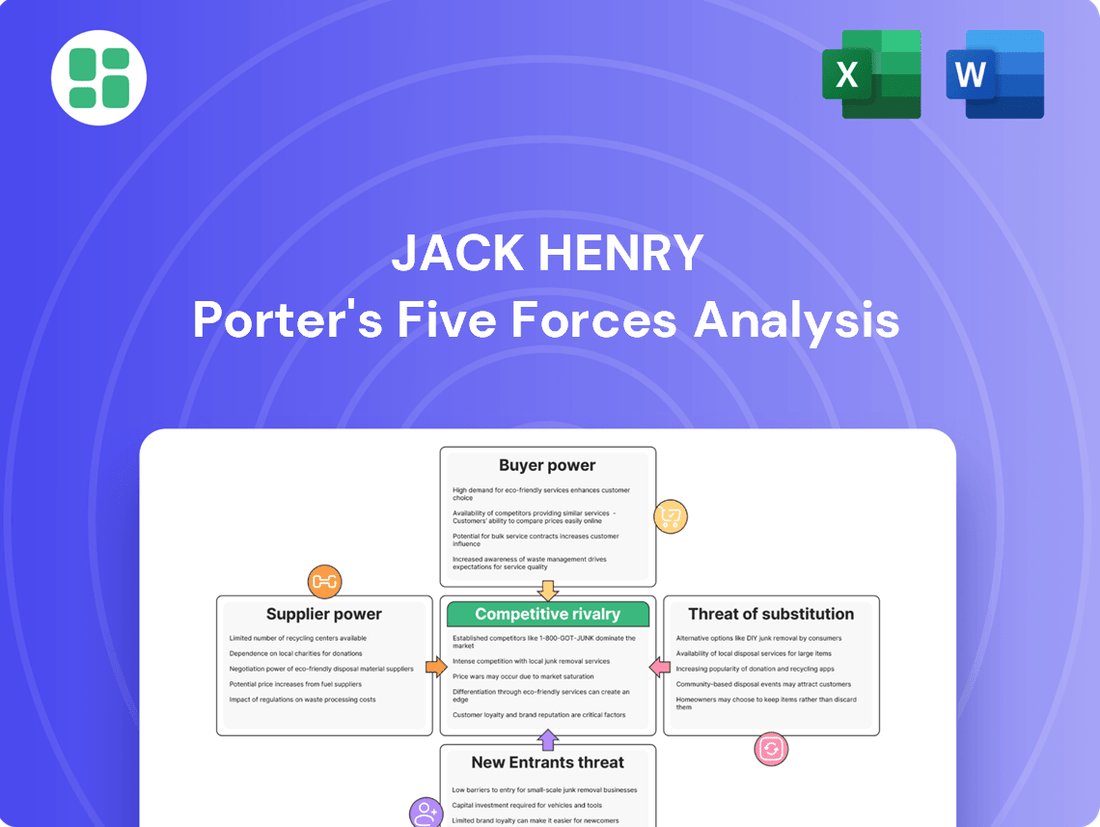
Jack Henry Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Jack Henry Bundle
Jack Henry's competitive landscape is shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the financial technology sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Jack Henry’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Jack Henry relies on specialized technology components, such as advanced cloud infrastructure and robust cybersecurity solutions, from third-party vendors. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be significant, particularly when their offerings are proprietary or critical to Jack Henry's operations, potentially influencing costs and the pace of innovation.
The market for highly skilled professionals, crucial for Jack Henry's operations, is intensely competitive. Think software developers, cybersecurity gurus, and fintech wizards – these are in-demand roles.
When labor markets are tight, these talented individuals wield significant bargaining power. This translates directly into upward pressure on wages and can make attracting top talent a real hurdle for Jack Henry, impacting both operational expenses and the pace of project delivery.
Jack Henry, as a crucial player in payment processing, directly engages with dominant payment networks such as Visa, Mastercard, and the Automated Clearing House (ACH) system. These networks wield considerable influence because of their entrenched market positions and their indispensable function within the financial infrastructure. Their power translates into setting fees, dictating technical specifications, and establishing operational guidelines that Jack Henry must follow, impacting its cost structure and service delivery.
Access to Proprietary Data and Regulatory Updates
Jack Henry's reliance on proprietary data and regulatory updates for its risk management and compliance solutions highlights a key area of supplier influence. Suppliers providing unique financial data feeds or crucial regulatory changes can wield significant power if their offerings are difficult to substitute.
This dependence means that if a key data provider or regulatory information source significantly increases prices or restricts access, Jack Henry could face higher operating costs or compliance challenges. For instance, in 2024, the increasing complexity of financial regulations, such as those related to anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, necessitates access to highly specific and often proprietary data sets.
- Data Dependency: Jack Henry's core services are built upon the accurate and timely delivery of financial data.
- Regulatory Nuances: Keeping pace with evolving regulations requires specialized data and insights from niche providers.
- Supplier Leverage: Firms with unique data or regulatory intelligence can command higher prices or more favorable terms.
- Market Impact: In 2024, the cost of specialized financial data services saw an average increase of 5-8% across the industry, impacting companies like Jack Henry.
Hardware and Cloud Infrastructure Providers
Hardware and cloud infrastructure providers hold moderate bargaining power over Jack Henry. While the market features several large, established vendors, Jack Henry's increasing reliance on cloud-native solutions and its strategic goal to have 92% of its client base on private cloud by the end of 2024 creates a degree of dependency. This reliance on key infrastructure partners, coupled with the long-term nature of many of these contracts, can influence pricing and service terms.
The dynamic shifts as Jack Henry continues its digital transformation. The company's investment in cloud infrastructure, aiming for a significant portion of its operations to be cloud-native, means these suppliers are critical to its service delivery. For instance, in 2023, Jack Henry reported that its cloud-based solutions were a key growth driver, highlighting the importance of these infrastructure partners in achieving its strategic objectives.
- Moderate Supplier Power: Several large vendors exist, but Jack Henry's increasing cloud adoption creates dependencies.
- Cloud Migration Impact: The push for 92% of clients on private cloud by year-end 2024 strengthens supplier leverage due to long-term commitments.
- Strategic Importance: Reliable hardware and cloud infrastructure are fundamental to Jack Henry's operational backbone and data center functions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Jack Henry is a critical factor, especially concerning specialized technology and data. Companies providing proprietary software, unique financial data feeds, or essential regulatory intelligence can significantly influence Jack Henry's costs and operational efficiency. In 2024, the increasing demand for sophisticated cybersecurity solutions meant that specialized providers in this area saw increased leverage, potentially leading to higher contract costs for Jack Henry.
Jack Henry's reliance on dominant payment networks like Visa and Mastercard also represents a significant supplier power dynamic. These networks are integral to payment processing, allowing them to dictate terms and fees. Furthermore, the market for highly skilled tech talent, including developers and cybersecurity experts, is competitive, giving these professionals considerable bargaining power, which can drive up labor costs for Jack Henry.
| Supplier Type | Influence Level | Impact on Jack Henry | 2024 Trend/Fact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology Vendors (e.g., Cloud, Cybersecurity) | High | Pricing, innovation pace, operational reliance | Increased demand for cybersecurity solutions led to higher vendor pricing. |
| Financial Data Providers (Proprietary/Regulatory) | High | Operating costs, compliance, service quality | Average increase of 5-8% in specialized financial data services cost. |
| Dominant Payment Networks (Visa, Mastercard) | Very High | Fees, technical specifications, operational guidelines | Continued dominance in transaction processing dictates terms. |
| Skilled Labor Market (Developers, Cybersecurity) | High | Wages, talent acquisition costs, project timelines | Tight labor market for fintech professionals drove up recruitment and retention costs. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition and market dynamics within the financial technology sector, specifically analyzing Jack Henry's competitive position and strategic advantages.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic visual representation of Porter's Five Forces, allowing for immediate strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Jack Henry's core processing platforms are intricately woven into the daily operations of financial institutions, making them incredibly difficult to replace. These systems are not just software; they are the backbone of banking, handling everything from account management to transaction processing.
The sheer complexity, substantial cost, and lengthy timelines associated with migrating these core systems significantly diminish a customer's ability to negotiate terms once they are on board. For instance, a typical core system conversion can take years and cost millions, alongside the inherent risk of disrupting critical services.
This deep integration and the associated high switching costs effectively lock in customers, thereby reducing their bargaining power. In 2024, financial institutions continue to face these realities, as the investment in and reliance on established core banking technology remain paramount.
Jack Henry & Associates' customer base is largely composed of community banks and credit unions. This means that individually, these clients have relatively little power to negotiate terms or prices with Jack Henry. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Jack Henry served over 3,200 financial institutions, highlighting the dispersed nature of its clientele.
The sheer number of these smaller institutions means that no single customer or even a small consortium of them can significantly sway Jack Henry's operational decisions or pricing structures. This fragmentation effectively dilutes any potential for collective bargaining, making it difficult for customers to exert substantial leverage.
Jack Henry's suite of services, encompassing core processing, digital banking platforms, and robust risk management solutions, forms the operational backbone for countless financial institutions. These offerings are not merely supplementary; they are fundamental to the daily functioning and strategic growth of its clients.
This mission-critical dependency significantly curtails the bargaining power of Jack Henry's customers. Financial institutions rely on the seamless integration and consistent performance of these services, making abrupt changes or aggressive price negotiations disruptive and often unfeasible. In 2023, Jack Henry reported revenue of $1.95 billion, underscoring the scale and importance of its client relationships.
Long-Term Contractual Relationships
Jack Henry's strategy of securing clients through multi-year contracts significantly dampens customer bargaining power. These agreements, often spanning several years, create a predictable revenue stream for Jack Henry, insulating them from short-term demands. For example, many of their core platform contracts are typically 5 to 7 years in length.
These long-term commitments make switching providers a complex and costly endeavor for financial institutions. The integration of new systems, data migration, and staff retraining involved in changing core banking software or payment processing platforms creates substantial switching costs. This friction effectively locks in customers, reducing their ability to negotiate better terms frequently.
- Multi-Year Contracts: Jack Henry typically enters into agreements lasting several years, ensuring stable revenue.
- Reduced Switching Costs: The complexity and expense associated with changing providers limit customer flexibility.
- Market Position Reinforcement: Long-term contracts solidify Jack Henry's standing by retaining its client base.
- Revenue Predictability: These contracts provide a reliable income forecast, crucial for strategic planning.
Integrated Value Proposition
Jack Henry's integrated value proposition significantly weakens customer bargaining power. By offering a seamless suite of solutions, the company reduces the incentive for clients to seek out and integrate disparate "best-of-breed" products from multiple vendors.
This consolidation translates into tangible benefits for financial institutions. For instance, a 2024 survey by J.D. Power found that customers of integrated core banking systems reported higher satisfaction scores compared to those using fragmented solutions. This suggests that the operational efficiencies and simplified vendor management provided by Jack Henry's approach directly impact client loyalty and reduce their willingness to switch.
- Reduced Vendor Management: Customers avoid the complexity and cost of managing relationships with numerous technology providers.
- Operational Efficiencies: Seamless integration leads to smoother workflows and fewer system compatibility issues.
- Lower Integration Costs: Bundled solutions typically have lower upfront and ongoing integration expenses than piecing together multiple systems.
- Enhanced Data Flow: Integrated platforms facilitate better data sharing and analysis across different banking functions.
Jack Henry's customers, primarily community banks and credit unions, possess limited individual bargaining power due to their smaller size and the dispersed nature of the client base. With over 3,200 financial institutions served as of early 2024, no single entity can significantly influence pricing or terms. This fragmentation dilutes any potential for collective negotiation, making it difficult for clients to exert substantial leverage against the company.
Full Version Awaits
Jack Henry Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual Jack Henry Porter's Five Forces Analysis, a comprehensive assessment of the competitive landscape within the financial technology sector. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing valuable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of substitute products.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The financial technology sector, particularly in core processing and digital banking, is highly competitive. Established giants like Fiserv and FIS, along with international players such as Temenos, dominate the landscape. These firms are locked in a constant battle for market share, driving innovation and service enhancements.
This intense rivalry means that companies like Jack Henry must continuously invest in new technologies and customer experiences to remain competitive. For instance, in 2023, Fiserv reported revenue of $17.7 billion, showcasing the scale and financial power of these established players, which puts pressure on all market participants to deliver superior value.
Competitive rivalry in the financial technology sector is intense, fueled by the constant need for product innovation. Companies are pouring resources into areas like cloud-native platforms and AI to offer unique solutions. For instance, in 2024, many fintech firms reported significant R&D spending increases, with some dedicating over 15% of their revenue to innovation to stay ahead of rivals and meet the rapidly changing expectations of financial institutions and their customers.
The core banking software market is projected to grow from $13.32 billion in 2024 to $14.43 billion in 2025, a respectable CAGR of 8.3%. However, this growth doesn't stem from a surge in new banks. Instead, it signifies a fierce battle for existing market share among established players.
This dynamic intensifies competition, forcing companies like Jack Henry to invest heavily in sales and marketing to poach customers from rivals. The mature nature of the segment means that winning new business often directly translates to a competitor losing business, making every deal crucial.
Pricing Sensitivity and Bundling Strategies
Even with substantial switching costs in the financial technology sector, competitive rivalries can still drive significant pricing sensitivity. Financial institutions, under pressure to control operational expenditures, are increasingly scrutinizing vendor costs. For instance, in 2024, many community banks reported a heightened focus on cost optimization within their core banking and digital solutions, directly impacting their willingness to pay premium prices for technology services.
This competitive landscape compels rivals to adopt aggressive pricing tactics or develop attractive bundled offerings. These strategies aim to lure new customers or secure the loyalty of existing ones, potentially eroding Jack Henry's market share and profitability. Companies like Fiserv and FIS have been observed in 2024 to offer integrated packages covering everything from core processing to digital payments, often at a discounted rate compared to standalone solutions.
- Pricing Sensitivity: Financial institutions are actively seeking to reduce operational costs, leading to increased price sensitivity for technology solutions.
- Bundling Strategies: Competitors are leveraging bundled product offerings to gain market traction and retain clients, creating pricing pressure.
- Impact on Profitability: Aggressive pricing and bundling by rivals can directly affect Jack Henry's revenue and profit margins.
- Market Dynamics: The need for cost optimization among financial institutions fuels a competitive environment where pricing and product integration are key differentiators.
Industry Consolidation and M&A Activity
The financial services technology sector is a hotbed for mergers and acquisitions. In 2024, we've seen significant consolidation as larger companies acquire smaller ones to gain market share and expand their offerings. This trend is driven by the pursuit of economies of scale and a desire to create more comprehensive product suites.
This M&A activity directly impacts competitive rivalry. When big players merge, they often become even more dominant, intensifying the competition for clients and skilled employees. For instance, the acquisition of a smaller fintech firm by a major player can instantly boost the latter's capabilities in a specific area, forcing other competitors to adapt or seek their own strategic partnerships.
- Industry Consolidation: The financial technology space is witnessing a steady stream of mergers and acquisitions, aiming to consolidate market share and enhance product portfolios.
- Economies of Scale: Companies are actively pursuing M&A to achieve greater operational efficiencies and cost reductions through increased scale.
- Reshaping Competition: These consolidation efforts are leading to the emergence of more powerful competitors, thereby intensifying the battle for customer acquisition and retention.
- Talent and Client Wars: The heightened M&A activity also escalates the competition for top talent and critical client relationships within the industry.
The financial technology sector is characterized by intense competition, with established giants like Fiserv and FIS constantly vying for market share. This rivalry necessitates continuous investment in innovation, as seen with increased R&D spending by many fintech firms in 2024, often exceeding 15% of revenue.
The core banking software market, projected to grow at an 8.3% CAGR from 2024 to 2025, reflects this fierce competition for existing clients rather than new market entrants. Companies must aggressively pursue sales and marketing to gain customers, as winning new business directly impacts competitors' market share.
Furthermore, significant M&A activity in 2024 is consolidating the industry, creating larger, more dominant players. This trend intensifies the competition for clients and talent, forcing companies to adapt through strategic partnerships or face increased pressure from consolidated rivals.
| Company | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Focus Areas | Competitive Actions in 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiserv | 17.7 | Core Processing, Digital Banking | Aggressive bundling of services, acquisitions to expand offerings |
| FIS | (Not specified for 2023, but major competitor) | Payment Solutions, Banking Software | Focus on integrated packages, potential strategic partnerships |
| Temenos | (Not specified for 2023, but major competitor) | Cloud-Native Core Banking | Continued investment in AI and cloud technology for differentiation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While community banks and credit unions, Jack Henry's core customers, are unlikely to develop complex core banking systems in-house, larger financial institutions might explore this. The sheer cost and time investment, however, often make it impractical. For instance, developing a new core banking platform can cost hundreds of millions of dollars and take years to implement, a barrier most institutions cannot overcome.
Some smaller or less technologically advanced financial institutions may still heavily rely on outdated legacy systems or extensive manual processes. These represent less efficient and riskier alternatives to modern, integrated solutions. For example, in 2024, a significant portion of community banks, particularly those with assets under $1 billion, continued to grapple with the costs and complexities of maintaining legacy core banking systems, hindering their ability to offer competitive digital services.
While these are indirect substitutes, the prevailing industry trend strongly favors modernization, diminishing their long-term threat. Financial institutions that fail to upgrade risk falling behind in terms of operational efficiency, customer experience, and regulatory compliance, making them less attractive to both customers and investors.
The threat of substitutes for Jack Henry's core offerings is relatively low, especially for mission-critical banking functions. While financial institutions might consider generic enterprise resource planning (ERP) or customer relationship management (CRM) software for non-core operations, these solutions typically fall short. For instance, in 2024, the banking sector's stringent regulatory environment, including compliance with regulations like the Bank Secrecy Act and evolving data privacy laws, demands specialized features that generic software often lacks. These generic platforms also struggle to match the robust security protocols and specialized financial transaction processing capabilities that are fundamental to Jack Henry's integrated banking solutions.
Fragmented 'Best-of-Breed' Approach
The threat of substitutes is amplified by a fragmented 'best-of-breed' approach within the financial technology sector. Financial institutions might consider piecing together specialized solutions from various niche vendors for core banking, digital platforms, and payment processing. This strategy, while offering customization, introduces substantial integration challenges and increases the burden of managing multiple vendor relationships. Furthermore, it can create greater security risks compared to a unified offering.
For instance, in 2024, the average financial institution reported managing over 50 third-party vendor relationships, with a significant portion dedicated to technology solutions. This complexity can deter institutions from adopting a fragmented model, especially when vendors like Jack Henry offer comprehensive, integrated suites that streamline operations and potentially reduce overall risk exposure.
- Increased Integration Complexity: Combining disparate systems often leads to costly and time-consuming integration projects.
- Vendor Management Overhead: Managing multiple contracts, service level agreements, and support channels for different vendors is resource-intensive.
- Heightened Security Vulnerabilities: Each new integration point can introduce potential security gaps that require diligent monitoring and management.
- Operational Inefficiencies: A lack of seamless data flow between best-of-breed solutions can hinder operational efficiency and customer experience.
Outsourcing to Non-Platform BPO Providers
While financial institutions might engage Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) providers for specific operational tasks, these arrangements typically focus on execution rather than the core technology infrastructure. This means they don't directly substitute Jack Henry's integrated software solutions, which offer a complete technological foundation.
These non-platform BPO providers offer a limited substitute, primarily addressing labor arbitrage for routine tasks. For instance, in 2024, the global BPO market was valued at approximately $270 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to customer service and back-office operations. However, these services lack the technological depth and integration capabilities that Jack Henry's platform provides, making them a less potent threat to the core business.
- Limited Scope: Non-platform BPO primarily handles task execution, not the underlying technology.
- Lack of Integration: These providers do not offer the comprehensive, integrated software suites that Jack Henry specializes in.
- Focus on Labor: The primary value proposition is often cost reduction through labor arbitrage, not technological advancement.
The threat of substitutes for Jack Henry's core banking solutions is generally low. While financial institutions could theoretically build their own systems, the immense cost, time, and specialized expertise required make this impractical for most. For example, developing a new core banking platform can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars and take several years, a significant barrier.
Generic software like ERP or CRM systems are not viable substitutes for core banking functions due to stringent regulatory demands and the need for specialized financial transaction processing. In 2024, the banking sector's complex compliance landscape, including data privacy laws, necessitates tailored features that general software often lacks.
The rise of a fragmented 'best-of-breed' approach in fintech, where institutions might combine niche solutions, also presents a threat. However, this strategy introduces significant integration challenges and increased security risks. In 2024, the average financial institution managed over 50 third-party vendor relationships, highlighting the complexity that integrated solutions like Jack Henry's aim to simplify.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the financial technology sector, especially for core banking systems, requires a massive upfront investment. Think about the costs for research and development, building secure and reliable infrastructure, and making sure everything meets strict regulatory requirements. For instance, developing a new core banking platform can easily cost tens of millions, if not hundreds of millions, of dollars.
New companies need serious financial muscle to create platforms that are not only scalable and secure but also competitive enough to go head-to-head with giants like Jack Henry. Without deep pockets, it's incredibly difficult to even get a foot in the door and build the kind of robust technology that financial institutions depend on.
The financial sector's intricate web of regulations, including Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), data privacy, and the push for instant payments, presents a formidable hurdle. New companies must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these complex rules, which can be a significant barrier to entry.
For instance, in 2024, the cost of regulatory compliance for financial institutions continued to rise, with many reporting increased spending on technology and personnel to manage these obligations. Obtaining the necessary licenses and building robust systems that meet rigorous security and audit requirements demand substantial capital and expertise, deterring many potential new entrants.
Financial institutions, particularly those dealing with sensitive customer data and mission-critical operations, place an immense premium on trust and a proven track record. This inherent risk aversion means that new entrants face a significant hurdle in convincing these organizations to switch from established, trusted technology providers.
Established players like Jack Henry have cultivated decades of trust and built deep, long-standing relationships with their client base. These relationships are not easily replicated by newcomers, who lack the battle-tested reputation and the ingrained understanding of client needs that come with years of service. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions continue to demonstrate a preference for vendors with a demonstrable history of reliability and security, often prioritizing existing partnerships over unproven solutions.
Integration Complexity and Ecosystem Development
The integration complexity of Jack Henry's offerings presents a substantial barrier to new entrants. Their solutions are deeply embedded within a vast financial ecosystem, necessitating seamless interaction with a multitude of third-party applications and services. This intricate web of integrations requires significant investment and time for any newcomer to replicate.
New players must not only develop robust integration capabilities but also cultivate a broad network of partnerships. This is particularly challenging given the highly diverse and often legacy IT infrastructures of financial institutions, making a one-size-fits-all integration approach impractical. For instance, in 2023, the average financial institution worked with over 100 fintech partners, highlighting the scale of this challenge.
- Integration Complexity: Jack Henry's solutions require deep integration with numerous existing financial systems and third-party applications.
- Ecosystem Development: New entrants must build a comparable network of partnerships and integration capabilities, a time-consuming and costly endeavor.
- IT Diversity: The varied and often complex IT environments of financial institutions make replicating Jack Henry's integration success a significant hurdle.
- Market Share Impact: The entrenched nature of these integrations makes it difficult for new entrants to displace established players like Jack Henry.
Talent Acquisition and Retention Challenges
The fintech sector faces significant hurdles in attracting and keeping top-tier professionals. Developing advanced financial technology demands experts in cybersecurity, data analytics, and regulatory compliance. New companies must vie with established players for this limited pool of talent, driving up recruitment costs and reinforcing entry barriers.
In 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning specialists in finance saw a substantial increase, with job postings for these roles growing by an estimated 40% compared to the previous year. This intense competition for skilled individuals directly impacts the cost and feasibility for new entrants aiming to build innovative financial solutions.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Cybersecurity analysts, data scientists, and regulatory compliance officers are in critical demand.
- Increased Recruitment Costs: Competing for scarce talent with established firms drives up salary expectations and benefits packages.
- Impact on Innovation Speed: Difficulty in acquiring necessary talent can slow down the development and deployment of new financial technologies.
- Retention as a Key Challenge: Keeping highly sought-after employees requires competitive compensation and a strong company culture, adding to operational expenses for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the core banking technology sector, where Jack Henry operates, remains relatively low due to substantial capital requirements and significant regulatory burdens. Developing a competitive core banking platform can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a prohibitive sum for most startups. Furthermore, navigating the complex and evolving regulatory landscape, including data privacy and security mandates, demands extensive expertise and financial investment, acting as a strong deterrent.
Established trust and deep client relationships also present a formidable barrier. Financial institutions prioritize reliability and security, often opting for vendors with a proven track record. Jack Henry's decades of experience and ingrained partnerships make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions continued to favor established vendors with a history of stability, underscoring the challenge for new entrants.
The integration complexity of existing financial systems and the need for a broad partner ecosystem further solidify the barriers. New entrants must invest heavily in replicating Jack Henry's extensive integration capabilities and cultivating a network of third-party relationships, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. The demand for specialized talent in areas like cybersecurity and AI also intensifies competition for skilled professionals, raising recruitment costs for new players.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Developing core banking tech costs hundreds of millions. | Prohibitive for most startups. | Continued high R&D spending in fintech. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex compliance (KYC, AML, data privacy). | Requires significant investment in expertise and systems. | Increased compliance spending by financial institutions. |
| Established Trust & Relationships | Financial institutions prioritize proven reliability. | Difficult for new entrants to displace incumbents. | Preference for vendors with long-standing track records. |
| Integration Complexity & Ecosystem | Deep integration with numerous systems and partners. | Costly and time-consuming to replicate. | Average FI works with over 100 fintech partners. |
| Talent Acquisition | High demand for specialized skills (cybersecurity, AI). | Drives up recruitment costs and slows innovation. | 40% increase in demand for AI/ML specialists in finance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific data, including market research reports from leading firms, financial disclosures from publicly traded companies, and government economic statistics. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive pressures.