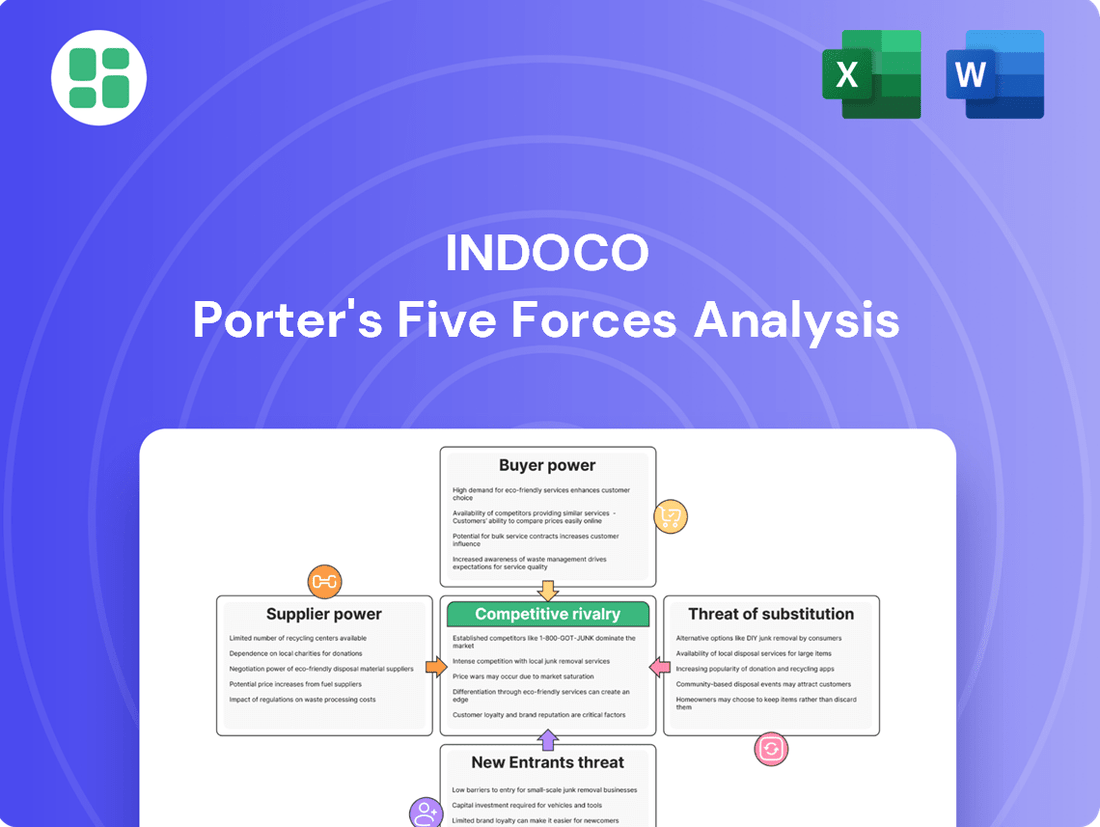
Indoco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Indoco Bundle
Indoco's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market. The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Indoco’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Indoco Remedies, especially for crucial Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and raw materials, leans towards moderate to high. Despite India being a substantial player in global API production, accounting for 8.8% of worldwide output, the industry still shows a marked dependence on specific geographic areas, particularly China.
China's significant role in the global generic API supply chain, holding approximately 80% of the market share in 2023, grants certain API manufacturers considerable leverage. This is particularly true when it comes to specialized or high-potency APIs, where fewer suppliers can meet the stringent quality and production requirements.
The availability of substitute inputs for Indoco Remedies presents a moderate bargaining power for suppliers. While many basic chemicals and organic raw materials have numerous sources, the pharmaceutical sector relies on specialized Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and excipients. These critical components often have fewer alternative suppliers, especially for high-purity grades required for drug manufacturing.
For instance, during 2024, the global supply chain for certain specialized pharmaceutical intermediates experienced tightness due to geopolitical factors and increased demand. This situation can elevate the leverage of suppliers who can consistently provide these essential, less substitutable inputs, potentially impacting Indoco's cost structure and production timelines.
Switching costs for Indoco Remedies to change suppliers, especially for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), can be substantial. This is largely due to the rigorous regulatory hurdles and quality assurance protocols inherent in the pharmaceutical industry. For instance, the process of approving a new API supplier typically involves extensive validation studies, site audits, and potentially even re-submissions to regulatory agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European health authorities.
These validation and re-filing processes are not only time-consuming but also represent a significant financial investment for Indoco Remedies. The extended timelines and associated costs can create a strong dependency on established, pre-approved suppliers. This reliance directly translates into increased bargaining power for these suppliers, as Indoco Remedies faces considerable friction in seeking alternative sources.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers moving into finished dosage form manufacturing for pharmaceutical companies like Indoco is generally low, though not entirely absent. This is because producing finished drugs requires substantial investment in areas like formulation, gaining regulatory approvals, and establishing marketing and distribution networks, which are quite different from the core business of manufacturing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs).
While some major API producers might contemplate this expansion, the barriers to entry are significant. For instance, the pharmaceutical industry's regulatory landscape, especially for finished products, is complex and varies by region. In 2024, obtaining approvals for new drug formulations can take several years and millions of dollars, making it a daunting prospect for many API-only manufacturers.
However, a more direct concern could arise from Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) that already produce both APIs and finished dosage forms. If these CMOs decide to expand their own branded product portfolios rather than just manufacturing for others, they could indeed present a more tangible competitive threat by directly entering Indoco's market space.
The bargaining power of suppliers, in this context, is influenced by the capital expenditure required for forward integration:
- Significant Capital Investment: Moving into finished dosage forms requires substantial investment in R&D, manufacturing facilities compliant with GMP standards for finished products, and extensive regulatory filings.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining marketing authorization for finished products in key markets like the US or EU is a lengthy and costly process, often taking 5-10 years and millions in development.
- Marketing and Distribution Infrastructure: Suppliers would need to build or acquire capabilities in sales, marketing, and distribution, which are distinct skill sets from API production.
- Potential for CMO Expansion: CMOs with existing dual capabilities represent a more immediate, albeit still limited, threat if they choose to leverage their infrastructure for proprietary product lines.
Importance of Indoco Remedies to Suppliers
Indoco Remedies' significance to its suppliers is not uniform; it hinges on the supplier's scale and product range. For smaller, niche manufacturers of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), Indoco can represent a substantial portion of their sales, thereby diminishing their negotiating strength.
Conversely, major global API suppliers, with diversified customer bases, may find Indoco's business to be a smaller segment of their overall revenue. This situation grants these larger suppliers greater leverage in their dealings with Indoco.
The pharmaceutical industry's increasing focus on diversifying supply chains and reducing dependence on single sources, coupled with Indian government policies encouraging domestic API manufacturing, is gradually strengthening the position of companies like Indoco Remedies relative to some of their suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: For specialized API producers, Indoco's orders can be crucial, limiting their pricing power.
- Global Supplier Leverage: Large, diversified API providers may have less reliance on Indoco, increasing their bargaining power.
- Industry Trends: A move towards supply chain diversification and India's 'Make in India' initiative for APIs could improve Indoco's supplier negotiation position.
Indoco Remedies faces moderate to high bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly for specialized Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and critical raw materials. While India is a significant global API producer, reliance on certain regions, like China which held about 80% of the generic API market share in 2023, concentrates power with some suppliers.
The availability of substitutes for these specialized inputs is limited, as pharmaceutical manufacturing demands high-purity, compliant materials. Switching costs are substantial due to rigorous regulatory validation processes, making it difficult and expensive for Indoco to change suppliers. For instance, re-validating an API supplier with agencies like the FDA can take years and significant investment.
While forward integration by API suppliers into finished dosage forms is generally a low threat due to high capital and regulatory barriers, Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) with existing dual capabilities pose a more direct, albeit limited, risk if they expand their own proprietary product lines. Indoco's own significance to its suppliers varies; smaller, niche suppliers may have less leverage than larger, diversified global players.
| Factor | Indoco Remedies' Position | Supplier Leverage |
| Dependence on Specialized Inputs | High | Moderate to High |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low for specialized APIs | High |
| Switching Costs | High (regulatory, validation) | High |
| Supplier Concentration (e.g., China's API share) | Moderate dependence | Moderate to High |
| Indoco's Significance to Supplier | Varies (high for niche, low for large) | Varies (low for niche, high for large) |
What is included in the product
Indoco's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each Porter's Force, empowering proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Indoco Remedies operates across diverse markets, supplying finished dosage forms and offering contract manufacturing. While its broad customer base in India, encompassing distributors, hospitals, and pharmacies, generally limits individual customer leverage, significant volume from large institutional buyers or key international contract manufacturing clients can indeed shift the balance.
Customers of Indoco Remedies face a moderate to high availability of substitute pharmaceutical products, particularly within the Indian market. For generic formulations, a substantial segment of the industry, a multitude of competitors offer comparable drugs, directly enhancing customer choice and amplifying price sensitivity. This broad availability means customers can readily switch providers if prices become less attractive or if product quality falters, exerting significant pressure on Indoco's pricing power.
Switching costs for Indoco Remedies' customers, such as pharmacies and hospitals, are generally low, particularly for generic drugs. While existing relationships and efficient supply chains are factors, price and regulatory adherence often dictate purchasing decisions.
For instance, in the highly competitive generic pharmaceutical market, if a competitor offers a comparable product at a lower price or with better availability, customers can readily shift their business. This ease of switching is a significant consideration for Indoco.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity in the pharmaceutical sector, especially for generics, is a significant factor. In markets like India, where affordability is paramount, this sensitivity directly impacts sales volumes and pricing strategies. For instance, the Indian pharmaceutical market is projected to reach $130 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand for cost-effective medicines.
Government interventions further amplify this pressure. Policies such as drug price controls and mandates for generic drug substitution directly encourage consumers to opt for lower-cost alternatives. This creates a highly competitive pricing environment, forcing companies to optimize their cost structures to maintain profitability.
For contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) within the industry, client price sensitivity is equally pronounced. Clients actively seek cost-effective solutions to minimize their own research and development expenditures. This focus on efficiency and value for money means CMOs must demonstrate clear cost advantages to secure and retain business.
- High Price Sensitivity in Generics: The generic drug segment is particularly vulnerable to price fluctuations, as consumers actively seek the most affordable options.
- Impact of Government Policies: Drug price controls and generic substitution laws in countries like India directly push prices down, increasing customer bargaining power.
- Cost-Effectiveness for CMOs: Clients engaging contract manufacturing services prioritize cost savings, making price a critical factor in their selection of partners.
- Market Growth and Affordability: The significant growth projected for markets like India is largely fueled by the demand for affordable healthcare, underscoring customer price sensitivity.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers in the pharmaceutical industry, where customers might start their own manufacturing, is typically low. This is largely due to the substantial capital requirements, intricate regulatory landscapes, and the need for highly specialized technical knowledge inherent in drug production.
However, the situation can shift for large pharmaceutical companies that currently rely on contract manufacturing. If bringing production in-house becomes more strategically sound or financially beneficial, especially for products with significant demand, these companies may indeed consider it. For instance, in 2024, the global contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $170 billion, indicating a substantial existing reliance on external production, which could be a precursor to backward integration if market dynamics change.
Consider these factors regarding customer backward integration:
- High Capital Outlay: Establishing pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities requires billions in investment for infrastructure, equipment, and quality control systems, posing a significant barrier for most customers.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating stringent regulations from bodies like the FDA or EMA, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), demands extensive expertise and compliance efforts.
- Specialized Expertise: Pharmaceutical manufacturing involves complex processes, research and development, and skilled labor, which are difficult and costly for external entities to replicate quickly.
- Strategic Shifts: While generally low, the threat can increase if a major customer, like a large hospital network or a dominant pharmacy chain, perceives a significant cost or control advantage in producing certain drugs internally, particularly generics.
Customers of Indoco Remedies, especially those in the generics market, wield considerable bargaining power due to high price sensitivity and the availability of numerous substitutes. This pressure is amplified by government policies promoting affordability, making it crucial for Indoco to maintain competitive pricing and efficient operations. While backward integration by customers is generally low due to high barriers, significant demand shifts could alter this landscape.
| Factor | Indoco's Position | Customer Bargaining Power |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High, especially in generics | High |
| Availability of Substitutes | High in generics | High |
| Switching Costs | Low for most customers | High |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low overall, but potential for large clients | Low to Moderate |
What You See Is What You Get
Indoco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Indoco Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a thorough examination of the competitive landscape, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You'll gain actionable insights to inform your strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian pharmaceutical market is incredibly crowded, featuring a vast array of domestic and international companies. Indoco Remedies faces stiff competition from major players such as Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Cipla, and Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, alongside a multitude of smaller and mid-sized businesses operating across different therapeutic segments and contract manufacturing services. This intense competition, particularly within the generic drug sector, significantly heightens rivalry.
The Indian pharmaceutical market is on a strong growth trajectory, with projections indicating it could reach around $130 billion by 2030. This expansion is fueled by increasing rates of lifestyle diseases, a growing elderly population, and broader access to healthcare services.
This robust market expansion, while creating significant opportunities, simultaneously intensifies competitive rivalry. As the industry expands, more players are drawn in, leading to a heightened struggle for market share among existing and new participants.
Further intensifying this dynamic is the burgeoning contract manufacturing sector within pharmaceuticals. This segment is anticipated to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 9.6% to 9.8% between 2025 and 2035, attracting further investment and competition.
In the generic pharmaceutical sector, product differentiation is inherently limited because the active pharmaceutical ingredients are chemically the same. This means companies like Indoco often compete on price, perceived quality, and the dependability of their supply chains. For instance, in 2024, the global generic drugs market was valued at approximately $450 billion, highlighting the scale of this price-sensitive competition.
Indoco's strategy involves focusing on specific therapeutic areas and offering contract manufacturing services. However, truly standing out beyond meeting regulatory standards and maintaining high manufacturing quality is difficult in this segment. The low switching costs for customers buying generic medications mean that if a competitor offers a slightly lower price or a more readily available supply, customers can easily shift their business, intensifying competitive rivalry.
Strategic Stakes and Exit Barriers
The strategic stakes in the Indian pharmaceutical market are incredibly high, fueled by its rapid growth and its status as a significant global pharmaceutical hub. Companies are pouring substantial resources into advanced manufacturing, cutting-edge research and development, and stringent regulatory adherence to secure and retain their market positions.
These significant investments translate into formidable exit barriers for pharmaceutical firms operating in India. The specialized nature of assets, including state-of-the-art manufacturing plants and dedicated R&D laboratories, coupled with the necessity of maintaining critical regulatory approvals, makes exiting the market a complex and financially burdensome undertaking. This difficulty in leaving the market naturally intensifies the competitive rivalry among the established players.
- High Strategic Stakes: India's pharmaceutical market is projected to reach $130 billion by 2030, underscoring the immense growth potential and strategic importance for companies.
- Significant Investment: Pharmaceutical companies in India typically invest between 5-10% of their revenue in R&D, demonstrating a deep commitment to innovation and market presence.
- Elevated Exit Barriers: Specialized manufacturing facilities, often built to meet global Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, represent substantial sunk costs, making divestment challenging.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Maintaining approvals from regulatory bodies like the US FDA and EMA for exported products creates a sticky situation, as abandoning these markets would mean losing valuable international revenue streams.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
The pharmaceutical sector faces intense rivalry driven by a stringent regulatory landscape. Compliance with global standards like USFDA, UKMHRA, and EU GMP necessitates substantial and ongoing investment, directly impacting a company's ability to compete.
For instance, Indoco Remedies has experienced regulatory scrutiny, including observations at its Goa facility, which can hinder market access and sales. This underscores how adherence to regulations, or lack thereof, significantly shapes competitive positioning.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Strict quality standards and lengthy approval processes act as significant barriers to entry, but also intensify competition among existing players.
- Compliance Costs: Maintaining compliance requires continuous investment in facilities, processes, and personnel, impacting profitability and operational flexibility.
- Impact of Non-Compliance: Regulatory observations or warning letters can lead to production halts, product recalls, and loss of market share, as seen with past issues at various pharmaceutical plants globally.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with robust compliance systems and a history of regulatory adherence gain a competitive edge, fostering trust and market preference.
Competitive rivalry within Indoco Remedies' operating environment is exceptionally high due to the fragmented nature of the Indian pharmaceutical market and the global generic drug industry. Companies frequently compete on price, supply chain reliability, and adherence to stringent quality standards, with limited product differentiation in generics.
| Key Competitor | Market Share (Approx. 2024) | Therapeutic Focus |
| Sun Pharmaceutical Industries | ~8-10% (India) | Broad spectrum, specialty |
| Cipla | ~6-7% (India) | Respiratory, anti-infectives |
| Dr. Reddy's Laboratories | ~4-5% (India) | Oncology, cardiovascular |
| Indoco Remedies | ~0.5-1% (India) | Dermatology, respiratory, CNS |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitute products for Indoco Remedies is notably moderate to high, largely due to the widespread availability of generic drugs. These generic alternatives often provide comparable therapeutic benefits at substantially reduced costs, presenting a compelling value proposition for both patients and healthcare providers.
This inherent price-performance advantage of generic medications exerts consistent pressure on companies like Indoco that offer branded or premium-priced formulations. For instance, in 2023, the global generic drugs market was valued at approximately $430 billion, underscoring the significant market share captured by these cost-effective alternatives.
The increasing availability and adoption of generic and biosimilar drugs represent a substantial threat to pharmaceutical companies like Indoco. India's prominent role as a global hub for generic drug manufacturing means this trend directly impacts companies operating within the country.
When patents on original, branded medications expire, the market rapidly sees an influx of cheaper generic versions, leading to heightened price competition. This dynamic directly affects profit margins for both innovator and generic drug producers.
Furthermore, the burgeoning market for biosimilars, especially in therapeutic areas such as anti-obesity treatments, amplifies this competitive pressure. For instance, as of early 2024, the market for biosimilars is projected to grow significantly, with some reports indicating a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15% over the next five years, further intensifying the threat of substitution.
Beyond traditional pharmaceuticals, alternative therapies and lifestyle changes pose a significant threat of substitution. For chronic conditions or general wellness, patients increasingly explore options like Ayurveda, acupuncture, or dietary interventions. For instance, the global wellness market, which includes these lifestyle aspects, reached an estimated $5.6 trillion in 2023, indicating a strong consumer shift towards non-pharmaceutical solutions.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences are increasingly leaning towards holistic health and preventative care, sometimes favoring natural remedies over conventional pharmaceuticals. This shift poses a threat to companies like Indoco, which primarily offer traditional drug products. A significant change in consumer mindset could reduce demand for certain Indoco offerings, potentially boosting the appeal of non-pharmaceutical substitutes or over-the-counter (OTC) options perceived as gentler.
For instance, the global wellness market, which encompasses natural and alternative health solutions, was valued at approximately $4.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to continue its robust growth. This expansion highlights a growing consumer willingness to explore alternatives to traditional medicine.
- Growing Wellness Market: The global wellness market's significant size and continued expansion indicate a strong consumer interest in health solutions beyond traditional pharmaceuticals.
- Preference for Natural Remedies: An increasing segment of consumers actively seeks out natural or perceived "benign" alternatives for health management.
- Impact on Pharmaceutical Demand: Shifts in consumer mindset can directly affect demand for specific therapeutic areas within Indoco's product portfolio.
- Rise of OTC Alternatives: The availability and marketing of effective OTC products that address similar health concerns can also draw consumers away from prescription or branded alternatives.
Regulatory Support for Substitutes
Government policies actively foster the adoption of substitutes, particularly in healthcare, by aiming to lower overall costs. For instance, in 2024, many national health services continued to emphasize the use of generic medications, with some countries reporting generic utilization rates exceeding 80% for commonly prescribed drugs.
Regulatory bodies streamline the approval pathways for generic drugs and biosimilars. This expedited process, observed globally in 2024, reduces the time to market for these lower-cost alternatives, directly challenging the market share of originator products. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for example, approved over 100 new generic drug applications in the first half of 2024 alone.
These regulatory actions create a more favorable competitive landscape for substitutes:
- Government mandates encouraging generic prescribing.
- Reduced regulatory hurdles for biosimilar approvals.
- Incentives for pharmacies to dispense generics.
- Price controls or reference pricing favoring cheaper alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Indoco Remedies is significant, fueled by the widespread availability and cost-effectiveness of generic drugs, which offer comparable therapeutic outcomes at lower prices. This pressure is amplified by the growing market for biosimilars, particularly in advanced therapeutic areas, and the increasing consumer interest in alternative health and wellness solutions.
The global generic drugs market's substantial valuation, around $430 billion in 2023, highlights the competitive landscape. Furthermore, the wellness market, valued at $5.6 trillion in 2023, demonstrates a growing consumer preference for non-pharmaceutical interventions.
Government policies and streamlined regulatory approvals for generics and biosimilars, with over 100 generic drug applications approved by the FDA in the first half of 2024, further bolster the position of substitutes.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Indoco |
| Generic Drugs | Lower-cost alternatives to branded medications. | Increased price competition, potential margin erosion. |
| Biosimilars | Highly similar versions of biologic drugs. | Challenges in specialized therapeutic areas, market share dilution. |
| Alternative Therapies | Holistic health, natural remedies, lifestyle changes. | Reduced demand for conventional pharmaceuticals, shift in consumer preference. |
| OTC Products | Over-the-counter medications addressing similar ailments. | Draws consumers away from prescription or branded alternatives. |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical sector, particularly in finished dosage forms and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), demands significant capital. This includes hefty investments in research and development, advanced manufacturing plants, robust quality control systems, and comprehensive compliance infrastructure. For instance, establishing a new API manufacturing facility compliant with global regulatory standards can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, if not hundreds.
Indoco Remedies has already made substantial investments in its manufacturing capabilities and technological infrastructure. Consequently, any new entrant aiming to compete effectively would require a similar, considerable financial outlay to match Indoco's scale and technological sophistication, presenting a significant barrier.
The pharmaceutical industry presents significant barriers to entry due to extensive regulatory oversight. Companies must navigate complex approval processes for drug development, manufacturing, and marketing, as mandated by bodies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). For instance, bringing a new drug to market typically involves years of clinical trials, with success rates often below 10%, making the investment substantial and risky for newcomers.
Established pharmaceutical players, including Indoco Remedies, possess robust distribution networks and established relationships with healthcare providers, pharmacies, and government bodies. For instance, Indoco's presence in over 55 countries highlights its extensive reach. Newcomers would need substantial investment and time to replicate this infrastructure and gain market trust.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players like Indoco Remedies leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, raw material procurement, and research and development. For instance, in 2023, Indoco Remedies reported a production capacity of 3.7 billion tablets/capsules and 350 million liquid or semi-solid dosage forms, a scale that is challenging for newcomers to match immediately.
Furthermore, these established companies benefit from an accumulated experience curve. This translates to greater efficiency in drug development processes, smoother navigation of complex regulatory landscapes, and proven strategies for market penetration. New entrants would face considerably higher initial capital outlays and a much steeper learning curve, hindering their ability to compete effectively on price or operational efficiency against established firms.
- Economies of Scale: Indoco's large-scale production facilities in 2023 contributed to cost efficiencies, making it harder for new, smaller players to undercut prices.
- Experience Curve: Decades of experience in navigating pharmaceutical regulations and market dynamics provide Indoco with a significant competitive advantage over nascent entrants.
- R&D Investment: Established players can spread substantial R&D costs over a larger output, a luxury new entrants often cannot afford, leading to higher initial product costs.
Brand Loyalty and Product Differentiation
Brand loyalty significantly impacts the threat of new entrants in the pharmaceutical sector. While the generic market may see less entrenched loyalty, established players in branded or specialized therapeutic areas have cultivated trust and recognition over extended periods. For instance, in 2024, major pharmaceutical companies continued to leverage their long-standing reputations, particularly in critical care segments, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share without substantial differentiation.
New entrants face the considerable challenge of overcoming this existing brand loyalty. They must invest heavily in marketing and promotion to build awareness and trust. Furthermore, differentiating products in a crowded marketplace, even within generics, requires a compelling value proposition, such as superior quality, unique formulations, or more accessible pricing strategies. The success of a new entrant often hinges on its ability to clearly communicate its unique selling points and establish credibility quickly.
- Established brands command significant customer trust, particularly in specialized therapeutic areas.
- New entrants must overcome years of reputation building by incumbents.
- Differentiating products requires substantial marketing investment and a clear value proposition.
- Contract manufacturing services also benefit from established relationships and proven track records, posing a barrier to new contract manufacturers.
The threat of new entrants for Indoco Remedies is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles. Significant investments are needed for R&D, advanced manufacturing, and compliance, often running into tens of millions of dollars for API facilities. Indoco's existing scale, with a 2023 production capacity of 3.7 billion tablets/capsules, presents a formidable economic barrier.
Established players like Indoco benefit from extensive distribution networks and strong relationships with healthcare providers, which take considerable time and investment for newcomers to replicate. For example, Indoco's presence in over 55 countries underscores this advantage. Furthermore, brand loyalty, especially in specialized therapeutic areas, makes it challenging for new entrants to gain market share without substantial differentiation and marketing investment.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for R&D, manufacturing, and compliance. | Significant barrier, requiring substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex approval processes (FDA, EMA) for development and manufacturing. | Time-consuming and costly, increasing risk for newcomers. |
| Economies of Scale | Indoco's large-scale production (3.7 billion units in 2023) leads to lower costs. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies. |
| Distribution & Relationships | Established networks and trust with healthcare providers. | Difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to build. |
| Brand Loyalty | Customer trust cultivated over time, especially in branded segments. | Requires significant marketing and differentiation efforts to overcome. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from Indoco Remedies' annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate industry-specific reports from market research firms and pharmaceutical trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.