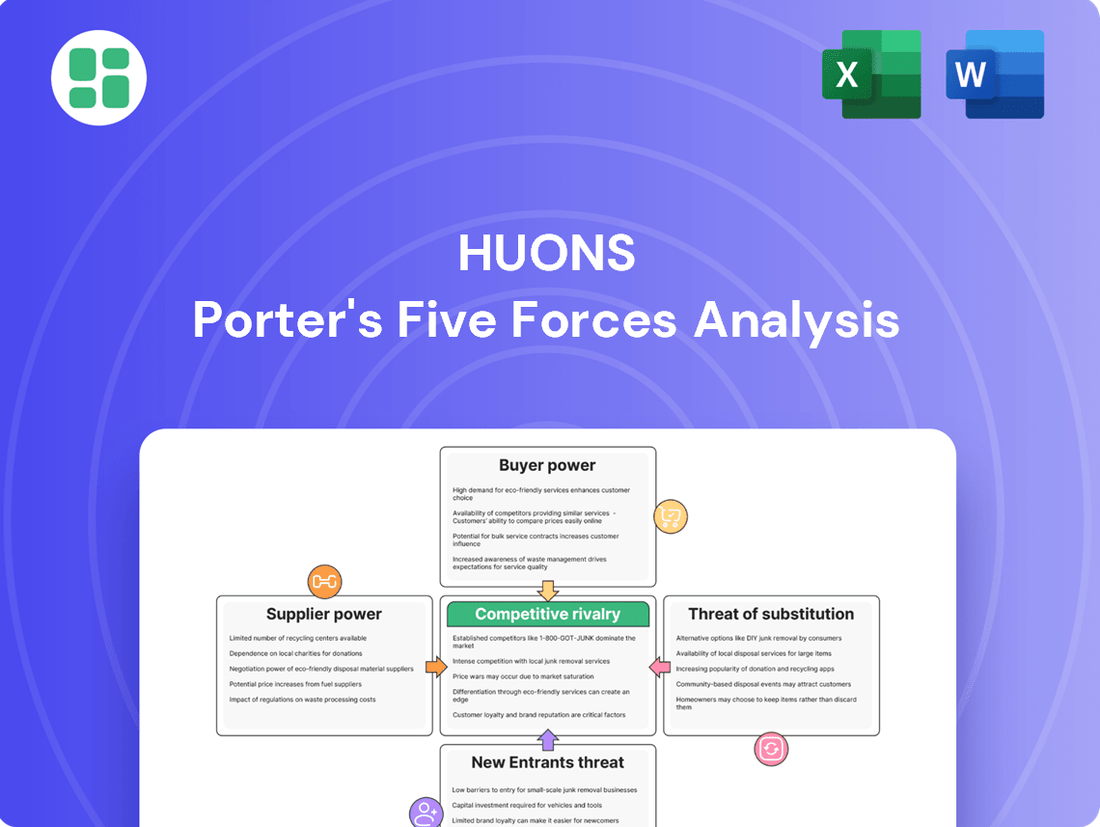
Huons Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Huons Bundle
Huons operates in a dynamic pharmaceutical landscape, where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals how buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants significantly shape its market. The intensity of rivalry and the availability of substitutes further define the strategic terrain.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Huons’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Huons' dependence on specialized suppliers for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other crucial raw materials significantly influences its operational costs. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be considerable, especially when dealing with patented or highly specialized APIs for which Huons has few alternative sourcing options. This limited availability can directly translate into higher input costs for the company, impacting its profitability margins.
The stringent requirement for Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) certification further narrows the pool of eligible suppliers for Huons. This regulatory necessity not only restricts the company's supplier choices but also amplifies the leverage held by those suppliers who meet these demanding standards. For instance, in 2023, the global API market experienced price increases due to supply chain disruptions and heightened demand for specific therapeutic categories, a trend that likely affected Huons' procurement costs for key ingredients.
Suppliers of advanced manufacturing equipment and proprietary technologies, crucial for Huons' injection lines and biopharmaceutical production, wield considerable bargaining power. These specialized assets demand significant capital outlay, and the high costs associated with switching providers create a strong dependency for Huons.
Huons' ongoing investments in new production facilities, such as its expansion projects, directly highlight its reliance on these key technology and equipment providers. This reliance can translate into higher equipment costs or less favorable terms if these suppliers face limited competition.
While Huons provides contract manufacturing, it also relies on external CROs for specific research and clinical trial stages, or specialized CDMOs for unique production requirements. The bargaining power of these external service providers is elevated when they possess specialized knowledge, cutting-edge facilities, or proprietary technologies that are essential for Huons' research and development pipeline. For instance, Huonslab, a subsidiary, is actively engaged in clinical trials that could necessitate outsourcing certain phases to these specialized organizations.
Skilled Labor and R&D Talent
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly concerning skilled labor and R&D talent, is a significant factor for Huons. The South Korean healthcare and biopharmaceutical sector is intensely focused on innovation, making highly qualified researchers, scientists, and specialized manufacturing staff exceptionally valuable. This high demand translates directly into increased bargaining power for these individuals, influencing Huons' labor costs through competitive compensation packages and intensive recruitment strategies.
South Korea's robust commitment to research and development further amplifies the importance of this skilled labor pool. For instance, in 2023, South Korea's R&D expenditure reached approximately 5.17% of its GDP, a figure that underscores the nation's dedication to scientific advancement and the critical role of skilled personnel within this ecosystem. This environment necessitates that companies like Huons actively manage their talent acquisition and retention to maintain a competitive edge.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: The biopharmaceutical industry requires niche expertise, giving skilled professionals leverage.
- Competitive Salary Landscape: Companies often compete fiercely for top talent, driving up wages.
- R&D Investment Impact: Significant R&D spending by the South Korean government and private sector highlights the value placed on innovation and the talent that fuels it.
- Talent Retention Challenges: Retaining highly skilled employees is crucial, as their departure can disrupt R&D pipelines and operational continuity.
Regulatory Compliance and Consulting Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in the pharmaceutical and medical device sector, particularly concerning regulatory compliance, is significant for companies like Huons. Adhering to stringent regulations from bodies such as the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is paramount for market access and product approval. Huons' strategic focus on obtaining FDA approvals for its injectable drug portfolio and increasing international sales directly amplifies its dependence on specialized regulatory consulting services.
These expert consultants, possessing in-depth knowledge of complex global regulatory landscapes, can command higher fees and exert influence due to the critical nature of their services. For instance, the cost of regulatory affairs consulting can represent a substantial portion of a company's research and development budget, especially during the clinical trial and submission phases. In 2024, the global regulatory affairs outsourcing market was valued at approximately $12.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of over 8% through 2030, underscoring the growing reliance and supplier power in this niche.
- High Demand for Specialized Expertise: The intricate and ever-evolving nature of pharmaceutical regulations creates a strong demand for specialized consulting services, giving these suppliers significant leverage.
- Criticality of Compliance: Failure to comply with regulatory standards can lead to product recalls, fines, and market exclusion, making adherence non-negotiable and increasing a company's reliance on expert guidance.
- Cost of Non-Compliance: The financial and reputational costs associated with regulatory missteps far outweigh the fees paid to compliance consultants, further empowering these service providers.
- Global Regulatory Divergence: Navigating differing regulations across multiple international markets, as Huons aims to do with its exports, necessitates diverse and expert regulatory support, concentrating power among specialized firms.
Huons faces considerable supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on specialized APIs and GMP-certified suppliers, which limits sourcing options and can drive up input costs. The company's need for advanced manufacturing equipment and proprietary technologies from a select few providers further solidifies supplier leverage, as switching costs are high. Additionally, the intense competition for skilled R&D and manufacturing talent in South Korea, a nation with significant R&D investment, empowers these professionals, impacting Huons' labor expenses.
The increasing global regulatory complexity and Huons' expansion into international markets elevate the bargaining power of specialized regulatory consulting services. These experts are essential for navigating diverse compliance landscapes, making their fees a significant factor in R&D budgets. For instance, the global regulatory affairs outsourcing market was valued at around $12.5 billion in 2024, indicating substantial supplier influence in this critical area.
| Supplier Type | Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Huons |
|---|---|---|
| API & Raw Material Suppliers | Limited availability of patented/specialized ingredients, GMP certification requirements | Higher input costs, potential supply chain disruptions |
| Equipment & Technology Providers | Proprietary technologies, high switching costs for specialized assets | Increased capital expenditure, less favorable terms |
| Skilled Labor (R&D, Manufacturing) | High demand in a research-intensive sector, competitive compensation | Elevated labor costs, intensive talent acquisition/retention strategies |
| Regulatory Consultants | Complex global regulations, critical need for compliance expertise | Significant consulting fees, essential for market access |
What is included in the product
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the competitive forces shaping Huons' market, detailing threats from new entrants, substitutes, buyer and supplier power, and existing rivalry.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive dashboard that adapts to your specific industry and strategic context.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies are significant buyers of Huons' prescription drugs and medical devices, giving them substantial bargaining power. Their ability to purchase in large volumes and switch between suppliers means they can effectively negotiate for more favorable pricing and contract terms. In 2023, Huons' prescription drug segment, which directly serves these institutional customers, represented a core part of its revenue, highlighting the importance of managing these relationships.
Distributors and wholesalers are key players for Huons, acting as gatekeepers to diverse markets, both at home and abroad. Their established connections and influence over where products are displayed give them considerable sway over Huons' market penetration and overall sales. For instance, in 2024, Huons has been strategically focusing on strengthening these relationships to boost its international sales, aiming to tap into new distribution channels.
For Huons' contract manufacturing services, client pharmaceutical companies often wield significant bargaining power. This is largely due to the global availability of numerous contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), allowing clients to shop around for the best pricing and specific expertise. Huons must therefore focus on delivering high-quality services and maintaining cost-effectiveness to remain competitive.
The competitive landscape for CDMO services means clients can easily switch providers if they find better terms or specialized capabilities elsewhere. This dynamic necessitates that Huons, and its expanding subsidiary PanGen Biotech, consistently demonstrate value and reliability to retain and attract business in this segment.
Government and National Health Insurance (NHI) System
The South Korean government, through its National Health Insurance (NHI) system, holds substantial bargaining power as a customer for pharmaceutical companies like Huons, particularly for prescription drugs reimbursed by public insurance. This influence extends to setting drug prices, determining reimbursement rates, and deciding which medications are included in national formularies, directly impacting Huons' revenue streams and profitability in its ethical drug segment.
The NHI system's strategic initiatives, such as those outlined for the 2024-2028 period, aim to optimize pharmaceutical spending. For instance, the government has been actively pursuing policies to encourage the use of generics and biosimil, which can put downward pressure on the prices of branded drugs. In 2023, the total expenditure on pharmaceuticals in South Korea reached approximately 25 trillion KRW (roughly $19 billion USD), with a significant portion of this coming from NHI reimbursements, underscoring the government's considerable purchasing leverage.
- Price Negotiation: The NHI system directly negotiates prices for drugs, limiting the pricing power of pharmaceutical manufacturers.
- Reimbursement Policies: Decisions on which drugs are covered and at what level significantly influence market access and sales volume.
- Formulary Management: Inclusion or exclusion from the NHI formulary is critical for a drug's commercial success.
- Cost Containment Measures: Government-led initiatives to control healthcare spending can lead to increased pressure on drug prices and profit margins.
End-Consumers (for OTC and Cosmeceuticals)
While individual end-consumers of Huons' over-the-counter products and cosmeceuticals possess limited direct bargaining power, their collective influence is substantial. This is particularly evident in the aesthetics and wellness sectors, where trends often dictate purchasing behavior.
Huons must actively manage its brand and engage with consumers to navigate this dynamic. In 2024, the global beauty and personal care market was valued at approximately $500 billion, with a significant portion driven by consumer preferences and social media influence, highlighting the importance of brand perception for companies like Huons.
- Consumer Influence: Individual consumers have low bargaining power, but their collective choices shape market demand.
- Trend Responsiveness: The aesthetics and wellness segments are highly susceptible to social media trends and K-beauty influence.
- Brand Loyalty: Building and maintaining strong brand loyalty is crucial for mitigating customer power.
- Market Data: The global beauty market's significant size underscores the impact of consumer sentiment on revenue.
The bargaining power of customers for Huons is significant, primarily driven by large institutional buyers like hospitals and the South Korean government's National Health Insurance (NHI) system. These entities can negotiate prices, influence market access through formulary decisions, and drive demand for generics, directly impacting Huons' revenue and profitability in its core prescription drug segment.
Distributors and client pharmaceutical companies also exert considerable influence, especially in contract manufacturing. Their ability to switch providers based on pricing and specialized capabilities means Huons must consistently deliver value and maintain cost-effectiveness. Even individual consumers, while having low direct power, collectively shape demand in the lucrative beauty and wellness markets, necessitating strong brand management.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Influences | Impact on Huons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitals, Clinics, Pharmacies | High | Volume purchasing, supplier switching | Price negotiation, contract terms |
| South Korean NHI System | Very High | Price setting, reimbursement, formulary inclusion | Revenue, profitability, market access |
| Distributors & Wholesalers | High | Market access, channel control | Sales volume, market penetration |
| Client Pharmaceutical Companies (CDMO) | High | Provider switching, pricing, expertise | Contract retention, service pricing |
| End-Consumers (OTC, Cosmeceuticals) | Low (individually), High (collectively) | Trends, brand perception, social media | Brand loyalty, market demand |
Preview Before You Purchase
Huons Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Huons Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. You are viewing the exact document you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden elements. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate use, providing valuable insights into Huons' industry dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The South Korean pharmaceutical and healthcare sector is fiercely competitive, with a crowded landscape of both local businesses and global giants. Huons navigates this intense environment across its key segments like ophthalmology, dermatology, and aesthetics, where a multitude of companies are constantly striving to capture market share.
The pharmaceutical industry's competitive landscape is significantly shaped by a relentless drive for innovation, fueled by substantial Research and Development (R&D) investments. This intense focus on discovering novel drug candidates and cutting-edge technologies compels companies to constantly push boundaries. South Korea, a key player in this sector, consistently ranks high in clinical trials and new drug discoveries, underscoring the imperative for firms like Huons to maintain robust R&D spending to stay ahead.
Huons' commitment to R&D is evident in its financial performance, with R&D expenses showing an increase in the first quarter of 2025. This strategic investment is crucial for Huons to develop a competitive pipeline of new products and maintain its market position amidst fierce industry rivalry.
Competitive rivalry at Huons is shaped by a dual strategy: pursuing product differentiation through innovative, patented treatments and competing in the generics market where price is paramount. This means Huons faces distinct competitive pressures, from R&D-intensive battles for novel therapies to cost-driven competition for established drug formulations.
In the differentiated segment, competition centers on the unique value proposition of patented products. Conversely, the generics market, particularly for injections which Huons exports, intensifies rivalry based on manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For instance, the global generic drug market was valued at approximately $470 billion in 2023, with significant growth expected, highlighting the intense price competition Huons navigates in this space.
Dynamic Market Growth in Specific Segments
While the broader South Korean pharmaceutical sector demonstrates consistent growth, the aesthetics segment is booming, driven by a surge in demand for cosmetic procedures. This rapid expansion acts as a magnet for new entrants, consequently intensifying rivalry within these particularly profitable niches.
The Korean aesthetic market is anticipated to experience substantial growth, with projections indicating a significant upward trajectory by 2032. This robust expansion is a key factor in elevating competitive pressures among existing and emerging players.
- Rapid Growth in Aesthetics: The South Korean aesthetics market is a prime example of dynamic segment expansion within the pharmaceutical industry.
- Increased Player Influx: Lucrative growth in aesthetics attracts new companies, heightening competition.
- Projected Market Expansion: The Korean aesthetic market is forecast for significant growth by 2032, signaling continued competitive intensity.
Strategic Alliances and M&A Activities
Huons actively navigates a competitive landscape heavily influenced by strategic alliances and mergers and acquisitions (M&A). These activities are crucial for companies aiming to bolster market share, broaden their product offerings, and secure advanced technologies. For instance, Huons' move to increase its stake in PanGen Biotech exemplifies a strategy to foster group synergies and strengthen its overall competitive stance.
The pharmaceutical and biotech sectors, where Huons operates, frequently see consolidation. In 2024, the global M&A market in healthcare saw continued activity, with significant deal-making focused on areas like biopharmaceuticals and medical devices. These transactions often aim to achieve economies of scale, expand R&D pipelines, and access new markets.
- Market Consolidation: Companies pursue M&A to gain a larger share of a fragmented market.
- Portfolio Diversification: Acquisitions allow companies to enter new therapeutic areas or expand their product lines.
- Technological Advancement: Strategic partnerships and acquisitions are key to acquiring innovative technologies and intellectual property.
- Synergy Realization: Huons' increased stake in PanGen Biotech highlights the pursuit of operational and financial synergies.
Huons faces intense rivalry from numerous domestic and international players across its specialized segments. The company strategically differentiates itself through patented innovations while also competing on price in the generics market, particularly for its exported injections. This dual approach means Huons must constantly balance R&D investment with manufacturing efficiency to maintain its competitive edge.
The burgeoning South Korean aesthetics market, projected for substantial growth, attracts new entrants, intensifying competition in profitable niches. Huons' strategy of increasing its stake in PanGen Biotech reflects the broader industry trend of consolidation through M&A in 2024, aimed at expanding product portfolios and securing advanced technologies.
| Segment | Competitive Focus | Example Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Differentiated Products (e.g., Ophthalmology) | Innovation, patented treatments, R&D | South Korea ranks high in clinical trials and new drug discoveries. |
| Generics Market (e.g., Injections) | Price, manufacturing efficiency, cost-effectiveness | Global generic drug market valued at ~$470 billion in 2023. |
| Aesthetics | New entrants, market share capture, growth opportunities | Korean aesthetics market anticipated for significant growth by 2032. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many of Huons' prescription drugs, especially those with expired patents, generic alternatives represent a substantial threat. These generics offer comparable therapeutic benefits at a considerably lower price point, directly impacting Huons' market share and pricing power.
The growing availability of biosimilars further intensifies this substitution threat, particularly for Huons' biological drugs. For instance, the global biosimilars market was valued at approximately $22.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $90.0 billion by 2030, highlighting the significant competitive pressure.
Huons' strategic move with its subsidiary, PanGen Biotech, which actively develops EPO biosimilars, demonstrates a clear understanding of this market dynamic. This internal development aims to counter the external threat by participating in the biosimilar space.
In areas like health functional foods and managing chronic conditions, alternative therapies and lifestyle changes can step in for traditional pharmaceuticals. This is particularly relevant in South Korea, where consumers are increasingly focused on preventing illness rather than just treating it.
The South Korean market for health functional foods reached an estimated 5.9 trillion KRW in 2023, indicating a strong consumer preference for non-pharmaceutical health solutions. This trend suggests that pharmaceutical companies like Huons face a significant threat from these alternative health approaches.
Advancements in medical device technology present a growing threat of substitution for traditional drug treatments. For example, innovative diagnostic tools or minimally invasive therapeutic devices can now address conditions previously managed solely by pharmaceuticals. This trend is particularly evident in rapidly evolving sectors like digital health, which saw significant growth in South Korea during 2024, offering new avenues for patient care that bypass or complement drug regimens.
Cosmetic Procedures vs. Cosmeceuticals
More invasive or advanced non-surgical cosmetic procedures offered by clinics can act as a substitute for topical cosmeceuticals and less invasive injectable treatments. The global aesthetic market is substantial, with reports indicating it reached approximately $15.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This broad market encompasses a wide array of options, from dermal fillers and botulinum toxin injections to advanced laser treatments and chemical peels, all competing for consumer attention and spend in the pursuit of aesthetic enhancement.
These more intensive procedures offer more dramatic and immediate results compared to daily topical applications. For instance, while a high-end serum might promise gradual skin texture improvement, a laser resurfacing treatment can deliver more pronounced rejuvenation in a single session. This creates a direct competitive pressure, as consumers may opt for a clinic-based procedure that addresses their concerns more rapidly, even if it involves a higher upfront cost and potential downtime.
The threat is amplified by the increasing accessibility and acceptance of these advanced treatments. Many clinics now offer financing options, making them more attainable for a wider demographic. Furthermore, the continuous innovation in aesthetic technology means new and improved procedures are regularly introduced, further broadening the range of substitutes available to consumers looking for cosmetic improvements.
- Market Diversification: The aesthetics market is not monolithic; it includes surgical, minimally invasive, and non-invasive treatments, each with varying degrees of efficacy and cost.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in laser technology, energy-based devices, and injectables continually enhance the effectiveness and appeal of professional procedures.
- Consumer Preference Shifts: A growing segment of consumers prioritizes immediate and significant results, making more intensive procedures attractive substitutes for topical solutions.
- Economic Factors: While upfront costs can be higher for procedures, the perceived value and speed of results can justify the investment for many consumers, influencing their choices away from cosmeceuticals.
Digital Health Solutions and Telemedicine
Emerging digital health solutions pose a significant threat of substitution for traditional pharmaceutical interventions. AI-driven diagnostics, digital therapeutics, and telemedicine platforms offer alternative methods for health management and treatment. For instance, the South Korea smart healthcare market is projected for substantial growth, fueled by increasing digitalization, indicating a shift towards these new modalities.
These digital health solutions can provide comparable or even superior outcomes to conventional drugs in certain cases, often at a lower cost or with greater convenience. This accessibility and potential cost-effectiveness make them attractive substitutes for patients and healthcare providers alike.
- Digital Therapeutics: These are software-based interventions designed to prevent, manage, or treat medical disorders or diseases.
- Telemedicine Growth: The global telemedicine market is experiencing rapid expansion, with projections indicating continued strong growth through 2025 and beyond.
- AI in Healthcare: Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated into diagnostic tools and treatment planning, offering alternatives to traditional medical approaches.
- South Korea Smart Healthcare: This market segment is a key indicator of the trend, with significant investment and adoption of digital health technologies.
The threat of substitutes for Huons' products is multifaceted, encompassing both direct pharmaceutical alternatives and broader health solutions. Generic drugs and biosimilars significantly erode market share and pricing power, as seen with the projected growth of the biosimilars market. Furthermore, the increasing consumer interest in health functional foods and preventative lifestyle changes in South Korea, where this market reached approximately 5.9 trillion KRW in 2023, offers non-pharmaceutical avenues for health management.
Advanced medical devices and digital health solutions also present a growing substitution threat. Innovations in minimally invasive procedures and AI-driven diagnostics offer alternatives to traditional drug treatments. The South Korean smart healthcare market's expansion in 2024 underscores this shift towards digital and technologically advanced health management, potentially bypassing or complementing pharmaceutical interventions.
In the aesthetics sector, more invasive or advanced non-surgical procedures compete directly with Huons' cosmeceutical offerings. The global aesthetic market, valued around $15.9 billion in 2023, demonstrates a strong consumer demand for rapid and significant results, often favoring clinic-based treatments over topical solutions.
| Substitution Area | Key Drivers | Market Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Generic Drugs & Biosimilars | Lower cost, comparable efficacy | Global biosimilars market projected to reach $90.0 billion by 2030 (from $22.0 billion in 2023) |
| Health Functional Foods & Lifestyle | Preventative health focus, consumer preference | South Korea health functional foods market reached 5.9 trillion KRW in 2023 |
| Medical Devices & Digital Health | Technological advancement, convenience, alternative outcomes | South Korea smart healthcare market showing significant growth in 2024 |
| Advanced Aesthetic Procedures | Immediate results, accessibility, technological innovation | Global aesthetic market ~ $15.9 billion in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The pharmaceutical and medical device sectors in South Korea present substantial challenges for newcomers due to rigorous regulatory requirements. The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) oversees complex and lengthy drug approval pathways, a significant deterrent for potential entrants.
In 2024, the time taken for new drug approvals in South Korea remained a critical factor, with some complex biologics facing review periods extending over several years. This extended timeline, coupled with substantial investment needed for compliance and clinical trials, effectively limits the number of new companies that can realistically enter the market.
Developing new pharmaceuticals and medical devices demands enormous capital for research, rigorous clinical trials, and building GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities. For instance, bringing a single new drug to market can cost upwards of $2.6 billion, with development timelines often exceeding a decade. These substantial financial outlays and lengthy R&D periods erect significant barriers, making it incredibly challenging for new players to enter the market. Huons is actively bolstering its competitive position by investing in new production lines, demonstrating its commitment to innovation and market leadership.
New companies entering the pharmaceutical market, like Huons operates in, often struggle with the immense challenge of establishing widespread distribution networks. Incumbent firms, such as Huons, have spent years building strong relationships with hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, ensuring their products reach end-users efficiently. This established infrastructure is a significant barrier for newcomers.
Furthermore, brand recognition plays a crucial role. Huons, with its history and presence in the market, has cultivated trust among healthcare providers and patients. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and sales to build a similar level of credibility and awareness, a costly and time-consuming endeavor. For instance, in 2024, pharmaceutical companies spent an average of 20% of their revenue on sales and marketing, highlighting the significant investment required to gain market traction.
Intellectual Property Protection for Existing Products
Existing patents and proprietary technologies for innovative drugs and formulations are a significant barrier for new entrants looking to replicate Huons' successful products. As of 2024, Huons actively invests in research and development, securing approvals for its unique offerings, which further solidifies its competitive standing.
Huons' commitment to R&D, evidenced by its substantial investment in new drug development, creates a formidable moat. For example, in 2023, the company allocated a significant portion of its revenue to R&D, aiming to expand its pipeline of differentiated pharmaceuticals.
- Strong Patent Portfolio: Huons maintains a robust portfolio of patents covering its key pharmaceutical products and manufacturing processes.
- Proprietary Formulations: The company possesses unique drug formulations that are difficult and costly for competitors to develop and gain regulatory approval for.
- R&D Investment: Huons' consistent investment in research and development, exceeding industry averages in certain therapeutic areas, fuels its innovation pipeline.
- Regulatory Approvals: Successfully navigating complex regulatory pathways for novel drugs provides a significant time and cost advantage over potential new entrants.
Access to Specialized Talent and Technology
The healthcare and biopharmaceutical sectors are characterized by an intense need for highly specialized talent. New companies entering this arena often face significant hurdles in attracting and retaining top-tier scientific, technical, and manufacturing professionals. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of skilled biopharmaceutical researchers was estimated to be around 10%, impacting R&D timelines and innovation capacity.
Furthermore, access to cutting-edge technologies and proprietary platforms presents another substantial barrier. Developing or acquiring these advanced capabilities requires substantial capital investment and often involves complex licensing agreements, making it difficult for nascent players to compete effectively with established firms that already possess these critical assets.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: Difficulty in recruiting experienced scientists and engineers in specialized fields like gene editing or AI-driven drug discovery.
- Technology Access Costs: High expenses associated with licensing advanced manufacturing equipment or proprietary drug discovery software.
- Intellectual Property Hurdles: Navigating complex patent landscapes and the cost of developing novel intellectual property.
- Regulatory Expertise: The necessity of specialized knowledge to navigate stringent FDA or EMA approval processes, which can take years and significant investment.
The threat of new entrants for Huons is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements and extensive regulatory hurdles. The pharmaceutical industry demands massive upfront investment in research, clinical trials, and compliant manufacturing, with bringing a single drug to market costing upwards of $2.6 billion. In 2024, the protracted drug approval process by the MFDS, sometimes taking years for complex biologics, further deters new players.
Established distribution networks and brand loyalty also present substantial barriers. Huons' long-standing relationships with healthcare providers are difficult for newcomers to replicate, and the significant marketing spend, averaging 20% of revenue in 2024 for pharma companies, is a considerable obstacle to building brand recognition.
Huons' strong patent portfolio and ongoing R&D investments, which saw significant allocation of revenue in 2023, create a formidable competitive advantage. The need for specialized talent, with a global shortage of biopharmaceutical researchers estimated at 10% in 2024, and the high cost of accessing advanced technologies further solidify the barriers to entry.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Time (Illustrative) |
| Capital Requirements | R&D, Clinical Trials, Manufacturing Facilities | >$2.6 Billion per drug |
| Regulatory Approvals | MFDS Drug Approval Process | Years for complex biologics |
| Distribution Networks | Established relationships with hospitals/clinics | Years to build |
| R&D and Patents | Developing novel IP and formulations | Significant ongoing investment |
| Talent Acquisition | Specialized scientific and technical staff | 10% global shortage (2024) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert interviews. This multi-faceted approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.