Gruma Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gruma Bundle
Gruma's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate the corn masa and tortilla chip market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Gruma’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Gruma's reliance on corn, a global commodity, means the bargaining power of suppliers is generally moderate. While corn is widely available, specialized varieties or specific quality standards for nixtamalized corn flour could concentrate power among a few key suppliers, potentially increasing their leverage.
However, Gruma's immense scale as the world's largest producer of corn flour and tortillas significantly mitigates this. In 2024, Gruma's substantial purchasing volume allows it to negotiate highly favorable terms with its corn suppliers, effectively reducing individual supplier bargaining power.
Global supply chains are facing unprecedented volatility due to geopolitical tensions and the escalating impact of climate change. Disruptions to major trade routes, like those seen in the Red Sea in early 2024, can significantly increase shipping costs and lead times for essential raw materials like corn and wheat, which are critical for Gruma's operations.
These external shocks directly bolster the bargaining power of suppliers who can guarantee consistent and reliable delivery of these key inputs. For instance, a supplier with diversified sourcing or robust logistics capabilities in a more stable region can command higher prices when Gruma faces potential shortages or significant transit delays.
Supplier switching costs for Gruma can influence the bargaining power of their suppliers. If Gruma faces significant expenses when changing corn suppliers or other essential input providers, such as implementing new quality control processes, adjusting logistics, or renegotiating agreements, it strengthens the leverage of their current suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the global corn market saw price volatility, making the cost and complexity of switching suppliers a key consideration for large food processors like Gruma.
Backward Integration Potential
Gruma's potential for backward integration into large-scale corn farming, while theoretically possible, faces significant practical hurdles. The sheer scale of land acquisition, substantial capital investment, and the specialized agricultural expertise required make extensive farming operations challenging. This inherent limitation suggests that Gruma will likely maintain a degree of reliance on external corn suppliers, thus preserving some bargaining power for those suppliers.
For instance, while Gruma is a dominant player in corn flour and tortilla production, the agricultural sector demands different operational models. The cost and complexity of managing vast tracts of farmland, dealing with weather volatility, and navigating agricultural regulations can be prohibitive. This means that while Gruma can influence some aspects of its supply chain, complete control over corn sourcing through direct farming is not a readily achievable strategy for the entirety of its needs.
- Limited Farming Expertise: Gruma's core competency lies in food processing, not large-scale agriculture, requiring significant investment in new skill sets.
- Capital Intensity: Acquiring and managing agricultural land requires substantial upfront capital, potentially diverting resources from core business activities.
- Geographic Dispersion: Sourcing corn globally means managing diverse agricultural regions, each with unique challenges and regulations.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers. For Gruma, a major producer of corn flour and tortillas, the primary input is corn. While other grains like wheat are used for different types of tortillas, the direct substitutes for corn in its core product lines are relatively limited. This scarcity of direct alternatives for its main raw material can empower corn suppliers.
In 2024, the global corn market experienced price volatility. For instance, U.S. corn prices fluctuated, influenced by weather patterns and global demand, impacting Gruma's input costs. The limited substitutability of corn for its flagship products means suppliers have a stronger hand in negotiating prices and terms.
- Limited Direct Substitutes: For Gruma's core corn-based products, direct input substitutes for corn are scarce.
- Alternative Grains Exist: Wheat flour is a substitute for producing wheat tortillas, diversifying product offerings but not directly replacing corn in its primary use.
- Supplier Leverage: The lack of readily available direct substitutes for corn strengthens the bargaining power of corn suppliers to Gruma.
- Market Dynamics: Global corn prices, influenced by factors like weather and demand, directly affect Gruma's input costs and the supplier's negotiating position.
Gruma's substantial scale as a major global purchaser of corn generally limits supplier bargaining power. However, disruptions in 2024, such as increased shipping costs due to geopolitical events, empowered suppliers who could guarantee consistent delivery, allowing them to command higher prices.
The limited availability of direct substitutes for corn in Gruma's core products, coupled with the significant costs and complexities of switching suppliers, further strengthens the leverage of corn producers, particularly during periods of market volatility like the price fluctuations observed in the corn market throughout 2024.
Gruma's core competency in food processing, rather than large-scale agriculture, presents practical barriers to backward integration, ensuring continued reliance on external suppliers and preserving their bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Gruma's Supplier Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Gruma's Scale | Reduces supplier power due to high purchasing volume | Significant, enabling favorable terms |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increases supplier power by creating scarcity/delays | High, due to geopolitical tensions and climate impacts |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier power if costs are high | Moderate, due to complexity and potential price volatility |
| Limited Substitutes for Corn | Strengthens supplier power | High, for Gruma's core products |
What is included in the product
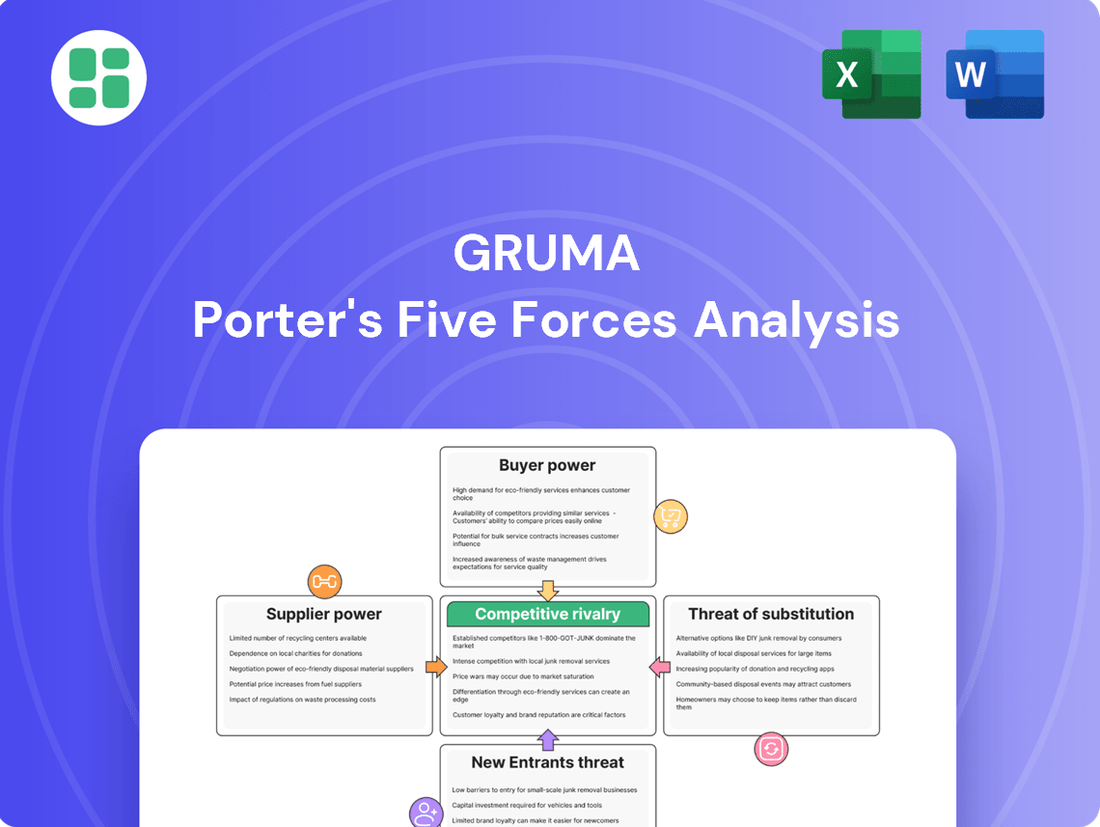
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within Gruma's operating environments by examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Gruma's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive pressures—perfect for quickly identifying and addressing market pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Gruma's customer base is a mixed bag. On one hand, large players like major supermarket chains and big foodservice operators can demand better pricing due to their sheer volume, potentially squeezing Gruma's margins. For instance, in 2024, the top five U.S. grocery retailers accounted for over 40% of the market, giving them significant leverage.
However, Gruma also serves a vast number of smaller, independent businesses and direct consumers. This fragmentation means that no single small customer has much power to dictate terms. Think of the thousands of smaller restaurants or local grocery stores that carry Gruma products; their individual purchasing power is minimal, which helps to offset the influence of the larger accounts.
Gruma faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly driven by price sensitivity among foodservice clients. This means Gruma must carefully manage its pricing to remain competitive, as customers can easily switch if costs rise.
The market offers numerous alternatives, especially for corn flour tortillas, including other brands and the option for customers to produce them in-house. This abundance of choices further strengthens the customers' ability to negotiate or seek out lower-priced options, directly impacting Gruma's market share and profitability.
Gruma's robust brand portfolio, featuring Maseca and Mission, cultivates considerable consumer loyalty worldwide. This established loyalty, coupled with product differentiation efforts like enhanced quality and healthier alternatives, somewhat lessens customer bargaining power by decreasing their propensity to switch brands.
Customer's Information and Switching Costs
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, with easy access to details about product ingredients, pricing comparisons, and available alternatives. This transparency significantly shifts power towards the buyer.
For Gruma's larger, industrial clients, such as tortillerias, switching suppliers can incur costs. These might include ensuring consistent product quality and recalibrating their own production processes. Gruma has strategically worked to increase these switching costs in certain markets, making it less appealing for customers to move to competitors.
- Information Accessibility: In 2024, online platforms and consumer review sites provide unprecedented levels of product information, empowering customers to make more informed purchasing decisions.
- Switching Costs for Industrial Customers: For a large food manufacturer like Gruma, the cost for a tortilleria to switch from Gruma's corn flour to another supplier could involve significant investment in re-testing and process validation to ensure the new flour meets existing quality and performance standards.
- Gruma's Strategy: Gruma's focus on product consistency and building strong relationships aims to embed its products within customer operations, thereby raising the perceived cost of switching.
Volume of Purchases by Key Customers
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the volume of purchases made by key clients. Large distributors, major supermarket chains, and significant foodservice operators regularly procure substantial quantities of Gruma's products. This considerable purchasing volume grants them considerable leverage when negotiating terms such as pricing, delivery schedules, and even specific product attributes.
This customer leverage is evident in Gruma's performance. For instance, the company experienced a contraction in its sales volume within the crucial foodservice channel during 2024. This downturn underscores how sensitive Gruma's business can be to the demands and purchasing power of its major clients in this sector.
- High Volume Purchases: Key customers like large distributors and supermarket chains buy in bulk, increasing their negotiating strength.
- Price Sensitivity: Significant purchase volumes allow these customers to demand more favorable pricing from Gruma.
- Influence on Terms: Customers can dictate delivery terms and product specifications due to their substantial order sizes.
- Channel Performance Impact: A contraction in sales volume, as seen in Gruma's foodservice channel in 2024, directly reflects the impact of customer bargaining power.
Gruma navigates a complex customer landscape where large buyers, like major grocery chains in 2024 that controlled over 40% of the U.S. market, wield significant pricing power due to their volume. This pressure is amplified by the ease with which customers can switch to competitors or even produce items like tortillas in-house, especially given the abundance of alternatives. While Gruma's strong brand loyalty, exemplified by Maseca and Mission, and efforts to increase switching costs for industrial clients offer some defense, the overall customer bargaining power remains a key consideration for pricing and channel strategy.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Gruma |
|---|---|---|
| Large Supermarket Chains & Foodservice Operators | High Volume Purchases, Price Sensitivity, Market Concentration | Leads to price negotiations, potential margin pressure, and channel performance fluctuations (e.g., 2024 foodservice sales volume contraction). |
| Independent Businesses & Direct Consumers | Low Individual Volume, Fragmented Market | Minimal individual bargaining power, offsetting some pressure from larger clients. |
| Industrial Customers (e.g., Tortillerias) | Switching Costs (quality validation, process recalibration), Product Consistency Needs | Gruma aims to increase these costs through strong relationships and consistent product, reducing customer ability to switch easily. |
What You See Is What You Get
Gruma Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a comprehensive breakdown of Gruma's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Gruma's position as the global leader in corn flour and tortilla production signifies a highly concentrated market. In Mexico, Gruma commands an impressive 50% to 90% of sales in certain regions, establishing it as a formidable incumbent with substantial market power.
Gruma operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, with a vast array of global and local players vying for market share. This includes giants like Nestlé and Grupo Bimbo, who possess significant resources and established distribution networks, alongside numerous smaller, agile regional companies and the ever-present threat of private label brands from major retailers.
The sheer diversity of these competitors means that Gruma faces rivalry not just on a global scale but also within specific product segments and geographic markets. For instance, while Gruma is a leader in corn flour and tortillas, it must contend with different sets of competitors in its various international operations, each with unique strengths and market penetration strategies.
In 2024, the global packaged food market, where Gruma primarily competes, is projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, underscoring the immense scale and the intensity of competition. This broad market encompasses a wide range of products, from staple grains to convenience foods, ensuring that Gruma is constantly challenged by a multitude of entities with varying business models and competitive advantages.
Gruma's competitive edge is significantly shaped by its commitment to product differentiation. The company emphasizes the quality and traditional authenticity of its offerings, particularly its nixtamalized corn flour, a key ingredient that sets its masa harina apart. This focus on heritage and quality resonates with consumers seeking genuine culinary experiences.
Beyond tradition, Gruma is actively innovating in the 'better-for-you' segment, introducing healthier product lines that cater to evolving consumer preferences. This includes options with reduced sodium, whole grains, or alternative flours, addressing growing health consciousness in the market.
The company consistently invests in research and development to introduce new flavors, textures, and dietary alternatives. For instance, in 2024, Gruma continued to explore plant-based ingredients and gluten-free options to broaden its appeal and maintain a leading position in a dynamic food industry.
Pricing Strategies and Market Share Dynamics
Competitive rivalry within the tortilla and corn flour industry, where Gruma operates, often intensifies through aggressive pricing strategies. In certain markets, Gruma has historically maintained higher average prices compared to its rivals, suggesting a degree of market power derived from brand loyalty or product differentiation. However, this pricing advantage can be challenged by economic downturns that weaken consumer spending.
The pressure from a less robust consumer environment has indeed led to Gruma experiencing market share erosion in key regions. For instance, in the U.S. market, Gruma's market share has seen some decline, a trend also observed in Mexico. This suggests that while Gruma possesses pricing strength, it is not immune to competitive pressures exacerbated by economic headwinds.
- Pricing Power vs. Consumer Sensitivity: Gruma's ability to command higher prices in some segments is counterbalanced by consumer sensitivity to economic conditions, impacting market share.
- Regional Market Share Shifts: Data from 2024 indicates Gruma faced challenges in maintaining its market share in the U.S. and Mexico due to intensified competition and a weaker consumer environment.
- Competitive Response to Economic Downturns: Competitors may leverage Gruma's higher price points during economic downturns to gain market share by offering more budget-friendly alternatives.
Geographic Reach and Distribution Networks
Gruma's expansive geographic reach, spanning operations in North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Oceania, is a formidable barrier to entry. This global footprint, supported by over 100 plants and a robust distribution network, allows Gruma to serve diverse markets efficiently, a scale that smaller competitors find difficult to replicate.
Competitors often find themselves at a disadvantage due to a more limited geographic presence. For instance, while Gruma has a strong presence in the United States, a key market, many rivals focus on regional strengths, making it challenging to compete on a global scale for market share and economies of scale.
- Gruma's Global Footprint: Operations in over 100 countries as of late 2023.
- Distribution Network Scale: Extensive logistics infrastructure enabling broad market access.
- Competitive Disadvantage for Rivals: Limited geographic reach hinders ability to match Gruma's market penetration and cost efficiencies.
Gruma faces intense rivalry from a broad spectrum of competitors, ranging from global food conglomerates like Nestlé to agile regional players and private label brands. This competitive pressure is amplified by the sheer size of the global packaged food market, projected to exceed $1.1 trillion in 2024, creating a dynamic environment where differentiation and innovation are crucial for maintaining market share.
While Gruma benefits from brand loyalty and product quality, particularly its nixtamalized corn flour, it must continually adapt to evolving consumer preferences, including a growing demand for healthier options. The company's strategic investments in R&D for plant-based and gluten-free products in 2024 highlight this ongoing effort to stay ahead of the curve.
Economic conditions in 2024 have tested Gruma's pricing power, with some market share erosion observed in key markets like the U.S. and Mexico. This indicates that while Gruma can command premium prices, competitive offerings that are more budget-friendly can gain traction during periods of economic sensitivity, forcing Gruma to balance its premium positioning with market realities.
Gruma's extensive global presence, with over 100 plants and a robust distribution network, presents a significant competitive advantage, making it difficult for rivals with more limited geographic reach to compete effectively on scale and cost efficiencies.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Competitive Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Global Food Conglomerates | Nestlé, Grupo Bimbo | Significant resources, established distribution, broad product portfolios |
| Regional Players | Various local brands | Niche market focus, agility, strong local ties |
| Private Label Brands | Retailer-owned brands | Price sensitivity appeal, direct consumer access |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitutes for corn flour and tortillas are other staple foods such as bread, rice, and potatoes. These alternatives fulfill similar dietary needs and are often selected by consumers based on cultural preferences, prevailing prices, or regional availability.
In 2024, global rice consumption was projected to reach approximately 520 million metric tons, while potato production neared 377 million metric tons, underscoring their significant role as alternative carbohydrate sources. The price volatility of these staples, influenced by weather patterns and global supply chains, directly impacts their attractiveness relative to corn-based products.
Within the flatbread market, wheat tortillas, pita bread, naan, and other varieties represent significant substitutes for Gruma's corn tortillas. Consumers might opt for these alternatives due to taste preferences, specific culinary uses, or a perceived advantage in health benefits, such as the availability of gluten-free options.
For Gruma, a significant threat comes from consumers making their own tortillas at home. This is especially true in areas with deep-rooted culinary traditions where homemade food is highly valued. For instance, in Mexico, where corn is a staple, many households still prepare tortillas from scratch, bypassing commercial products.
Health and Dietary Trends
The growing emphasis on health and wellness significantly impacts the tortilla market. Consumers are increasingly seeking out options that align with specific dietary needs and preferences, such as gluten-free, whole grain, or minimally processed foods. This trend can divert demand away from traditional corn and flour tortillas towards alternatives like lettuce wraps, rice paper, or even entirely different meal categories perceived as healthier.
Gruma is actively addressing this threat through its 'better-for-you' product lines. For instance, Maseca, a key brand, has introduced whole grain and reduced sodium varieties. In 2023, the global gluten-free products market was valued at approximately USD 25.3 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a substantial market for alternatives that Gruma's competitors can target.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: A rise in health-conscious consumers favors foods with perceived health benefits, potentially reducing demand for conventional tortillas.
- Availability of Alternatives: The market offers numerous substitutes, from other grain-based wraps to vegetable-based options, catering to diverse dietary needs.
- Gruma's Mitigation Strategy: The company's investment in 'better-for-you' product development, like whole grain and lower-sodium tortillas, aims to retain market share.
- Market Growth in Health Foods: The expanding market for health-focused food products, including gluten-free and minimally processed items, highlights the competitive pressure from substitutes.
Convenience and Prepared Food Options
The increasing availability of convenient prepared food options presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional meal components like tortillas. Meal kit delivery services, such as HelloFresh and Blue Apron, offer pre-portioned ingredients and recipes, directly competing for consumers seeking quick and easy meal solutions. In 2024, the global meal kit delivery market was valued at approximately $15 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a strong consumer preference for these alternatives.
Grocery stores have also expanded their prepared foods sections, offering ready-to-eat meals and meal components that bypass the need for traditional cooking ingredients. This trend is supported by data showing a steady increase in consumer spending on these items. For instance, in the US, sales of prepared foods in supermarkets have seen consistent year-over-year growth, capturing a larger share of the consumer's food dollar.
Fast-casual restaurants, like Chipotle and Qdoba, provide convenient and customizable meal experiences, often featuring tortilla-based products but as a complete meal solution rather than a component. These establishments cater to consumers looking for quick, affordable, and satisfying meals, directly diverting spending that might otherwise go towards purchasing ingredients like tortillas for home preparation. The fast-casual sector continues to be a dominant force in the food industry, with many chains reporting robust sales figures in 2024, underscoring their competitive appeal.
- Meal Kit Market Growth: The global meal kit delivery market reached around $15 billion in 2024, demonstrating a strong consumer shift towards convenient meal solutions.
- Grocery Prepared Foods: Supermarkets are increasingly offering a wide array of prepared foods, directly competing with traditional grocery items and home cooking.
- Fast-Casual Dominance: Fast-casual restaurants, offering complete meals, continue to capture consumer spending, acting as a significant substitute for meal components.
The threat of substitutes for Gruma's corn flour and tortillas is multifaceted, encompassing other staple foods, alternative flatbreads, and even the trend of home preparation. Consumers have readily available alternatives like rice, potatoes, and wheat-based products, which serve similar dietary functions and are often chosen based on cost, availability, or cultural fit. In 2024, global rice consumption was projected to exceed 520 million metric tons, highlighting its substantial role as a carbohydrate substitute.
Furthermore, the rise of health-conscious eating has introduced substitutes such as lettuce wraps and rice paper, alongside a growing demand for gluten-free and whole-grain options. Gruma is proactively responding by expanding its healthier product lines, recognizing that the global gluten-free market, valued at roughly USD 25.3 billion in 2023, represents a significant area where consumer preferences are shifting away from traditional offerings.
Convenience is another major driver of substitution. Meal kit services and expanded prepared food sections in grocery stores offer consumers ready-made meal solutions, reducing the need for traditional ingredients like tortillas. The fast-casual dining sector, with players like Chipotle, also captures consumer spending by providing complete, convenient meals, further intensifying the competitive landscape for Gruma's core products.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | 2024 Market Insight | Consumer Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other Staple Foods | Rice, Potatoes | Rice consumption projected >520M metric tons | Cost, Availability, Cultural Preference |
| Alternative Flatbreads | Wheat Tortillas, Pita, Naan | N/A (Broad Category) | Taste, Culinary Use, Perceived Health Benefits |
| Health-Conscious Options | Lettuce Wraps, Rice Paper, Gluten-Free Products | Global Gluten-Free Market valued at ~$25.3B (2023) | Dietary Needs, Wellness Trends |
| Convenience & Prepared Foods | Meal Kits, Grocery Prepared Meals, Fast-Casual Restaurants | Meal Kit Market ~$15B (2024) | Time Savings, Ease of Preparation |
Entrants Threaten
The food manufacturing industry, particularly for large-scale operations like Gruma's corn flour and tortilla production, necessitates significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in advanced processing plants, specialized machinery, and robust distribution networks to compete effectively.
These substantial capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, effectively deterring many potential new players from entering the market. For instance, establishing a modern tortilla production facility can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, a figure that limits the pool of viable entrants.
Gruma's established brands, such as Maseca and Mission, have cultivated deep consumer loyalty and widespread recognition over many years. This strong brand equity presents a formidable barrier for any new company attempting to enter the market, requiring substantial investment in marketing and brand building to even approach Gruma's level of consumer trust and awareness.
Gruma's position as a global leader grants significant economies of scale in sourcing, production, and logistics. This translates to lower per-unit costs, creating a substantial barrier for new entrants who struggle to match these efficiencies and compete on price without eroding their margins.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Gruma, a global leader in corn flour and tortillas, benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with retailers and foodservice operators. For instance, in 2024, Gruma's extensive distribution network covered over 100,000 points of sale across more than 100 countries, a testament to decades of investment in logistics and customer partnerships.
New entrants face significant hurdles in replicating this access. Building comparable supply chains and securing shelf space in major supermarkets or contracts with large restaurant chains requires substantial capital and time, often proving prohibitive for emerging competitors.
- Established Distribution Networks: Gruma's global reach and established relationships with over 100,000 retail and foodservice points of sale in 2024 present a formidable barrier.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: New entrants would need to invest heavily to develop the sophisticated and cost-effective supply chains that Gruma currently leverages worldwide.
- Retailer and Foodservice Partnerships: Securing favorable terms and consistent access to key distribution channels is exceptionally difficult for companies lacking Gruma's established track record and market presence.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The food industry presents a formidable barrier to entry due to extensive regulatory oversight. New companies must meticulously adhere to stringent health, safety, and labeling requirements. For instance, in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandates compliance with the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), which imposes significant operational and documentation burdens.
Navigating these complex regulations demands substantial investment in compliance infrastructure and expertise. Obtaining necessary certifications, such as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) or organic certifications, further adds to the initial costs and time-to-market.
- Regulatory Complexity: The food sector is heavily regulated, requiring new entrants to understand and comply with a web of national and international food safety laws.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting these standards involves significant upfront investment in facilities, processes, and personnel training, often running into millions of dollars for large-scale operations.
- Certification Requirements: Obtaining crucial certifications like HACCP or ISO 22000 can be a lengthy and expensive process, acting as a substantial hurdle for smaller or less-resourced new entrants.
- Product Recalls and Liability: The potential for costly product recalls and liability issues due to non-compliance further deters new entrants who may lack established risk management systems.
The threat of new entrants for Gruma is generally low due to several significant barriers. High capital requirements for advanced manufacturing facilities and distribution networks, estimated in the tens of millions for a modern tortilla plant, deter many potential competitors.
Gruma's strong brand loyalty, exemplified by its Maseca and Mission brands, necessitates substantial marketing investment for newcomers to gain traction. Furthermore, Gruma's economies of scale in production and sourcing, coupled with its extensive global distribution network reaching over 100,000 points of sale in 2024, create a significant cost advantage and market access hurdle.
Navigating complex food safety regulations, such as the FDA's FSMA in the US, and obtaining certifications like HACCP add considerable compliance costs and time, further limiting the appeal for new entrants.
| Barrier | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing large-scale corn flour and tortilla production facilities. | Tens of millions of dollars for a modern plant. |
| Brand Loyalty | Building consumer trust and recognition against established brands like Maseca and Mission. | Significant marketing and advertising investment required. |
| Economies of Scale | Matching Gruma's cost efficiencies in sourcing, production, and logistics. | Difficult for new entrants to achieve comparable per-unit costs. |
| Distribution Networks | Replicating Gruma's access to over 100,000 points of sale globally (as of 2024). | Requires substantial investment in logistics and retailer partnerships. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to food safety standards (e.g., FSMA) and obtaining certifications (e.g., HACCP). | Millions in compliance infrastructure, personnel, and certification processes. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Gruma Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from Gruma's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.