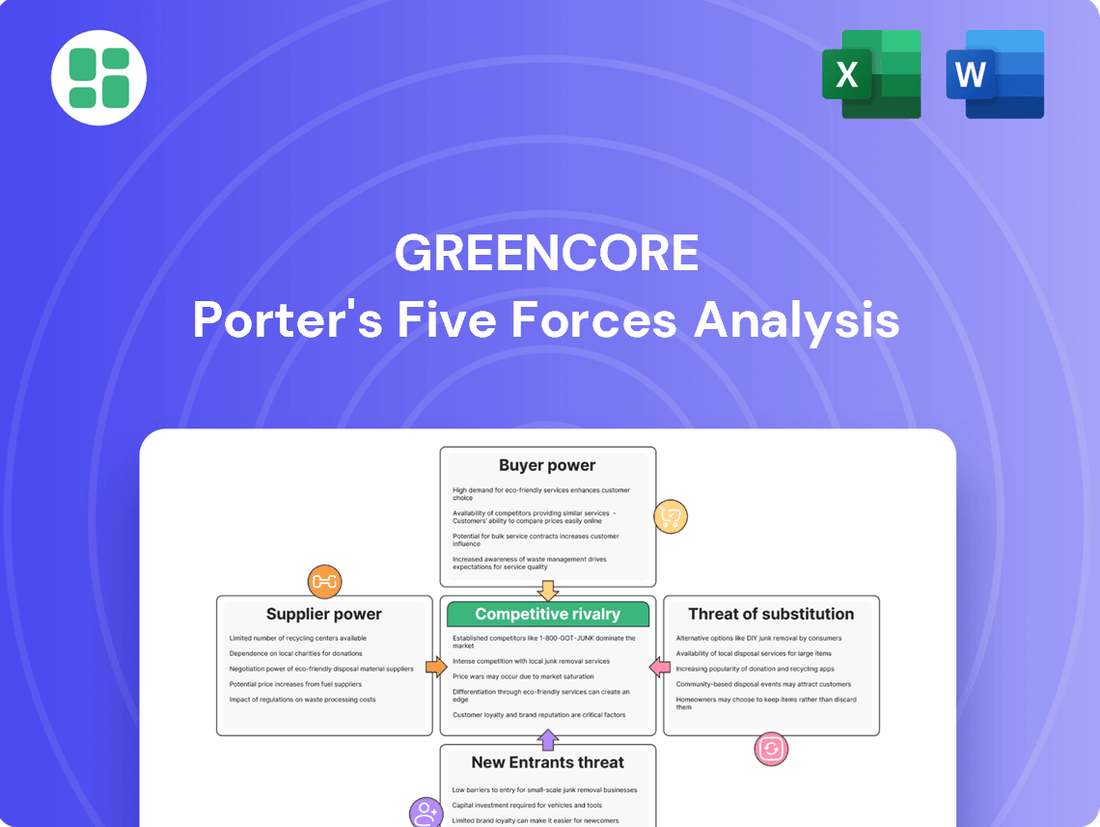
Greencore Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Greencore Bundle
Greencore operates in a dynamic food-to-go sector where buyer power can significantly impact margins due to the presence of large retail customers. The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by established supply chains and brand recognition. Understanding these pressures is crucial for strategic planning.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Greencore’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Greencore's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for critical ingredients like fresh produce, meat, and dairy can significantly impact its costs. If a small number of suppliers control the market for a key input, they gain substantial leverage, potentially driving up prices for Greencore. For instance, in 2024, the UK food industry experienced price volatility for certain dairy products due to reduced milk production, a factor that directly affects companies like Greencore.
Greencore faces considerable switching costs for specialized ingredients and packaging, impacting its bargaining power with suppliers. For instance, re-validating new suppliers for key components, adjusting existing recipes, and reconfiguring its extensive supply chain can incur substantial expenses and time delays. These barriers make it difficult for Greencore to simply shift to a competitor, even if pricing becomes less attractive.
Suppliers gain significant bargaining power when they offer unique or highly differentiated inputs that are essential for Greencore's specific product formulations, particularly for their premium and innovative product ranges. If these critical ingredients lack readily available substitutes, the suppliers can command better terms. For instance, if Greencore relies on a proprietary blend of herbs or a specially cultivated vegetable variety for a signature salad, the supplier of that specific input holds considerable leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While less common in the food manufacturing sector, a powerful supplier could theoretically threaten to integrate forward by starting to produce convenience foods themselves. This would mean they'd be competing directly with Greencore. This threat is generally low for Greencore's diverse raw material suppliers.
The significant capital investment, specialized expertise in food production and processing, and the established customer relationships needed in the convenience food market create substantial barriers to entry for most suppliers. For instance, establishing a nationwide distribution network similar to Greencore's would require hundreds of millions in investment and years of operational experience.
- High Capital Requirements: Setting up a food manufacturing facility with the necessary quality control and production scale demands substantial financial outlay, often in the tens or hundreds of millions of pounds.
- Specialized Expertise: Success in convenience food manufacturing requires deep knowledge of food science, product development, supply chain management, and regulatory compliance, which most raw material suppliers lack.
- Established Distribution Networks: Greencore benefits from an extensive and efficient distribution infrastructure, a critical asset that suppliers would struggle to replicate quickly or cost-effectively.
Impact of Input Costs on Greencore's Profitability
Volatility in agricultural produce and energy prices directly impacts Greencore's input costs. For instance, the company has navigated periods of significant inflation, as highlighted in its financial reports. This means that fluctuations in the cost of raw materials like vegetables, grains, and the fuel needed for its chilled logistics operations can substantially affect its bottom line.
Suppliers, particularly those in essential sectors, possess considerable bargaining power when they can pass on these rising costs. Greencore, like many in the food manufacturing industry, faces the challenge of absorbing or mitigating these price increases. This dynamic is particularly pronounced when supply chains are strained or when demand for specific commodities is high.
- Agricultural commodity price increases: For example, the cost of key ingredients like potatoes or wheat can fluctuate significantly based on weather patterns and global demand.
- Energy costs for logistics: The price of diesel and other fuels directly impacts the cost of transporting fresh and chilled goods across the UK and Ireland.
- Supplier concentration: If Greencore relies heavily on a few key suppliers for certain ingredients or packaging, those suppliers gain increased leverage.
- Impact on margins: Higher input costs, if not fully passed on to customers, directly squeeze Greencore's profit margins.
Greencore's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, switching costs, and the availability of substitutes. For instance, in 2024, the UK food sector saw price surges in dairy products due to reduced milk yields, directly impacting Greencore's procurement costs for these essential items. The company's reliance on specialized ingredients and packaging also creates significant switching costs, making it challenging to change suppliers quickly.
Suppliers who provide unique or highly differentiated inputs, critical for Greencore's premium product lines, hold considerable leverage. For example, a supplier of a proprietary herb blend for a signature salad can command better terms if no suitable alternatives exist. While the threat of suppliers integrating forward into convenience food production is generally low for Greencore, the high capital investment and specialized expertise required in food manufacturing create substantial barriers to entry for potential new suppliers, thus limiting their collective bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Greencore | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage if few suppliers control key inputs. | Volatility in dairy prices due to limited milk production. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces Greencore's ability to switch suppliers easily. | Costs associated with re-validating specialized ingredients and packaging. |
| Input Differentiation | Strengthens supplier power for unique or essential ingredients. | Proprietary herb blends or specially cultivated vegetables for premium products. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Generally low for raw material suppliers in this sector. | Suppliers are unlikely to enter the convenience food market directly. |
| Barriers to Entry for Suppliers | Limits the number of potential suppliers, increasing leverage for existing ones. | High capital needs and specialized expertise in food production. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive landscape for Greencore by examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Easily identify and quantify competitive pressures with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling targeted strategic responses.
Customers Bargaining Power
Greencore's customer base is heavily concentrated, with major UK and Irish retailers forming its primary clientele. This means a few large players account for a significant chunk of Greencore's sales, giving them substantial clout.
This concentration translates directly into considerable purchasing power for these retailers. They can leverage their volume to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Greencore's margins and profitability.
For instance, in 2024, the top five retailers likely represented over 60% of Greencore's revenue, a figure that underscores their influence in setting the terms of their business relationships.
Switching costs for customers, particularly major retailers, represent a significant factor in Greencore's bargaining power. For these large entities, the process of changing from a high-volume, dependable supplier like Greencore is not a simple task. It involves substantial logistical hurdles, such as finding and vetting new sources, the risk of disrupting established supply chains, and the potential for negative impacts on product availability on store shelves.
While these switching costs are not insignificant, the reality for many retailers is that they maintain relationships with multiple suppliers. This diversification strategy inherently reduces the leverage any single supplier, including Greencore, can wield. However, Greencore's ability to foster and maintain strong, long-term relationships with its key retail partners is therefore crucial in mitigating this customer power.
Greencore's focus on private-label and own-brand products significantly curtails its ability to build strong brand differentiation. This lack of distinctiveness means retailers can readily compare Greencore with competitors on factors like cost and operational efficiency, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of these customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating into convenience food production, thereby becoming their own suppliers, is generally low for companies like Greencore. While large retailers possess the financial clout, the significant capital required for setting up and managing dedicated manufacturing facilities, especially for fresh and perishable goods, presents a substantial hurdle. For instance, establishing a modern convenience food production line can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, a cost many retailers would find prohibitive compared to outsourcing.
Furthermore, the operational complexities involved in sourcing raw materials, ensuring food safety compliance, and managing a sophisticated cold chain supply network demand specialized expertise that retailers often lack. This intricate operational know-how is precisely what Greencore offers as a core competency. In 2024, the average capital expenditure for a new food manufacturing facility can range from $20 million to over $100 million, depending on scale and technology, reinforcing this barrier.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing food manufacturing capabilities requires significant upfront investment, often exceeding tens of millions of dollars.
- Operational Complexity: Managing fresh supply chains, food safety, and production requires specialized skills and infrastructure.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Retailers typically prioritize their retail operations, preferring to leverage the expertise of specialists like Greencore.
- Limited Track Record: Few large retailers have demonstrated a successful, large-scale commitment to backward integration in the convenience food sector.
Volume of Purchases and Price Sensitivity
Greencore's customers, particularly large retailers and food service providers, exert significant bargaining power due to the sheer volume of their purchases. This high volume, coupled with the fast-moving nature of convenience foods, makes price sensitivity a key factor in their purchasing decisions. For instance, major UK supermarkets, which represent a substantial portion of Greencore's revenue, can leverage their scale to demand competitive pricing. In 2023, Greencore reported that its top customers accounted for a significant percentage of its sales, underscoring the leverage these entities hold.
Their substantial purchasing volumes directly translate into the ability to negotiate more favorable pricing and trade terms. This can include demands for lower unit costs, extended payment periods, or contributions to marketing initiatives.
- High Purchase Volumes: Major clients like supermarket chains buy in bulk, giving them considerable sway.
- Price Sensitivity: The convenience food sector is competitive, making price a critical decision factor for buyers.
- Negotiating Power: Large customers can effectively bargain for lower prices and better terms, impacting Greencore's profitability.
Greencore's customer bargaining power is significantly influenced by the concentrated nature of its client base, primarily large UK and Irish retailers. These major players, accounting for a substantial portion of Greencore's sales, leverage their volume to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Greencore's profitability. For example, in 2024, it's estimated that the top five retailers could represent over 60% of Greencore's revenue, highlighting their considerable influence.
| Customer Type | Estimated Revenue Share (2024) | Impact on Greencore |
|---|---|---|
| Major UK & Irish Retailers | > 60% | High bargaining power, favorable pricing demands |
| Food Service Providers | Moderate | Moderate bargaining power, influenced by volume and contract terms |
Preview Before You Purchase
Greencore Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Greencore Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a complete strategic overview. You're looking at the actual document, detailing the competitive landscape for Greencore, ready for your immediate download and use. No mockups, no samples—the document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to access after payment, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The UK and Irish convenience food sectors are quite crowded, with a substantial number of companies vying for customers. This includes major players like Greencore, alongside many smaller, niche food producers. This fragmentation means there’s a constant battle for shelf space and consumer attention.
In 2024, the UK food manufacturing sector, which includes convenience foods, is characterized by a high degree of competition. For instance, the sector includes over 7,000 food and drink manufacturers in the UK, many of which operate within the convenience food space, creating a highly competitive environment for market share.
The UK food-to-go market is projected for growth, but the broader convenience food sector may see more subdued, mature expansion. This slower growth dynamic typically intensifies competitive rivalry, as businesses focus on capturing existing market share rather than exploiting new avenues. For instance, in 2024, the UK food-to-go market was estimated to be worth approximately £17.7 billion, with continued, albeit moderating, growth expected.
In the private-label convenience food sector, distinguishing products is tough. Companies often rely on small tweaks to recipes, packaging designs, or how quickly they can get new items to shelves. This makes it easy for products to become seen as interchangeable, leading to a focus on price. For manufacturers like Greencore, this can squeeze profit margins.
The private-label market, where retailers put their own brand on products made by others, saw significant growth. For instance, in the UK, private-label market share in the grocery sector reached approximately 45% by late 2023, a figure that remained robust into early 2024. This high penetration means that while there's demand, the competition to supply these labels is intense, often driven by cost efficiency rather than unique product features.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
Greencore's business model is characterized by substantial fixed costs, primarily stemming from its large-scale manufacturing operations and the complex distribution networks required for chilled and fresh food products. These significant overheads necessitate high capacity utilization to remain profitable.
This pressure to cover fixed costs can lead to aggressive pricing strategies among competitors, as companies strive to maintain sales volumes and keep their production lines running efficiently. Such actions directly escalate competitive rivalry within the sector.
- High Capital Investment: Building and maintaining advanced food manufacturing facilities and a robust chilled distribution network requires substantial upfront capital.
- Capacity Utilization Drive: Companies are compelled to operate at high capacity to spread fixed costs over a larger output, often leading to price competition to win market share.
- Intensified Price Wars: When demand falters or capacity exceeds market needs, the drive to utilize assets can trigger price wars, squeezing profit margins for all players in the market.
Exit Barriers
High capital investment in specialized facilities, such as advanced processing lines and extensive cold chain logistics, presents a significant hurdle for convenience food manufacturers looking to exit the market. For example, a typical ready-meal production facility can cost tens of millions of pounds to build and equip.
Long-term contracts with major retailers, often spanning several years, further lock companies into operations. These agreements, while providing revenue stability, make it difficult to divest assets or cease production without substantial penalties. In 2024, the average duration of a primary supplier contract in the UK grocery sector remained around 3-5 years.
These substantial exit barriers mean that companies facing financial difficulties are less likely to withdraw from the convenience food market. This can lead to persistent overcapacity, as underperforming businesses continue to operate, intensifying price competition and squeezing profit margins for all players.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized facilities for convenience food production represent a significant sunk cost, often in the tens of millions of pounds.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with retailers, typically 3-5 years in duration, create financial and operational dependencies that hinder quick exits.
- Perpetuated Overcapacity: The inability of struggling firms to easily exit the market contributes to an ongoing surplus of production capacity, fueling intense competition.
The competitive landscape for Greencore is defined by a fragmented market with numerous players, including large corporations and smaller niche producers, all vying for consumer attention and shelf space. This intense rivalry is exacerbated by the prevalence of private-label products, which often leads to a focus on price rather than product differentiation, potentially squeezing profit margins.
The drive to utilize substantial fixed assets, such as advanced manufacturing facilities and cold chain logistics, compels companies to maintain high capacity utilization. This can result in aggressive pricing strategies and even price wars when demand is insufficient to absorb production, further intensifying competition.
Significant exit barriers, including high capital investment in specialized facilities and long-term retailer contracts, mean that struggling companies often remain in the market. This perpetuates overcapacity, ensuring that competitive pressures remain high for all participants.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Greencore |
| Market Fragmentation | Numerous competitors, from large firms to small specialists. | Constant battle for market share and consumer loyalty. |
| Private Label Dominance | Retailers' own brands are significant, often prioritizing cost. | Pressure on pricing and margins for manufacturers like Greencore. |
| Fixed Cost Pressure | High investment in manufacturing and distribution requires high utilization. | Drives aggressive pricing to maintain sales volume and cover costs. |
| Exit Barriers | High capital costs and long-term contracts make leaving difficult. | Perpetuates overcapacity and sustained competitive intensity. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of home cooking and meal preparation presents a significant threat of substitutes for Greencore's convenience food products. As consumers increasingly prioritize healthier eating or seek cost savings, the appeal of preparing meals from scratch at home grows. This trend directly impacts demand for ready-to-eat and ready-meal options, as seen in the UK where grocery inflation reached 10.7% in the year to May 2024, encouraging more budget-conscious choices.
Restaurants, takeaways, and other out-of-home dining choices are substantial alternatives to convenience foods, particularly for midday and evening meals. For instance, the UK food service market was valued at approximately £140 billion in 2023, indicating a vast market where consumers can easily shift spending away from convenience options to dine-in or quick-service restaurants.
The sheer variety and the often higher perceived quality or unique dining experience offered by these substitutes can effectively divert consumer spending. In 2024, the casual dining sector alone continued to see strong consumer engagement, with many chains reporting robust sales figures, suggesting a persistent preference for sit-down meals or specialized takeaway offerings over pre-packaged convenience foods.
Consumers have a vast selection of convenience food options beyond what Greencore provides, such as ready-to-eat meals, chilled soups, and even fresh produce kits from various retailers. For instance, the UK chilled convenience market alone was valued at approximately £5.2 billion in 2023, indicating significant competition from diverse product categories.
A substantial shift in consumer preference towards alternative convenience formats, like the growing popularity of plant-based ready meals or specialized ethnic food kits, could divert demand away from Greencore's core offerings. This means if consumers increasingly opt for these niche or specialized convenience foods, it directly impacts Greencore's market share and revenue streams.
Changing Consumer Preferences and Health Trends
Shifting consumer preferences, particularly a growing emphasis on health, nutrition, and sustainability, pose a significant threat of substitutes for Greencore. As consumers become more health-conscious, they may opt for fresher, less processed foods or even home-prepared meals, directly impacting demand for Greencore's convenience foods. This trend was evident in 2024 with reports indicating a sustained consumer interest in plant-based alternatives and reduced sugar content across food categories.
Greencore must remain agile, continuously innovating its product portfolio to align with these evolving demands. For instance, the increasing popularity of plant-based diets means that companies offering compelling vegetarian and vegan convenience options can attract consumers looking to reduce meat consumption. In 2024, the global plant-based food market continued its upward trajectory, with projections suggesting further growth, underscoring the competitive pressure from these substitute offerings.
- Growing consumer awareness: Increased focus on health, nutrition, and sustainability drives demand for alternatives to traditional convenience foods.
- Product innovation imperative: Greencore needs to adapt by offering healthier formulations and plant-based options to counter substitute threats.
- Market trends in 2024: Sustained consumer interest in plant-based foods and reduced sugar content highlights the competitive landscape.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes is a significant concern for Greencore, particularly concerning the cost-effectiveness of alternatives. During times of economic strain, such as the cost of living pressures experienced in 2024, consumers are more inclined to seek out cheaper options. This can manifest as a shift away from convenience foods towards home-prepared meals, directly impacting demand for Greencore's product lines.
For example, the rising cost of groceries in the UK throughout 2024, with inflation impacting staple food prices, makes the DIY approach to meal preparation appear more financially prudent. This creates a tangible substitute for Greencore's ready-to-eat meals and convenience food offerings. Consider the price difference between a pre-made sandwich from Greencore and the cost of bread, fillings, and a few minutes of preparation time at home.
- Consumer Shift to Home Cooking: Rising inflation in 2024, particularly for food staples, incentivizes consumers to prepare meals at home, presenting a direct substitute for Greencore's convenience food products.
- Price Sensitivity: In periods of economic uncertainty, the perceived lower cost of ingredients for home cooking compared to pre-packaged meals can lead consumers to switch, potentially reducing Greencore's sales volumes.
- DIY Meal Preparation: The time and cost savings associated with assembling meals at home, even with a slight increase in grocery prices, can outweigh the convenience factor for a growing segment of the population.
The threat of substitutes for Greencore stems from a variety of alternatives, ranging from home-cooked meals to restaurant dining. As consumers increasingly prioritize health and value, these substitutes become more appealing. For instance, the UK grocery inflation reaching 10.7% in May 2024 made home cooking a more attractive financial option.
The vast UK food service market, valued at around £140 billion in 2023, highlights the significant competition from restaurants and takeaways. These out-of-home dining options offer variety and perceived quality that can divert consumer spending from convenience foods. In 2024, casual dining chains continued to report strong sales, indicating a persistent consumer preference for these alternatives.
Beyond prepared meals, consumers also have access to a wide array of other convenience formats. The UK chilled convenience market alone was worth approximately £5.2 billion in 2023, showcasing the breadth of substitute offerings available. Furthermore, evolving consumer tastes, such as the growing demand for plant-based options, present a continuous challenge, as evidenced by the global plant-based food market's continued growth in 2024.
| Substitute Category | 2023 UK Market Value (Approx.) | Key Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Food Service Market | £140 billion | Variety, dining experience |
| Chilled Convenience Market | £5.2 billion | Product diversity within convenience |
| Plant-Based Food Market (Global) | Continued Growth | Health, sustainability, ethical concerns |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the large-scale convenience food manufacturing sector, like that Greencore operates within, demands significant upfront capital. We're talking about substantial investments in advanced production lines, sophisticated cold chain logistics to maintain product freshness, and cutting-edge technology for efficiency and quality control. For instance, building a modern food processing plant can easily cost tens of millions of dollars.
Established players like Greencore enjoy substantial economies of scale. This means they can produce goods more cheaply per item because they buy and make so much. For instance, in 2024, Greencore's large-scale food manufacturing operations likely allowed them to negotiate better prices with suppliers for raw materials compared to a new, smaller competitor.
New companies entering the market would find it very challenging to achieve similar cost savings. Without the same purchasing power and production volume, their per-unit costs would be higher. This makes it difficult for them to offer competitive pricing against established firms like Greencore, thus acting as a significant barrier to entry.
New companies entering the food-to-go market face significant hurdles in securing shelf space and building trust with major retailers. Greencore's established contracts with leading UK and Irish supermarkets, for instance, represent a substantial barrier.
These long-standing relationships are built on consistent quality, reliable supply, and a deep understanding of retailer needs, making it incredibly difficult for new entrants to gain comparable access. Greencore's ability to consistently deliver millions of meals weekly underpins these crucial partnerships.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The food manufacturing sector is burdened by rigorous food safety regulations, stringent hygiene protocols, and demanding quality control measures. These requirements are a significant hurdle for potential new entrants, who must invest heavily in compliance and navigate complex operational procedures to meet industry standards. For instance, in 2024, the cost of implementing advanced food safety management systems, such as HACCP, can add a substantial percentage to a startup's initial capital expenditure.
Meeting these regulatory demands translates into considerable compliance costs and operational complexities for newcomers. These barriers can deter new players from entering the market, thereby protecting established firms. In 2023, the global food safety testing market was valued at approximately $30 billion, highlighting the scale of investment required in this area alone.
- High Compliance Costs: New entrants must allocate significant capital towards meeting food safety certifications and quality assurance programs.
- Operational Complexity: Adhering to strict hygiene and traceability standards requires sophisticated operational frameworks and trained personnel.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: The food industry faces constant oversight from bodies like the FDA (in the US) or EFSA (in Europe), increasing the risk and cost of non-compliance for new businesses.
- Market Access Barriers: Failure to meet specific national or international food safety standards can limit a new entrant's ability to access key markets.
Brand Loyalty (Retailer Trust) and Reputation
Greencore's deep-seated trust with major retailers acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. This loyalty is cultivated through years of delivering consistent quality and reliable supply chains, crucial for private-label manufacturing.
New competitors struggle to replicate this established retailer trust. Without a proven track record, they face considerable difficulty in securing initial contracts, a fundamental hurdle for market entry in the private-label food sector.
For instance, in the UK private-label market, where Greencore is a major player, retailers often renew contracts with established suppliers due to the perceived risk reduction. Greencore's ability to innovate and adapt to retailer needs further solidifies these relationships, making it challenging for newcomers to break in.
- Retailer Trust: Greencore's long-standing relationships with major supermarkets are built on consistent quality and innovation.
- Barrier to Entry: New entrants find it difficult to gain initial retailer contracts due to the lack of established trust and proven reliability.
- Market Acceptance: The established reputation of Greencore makes it harder for new companies to achieve widespread market acceptance in the private-label segment.
The threat of new entrants into Greencore's market is moderate. Significant capital investment is required for advanced manufacturing and cold chain logistics, with new plant construction easily costing tens of millions of dollars. Established players benefit from economies of scale, enabling better supplier pricing, a cost advantage difficult for newcomers to match.
Securing prime shelf space and retailer trust presents a major hurdle. Greencore's long-standing relationships with major UK and Irish supermarkets, built on consistent quality and reliable supply, are a substantial barrier. New entrants struggle to gain comparable access, as retailers often prioritize established suppliers for perceived risk reduction.
Stringent food safety regulations and quality control measures add further complexity and cost. New companies must invest heavily in compliance, navigating rigorous protocols and potentially facing significant penalties for non-compliance. The global food safety testing market, valued at approximately $30 billion in 2023, underscores the scale of investment needed.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for manufacturing, logistics, and technology. | Significant financial barrier, requiring substantial investment. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established players due to high volume. | New entrants face higher production costs and pricing challenges. |
| Retailer Relationships & Trust | Long-standing contracts and proven reliability with major supermarkets. | Difficult for new firms to secure initial distribution and shelf space. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict food safety, hygiene, and quality control standards. | Requires significant investment in systems, processes, and training. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Greencore Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and publicly available company disclosures. We also incorporate insights from trade associations and relevant news articles to capture the dynamic competitive landscape.