Spartan Delta Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Spartan Delta Bundle
Spartan Delta's competitive landscape is shaped by a delicate balance of supplier power, buyer bargaining, and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Spartan Delta’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Spartan Delta, operating in the Western Canadian oil and gas sector, faced a concentrated supplier base for essential drilling, completion, and seismic services. This concentration meant that a few key players often held substantial market share, reducing the choices available to exploration and production companies like Spartan Delta.
Such market dynamics can translate into increased costs for vital operational inputs. For instance, during periods of robust demand or when supply is constrained, these specialized service providers can leverage their market position, driving up prices and directly impacting Spartan Delta's operational expenses and profitability.
Switching oil and gas suppliers often incurs significant expenses for operators. These costs can include retooling existing equipment to be compatible with new materials or processes, retraining staff on different operational procedures, and the potential downtime associated with the transition. For instance, a study in 2024 highlighted that the average cost for a mid-sized oil producer to switch to a new drilling fluid supplier could range from $500,000 to $1.5 million, depending on the complexity of the integration.
These substantial switching costs effectively limit the bargaining power of companies like Spartan Delta. When it becomes expensive and disruptive to change providers, operators are less likely to seek out alternative suppliers, even if those alternatives offer marginally better pricing or terms. This inertia strengthens the hand of existing suppliers, allowing them to maintain their pricing power and influence over contract negotiations.
Suppliers of advanced drilling technology, specialized software, and environmental services hold significant bargaining power due to their unique expertise. This specialized knowledge is critical for Spartan Delta's efficient and compliant operations, making these suppliers indispensable.
The proprietary nature of their technology and expertise limits Spartan Delta's ability to negotiate prices or terms. Often, readily available or comparable substitutes are scarce, reinforcing the suppliers' leverage in the market.
Impact of Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Suppliers offering critical environmental compliance solutions, such as those specializing in carbon capture and storage (CCS) or advanced water treatment, are increasingly influential. As regulatory landscapes tighten, companies like Spartan Delta, which prioritize sustainable operations, become more dependent on these specialized providers to meet stringent environmental standards. This dependence directly translates into enhanced bargaining power for these suppliers.
For instance, the global carbon capture market was valued at approximately USD 6.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, driven by climate change mitigation efforts. This growth underscores the increasing demand for CCS technologies and, consequently, the bargaining leverage of companies at the forefront of this sector. Spartan Delta’s commitment to reducing its environmental footprint means these suppliers are not just vendors but essential partners in achieving operational and regulatory objectives.
- Increased Reliance on Specialized Environmental Services: Companies face growing pressure to adhere to evolving environmental regulations, making suppliers of CCS and water management solutions indispensable.
- Supplier Leverage in Compliance Negotiations: The specialized nature of environmental compliance technologies grants these suppliers significant negotiating power, especially when regulatory deadlines loom.
- Strategic Importance of Environmental Partners: Spartan Delta's dedication to responsible resource development elevates the strategic importance and bargaining strength of suppliers who enable them to meet environmental stewardship goals.
Commodity Price Fluctuations on Supplier Power
Commodity price fluctuations significantly impact the bargaining power of suppliers in the oil and gas sector. Prolonged periods of low oil and gas prices, such as those experienced in recent years, can diminish supplier leverage. For instance, during a downturn, exploration and production (E&P) companies often curtail capital expenditures, directly reducing the demand for services and equipment from suppliers. This reduced demand can force suppliers to offer more competitive pricing to secure business.
However, this dynamic can shift rapidly. As the Canadian oil and gas sector looks towards 2025 with expectations of increased production and capital investment, suppliers are poised to regain stronger bargaining positions. This anticipated surge in demand for services, drilling equipment, and specialized labor will likely empower suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms and potentially increase their prices. For example, a projected rise in capital spending by Canadian E&P firms in 2025 could see increased activity across the board, from well completions to midstream infrastructure development.
- Supplier Leverage: Generally high, but tempered by prolonged low commodity prices.
- Impact of Downturns: Reduced E&P capital expenditure leads to lower demand for supplier services.
- 2025 Outlook: Anticipated increase in Canadian oil and gas production and investment is expected to strengthen supplier bargaining power.
- Market Shift: Renewed demand in 2025 will likely enable suppliers to command higher prices and better contract terms.
Spartan Delta's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly influenced by the concentration of key service providers in the Western Canadian oil and gas sector. High switching costs, often in the hundreds of thousands to over a million dollars for mid-sized producers, lock companies into existing relationships, bolstering supplier leverage.
Suppliers of specialized technology and critical environmental compliance solutions, such as carbon capture, hold considerable sway due to their unique expertise and the scarcity of viable alternatives. The growing global demand for these services, with the carbon capture market valued at approximately USD 6.0 billion in 2023, further amplifies their negotiating strength.
While prolonged low commodity prices can weaken supplier power by reducing demand, the outlook for 2025 suggests a reversal. Anticipated increases in Canadian oil and gas production and capital investment are expected to empower suppliers, enabling them to command higher prices and more favorable contract terms.
| Factor | Impact on Spartan Delta | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Reduces negotiation flexibility | Few key players in drilling, completion, seismic services |
| Switching Costs | Increases reliance on existing suppliers | $500k - $1.5M for mid-sized E&P to switch drilling fluid suppliers (2024 est.) |
| Specialized/Environmental Services | High supplier leverage due to critical expertise | Carbon Capture market ~$6.0B (2023); growing demand |
| Commodity Price Outlook (2025) | Expected to strengthen supplier power | Projected increase in Canadian E&P capital spending |
What is included in the product
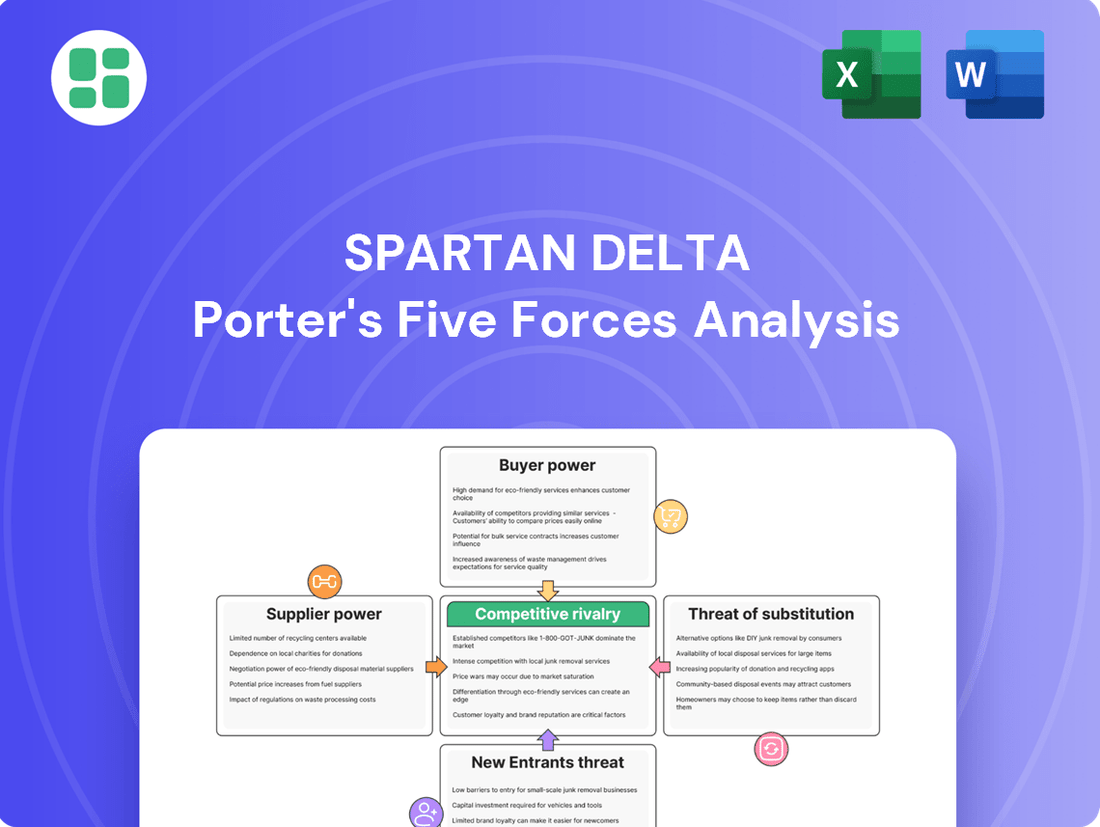
Analyzes the five competitive forces impacting Spartan Delta, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces analysis that highlights your most critical pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Spartan Delta's primary customers for crude oil and natural gas are large entities like refiners and utility companies. However, the sheer scale of the global and North American commodity markets means that no single buyer typically wields significant power over a producer like Spartan Delta. This broad customer base limits any individual customer's ability to dictate pricing for raw commodities.
Oil and natural gas are essentially undifferentiated commodities; their pricing is dictated by the broader forces of global and regional supply and demand, not by individual customer bargaining. This means that a single buyer has very little power to negotiate prices down for these essential resources.
The ongoing expansion of critical pipeline infrastructure, such as the Trans Mountain Expansion (TMX) and Coastal GasLink, is a game-changer for Western Canadian producers. By providing enhanced access to a wider array of markets, including those in Asia, these projects significantly reduce reliance on any single buyer.
This improved and diversified market access directly bolsters the bargaining position of producers. When producers can easily reach multiple international and domestic markets, they are less vulnerable to the demands of any one customer, thereby diminishing customer bargaining power.
While individual customers might easily switch between generic commodity suppliers, the energy sector's complex infrastructure creates significant indirect switching costs. For instance, a refinery designed for specific crude oil grades requires substantial investment to reconfigure for different types, effectively locking it into certain supply chains. This can provide producers with a degree of stability within their niche markets.
Regulatory Environment and Demand Drivers
Customer demand for natural gas is significantly shaped by government policies and broader economic trends. For example, Alberta's natural gas producers benefit from robust demand driven by liquefied natural gas (LNG) export facilities and the power generation sector. This strong demand, particularly in 2024, directly enhances the bargaining power of these customers.
However, the long-term landscape is being influenced by environmental regulations and the ongoing energy transition. Initiatives focused on decarbonization could gradually shift customer preferences away from natural gas, potentially altering the bargaining power dynamics over time.
- Government policies and energy transition initiatives are key drivers of customer demand.
- Increased demand for natural gas from LNG exports and power generation in Alberta strengthens customer bargaining power.
- Environmental regulations promoting decarbonization may shift customer preferences in the long run.
- In 2024, Alberta's natural gas producers saw strong demand, bolstering customer leverage.
Consolidation Among Buyers
Consolidation among buyers, such as large refiners or pipeline operators, can significantly amplify their bargaining power. This is particularly relevant in commodity markets where a few dominant players can dictate terms. However, for upstream producers like Spartan Delta, the impact is often tempered by the vast number of buyers and the competitive landscape. For instance, in the North American energy sector, the sheer volume of transactions and the diversity of purchasers generally diffuse buyer concentration, limiting the leverage of any single consolidated entity over producers.
- Buyer Consolidation Impact: Increased bargaining power for large refiners or pipeline operators.
- Mitigating Factors: Competitive downstream/midstream sectors and diverse buyer base in North America.
- Spartan Delta's Position: Generally benefits from a broad market, reducing the impact of buyer consolidation.
- Market Dynamics: High transaction volumes and numerous buyers limit individual buyer leverage.
The bargaining power of customers for Spartan Delta is generally low due to the commodity nature of oil and gas and a diverse buyer base. While large refiners can exert some influence, the vast North American market and extensive infrastructure limit any single buyer's ability to dictate terms. However, specific market conditions, like strong demand from LNG exports in Alberta during 2024, can temporarily shift leverage towards customers.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Spartan Delta's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Nature | Low; prices set by market forces | Limited ability to differentiate |
| Buyer Concentration | Potentially high for large refiners | Mitigated by broad market access |
| Market Access (e.g., TMX) | Reduces reliance on specific buyers | Strengthens producer position |
| Demand Drivers (e.g., LNG in 2024) | Can increase customer leverage | Varies with specific commodity demand |
Preview Before You Purchase
Spartan Delta Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Spartan Delta Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability. You're looking at the final, ready-to-use analysis, providing all the insights you need without any hidden placeholders or further customization required.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Spartan Delta operates within the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB), a region characterized by a mature and highly fragmented oil and gas exploration and production landscape. This environment hosts a significant number of competitors, ranging from large, integrated energy corporations to smaller, specialized junior companies, all vying for resources and market presence.
The sheer volume of players in the WCSB fuels intense competitive rivalry. This rivalry is particularly acute when it comes to securing access to desirable drilling locations and expanding market share, impacting pricing and operational efficiency for all participants.
In the oil and natural gas sector, products are largely homogenous, meaning companies compete intensely on cost and efficiency rather than product differentiation. This lack of distinction means buyers are indifferent to the source of their fuel, as long as quality standards are met. For instance, in 2024, the benchmark West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil price fluctuated significantly, underscoring the sensitivity to supply and demand dynamics rather than brand loyalty.
This commodity nature forces producers like Spartan Delta to focus on operational excellence and cost management to maintain profitability. Companies that can extract and deliver oil and gas at a lower cost per barrel or per unit of energy have a distinct advantage in this highly competitive landscape. Efficiency gains, technological adoption, and strategic access to infrastructure are therefore critical differentiators.
The Canadian energy sector is experiencing significant consolidation, with companies prioritizing acquisitions over exploration to gain reserves. Spartan Delta's own strategic acquisitions and subsequent reorganization highlight this trend, demonstrating how firms are actively repositioning to enhance value and achieve greater economies of scale in a competitive landscape.
Capital Intensity and Access to Funding
The oil and gas sector demands substantial capital for exploration, drilling, and infrastructure, making capital intensity a significant barrier. Companies like Spartan Delta, which prioritize generating free funds flow, gain a crucial edge by being able to self-finance growth and weather market volatility. This financial discipline is essential for sustained competition in an industry where project financing is paramount.
Access to capital directly influences a company's ability to undertake large-scale projects and maintain production levels. In 2024, many energy companies faced higher borrowing costs, emphasizing the importance of robust balance sheets and efficient capital allocation. Spartan Delta's strategy of focusing on free funds flow generation in 2024 directly addresses this challenge, positioning them to invest in opportunities without over-reliance on external debt.
- High Capital Requirements: Exploration and production in the oil and gas industry necessitate billions of dollars in upfront investment.
- Funding Access as a Differentiator: Companies with strong credit ratings and access to diverse funding sources can secure favorable terms for capital projects.
- Spartan Delta's Financial Strategy: In 2024, Spartan Delta's emphasis on free funds flow aimed to bolster its financial flexibility and reduce reliance on external financing, enhancing its competitive standing.
- Industry Trend: Many exploration and production companies are increasingly prioritizing balance sheet strength and cash flow generation to navigate capital market conditions.
Regulatory Burden and ESG Pressures
Increasing regulatory burdens, such as evolving carbon pricing mechanisms and stricter emissions caps, are adding layers of complexity and cost to operations, thereby intensifying competition within the sector. For instance, in 2024, many energy companies faced new reporting requirements related to Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, directly impacting operational budgets.
Companies that proactively adapt to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) pressures, through strategic investments in areas like carbon capture technologies or significant reductions in methane emissions, are carving out a competitive advantage. This focus on sustainability is becoming a key differentiator, pushing companies to innovate beyond mere production volume metrics.
- 2024 saw a notable increase in proposed climate-related disclosures, impacting capital allocation decisions.
- Companies investing in methane reduction technologies reported an average of 5% lower operational costs in pilot programs during the year.
- ESG-focused funds continued to attract significant inflows, signaling investor preference for sustainable operations.
The competitive rivalry within the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin is fierce due to the homogenous nature of oil and gas products. Companies like Spartan Delta must excel in cost efficiency and operational excellence to stand out. This intense competition is further amplified by the significant capital requirements and increasing regulatory pressures, making financial flexibility and ESG adaptation crucial for sustained success.
| Metric | Spartan Delta (2024 Estimate) | Industry Average (2024 Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Production Cost per BOE (USD) | $15.50 | $17.00 |
| Free Funds Flow Yield | 8.5% | 6.2% |
| ESG Investment as % of CapEx | 12% | 9% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The long-term threat of substitutes for oil and natural gas is increasingly driven by the rapid growth of renewable energy. Sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power are becoming more competitive, especially for electricity generation.
In 2024, global renewable energy capacity additions are projected to reach new highs, with solar photovoltaic leading the charge. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that solar PV alone accounted for over two-thirds of all renewable capacity additions in 2023, a trend expected to continue and accelerate.
Government policies and ongoing technological advancements are further bolstering the integration of renewables into the global energy mix. This acceleration poses a significant, albeit evolving, threat to traditional fossil fuel demand over the long term.
Biofuels, such as ethanol and renewable diesel, are emerging as significant substitutes, particularly within the transportation industry. Canada's commitment to these cleaner alternatives is evident in its increasing investments and consumption growth. For instance, by the end of 2023, Canada's renewable diesel production capacity was projected to reach approximately 4.4 billion liters annually, a substantial increase from previous years.
This escalating adoption of biofuels, coupled with the accelerating market penetration of electric vehicles, presents a tangible long-term threat to the demand for crude oil and its refined petroleum products. The Canadian government's targets, like aiming for 15% renewable content in gasoline and diesel by 2030, underscore this shift and its potential impact on traditional fuel markets.
Hydrogen is emerging as a significant substitute in the energy sector, particularly in Canada, where substantial investments are being made. While not yet a dominant force, its potential to decarbonize industries could eventually challenge natural gas in power generation and industrial processes.
By 2024, global investment in hydrogen projects was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, signaling a serious commitment to its development. This growing momentum suggests that hydrogen could become a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, impacting sectors currently reliant on natural gas.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Improvements in energy efficiency are a significant substitute threat to Spartan Delta's oil and gas business. For instance, advancements in vehicle fuel economy and the adoption of electric vehicles directly reduce the demand for gasoline and diesel. In 2024, global investments in energy efficiency are projected to reach over $500 billion, a testament to the growing focus on reducing energy consumption across all sectors.
Government policies and increasing consumer awareness further amplify this threat. Many nations are setting ambitious energy efficiency targets and promoting conservation measures. For example, the European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive aims to improve energy efficiency by at least 11.7% by 2030 compared to 2020 projections. This focus on conservation directly dampens the potential market size for new oil and gas production.
- Reduced Demand: Enhanced efficiency in industries and transportation directly lowers the need for fossil fuels.
- Policy Support: Government mandates and incentives for energy conservation bolster the substitute threat.
- Consumer Behavior: Growing public awareness about climate change encourages more energy-conscious choices, impacting demand.
- Technological Advancement: Innovations in areas like smart grids and efficient appliances further reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
Policy-Driven Transition to Lower-Carbon Systems
Government policies focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, such as net-zero targets by 2050, are a major driver for the threat of substitutes. These policies, including carbon taxes and emissions caps, actively encourage a move towards lower-carbon energy sources and technologies. For instance, in 2024, many nations are implementing or strengthening carbon pricing mechanisms, which directly increases the cost of carbon-intensive activities, making alternatives more attractive.
The push for decarbonization creates a significant threat by making cleaner substitutes more competitive. Incentives for renewable energy adoption and electric vehicles, for example, are accelerating the transition away from fossil fuels. By 2024, global investment in clean energy technologies reached record highs, demonstrating a clear market shift driven by these policy initiatives.
- Policy Impact: Government mandates and incentives directly elevate the viability and adoption of lower-carbon substitutes.
- Economic Shift: Carbon pricing and emissions regulations make traditional energy sources less economically favorable, driving demand for alternatives.
- Technological Advancement: Policy support fuels research and development in clean technologies, improving their performance and reducing costs, thereby increasing their substitutability.
- Market Transformation: The collective effect of these policies is a systemic change in consumer and industrial behavior, favoring sustainable options over conventional ones.
The threat of substitutes for oil and natural gas is intensifying due to the rapid expansion of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, which are becoming increasingly cost-competitive for electricity generation. By 2024, global renewable energy capacity additions were projected to hit record levels, with solar PV leading this growth, accounting for over two-thirds of all additions in 2023 according to the IEA.
Biofuels, such as renewable diesel, are also gaining traction, particularly in the transportation sector. Canada's renewable diesel production capacity was expected to reach approximately 4.4 billion liters annually by the end of 2023, reflecting a significant increase and a direct challenge to traditional fuel demand.
Furthermore, advancements in energy efficiency, driven by government policies and consumer awareness, directly reduce the overall demand for fossil fuels. Global investments in energy efficiency were projected to exceed $500 billion in 2024, highlighting a significant trend that dampens the market for new oil and gas production.
| Substitute Category | Key Developments (2023-2024) | Impact on Oil & Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Record capacity additions, solar PV dominance (IEA) | Decreasing demand for fossil fuels in power generation |
| Biofuels | Growing production capacity (e.g., Canada's ~4.4 billion liters/year by end-2023) | Direct substitution for gasoline and diesel in transportation |
| Energy Efficiency | Over $500 billion global investment projected for 2024 | Reduced overall energy consumption, lowering demand for all energy sources |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for companies like Spartan Delta, operating in the oil and gas sector, is significantly mitigated by exceptionally high capital requirements. Exploration and production (E&P) activities demand enormous upfront investments, ranging from geological surveys and drilling operations to the construction of essential infrastructure like pipelines and processing plants. For instance, a single offshore oil platform can cost billions of dollars to build and deploy, a sum prohibitive for most aspiring companies.
New entrants in the Canadian energy sector confront significant regulatory and environmental barriers. Navigating federal and provincial laws, including rigorous environmental impact assessments and permitting processes, demands substantial time and financial resources. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain key permits for new energy projects in Canada continued to be lengthy, often exceeding 18-24 months, a clear deterrent to smaller or less capitalized new players.
Securing access to commercially viable land and proven oil and gas reserves presents a substantial hurdle for new companies entering the sector. This scarcity of prime acreage, particularly in established producing regions like Western Canada, means that most attractive opportunities are already controlled by incumbent companies, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a competitive footing.
Spartan Delta's own strategy highlights this challenge, as the company actively pursued strategic acquisitions to bolster its land holdings and reserve base. For instance, in 2023, Spartan Delta completed several acquisitions, adding significant production and undeveloped acreage, demonstrating the necessity of acquiring existing positions rather than relying solely on new exploration in a mature market.
Technological Expertise and Infrastructure
Technological expertise is a significant barrier for new entrants in the oil and gas sector, particularly in complex regions like the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. Companies need advanced knowledge in horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing to operate efficiently and profitably. For instance, the average horizontal well length in the Montney formation, a key area within the basin, has steadily increased, demanding sophisticated completion techniques.
Access to and the cost of building out essential infrastructure, such as pipelines and processing facilities, also present a substantial hurdle. New players must either secure access to existing midstream networks, which can be costly and competitive, or invest heavily in their own. In 2024, the capital expenditure required for new pipeline projects in Canada remained substantial, reflecting the ongoing need for expanded capacity and the associated regulatory and construction challenges.
- Specialized Skills: Horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing require highly skilled personnel and specialized equipment.
- Infrastructure Costs: Building or accessing pipelines and processing facilities involves significant capital investment.
- Operational Complexity: The WCSB's geology demands advanced technological solutions for resource extraction.
- Capital Intensity: The high upfront costs deter many potential new entrants.
Established Player Dominance and Consolidation
The dominance of established players and ongoing industry consolidation present a significant barrier to entry. Companies like Suncor Energy and Canadian Natural Resources, major players in the Canadian oil and gas sector, benefit from substantial economies of scale, giving them a cost advantage that newcomers struggle to match. For instance, in 2023, these integrated energy giants reported billions in revenue, reflecting their entrenched market positions and operational efficiencies. This trend means that any new entrant would face immense pressure to compete on price and volume from these already powerful entities.
Furthermore, the capital-intensive nature of the energy industry, particularly in exploration and production, requires massive upfront investment. This financial hurdle is amplified by the consolidation trend, where larger, well-capitalized companies are actively acquiring smaller competitors. This reduces the number of independent entities and consolidates market power, making it even more challenging for a truly new, independent company to emerge and gain traction. The reduced availability of acquisition targets for aspiring entrants further solidifies the position of existing large-scale operators.
- Established Player Dominance: Large companies possess significant market share and economies of scale, creating a high barrier for new entrants.
- Consolidation Trend: Ongoing mergers and acquisitions by larger entities reduce opportunities for new companies to enter and grow.
- Capital Intensity: The energy sector requires substantial initial investment, a challenge exacerbated by the financial strength of incumbents.
- Reduced Acquisition Targets: Industry consolidation limits the availability of smaller companies for potential acquisition by new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Spartan Delta in the Canadian oil and gas sector is considerably low due to immense capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the necessity of securing prime acreage. These factors, combined with the need for advanced technological expertise and access to established infrastructure, create substantial barriers. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to develop a new oil sands project in Canada remained in the billions, a figure that effectively deters most new players.
The dominance of established companies, bolstered by ongoing industry consolidation, further solidifies this low threat. Larger players benefit from significant economies of scale and entrenched market positions, making it difficult for newcomers to compete. Spartan Delta's own strategic acquisitions in 2023, adding considerable production and undeveloped acreage, underscore the industry's reliance on acquiring existing assets rather than organic entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example (2023-2024 Data) |
| Capital Requirements | Extremely high upfront investment for exploration, infrastructure, and operations. | Billions of dollars for new projects; offshore platform costs can exceed $1 billion. |
| Regulatory & Environmental | Lengthy and complex permitting and compliance processes. | Average 18-24 months for key energy project permits in Canada. |
| Land & Reserve Access | Scarcity of commercially viable acreage controlled by incumbents. | Prime land in Western Canada already secured by major producers. |
| Technological Expertise | Need for advanced skills in drilling and extraction techniques. | Increasing complexity and length of horizontal wells in key formations. |
| Infrastructure Access | Costly to build or access pipelines and processing facilities. | Substantial capital expenditure required for new pipeline projects. |
| Established Player Dominance | Economies of scale and market power of large incumbents. | Major players like Suncor and CNRL reporting billions in revenue in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Spartan Delta Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, publicly available financial statements, and reputable trade publications.
We leverage insights from government economic data, competitor annual reports, and specialized industry databases to provide a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the competitive landscape.