertrains utilize fundamentally different components compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, directly impacting Aisin's established product lines.
This technological shift poses a substantial risk to demand for Aisin's conventional powertrain components and engine-related products. For instance, the growing preference for EVs means fewer transmissions and exhaust systems, core areas for Aisin. By 2025, it's anticipated that EVs will constitute a significant portion of new vehicle sales in key markets, a trend that will continue to erode the market for ICE-specific parts.
The automotive industry's relentless pursuit of better fuel economy and lower emissions is a major driver for the adoption of lightweight materials such as composites and advanced alloys. These innovative materials offer a viable alternative to traditional steel and aluminum components, directly impacting Aisin's core business in body and chassis systems.
The increasing demand for these substitutes is underscored by market projections; for instance, the global automotive lightweight materials market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023 and is expected to see robust growth, reaching an estimated $150 billion by 2028. This trend directly challenges Aisin's existing product portfolio by presenting alternative solutions that can perform similar functions with reduced weight.
The automotive industry's shift towards highly integrated vehicle systems and modular designs presents a significant threat of substitution for component suppliers like Aisin. As original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) consolidate multiple functions into fewer, more complex modules, the demand for individual, discrete components diminishes. This trend could lead to a reduced overall part count in vehicles, directly impacting Aisin's traditional product lines.
For instance, the increasing prevalence of electric vehicles (EVs) often features simplified architectures with fewer moving parts compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. Aisin's reliance on traditional powertrain components, such as transmissions and driveline systems, faces substitution from these more integrated EV powertrains. In 2024, EVs continued to gain market share, with global sales projected to reach over 17 million units, highlighting the accelerating nature of this substitution threat.
Public transportation and ride-sharing services
The increasing adoption of public transportation and ride-sharing services presents a significant indirect threat to Aisin Seiki. As more individuals opt for these alternatives over private vehicle ownership, the overall demand for automotive components, Aisin's core business, could diminish. For instance, in 2024, major cities are seeing a continued rise in ride-sharing usage, with platforms like Uber and Lyft reporting substantial increases in passenger trips compared to pre-pandemic levels. This trend suggests a potential long-term reduction in the number of vehicles manufactured and, by extension, the components Aisin supplies.
This shift in mobility patterns impacts Aisin by potentially lowering the volume of new vehicle production, a key driver of its component sales. While not a direct substitute for a car part, the broader societal move towards shared mobility reduces the need for individual car ownership. For example, in 2024, many urban areas are expanding their public transit infrastructure, making it a more viable and attractive option for daily commutes, further eroding the necessity for personal vehicles.
The threat of substitutes, in this context, is about the evolving landscape of personal transportation.
- Reduced Vehicle Ownership: Growing reliance on public transit and ride-sharing could lead to fewer cars being purchased.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Convenience and cost-effectiveness of alternatives may steer consumers away from traditional car ownership.
- Impact on Component Demand: A decline in new vehicle sales directly translates to lower demand for automotive parts like those produced by Aisin.
- Urban Mobility Trends: In 2024, cities continue to invest in public transport and support ride-sharing, reinforcing this substitution trend.
DIY and aftermarket alternatives
The threat of DIY and aftermarket alternatives for standard automotive components poses a challenge to Aisin Seiki. Vehicle owners can opt for less expensive parts from smaller manufacturers or even undertake repairs themselves, bypassing Aisin's original equipment. For instance, the global automotive aftermarket was valued at approximately $450 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a significant market for these alternatives.
Aisin is actively addressing this substitution threat by strategically expanding its own aftermarket parts offerings and enhancing its service capabilities. This dual approach aims to provide competitive and accessible options for consumers while maintaining Aisin's brand quality and reliability. By increasing its presence in the aftermarket, Aisin seeks to capture a larger share of this segment, mitigating the impact of independent repair options.
- DIY and aftermarket parts offer lower-cost alternatives to OEM components for routine maintenance and repairs.
- The global automotive aftermarket's substantial and growing valuation, estimated at over $450 billion in 2023, highlights the significant market for substitutes.
- Aisin Seiki is counteracting this threat by broadening its aftermarket product lines and improving its service network.
- This strategy aims to retain customer loyalty and market share by offering a compelling alternative to independent aftermarket suppliers.
The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) presents a significant substitution threat to Aisin Seiki's traditional powertrain components. As global EV sales are projected to exceed 20 million units in 2024, demand for Aisin's transmissions and driveline systems for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles faces a direct challenge. This technological shift means fewer components are needed for these evolving vehicle architectures.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the automotive parts manufacturing sector, particularly as a Tier 1 supplier akin to Aisin, demands immense capital. This includes setting up state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, acquiring sophisticated machinery, and investing heavily in research and development. For instance, establishing a new, fully automated automotive component plant in 2024 could easily cost upwards of $200 million, a figure that presents a formidable hurdle for potential new competitors.
The automotive component sector is a hotbed of innovation, requiring substantial investment in research and development to stay ahead of the curve, especially with the rapid advancements in electric vehicles and autonomous driving systems. Newcomers face a steep climb to match the technological prowess already established by industry leaders.
Aisin Seiki consistently allocates a significant portion of its revenue to R&D, underscoring the immense capital and expertise needed to enter this competitive space. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Aisin reported R&D expenses amounting to ¥130.3 billion, demonstrating a strong commitment to technological advancement.
Established relationships with OEMs represent a significant barrier for new entrants in the automotive supply chain. Companies like Aisin Seiki have cultivated decades-long partnerships with major car manufacturers, creating a deeply integrated and trust-based ecosystem. These relationships are not easily replicated, as they involve rigorous qualification processes, extensive product development collaboration, and seamless integration into the OEM's production lines.
Newcomers struggle to penetrate this established network due to the high switching costs and the inherent risks associated with disrupting proven supply chains. The trust and reliability built over years are invaluable assets. For instance, Aisin's enduring 41-year partnership with General Motors underscores the longevity and strength of such OEM relationships, making it exceptionally challenging for new suppliers to gain a foothold.
Economies of scale and experience curve effects
Aisin Seiki, as a major global automotive parts manufacturer, leverages substantial economies of scale. This allows them to negotiate better prices for raw materials and components, and spread fixed costs like research and development over a larger production volume. For instance, in 2023, Aisin reported consolidated net sales of ¥4,522.3 billion, indicating a significant operational footprint that new entrants would find difficult to match.
The experience curve effect further solidifies Aisin's competitive advantage. As a company with decades of manufacturing experience, Aisin has refined its production processes, leading to increased efficiency and lower per-unit costs. This accumulated knowledge and operational expertise make it challenging for new companies to enter the market and achieve comparable cost structures quickly.
- Economies of Scale: Aisin's ¥4.5 trillion in consolidated net sales for 2023 demonstrates its massive production and procurement power, leading to lower per-unit costs that new entrants cannot easily replicate.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational refinement have allowed Aisin to optimize manufacturing processes, reducing costs and improving quality, a benefit that newcomers would take years to build.
- Barriers to Entry: The combination of scale and experience creates a significant cost barrier, making it difficult for new, smaller players to compete on price against established giants like Aisin.
Regulatory hurdles and safety standards
The automotive sector is heavily regulated, with stringent safety, environmental, and quality standards that vary by region. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to enforce its Euro 7 emissions standards, requiring significant investment from manufacturers to ensure compliance. New entrants face substantial costs and lengthy timelines to meet these global benchmarks, making market entry a formidable challenge.
Compliance with these rigorous requirements acts as a significant barrier to entry. Companies must allocate considerable resources towards research, development, and testing to satisfy regulations like the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration's Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. This financial and time commitment deters many potential new players from entering the established automotive supply chain.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must invest millions to meet global safety and emissions standards.
- Time to Market: Navigating complex regulatory frameworks can add years to product development cycles.
- Certification Requirements: Obtaining necessary certifications, like ISO 9001 for quality management, is a prerequisite and an added expense.
- Evolving Standards: Continuous updates to regulations, such as those for electric vehicle battery safety, necessitate ongoing investment.
The threat of new entrants in the automotive parts sector, particularly for a Tier 1 supplier like Aisin Seiki, is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, estimated at over $200 million for a new automated plant in 2024, immediately deter smaller players. Furthermore, established OEM relationships, built over decades and involving high switching costs, create a significant hurdle for newcomers trying to integrate into existing supply chains.
Aisin's strong brand reputation and extensive experience curve, honed over years of operational refinement, also contribute to this low threat. The company's ¥130.3 billion in R&D spending for fiscal year 2023 highlights the continuous innovation needed, a costly endeavor for new entrants. Navigating complex and evolving global regulations, such as EU emissions standards, adds further significant costs and time delays, effectively limiting the pool of potential new competitors.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Aisin Seiki is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports from firms like IHS Markit, and official company disclosures. We also incorporate data from automotive trade publications and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.