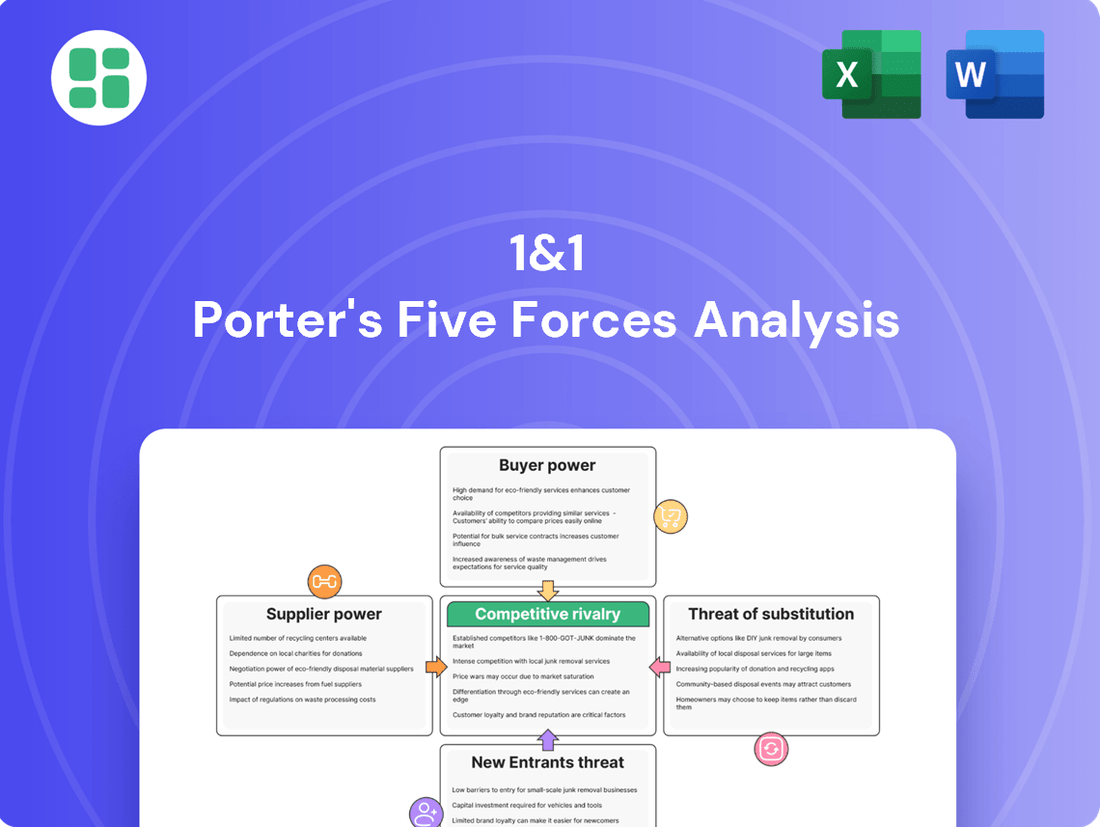
1&1 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
1&1 Bundle
1&1 faces moderate rivalry from established hosting providers and emerging cloud services, while the threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by high capital requirements. Buyer power is significant due to the commoditized nature of basic hosting, but 1&1 can leverage its integrated service offerings to differentiate.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping 1&1’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
1&1 AG's ambition to build its own Open RAN mobile network is tempered by its reliance on infrastructure partners for crucial elements like national roaming and parts of the network rollout. This dependence means 1&1 is not entirely insulated from external factors affecting its infrastructure development.
Delays in connecting mobile masts to fiber optic networks and challenges with specific network components have demonstrably slowed 1&1's rollout progress. For instance, the company has highlighted issues with passive infrastructure providers, including partners like Vantage Towers, which directly impacts the speed and efficiency of their network expansion.
Wholesale network access significantly impacts 1&1's bargaining power with suppliers. Historically, 1&1 depended on national roaming agreements, primarily with Telefónica, and more recently with Vodafone, to provide its customers with nationwide coverage. This reliance grants substantial leverage to these established network operators, as 1&1 requires their existing infrastructure to bridge coverage gaps while its own network is still under development.
As of 2024, 1&1 is actively expanding its own 5G network, aiming for significant coverage milestones. However, until this network is fully established, the company remains reliant on wholesale access, particularly for areas not yet covered by its proprietary infrastructure. This ongoing dependence means that terms and pricing for these wholesale agreements, especially with major players like Vodafone, can directly influence 1&1's cost structure and competitive pricing strategies.
1&1's commitment to Open RAN, utilizing over 80 partners with roughly 50% based in Germany, significantly diversifies its supplier base. This strategy is designed to mitigate the power of any single dominant manufacturer. However, the specialized and evolving nature of Open RAN means that certain providers of critical hardware and software components still wield considerable influence.
Fiber Optic Network Suppliers
The bargaining power of fiber optic network suppliers for a company like 1&1, with its subsidiary 1&1 Versatel operating a substantial network for corporate clients, can be significant. 1&1 Versatel's ongoing modernization, including upgrades with Adtran FSP 3000 technology, highlights a dependence on specific technology providers for critical network enhancements and expansion. This reliance can give these suppliers leverage in pricing and terms, directly impacting 1&1's operational capabilities and capital expenditure.
Key considerations for 1&1 regarding supplier power include:
- Technological Dependence: The specialized nature of fiber optic hardware and software means fewer suppliers can meet the advanced requirements for network upgrades and maintenance, concentrating power with those providers.
- Switching Costs: Migrating to different network technologies or suppliers can be complex and costly, locking 1&1 into existing vendor relationships.
- Supplier Concentration: If the market for high-performance fiber optic equipment is dominated by a few major players, these suppliers will have greater influence over pricing and contract negotiations.
Regulatory Requirements and Spectrum
The German government, acting through the Bundesnetzagentur, wields considerable power as the primary supplier of radio frequency spectrum. This power is evident in the significant costs associated with acquiring and extending spectrum usage rights. For instance, the 2021 spectrum auction for 5G frequencies generated approximately €1.1 billion for the German government, with 1&1 alone investing hundreds of millions of euros to secure its allocated bands.
These regulatory requirements extend beyond mere financial outlay. Telecommunication providers are often burdened with extensive build-out obligations, mandating specific network coverage targets within defined timeframes. Failure to meet these obligations can result in penalties, further increasing the operational risk and cost for companies like 1&1. For example, the 2019 spectrum auction included commitments for nationwide 5G coverage by the end of 2022, a challenging target for all participants.
The bargaining power of spectrum suppliers is further amplified by the limited availability of this crucial resource. Spectrum is a finite asset, and its allocation is a government prerogative. This scarcity means that when new spectrum becomes available or existing licenses are up for renewal, suppliers can dictate terms that heavily influence the cost structure and strategic planning of mobile network operators.
- Spectrum Auctions: The German government, via Bundesnetzagentur, controls spectrum allocation.
- Financial Burden: Spectrum acquisition and renewal involve substantial fees, impacting operator costs.
- Build-out Obligations: Operators face stringent network deployment requirements, adding operational complexity and cost.
- Limited Resource: The finite nature of spectrum enhances the supplier's bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for 1&1 is a critical factor in its Open RAN mobile network build-out. Dependence on wholesale roaming partners like Vodafone for coverage until its own network is fully established grants these established operators significant leverage. Furthermore, specialized fiber optic network providers and critical Open RAN component manufacturers can exert considerable influence due to technological dependencies and high switching costs.
The German government, as the sole supplier of radio frequency spectrum, holds substantial power. This is demonstrated by the significant costs of spectrum acquisition, such as the €1.1 billion generated in the 2021 5G auction, and the stringent build-out obligations imposed on operators like 1&1, which require substantial investment and adherence to deployment timelines.
| Supplier Type | Leverage Factors | Impact on 1&1 |
|---|---|---|
| Wholesale Roaming Partners (e.g., Vodafone) | Existing infrastructure, nationwide coverage | Higher pricing for access, potential limitations on service expansion until own network is ready |
| Fiber Optic Network Providers | Technological specialization, high switching costs | Influence on pricing and terms for network upgrades and expansion |
| Open RAN Component Manufacturers | Specialized, evolving technology | Potential for concentrated power among key providers of critical hardware/software |
| German Government (Spectrum) | Limited resource availability, regulatory control | Substantial costs for spectrum, strict build-out obligations, penalties for non-compliance |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting 1&1, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and ultimately, 1&1's strategic position.
Instantly identify and quantify the impact of each of Porter's Five Forces on your industry, allowing for targeted strategies to mitigate competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
The German telecommunications landscape is a battleground, with giants like Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, and Telefónica vying for customers alongside 1&1. This crowded market means consumers have plenty of options for broadband and mobile services. In 2023, Germany's broadband penetration rate was over 94%, highlighting the widespread availability of services and thus, customer choice.
Customers in Germany, especially those opting for discount brands, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are highly attuned to pricing differences and readily switch providers for better deals.
For 1&1, this price sensitivity translates into a constant need to monitor competitor pricing and promotional activities. For instance, in 2024, the German telecommunications market saw intense price competition, with providers frequently offering bundled discounts on mobile and internet services.
This competitive landscape forces 1&1 to maintain aggressive pricing to retain its customer base. High churn rates are a direct consequence of failing to meet customer price expectations, making pricing strategy a critical factor for sustained growth.
Customers in the mobile services sector, including those of 1&1, often face low switching costs. While moving from a complex fixed-line setup might involve some effort, the widespread availability of mobile number portability means customers can easily switch providers without losing their existing number. This ease of transition significantly boosts their bargaining power, as they can readily seek out better pricing or service packages from competitors.
Availability of Bundled Services
The increasing trend of bundled services, combining internet, TV, and mobile plans, significantly enhances customer bargaining power in the German telecommunications market. Customers can readily switch to providers offering attractive all-in-one packages, creating pressure on companies like 1&1 to remain competitive on price and service integration.
This availability of comprehensive solutions means customers have more leverage. They can effectively compare offerings and demand better value, forcing 1&1 to continuously innovate and refine its bundled product strategies to retain its customer base.
- Bundled Offerings Drive Customer Choice: German telecom providers are actively promoting bundled services, making it easier for consumers to consolidate their communication needs.
- Cost and Convenience Influence Switching: Customers prioritize cost savings and the convenience of a single provider, directly impacting their willingness to switch if better bundled deals are available.
- 1&1 Faces Competitive Pressure: The prevalence of bundled services necessitates that 1&1 maintain highly competitive pricing and feature-rich packages to counter the bargaining power of its customers.
Customer Contract Trends
Customer contract trends for 1&1 AG in the first half of 2025 reveal a nuanced picture of buyer power. While broadband contracts saw a slight decrease, mobile contracts held steady, suggesting customers are actively evaluating their choices based on value and service. This resilience in the mobile sector, despite a competitive market, highlights a willingness to stick with providers offering perceived advantages.
The slight dip in broadband contracts indicates customers are not hesitant to switch if better offers or service quality are available. This sensitivity to value propositions is a key indicator of significant customer bargaining power. 1&1's performance reflects a market where consumers are well-informed and responsive to competitive pressures.
- Broadband contract decline: 1&1 AG experienced a minor reduction in broadband subscriptions during the first half of 2025.
- Mobile contract stability: In contrast, the company maintained a stable number of mobile contracts within the same period.
- Customer price sensitivity: The trends suggest customers are actively comparing offers and are willing to migrate for better value or service.
- Competitive market impact: Intense competition and aggressive customer acquisition strategies by rivals are influencing these contract decisions.
Customers in Germany's telecommunications sector wield considerable bargaining power due to a highly competitive market with numerous providers offering similar services. This intense rivalry, evident in 2024 with aggressive bundled discounts, compels companies like 1&1 to maintain competitive pricing and attractive service packages to retain subscribers. The ease with which customers can switch providers, facilitated by mobile number portability and the growing trend of bundled services, further amplifies their leverage, demanding continuous innovation and value from 1&1.
| Factor | Impact on 1&1 | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Market Competition | High | Germany's telecommunications market is crowded with major players like Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, and Telefónica. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Customers, especially in the discount segment, are highly responsive to price differences and readily switch for better deals. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Mobile number portability makes switching providers seamless, reducing customer commitment. |
| Bundled Services | Increases Power | Customers can easily compare and switch to providers offering attractive all-in-one packages (internet, TV, mobile). |
| Contract Trends (H1 2025) | Indicates active evaluation | Slight decline in broadband contracts for 1&1 AG suggests customers are migrating for better value or service quality. |
Full Version Awaits
1&1 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete 1&1 Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you're viewing is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises. You can confidently use this comprehensive report to understand the strategic landscape and competitive dynamics affecting 1&1.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The German telecommunications landscape is fiercely competitive, dominated by giants like Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, and Telefónica (O2). These established players hold significant market share, making it challenging for newer entrants to gain traction. 1&1 AG is actively working to establish itself as a fourth major national network operator, intensifying this rivalry.
Deutsche Telekom, in particular, demonstrates strong leadership across both mobile and fixed-line services, underscoring the market's concentrated nature. As of early 2024, Deutsche Telekom reported over 42 million mobile customers in Germany, showcasing its substantial presence and the high barrier to entry for competitors seeking to challenge its dominance.
Competitive rivalry in the German telecommunications sector is fierce, driven by substantial investments in network expansion, especially for fiber optic and 5G technologies. Major players, including 1&1, are aggressively rolling out 5G, fueling a race for technological leadership and market share.
This intense competition means operators are constantly upgrading their infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, significant capital expenditures were directed towards enhancing 5G capabilities and expanding fiber optic networks to meet growing data demands.
Competitors in the telecommunications sector frequently employ aggressive pricing tactics and create bundled service packages to win and keep customers. These offerings often include unlimited data plans and combined internet, TV, and mobile services. For instance, in 2024, many providers continued to push unlimited data plans, with average monthly costs for such plans in Germany ranging from €30 to €50, depending on network speed and additional features. This intense competition forces 1&1 to continually evaluate its own pricing and service bundles to remain competitive and retain its market share.
1&1's Open RAN Strategy
1&1's ambitious Open RAN strategy positions it uniquely as Europe's first fully virtualized mobile network operator, aiming for digital sovereignty and enhanced energy efficiency. This disruptive approach directly challenges established players by offering a more flexible and potentially cost-effective network architecture.
However, the rollout has encountered hurdles, impacting its initial competitive edge. For instance, by the end of 2023, 1&1 had deployed approximately 1,000 Open RAN sites, a pace that, while significant, has been slower than initially projected, affecting its ability to rapidly gain market share against incumbent operators with more mature networks.
- Disruptive Entry: 1&1's Open RAN model introduces a new competitive dynamic, leveraging virtualization for agility.
- Digital Sovereignty & Efficiency: The strategy prioritizes control over network infrastructure and aims for reduced energy consumption, a key differentiator.
- Rollout Challenges: Delays in site deployment, with around 1,000 Open RAN sites operational by year-end 2023, have tempered its immediate competitive impact.
- Impact on Rivalry: These challenges mean that while the long-term threat to incumbents is substantial, the immediate competitive rivalry is still in its formative stages.
Regulatory Environment Fostering Competition
The German regulatory environment, particularly as managed by the Bundesnetzagentur, actively cultivates competition within the telecommunications sector. This approach is designed to spur innovation and encourage the expansion of infrastructure.
Key legislation, such as the Telecommunications Act, plays a crucial role in fostering a varied supplier and product ecosystem. This ensures that a competitive marketplace remains central to the industry's dynamics.
- Bundesnetzagentur's Mandate: The German Federal Network Agency is tasked with promoting competition and innovation in telecommunications.
- Telecommunications Act: This act encourages a diverse range of service providers and technological offerings.
- Market Impact: Policies aim to prevent market dominance and ensure fair access for new entrants, driving down prices and improving service quality for consumers.
Competitive rivalry in Germany's telecom sector is intense, with established players like Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, and Telefónica holding significant market share. 1&1 AG's push to become a fourth national network operator intensifies this dynamic, driving substantial investments in 5G and fiber optic expansion. Aggressive pricing and bundled services are common, with unlimited data plans often costing between €30-€50 monthly in 2024, forcing companies to constantly adapt their offerings.
| Competitor | Mobile Customers (approx. early 2024) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Deutsche Telekom | 42+ million | Broad network coverage, fixed-line services |
| Vodafone | ~17 million (mobile) | Converged services, 5G rollout |
| Telefónica (O2) | ~15 million (mobile) | Network modernization, customer acquisition |
| 1&1 AG | ~13 million (mobile) | Open RAN, 5G network build-out |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of over-the-top (OTT) communication services like WhatsApp and Zoom presents a substantial threat to traditional telecom revenue. These platforms offer free or low-cost alternatives for messaging and voice/video calls, directly substituting revenue generated from traditional mobile and fixed-line services. For instance, in 2024, global mobile data traffic continued its upward trajectory, driven by video streaming and messaging apps, further eroding reliance on voice minutes.
Public Wi-Fi and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) represent a growing threat of substitutes for traditional broadband and mobile services. While not a complete replacement for a bundled plan, these alternatives can chip away at market share, particularly for light users or in specific geographic locations. For instance, the widespread availability of free public Wi-Fi in cafes, airports, and public spaces can reduce the need for mobile data consumption when users are on the go.
Fixed Wireless Access, leveraging cellular networks to provide home internet, is also gaining traction. In 2024, FWA deployments continued to expand, offering a viable alternative to cable or fiber, especially in areas where traditional infrastructure is less developed or more expensive to deploy. This can limit the perceived value of traditional fixed broadband plans, forcing providers to compete more aggressively on price and service offerings.
The ongoing rollout of 5G, and the anticipation of 6G, significantly enhances mobile broadband's ability to act as a substitute for traditional fixed-line internet. This is especially true for consumers with moderate data needs or in regions where fiber optic infrastructure development is lagging. For instance, in 2024, 5G adoption continued to climb, with global 5G connections projected to surpass 1.5 billion by year-end, according to various industry reports.
This technological shift is fostering a growing preference for mobile-first or mobile-only connectivity solutions among a segment of the population. As mobile speeds and reliability improve, the perceived necessity of a wired connection diminishes, potentially impacting the subscriber base of fixed-line providers. By the end of 2023, mobile data traffic globally had already seen substantial year-over-year increases, underscoring the growing reliance on wireless connectivity.
Alternative Entertainment and Information Channels
The proliferation of streaming services and online content platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional TV packages. Consumers are increasingly diverting spending towards Over-The-Top (OTT) services like Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime Video, which offer a vast library of on-demand content. This shift directly impacts telecom providers whose core business often includes bundled TV packages.
The accessibility and perceived value of these streaming alternatives are key drivers. For instance, by mid-2024, the global streaming market was projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating substantial consumer investment in these substitute channels. This makes it harder for traditional TV providers to retain subscribers solely on the basis of channel bundles.
- Streaming Dominance: Services like Netflix and Disney+ have captured a significant share of entertainment budgets, offering flexibility and a wide selection.
- Consumer Preference Shift: There's a clear trend towards on-demand viewing over scheduled programming, favoring streaming platforms.
- Content Diversification: Online platforms are not only replicating traditional content but also producing exclusive, high-quality original series and films, further enhancing their appeal.
Satellite Internet and Niche Connectivity Solutions
For specific rural or remote areas in Germany where traditional broadband infrastructure is lacking, satellite internet services and other niche connectivity solutions pose a potential threat of substitutes. These alternatives can fulfill the basic connectivity needs of certain customer segments, offering a viable option when wired connections are unavailable or prohibitively expensive to deploy.
While the overall threat might be limited in densely populated areas of Germany, these niche solutions are particularly relevant for specific user groups. For instance, in 2024, approximately 10% of German households were still located in areas with limited broadband availability, creating a market for alternative providers.
- Satellite Internet: Offers a global solution for remote areas, with providers like Starlink expanding their reach.
- Niche Connectivity: Includes fixed wireless access and specialized mobile solutions catering to underserved regions.
- Market Penetration: While small in Germany's overall market, these substitutes are critical for specific geographical segments.
- Cost-Benefit: The decision to switch often hinges on the cost of satellite or niche solutions versus the lack of traditional broadband options.
The threat of substitutes for traditional telecommunication services is significant, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Over-the-top (OTT) communication platforms like WhatsApp and Zoom directly challenge revenue streams from voice and messaging services, with global mobile data traffic in 2024 continuing its upward trend, fueled by these very applications. Public Wi-Fi and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) also chip away at market share, especially in areas with less developed traditional infrastructure, as seen with the continued expansion of FWA in 2024, offering a competitive alternative to cable and fiber. The increasing capabilities of 5G networks, with global connections projected to exceed 1.5 billion by the end of 2024, further bolster mobile broadband's role as a substitute for fixed-line internet, especially for users with moderate data needs.
| Substitute Category | Impact on Telecom | Key Drivers | 2024 Data/Projections |
|---|---|---|---|
| OTT Communication (WhatsApp, Zoom) | Erodes voice and messaging revenue | Free/low-cost alternatives, convenience | Global mobile data traffic growth |
| Public Wi-Fi | Reduces mobile data consumption | Ubiquitous availability in public spaces | Increased usage in cafes, airports |
| Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | Competes with fixed broadband | Alternative to cable/fiber, especially in underserved areas | Continued deployment and expansion |
| Advanced Mobile Broadband (5G) | Substitutes for fixed-line internet | Improving speeds and reliability, 5G adoption | Global 5G connections > 1.5 billion |
Entrants Threaten
The German telecommunications market presents a formidable barrier to entry due to substantial capital requirements. Establishing a network operator necessitates significant investment in acquiring spectrum licenses, which alone can cost billions of euros, as seen in past auctions. Furthermore, the rollout of 5G and fiber optic infrastructure demands tens of billions of euros in capital expenditure, alongside considerable operational setup costs.
The German telecom market presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its intricate regulatory landscape. The Bundesnetzagentur, Germany's Federal Network Agency, oversees crucial aspects like spectrum allocation, network security standards, and fostering fair competition. Successfully navigating this complex web of rules and securing the necessary operating licenses is a significant challenge for any aspiring new entrant.
The need for extensive infrastructure and coverage presents a significant barrier to entry in the telecommunications sector. New players must invest billions in building out their own networks, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. For instance, 1&1's own experience highlights these challenges, as they have faced considerable hurdles in establishing their nationwide network to compete with established giants like Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone, and Telefónica.
Established Brand Loyalty and Customer Base
Established brand loyalty and a deeply entrenched customer base present a significant barrier for new entrants. Incumbent operators, like those in the telecommunications sector, often benefit from decades of brand recognition and trust, making it challenging for newcomers to attract customers. For instance, in 2024, major telecom providers consistently reported high customer retention rates, often exceeding 90% for their most loyal segments, demonstrating the power of this loyalty.
Newcomers would need to invest heavily in marketing and develop compelling, differentiated offerings to even begin chipping away at this existing loyalty. Consider the advertising spend in 2024; major players allocated billions to maintain their brand visibility and customer relationships. Overcoming this inertia requires not just competitive pricing but also a superior customer experience and unique value propositions.
- Strong Brand Recognition: Incumbents have cultivated strong brand equity over many years, fostering customer trust and familiarity.
- Established Customer Base: Existing subscribers represent a stable revenue stream and a significant hurdle for new entrants to capture market share.
- Distribution Channels: Incumbents possess well-developed sales and service networks, providing convenient access for customers.
- Customer Inertia: Switching costs, both perceived and actual, can deter customers from moving to a new provider, even with attractive offers.
Access to Wholesale Networks and Interconnection
Newcomers to the telecommunications sector face significant hurdles in gaining access to established wholesale networks and interconnection agreements. While regulatory frameworks often mandate fair access, negotiating favorable terms with incumbent operators can be a complex and time-consuming process for companies without their own extensive infrastructure. This can directly impact their cost structure and the quality of services they can offer to customers, especially in terms of national roaming capabilities.
For instance, in 2024, the average wholesale interconnection rate for mobile voice services in the EU remained a point of negotiation, with significant variations between member states. New entrants often find themselves at a disadvantage when seeking to establish these crucial links, as existing players leverage their market power. This lack of immediate, cost-effective access to essential network components can stifle competition and prolong the time it takes for new providers to gain a meaningful market share.
- Wholesale Network Access: New entrants often rely on existing infrastructure for services like mobile data and voice, requiring agreements with established network operators.
- Interconnection Challenges: Securing favorable interconnection rates and terms with incumbents can be difficult, impacting cost-competitiveness.
- Roaming Agreements: The ability to offer national roaming is crucial for coverage, but negotiating these deals can be a barrier for new players.
- Regulatory Influence: While regulations aim for fair access, the practical implementation and negotiation of terms remain a significant hurdle for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the German telecommunications market is significantly low due to immense capital requirements for infrastructure and spectrum licenses, often running into billions of euros. Navigating the complex regulatory environment overseen by the Bundesnetzagentur further deters new players, requiring extensive legal and operational expertise.
Established brand loyalty and existing customer bases, with retention rates often exceeding 90% for loyal segments in 2024, create a substantial hurdle. Newcomers must overcome decades of brand equity and customer inertia, necessitating massive marketing investments and superior value propositions to gain traction.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Spectrum licenses and network build-out (5G, fiber) demand billions in investment. | Extremely High Barrier |
| Regulatory Landscape | Complex rules for spectrum, security, and competition managed by Bundesnetzagentur. | High Barrier |
| Infrastructure & Coverage | Building nationwide networks is time-consuming and capital-intensive. | High Barrier |
| Brand Loyalty & Customer Base | Incumbents benefit from trust and high retention rates (over 90% in 2024). | High Barrier |
| Access to Wholesale Networks | Negotiating favorable interconnection and roaming agreements is challenging. | Medium to High Barrier |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our 1&1 Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and publicly available financial statements. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.