AIRBUS PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AIRBUS Bundle
Navigate the complex global landscape impacting AIRBUS with our expert PESTEL Analysis. Understand how political stability, economic fluctuations, and technological advancements are shaping the aerospace giant's future. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to refine your market strategy and gain a competitive edge. Download the full version now for deep-dive insights.
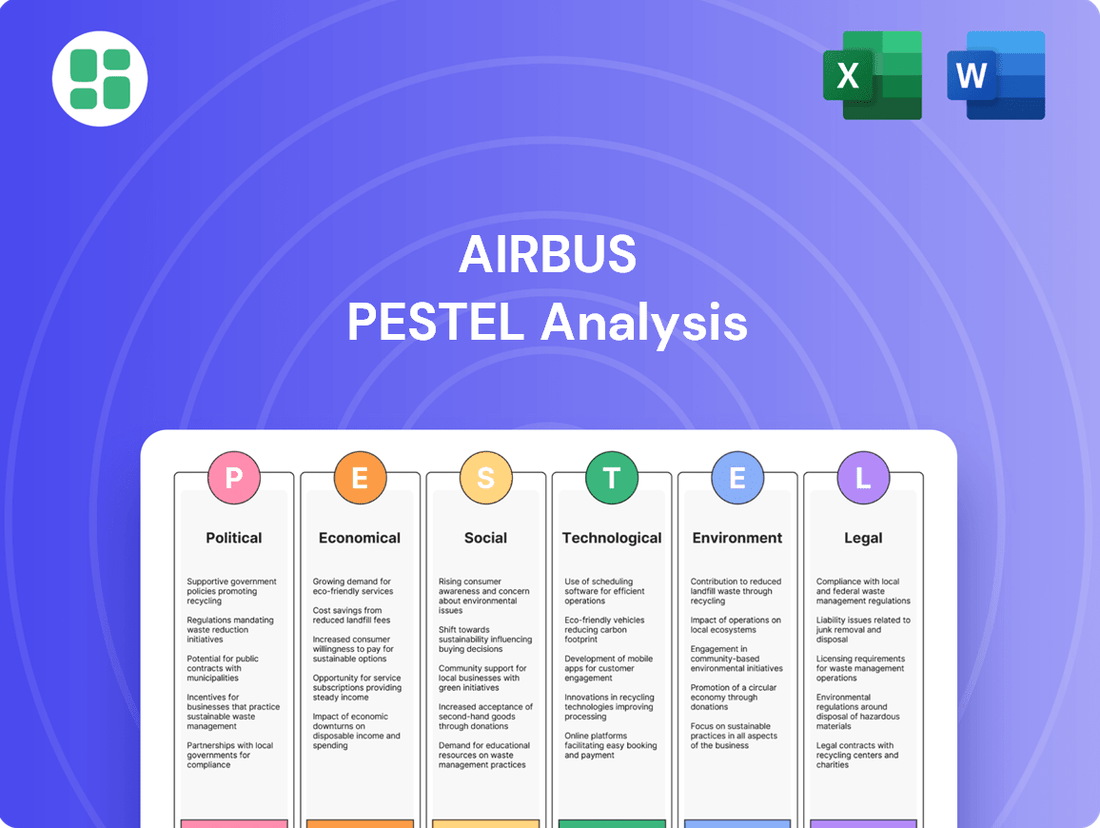
Political factors
Government contracts significantly bolster Airbus's Defence and Space division. In 2024 alone, the company saw a record order intake, including a crucial deal for 25 Eurofighter jets for Spain, underscoring robust defense sector demand.
Further cementing its position, Airbus secured a €2.1 billion German contract in July 2024 for advanced military satellite development and operation. This demonstrates substantial government investment in next-generation defense capabilities.
Adding to this momentum, a French armed forces contract awarded in February 2025 to an Airbus-led consortium for the RIFAN stage 3 IP Network is valued up to 480 million euros over ten years, showcasing continued long-term government commitment.
International trade policies, particularly tariffs, significantly influence Airbus's operational costs and market access. For instance, Airbus's 2025 financial guidance specifically omits any impact from potential new tariffs, highlighting the company's concern. CEO Guillaume Faury has stated that tariffs would be a lose-lose scenario due to Airbus's substantial U.S. manufacturing and export footprint.
A recent positive development is the political agreement between the EU and the US to reinstate a zero-tariff approach for civil aircraft. This move fosters a more predictable and stable trade environment for major aerospace players like Airbus, potentially reducing the risk of price volatility and market disruptions.
Geopolitical instability, particularly the ongoing conflict in Eastern Europe, has spurred a significant increase in global defense spending. This trend directly benefits Airbus, as nations bolster their military capabilities with demand for transport, surveillance, and communication systems. For instance, NATO members committed to increasing defense spending, with many aiming for 2% of GDP, a commitment reinforced at the 2024 Vilnius summit.
The heightened focus on national security and the evolving nature of warfare, including cybersecurity and AI, further align with Airbus's strategic investments and product development. This environment supports growth in Airbus's Defense and Space division, as countries seek advanced solutions to address emerging threats. The global defense market was valued at approximately $2.2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating sustained demand for Airbus's offerings.
Export Controls and Regulations
Airbus operates within the aerospace and defense industries, making it subject to rigorous international export controls and regulations. These regulations are designed to manage the cross-border movement of sophisticated technologies and military hardware. For instance, the Wassenaar Arrangement, a multilateral export control regime, impacts the transfer of dual-use goods and technologies, affecting Airbus’s global supply chain and customer base.
Navigating these complex rules is paramount for Airbus to retain access to key markets and prevent significant financial penalties. The company must continuously adapt its compliance strategies in response to shifting geopolitical landscapes and evolving national security interests. A failure to adhere to these controls, such as those managed by the Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) in the United States, can lead to severe sanctions.
- Export Control Compliance: Airbus must meticulously follow regulations like ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) and EAR (Export Administration Regulations) to ensure legal international sales.
- Geopolitical Impact: Trade tensions and sanctions between major economic blocs can directly restrict Airbus's ability to export aircraft and defense systems, impacting order books.
- Technological Safeguards: Regulations often mandate strict controls on the technology embedded in Airbus products, requiring robust cybersecurity and end-user verification measures.
- Market Access Restrictions: Non-compliance or changes in export policies can lead to the denial of export licenses, effectively closing off lucrative markets for Airbus.
Government Subsidies and State Aid
Government subsidies and state aid have long been a contentious issue in the aerospace sector, with significant historical disputes involving major manufacturers like Airbus and Boeing. While specific new subsidy announcements for 2024-2025 are not publicly detailed, the broader context of trade agreements and political negotiations, such as the EU-US tariff resolution, continues to influence market dynamics. Airbus actively monitors these political developments to ensure a level playing field and to identify opportunities for governmental support in crucial areas like research, development, and manufacturing.
These political factors directly impact Airbus's operational environment. For instance, the resolution of the long-standing Airbus-Boeing subsidy dispute, which saw tariffs imposed and later suspended, highlights the sensitivity of state aid in international trade. The European Union has continued to support its aerospace industry through various programs, including Horizon Europe, which funds research and innovation. In 2023, the EU allocated €10.5 billion to Horizon Europe, with a significant portion directed towards advanced manufacturing and aerospace technologies, potentially benefiting Airbus's R&D efforts.
- Ongoing Trade Negotiations: The EU and US continue to engage in discussions regarding trade practices, which could impact future aerospace industry regulations and support mechanisms.
- EU Research Funding: Programs like Horizon Europe provide substantial funding for aerospace innovation, with billions allocated annually for R&D projects.
- National Aerospace Strategies: Individual European nations often have their own aerospace strategies that can involve direct or indirect support for companies like Airbus, influencing production and export capabilities.
Government contracts remain a cornerstone for Airbus, particularly in its defense segment. The company's 2024 performance included a significant €2.1 billion German contract for satellite development and a substantial French armed forces contract in early 2025 for network infrastructure valued up to €480 million over ten years.
International trade policies, including the recent EU-US agreement for zero tariffs on civil aircraft, create a more stable operating environment. However, Airbus remains vigilant, with its 2025 financial guidance excluding potential tariff impacts, reflecting ongoing concerns about trade friction.
Geopolitical events, such as the conflict in Eastern Europe, are driving increased global defense spending, benefiting Airbus. NATO members' renewed commitment to spending 2% of GDP on defense, reinforced in 2024, signals sustained demand for military aerospace solutions.
Airbus operates under stringent international export controls, such as the Wassenaar Arrangement and US ITAR/EAR regulations. Compliance is critical for market access and avoiding penalties, requiring constant adaptation to evolving national security interests and geopolitical shifts.
| Factor | Impact on Airbus | 2024-2025 Data/Trend |
| Government Contracts | Boosts Defence and Space division | €2.1bn German satellite contract (2024); €480m French network contract (2025) |
| Trade Policies | Affects costs and market access | EU-US zero-tariff agreement for civil aircraft; Airbus guidance excludes tariff impact |
| Geopolitical Instability | Drives defense spending | NATO 2% GDP defense spending commitment reinforced (2024) |
| Export Controls | Governs international sales | Wassenaar Arrangement, ITAR, EAR compliance critical |
What is included in the product
This comprehensive PESTLE analysis examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors influencing Airbus, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
A concise, actionable summary of Airbus's PESTLE factors, designed to proactively identify and mitigate potential disruptions before they impact operations.
Economic factors
Global economic growth is a significant driver for air travel demand, and Airbus forecasts a strong future. Their Global Market Forecast for 2025-2044 anticipates a need for 43,420 new passenger and freighter aircraft, suggesting the current fleet will nearly double. This projection is underpinned by the commercial aviation sector's full recovery in demand during 2024, marking a robust rebound in global air passenger traffic.
This positive trend in air travel is directly linked to expanding global economic activity and enhanced connectivity. Emerging markets, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region and China, are expected to be key contributors to this growth, fueling the demand for new aircraft and supporting Airbus's ambitious market outlook.
Global fuel prices, particularly jet fuel, are a major determinant of airline profitability and a key factor in their aircraft acquisition strategies. For instance, in early 2024, jet fuel prices saw considerable volatility, with benchmarks like the Singapore jet fuel price fluctuating around $90-$100 per barrel, impacting airline operating expenses directly.
Airbus is actively addressing this by championing Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF). While SAF currently carries a premium, with prices potentially 2-3 times that of conventional jet fuel, its increasing production and adoption are vital for reducing the industry's carbon footprint and potentially stabilizing long-term fuel costs.
Airbus, being a European company with worldwide sales, is heavily influenced by changes in currency exchange rates, especially between the Euro and the US Dollar. These fluctuations directly impact its financial performance and the value of its international contracts.
In the first quarter of 2025, favorable foreign exchange effects boosted commercial aircraft revenues by 4%. This positive currency impact helped to balance out a decrease in the number of aircraft delivered during the same period.
The strengthening of the US dollar also had a significant effect on Airbus's financial standing. By the close of 2024, this currency movement contributed to an increase in the overall value of the company's consolidated order backlog.
Interest Rates and Airline Financing
Rising interest rates pose a direct challenge to airlines by increasing the cost of capital. This can make financing new aircraft purchases, a significant capital expenditure for carriers, more expensive. Consequently, airlines might delay or re-evaluate fleet modernization plans, impacting demand for new aircraft from manufacturers like Airbus.
Despite these economic headwinds, Airbus maintains a robust position, evidenced by its substantial order backlog. As of June 2025, Airbus had an order backlog of 8,754 commercial aircraft. This impressive figure underscores the enduring demand for new, fuel-efficient aircraft, driven by airlines' strategic imperatives to upgrade fleets and meet projected passenger growth.
- Increased Borrowing Costs: Higher interest rates directly translate to more expensive debt for airlines, potentially straining their financial capacity for large aircraft investments.
- Fleet Modernization Impact: Financing challenges could lead to deferred or scaled-back fleet renewal programs by airlines, affecting future aircraft orders.
- Airbus's Strong Backlog: Airbus's backlog of 8,754 commercial aircraft as of June 2025 demonstrates resilient airline commitment to upgrading fleets, even amidst economic volatility.
- Long-Term Demand Drivers: The ongoing need for fuel efficiency and capacity expansion continues to fuel demand for new aircraft, supporting manufacturers like Airbus.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Inflation
Airbus experienced significant supply chain disruptions throughout 2024 and into Q2 2025, primarily driven by engine component shortages impacting the A320 Family production. These bottlenecks resulted in a noticeable backloading of aircraft deliveries, delaying revenue recognition and potentially affecting order fulfillment timelines.
To mitigate these persistent issues and bolster production stability, Airbus is undertaking a strategic acquisition of key work packages from Spirit AeroSystems, with the deal anticipated to finalize by Q4 2025. This move aims to bring critical manufacturing processes in-house, thereby enhancing control and reducing reliance on external vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, Airbus is actively implementing strategies to build greater supply chain resilience against ongoing inflationary pressures. These measures include renegotiating pricing agreements with suppliers and establishing strategic inventory buffers to cushion against potential future shocks and cost increases.
- Engine Shortages: Persistent bottlenecks in 2024 and Q2 2025, particularly impacting A320 Family production.
- Delivery Backloading: Supply chain issues led to a shift in aircraft delivery schedules.
- Spirit AeroSystems Acquisition: Expected Q4 2025 closure to secure critical work packages.
- Resilience Measures: Re-pricing agreements and inventory buffers are being utilized to combat inflation.
Global economic expansion fuels air travel demand, with Airbus forecasting a need for 43,420 new aircraft between 2025 and 2044. This growth is strongly tied to economic activity in emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and China.
Fluctuations in jet fuel prices, such as the $90-$100 per barrel range seen in early 2024, directly impact airline operating costs and purchasing decisions.
Currency exchange rates, especially the Euro-US Dollar, significantly affect Airbus's financial results and backlog value, with favorable movements boosting revenues in Q1 2025.
Rising interest rates increase the cost of capital for airlines, potentially delaying fleet modernization and impacting new aircraft orders, although Airbus's substantial backlog of 8,754 aircraft as of June 2025 indicates continued demand.
What You See Is What You Get
AIRBUS PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Airbus delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the aerospace giant. Understand the strategic landscape Airbus operates within, from global trade policies to emerging market demands.
Sociological factors
Public confidence in air travel safety and security is the bedrock of the aviation sector's success. Even though Airbus consistently upholds stringent safety protocols, incidents involving other manufacturers can cast a shadow over the entire industry, intensifying public scrutiny and leading to tighter regulatory frameworks. For instance, in 2023, the FAA reported an increase in tarmac delays and cancellations, partly due to staffing shortages, which can indirectly impact passenger perception of operational reliability.
Maintaining an impeccable reputation for quality and safety is therefore crucial for Airbus to retain the trust of both passengers and airlines. A strong safety record directly translates into sustained demand for their aircraft. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) reported a significant improvement in jet hull loss rates, reaching an all-time low in 2023, demonstrating the industry's commitment to safety, which indirectly bolsters public trust in manufacturers like Airbus.
Societal shifts are profoundly altering air travel. A significant driver is the growing consumer demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious travel options. This preference directly influences airlines' purchasing decisions and spurs innovation in aircraft design, pushing manufacturers like Airbus to prioritize eco-friendly solutions.
Consumers are more aware than ever of aviation's environmental footprint. This heightened awareness compels companies such as Airbus to invest heavily in developing fuel-efficient aircraft and exploring groundbreaking technologies, including hydrogen propulsion. For instance, Airbus has set ambitious goals, aiming for its aircraft to be carbon-neutral by 2050, with significant investment in sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) and advanced aerodynamic designs expected to contribute to this target.
This evolving landscape necessitates a strong emphasis on green technologies and clear, transparent sustainability reporting. Airlines and manufacturers alike are under pressure to demonstrate their commitment to reducing emissions, making sustainability a key competitive differentiator and a critical factor in consumer choice.
The aerospace sector, including Airbus, faces a critical need for specialized skills, with a significant portion of its experienced workforce nearing retirement. Reports from 2024 indicate a persistent skills gap in areas like advanced manufacturing and digital engineering, impacting production timelines and innovation.
Airbus's global operations necessitate a diverse workforce, but attracting and retaining top engineering and technical talent remains a key sociological challenge. In 2024, the company continued to invest heavily in apprenticeship programs and university partnerships to build a pipeline of future skilled employees.
Globalization and Air Connectivity
Globalization continues to fuel the need for better air travel connections, supporting global trade, tourism, and cultural understanding. Airbus's projections for 2024-2043 indicate a substantial rise in demand for both passenger and cargo planes, especially in emerging economies.
This growing interconnectedness highlights air transport's crucial role in linking people and driving worldwide economic growth. For instance, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) reported that air cargo volumes in early 2024 were showing signs of recovery, with a notable uptick in international routes.
- Global passenger traffic is expected to double by 2043 compared to 2019 levels, according to Airbus's Global Market Forecast.
- Emerging markets in Asia are projected to account for a significant portion of this new aircraft demand.
- The ease of travel fostered by air connectivity directly supports the expansion of global supply chains and business operations.
Corporate Social Responsibility Expectations
Airbus faces mounting pressure from society to uphold robust corporate social responsibility (CSR). This includes demonstrating ethical business practices, actively engaging with communities, and prioritizing environmental care. These expectations are shaping how the company operates and communicates its value.
Reflecting these societal demands, Airbus has outlined a comprehensive sustainability strategy. A key goal is to significantly reduce the environmental footprint of its operations and products. For instance, by 2035, Airbus aims to have a zero-emission commercial aircraft in service, a testament to its commitment to a greener future.
The company's dedication extends to social impact through the Airbus Foundation. This foundation actively supports humanitarian aid and community development projects. In 2023, the Foundation supported over 30 projects globally, reinforcing Airbus's commitment to being a responsible corporate citizen.
- Ethical Conduct: Ensuring transparency and integrity in all business dealings.
- Community Engagement: Investing in local communities through various programs and partnerships.
- Environmental Stewardship: Pursuing ambitious goals for emissions reduction and sustainable aviation fuel adoption.
Societal expectations are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, pushing Airbus and the broader aviation industry towards eco-friendly innovations. This includes a strong demand for fuel-efficient aircraft and the exploration of new propulsion technologies like hydrogen. Airbus's commitment is evident in its 2050 carbon-neutral goal, supported by investments in sustainable aviation fuels and advanced designs.
The aerospace sector, including Airbus, is also grappling with a significant skills gap, particularly in advanced manufacturing and digital engineering. Attracting and retaining specialized talent remains a key challenge, prompting companies to invest in training and educational partnerships to build a future workforce. This also impacts the global demand for air travel, with projections indicating a substantial rise in aircraft needs, especially from emerging economies.
Corporate social responsibility is another critical factor, with society demanding ethical practices, community engagement, and environmental stewardship from companies like Airbus. This translates into concrete goals, such as Airbus's aim for a zero-emission commercial aircraft by 2035 and ongoing support for humanitarian projects through its foundation.
Technological factors
Airbus is heavily invested in sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and advanced propulsion, recognizing their critical role in decarbonizing the industry. The company aims for commercial entry of its hydrogen-powered aircraft around 2040, focusing on fuel cell technology and developing necessary infrastructure.
Airbus is heavily invested in Industry 4.0, driving digitalization and automation across its manufacturing. This strategic shift aims to boost efficiency and innovation throughout its operations.
The company is implementing advanced digital technologies and AI to enhance supply chain visibility and optimize production. For instance, predictive maintenance powered by AI is becoming crucial for aircraft longevity and operational reliability.
Airbus is actively developing a robust digital backbone, a foundational element for its future manufacturing and operational advancements. This digital infrastructure is key to staying competitive in the evolving aerospace landscape.
Airbus is heavily invested in developing and integrating new materials, with significant R&D spending in 2024 and projected for 2025. Their focus is on lighter, stronger, and more environmentally friendly composites and alloys.
These advanced materials are critical for improving fuel efficiency. For instance, the A320neo family, which extensively uses composites, boasts a 15% reduction in fuel burn compared to its predecessor.
The drive for sustainability means innovations in materials directly support Airbus’s goal to reduce CO2 emissions per passenger-km by 25% by 2030, with new materials playing a pivotal role in achieving these ambitious targets.
Cybersecurity Threats and Data Protection
As aerospace systems become increasingly interconnected and digitalized, cybersecurity threats pose a significant risk to operations, intellectual property, and even national security. Airbus, like other major players, must continually invest in robust cybersecurity innovations to safeguard its complex systems, which often include sensitive military communication networks and proprietary data. The escalating sophistication of cyberattacks necessitates enhanced protection measures across the entire digital infrastructure.
The aerospace sector is experiencing a notable surge in cyberattacks, with reports indicating a substantial increase in attempts to breach defense and aviation networks. For instance, a 2023 report by a leading cybersecurity firm highlighted a 40% year-over-year increase in attempted attacks targeting critical infrastructure, including aerospace and defense. Airbus must therefore adhere to evolving regulations and frameworks, such as those mandated by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and national defense bodies, to ensure the integrity and security of its operations.
- Increased Investment: Airbus is expected to allocate significant capital towards advanced cybersecurity solutions, including AI-driven threat detection and quantum-resistant encryption, to counter sophisticated attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to stringent data protection regulations like GDPR and sector-specific cybersecurity standards is paramount for maintaining operational licenses and customer trust.
- Industry Trends: The aerospace industry's growing reliance on IoT devices and cloud-based platforms expands the attack surface, making proactive cybersecurity strategies essential.
- Data Protection Focus: Protecting intellectual property, including design blueprints and flight data, is a critical concern, with potential financial losses from data breaches running into billions of dollars for major aerospace firms.
Innovation in Autonomous Flight and Urban Air Mobility (UAM)
The aerospace industry is witnessing a significant push towards autonomous flight systems, a trend Airbus is actively pursuing to mitigate crew shortages and enhance operational safety and efficiency. This technological advancement is crucial for future aviation models.
Airbus is also deeply invested in Urban Air Mobility (UAM), particularly with its development of electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft. The eVTOL market is poised for substantial expansion, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years.
These innovations in autonomous flight and UAM are not just theoretical; they represent tangible future pathways for both passenger air travel and cargo logistics. For instance, the global UAM market was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach over USD 10 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of around 25%.
- Autonomous Flight: Addresses pilot shortages and aims for improved safety and efficiency.
- Urban Air Mobility (UAM): Focuses on eVTOL technology for city-based transport.
- Market Growth: UAM market expected to surge, reaching over USD 10 billion by 2028.
- Airbus's Role: Actively developing and investing in these future aviation technologies.
Airbus is heavily investing in advanced materials, with significant R&D spending in 2024 and projected for 2025, focusing on lighter, stronger, and more environmentally friendly composites and alloys. These materials are crucial for improving fuel efficiency, with the A320neo family, utilizing composites, demonstrating a 15% reduction in fuel burn. This aligns with Airbus’s goal to reduce CO2 emissions per passenger-km by 25% by 2030.
The company is also a leader in sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) and advanced propulsion, aiming for commercial entry of its hydrogen-powered aircraft around 2040, concentrating on fuel cell technology and infrastructure development.
Airbus is embracing Industry 4.0, driving digitalization and automation across manufacturing to boost efficiency and innovation. This includes implementing advanced digital technologies and AI for supply chain visibility and predictive maintenance, enhancing aircraft longevity and reliability.
Further, Airbus is actively developing autonomous flight systems to address pilot shortages and improve safety and efficiency, alongside significant investment in Urban Air Mobility (UAM) and eVTOL aircraft development, a market projected to exceed USD 10 billion by 2028.
| Technological Factor | Airbus Focus/Investment | Impact/Goal | Data Point/Projection |
| Advanced Materials | R&D in composites, alloys | Improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions | A320neo: 15% fuel burn reduction; Target: 25% CO2 reduction/pkm by 2030 |
| Sustainable Propulsion | Hydrogen aircraft development, SAF | Decarbonization of aviation | Commercial entry of hydrogen aircraft targeted around 2040 |
| Industry 4.0 & Digitalization | Automation, AI, predictive maintenance | Enhanced manufacturing efficiency, operational reliability | AI for predictive maintenance |
| Autonomous Flight & UAM | eVTOL development, autonomous systems | Mitigate crew shortages, enhance safety, new transport modes | UAM market projection: > USD 10 billion by 2028 |
Legal factors
Airbus navigates a landscape heavily shaped by aviation safety regulations, overseen by bodies like the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). These stringent rules dictate everything from design and manufacturing to operational procedures, ensuring passenger and crew safety. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, grounding of aircraft, and significant reputational damage.
Recent events in the aviation sector have intensified regulatory scrutiny, prompting potential updates to safety standards and certification pathways for all manufacturers, including Airbus. For instance, following the 737 MAX incidents, the FAA and EASA implemented more rigorous oversight and required extensive modifications. This evolving regulatory environment necessitates continuous investment in compliance and adaptation to maintain market access and operational licenses globally.
As one of the two primary global commercial aircraft manufacturers, Airbus operates under strict antitrust and competition laws across numerous countries. These regulations are designed to prevent monopolies and ensure a level playing field, especially as the industry has seen consolidation and ongoing competition. For instance, the European Commission closely monitors mergers and acquisitions within the aerospace sector to safeguard fair competition.
Navigating these legal landscapes is crucial for Airbus to maintain its market standing and avoid significant legal repercussions. Failure to comply with competition laws can result in substantial fines, operational restrictions, and damage to its reputation, impacting its ability to secure contracts and partnerships. Recent regulatory scrutiny, such as investigations into potential anti-competitive practices in the defense sector, highlights the ongoing importance of diligent legal adherence.
Airbus's competitive edge is built upon a vast collection of intellectual property, encompassing patents for its cutting-edge aircraft, helicopter, and space technologies, alongside trademarks and design rights. This extensive IP portfolio is fundamental to its market position.
Safeguarding these valuable assets through strong legal frameworks is paramount to deterring infringement and ensuring continued innovation. Airbus's substantial investments in research and development underscore the critical importance of IP protection as a core legal priority. For instance, in 2023, Airbus reported R&D expenses of €2.5 billion, highlighting its commitment to developing new technologies that require robust IP protection.
Labor Laws and Union Relations
Airbus navigates a complex web of labor laws across its global operations, impacting everything from employee contracts and working hours to safety standards and compensation. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to adhere to the EU's Working Time Directive, which limits the average working week to 48 hours, while also managing country-specific nuances in regions like the United States with its Fair Labor Standards Act.
Maintaining positive relationships with its diverse workforce, often represented by unions, is a critical legal and operational imperative for Airbus. In 2024, significant union agreements were in place across major manufacturing hubs like France, Germany, and the UK, influencing collective bargaining and dispute resolution processes. The company's ability to foster stable labor relations directly impacts its production schedules and avoids costly industrial actions.
Key considerations for Airbus regarding labor laws and union relations include:
- Compliance with diverse national labor regulations: Adhering to varying employment acts and worker protection laws in over 150 countries where it operates.
- Collective bargaining agreements: Managing ongoing negotiations and existing contracts with major labor unions representing its thousands of employees globally.
- Workplace safety and health standards: Ensuring compliance with stringent legal requirements for employee well-being in manufacturing and engineering environments.
- Managing cross-border employment issues: Addressing legal complexities related to expatriate workers and international labor mobility.
Product Liability and Warranty Laws
Airbus operates under strict product liability and warranty laws due to the critical safety and high value of its aircraft. These regulations mandate that manufacturers guarantee their products meet rigorous safety and quality benchmarks. For instance, in 2023, the European Union continued to refine its product safety regulations, impacting how manufacturers like Airbus must demonstrate compliance and handle potential defects.
The company must actively manage these legal exposures through comprehensive testing protocols, robust quality assurance processes, and clearly defined warranty terms. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage. In 2024, ongoing litigation related to aircraft performance and manufacturing defects across the aerospace sector underscores the importance of these legal frameworks.
- Stringent Safety Standards: Airbus must comply with international aviation safety regulations, such as those set by EASA and the FAA, which dictate design, manufacturing, and maintenance requirements.
- Warranty Obligations: The company provides extensive warranties on its aircraft and components, covering defects in materials and workmanship, which can represent a significant financial commitment.
- Product Recalls and Liability: In cases of identified safety defects, Airbus may face costly product recalls and substantial liability claims from airlines and passengers, as seen in past incidents involving specific aircraft models.
Airbus's operations are deeply entwined with international and national trade laws, impacting its global supply chain and sales agreements. Compliance with export controls, sanctions, and trade tariffs is essential for maintaining market access and avoiding penalties. For example, in 2024, ongoing geopolitical shifts continued to influence trade policies, requiring Airbus to adapt its strategies to navigate potential disruptions and ensure compliance with evolving international trade regulations.
The company must also adhere to intellectual property laws to protect its innovations and technological advancements. In 2023, Airbus reported spending €2.5 billion on research and development, underscoring the critical need for robust patent protection and legal safeguards against infringement. This commitment to innovation necessitates vigilant legal management of its extensive IP portfolio across its aerospace, defense, and space divisions.
Airbus faces significant legal exposure related to product liability and warranty obligations due to the critical safety and high value of its aircraft. In 2024, the aerospace industry continued to grapple with the implications of past incidents, reinforcing the importance of rigorous compliance with safety standards and comprehensive warranty management. Failure to meet these legal benchmarks can lead to substantial financial repercussions and reputational damage.
Environmental factors
Airbus is actively aligning with global climate objectives, including the aviation industry's commitment to net-zero emissions by 2050 and the Paris Agreement. This commitment translates into concrete, near-term goals. For instance, Airbus aims to slash its absolute Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions by a significant 63% by 2030, using 2015 as its baseline year.
Furthermore, the company is addressing emissions generated by its products once they are in use. Airbus has set a target to reduce Scope 3 emissions from the use of sold products by 46% per revenue passenger kilometer (RPK) by 2035. These ambitious targets underscore Airbus's proactive approach to environmental stewardship within the aviation sector.
Noise pollution remains a persistent environmental challenge for communities situated near airports, directly impacting the operational feasibility and public perception of aviation. Aircraft manufacturers, including Airbus, are actively engaged in developing quieter engine technologies and aerodynamic designs to meet increasingly stringent noise regulations.
The European Union's regulations, for instance, continue to push for reduced noise levels, with ongoing discussions and potential revisions expected around 2024-2025. Airbus's commitment to this area is demonstrated through significant R&D investments aimed at achieving these compliance standards, crucial for maintaining social license to operate and ensuring future air traffic growth.
Airbus champions a full lifecycle approach to environmental stewardship, deeply embedding waste management and recycling into its manufacturing processes. The company leverages ISO 14001 certified environmental management systems to actively shrink its industrial footprint, prioritizing responsible material sourcing and optimizing material utilization during production.
These initiatives are crucial for sustainability, with Airbus reporting a significant reduction in waste generation per aircraft produced over the years. For example, by 2023, they aimed to achieve a 10% reduction in waste sent to landfill compared to 2019 levels across their major European sites.
Beyond production, Airbus extends its commitment to maximizing the reuse and recycling of aircraft components at the end of their service life, recognizing the substantial material value locked within retired aircraft.
Sustainable Supply Chain Requirements
Airbus is intensifying efforts to ensure its supply chain meets stringent sustainability criteria, focusing on ethical sourcing and responsible production to reduce environmental impact. This commitment extends to material selection, prioritizing components that enhance aircraft fuel efficiency and overall environmental performance. For instance, Airbus has set targets for increasing the use of sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) within its operations and supply chain, aiming for 10% SAF usage by 2030.
Enhanced supply chain visibility is becoming a critical trend in aerospace, enabling better tracking and management of sustainability metrics. Airbus's proactive approach involves close collaboration with suppliers to drive improvements in areas like carbon emissions, waste reduction, and water usage. By 2024, the company aims to have 90% of its key suppliers report their environmental data through a standardized platform.
- Supplier Engagement: Airbus actively engages with over 1,500 suppliers globally to integrate sustainability into procurement processes.
- Material Innovation: A significant portion of Airbus's R&D budget, often exceeding €1 billion annually, is directed towards developing lighter, more sustainable materials for aircraft.
- SAF Integration: By the end of 2024, Airbus plans to have its entire fleet capable of flying with a 50% SAF blend, with a roadmap towards 100% SAF compatibility by 2030.
Biodiversity Impact of Operations
Airbus acknowledges its environmental footprint extends beyond carbon emissions to encompass biodiversity. While direct operational impacts on biodiversity are not detailed in recent public statements, the company's broader sustainability framework and its support for environmental projects, like those undertaken by the Airbus Foundation, suggest a growing consideration for ecological preservation. For instance, the foundation's involvement in initiatives aimed at protecting endangered species signifies a commitment to mitigating negative environmental externalities.
The company’s commitment to environmental responsibility is reflected in its broader sustainability goals, which implicitly include biodiversity considerations. Airbus's focus on eco-efficient aircraft design and sustainable aviation fuels also contributes indirectly to reducing pressure on natural habitats. By promoting cleaner aviation technologies, Airbus aims to minimize the overall environmental impact of air travel, thereby supporting biodiversity conservation efforts globally.
Airbus's engagement with environmental stewardship, while primarily focused on emissions and fuel efficiency, also touches upon biodiversity. The Airbus Foundation's support for various environmental causes, including wildlife conservation, demonstrates an awareness of the interconnectedness between industrial activity and ecological health. This indirect approach to biodiversity impact management is a key aspect of their corporate social responsibility strategy.
Airbus is deeply committed to environmental sustainability, targeting net-zero emissions by 2050 and a 63% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 2030 against a 2015 baseline. The company is also focused on reducing Scope 3 emissions from the use of sold products, aiming for a 46% decrease per RPK by 2035.
Noise pollution is a key concern, with Airbus investing in quieter engine and aerodynamic technologies to meet evolving EU noise regulations, with potential revisions anticipated around 2024-2025.
Airbus implements robust waste management and recycling practices, utilizing ISO 14001 certified systems to reduce its industrial footprint and aiming for a 10% waste reduction to landfill by 2023 compared to 2019.
The company is also enhancing supply chain sustainability, with a goal for 90% of key suppliers to report environmental data by 2024 and aiming for 10% SAF usage in its operations and supply chain by 2030.
| Environmental Target | Metric | Target Year | Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 & 2 Emissions Reduction | 63% absolute reduction | 2030 | 2015 |
| Scope 3 Emissions Reduction (Use of Sold Products) | 46% per RPK | 2035 | N/A |
| Waste to Landfill Reduction | 10% | 2023 | 2019 |
| Supplier Environmental Data Reporting | 90% of key suppliers | 2024 | N/A |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Usage | 10% | 2030 | N/A |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Airbus PESTLE Analysis utilizes a comprehensive blend of official government publications, leading aerospace industry reports, and reputable financial news outlets. This ensures a robust understanding of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the aviation sector.