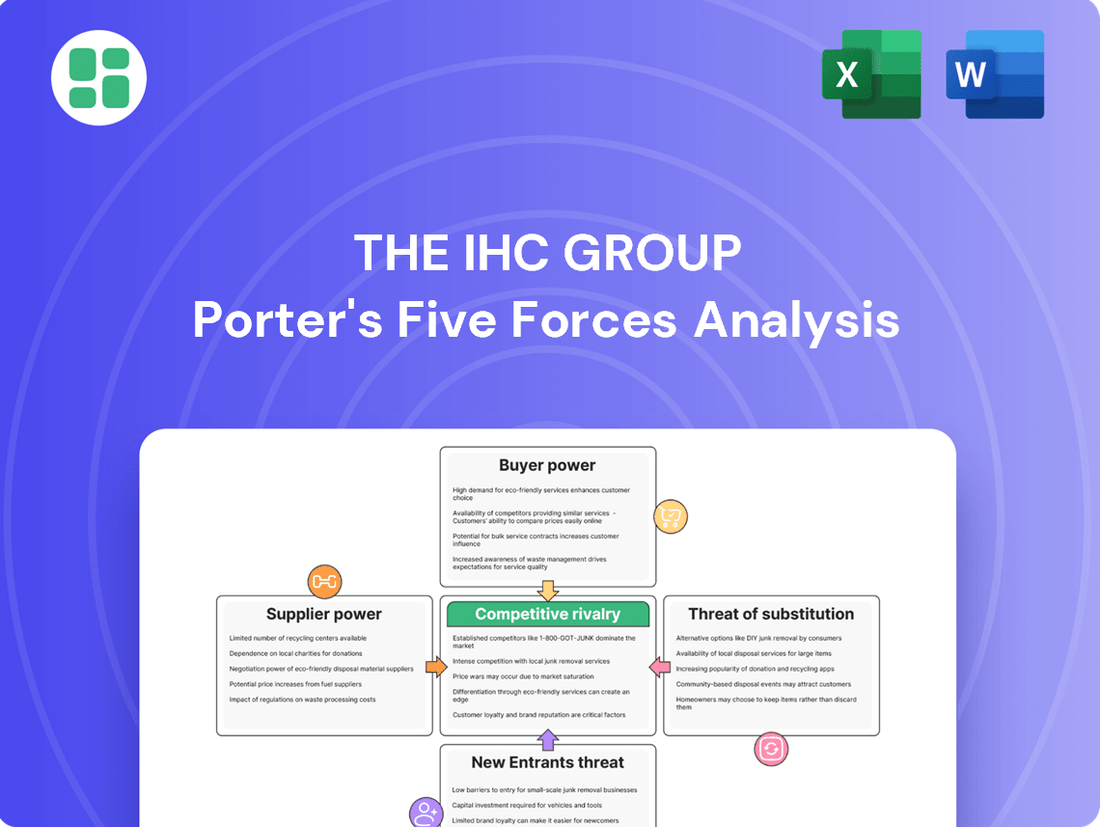
The IHC Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
The IHC Group Bundle
The IHC Group operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive terrain.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore The IHC Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of reinsurance providers presents a considerable influence over IHC Group. This is primarily because IHC relies on these entities to offload a portion of its insurance-related risks. The medical stop-loss sector, a critical segment for IHC, has seen an uptick in claims and associated costs.
This increasing cost environment for medical stop-loss is a key factor. It suggests that reinsurers may be in a stronger position to negotiate higher rates for 2025. This leverage could translate into increased costs for IHC as it seeks to secure reinsurance coverage.
For medical stop-loss insurance, healthcare providers are indirect suppliers whose pricing directly influences claims costs for insurers like The IHC Group. As the cost of complex medical treatments, such as advanced surgeries, specialized pharmaceuticals, and intensive care, continues to climb, providers gain leverage to command higher prices. This upward pressure on healthcare expenses directly translates to increased claims for stop-loss policies, impacting profitability for IHC.
In 2024, the U.S. experienced significant increases in healthcare expenditures, with projections indicating continued growth in medical inflation. For instance, the average cost of a hospital stay has seen a notable rise, driven by factors like staffing shortages and the increasing use of expensive medical technologies. This trend empowers healthcare systems to negotiate higher reimbursement rates, which in turn, increases the potential claims IHC must cover under its stop-loss products.
The increasing integration of advanced analytics and AI within the insurance sector significantly bolsters the bargaining power of technology and software vendors. As IHC Group, like many insurers, leans on sophisticated platforms for critical functions such as claims prediction and underwriting, specialized software providers can leverage this dependence. For instance, in 2024, the global AI in insurance market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, underscoring the critical nature of these technologies and the leverage held by their suppliers.
Brokerage and Distribution Networks
The IHC Group, like many insurance providers, depends heavily on brokers and established distribution networks to connect with its target customers for life and health insurance. These intermediaries are crucial for market access.
Networks that boast strong client relationships and extensive market penetration can wield significant influence. They can negotiate commission rates and other terms because of their ability to deliver a consistent flow of business to insurers.
In 2024, the insurance brokerage sector continued to consolidate. For instance, major insurance brokers reported significant revenue growth, underscoring their market power. This trend suggests that a strong distribution network can indeed command better terms.
- Dependence on Intermediaries: IHC's reliance on brokers and distribution channels for customer acquisition is a key factor.
- Network Strength Influence: The reach and client loyalty of these networks directly translate into bargaining leverage.
- Negotiating Power: Strong networks can dictate commission structures and service agreements due to their market access.
- Market Consolidation Impact: Industry trends in 2024, showing broker revenue growth, highlight the increasing power of these distribution entities.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, wield significant influence over insurance companies like The IHC Group. Changes in state and federal regulations, for instance, can mandate costly compliance measures, impacting operational expenses and effectively setting terms for insurers. In 2024, the insurance industry continued to navigate a complex web of evolving regulations, with areas like data privacy and cybersecurity seeing increased scrutiny, leading to potential investments in new technologies and compliance protocols.
These regulatory impositions can range from solvency standards that require insurers to maintain higher capital reserves to new data governance rules that necessitate robust information management systems. Such requirements can directly increase the cost of doing business, akin to a supplier demanding higher prices, thereby impacting an insurer's profitability and strategic flexibility.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Insurers face growing expenses related to adhering to new state and federal mandates, such as those concerning data security and consumer protection.
- Capital Requirements: Regulatory bodies often dictate solvency standards, forcing companies to hold more capital, which can limit investment capacity.
- Operational Adjustments: New rules may require significant changes to business processes, technology investments, and personnel training, adding to overhead.
- Market Entry Barriers: Stringent regulatory environments can act as a barrier to entry for new competitors, indirectly benefiting established players but also limiting innovation.
The bargaining power of suppliers for The IHC Group is multifaceted, encompassing reinsurance providers, healthcare entities, technology vendors, and distribution networks. Reinsurers can exert significant influence, particularly as medical stop-loss claims and costs rise, as seen with increasing healthcare expenditures in 2024. Healthcare providers, as indirect suppliers, gain leverage through escalating treatment costs, directly impacting IHC's claims. Furthermore, the growing reliance on specialized technology for analytics and underwriting empowers software vendors, a trend highlighted by the substantial global AI in insurance market value. Finally, the consolidation within the insurance brokerage sector in 2024 has amplified the negotiating power of strong distribution networks, allowing them to secure more favorable terms.
| Supplier Type | Influence Factor | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Reinsurance Providers | Risk transfer, claims costs | Rising medical stop-loss claims and costs empower reinsurers to negotiate higher rates. |
| Healthcare Providers | Cost of medical treatments | Increased complexity and cost of medical procedures directly inflate claims for stop-loss policies. |
| Technology/Software Vendors | AI/Analytics platform dependence | The $10.5 billion global AI in insurance market in 2024 underscores vendor leverage due to critical technology reliance. |
| Brokers/Distribution Networks | Market access, client relationships | Industry consolidation and revenue growth in 2024 for brokers indicate increased negotiating power for distribution channels. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for The IHC Group dissects the competitive intensity within its operating environment, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive, visual breakdown of the IHC Group's Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual customers in the short-term medical and supplemental health insurance sectors often exhibit significant price sensitivity, especially as healthcare expenses continue to rise. For instance, in 2024, many consumers are actively seeking the most cost-effective coverage options to manage out-of-pocket medical expenses.
The proliferation of online insurance marketplaces empowers these individuals by making it easier to compare policies from various providers. This increased transparency and the sheer volume of available plans directly enhance their bargaining power, as they can readily identify and switch to more affordable alternatives.
However, the practicalities of switching health insurance can be complex. High switching costs, particularly concerning the continuity of care and the potential disruption to ongoing medical treatments, can significantly temper a customer's willingness to change providers, thereby mitigating their bargaining power in certain situations.
Employer groups, particularly larger ones, wield considerable bargaining power when procuring medical stop-loss and group term life insurance. These groups often employ specialized benefits consultants who can negotiate favorable terms, attachment points, and tailored coverage. For instance, in 2023, the average employer spent $1,323 per employee on stop-loss insurance, a figure that can be influenced by negotiation.
Customers today have unprecedented access to information about health insurance, thanks to online comparison tools and review sites. This heightened awareness means they can easily research pricing, policy details, and the track record of insurers, including companies like The IHC Group. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of consumers actively used digital platforms to research health insurance plans, a trend that continues to grow.
This readily available data significantly boosts the bargaining power of customers. They can now objectively compare offerings, putting pressure on The IHC Group and its competitors to provide transparent pricing and comprehensive coverage to remain competitive. The ability to easily see how one plan stacks up against another empowers individuals to demand better value.
Switching Costs and Continuity of Care
The bargaining power of customers within the healthcare industry, particularly for entities like The IHC Group, is significantly influenced by switching costs. Despite growing consumer awareness and a desire for better value, many patients find the process of changing healthcare providers to be complex and fraught with potential drawbacks. This complexity often serves as a significant barrier, effectively dampening their ability to exert strong bargaining power.
These switching costs aren't merely financial; they encompass the practical challenges of transferring medical records, the potential disruption to ongoing treatment plans, and the anxiety surrounding unexpected out-of-pocket expenses during the transition. For instance, a patient undergoing a chronic condition management plan might hesitate to switch if it means re-establishing care with a new physician, potentially facing delays in diagnosis or treatment adjustments. This perceived inconvenience or risk can often outweigh the allure of potential cost savings or improved service elsewhere.
Consider the data from 2024, where studies indicated that over 60% of patients expressed concerns about the administrative burden involved in switching healthcare providers. Furthermore, a significant portion reported anxiety about maintaining the continuity of care, especially for those with complex medical histories. These factors collectively reinforce the inertia that limits the effective exercise of customer bargaining power in the healthcare sector.
- High Switching Costs: Patients face hurdles like transferring medical records and re-establishing relationships with new doctors.
- Continuity of Care Concerns: Patients worry about disruptions to ongoing treatment and potential gaps in their medical management.
- Financial Uncertainty: The risk of unexpected medical bills during a transition deters many from switching providers.
- Reduced Bargaining Power: The inconvenience and risk associated with switching often outweigh potential benefits, limiting customer leverage.
Broker Influence and Advisory Role
Customers often lean on brokers and financial advisors to understand the intricacies of insurance, especially for group and specialized plans. These professionals, representing the customer's interests, can consolidate demand and negotiate terms with insurance providers, thereby amplifying the collective bargaining power of their clientele.
For instance, in 2024, the reliance on financial advisors for retirement planning and investment decisions remained high, with reports indicating that a significant percentage of individuals sought professional guidance for managing their assets. This reliance translates directly into increased leverage for customers when selecting insurance products or negotiating group benefits, as advisors can present a unified front with aggregated client needs.
- Broker Dependency: Customers often lack the expertise to navigate complex insurance policies, making them reliant on brokers.
- Demand Aggregation: Brokers can pool customer demand, creating a larger negotiating bloc.
- Negotiating Leverage: This aggregated demand strengthens the bargaining position of customers when dealing with insurers.
- Informed Choices: Advisors help clients make informed decisions, driving competition among insurers to offer better terms.
While individual customers can compare prices, their bargaining power is often limited by high switching costs and the complexity of health insurance. For example, in 2024, many consumers found the administrative burden of changing providers, along with concerns about continuity of care, to be significant deterrents.
Employer groups, however, represent a stronger customer segment. In 2023, larger employers, often aided by benefits consultants, could negotiate terms for medical stop-loss insurance, with average per-employee spending at $1,323, indicating a substantial market where negotiation is common.
The increasing use of online comparison tools in 2024 empowers consumers by providing greater transparency. This ease of access to information about pricing and policy details allows customers to more effectively pressure insurers like The IHC Group for better value and clearer offerings.
Full Version Awaits
The IHC Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of The IHC Group, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you are viewing is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after completing your purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The health and life insurance sectors present a dual nature: fragmented in specialized areas but highly concentrated among major players, especially in lucrative commercial and Medicare Advantage markets. This dynamic means that even for companies like IHC Group, which strategically targets niches such as medical stop-loss and supplemental health, the competitive landscape remains intensely challenging due to the presence of large, established national insurers.
The insurance sector, particularly for stop-loss coverage, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These stem from essential functions like underwriting, managing claims, and adhering to stringent regulatory frameworks. These high overheads create a powerful incentive for insurers to expand their customer base and achieve economies of scale, often driving intense price competition or encouraging consolidation through mergers and acquisitions.
This dynamic is evident in recent market trends. For instance, data from 2024 indicates a noticeable increase in market concentration within the stop-loss carrier segment. This heightened concentration directly fuels more aggressive competitive rivalry, as fewer, larger players vie for market dominance.
Competitive rivalry within the health insurance sector, particularly for entities like The IHC Group, is significantly fueled by product differentiation. Insurers are actively distinguishing themselves by offering unique medical stop-loss structures, specialized supplemental health benefits, and comprehensive integrated wellness programs. This focus on unique offerings allows companies to carve out niche markets and appeal to specific customer needs, directly impacting competitive intensity.
Innovation, often powered by technological advancements, is a critical driver of this differentiation. For instance, the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics by insurers is transforming product design and service delivery. Companies are leveraging these tools to create more personalized and efficient health solutions, thereby gaining a competitive edge. As of early 2024, the health insurance technology market is experiencing robust growth, with investments in AI and data analytics projected to accelerate innovation across the industry.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Burden
The insurance sector is heavily regulated, with state and federal agencies constantly updating requirements. This complex environment demands substantial investment in compliance, acting as a significant barrier to entry for smaller firms and a strategic advantage for established players adept at navigating these rules. For instance, in 2024, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) continued to refine data security and privacy regulations, requiring insurers to update their operational frameworks.
This regulatory burden directly influences competitive dynamics. Companies that can efficiently manage compliance can allocate more resources to innovation and customer service, thereby gaining a competitive edge. Conversely, those struggling with these demands may see their market share erode. The cost of compliance for the insurance industry in the US was estimated to be in the tens of billions of dollars annually, with ongoing investments needed to meet new mandates.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Insurers face significant expenses related to adhering to state and federal regulations, including licensing, reporting, and capital requirements.
- Barrier to Entry: The complexity and cost of regulatory compliance can deter new entrants, particularly smaller companies, into the insurance market.
- Differentiator: Companies with robust compliance infrastructure and expertise can leverage this as a competitive advantage, demonstrating stability and trustworthiness to consumers and regulators.
- Evolving Landscape: Continuous updates to regulations, such as those concerning data privacy and cybersecurity, necessitate ongoing adaptation and investment, impacting strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Impact of Rising Healthcare Costs and Claims
The IHC Group faces intensified competitive rivalry due to escalating healthcare expenses and a rise in both the frequency and cost of claims, particularly within the medical stop-loss sector. This trend puts pressure on insurers to differentiate beyond just pricing.
Insurers are now competing fiercely on their prowess in risk management, cost containment strategies, and maintaining profitability amidst a difficult claims landscape. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of employer-sponsored health insurance in the U.S. continued its upward trajectory, impacting the pricing and profitability models for companies like IHC.
- Rising Claims: The medical stop-loss market, a key area for IHC, has seen a notable increase in large claims, impacting profitability.
- Cost Containment Focus: Competitors are heavily investing in cost-containment solutions and network management to offset rising healthcare expenditures.
- Premium Pressure: The upward pressure on premiums due to higher claims forces insurers to compete more aggressively on value and service, not just price.
- Profitability Challenges: Maintaining healthy profit margins becomes more challenging as claim costs outpace premium adjustments, intensifying the competitive fight for market share.
Competitive rivalry in the health insurance sector, particularly for companies like The IHC Group, is intensified by a market structure that, while fragmented in certain specialties, is dominated by large, established national players. This means even niche insurers face significant competition from well-resourced incumbents, driving a need for strategic differentiation beyond mere price competition.
The intense rivalry is further fueled by high fixed costs associated with underwriting, claims management, and regulatory compliance, pushing companies to seek economies of scale. This dynamic was evident in 2024, with increased market concentration in the stop-loss segment, intensifying the competition among fewer, larger entities vying for market share.
Product innovation and technological advancements, such as the adoption of AI and advanced analytics, are key battlegrounds. Companies are leveraging these tools to offer more personalized and efficient health solutions, a trend supported by robust growth in the health insurance technology market in early 2024.
The pressure to differentiate is compounded by rising healthcare costs and claims, forcing insurers to compete on risk management and cost containment strategies. For example, the continued upward trend in the average cost of employer-sponsored health insurance in the U.S. during 2024 placed additional pressure on pricing and profitability models.
SSubstitutes Threaten
For employers, a significant substitute for traditional fully insured or stop-loss protected health plans is to entirely self-fund their benefits without purchasing stop-loss insurance. This approach, while carrying higher risk, especially for catastrophic claims, offers employers maximum control over their healthcare spending and potentially lower administrative costs. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of large employers, often those with over 200 employees, are considering or already implementing self-funded models to gain this flexibility.
Government-provided healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, represent significant substitutes for private health insurance. These programs can fulfill many of the same needs as individual health insurance plans, especially for specific demographics like seniors and low-income individuals. For instance, Medicare enrollment in 2023 reached approximately 65 million beneficiaries, demonstrating its widespread reach and impact on the insurance market.
State-level health insurance exchanges, established under the Affordable Care Act, also act as substitutes by offering subsidized private plans. These exchanges provide an alternative pathway for individuals to obtain coverage, potentially diverting demand from traditional private insurance products. In 2024, over 21 million Americans enrolled in plans through the ACA marketplaces, highlighting the substantial market share captured by these government-facilitated options.
Changes in government policy, such as expanding eligibility for public programs or introducing new public options, could further intensify the threat of substitutes. If these government programs become more comprehensive or accessible, they may reduce the perceived value or necessity of private health insurance for a larger segment of the population. This dynamic poses a continuous challenge for companies like IHC, requiring them to adapt their offerings and value propositions.
Direct Primary Care (DPC) and concierge medicine present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance models, particularly for individuals seeking more personalized and accessible primary care. These models, which involve a direct monthly or annual fee from patients to physicians, can reduce reliance on comprehensive insurance for routine services. For instance, the DPC industry has seen significant growth, with estimates suggesting over 2,000 DPC practices operating in the US by late 2023, catering to a segment of the population that values direct physician access and potentially lower out-of-pocket costs for primary care compared to high-deductible plans.
Wellness Programs and Preventive Care Initiatives
The rise of wellness programs and preventive care initiatives presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional insurance models like those offered by The IHC Group. Employers and individuals are increasingly investing in proactive health management, aiming to reduce overall healthcare utilization and associated costs. This shift from simply transferring risk to actively mitigating it could lessen the demand for certain types of insurance, particularly those focused on managing the consequences of poor health.
For instance, by 2024, many companies are expanding their wellness offerings. A survey by the National Business Group on Health indicated that 80% of employers offered some form of wellness program in 2023, with a projected increase in investment in preventive care services. This focus on keeping people healthy can reduce the need for extensive medical treatments, thereby impacting the market for health insurance products.
- Reduced Demand for Certain Insurance Products: As preventive care gains traction, the need for insurance covering conditions that could have been avoided may decrease.
- Shift in Consumer Behavior: Individuals are becoming more proactive in managing their health, viewing wellness as an alternative to relying solely on insurance for medical needs.
- Cost-Saving Focus for Employers: Businesses are prioritizing wellness to control healthcare spending, making insurance a less attractive solution if preventive measures prove effective.
Financial Self-Reliance and Savings Accounts
For less severe health risks or specific supplemental needs, individuals might choose financial self-reliance over purchasing additional insurance. This can involve utilizing health savings accounts (HSAs) or other personal savings vehicles.
The growing appeal of HSAs, largely due to their tax advantages, directly impacts the demand for certain supplemental health insurance products. For instance, in 2024, the number of individuals with HSAs continued to climb, with projections indicating further growth.
- HSAs offer tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
- This financial flexibility allows individuals to cover a range of healthcare costs without relying on traditional insurance for every need.
- The increasing adoption of HSAs signals a shift towards more personalized healthcare finance management, potentially reducing the market for some insurance alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for health insurance is significant, encompassing self-funding, government programs, and alternative care models. For instance, by 2024, a substantial portion of large employers are considering or implementing self-funded health plans to gain control over costs and flexibility, bypassing traditional insurance altogether. This trend, coupled with the widespread reach of government programs like Medicare, which served approximately 65 million beneficiaries in 2023, indicates a growing preference for alternatives that may offer greater control or cater to specific demographic needs.
Furthermore, direct primary care and concierge medicine models are emerging as substitutes, particularly for individuals seeking more personalized healthcare. These models, where patients pay a direct fee to physicians, can reduce reliance on comprehensive insurance for routine services. By late 2023, over 2,000 DPC practices were estimated to be operating in the US, demonstrating a growing segment of the market opting for direct access and potentially lower out-of-pocket costs for primary care.
The increasing popularity of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) also presents a substitute for certain supplemental insurance products. HSAs offer tax advantages, allowing individuals to cover a range of healthcare costs without relying on traditional insurance for every need. The continued growth in HSA adoption by 2024 signals a shift towards personalized healthcare finance management, potentially impacting the market for some insurance alternatives.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Penetration/Growth Indicator (Approximate) | Impact on Traditional Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Funding (Employers) | Employers bear direct risk for claims, bypassing insurance carriers. | Significant portion of large employers considering/implementing by 2024. | Reduces demand for fully insured or stop-loss products. |
| Government Programs (Medicare/Medicaid) | Publicly funded healthcare coverage for specific populations. | Medicare beneficiaries reached ~65 million in 2023. | Fulfills needs for seniors and low-income individuals, diverting demand. |
| ACA Marketplaces | Subsidized private plans offered through state exchanges. | Over 21 million Americans enrolled in 2024. | Provides an alternative pathway for individual coverage. |
| Direct Primary Care (DPC) | Patients pay direct fees to physicians for primary care services. | Over 2,000 DPC practices by late 2023. | Reduces reliance on insurance for routine primary care. |
| Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) | Tax-advantaged savings accounts for medical expenses. | Continued climbing in individual adoption by 2024. | Can cover costs, reducing need for supplemental insurance. |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector, particularly areas like medical stop-loss and life insurance, demands massive financial reserves. These are crucial for covering potential claims and adhering to strict solvency regulations. For instance, in 2024, the average capital requirement for a new health insurance carrier to enter the U.S. market can easily exceed $10 million, and for life insurers, it's often much higher, sometimes reaching hundreds of millions.
The insurance sector is a minefield of regulations, with rules set by both state and federal governments. New companies must navigate a labyrinth of licensing, compliance, and continuous oversight. This complexity alone requires substantial investment in legal and administrative expertise, acting as a strong deterrent to potential newcomers.
Established insurers, including The IHC Group, benefit significantly from deep-rooted brand loyalty and robust distribution networks. These existing players have cultivated customer trust over years, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry continued to see high customer retention rates for established brands, often exceeding 80% for life insurance policies.
New entrants must overcome the substantial hurdle of building brand credibility and establishing effective distribution channels. This typically demands considerable financial investment and a lengthy period to replicate the reach of established firms, which often rely on a vast array of independent agents and brokers.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Incumbent insurance companies, like those within The IHC Group, leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to spread fixed costs across a larger volume of policies for underwriting, claims processing, and administrative tasks. For instance, a large insurer might have a claims processing cost per claim that is substantially lower than a startup due to specialized software and dedicated teams. This efficiency directly impacts their ability to offer competitive premiums.
Furthermore, established players benefit from an experience curve. Years of data collection and analysis have honed their skills in risk assessment and accurate pricing. This accumulated knowledge enables them to better predict claim frequencies and severities, leading to more profitable underwriting. New entrants, lacking this historical data and expertise, face a steeper learning curve and often misprice risks, impacting their initial profitability and competitiveness.
- Economies of Scale: Larger insurers can negotiate better rates with reinsurers and suppliers, further reducing operational costs compared to smaller or new entrants.
- Experience Curve Advantage: Decades of underwriting and claims data allow incumbents to refine pricing models, leading to a more accurate prediction of losses and improved profitability.
- Barriers to Entry: The difficulty for new entrants to match these cost efficiencies and pricing accuracy creates a significant barrier, protecting incumbent market share.
Data and Technology Barriers
The increasing dependence on sophisticated data analytics, artificial intelligence, and interconnected technology platforms presents a substantial hurdle for new market entrants. Established firms like IHC Group leverage these advanced systems for operational efficiency and competitive pricing, requiring significant upfront investment from newcomers.
To effectively compete, new entrants must allocate substantial capital towards building robust technology infrastructure and cultivating advanced data management capabilities. For instance, the global AI market was projected to reach over $200 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of investment required to develop competitive AI-driven solutions.
- High Capital Expenditure: Newcomers face considerable costs in acquiring and implementing cutting-edge technology and data analytics tools.
- Talent Acquisition: A shortage of skilled professionals in data science and AI further exacerbates the entry barrier, driving up labor costs.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating new technologies with existing business processes can be complex and time-consuming for unproven entities.
The threat of new entrants into the insurance market, particularly for companies like The IHC Group, is generally considered moderate to low. Significant capital requirements, stringent regulatory landscapes, and the need for established distribution networks and brand loyalty create substantial barriers. Newcomers must also contend with the advanced technological infrastructure and data analytics capabilities that incumbents already possess, demanding considerable investment to even approach parity.
| Barrier Category | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Need for substantial financial reserves to cover claims and meet solvency regulations. | High barrier, requiring significant upfront investment. | Minimum capital for new U.S. health insurer: $10M+; Life insurer: $100M+. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating state and federal licensing, compliance, and oversight. | High barrier, demanding extensive legal and administrative resources. | Compliance costs can add 5-10% to initial operating expenses. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established trust and extensive agent/broker networks. | Moderate to high barrier, requiring time and investment to build. | Customer retention for established life insurers often exceeds 80%. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs and refined risk assessment from accumulated data. | High barrier, impacting pricing competitiveness. | Large insurers can achieve 15-25% lower claims processing costs per claim. |
| Technology & Data Analytics | Investment in AI, data platforms, and skilled talent. | High barrier, requiring significant capital and expertise. | Global AI market projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for The IHC Group is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings. We also leverage macroeconomic data and financial databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.