HANA Micron Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HANA Micron Bundle
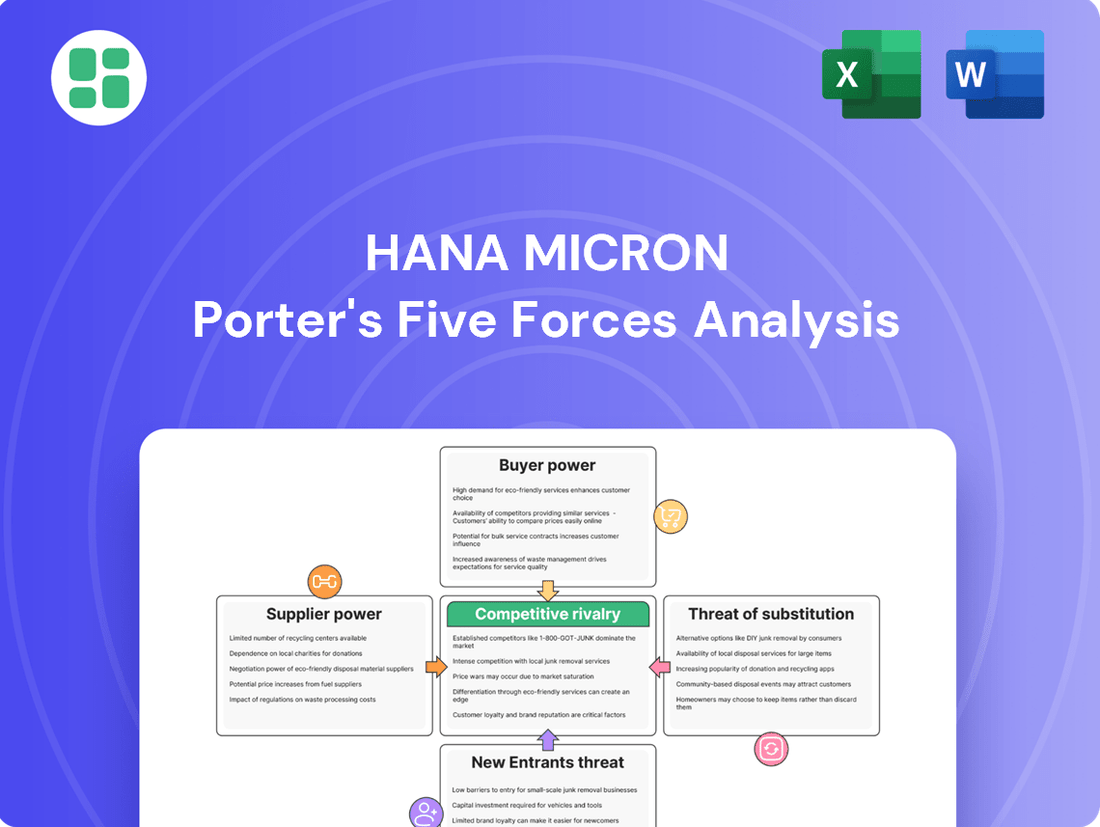
Understanding the competitive landscape for HANA Micron requires a deep dive into Porter's Five Forces. This framework helps dissect the industry's profitability and HANA Micron's strategic positioning by examining buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping HANA Micron’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hana Micron's reliance on specialized semiconductor packaging and testing equipment, like advanced bonding machines and lithography tools, means a few key suppliers often dominate the market. This concentration of suppliers for critical inputs gives them considerable bargaining power.
For instance, the market for certain high-precision semiconductor manufacturing equipment is known for its limited number of global providers. This allows these suppliers to influence pricing and dictate terms, potentially impacting Hana Micron's cost structure and production schedules.
The proprietary nature of certain advanced manufacturing equipment and critical materials used by Hana Micron can significantly limit its sourcing options. When suppliers offer unique components or technologies that are difficult to replicate or substitute, their bargaining power increases. This uniqueness makes it challenging for Hana Micron to switch to alternative suppliers without incurring substantial costs.
High switching costs, encompassing expenses related to re-qualifying new suppliers, integrating new materials, and potential disruptions to production timelines, further bolster the suppliers' leverage. For instance, the specialized nature of inputs for advanced semiconductor packaging technologies means that finding and onboarding a new supplier can be a lengthy and costly process, pushing Hana Micron to maintain relationships with existing providers even if terms are less favorable.
While direct forward integration by suppliers into OSAT services is a significant undertaking due to high capital requirements and established customer ties, the theoretical possibility still exists for highly specialized suppliers. This potential, however remote, can subtly enhance their bargaining leverage.
The semiconductor industry's intricate supply chain means that vertical integration at any stage can alter power balances. For instance, a supplier of advanced packaging materials might consider offering integrated solutions, thereby encroaching on existing OSAT providers' market share.
Importance of Supplier Technology and Innovation
Suppliers providing advanced packaging and testing technologies are vital for Hana Micron's competitiveness, particularly as demand for AI and high-performance computing chips escalates. Their ongoing innovation directly influences Hana Micron's capacity to innovate and maintain its market position, granting these suppliers significant bargaining power. For instance, the global semiconductor packaging market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, highlighting the importance of these specialized suppliers.
The ability to access and integrate the latest technological advancements in areas like advanced packaging solutions, such as fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) or chiplets, is a key differentiator for Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) companies like Hana Micron. Suppliers that can consistently deliver these cutting-edge capabilities effectively hold considerable sway over their customers.
- Technological Dependence: Hana Micron's reliance on specialized suppliers for advanced packaging and testing equipment means these suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms.
- Innovation Link: The pace of innovation by equipment suppliers directly impacts Hana Micron's ability to offer next-generation semiconductor solutions.
- Market Growth: With the semiconductor industry, particularly AI-driven segments, experiencing robust growth, suppliers of critical technologies are well-positioned to exert influence.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. When alternative materials or less specialized equipment exist, buyers can switch suppliers more easily, thereby reducing the power of any single supplier.
However, for highly specialized inputs crucial to advanced semiconductor packaging and testing, the landscape shifts. HANA Micron's reliance on these specialized components means fewer readily available substitutes. This scarcity inherently strengthens the bargaining power of its suppliers, especially as advanced packaging becomes increasingly critical for performance and differentiation in the semiconductor industry.
- Specialized Inputs: HANA Micron's need for advanced packaging materials and testing equipment often involves proprietary technologies or unique manufacturing processes.
- Limited Alternatives: The highly technical nature of these inputs restricts the number of suppliers capable of meeting stringent quality and performance requirements.
- Supplier Leverage: In 2024, the demand for advanced semiconductor packaging solutions outpaced supply for certain critical materials, giving suppliers greater pricing and negotiation leverage. For instance, shortages in specific high-purity chemicals used in advanced packaging processes have been reported, impacting lead times and costs for manufacturers like HANA Micron.
- Strategic Importance: As the semiconductor industry pushes for miniaturization and enhanced functionality, the importance of specialized packaging inputs grows, further consolidating supplier power in these niche markets.
Hana Micron's reliance on a concentrated group of suppliers for specialized semiconductor packaging and testing equipment, such as advanced bonding machines and lithography tools, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. This is particularly evident in 2024, where demand for cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing capabilities has intensified, leading to extended lead times and increased costs for critical components.
The proprietary nature of many of these essential inputs, coupled with high switching costs for Hana Micron, further amplifies supplier leverage. For example, the global market for certain high-precision semiconductor manufacturing equipment is dominated by a few key players, allowing them to dictate pricing and terms, impacting Hana Micron's operational expenses and production schedules.
The strategic importance of these suppliers is underscored by the rapid growth in sectors like AI and high-performance computing, where advanced packaging is a key differentiator. Suppliers capable of delivering next-generation solutions, such as fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) or chiplets, hold considerable sway. The global semiconductor packaging market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and continues its upward trajectory, highlighting the critical role and influence of these specialized providers.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Hana Micron | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of Suppliers | Limited sourcing options, increased pricing power for suppliers | Dominance of a few key equipment providers |
| Proprietary Technology/Inputs | High switching costs, reduced buyer flexibility | Scarcity of advanced packaging materials reported |
| Innovation Pace | Directly affects Hana Micron's competitiveness | Strong demand for AI-driven semiconductor solutions |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting HANA Micron, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces on a single, intuitive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hana Micron's customer base is largely composed of major semiconductor players, including Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) and fabless companies. These clients frequently place substantial orders, particularly for memory and System-on-Chip (SoC) components.
The concentration of Hana Micron's revenue among a few key customers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, if a single client represents over 10% of Hana Micron's total sales, that customer can exert considerable influence, potentially leading to downward price pressure on Hana Micron's offerings.
Large integrated device manufacturers (IDMs) like Intel and Samsung possess their own in-house packaging and testing facilities. This capability grants them considerable leverage over outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) providers, as they can choose to bring operations back in-house if pricing or service levels are not met. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see significant investment in advanced packaging technologies by major IDMs, underscoring their commitment to vertical integration.
This inherent threat of vertical integration compels OSAT companies to maintain competitive pricing structures and continuously invest in cutting-edge services and technologies. The ability of a major chip designer to perform its own advanced packaging, which is becoming increasingly critical for performance, directly influences the bargaining power it holds when negotiating with external OSAT partners.
Customers often face minimal costs when switching between Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) providers, particularly for common packaging and testing needs. This low barrier to entry means clients can easily shop around for better deals. For instance, in 2024, many OSAT customers reported that the effort and expense of transferring production lines or re-qualifying components were negligible for standard offerings.
This ability to switch readily empowers customers to negotiate aggressively on price. If a particular OSAT provider's pricing or service levels aren't competitive, customers can simply move their business elsewhere. The OSAT industry is quite fragmented, with numerous significant players, intensifying this competitive dynamic and further amplifying customer bargaining power.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Hana Micron. The semiconductor industry, where Hana Micron's clients operate, is notoriously competitive. This intense competition forces chip manufacturers to be extremely mindful of their own costs, including the expenses associated with packaging and testing services. Consequently, these customers leverage their substantial purchasing volume to negotiate aggressively for lower prices from OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) providers like Hana Micron.
This downward pressure on pricing is further exacerbated by the inherent cyclicality of the semiconductor market. During downturns, demand for chips falls, giving customers even more leverage to demand cost reductions. For instance, in 2023, the global semiconductor market experienced a contraction, which would have intensified price negotiations for OSAT services.
- High Competition Among Semiconductor Firms: Drives a constant need to reduce costs in the supply chain.
- Customer Leverage: Large chip manufacturers use their significant order volumes to negotiate lower prices for packaging and testing.
- Industry Cyclicality: Downturns in the semiconductor market amplify customer price sensitivity and negotiation power.
Standardization of Services
When packaging and testing services become highly standardized, customers gain significant leverage. This lack of differentiation among Original Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) providers means buyers can easily switch suppliers based on price. For instance, in 2024, the OSAT market saw intense competition, with many players offering similar core services, making price a primary decision factor for many clients.
This commoditization directly amplifies customer bargaining power. Buyers can readily compare quotes from multiple OSAT companies, pushing down prices and squeezing profit margins for providers. If a service is easily replicated, a customer demanding a lower price has a strong position because they can find another supplier willing to meet their terms.
Hana Micron's strategy to counter this involves focusing on advanced, differentiated technologies. By offering specialized packaging solutions or testing capabilities that competitors cannot easily match, Hana Micron can reduce the degree to which its services are perceived as standardized. This differentiation is crucial for maintaining pricing power and mitigating the inherent bargaining strength of customers in a commoditized market.
- Standardization Leads to Price Sensitivity: In 2024, the OSAT sector experienced a notable trend where the availability of similar packaging and testing services allowed customers to prioritize cost, increasing their negotiation power.
- Customer Leverage in Commoditized Markets: When services lack unique features, customers can easily switch providers, forcing suppliers to compete aggressively on price, thereby enhancing customer bargaining power.
- Hana Micron's Differentiation Strategy: Hana Micron aims to mitigate customer bargaining power by investing in and highlighting its advanced technological capabilities, creating unique value propositions that are harder for competitors to replicate.
Hana Micron's customers, primarily major semiconductor firms, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the competitive nature of the chip industry. This leverage intensifies during market downturns, as seen in 2023's semiconductor contraction, where customers pushed for cost reductions.
The ease with which customers can switch between Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) providers, especially for standard services, further amplifies their negotiation strength. In 2024, minimal switching costs for common offerings allowed clients to readily seek better pricing, a trend that continues to pressure OSAT margins.
As OSAT services become more commoditized, customers gain leverage by easily comparing prices across providers. Hana Micron counters this by investing in advanced, differentiated technologies, aiming to reduce service standardization and maintain pricing power against these strong customer demands.
| Factor | Impact on Hana Micron | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for large clients | Key clients representing >10% of revenue exert significant price pressure. |
| Threat of Vertical Integration | Need for competitive pricing and innovation | IDMs like Intel and Samsung continue investing in advanced packaging in 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs empower price negotiation | Minimal costs for transferring standard production lines reported by OSAT customers in 2024. |
| Market Cyclicality | Increased customer leverage during downturns | 2023's semiconductor contraction intensified price negotiations for OSAT services. |
| Service Standardization | Commoditization leads to price sensitivity | Intense competition in 2024 OSAT market with many offering similar core services. |
Preview Before You Purchase
HANA Micron Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete HANA Micron Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the semiconductor industry. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file. This comprehensive analysis will equip you with critical insights into market dynamics, buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and industry rivalry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The OSAT market is incredibly crowded, with a significant number of companies competing for business. Think of giants like ASE Technology Group, Amkor Technology, and JCET Group, but also many smaller, specialized outfits. This sheer volume of players means intense competition, as everyone is fighting to grab a bigger piece of the pie. In 2023, the OSAT market was valued at approximately $52.6 billion, with Asia-Pacific dominating, accounting for over 60% of the global market share.
The semiconductor industry is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a strong upward trajectory through 2024 and 2025, largely fueled by the AI revolution and the demand for high-bandwidth memory (HBM). Despite this overall expansion, the Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) sector can still face challenges related to capacity utilization. For instance, in early 2024, while demand for advanced packaging like HBM surged, other segments of the OSAT market might have seen slower uptake, leading to potential imbalances.
When the installed capacity in the OSAT industry exceeds the actual demand, competitive rivalry intensifies significantly. Companies then engage in aggressive competition for the available business, which can unfortunately result in price reductions or price wars. This dynamic was observed in certain segments of the OSAT market in late 2023 and early 2024, where companies with excess capacity sought to secure orders, impacting profitability.
The semiconductor packaging and testing sector is inherently capital-intensive, demanding massive investments in cutting-edge machinery and infrastructure. This heavy upfront expenditure translates into substantial fixed costs for companies like Hana Micron. For instance, establishing advanced packaging facilities, such as those Hana Micron is developing in Vietnam, requires hundreds of millions of dollars in capital outlay.
These high fixed costs act as significant exit barriers. Companies are compelled to continue production even when market demand softens to spread these costs over a larger volume, preventing them from simply shutting down operations. This dynamic intensifies competitive rivalry, as firms fight to maintain market share and cover their ongoing expenses, even in less favorable economic conditions.
Product Differentiation and Specialization
Competitive rivalry in the OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) sector is intensifying, with product differentiation becoming a key battleground. This goes beyond traditional assembly to sophisticated offerings like 2.5D/3D packaging, chiplets, and heterogeneous integration.
Companies excelling in specialized, high-performance, and cost-efficient advanced packaging, especially for demanding AI and HPC workloads, are carving out significant advantages. For instance, in 2024, the demand for advanced packaging solutions, crucial for AI accelerators, surged, with market research indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% for these specific segments.
- Advanced Packaging Growth: The market for advanced packaging, including 2.5D and 3D, is projected to grow substantially, driven by AI and high-performance computing needs.
- Specialization as a Differentiator: OSAT providers focusing on niche, high-value services like chiplet integration are gaining market share.
- Cost-Effectiveness in Innovation: Balancing cutting-edge technology with competitive pricing is vital for differentiation in 2024.
Geographic and Strategic Expansions
Competitors are aggressively broadening their reach both geographically and in terms of services offered. This expansion is often a response to geopolitical shifts and client demands for more resilient, diversified supply chains. For instance, Hana Micron's significant investment in Vietnam reflects a broader trend where major industry players are establishing or enhancing operations in emerging markets, intensifying competition in both established and nascent territories.
This strategic maneuvering directly impacts competitive rivalry. As more companies establish presences in key regions like Vietnam, the market becomes more crowded, potentially leading to price wars and a greater need for differentiation. Hana Micron's 2024 expansion efforts in Vietnam, aiming to bolster its outsourced semiconductor packaging and testing (OSAT) capabilities, are a prime example of this heightened competitive dynamic.
- Geographic Expansion: Competitors are increasing their presence in new markets, mirroring Hana Micron's moves into Vietnam.
- Service Portfolio Growth: Companies are broadening their offerings to meet evolving client needs for integrated supply chain solutions.
- Client-Driven Diversification: Demand for supply chain resilience is a key motivator for competitors' expansion strategies.
- Increased Market Saturation: The influx of competitors into regions like Vietnam intensifies rivalry and necessitates strategic adaptation.
The intense competition within the OSAT market, valued at $52.6 billion in 2023, is driven by numerous players, from giants like ASE Technology to smaller specialists. This rivalry is amplified by the capital-intensive nature of the industry, with significant investments in advanced machinery creating high fixed costs and exit barriers, forcing companies to compete fiercely even during demand slowdowns.
Differentiation through advanced packaging, such as 2.5D/3D integration for AI and HPC workloads, is becoming crucial, with this segment projected to grow over 10% annually in 2024. Competitors are also expanding geographically and service portfolios, with Hana Micron's Vietnam expansion reflecting a broader trend that intensifies rivalry in both established and emerging markets.
| Key Competitors (OSAT) | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) | Growth Driver Example | Geographic Expansion Trend |
| ASE Technology Group | N/A (Private) | AI Chip Packaging | Asia-Pacific Focus |
| Amkor Technology | N/A (Public) | HBM Integration | Global Operations |
| JCET Group | N/A (Public) | Advanced Packaging Solutions | China & Emerging Markets |
| Hana Micron | N/A (Public) | Vietnam Facility Investment | Southeast Asia Expansion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) such as Intel and Samsung can conduct their own packaging and testing, acting as a significant substitute for outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) providers like Hana Micron. This in-house capability allows IDMs to bring critical manufacturing steps under their direct control.
While outsourcing often provides cost advantages and access to specialized know-how, IDMs retain the option to expand their internal packaging and testing operations. This strategic move is particularly relevant for high-volume or mission-critical products, enabling them to lessen their dependence on external OSAT partners.
For example, in 2023, major IDMs continued to invest in advanced packaging technologies, with companies like Intel showcasing their own integrated solutions. This trend highlights the ongoing threat of substitution, as these giants can internalize services previously offered by companies like Hana Micron, potentially impacting market share and revenue streams.
Leading foundries such as TSMC and Samsung are increasingly integrating advanced packaging services like CoWoS and SoIC directly into their wafer fabrication offerings. This move presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) providers.
Chip designers, particularly those working on complex AI chips, may find it more efficient and cost-effective to opt for a comprehensive, one-stop solution directly from the foundry. This integrated approach bypasses the need to engage separate OSAT companies, thereby reducing supply chain complexity and potential delays.
For instance, TSMC's advanced packaging services are crucial for high-performance computing and AI applications, a segment where demand is rapidly growing. In 2024, the advanced packaging market is projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, with foundries capturing a larger share as they enhance their integrated offerings.
Innovations in chip architectures, like monolithic dies and advanced system-on-chip (SoC) designs, are simplifying packaging by reducing the need for multiple discrete components. This trend, particularly prominent in the development of next-generation processors and AI accelerators, could theoretically lessen the demand for certain outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) services. For instance, the increasing integration within a single silicon die directly addresses a key value proposition of traditional packaging solutions.
However, this potential threat is often counterbalanced by the growing complexity in other areas of semiconductor manufacturing. While packaging complexity might decrease in some segments, the demand for advanced testing, intricate wafer-level packaging, and specialized substrate technologies is simultaneously rising. The global OSAT market, projected to reach approximately $70 billion in 2024, demonstrates this ongoing demand, with growth driven by advanced packaging needs for high-performance computing and mobile devices.
Software-based Solutions Reducing Hardware Testing Needs
The threat of substitutes is amplified by advancements in software-based solutions that can reduce the need for extensive hardware testing. Innovations in design for test (DFT) and built-in self-test (BIST) are enabling chips to perform more self-validation. This trend, coupled with sophisticated simulation tools, could diminish the reliance on external testing services, potentially impacting companies like Hana Micron.
For instance, the increasing complexity of integrated circuits (ICs) necessitates more efficient testing methodologies. By embedding testing capabilities directly into the chip design, manufacturers can streamline the validation process. This shift means that a significant portion of what was once done through physical, external testing can now be handled internally through software and embedded logic.
- Increased DFT/BIST Adoption: Leading semiconductor firms are investing heavily in on-chip testing, with DFT techniques becoming standard practice in modern IC design.
- Simulation Accuracy: Advanced simulation software can now predict a substantial percentage of potential hardware failures, reducing the need for exhaustive physical test runs.
- Cost Reduction for Chipmakers: By minimizing reliance on external test houses, chip manufacturers can achieve significant cost savings, making in-house or software-driven testing more attractive.
Alternative Manufacturing Models or Technologies
While not a direct substitute for current semiconductor packaging, radical shifts in manufacturing paradigms, such as entirely new material systems or the widespread adoption of quantum computing, could, in the very long term, diminish the reliance on traditional packaging and testing methods. For instance, advancements in areas like chiplets and heterogeneous integration, which are already gaining traction, represent an evolution rather than a substitution of existing packaging technologies. These trends are actually increasing the complexity and value of advanced packaging solutions.
In the immediate future, advanced packaging is becoming more, not less, critical for performance gains and integration. The semiconductor industry, including players like Micron Technology, is heavily investing in these advanced packaging techniques to overcome the limitations of traditional scaling. For example, Micron's 2024 capital expenditures are expected to be significant, with a portion earmarked for advanced manufacturing and packaging capabilities to support high-performance computing and AI workloads.
- Radical Manufacturing Shifts: Long-term threats could emerge from entirely new material systems or quantum computing, potentially altering the need for current packaging.
- Immediate Relevance: Advanced packaging is currently becoming more critical, not less, as seen in industry investments.
- Heterogeneous Integration: Trends like chiplets represent an evolution of packaging, increasing its importance rather than substituting it.
- Industry Investment: Companies like Micron are investing heavily in advanced packaging to meet demand for high-performance computing and AI.
Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) and leading foundries are increasingly offering advanced packaging services directly, acting as substitutes for traditional outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) providers. This trend is driven by the desire for greater control over critical manufacturing steps and the efficiency of one-stop solutions, especially for complex chips. For instance, TSMC's integrated packaging services are vital for high-performance computing and AI, a market segment expected to grow significantly, with foundries capturing an increasing share of the advanced packaging market in 2024.
Innovations in chip design, such as monolithic dies and advanced system-on-chip (SoC) designs, can simplify packaging by integrating more functionality onto a single silicon die. This reduces the need for separate components and, consequently, some traditional outsourced assembly and testing services. However, the overall demand for advanced testing and intricate wafer-level packaging is rising, with the global OSAT market projected to reach around $70 billion in 2024, fueled by these complex needs.
Software-based solutions like design for test (DFT) and built-in self-test (BIST) are also emerging as substitutes by enabling more on-chip validation, potentially reducing reliance on external testing. This allows chipmakers to streamline validation and achieve cost savings. Leading semiconductor firms are indeed investing heavily in these on-chip testing techniques, making them standard practice in modern IC design to handle the increasing complexity of integrated circuits.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | Impact on OSAT Providers | Key Drivers | Example/Data Point |
| IDM/Foundry Integration | IDMs and foundries offer in-house packaging and testing. | Reduced demand for outsourced services. | Control, efficiency, one-stop solutions. | TSMC's advanced packaging for AI chips. |
| Chip Design Simplification | Monolithic dies and SoCs reduce the need for separate packaging. | Potential decrease in demand for certain assembly steps. | Integration, simplification. | Increased functionality on a single silicon die. |
| Software-Based Testing | DFT and BIST enable on-chip validation. | Less reliance on external testing services. | Cost savings, streamlined validation. | Increased adoption of DFT in IC design. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the semiconductor packaging and testing industry, where HANA Micron operates, requires substantial upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing facilities, sophisticated testing equipment, and stringent cleanroom environments. For instance, the cost of a single advanced semiconductor packaging line can run into tens of millions of dollars, making it a significant barrier for newcomers.
The semiconductor industry, particularly for advanced memory solutions like those produced by Micron, demands a highly specialized technical workforce. New entrants face a significant hurdle in acquiring talent proficient in complex semiconductor fabrication, advanced materials science, and stringent quality control protocols. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor talent shortage remained a critical issue, with estimates suggesting a deficit of hundreds of thousands of skilled workers.
Established OSAT players, such as Hana Micron, have cultivated deep-seated relationships and a high degree of trust with key semiconductor manufacturers. This loyalty is built on years of consistent performance and reliable service within a critical industry.
Newcomers entering the OSAT market would find it exceptionally challenging to displace these entrenched connections. The significant capital investment and meticulous qualification processes required by major chipmakers mean they are hesitant to switch suppliers without compelling evidence of superior capability and unwavering dependability.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to emphasize supply chain security and risk mitigation. Companies like TSMC and Samsung, major Hana Micron clients, are known for their rigorous vendor selection criteria, often favoring partners with extensive experience and a proven history of meeting stringent quality and delivery standards.
Economies of Scale Enjoyed by Incumbents
Established OSAT firms leverage substantial economies of scale, particularly in procurement and advanced manufacturing processes. This allows them to negotiate better terms with suppliers and spread fixed costs over a larger output, leading to lower per-unit production costs. For instance, a major OSAT player might achieve a 10-15% cost advantage on raw materials compared to a startup due to bulk purchasing power.
These scale advantages extend to research and development. Incumbents can invest heavily in cutting-edge technologies and process improvements, which new entrants would find prohibitively expensive to replicate. This R&D spending, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars annually for leading companies, creates a significant barrier to entry, as new firms would need immense capital to compete on technological innovation.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbents benefit from lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production.
- Procurement Power: Large OSAT companies secure better pricing on materials through bulk orders.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Established players optimize production lines for maximum output and minimal waste.
- R&D Investment: Significant capital allows incumbents to lead in technological advancements, deterring new entrants.
Complex Regulatory and Intellectual Property Landscape
The semiconductor industry presents a formidable barrier to new entrants due to its intricate regulatory environment and extensive intellectual property (IP) protections. Companies must adhere to rigorous quality control measures, environmental standards, and a complex web of patents, which require significant investment in legal expertise and compliance infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor industry spent an estimated $70 billion on research and development, a substantial portion of which is tied to IP creation and protection.
Navigating this landscape demands not only substantial capital but also a deep understanding of global trade regulations and patent law. Failure to comply or accidental infringement can lead to costly litigation and market exclusion. The sheer density of existing patents, covering everything from chip design to manufacturing processes, means that any newcomer faces a high probability of infringing on established IP, necessitating extensive patent clearance or licensing agreements, adding further to upfront costs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with standards like TSMC's stringent quality controls and environmental regulations (e.g., REACH in Europe) requires significant upfront investment.
- IP Landscape: The semiconductor sector is heavily patented; in 2023, patent filings in the US alone exceeded 50,000 for semiconductor-related technologies, making it challenging to operate without licensing.
- Litigation Risk: Avoiding patent infringement lawsuits, which can cost millions, is a critical concern for any new player.
The threat of new entrants into the semiconductor packaging and testing (OSAT) sector, where Hana Micron operates, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements. Establishing state-of-the-art facilities and acquiring specialized equipment demands hundreds of millions of dollars, a prohibitive cost for most potential competitors. Furthermore, the industry's reliance on a highly skilled workforce, coupled with existing strong customer relationships built on trust and performance, creates substantial barriers.
| Barrier Category | Description | Example Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in advanced manufacturing and testing equipment. | Cost of an advanced packaging line: Tens of millions USD. |
| Technical Expertise | Need for specialized skills in fabrication, materials science, and quality control. | Global semiconductor talent shortage estimated in hundreds of thousands of skilled workers. |
| Customer Relationships | Entrenched loyalty and trust with major semiconductor manufacturers. | Major clients like TSMC/Samsung have rigorous vendor qualification processes. |
| Economies of Scale | Incumbents benefit from lower per-unit costs through high-volume production and procurement power. | Potential 10-15% cost advantage on raw materials for large players via bulk purchasing. |
| Intellectual Property & Regulation | Complex IP landscape and stringent regulatory compliance add to costs and risks. | Semiconductor R&D spending: ~$70 billion globally in 2024. US semiconductor patent filings: >50,000 in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our HANA Micron Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Micron's official financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and IDC, and public statements from competitors and key suppliers.