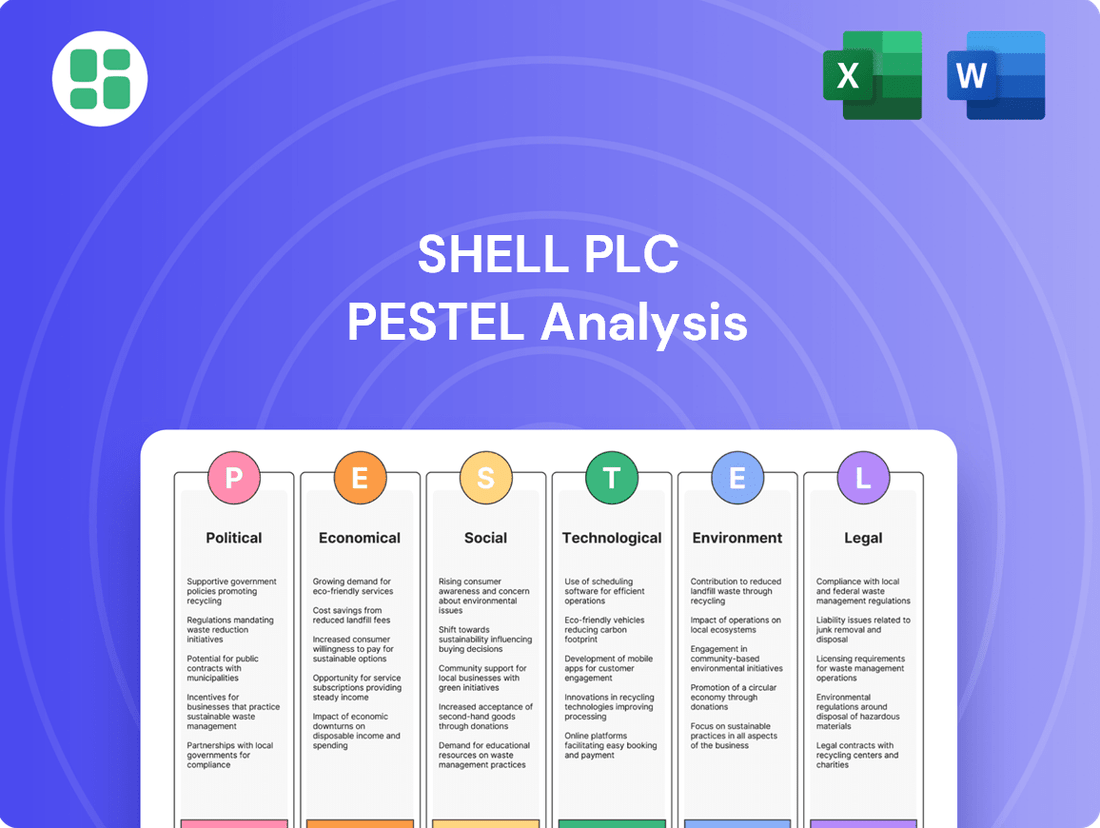
Shell Plc PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Shell Plc Bundle
Navigate the complex world of Shell Plc with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political shifts, economic volatility, and evolving social trends are shaping the energy giant's future. Unlock actionable insights to inform your strategy and gain a competitive edge. Download the full version now for a complete breakdown.
Political factors
Governments globally are increasingly prioritizing the energy transition, enacting policies that promote renewable energy sources and impose stricter regulations on carbon emissions. For instance, the EU's Fit for 55 package aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels, directly influencing energy companies like Shell. These initiatives create both opportunities and challenges for Shell, shaping its investment strategies in areas like hydrogen, biofuels, and offshore wind, while also impacting the economics of its existing fossil fuel assets.
Global geopolitical events, including regional conflicts and trade tensions, directly influence the energy sector by disrupting supply chains, impacting energy prices, and shaping investment climates. For Shell, a major player in the global energy market, these instabilities present both risks and opportunities, particularly regarding the security of its oil and gas infrastructure and its ongoing efforts to diversify its energy portfolio.
For instance, the ongoing conflict in Eastern Europe has led to significant volatility in global oil and gas prices, with Brent crude futures fluctuating around $80-$90 per barrel in early 2024, impacting Shell's operational costs and revenue streams. Shell's strategic investments in renewable energy sources, such as offshore wind projects in the North Sea, are partly a response to these geopolitical uncertainties, aiming to create a more resilient business model less dependent on fossil fuels.
Changes in international trade policies, including tariffs and trade agreements, directly impact Shell's costs for importing and exporting energy products and advanced technologies. For instance, in early 2024, ongoing trade tensions between major economies continued to create uncertainty around the stability of global supply chains for critical components used in LNG infrastructure and renewable energy projects.
Shell's extensive global operations mean its competitiveness is significantly sensitive to these evolving trade policies. Tariffs on imported materials or equipment can increase capital expenditure for new projects, while favorable trade agreements can reduce operational costs and open new market opportunities. For example, the European Union's efforts to diversify energy sources in 2024, partly through new trade pacts, could offer Shell advantages in its European liquefied natural gas (LNG) market share.
Adapting to these policy shifts is crucial for Shell to maintain profitable trade flows. The company's strategic planning must account for potential disruptions or benefits arising from trade disputes or new bilateral and multilateral agreements. By closely monitoring and proactively responding to changes in tariffs and trade pacts, Shell can better manage its international business and secure its supply chains.
Regulatory changes in exploration and production
Governments globally are continually revising rules for oil and gas exploration and production. These updates cover areas like licensing, environmental protection, and safety protocols. For Shell, this means potential increases in operating expenses, restrictions on accessing new reserves, and new compliance obligations that directly affect its upstream activities.
Staying informed about these evolving regulations is crucial for Shell's ongoing operations and future growth plans. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to refine methane emission standards for the oil and gas sector, impacting operational practices and requiring new monitoring technologies. Similarly, in the North Sea, the UK government's focus on energy security and net-zero targets has led to new licensing rounds with stricter environmental conditions, influencing investment decisions for projects like Shell's participation in the Jackdaw field development.
- Increased Compliance Costs: New environmental regulations, such as stricter methane emission controls, can necessitate investment in advanced monitoring equipment and process modifications, potentially adding millions to operational budgets.
- Access to Reserves: Changes in licensing policies or the designation of protected areas can limit Shell's ability to explore and develop previously identified reserves, impacting future production volumes.
- Operational Adjustments: Enhanced safety regulations or requirements for specific technologies, like blowout preventers with advanced safety features, can mandate changes in drilling practices and equipment, affecting project timelines and costs.
International relations and sanctions
International relations and sanctions significantly impact Shell's global operations. For instance, sanctions imposed on Russia following the 2022 invasion of Ukraine led Shell to announce its exit from joint ventures with Gazprom and its withdrawal from the Sakhalin-2 LNG project. This decision, impacting billions in assets, highlights the direct financial and operational consequences of geopolitical shifts.
These geopolitical tensions can restrict Shell's access to crucial energy resources and markets, forcing strategic adjustments. The ongoing volatility in global energy markets, influenced by sanctions and international disputes, necessitates continuous risk assessment and potential portfolio restructuring to mitigate exposure.
Shell must closely monitor evolving international relations to navigate sanctions regimes effectively. This includes understanding the implications of sanctions on supply chains, trade routes, and investment opportunities in key energy-producing regions.
- Geopolitical Risk Mitigation: Shell's 2023 financial statements noted significant impacts from geopolitical events, including the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and related sanctions, which necessitated impairments and adjustments to its Russian business operations.
- Market Access Restrictions: Sanctions can limit Shell's ability to procure or sell oil and gas in affected countries, disrupting established trade flows and requiring the development of alternative market strategies.
- Divestment Strategies: In response to sanctions and geopolitical pressures, companies like Shell have been compelled to divest assets in certain regions, impacting long-term growth strategies and capital allocation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Shell must ensure strict adherence to all international sanctions, which involves complex compliance frameworks and potential penalties for non-compliance, adding operational overhead.
Government policies are increasingly steering energy markets towards decarbonization, with initiatives like the EU's Green Deal and the US Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 encouraging renewable energy investments. For Shell, this translates into strategic shifts, with significant capital allocation towards low-carbon solutions, such as its investments in offshore wind and hydrogen projects, aiming to align with net-zero targets. These policy directions directly influence the economic viability of traditional fossil fuel operations and necessitate robust adaptation strategies.
Geopolitical instability, exemplified by the ongoing conflict in Eastern Europe and its impact on global energy supply chains, continues to create price volatility. In early 2024, Brent crude oil prices fluctuated, underscoring the need for energy security and diversification. Shell's strategic response includes bolstering its liquefied natural gas (LNG) portfolio and expanding renewable energy capacity to mitigate risks associated with these disruptions.
Evolving trade policies and international relations significantly shape Shell's global operational costs and market access. For instance, ongoing trade tensions in early 2024 created uncertainty regarding the supply of critical components for energy infrastructure. Shell's ability to navigate these complexities, including adapting to new trade agreements and potential tariffs, is crucial for maintaining competitive energy flows and securing its supply chains.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors influencing Shell Plc, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
The PESTLE analysis for Shell Plc offers a clear, summarized version of complex external factors, simplifying strategic discussions and ensuring all stakeholders grasp key market dynamics and potential risks.
Economic factors
Fluctuations in global oil and gas prices are a primary economic driver for Shell, directly impacting its revenues, profitability, and investment capacity in both fossil fuels and renewable projects. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, Shell reported adjusted earnings of $7.7 billion, a decrease from $9.6 billion in the same period of 2023, partly influenced by lower commodity prices.
Sustained periods of high or low prices necessitate adaptive financial strategies, including capital allocation adjustments and cost management initiatives. Shell's 2024 capital expenditure plan of $23-25 billion reflects this, balancing investments in traditional energy sources with a growing focus on lower-carbon solutions, a strategy directly shaped by the prevailing price environment.
The overall health of the global economy significantly impacts Shell's performance. During 2024, projections indicated continued, albeit moderate, global economic growth. For instance, the IMF forecasted global GDP growth of 3.2% for 2024, a slight uptick from 2023. This growth generally translates to increased energy demand across industrial, transportation, and consumer sectors, which benefits Shell's sales volumes and profitability.
However, the specter of economic slowdowns or recessions poses a direct threat. A recession typically leads to reduced industrial output and lower consumer spending, both of which curtail energy consumption. This directly affects Shell's sales volumes and can put downward pressure on profit margins. For example, a significant global recession, similar to the sharp contraction experienced in 2020, would likely see a noticeable dip in Shell's revenue streams.
Conversely, periods of robust economic expansion create favorable conditions for Shell. Increased manufacturing activity, higher transportation needs, and greater consumer purchasing power all drive up demand for oil and gas products. This can create opportunities for Shell to increase production, invest in new projects, and potentially achieve higher profit margins, as seen in periods of strong global growth prior to 2024.
Rising inflation directly impacts Shell's operational costs. For instance, in early 2024, global inflation rates remained a concern, with the IMF projecting a global average of 5.8% for 2024, though moderating from 2023. This means the cost of procuring raw materials like crude oil and natural gas, as well as labor and logistics, can increase significantly, squeezing profit margins if not passed on to consumers.
Changes in interest rates, particularly those set by major central banks like the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, have a substantial effect on Shell's financial strategy. As of mid-2024, interest rates in many developed economies were still elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels, increasing the cost of borrowing for Shell's capital-intensive projects, such as new offshore drilling or renewable energy infrastructure development. This higher cost of capital can influence investment decisions and the overall attractiveness of Shell's financial performance to investors.
Currency exchange rate fluctuations
Currency exchange rate fluctuations significantly impact Shell's financial results. As a global energy giant, its revenues and expenses are denominated in various currencies, and these are translated into U.S. dollars for reporting. For instance, a stronger U.S. dollar against currencies like the Euro or British Pound can reduce the reported value of earnings generated in those regions. Conversely, a weaker dollar can boost reported earnings.
In 2024, the volatility in major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, presented ongoing challenges. For example, if Shell earns substantial revenue in Euros, and the Euro depreciates against the U.S. dollar, those Euro earnings translate into fewer U.S. dollars, directly impacting reported profits. This exposure affects not only profitability but also the comparative cost of operations across different geographical segments.
- Impact on Revenue: A stronger USD can decrease the reported value of international sales.
- Impact on Expenses: Conversely, a weaker USD can increase the cost of dollar-denominated imports for non-U.S. operations.
- Competitive Positioning: Exchange rate shifts can alter the cost competitiveness of Shell's products in different markets.
- Financial Reporting: Translation adjustments due to currency movements are a regular feature in Shell's financial statements.
Investment in renewable energy
The economic viability of renewable energy investments for Shell is shaped by fluctuating market prices for commodities like oil and gas, which can impact the relative attractiveness of transitioning to renewables. Government incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, play a crucial role in de-risking these investments. For instance, in 2024, the US Inflation Reduction Act continues to provide significant tax credits for renewable energy projects, bolstering their economic case.
Shell's strategic shift towards energy transition necessitates considerable capital allocation towards areas like biofuels, hydrogen, and renewable electricity generation. In 2024, Shell announced plans to invest billions in low-carbon energy solutions, including expanding its renewable power portfolio and developing hydrogen infrastructure. The cost of capital is a critical factor, with higher interest rates potentially increasing the hurdle rate for these long-term projects, though government support can help mitigate this.
- Market Conditions: Volatility in fossil fuel prices directly impacts the economic competitiveness of renewable energy investments.
- Government Incentives: Policies like tax credits and subsidies are vital for improving the financial returns of renewable projects.
- Cost of Capital: Interest rates and financing availability significantly influence the overall profitability and feasibility of large-scale renewable energy projects.
- Shell's Capital Expenditure: Billions are being allocated by Shell in 2024 towards biofuels, hydrogen, and renewable electricity, underscoring the economic importance of these sectors.
Global economic growth directly influences energy demand, with projections for 2024 suggesting moderate expansion, which generally benefits Shell's sales volumes. However, economic downturns or recessions can significantly reduce energy consumption, impacting Shell's revenue and profitability, as seen in past contractions.
Inflationary pressures in 2024 increased operational costs for Shell, affecting expenses for raw materials, labor, and logistics. Elevated interest rates in developed economies also raised the cost of borrowing for capital-intensive projects, influencing investment decisions and shareholder returns.
Currency fluctuations, particularly in major pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD throughout 2024, impacted Shell's reported earnings and the comparative cost of its operations across different regions.
The relative economic attractiveness of renewable energy investments for Shell is influenced by fossil fuel prices and government incentives, such as those provided by the US Inflation Reduction Act in 2024, which aim to de-risk and bolster renewable energy projects.
| Economic Factor | 2024 Impact on Shell | Data Point/Trend |
| Global GDP Growth | Supports energy demand | IMF projected 3.2% global GDP growth for 2024 |
| Inflation | Increases operational costs | Global average inflation projected at 5.8% for 2024 (IMF) |
| Interest Rates | Raises cost of capital | Elevated rates in developed economies impacting borrowing costs |
| Currency Exchange Rates | Affects reported earnings | Volatility in EUR/USD and GBP/USD pairs observed in 2024 |
| Commodity Prices | Drives revenue and investment decisions | Q1 2024 adjusted earnings of $7.7 billion, down from $9.6 billion in Q1 2023 |
Full Version Awaits
Shell Plc PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Shell Plc delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the global energy giant. Understand the critical external forces shaping Shell's strategy and future.
Sociological factors
Societal views on fossil fuels are shifting, with a growing preference for renewable energy. This change directly impacts Shell by influencing consumer choices, investor confidence, and the regulatory landscape. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers in Europe are more likely to choose energy providers with strong renewable commitments.
A negative public image regarding fossil fuel reliance can erode Shell's social license to operate, potentially leading to protests or operational disruptions. Conversely, Shell's investments in renewables, such as its 2024 commitment to invest $5 billion in clean energy solutions, can bolster its brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious customers and investors.
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, with a significant portion of the global population actively seeking out environmentally friendly products and services. This growing awareness directly impacts the energy sector, pushing companies like Shell to respond to a clear demand for cleaner alternatives.
In 2024, surveys indicated that over 60% of consumers consider sustainability a key factor in their purchasing decisions, a figure that has steadily climbed over the past few years. This trend necessitates strategic shifts for energy giants, compelling them to invest heavily in renewable energy sources and low-carbon technologies to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations.
Shell's response includes substantial investments in areas like electric vehicle charging infrastructure and the development of biofuels. For instance, by the end of 2025, Shell aims to have over 100,000 EV charging points globally, demonstrating a tangible commitment to adapting its business model to align with consumer demand for sustainable energy solutions.
Shell faces a shifting workforce landscape. As the global population ages, many experienced workers in the oil and gas sector are nearing retirement, potentially creating a knowledge drain. For instance, in 2024, the average age of workers in the energy sector in many developed nations is over 50, highlighting the urgency to transfer skills.
Simultaneously, Shell's pivot towards renewable energy necessitates a new skillset. There's a growing demand for professionals in areas like solar panel installation, wind turbine maintenance, and battery technology development, skills not traditionally central to the fossil fuel industry. This creates a significant skills gap that requires proactive training and recruitment initiatives to ensure Shell can effectively implement its energy transition strategy.
Corporate social responsibility expectations
Stakeholders, from investors to local communities, are pushing Shell to go beyond just following the rules regarding corporate social responsibility. They want to see genuine efforts in ethical operations and community support, which directly impacts Shell's public image and its operational freedom.
These expectations translate into tangible pressures. For instance, in 2024, Shell faced continued scrutiny over its environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, with a significant portion of shareholder votes in its 2024 annual general meeting focusing on climate-related resolutions. This indicates a strong demand for proactive engagement in sustainable development.
- Investor Scrutiny: In 2024, many institutional investors, managing trillions in assets, have integrated ESG criteria more deeply into their investment decisions, directly influencing capital allocation towards companies with robust CSR programs.
- Employee Expectations: A 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of employees globally consider a company's social and environmental impact when choosing an employer, highlighting the importance of CSR for talent attraction and retention at Shell.
- Community Impact: Shell's ongoing social license to operate in various regions hinges on its demonstrated commitment to local communities, including job creation and environmental stewardship, as evidenced by community investment programs reported in its 2023 sustainability report.
- Reputational Risk: Failure to meet evolving CSR expectations can lead to significant reputational damage, impacting brand value and consumer trust, a critical factor in the competitive energy market.
Health and safety concerns
Societal concerns about health and safety are paramount for Shell, especially given the inherent risks in oil and gas operations. The company must maintain stringent safety standards and openly communicate its efforts to mitigate risks to employees, communities, and the environment. A robust safety culture is not just a compliance issue but a critical factor in maintaining public trust and operational continuity.
Shell's commitment to health and safety directly impacts its reputation and financial performance. Incidents can lead to significant fines, costly clean-ups, and long-term damage to brand image, deterring investors and customers. For instance, in 2023, Shell reported a total recordable injury frequency rate (TRIFR) of 0.54 per million hours worked across its global operations, a figure it continually strives to reduce.
- Public Health Impact: Societal scrutiny focuses on potential health impacts from emissions and industrial activities, requiring Shell to invest in cleaner technologies and transparently report on environmental performance.
- Operational Safety: Maintaining a zero-harm workplace is a core objective, with significant resources dedicated to training, equipment, and process safety management to prevent accidents.
- Reputational Risk: A strong safety record is vital for public perception and investor confidence; conversely, accidents can trigger widespread criticism and regulatory intervention.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to evolving health and safety regulations across different jurisdictions is a constant challenge, demanding proactive adaptation and investment in compliance measures.
Societal expectations are increasingly driving demand for sustainable energy solutions, influencing consumer preferences and investor decisions. Shell's proactive investments in renewables, such as its 2024 commitment of $5 billion towards clean energy, aim to align with this trend and bolster its brand image. By 2025, the company plans to deploy over 100,000 electric vehicle charging points globally, reflecting a tangible adaptation to consumer demand for greener alternatives.
The energy sector workforce is undergoing a transformation, with an aging demographic in traditional roles and a growing need for new skills in renewables. Shell is addressing this by focusing on training and recruitment for areas like solar and wind energy, acknowledging the potential knowledge gap as experienced workers retire. This shift is critical for the company's successful energy transition strategy.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a key focus for stakeholders, with investors and communities demanding ethical operations and community support from Shell. In 2024, shareholder votes at Shell's annual general meeting highlighted significant concern over its ESG performance, particularly climate-related resolutions. This demonstrates a strong societal push for proactive engagement in sustainable development.
Health and safety remain paramount concerns, with society expecting stringent standards from Shell, especially in its oil and gas operations. The company's commitment to safety impacts its reputation and financial stability, as incidents can lead to fines and reputational damage. In 2023, Shell reported a total recordable injury frequency rate of 0.54 per million hours worked, a metric it actively seeks to improve.
| Societal Factor | Impact on Shell | Supporting Data/Initiatives (2024/2025 Focus) |
| Demand for Sustainability | Shifts consumer preference and investor allocation towards renewables. | 60%+ consumers in Europe favor renewable energy providers (2024 survey). Shell's $5B clean energy investment commitment (2024). Aim for 100,000+ EV charging points globally by end of 2025. |
| Workforce Demographics & Skills | Potential knowledge drain from retiring workers; need for new skills in renewables. | Average age of energy sector workers in developed nations over 50 (2024). Focus on training for solar, wind, and battery tech roles. |
| Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) | Pressure for ethical operations and community support impacts public image and license to operate. | Significant shareholder focus on ESG and climate resolutions at 2024 AGM. 70%+ employees consider company's impact when choosing employer (2024 survey). |
| Health & Safety Expectations | Stringent standards required to maintain public trust and operational continuity. | Shell's 2023 TRIFR was 0.54 per million hours worked. Societal scrutiny on emissions and industrial activity impacts investment in cleaner technologies. |
Technological factors
Technological advancements in carbon capture and storage (CCS) are critical for Shell's ambition to lower emissions from its oil and gas activities and sectors that are difficult to decarbonize. Shell's 2024 outlook highlights significant R&D spending in CCS, aiming to capture 25 million tonnes per annum of CO2 by 2035.
Investing in and effectively implementing CCS technologies not only bolsters the environmental credentials of Shell's existing business but also opens avenues for new revenue streams. For instance, Shell's Quest CCS facility in Canada has been operational since 2015, demonstrating the viability of the technology and its potential for commercialization.
Continuous innovation in renewable energy technologies, like more efficient solar panels and advanced battery storage, directly affects the cost-effectiveness and scalability of Shell's renewable energy projects. Tracking and investing in these advancements are vital for Shell's competitive standing in the evolving low-carbon energy market.
For instance, by the end of 2024, global renewable energy capacity is projected to reach over 5,000 GW, with solar and wind dominating growth. Shell's strategic investments in companies developing next-generation battery technology, aiming for higher energy density and faster charging, are crucial for integrating intermittent renewables into the grid and supporting its electric vehicle charging infrastructure expansion.
Technological advancements continue to be a critical driver for Shell's upstream operations, focusing on both efficiency gains and environmental impact reduction. Innovations in areas like advanced drilling techniques and digital subsurface imaging are key to unlocking more resources and optimizing production from existing fields.
For instance, Shell has been investing in technologies to reduce methane emissions, a significant environmental concern in oil and gas extraction. In 2023, the company reported progress in its methane intensity reduction targets, aiming for industry-leading performance. These efforts not only address regulatory pressures but also improve operational integrity and reduce potential revenue loss from leaks.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in subsurface analysis is enhancing reservoir characterization and predictive maintenance, leading to more informed decision-making and reduced downtime. This digital transformation in exploration and production is vital for Shell to maintain its competitive edge in a dynamic global energy market.
Digitalization and AI in operations
Shell's embrace of digitalization and artificial intelligence (AI) is a key technological driver, promising to revolutionize its operations. By integrating AI, Shell aims to boost efficiency across the board, from the initial stages of exploration to the final delivery of products. This technology is also crucial for predictive maintenance, allowing the company to anticipate equipment failures and minimize downtime, a critical factor in the energy sector.
The application of AI within Shell's vast network can unlock significant cost efficiencies and optimize performance. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze massive datasets from exploration activities to identify promising reserves more effectively. In production, AI can optimize well performance and resource extraction. Furthermore, AI-powered analytics are being deployed in refining processes to improve yield and reduce energy consumption, and in supply chain management to enhance logistics and inventory control.
Shell has been actively investing in these areas. For example, in 2023, the company highlighted its use of AI and digital twins for optimizing offshore platform operations, leading to improved safety and efficiency. Shell's commitment to digital transformation is further evidenced by its partnerships with technology providers and its internal development of digital capabilities, aiming to leverage data for smarter, faster decision-making in a competitive global market. The company's strategy increasingly relies on these technological advancements to navigate the complexities of the energy transition and maintain a competitive edge.
- Enhanced Efficiency: AI-driven automation in exploration, production, and refining can streamline processes, reducing operational lead times.
- Predictive Maintenance: Implementing AI to forecast equipment failures in offshore platforms and refineries can prevent costly unplanned shutdowns, improving uptime.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Advanced analytics powered by AI enable more informed strategic choices across the entire value chain, from resource discovery to market distribution.
- Cost Optimization: Digitalization and AI are projected to deliver substantial cost savings through optimized resource allocation and reduced waste in operations.
Hydrogen production and infrastructure
Shell's strategic positioning in the evolving energy landscape is heavily influenced by advancements in hydrogen production. The company is actively exploring both green hydrogen, produced using renewable electricity, and blue hydrogen, generated from natural gas with carbon capture. These technologies are pivotal for Shell's goal of becoming a significant player in the hydrogen economy, aiming to provide cleaner energy solutions.
The development of robust infrastructure for hydrogen storage and distribution is equally crucial. Without adequate pipelines, refueling stations, and storage facilities, the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a fuel remains a significant challenge. Shell's investments in these areas are therefore essential for unlocking the potential of hydrogen as a key component of future energy systems.
By 2024, global investment in clean hydrogen projects was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, with significant growth anticipated through 2030. Shell's participation in projects like the Holland Hydrogen I plant, which aims to be Europe's largest green hydrogen facility upon completion, underscores its commitment to scaling these nascent technologies. This facility alone is expected to produce up to 60 megawatts of renewable hydrogen, demonstrating a tangible step towards commercializing green hydrogen.
- Green Hydrogen Production: Shell is investing in electrolysis technologies powered by renewable energy sources to produce zero-emission hydrogen.
- Blue Hydrogen Development: The company is also exploring blue hydrogen production, which involves capturing carbon emissions from natural gas reforming.
- Infrastructure Investment: Significant capital is being allocated to build out the necessary infrastructure for hydrogen storage, transportation, and distribution networks.
- Market Growth: The global hydrogen market is projected for substantial expansion, with Shell aiming to capture a significant share by developing scalable production and supply chains.
Technological advancements in carbon capture and storage (CCS) are crucial for Shell's emission reduction goals, with R&D spending focused on capturing 25 million tonnes per annum of CO2 by 2035. Shell's Quest CCS facility in Canada, operational since 2015, demonstrates the commercial viability of this technology.
Innovations in renewable energy, such as more efficient solar panels and advanced battery storage, are vital for Shell's competitive edge in the low-carbon market. Global renewable energy capacity is projected to exceed 5,000 GW by the end of 2024, with Shell investing in next-generation battery technology to support grid integration and EV charging infrastructure.
Digitalization and AI are revolutionizing Shell's operations, from exploration to product delivery, enhancing efficiency and enabling predictive maintenance. AI algorithms optimize exploration, production, refining, and supply chain management, with Shell using AI and digital twins for offshore platform operations, as highlighted in 2023.
Legal factors
Shell faces increasingly stringent environmental regulations worldwide, impacting everything from its offshore drilling operations to its refining processes. For instance, the European Union's Fit for 55 package, aiming for a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, directly influences Shell's investment in lower-carbon energy sources and requires significant adaptation in its existing fossil fuel infrastructure. Failure to comply with these evolving emissions standards, which cover greenhouse gases, air quality, and water discharge, can lead to substantial fines and jeopardize its ability to secure necessary operating permits.
Shell's dominant position in the global energy market, particularly in oil and gas, means it faces intense scrutiny under antitrust and competition laws across numerous countries. For instance, in 2023, the European Commission continued its investigations into potential anti-competitive practices within the energy sector, which could impact Shell's operations and pricing strategies.
These regulations are designed to prevent market manipulation and ensure a level playing field, directly influencing Shell's ability to pursue mergers, acquisitions, and joint ventures. Any significant expansion or partnership must navigate these complex legal frameworks to avoid penalties and ensure compliance, impacting strategic growth plans.
Shell must navigate a complex web of labor laws globally, impacting everything from minimum wages to employee benefits. For instance, in 2024, the International Labour Organization reported that over 50 countries had updated their minimum wage laws, a trend Shell must actively monitor to ensure compliance across its operations, from the United States to Nigeria.
Adherence to robust worker protection standards is critical for mitigating legal challenges and maintaining a positive employer brand. In 2025, reports from organizations like the International Trade Union Confederation highlight ongoing scrutiny of working conditions in the energy sector, making proactive compliance and fair labor practices paramount for Shell's operational stability and reputation.
Data privacy and cybersecurity laws
Shell must carefully manage data privacy and cybersecurity laws as its operations become more digital. Regulations like the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and similar frameworks worldwide impose strict rules on how personal data is collected, processed, and stored. Failure to comply can result in substantial penalties; for instance, GDPR fines can reach up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Cybersecurity threats are a constant concern, and Shell's reliance on digital infrastructure makes it a target. A significant data breach could lead to severe financial losses, damage its brand reputation, and disrupt critical energy operations. For example, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021, while not directly related to Shell, highlighted the immense economic and operational impact such incidents can have on critical infrastructure, with estimated costs in the millions of dollars.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Adherence to regulations like GDPR is essential to avoid fines, with potential penalties reaching 4% of global annual revenue.
- Cybersecurity Investment: Shell needs to invest heavily in cybersecurity to protect against increasingly sophisticated threats that could cause operational disruptions and financial damage.
- Reputational Risk: Data breaches can severely damage customer trust and Shell's overall brand image, impacting long-term business prospects.
- Operational Continuity: Robust data governance and cybersecurity measures are critical for ensuring the uninterrupted flow of energy services.
International energy treaties and agreements
Shell's extensive global operations are significantly shaped by a web of international energy treaties and agreements. These pacts, ranging from bilateral investment treaties to multilateral climate accords, establish the ground rules for cross-border energy trade, investment security, and how disputes are handled. For instance, agreements like the Paris Agreement, to which many of Shell's operating countries are signatories, directly influence the company's long-term strategy regarding emissions reduction and investment in lower-carbon technologies, impacting its capital allocation decisions through 2025 and beyond.
These legal frameworks are crucial for providing a predictable operating environment, which is vital for large-scale energy projects requiring substantial, long-term capital commitments. However, they also impose stringent obligations regarding environmental standards, resource management, and fair treatment of investments. Shell must continually monitor and adapt to evolving international legal landscapes, such as potential changes in trade tariffs or sanctions related to energy supply chains, which could affect its ability to move resources efficiently across borders.
Key international legal factors influencing Shell include:
- Energy Charter Treaty (ECT): While facing scrutiny and withdrawal by some members, the ECT historically provided investment protections for energy companies, including Shell, across signatory nations, though its future impact is evolving.
- Climate Change Agreements (e.g., Paris Agreement): These agreements set national targets for emissions reduction, indirectly pressuring companies like Shell to align their operations and investment strategies with decarbonization goals, a trend expected to intensify through 2025.
- Bilateral Investment Treaties (BITs): Shell operates in numerous countries with BITs that offer legal recourse and protection against expropriation or unfair treatment of its investments, providing a degree of stability for its global asset base.
- International Maritime Law: Governing Shell's extensive shipping operations, these laws ensure the safe and environmentally sound transport of oil, gas, and other products across international waters.
Shell's legal landscape is heavily influenced by evolving environmental regulations, with the EU's Fit for 55 package demanding significant emissions reductions by 2030. Non-compliance can result in substantial fines and permit issues, impacting its transition to lower-carbon energy. Furthermore, antitrust scrutiny, as seen in ongoing European Commission investigations in 2023, affects Shell's pricing and strategic expansion, requiring careful navigation of competition laws.
Labor laws globally, including minimum wage updates reported by the ILO in 2024, necessitate constant monitoring for compliance across Shell's diverse workforce. Worker protection standards face ongoing scrutiny, as highlighted by the International Trade Union Confederation, making fair labor practices crucial for operational stability and reputation in 2025.
Data privacy laws like GDPR impose strict rules, with potential fines up to 4% of global annual turnover, underscoring the need for robust data protection. Cybersecurity is paramount, as demonstrated by the significant costs of incidents like the 2021 Colonial Pipeline attack, with Shell needing to invest heavily to prevent operational disruptions and reputational damage.
International energy treaties, such as the Paris Agreement, shape Shell's long-term strategy for decarbonization, influencing capital allocation through 2025. Agreements like the Energy Charter Treaty historically provided investment protections, though its future is evolving, while Bilateral Investment Treaties offer recourse against unfair treatment, securing its global asset base.
Environmental factors
Climate change and the global push for decarbonization are major environmental pressures for Shell. This means the company faces significant expectations to shift away from fossil fuels. For instance, in 2023, Shell announced its ambition to become a net-zero emissions energy business by 2050, a significant undertaking that requires substantial investment and strategic adaptation.
Meeting these demands involves setting aggressive targets for reducing emissions across its operations and value chain. Shell is actively investing in low-carbon technologies, such as renewable energy sources and hydrogen, to align with a net-zero future. By 2023, the company had already invested billions in low-carbon energy solutions, demonstrating a tangible commitment to this transition.
Shell's extensive exploration and production activities, especially in sensitive regions, can significantly affect local biodiversity and ecosystem health. For instance, their operations in areas like the Arctic or deep-sea environments carry inherent risks of habitat disruption and potential pollution incidents. Shell reported in their 2023 Sustainability Report that they continued to implement biodiversity action plans across various operational sites, aiming to minimize their footprint.
Managing these impacts is a critical component of Shell's environmental stewardship and is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance. The company is increasingly investing in mitigation strategies, such as habitat restoration projects and biodiversity offsets, to counterbalance unavoidable impacts. In 2024, Shell continued to engage with conservation organizations to refine its biodiversity management approaches, recognizing the growing stakeholder expectations for responsible resource development.
Shell's commitment to effective waste management and pollution control is paramount, covering everything from industrial waste and wastewater to emissions from its vast operations. The company is focused on minimizing its environmental footprint by employing sophisticated pollution control technologies and rigorous waste management protocols across its global sites.
In 2023, Shell reported a 5% reduction in its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions compared to 2016 levels, demonstrating progress in its pollution control efforts. The company also aims to reduce its operational waste, with specific targets for reducing the amount of waste sent to landfill.
Resource depletion concerns
Shell faces increasing pressure due to concerns about the depletion of finite natural resources, especially oil and gas. This reality is pushing the company to actively seek out and invest in new energy sources. For instance, in 2023, Shell announced plans to invest billions in renewable energy projects, aiming to diversify its portfolio beyond fossil fuels.
These resource depletion concerns directly influence Shell's strategy, encouraging significant investments in renewable alternatives. By 2024, the company projected a substantial increase in its capital expenditure allocated to low-carbon solutions, aiming for a more sustainable energy mix. This strategic shift is also fostering the development and integration of circular economy principles within Shell's operational framework, focusing on resource efficiency and waste reduction.
- Resource Scarcity Drive: Finite resource depletion is a primary driver for Shell's strategic pivot towards new energy avenues.
- Renewable Investment Surge: Shell is channeling billions into renewable energy, as seen in its 2023 investment plans, to counter fossil fuel limitations.
- Circular Economy Adoption: The company is increasingly embedding circular economy models to optimize resource use and minimize waste in its operations.
Water scarcity and management
Shell's operations, particularly in oil and gas extraction and refining, are inherently water-intensive. In regions grappling with increasing water scarcity, such as parts of the Middle East and North Africa where Shell has significant operations, this can lead to intense scrutiny from regulators and local communities. For instance, in 2023, several Middle Eastern countries experienced below-average rainfall, exacerbating existing water stress, which directly impacts the availability of water for industrial use.
To address this, Shell is focusing on robust water management strategies. This includes investing in technologies for water efficiency, such as advanced water recycling and reuse systems in its refineries. A key initiative is the adoption of dry drilling techniques where feasible, minimizing freshwater consumption. Shell reported that in 2024, it aimed to reduce its freshwater withdrawal intensity by 15% compared to a 2016 baseline across its global operations.
- Water Scarcity Impact: Regions like the Permian Basin in the US, a significant area for oil production, have faced drought conditions, increasing the cost and competition for water resources essential for hydraulic fracturing.
- Efficiency Investments: Shell is investing in technologies that allow for higher rates of water recycling in its operations, aiming to reduce reliance on freshwater sources.
- Operational Viability: Proactive water management is crucial for maintaining Shell's social license to operate and ensuring the long-term sustainability of its projects in water-stressed geographies.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Stricter regulations on water usage and discharge are becoming more common globally, requiring companies like Shell to demonstrate responsible water stewardship.
Shell faces intense pressure from climate change and the global drive for decarbonization, necessitating a significant shift away from fossil fuels. The company has committed to becoming a net-zero emissions energy business by 2050, a goal that requires substantial investment in low-carbon technologies like renewables and hydrogen. By 2023, Shell had already invested billions in these areas, underscoring its dedication to this transition.
The company's operations, particularly in oil and gas, pose risks to biodiversity and ecosystems, prompting the implementation of biodiversity action plans. Shell is also focused on robust waste and pollution control, reporting a 5% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions by 2023 compared to 2016 levels. Concerns over finite resource depletion are driving Shell's strategic pivot towards new energy avenues, with billions invested in renewables as of 2023.
Water scarcity is a growing challenge, especially in regions where Shell operates. To mitigate this, the company is investing in water efficiency technologies and aims to reduce its freshwater withdrawal intensity by 15% by 2024 from a 2016 baseline. These environmental factors are reshaping Shell's strategy, pushing for greater sustainability and resource management.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Shell Plc is built on a robust foundation of data from reputable sources including government energy agencies, international financial institutions, and leading market research firms. This ensures comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the global energy sector.