Xeris Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Xeris Bundle
Xeris Pharmaceuticals operates in a dynamic market shaped by several competitive forces. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning and identifying potential advantages or threats.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Xeris’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Xeris Pharmaceuticals' reliance on a limited number of suppliers for its specialized active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. These critical components are essential for Xeris's proprietary XeriSol and XeriJect drug delivery platforms, meaning a disruption or price increase from a key supplier could directly impact Xeris's operations and profitability. For instance, if a particular API required for a high-demand product is only available from two or three manufacturers globally, those suppliers hold considerable leverage.
Biopharmaceutical firms frequently rely on Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) for production, particularly for complex sterile injectable or infusible drug formulations. This reliance can significantly shift bargaining power towards CMOs.
The bargaining power of these suppliers hinges on the availability of qualified CMOs possessing specialized technology platforms and expertise. For instance, the market for aseptic fill-finish services, crucial for sterile injectables, is characterized by a limited number of highly specialized providers. In 2024, the global CMO market for biologics was estimated to be worth tens of billions of dollars, with specialized services commanding premium pricing due to high barriers to entry and stringent regulatory requirements.
A scarcity of CMOs capable of handling intricate processes, such as lyophilization or specialized containment for highly potent compounds, grants these suppliers considerable leverage. This leverage translates into their ability to influence pricing, delivery schedules, and contract terms, potentially increasing costs for biopharmaceutical companies and impacting their overall profitability.
Suppliers providing Xeris with proprietary technology, such as specialized drug delivery devices or manufacturing equipment, can wield considerable bargaining power. If these technologies are protected by patents or require unique manufacturing expertise, Xeris might face substantial costs and operational disruptions when attempting to switch to alternative suppliers. For instance, a supplier holding a patent on a critical component of Xeris's XeriSol platform would have a strong negotiating position, potentially impacting Xeris's production costs and efficiency.
Labor and Specialized Expertise
The biopharmaceutical sector's reliance on highly specialized talent, such as research scientists and regulatory affairs professionals, significantly shapes supplier power. A scarcity of these skilled individuals, or dependence on specialized contract research organizations (CROs) for critical functions like clinical trials, can elevate the bargaining leverage of these human capital providers. This directly influences operational costs and the pace of product development, with potential impacts on project timelines and overall profitability.
Consider the demand for biopharmaceutical talent. In 2024, the global biopharmaceutical market was valued at over $500 billion, a figure that underscores the immense need for specialized expertise to drive innovation and production within this complex industry. For instance, a report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 10% growth in the demand for biochemists and biophysicists between 2022 and 2032, indicating a persistent need for highly educated professionals.
- Talent Scarcity: A shortage of experienced biopharmaceutical researchers or manufacturing specialists can lead to increased recruitment costs and longer hiring cycles, empowering those with the requisite skills.
- CRO Dependence: Companies heavily reliant on CROs for essential services like Phase III clinical trials may face higher fees and less favorable contract terms due to the specialized nature and limited supply of these outsourcing partners.
- Impact on Costs: Increased labor costs and fees from specialized service providers directly translate to higher operating expenses for biopharmaceutical firms, potentially affecting R&D budgets and product pricing.
- Project Timelines: Delays in securing specialized talent or CRO capacity can extend research, development, and regulatory approval timelines, impacting a company's ability to bring new therapies to market efficiently.
Regulatory Requirements and Quality Standards
Suppliers to Xeris, particularly those in the pharmaceutical sector, must navigate a complex web of regulatory requirements. For instance, adherence to FDA Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is non-negotiable for companies producing injectable drugs, a core area for Xeris. This creates a barrier to entry for new suppliers and elevates the standing of those already demonstrating consistent compliance.
Suppliers who have established a track record of meeting these stringent quality standards and possess robust internal quality control systems naturally wield greater bargaining power. Their ability to consistently deliver products that meet regulatory scrutiny, especially for sensitive applications like drug delivery systems, makes them invaluable partners. This is particularly true for specialized components or active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) where few suppliers can meet the required specifications.
The cost and inherent risk involved in switching to a new, potentially unproven supplier can be significant for Xeris. This includes the expense of re-validating processes, potential disruptions to production, and the risk of quality issues arising from a new source. Consequently, Xeris may be compelled to accept less favorable terms from established, compliant suppliers to maintain operational stability and product integrity.
- Regulatory Compliance as a Differentiator: Suppliers meeting FDA GMP standards for injectable drug components command higher influence.
- Quality Control Systems: Proven robust quality control systems enhance supplier bargaining power due to reduced risk for Xeris.
- Switching Costs and Risk: The substantial costs and risks associated with supplier changeover incentivize Xeris to maintain relationships with compliant suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: For specialized components, Xeris's reliance on a limited number of compliant suppliers increases their leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Xeris Pharmaceuticals is elevated due to the specialized nature of its required components and the limited number of qualified providers. This is particularly true for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients essential for Xeris's proprietary drug delivery platforms.
The biopharmaceutical industry's reliance on highly specialized Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) for sterile injectables and complex formulations grants significant leverage to these service providers. In 2024, the global CMO market for biologics demonstrated this, with specialized services commanding premium pricing due to high barriers to entry and stringent regulatory demands.
Furthermore, suppliers of proprietary technology, such as unique drug delivery devices, and providers of specialized talent, like biopharmaceutical researchers, also hold substantial bargaining power. The scarcity of these skills and technologies, coupled with the high switching costs for Xeris, reinforces supplier influence over pricing and contract terms.
| Factor | Impact on Xeris | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized APIs/Excipients | Increased costs, potential supply disruptions | Limited global suppliers for niche components |
| CMO Services (Aseptic Fill-Finish) | Higher fees, less favorable terms | Global biologics CMO market valued in tens of billions; high demand for specialized services |
| Proprietary Technology Suppliers | Higher component costs, potential production delays if switching | Patent protection and unique manufacturing expertise create leverage |
| Specialized Talent/CROs | Increased labor/service costs, extended project timelines | Projected 10% growth in demand for biochemists/biophysicists (2022-2032) |
What is included in the product
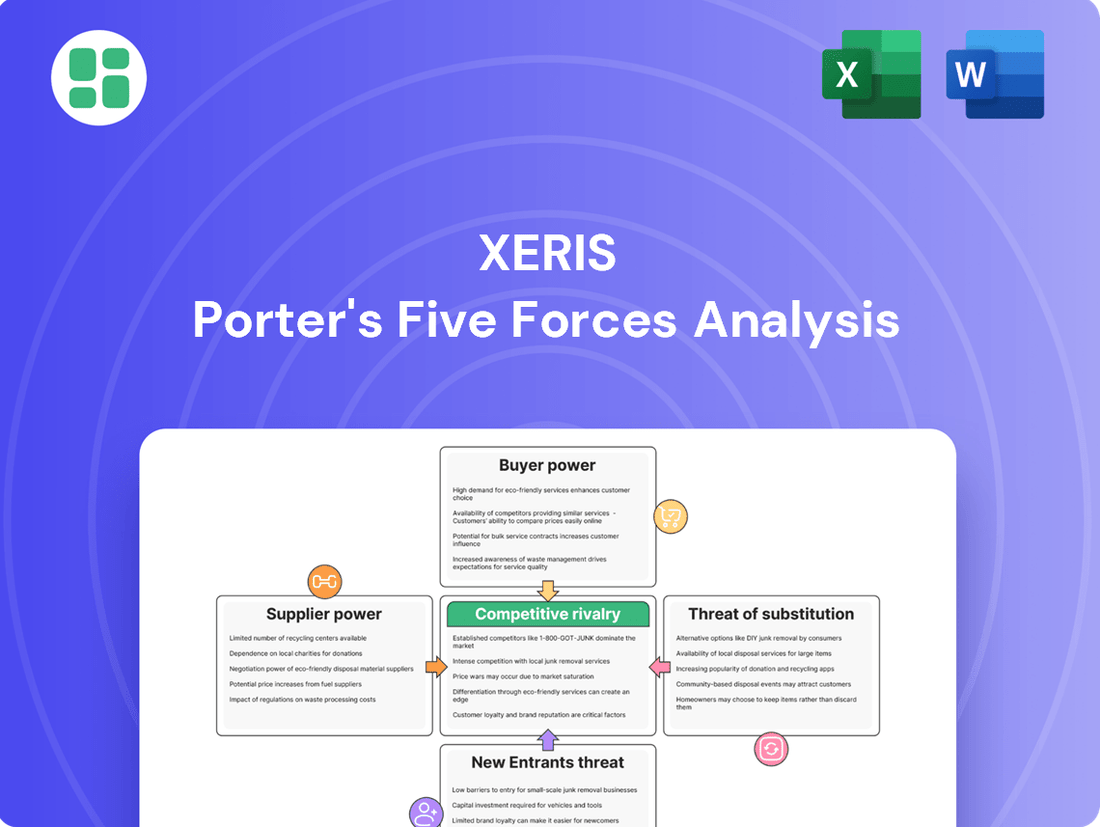
Xeris's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its market, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Xeris's customer base is primarily composed of powerful entities like healthcare systems, hospitals, pharmacies, and crucially, large payers such as insurance companies and government healthcare programs. These major players wield significant influence over Xeris's market penetration and profitability.
The bargaining power of these customers stems from their ability to dictate formulary inclusion, negotiate reimbursement rates, and control market access for Xeris's products. For instance, in 2024, major pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) continued to consolidate power, impacting drug pricing and access for manufacturers.
This concentration of purchasing power means Xeris must carefully manage relationships and pricing strategies to secure favorable terms. The ability of payers to bundle services or shift patient populations to alternative treatments further amplifies their leverage in negotiations with companies like Xeris.
Customers, particularly payers like insurance companies and government programs, are keenly focused on controlling healthcare expenses. This means Xeris faces significant pressure to justify the pricing of its products. In 2024, the average annual cost of specialty drugs continued to climb, creating a challenging environment for any pharmaceutical company. Xeris's value proposition hinges on proving that its ready-to-use insulin delivery systems not only offer convenience but also lead to better patient adherence and fewer complications, ultimately lowering overall healthcare spending.
The availability of therapeutic alternatives significantly impacts Xeris's customer bargaining power. While Xeris's technology offers convenience, patients and healthcare providers constantly assess other treatment options for conditions like diabetes and hypoglycemia. If comparable, more affordable drugs or management strategies are readily available, customers are less likely to accept a premium price for Xeris's offerings, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
Formulary Inclusion and Reimbursement Policies
For a drug to achieve widespread adoption, it's crucial for it to be listed on insurance formularies and benefit from favorable reimbursement policies. This process is often intricate and lacks transparency, granting significant leverage to payers. Exclusion from a formulary can drastically curtail a drug's market access and its potential for sales.
In 2024, the bargaining power of customers, particularly large insurance companies and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), remains a dominant force in the pharmaceutical industry. These entities negotiate aggressively on pricing and access for drugs, directly impacting manufacturer revenue. For instance, PBMs manage drug benefits for millions of Americans, giving them considerable clout in demanding discounts and rebates.
- Formulary Access: Inclusion on a formulary is a prerequisite for most patients to access a drug through their insurance.
- Reimbursement Rates: The level of reimbursement directly affects the net price a pharmaceutical company receives for its product.
- Negotiating Leverage: Payers, especially large ones, can dictate terms by threatening to exclude drugs or offer less favorable coverage.
- Market Penetration Impact: Formulary exclusion can severely limit a drug's market reach, impacting sales volume and revenue potential significantly.
Physician and Patient Demand
Physician and patient demand, while indirect, significantly impacts Xeris's customer bargaining power. When Xeris products demonstrate superior patient outcomes or ease of use, this can generate substantial pull-through demand. For instance, if a Xeris product significantly reduces injection frequency or improves patient comfort compared to alternatives, physicians are more likely to prescribe it, and patients will request it.
This physician and patient preference translates into leverage for Xeris when negotiating with healthcare providers and payers. Strong demand from end-users can diminish the ability of these intermediaries to dictate terms or force price concessions. In 2024, the increasing focus on patient-centric care and real-world evidence of product efficacy directly amplifies this dynamic for companies like Xeris.
- Physician Influence: Prescribing physicians act as key gatekeepers, their adoption driven by clinical efficacy and patient benefit.
- Patient Pull-Through: Positive patient experiences and demand for Xeris's convenient delivery systems can pressure providers.
- Market Differentiation: Products offering clear advantages in patient comfort or treatment adherence strengthen Xeris's negotiating stance.
- 2024 Trends: Increased emphasis on patient-reported outcomes and real-world data further empowers demand-driven influence.
Xeris's customers, primarily large healthcare systems, hospitals, pharmacies, and major payers like insurance companies, wield considerable bargaining power. Their ability to influence formulary inclusion, negotiate reimbursement rates, and control market access directly impacts Xeris's revenue. In 2024, the consolidation of power among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) intensified pricing pressures, as these entities manage benefits for millions, demanding significant discounts.
The focus on cost containment within healthcare systems means Xeris must demonstrate clear value, such as improved patient adherence and reduced overall treatment costs, to justify its pricing. The availability of alternative therapies also strengthens customer leverage, as Xeris's premium pricing is challenged if comparable, more affordable options exist. This dynamic is critical, as formulary exclusion can severely limit market penetration.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Xeris (2024 Focus) |
| Payers (Insurance, Government Programs) | Formulary control, reimbursement negotiation, cost containment focus | Intensified pricing pressure, demand for value demonstration (e.g., reduced overall healthcare spend) |
| Healthcare Systems/Hospitals | Purchasing volume, formulary decisions, adoption of new technologies | Negotiation on bulk pricing, influence on physician prescribing patterns |
| Pharmacies | Distribution channel control, patient access points | Influence on stocking and availability, potential for preferred stocking agreements |
What You See Is What You Get
Xeris Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact Xeris Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive upon purchase, ensuring complete transparency and no hidden surprises. You are viewing the final, professionally compiled document, ready for immediate download and application to your strategic planning needs. What you see here is precisely the comprehensive analysis you'll gain access to, offering actionable insights into Xeris's competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The biopharmaceutical arena, particularly for conditions like diabetes and hypoglycemia, is intensely crowded. Xeris faces a multitude of rivals, ranging from established pharmaceutical behemoths with extensive R&D budgets and market reach to agile, specialized biotech companies. This sheer volume ensures a dynamic competitive landscape where innovation and market penetration are constantly challenged.
Xeris's competitive battleground extends beyond direct competitors offering similar injectable formulations. The company must also contend with alternative drug delivery systems, such as oral medications or inhaled therapies, which may offer different patient convenience profiles. Furthermore, existing standard-of-care treatments, even if less advanced, represent a significant competitive force due to established patient and physician trust and reimbursement structures.
In 2024, the global diabetes care market alone was valued at over $60 billion, with significant portions dedicated to injectable therapies. Companies like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, major players in this space, reported substantial revenue growth from their insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonist portfolios, highlighting the scale of competition Xeris navigates. The ongoing development and approval of new diabetes and hypoglycemia treatments by these and other firms underscore the high level of rivalry.
Xeris Pharmaceuticals leverages its XeriSol and XeriJect proprietary technology platforms to create ready-to-use, stable injectable and infusible drug formulations. This advanced formulation technology significantly differentiates Xeris from competitors, offering enhanced convenience and potentially improved patient outcomes.
The strength of Xeris's patent protection for these technologies is a key factor in mitigating direct rivalry. In 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to see significant investment in R&D, with companies prioritizing novel drug delivery systems to gain a competitive edge and secure market share.
The biopharmaceutical sector faces fierce competition driven by substantial fixed costs in R&D, clinical trials, and manufacturing. Companies must achieve high sales volumes to recoup these investments, fostering aggressive pricing and marketing tactics.
Market Growth Rate and Existing Market Share
Xeris Biopharma's competitive rivalry is shaped by the growth rates of its target therapeutic markets and the established positions of its competitors. While Xeris has experienced significant revenue increases, for example, its revenue grew from $107.9 million in 2022 to $177.4 million in 2023, the intensity of competition varies. In rapidly expanding markets, new entrants can find space, but in more mature segments, companies like Xeris face a tougher battle for market share.
The competitive landscape for Xeris is characterized by the market share held by established pharmaceutical companies. For instance, in the diabetes market where Gvoke competes, major players like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly have substantial market dominance. This means Xeris must not only innovate but also strategically capture share from these entrenched competitors.
- Market Growth Dynamics: Therapeutic areas with higher growth rates, such as certain segments of obesity or rare diseases, can temper rivalry by allowing multiple players to gain traction. Conversely, slower-growing or saturated markets intensify competition for existing customers.
- Competitor Market Share: Xeris faces rivalry from companies with significant, often decades-long, market share in their respective therapeutic areas. For example, in the glucagon market, established players have built strong brand recognition and distribution networks.
- Product Differentiation: The degree to which Xeris's products, like Recorlev for Cushing's syndrome or Gvoke for hypoglycemia, are differentiated from competitor offerings directly impacts rivalry. Highly differentiated products can command better pricing and market position.
- R&D Investment and Pipeline: Competitors' ongoing investments in research and development and their pipeline of future products also influence rivalry. A strong competitor pipeline can signal future competitive threats for Xeris.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for healthcare providers and patients are a significant factor influencing competitive rivalry for Xeris Biopharma. These costs encompass a provider's familiarity with an existing drug, the necessary training for its administration, and how seamlessly it integrates into established treatment protocols. For instance, switching from a well-understood insulin delivery system to a new one requires retraining staff and potentially updating patient education materials.
While Xeris's innovative delivery systems aim to simplify administration, established competitors benefit from inertia. Many healthcare providers and patients are accustomed to existing methods, making the perceived switching cost lower for these familiar alternatives. This can intensify the rivalry as Xeris must demonstrate a clear and substantial advantage to overcome this ingrained preference.
- Familiarity with Existing Treatments: Healthcare professionals and patients often stick with treatments they know, reducing the perceived risk and effort associated with change.
- Training and Integration: Implementing new drug delivery systems requires staff training and integration into existing clinical workflows, adding to the overall switching cost.
- Perceived Cost-Benefit Analysis: Even if Xeris offers superior technology, the immediate costs and effort of switching may outweigh the long-term benefits in the eyes of some decision-makers.
The competitive rivalry for Xeris is intense, driven by numerous players in the biopharmaceutical sector, including large, established companies and smaller, specialized firms. This rivalry is further fueled by substantial R&D and manufacturing costs, necessitating high sales volumes and aggressive market strategies. Xeris must differentiate its offerings and overcome the inertia of existing treatments and patient familiarity to gain market share.
The market growth dynamics and competitor market share significantly shape the rivalry Xeris faces. While high-growth markets can accommodate multiple players, mature markets intensify competition for existing customers. Companies with substantial, long-standing market share present a formidable challenge, requiring Xeris to demonstrate clear product differentiation and a robust R&D pipeline to compete effectively.
Switching costs for healthcare providers and patients are a critical factor in competitive rivalry. Familiarity with existing treatments, the effort involved in staff training, and integration into clinical workflows can create significant barriers to adoption for new technologies. Xeris must offer a compelling cost-benefit analysis to persuade stakeholders to switch from established, well-understood alternatives.
| Competitor | Therapeutic Area Focus | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novo Nordisk | Diabetes, Obesity | $33.7 Billion | Ozempic, Rybelsus, Tresiba |
| Eli Lilly and Company | Diabetes, Obesity, Immunology | $34.1 Billion | Trulicity, Mounjaro, Jardiance |
| Sanofi | Diabetes, Cardiovascular, Vaccines | $47.0 Billion | Lantus, Toujeo, Dupixent |
| Xeris Biopharma | Diabetes, Hypoglycemia, Cushing's Syndrome | $177.4 Million | Gvoke, Recorlev |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Xeris's ready-to-use injectable and infusible drug formulations is a significant concern. Alternative drug delivery methods, such as oral medications, transdermal patches, or inhalers, can offer comparable therapeutic benefits with enhanced patient convenience or reduced costs. For instance, the global market for oral solid dosage forms, a primary substitute, is projected to reach over $160 billion by 2027, indicating a substantial existing and growing alternative.
The threat of generic and biosimilar competition is a significant concern for Xeris. Once patents expire, lower-priced alternatives can enter the market, impacting sales and profitability. For instance, the market for insulin, a key area for diabetes management, has seen substantial generic and biosimilar entry, driving down prices and increasing competitive intensity.
While Xeris's proprietary platforms offer some differentiation, its products, including those in its pipeline, are not immune. The company's experience with Keveyis, which faced competitive pressures, highlights this vulnerability. In 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to grapple with the economic impact of biosimilar approvals, with estimates suggesting significant savings for healthcare systems but increased pressure on originator drug manufacturers.
For conditions like diabetes and hypoglycemia, non-pharmacological interventions such as diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes can serve as effective substitutes for drug therapy, especially in the early stages or for preventative measures. This significantly broadens the competitive landscape beyond direct pharmaceutical rivals.
Alternative Therapeutic Approaches
The threat of substitutes for pharmaceutical companies like Xeris is significant, especially with rapid advancements in medical science. New therapeutic modalities, such as gene therapies and cell-based treatments, are emerging that could offer alternative or even superior ways to manage diseases currently treated with traditional drugs. For example, the global gene therapy market was valued at approximately $7.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift towards alternative approaches that could displace existing drug classes.
These innovative therapies often target the root cause of diseases rather than just managing symptoms, making them highly attractive to patients and healthcare providers. This potential for more definitive treatment outcomes poses a direct challenge to the long-term relevance of many conventional pharmaceutical products. The increasing investment in and development of these novel treatments underscore the growing competitive pressure from substitute therapeutic avenues.
Consider the impact on conditions like genetic disorders or certain cancers, where gene editing technologies are showing promising results. Companies focusing on these cutting-edge solutions could capture significant market share, diminishing the demand for established drug treatments. The threat is amplified as these new therapies become more accessible and cost-effective.
- Emerging Gene Therapies: The gene therapy market is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach tens of billions by the end of the decade.
- Cell-Based Treatments: Advancements in CAR T-cell therapy and other regenerative medicine approaches offer alternative disease management strategies.
- Targeting Root Causes: Novel therapies increasingly aim to correct underlying genetic defects, potentially rendering symptomatic treatments obsolete.
- Increased R&D Investment: Significant capital is flowing into biotech and advanced therapy research, accelerating the development of substitutes.
'Watch and Wait' or Symptomatic Management
For certain health conditions, especially those that are mild or don't occur frequently, patients and doctors might choose a 'watch and wait' strategy or focus solely on managing symptoms without using specific medications. This approach acts as a substitute, where the 'treatment' is non-drug related or very minimal.
This 'watch and wait' or symptomatic management can significantly impact the pharmaceutical industry. For instance, in 2024, many over-the-counter remedies for common colds and mild allergies, which often fall under symptomatic management, continued to see robust sales, indicating a preference for self-care over prescription drugs for less severe ailments.
- Reduced Prescription Volume: Mild conditions often don't require prescription drugs, directly decreasing the market for certain pharmaceuticals.
- Growth in OTC and Self-Care: This trend fuels the market for over-the-counter medications and health-related products.
- Patient Empowerment: Patients are increasingly taking control of their health, opting for less invasive interventions when appropriate.
- Focus on Lifestyle: For some conditions, lifestyle changes like diet or exercise are considered the primary 'treatment,' substituting pharmaceutical solutions.
The threat of substitutes for Xeris's injectable and infusible drugs is multifaceted, encompassing alternative delivery methods and non-pharmacological interventions. For example, the global market for oral solid dosage forms, a key substitute, was projected to exceed $160 billion by 2027, highlighting a substantial existing alternative. Furthermore, emerging gene and cell-based therapies, with the gene therapy market valued at approximately $7.9 billion in 2023, represent a growing challenge by offering potentially curative solutions that could displace symptom-management drugs.
| Substitute Category | Example | Market Size/Growth Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Drug Delivery | Oral Medications | Global oral solid dosage market projected over $160B by 2027 |
| Novel Therapeutic Modalities | Gene Therapies | Global gene therapy market valued at $7.9B in 2023, with substantial projected growth |
| Non-Pharmacological Interventions | Lifestyle Changes (Diet, Exercise) | Increasing patient focus on self-care and preventative health |
| Watchful Waiting/Symptomatic Management | Over-the-counter remedies | Robust sales of OTC medications for common ailments in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical industry presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high research and development (R&D) costs. Developing a new drug from discovery to market approval is a lengthy and incredibly expensive undertaking. For instance, estimates suggest the average cost to bring a new drug to market can exceed $2 billion, with some analyses pointing even higher when accounting for failed projects.
These substantial upfront investments cover extensive preclinical testing and multiple phases of rigorous clinical trials, often spanning a decade or more. This significant financial hurdle acts as a powerful deterrent, making it exceedingly difficult for new companies without substantial capital backing to challenge established players in the biopharmaceutical space.
The biopharmaceutical sector faces formidable barriers to entry, largely due to stringent regulatory approval processes. Agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandate extensive clinical trials and data submission to prove both safety and efficacy, a journey that can take years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, the average cost to develop a new drug was estimated to be around $2.6 billion in 2023, a figure that underscores the immense capital and expertise required before a product can even reach the market.
Xeris Pharmaceuticals' robust intellectual property portfolio, including its proprietary XeriSol and XeriJect technology platforms, acts as a formidable barrier to new entrants. These patents, along with specific product patents, effectively shield Xeris's innovations.
New companies entering the market face a difficult choice: invest heavily in developing entirely new compounds and delivery systems, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive, or pursue licensing agreements for Xeris's existing, protected technologies.
The lengthy lifespan of patents, often extending for decades, further solidifies this barrier, significantly delaying the potential market entry of competitors who would need to wait for patent expiry to legally replicate Xeris's offerings.
Need for Specialized Manufacturing and Distribution
The need for specialized manufacturing and distribution acts as a significant barrier to entry for new players in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly for companies like Xeris Biopharma. Manufacturing sterile injectable and infusible drugs demands substantial investment in highly specialized facilities, advanced equipment, and rigorous quality control systems. These operational requirements are not only costly to establish but also expensive to maintain, creating a high capital hurdle.
Furthermore, building effective sales, marketing, and distribution networks for pharmaceutical products is a complex and challenging undertaking. New entrants must navigate intricate regulatory landscapes and establish trust with healthcare providers and patients. For instance, companies aiming to replicate Xeris's capabilities in developing ready-to-use injectable formulations would face considerable upfront costs and time to market.
- High Capital Investment: Building cGMP-compliant sterile manufacturing facilities can cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Specialized Expertise: Requires highly skilled personnel in areas like aseptic processing, quality assurance, and regulatory affairs.
- Distribution Network Complexity: Establishing cold chain logistics and compliant pharmaceutical distribution channels is a significant undertaking.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining FDA approval for manufacturing processes and products is a lengthy and resource-intensive process.
Established Brand Loyalty and Physician Relationships
Established players like Xeris have cultivated deep-seated brand loyalty and strong relationships with physicians, healthcare providers, and patient advocacy groups. This trust, built over time, makes it challenging for new entrants to gain a foothold. For instance, Xeris's existing partnerships are crucial in a market where clinical experience and physician endorsement are paramount.
Newcomers must invest significantly to replicate the trust and acceptance that established companies enjoy. This often involves extensive marketing, clinical trials, and building a reputation from scratch. In 2024, the healthcare sector continued to see a high barrier to entry for new pharmaceutical and medical device companies, with many struggling to secure physician adoption even with innovative products.
- Physician Trust: Deep relationships with healthcare professionals are a significant barrier.
- Brand Loyalty: Existing patient and provider loyalty reduces the appeal of new entrants.
- Market Acceptance: Gaining acceptance requires overcoming established trust and clinical validation.
- High Entry Costs: New companies face substantial costs in building relationships and brand recognition.
The threat of new entrants for Xeris Pharmaceuticals is considerably low due to the immense capital required for research, development, and navigating stringent regulatory pathways. For instance, the average cost to bring a new drug to market was estimated to be around $2.6 billion in 2023, a figure that highlights the financial muscle needed to compete.
Xeris's strong intellectual property, including its proprietary XeriSol and XeriJect technology, creates a significant barrier, forcing potential competitors to either invest in entirely new, costly innovations or wait for patent expirations, which can extend for decades.
Furthermore, the specialized manufacturing and distribution requirements for sterile injectables, coupled with the need to build deep physician trust and brand loyalty, present substantial hurdles. In 2024, new pharmaceutical companies continued to face challenges in gaining physician adoption, even with innovative products, underscoring the difficulty of breaking into established markets.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data/Fact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D and manufacturing costs | Significant financial barrier | Average drug development cost: ~$2.6 billion (2023) |
| Intellectual Property | Patented technologies (XeriSol, XeriJect) | Limits replication and market entry | Patents can last for 20 years from filing |
| Regulatory Hurdles | FDA approval process | Time-consuming and costly | Clinical trials can span over a decade |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established relationships with healthcare providers | Difficult for newcomers to gain acceptance | Physician endorsement critical for market penetration |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Xeris Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.