IDEX Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
IDEX Bundle
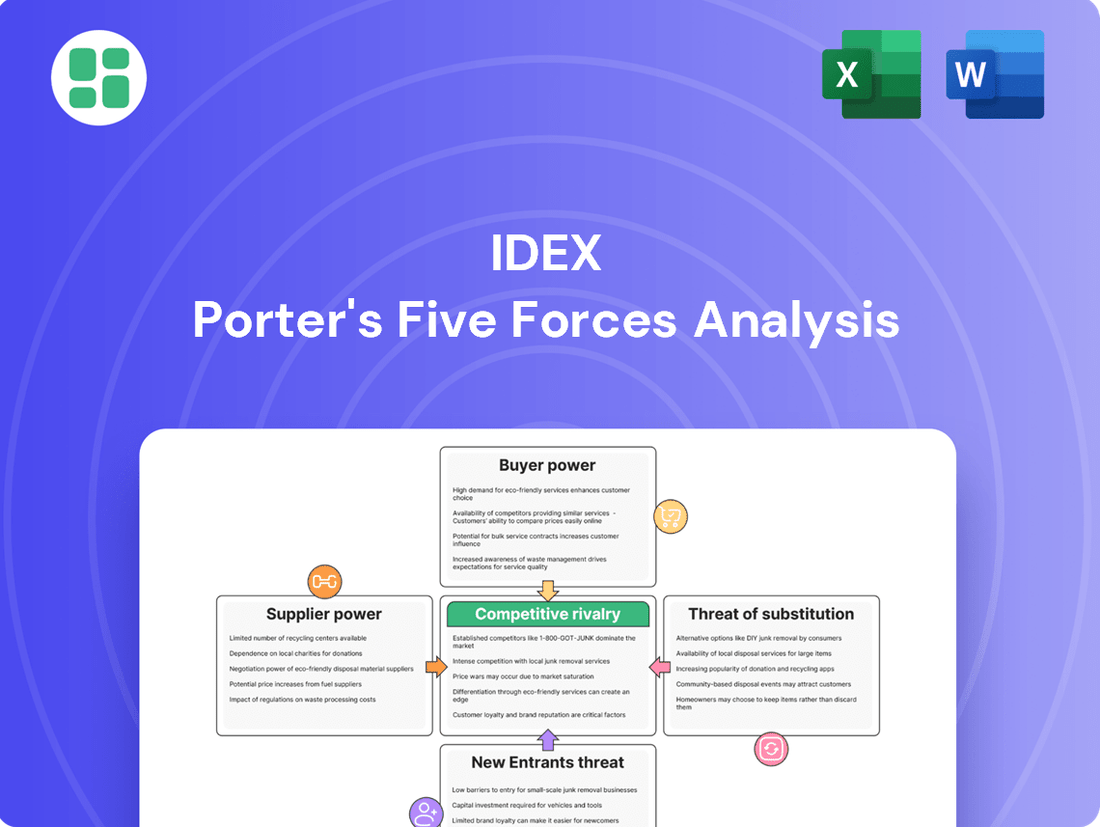
IDEX faces a dynamic competitive landscape shaped by the bargaining power of its buyers and the intensity of rivalry within its diverse markets. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its strategic path.
This brief overview only hints at the full picture. Unlock the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of IDEX's competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
IDEX Corporation's reliance on highly engineered products, often featuring proprietary technologies, means it frequently depends on specialized, high-precision components and unique raw materials. This dependency can significantly empower suppliers who are the sole or dominant providers of these critical inputs, giving them considerable leverage.
The scarcity of readily available alternative suppliers for these niche components can directly translate into higher input costs for IDEX. This situation also presents potential supply chain vulnerabilities, as disruptions from these specialized suppliers can have a disproportionate impact on IDEX's production and operations.
IDEX's reliance on suppliers for proprietary technology inputs can significantly influence its bargaining power. When these specialized components or intellectual property are critical to IDEX's product performance and differentiation, suppliers holding such unique assets can command higher prices or dictate more favorable terms. For instance, if a key sensor technology used in IDEX's fluid management systems is patented and has no readily available substitutes, that supplier has considerable leverage.
This situation can put pressure on IDEX's profit margins and operational flexibility. In 2023, the semiconductor industry, a potential supplier of critical components for some IDEX products, experienced continued supply chain challenges and price increases for advanced chips, illustrating the potential impact of proprietary technology suppliers. IDEX must therefore cultivate robust relationships with these key technology providers and explore avenues for in-house development or alternative sourcing to mitigate this supplier power.
Supplier concentration significantly influences IDEX's bargaining power. If IDEX relies on a limited number of suppliers for critical components or materials across its varied business units, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. This concentration can diminish price competition among suppliers, allowing them to potentially dictate terms and increase prices, directly impacting IDEX's cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
Switching Costs for IDEX
The bargaining power of suppliers for IDEX is significantly influenced by the switching costs associated with changing suppliers. If IDEX faces substantial expenses or operational disruptions when moving from one supplier to another, such as the need for retooling manufacturing equipment, requalifying new components, or undertaking product redesigns, then current suppliers hold greater leverage. These high switching costs can effectively create a lock-in effect, making it challenging for IDEX to seek out or transition to potentially more cost-effective or technologically advanced alternatives. This dependency can weaken IDEX's negotiating position, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or terms from its existing supplier base.
For instance, in industries where specialized components are critical to IDEX's product performance, the effort and investment required to vet and integrate a new supplier can be prohibitive. This situation grants suppliers a stronger hand in dictating terms, as IDEX may be reluctant to incur the significant upfront costs and potential production delays associated with a supplier change. The more complex and integrated the supply chain, the higher these switching costs tend to be, thereby amplifying supplier power.
- High Switching Costs: Significant expenses or operational disruptions for IDEX when changing suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: Increased power for existing suppliers due to the difficulty of switching.
- Negotiating Disadvantage: IDEX may face less favorable terms and pricing.
- Industry Dependence: Specialized components or integrated supply chains can exacerbate these switching costs.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration poses a significant risk to IDEX, potentially amplifying their bargaining power. If a crucial supplier possesses the resources and motivation to begin producing goods that directly compete with IDEX's offerings, they could transition from a supplier to a direct rival.
This scenario would compel IDEX to cultivate robust supplier relationships and possibly concede more advantageous terms to ensure continued supply. For instance, if a key component manufacturer for IDEX's fluidic solutions were to develop and market their own integrated systems, they would gain considerable leverage over IDEX, potentially dictating pricing and supply terms.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into IDEX's markets increases their power.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: Suppliers becoming direct competitors can force IDEX into less favorable agreements.
- Relationship Management: IDEX must maintain strong ties with suppliers who have forward integration capabilities.
IDEX Corporation faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on specialized, high-precision components and proprietary technologies. This dependency, coupled with high switching costs and potential supplier forward integration, can lead to increased input prices and supply chain vulnerabilities.
| Factor | Impact on IDEX | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited supplier options increase leverage. | In 2024, IDEX's reliance on a few key semiconductor suppliers for advanced sensors could lead to price increases if supply remains constrained. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers weaken IDEX's negotiating position. | The need for retooling and component requalification for IDEX's specialized pumps can make switching suppliers prohibitively expensive. |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers of unique inputs command higher prices. | A supplier of a patented fluid metering technology for IDEX's medical devices has significant power due to lack of alternatives. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers becoming competitors can dictate terms. | If a key material supplier for IDEX's sealing solutions were to offer finished sealing assemblies, they could leverage this to gain more favorable terms from IDEX. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting IDEX, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force.
Customers Bargaining Power
IDEX’s focus on niche markets, leveraging specialized engineering and proprietary technologies, creates a strong value proposition. For instance, in its fire suppression systems, IDEX's advanced solutions are critical for safety and operational continuity, making customers highly reliant on their offerings.
While this specialization inherently limits customer bargaining power, customers in these critical niches might still exert some influence if they have even limited alternative suppliers or if IDEX's products represent a significant portion of their own costs. However, the high value and unique benefits provided by IDEX’s specialized products generally reduce customer price sensitivity.
Customer concentration significantly impacts bargaining power. If IDEX relies heavily on a few major clients, these customers can wield considerable influence. For instance, if a single customer represents over 10% of IDEX's total revenue, their ability to negotiate favorable terms, such as price reductions or extended credit, becomes a substantial concern.
In 2023, IDEX's top ten customers accounted for approximately 25% of its total revenue. This level of concentration means that these key clients have the leverage to demand better pricing or more tailored product offerings. Such demands can directly squeeze IDEX's profit margins and limit its pricing flexibility.
IDEX's products, like precision pumps and fluidic systems, are often essential, mission-critical components for their customers. This means that if these parts fail, the customer's entire operation can be significantly disrupted. For instance, in medical devices or industrial automation, the reliability of an IDEX pump is paramount.
The specialized nature and high criticality of IDEX's offerings make it difficult for customers to switch to alternative suppliers. Finding a replacement that meets the same stringent performance and quality standards can be a lengthy and costly process. This inherent switching cost directly diminishes the customer's bargaining power.
In many of these applications, customers prioritize unwavering reliability and superior performance over minor price differences. For example, a fire suppression system manufacturer will likely choose IDEX's specialized valves based on their proven track record, rather than opting for a cheaper, less dependable option. This focus on performance further strengthens IDEX's position.
Customer Switching Costs
For IDEX's customers, the cost of switching to a different supplier can be substantial. This often involves significant expenses associated with re-engineering existing systems, undergoing rigorous re-certification processes for new equipment, or investing in comprehensive retraining for their staff. These financial and operational hurdles effectively dampen a customer's inclination to explore alternative vendors, thus diminishing their leverage in negotiations with IDEX.
The impact of these switching costs is amplified when customers utilize highly integrated solutions from IDEX. In such scenarios, replacing one component might necessitate a complete overhaul of interconnected systems, making the transition prohibitively expensive and complex. This lock-in effect strengthens IDEX's position by making it less practical for customers to switch, even if alternative offerings appear marginally cheaper.
- High Re-engineering Costs: Customers may need to redesign product lines or manufacturing processes to accommodate a new supplier's components.
- Certification and Compliance Expenses: Switching suppliers in regulated industries often requires costly and time-consuming re-certification of products and processes.
- Training and Integration Investments: Personnel require retraining on new equipment or software, and integrating new systems can be a significant undertaking.
- Impact on Integrated Solutions: The more deeply IDEX's products are integrated into a customer's operations, the higher the switching costs become.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity for IDEX products, while generally tempered by their mission-critical nature, can fluctuate. In 2024, industries experiencing significant economic headwinds or heightened competitive pressures might push back on pricing, even for highly specialized solutions. For instance, if a key customer segment like oil and gas exploration faces a sharp decline in commodity prices, their ability and willingness to absorb higher equipment costs could diminish.
However, the inherent value and essential function of IDEX's offerings, such as advanced fluidics and engineered solutions, often create a ceiling for this sensitivity. Customers rely on these components for safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance, making price a secondary consideration compared to performance and reliability. For example, in the medical device sector, where patient safety is paramount, the cost of a faulty component far outweighs the initial savings from a lower price point.
- Price Sensitivity Factors: Economic downturns and intense industry competition can increase customer pressure for lower prices.
- IDEX's Value Proposition: The mission-critical and high-value nature of IDEX's products often limits extreme price sensitivity.
- Industry Examples: Sectors like oil and gas may show more price sensitivity during commodity slumps, while medical devices prioritize reliability over cost.
The bargaining power of IDEX's customers is generally low due to the specialized, mission-critical nature of its products, which creates high switching costs and reduces price sensitivity. However, this power can increase if customers are concentrated, meaning a few large clients represent a significant portion of IDEX's revenue, or if specific industries face economic downturns, making them more price-conscious.
In 2023, IDEX's top ten customers accounted for approximately 25% of its revenue, indicating some customer concentration that could influence negotiations. While customers prioritize reliability, economic pressures in 2024, particularly in sectors like oil and gas, might lead to increased demands for better pricing, even for essential components.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | IDEX Specifics (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Product Criticality & Specialization | Lowers customer power | IDEX products are essential for safety and operations, with high performance demands. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | High costs for re-engineering, re-certification, and training make switching difficult. |
| Customer Concentration | Can increase customer power | Top 10 customers represented ~25% of 2023 revenue, giving them leverage. |
| Price Sensitivity | Generally low, but can increase | Economic headwinds in 2024 may heighten price sensitivity in some sectors like oil and gas. |
Preview Before You Purchase
IDEX Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview reveals the complete IDEX Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely the final, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
While IDEX Corporation strategically targets niche markets, the competition within these specialized segments is often quite fierce. Many of these competitors share similar core engineering capabilities and often cater to overlapping customer requirements, leading to direct confrontations for market share.
The intensity of this rivalry is directly tied to the number and scale of companies operating within each specific niche where IDEX has a presence. For instance, in the municipal fire apparatus market, IDEX faces established players with long-standing customer relationships and significant brand recognition, making it challenging to gain substantial ground without a differentiated offering.
In 2024, the industrial fluid handling sector, a key area for IDEX, saw continued consolidation and the emergence of specialized players focusing on high-margin applications. This dynamic intensifies rivalry as companies vie for dominance in these lucrative, albeit smaller, market pockets.
IDEX Corporation thrives on its specialized engineering prowess and a portfolio of proprietary technologies, setting its products apart in a competitive landscape. This focus on unique capabilities allows IDEX to command premium pricing and build strong customer loyalty.
The intensity of competition within IDEX's markets is largely fueled by a relentless pursuit of innovation. Companies that consistently introduce new products offering enhanced performance, greater reliability, and tailored solutions to specific customer needs tend to capture market share. For instance, in the fluid and control technologies segment, advancements in material science and miniaturization are critical for differentiation.
In 2023, IDEX reported a revenue of $2.3 billion, reflecting its ability to deliver value through its differentiated offerings. The company's strategic acquisitions, such as its acquisition of Zeus in 2022 for $3.1 billion, underscore its commitment to expanding its technological capabilities and product portfolio to stay ahead of rivals.
The growth rate within IDEX's diverse niche markets significantly shapes the intensity of competitive rivalry. In segments experiencing slower growth, such as certain industrial fluid handling components, competition for market share often escalates. This is because companies must aggressively pursue the limited opportunities available, leading to more direct and intense competitive actions among players like Dover Corporation and Flowserve.
Competitor Diversity
Competitive rivalry within the fluidics industry, where IDEX operates, is intensified by the diverse strategic approaches of its competitors. Some players prioritize aggressive pricing and high-volume production, aiming for market share through cost leadership. In contrast, IDEX often differentiates itself by focusing on high-value, specialized fluidic solutions, commanding premium pricing through innovation and performance. This strategic divergence means that competitive actions can vary significantly, ranging from price wars to technological advancements, creating a dynamic and complex competitive landscape.
This diversity in competitor strategies directly impacts the intensity of rivalry. For instance, in 2024, while some smaller competitors might engage in price cutting to gain traction in specific segments, IDEX's focus on engineered solutions for critical applications, such as in the semiconductor manufacturing or life sciences sectors, allows it to maintain strong margins. This creates a multi-faceted competitive environment where different players vie for dominance through distinct value propositions.
- Diverse Strategies: Competitors employ varied approaches, from low-cost production to specialized, high-value solutions, mirroring IDEX's own strategy.
- Varied Responses: This diversity leads to a spectrum of competitive actions, including price adjustments and innovation races, shaping market dynamics.
- Impact on IDEX: IDEX must navigate these varied strategies, balancing its premium offering with the pricing pressures from cost-focused rivals.
Acquisition Strategy
IDEX Corporation's acquisition strategy, exemplified by the 2024 purchase of Mott Corporation, directly impacts competitive rivalry. This inorganic growth tactic consolidates market share and introduces advanced technologies or new customer segments into IDEX's portfolio. Such moves often compel competitors to react, potentially through their own mergers and acquisitions or by accelerating research and development efforts to maintain parity.
The acquisition of Mott Corporation, a leader in filtration and fluidics solutions, by IDEX in 2024 for $770 million significantly reshaped the competitive landscape. This strategic move not only expanded IDEX's product offerings and technological capabilities but also bolstered its presence in key end markets.
- Market Consolidation: The Mott acquisition allowed IDEX to consolidate its position, potentially increasing the barriers to entry for smaller players.
- Technological Advancement: Integrating Mott's specialized filtration technologies provides IDEX with a competitive edge, forcing rivals to innovate or acquire similar capabilities.
- Competitive Response: Competitors in the fluid handling and filtration sectors are likely to scrutinize their own market positions and consider strategic responses, including M&A or enhanced R&D investment, to counter IDEX's strengthened market presence.
Competitive rivalry within IDEX's niche markets is intense, driven by companies with similar engineering capabilities and overlapping customer bases. In 2024, the fluid handling sector saw consolidation and specialized players emerge, intensifying competition for lucrative market pockets, with companies like Dover Corporation and Flowserve being key rivals.
IDEX differentiates itself through proprietary technologies and innovation, allowing for premium pricing, a strategy that contrasts with some rivals focusing on cost leadership. This leads to varied competitive actions, from price wars to technological advancements.
IDEX's acquisition of Mott Corporation in 2024 for $770 million consolidated market share and integrated advanced filtration technologies, prompting competitors to react through their own M&A or R&D acceleration.
| Competitor | Key Market Segment | 2024 Competitive Action Example |
|---|---|---|
| Dover Corporation | Industrial Fluid Handling | Focus on high-margin applications, potentially through new product launches. |
| Flowserve | Fluid & Control Technologies | Continued investment in R&D for enhanced performance and reliability. |
| Smaller Specialized Players | Niche Fluidics Solutions | Potential price adjustments in specific segments to gain market share. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for IDEX is significant, primarily stemming from alternative technologies that offer similar functionalities. Customers can often find different methods or systems to achieve fluid control or analytical results, bypassing the need for IDEX's specific pump or sensor technologies.
For instance, advancements in microfluidics or alternative sensor materials could present viable substitutes. The pace of technological innovation in related sectors directly impacts how easily customers can switch away from IDEX's offerings. In 2024, the market for advanced fluid handling solutions continues to see rapid development in areas like miniaturization and digital integration, potentially offering more accessible or cost-effective alternatives.
Customers often weigh the performance of a substitute against its price. If an alternative product delivers similar or even better results for less money, it represents a significant competitive pressure. For instance, if a new, lower-cost diagnostic tool emerges that performs nearly as well as IDEX's offerings in a specific market segment, customers might switch, especially if the price difference is substantial.
IDEX must continuously highlight its unique value proposition and the efficiency gains its specialized solutions provide. This means clearly communicating how IDEX's products, despite potentially higher upfront costs, lead to better outcomes or lower total cost of ownership in the long run. For example, a 2024 report on the laboratory diagnostics market indicated that while cost is a major factor, reliability and accuracy in critical applications can justify a premium for established players like IDEX.
The threat of substitutes for IDEX's products is significantly lowered due to the substantial switching costs customers face. These costs aren't just monetary; they often involve considerable operational disruption. For instance, a company integrating IDEX's specialized hydraulic or pneumatic components into their machinery might need to re-engineer entire production lines, re-qualify new parts with regulatory bodies, or invest in entirely new infrastructure to accommodate a different supplier's technology. This complexity makes a wholesale shift to a substitute solution a daunting prospect.
IDEX's strategy of embedding its solutions deeply within customer systems further amplifies these switching costs. Once a client’s operations are built around IDEX’s technology, the effort and expense required to extract and replace those components become prohibitively high. This creates a sticky customer base, effectively insulating IDEX from the immediate allure of alternative offerings that lack the same level of integration and established reliability. For example, in the industrial automation sector, where precision and uptime are paramount, the cost of downtime during a transition to a new, unproven component supplier can easily run into millions of dollars, a risk most businesses are unwilling to take.
Innovation of Substitutes
Continuous innovation in substitute offerings poses a significant threat. For instance, advancements in material science could yield alternative components that perform similarly to IDEX's products but at a lower cost or with enhanced features, directly impacting demand. Companies like 3M and DuPont are constantly exploring novel materials that could disrupt traditional industrial supply chains.
IDEX must remain vigilant about technological shifts. Developments in digital technologies, such as advanced simulation software or additive manufacturing (3D printing), could enable customers to design and produce their own solutions, bypassing the need for IDEX's specialized equipment or components. The growth of the 3D printing market, projected to reach over $60 billion by 2027, highlights this potential disruption.
The threat is amplified when these innovations offer a fundamentally different approach to solving customer problems. IDEX needs to track how competitors or new entrants are rethinking existing processes. For example, a shift towards integrated systems that reduce the number of individual components required could diminish the market for IDEX's core product lines.
- Monitoring Material Science: Companies like BASF are investing heavily in advanced polymers and composites that could offer superior performance or cost advantages over traditional materials used in IDEX's target markets.
- Digital Transformation Impact: The increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies allows for greater customization and on-demand production, potentially reducing reliance on established suppliers for specialized parts.
- Process Innovation: Innovations in manufacturing efficiency, such as lean manufacturing or automation, can lower the cost of producing substitute goods, making them more competitive against IDEX's offerings.
- Emerging Technologies: The rapid development in areas like nanotechnology or bio-inspired materials could unlock entirely new product categories that serve similar customer needs in novel ways.
Regulatory or Industry Shifts
Changes in regulations or industry norms can unexpectedly boost substitute products. For example, stricter environmental laws might push for different fluid handling systems, or new safety mandates could lead to the adoption of alternative rescue gear, even if IDEX's existing products perform well.
IDEX needs to stay agile, ensuring its product lines evolve to meet these changing sector requirements. For instance, if new emissions standards are introduced in 2024, companies might seek out technologies that reduce fluid leakage or emissions, potentially favoring competitors with more eco-friendly solutions.
- Regulatory Shifts: New environmental regulations in 2024 could favor alternative fluid handling technologies over IDEX's current offerings.
- Industry Practice Evolution: Changes in safety protocols might encourage the adoption of substitute rescue equipment, impacting IDEX's market share.
- Adaptability is Key: IDEX must proactively adjust its product development to align with emerging industry standards and customer demands driven by these shifts.
The threat of substitutes for IDEX is moderate but growing, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer needs. While IDEX's specialized products often have high switching costs, potential substitutes in areas like advanced materials and digital integration are becoming more viable. For example, the increasing sophistication of 3D printing allows for the creation of custom components that could, in some niche applications, replace standard parts. In 2024, the market for precision fluid handling continues to see innovation, with companies exploring miniaturization and alternative materials that could offer comparable performance at a lower cost or with added functionality.
However, IDEX's deep integration into customer systems and the associated high switching costs—including re-engineering and regulatory re-qualification—significantly mitigate this threat. For instance, in critical sectors like aerospace or medical devices, the cost and risk of switching from a proven IDEX component are substantial. The company's focus on reliability and performance in demanding applications further solidifies its position against many potential substitutes that may not meet stringent industry standards.
| Substitute Category | Potential Impact on IDEX | Key Drivers | 2024 Market Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Materials | Moderate | Cost reduction, enhanced performance | Increased R&D in composites and polymers |
| Digital Integration/IoT | Low to Moderate | Smart functionality, remote monitoring | Growing adoption in industrial automation |
| 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing | Low | Customization, rapid prototyping | Expansion into industrial and medical sectors |
| Alternative Fluid Handling Technologies | Moderate | Efficiency gains, environmental compliance | Focus on sustainable and energy-efficient solutions |
Entrants Threaten
The highly engineered nature of IDEX's specialized fluid and metering technologies, along with its extensive manufacturing footprint across more than 20 countries, points to a substantial capital investment hurdle for potential new entrants. For instance, establishing state-of-the-art R&D facilities and acquiring the precise, specialized machinery needed to produce these critical components would demand millions, if not hundreds of millions, of dollars.
IDEX's significant threat from new entrants is mitigated by its deeply ingrained proprietary technology and specialized engineering expertise. The company has cultivated decades of experience in fluid and metering, health and science, and fire and safety technologies, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to replicate this accumulated knowledge and intellectual property. For instance, IDEX's Health & Science segment, which includes critical components for medical devices, requires stringent regulatory compliance and advanced manufacturing processes that are not easily or quickly established by a new player.
IDEX's deep-seated customer relationships and strong brand loyalty present a significant barrier to new entrants. These established connections are built on trust and a proven track record of delivering mission-critical components across diverse industries.
For instance, in the highly regulated aerospace sector, where IDEX is a key supplier, the cost and time associated with qualifying new components and suppliers are substantial. Newcomers must overcome not only technical hurdles but also the inertia of existing, trusted partnerships, a process that can take years and significant investment, making it difficult to gain traction.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The threat of new entrants for IDEX is significantly mitigated by the rigorous regulatory landscape and certification demands in its key markets. Industries like life sciences, medical devices, and fire and rescue equipment are heavily regulated, requiring extensive testing, approvals, and adherence to strict quality standards. For example, obtaining FDA clearance for medical components can take years and cost millions of dollars, creating a substantial barrier to entry for potential competitors.
Navigating these complex approval processes is not only time-consuming but also financially burdensome. New companies must invest heavily in research and development, compliance, and quality assurance systems to meet the exacting requirements. This financial commitment, coupled with the extended timeline for market access, acts as a powerful deterrent, protecting IDEX's established market position.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants face significant upfront costs for R&D, manufacturing facilities compliant with industry standards, and obtaining necessary certifications.
- Lengthy Approval Cycles: Industries served by IDEX, such as aerospace and defense, often have multi-year certification processes that require extensive documentation and validation.
- Established Reputation and Trust: Existing players like IDEX benefit from a proven track record and established trust with customers, particularly in safety-critical applications where reliability is paramount.
- Intellectual Property: Proprietary technologies and patents held by IDEX further erect barriers, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate its product offerings or manufacturing processes.
Economies of Scale and Scope
IDEX's extensive global manufacturing footprint and broad product range enable significant economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs, like factory overhead and R&D, across a larger volume of goods, leading to lower per-unit production costs. For instance, in 2023, IDEX reported revenues of $2.4 billion, reflecting the scale of their operations.
Newcomers typically lack this scale. They would likely face higher per-unit costs in manufacturing, raw material sourcing, and distribution. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for them to compete on price with established players like IDEX, unless they target very specific, high-margin market segments or introduce truly innovative, cost-saving technologies.
- Economies of Scale: IDEX leverages its size to reduce per-unit costs in production and operations.
- Global Reach: A worldwide presence allows for optimized procurement and distribution networks.
- Product Diversification: A wide product portfolio spreads fixed costs, enhancing cost efficiencies.
- New Entrant Challenge: Smaller new entrants face higher initial costs, hindering price competitiveness.
The threat of new entrants for IDEX is generally low due to substantial barriers. These include high capital requirements for specialized manufacturing and R&D, lengthy regulatory approval processes in critical sectors like medical devices, and the need to build established customer trust and brand reputation. IDEX's proprietary technology and extensive experience further solidify its position.
For instance, IDEX's 2023 revenue of $2.4 billion highlights the scale of operations that new players must contend with. The company's global manufacturing footprint and diversified product lines contribute to economies of scale, making it difficult for smaller entrants to compete on cost. The aerospace sector alone, where IDEX is a key supplier, involves multi-year qualification processes for new components, adding significant time and expense for any newcomer.
| Barrier Type | Impact on New Entrants | IDEX's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Very High | Extensive manufacturing and R&D facilities |
| Regulatory Approvals | High (especially in Health & Science) | Established compliance and certification history |
| Proprietary Technology | High | Decades of specialized engineering expertise |
| Customer Relationships | High | Long-standing trust in mission-critical applications |
| Economies of Scale | Moderate to High | $2.4 billion in 2023 revenue, global operations |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our IDEX Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.
We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets, regulatory filings, and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape affecting IDEX.