Iluka Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Iluka Bundle
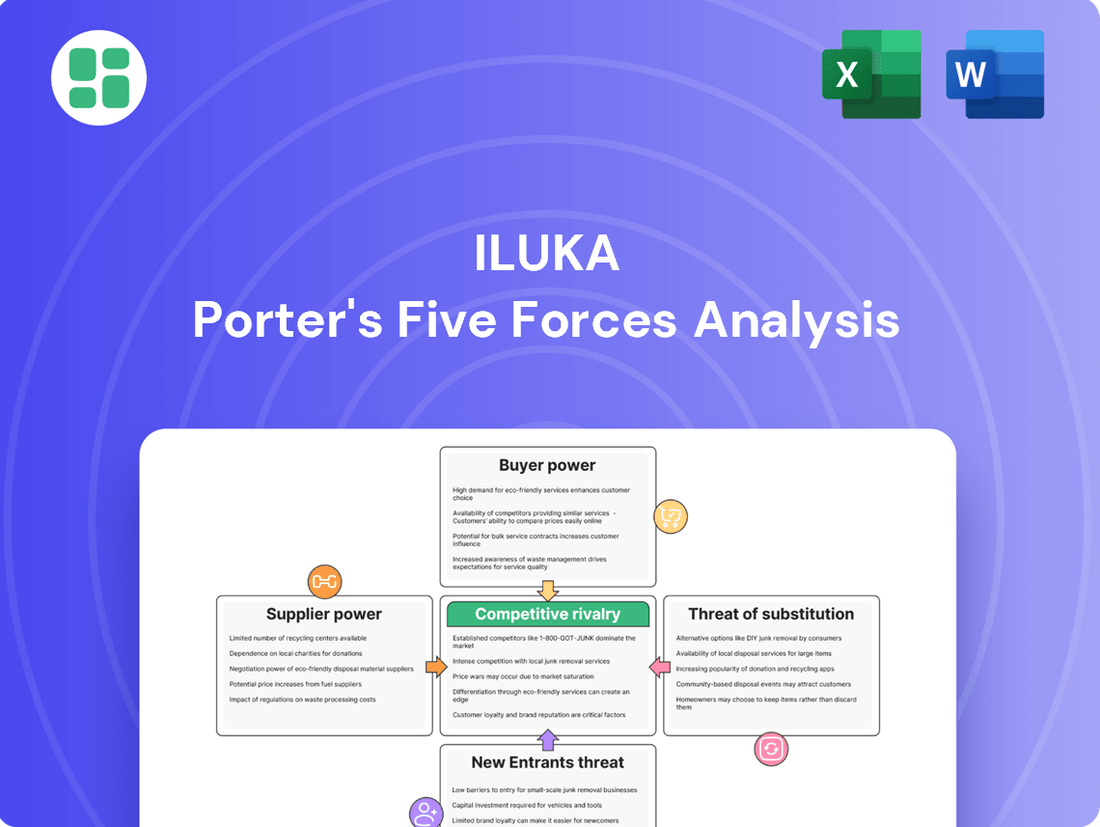
Iluka's competitive landscape is shaped by significant buyer power, particularly from its major customers in the zircon and titanium dioxide markets. Understanding the intensity of rivalry and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating Iluka's industry. The full analysis reveals the real forces shaping Iluka’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Iluka's reliance on specific raw materials like high-grade mineral sands and specialized mining equipment can grant significant leverage to its suppliers. While Iluka extracts many of its own mineral sands, it also processes third-party feedstocks, particularly for its rare earths refinery, meaning it doesn't have complete control over all its primary inputs.
The mining and processing of mineral sands, especially for synthetic rutile and rare earth refining, relies on highly specialized equipment and cutting-edge technology. Suppliers offering unique solutions, like those for underground mining or rare earth processing, can wield considerable bargaining power. This is largely due to the substantial costs and complexities involved in switching to alternative suppliers, coupled with a scarcity of comparable options for Iluka.
Iluka Resources relies heavily on a skilled workforce, including engineers, geologists, and specialized mining operators. The availability and cost of this talent directly influence operational efficiency and profitability. For instance, in 2023, Australia experienced ongoing labor shortages in specialized mining roles, a trend likely to persist into 2024, potentially driving up wages and giving workers more leverage.
Energy and Logistics Costs
Energy is a critical input for Iluka's mining and processing activities, making its cost base highly susceptible to energy price volatility. For instance, the average price of Brent crude oil, a key indicator for global energy costs, saw significant fluctuations throughout 2024, impacting operational expenditures.
The global reach of mineral sands trade introduces another layer of supplier power through logistics and transportation costs. These expenses are directly tied to fuel prices and the availability of shipping capacity. Iluka's strategic initiative, such as the development of the Balranald hybrid power system, aims to mitigate some of these energy-related cost pressures.
- Energy Price Impact: Fluctuations in global energy prices directly affect Iluka's production costs.
- Logistics Sensitivity: Dependence on global shipping means transportation costs, influenced by fuel prices, are a key supplier cost factor.
- Mitigation Strategies: Iluka is investing in solutions like the Balranald hybrid power system to reduce reliance on volatile energy markets.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance Services
The bargaining power of suppliers for environmental and regulatory compliance services is significant for critical minerals companies like Iluka. These specialized services are essential for maintaining operational licenses and adhering to increasingly strict sustainability mandates. For instance, in 2024, the global environmental consulting market was valued at approximately $48 billion, highlighting the substantial revenue streams available to providers in this sector.
Suppliers offering expertise in areas such as mine rehabilitation, emissions monitoring, and waste management technologies can exert considerable influence. Iluka's commitment to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles, a trend amplified throughout 2024, means that reliable and compliant service providers are in high demand. The cost of non-compliance can be substantial, including fines and reputational damage, further strengthening the hand of these critical suppliers.
- High Demand for Specialized Expertise: Suppliers with proven track records in critical minerals environmental management are sought after.
- Regulatory Necessity: Compliance with environmental laws is non-negotiable, making these services indispensable.
- ESG Commitments: Iluka's focus on sustainability increases reliance on suppliers who enable strong ESG performance.
- Potential for High Switching Costs: Transitioning to new compliance service providers can be complex and costly.
Iluka's suppliers, particularly those providing specialized mining equipment and rare earth processing technology, hold significant bargaining power. This leverage stems from the high costs and complexity associated with switching providers, compounded by a limited pool of comparable alternatives. The specialized nature of these inputs means Iluka cannot easily substitute them, granting suppliers considerable influence over pricing and terms.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Iluka's Vulnerability |
| Specialized Mining Equipment | Unique technology, high switching costs, limited providers | Reliance on specific machinery for efficient extraction |
| Rare Earth Processing Technology | Proprietary processes, high R&D investment, few alternatives | Dependence for value-added rare earth products |
| Skilled Labor (Geologists, Engineers) | Labor shortages in specialized mining roles (e.g., Australia 2023-2024) | Increased wage pressure impacting operational costs |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Iluka, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the mineral sands industry.
Quickly identify and quantify competitive pressures with a visual, interactive dashboard, allowing for immediate strategic adjustments to Iluka's market position.
Customers Bargaining Power
Iluka's customer base, while diverse across applications like ceramics and paints, shows significant concentration for its core mineral products. For instance, the demand for titanium dioxide feedstocks, such as rutile, is heavily reliant on the pigment industry, which historically consumes around 90% of this material. This concentration means a few large industrial buyers can wield considerable influence.
This situation grants substantial bargaining power to these major industrial customers. When a significant portion of demand comes from a limited number of players, especially within a fluctuating market, these buyers are in a strong position to negotiate pricing terms. This can put pressure on Iluka's profit margins.
Iluka's customers, particularly those in the ceramics and pigment manufacturing sectors, depend heavily on the consistent high quality of its zircon and rutile. These minerals are essential components in their production lines, meaning deviations in quality can significantly disrupt their operations. This critical reliance means customers have considerable bargaining power if Iluka fails to meet stringent specifications or if they can find suppliers offering comparable quality at a better price.
Customer bargaining power in the mineral sands sector, including for companies like Iluka, is significantly shaped by market dynamics. When there's an abundance of supply or during economic downturns, buyers tend to be more sensitive to price, leading them to push for reductions. This was evident in early 2024, where the zircon market experienced price volatility, with competitive offerings from other suppliers directly influencing the prices Iluka could achieve.
Diversification of Supply Chains
As geopolitical tensions and evolving trade policies continue to reshape global supply chains, customers are increasingly motivated to diversify their sources for critical minerals. This diversification directly impacts the bargaining power of customers by presenting them with a wider array of options, potentially reducing their reliance on any single supplier.
For example, the United States and the European Union have implemented anti-dumping measures against pigment imports originating from China. While this could initially benefit suppliers like Iluka by making their products more competitive, it also simultaneously empowers customers. They gain more leverage as tariffs or shifting trade dynamics create alternative supply routes, allowing them to negotiate better terms or switch suppliers if conditions become unfavorable.
- Diversified Sourcing: Customers can mitigate risks associated with single-source dependency, enhancing their negotiation position.
- Trade Policy Impact: Measures like anti-dumping duties create alternative supply options, increasing customer leverage.
- Supplier Competition: A more fragmented supply landscape intensifies competition among suppliers, benefiting customers.
Customer Sophistication and Direct Relationships
Iluka actively cultivates direct relationships with its key industrial customers, employing a disciplined marketing approach. This direct engagement allows for a deeper understanding of customer needs and market dynamics, which can help in managing customer power.
The customers Iluka serves are typically highly sophisticated. They possess a thorough understanding of prevailing market prices, the availability of alternative suppliers, and the broader global supply and demand landscape for mineral sands. This knowledge empowers them to negotiate terms more effectively.
For instance, in 2023, Iluka reported that approximately 70% of its synthetic rutile sales were secured through long-term contracts, demonstrating a strategic effort to lock in volumes and pricing. These agreements, like the take-or-pay contracts for synthetic rutile, are crucial in mitigating the bargaining power of customers by providing a degree of revenue certainty.
- Direct Customer Engagement: Iluka fosters direct relationships with major clients.
- Informed Customer Base: Sophisticated industrial customers are knowledgeable about market prices and alternatives.
- Contractual Mitigation: Long-term contracts, such as take-or-pay for synthetic rutile, reduce customer leverage.
- 2023 Contract Data: Around 70% of Iluka's synthetic rutile sales in 2023 were under long-term agreements.
Iluka's customers, particularly those in the pigment and ceramics industries, hold significant bargaining power due to the critical nature of its mineral products and market concentrations. This power is amplified when customers can source comparable materials from multiple suppliers or when market conditions favor buyers, as seen with price volatility in the zircon market in early 2024.
Iluka's strategic use of long-term contracts, such as the take-or-pay agreements for synthetic rutile, aims to counterbalance this customer leverage. In 2023, approximately 70% of Iluka's synthetic rutile sales were secured through such contracts, providing revenue certainty and mitigating the immediate impact of customer price negotiations.
The increasing trend of customers diversifying their mineral sources, partly influenced by geopolitical shifts and trade policies like anti-dumping measures, further empowers them. This diversification allows customers greater flexibility to negotiate terms and switch suppliers, directly impacting Iluka's pricing power and market position.
| Factor | Impact on Iluka | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration (Pigment Industry) | High reliance on a few large buyers for rutile. | Strong ability to negotiate pricing and terms. |
| Critical Input Dependency | Zircon and rutile are essential for customer production. | Customers can demand consistent quality and competitive pricing. |
| Market Volatility (e.g., Zircon 2024) | Price fluctuations create buyer sensitivity. | Customers push for price reductions during downturns. |
| Diversified Sourcing Trends | Customers seek multiple suppliers to reduce risk. | Increases options and negotiation power for customers. |
| Long-Term Contracts (2023 Data) | Secures volumes and pricing, mitigating immediate pressure. | Reduces short-term customer bargaining power on price. |
Same Document Delivered
Iluka Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Iluka Porter's Five Forces analysis details the competitive landscape of the mineral sands industry, offering insights into buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry. What you're previewing is precisely the same professionally formatted document that will be available to you instantly after purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Iluka Resources operates within a global mineral sands market, facing robust competition from several major players. Key rivals include Tronox Holdings plc, a significant producer of titanium dioxide and zircon, and Rio Tinto plc, a diversified mining giant with substantial mineral sands operations. Kenmare Resources plc and Base Resources Limited also represent important competitors, particularly in specific geographic regions or product segments. This landscape is dominated by a few large-scale producers, fostering intense rivalry for market share and pricing power, especially for high-demand products like zircon and titanium dioxide feedstocks.
While mineral sands are often viewed as commodities, differentiation is possible through superior product quality, unwavering consistency, and the development of specialized offerings. Iluka Resources, for instance, distinguishes itself by concentrating on high-grade zircon and rutile, and by venturing into the burgeoning rare earths sector. This strategic focus elevates Iluka beyond basic commodity trading, positioning it within the critical minerals space where specific applications drive value.
Competitive rivalry in the mineral sands industry, particularly for Iluka, is significantly shaped by producers' capacity utilization and their ability to ramp up new production. Iluka's current mining operations are running at full capacity, meaning existing output is maximized.
The planned expansion, including projects like the Balranald mine and the Eneabba rare earths refinery, will boost future production capacity. This increase in potential supply, if not matched by equivalent market demand growth, could lead to intensified price competition among existing and new players in the sector.
Strategic Diversification into Rare Earths
Iluka's strategic move into rare earth elements significantly alters the competitive landscape. By developing capabilities to supply separated rare earth oxides, Iluka is differentiating itself from competitors primarily focused on mineral sands, positioning itself as a critical supplier for the burgeoning high-tech sector.
This diversification directly addresses the threat of substitutes and enhances Iluka's bargaining power. In 2023, Iluka reported significant progress at its Eneabba rare earths refinery in Western Australia, with construction advancing on schedule, signaling a tangible commitment to this strategic pivot.
- Diversification Strategy: Iluka's entry into rare earths reduces dependence on volatile mineral sands markets.
- Market Position: Aims to be a key supplier of critical minerals for advanced technologies.
- Competitive Advantage: Competitors solely focused on mineral sands may struggle to match this integrated rare earths offering.
- Investment: Continued investment in projects like the Eneabba refinery underscores the seriousness of this competitive maneuver.
Geographical Concentration and Trade Policies
The mineral sands industry exhibits distinct geographical demand patterns, with the Asia Pacific region representing the largest market share. This concentration means that trade policies and tariffs can significantly alter the competitive landscape.
For instance, tariffs on Chinese pigment imports can create an advantage for producers in other regions, impacting global players like Iluka. These shifts can present both hurdles and avenues for growth, depending on a company's operational footprint and market access.
- Asia Pacific Dominance: The Asia Pacific region accounted for approximately 45% of the global mineral sands market in 2023, highlighting its critical demand center.
- Tariff Impact: In 2024, import tariffs imposed by various countries on titanium dioxide pigments, a key mineral sand derivative, have varied, with some tariffs reaching up to 15% on specific imports, influencing sourcing decisions and pricing.
- Jurisdictional Advantages: Favorable trade agreements or lower tariffs in certain production jurisdictions can lead to cost advantages, potentially shifting market share away from less favorably positioned competitors.
Iluka's competitive rivalry is intensified by its peers like Tronox and Rio Tinto, who also possess significant mineral sands operations, leading to a concentrated market. Iluka's strategy of focusing on high-grade products and expanding into rare earths, as evidenced by progress at its Eneabba refinery in 2023, helps it differentiate from competitors primarily focused on traditional mineral sands. This move into critical minerals positions Iluka to capture value in high-tech sectors, potentially altering the competitive dynamics. The company's current full capacity utilization means any future production increases, such as from the Balranald mine, could lead to more aggressive pricing strategies among market participants.
| Competitor | Key Products | 2023 Market Share (Est.) | Strategic Focus |
| Tronox Holdings plc | Titanium Dioxide, Zircon | 15-20% | Global TiO2 production, feedstock integration |
| Rio Tinto plc | Zircon, Titanium Dioxide Feedstock | 10-15% | Diversified mining, resource development |
| Kenmare Resources plc | Ilmenite, Zircon | 5-8% | African operations, specialty minerals |
| Base Resources Limited | Ilmenite, Rutile, Zircon | 3-5% | African operations, cost efficiency |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Synthetic rutile, created by processing ilmenite, presents a significant substitute for natural rutile, especially in the manufacturing of titanium dioxide pigments. This threat is managed by Iluka, a leading producer of synthetic rutile, which strategically offers both natural and synthetic options, thereby securing market share regardless of customer preference.
While titanium dioxide (TiO2) is the dominant white pigment, the threat of substitutes exists. Emerging alternative materials or advancements in pigment technology could offer comparable performance at a lower cost. For instance, research into novel composite materials or advanced ceramic pigments continues, although widespread industrial adoption remains nascent.
However, TiO2's established dominance is rooted in its superior opacity, brightness, and UV resistance, critical attributes across paints, plastics, and paper industries. The cost and complexity associated with retooling manufacturing processes and reformulating products present significant barriers to entry for most substitutes, limiting their immediate impact on TiO2's market position.
Zircon's unique properties, like its high melting point and chemical resistance, make it a cornerstone in ceramics and refractories. These sectors rely on zircon for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.
While materials such as calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, and calcium carbonate can substitute for zircon in certain niche refractory uses, they often fall short in performance or cost-effectiveness for broader applications. This limits the availability of a true, all-encompassing substitute.
Recycling and Circular Economy Initiatives
Increased recycling of zircon and titanium dioxide containing materials, alongside broader circular economy initiatives, could gradually diminish the need for newly mined mineral sands. This trend, while still in its early stages, represents a potential long-term substitution threat.
However, the sheer volume of current global consumption and the significant technical hurdles involved in efficiently recovering these specific minerals from finished products mean this is not an immediate concern. For instance, while global titanium dioxide demand was projected to reach approximately 10 million metric tons in 2024, the infrastructure for widespread mineral sand recycling is still developing.
The viability of substitutes is further limited by the specialized applications of zircon and titanium dioxide, where high purity and specific performance characteristics are often paramount. Current recycling efforts are more focused on less complex material streams.
Key considerations regarding this threat include:
- Nascent Substitution: The threat is currently low due to technical and economic feasibility challenges in recycling.
- Long-Term Potential: Circular economy advancements could impact demand for virgin resources over an extended period.
- Scale of Demand: High current consumption levels for titanium dioxide and zircon mean recycling needs to scale significantly to be impactful.
- Technical Hurdles: Efficiently extracting and purifying these minerals from diverse end-of-life products remains a significant obstacle.
Technological Advancements in End-User Industries
Technological advancements in end-user industries represent a potential substitute threat for mineral sands. For instance, shifts in ceramics or paint manufacturing that decrease the need for mineral sands, or allow for the use of lower-grade materials, could impact demand. Iluka's proactive engagement with these sectors aims to mitigate this by staying abreast of evolving requirements and ensuring product relevance.
In 2023, Iluka reported that its synthetic rutile production was around 230,000 tonnes, a figure that could be affected by process efficiencies in downstream industries. The company's strategy involves continuous dialogue with customers to anticipate and adapt to these technological shifts, thereby maintaining its competitive edge.
- Technological shifts in ceramics: Innovations could reduce reliance on titanium dioxide pigments derived from mineral sands.
- Paint and coatings evolution: New formulations might require less or different types of mineral sand inputs.
- Welding advancements: Changes in welding flux technologies could alter the demand for rutile.
- Iluka's customer engagement: Proactive partnerships help Iluka align its product offerings with industry changes.
While titanium dioxide (TiO2) dominates the white pigment market, emerging alternatives could pose a threat, though widespread adoption is currently limited by technical and cost barriers. For instance, Iluka, a major producer, strategically offers both natural and synthetic rutile, mitigating some of this risk by catering to diverse customer needs. The global TiO2 market, projected to exceed 10 million metric tons in 2024, highlights the scale of demand that any substitute would need to address.
The threat of substitutes for zircon is also constrained by its specialized applications, where high purity and performance are critical, making it difficult for materials like calcium oxide or magnesium oxide to fully replace it in demanding refractory uses. While recycling initiatives and circular economy principles present a long-term substitution potential, significant technical hurdles in efficient mineral recovery currently limit their immediate impact on virgin resource demand.
Technological shifts in end-user industries, such as advancements in ceramics or paint manufacturing that reduce the need for mineral sands, represent another potential threat. Iluka's proactive engagement with these sectors aims to stay ahead of evolving requirements, ensuring its product relevance in a changing market landscape.
| Substitute Type | Current Impact | Key Challenges | Iluka's Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Pigments | Low | Cost, performance parity, reformulation complexity | Offering synthetic rutile, customer collaboration |
| Recycling/Circular Economy | Very Low (immediate) | Technical recovery hurdles, infrastructure development | Monitoring long-term trends |
| End-User Technology Shifts | Low to Moderate | Industry-specific innovation pace | Proactive customer engagement, R&D |
Entrants Threaten
The mineral sands mining and processing sector demands massive upfront capital for exploration, mine development, and processing facilities. This high capital intensity, exemplified by Iluka's significant investments in projects such as Balranald, acts as a substantial deterrent for new players seeking to enter the market.
New entrants into the mineral sands industry, particularly those looking at Iluka's operational areas, confront a formidable gauntlet of regulatory and environmental requirements. These include rigorous environmental impact assessments, lengthy land access negotiations, and strict adherence to mining and environmental legislation. For instance, obtaining the necessary permits can take years and involve significant upfront investment, acting as a substantial deterrent for smaller or less capitalized potential competitors.
The mineral sands industry demands deep technical knowledge across geology, mining, processing, and market analysis. Iluka's decades of experience have fostered unique expertise, including proprietary advancements like remotely operated underground mining, creating a significant barrier for newcomers.
Established Supply Chains and Customer Relationships
Established players, such as Iluka Resources, benefit from deeply entrenched supply chains and robust, long-term relationships with major industrial clients. These networks are critical for consistent raw material sourcing and product distribution, giving incumbents a significant advantage.
Newcomers would face substantial hurdles in replicating these established connections. Building a global supply chain and securing reliable off-take agreements requires considerable time, investment, and the ability to overcome existing customer loyalty and brand preference. For instance, Iluka's long-standing partnerships in the titanium dioxide and zircon markets provide a barrier that is difficult for new entrants to surmount without significant capital and strategic maneuvering.
- Established Supply Chains: Iluka leverages a global network for sourcing and distribution, built over years.
- Customer Relationships: Long-standing ties with key industrial buyers create loyalty and preferential treatment.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants must invest heavily to build similar networks and gain customer trust.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Without these, new firms struggle to secure consistent sales and competitive pricing.
Resource Scarcity and Quality of Deposits
The availability of economically viable, high-grade mineral sands deposits is a significant constraint. Discovering and developing new deposits of sufficient quality and scale to challenge established players like Iluka, which operates the world's largest zircon mine, presents a formidable natural barrier. This scarcity directly impacts the threat of new entrants by limiting the raw material base available for new operations.
Iluka Resources, a leader in the mineral sands industry, reported that its Cataby mine in Western Australia produced approximately 315,000 tonnes of zircon in 2023. This highlights the scale required to compete effectively. The high capital expenditure and long lead times associated with exploration, mine development, and processing further deter potential new competitors.
- Limited High-Grade Deposits: The global supply of easily accessible, high-quality mineral sands is finite, creating a natural barrier.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing a new mineral sands operation requires substantial upfront investment in exploration, mining, and processing infrastructure.
- Iluka's Scale Advantage: Iluka's position as the operator of the world's largest zircon mine provides significant economies of scale and cost advantages, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price.
- Exploration Risk: The success rate for discovering economically viable mineral sands deposits is relatively low, increasing the risk for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the mineral sands sector is generally low due to significant capital requirements and established operational expertise. Iluka Resources' substantial investments in projects and its proprietary technologies create high barriers. Furthermore, securing necessary regulatory approvals and navigating complex environmental standards are time-consuming and costly hurdles for potential new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | Iluka's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment for exploration, mine development, and processing. | Iluka's significant project investments demonstrate this. |
| Regulatory & Environmental | Rigorous permits, land access, and compliance requirements. | Lengthy processes deter smaller, less experienced entrants. |
| Technical Expertise | Deep knowledge in geology, mining, processing, and proprietary tech. | Iluka's decades of experience and innovations like remote mining are key. |
| Supply Chain & Customer Relationships | Established networks and long-term client ties. | Iluka's global partnerships in TiO2 and zircon markets are a strong advantage. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Iluka leverages a combination of primary and secondary data, including Iluka's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and government geological surveys to assess raw material availability and supplier power.