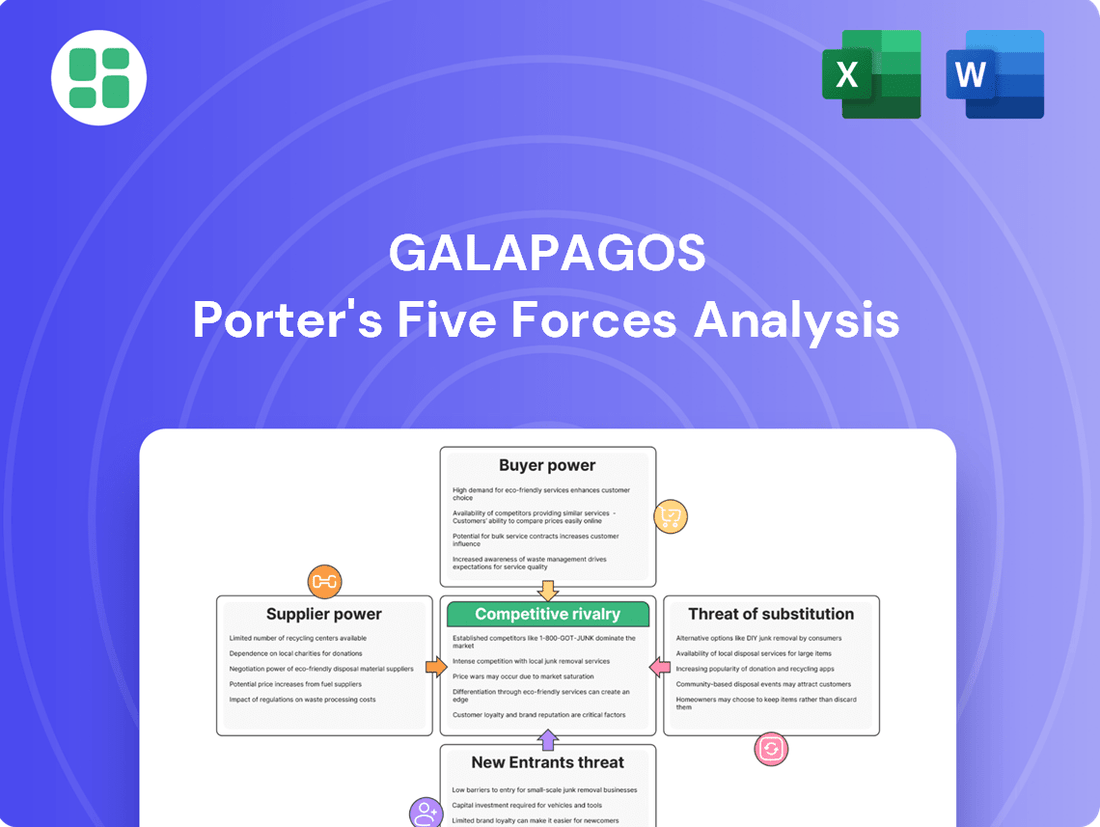
Galapagos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Galapagos Bundle
Galapagos's competitive landscape is shaped by the bargaining power of its buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry within the biotechnology sector. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its strategic path.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Galapagos’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Galapagos, a biotechnology firm, depends on highly specialized raw materials and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) for its drug development pipeline. The unique and often proprietary nature of these components means suppliers can wield considerable influence, particularly when alternative sources are scarce.
The bargaining power of these specialized suppliers is amplified by factors like limited production capacity and the complex regulatory hurdles involved in producing pharmaceutical-grade materials. For instance, a single supplier of a critical intermediate for a Galapagos drug candidate could command higher prices if few others can meet the stringent quality and volume requirements.
In 2024, the global pharmaceutical supply chain faced ongoing challenges, including increased demand for certain APIs and lingering effects of past disruptions. This environment generally favors suppliers of niche materials, potentially impacting Galapagos's cost of goods sold and the timeline for bringing new therapies to market.
Galapagos' reliance on Contract Research Organizations (CROs) for crucial clinical trial activities means these service providers hold significant sway. The CRO landscape is quite consolidated, with giants like IQVIA and Labcorp dominating, offering extensive global networks and a broad spectrum of services.
This concentration of power, coupled with a rising demand for outsourced clinical research and specialized skills in cutting-edge areas like cell and gene therapies, further strengthens the bargaining position of these key CRO players.
Suppliers of foundational intellectual property, like gene editing technologies or drug targets, hold sway through licensing. Galapagos’s reliance on its proprietary discovery platform means it might still need to license external IP, granting licensors leverage over terms and royalties. For instance, in 2024, the global biotechnology licensing market continued its robust growth, with deal values for early-stage assets often reflecting the scarcity and novelty of the underlying IP.
Specialized Equipment and Technology Providers
The biotechnology sector, particularly areas like cell therapy, is heavily reliant on highly specialized and advanced equipment. Providers of these critical technologies, such as cell therapy platforms, often operate with limited competition. This scarcity can translate into significant bargaining power for these suppliers, influencing pricing, service agreements, and the pace of technological upgrades. For Galapagos, whose strategy involves a decentralized cell therapy manufacturing network, this dependence on specialized infrastructure is a key consideration.
Galapagos's reliance on a select group of suppliers for its advanced manufacturing needs, including those for cell therapy, means these providers can exert considerable influence. For instance, the cost of specialized bioreactors or cell processing equipment can represent a substantial portion of a biotech company's capital expenditure. While specific figures for Galapagos's supplier contracts are proprietary, the broader industry trend shows that companies in this space often face high upfront investment for essential technology, underscoring supplier leverage.
- Limited Supplier Pool: The niche nature of advanced biotech equipment, like cell therapy manufacturing systems, restricts the number of viable providers.
- High Switching Costs: Transitioning to alternative suppliers for highly integrated and validated equipment can be costly and time-consuming, further solidifying supplier power.
- Technological Dependence: Companies like Galapagos depend on these specialized suppliers for the very core of their innovative therapies, granting suppliers significant leverage.
Skilled Labor and Scientific Expertise
The talent pool for highly specialized scientific and clinical expertise in biotechnology, particularly in areas like inflammatory, fibrotic diseases, and cell therapy, is quite limited. This scarcity directly translates into significant bargaining power for skilled researchers, clinicians, and technical staff.
This elevated bargaining power means that companies like Galapagos often face competitive pressures to offer higher salaries and more attractive benefits packages to secure and retain this crucial talent. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior research scientist in the biotech sector in key hubs like Boston or San Francisco could range from $150,000 to $200,000 annually, reflecting this demand.
- Limited Talent Pool: Niche areas in biotech, such as inflammatory and fibrotic diseases, have a restricted supply of highly specialized scientific and clinical professionals.
- Increased Operational Costs: The scarcity of skilled labor drives up compensation, directly impacting Galapagos' operational expenses through competitive salaries and benefits.
- Impact on Innovation: Access to top-tier scientific talent is critical for R&D success, and their bargaining power influences the company's ability to attract and retain the expertise needed for innovation.
Galapagos faces significant bargaining power from suppliers of specialized raw materials and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), particularly those with unique or proprietary components. The limited availability of alternative sources, coupled with stringent quality and regulatory demands in 2024, allows these suppliers to command higher prices, impacting Galapagos's cost of goods and development timelines.
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential within the Galapagos market by examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive threats and opportunities with a visual breakdown of each Porter's Force, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Galapagos's primary customers are healthcare systems and large payers like insurance companies and government health programs. These entities hold significant bargaining power because they purchase in large volumes and can dictate which drugs are included in formularies and at what reimbursement rates. For instance, in 2024, many national health services and private insurers continued to negotiate aggressively on drug prices, impacting the profitability of pharmaceutical companies.
Physicians and healthcare providers hold significant bargaining power within the pharmaceutical industry, even though they aren't the direct payers. Their influence is paramount because they are the gatekeepers who decide which treatments patients receive. In 2024, the increasing availability of diverse therapeutic options means physicians can more readily switch between or favor drugs based on factors like patient outcomes and ease of administration, directly impacting drug sales for companies like Galapagos.
This power is amplified by their deep understanding of clinical efficacy and safety data. Physicians rely on evidence-based medicine and often adhere to treatment guidelines established by medical societies, which can create barriers for new or less-established therapies. For instance, if a Galapagos drug lacks robust real-world evidence or fails to demonstrate a clear advantage over existing treatments in late 2024 studies, physicians may be hesitant to prescribe it, thereby limiting its market penetration.
The availability of alternative treatments significantly impacts customer bargaining power. If patients or healthcare providers have access to comparable therapies, whether they are generic versions, biosimilars, or treatments from rival pharmaceutical firms, their ability to negotiate prices with Galapagos increases. For instance, in 2024, the market penetration of biosimilars for several blockbuster biologic drugs continued to grow, offering significant cost savings and thus empowering payers and patients to demand lower prices from originators.
Should Galapagos's novel medicines not provide a demonstrably superior advantage in efficacy, safety profile, or overall cost-effectiveness compared to existing or emerging alternatives, customers are more likely to explore these other options. This diminishes Galapagos's leverage in setting prices, as the perceived value of their offerings is directly challenged by the accessibility and competitiveness of substitutes.
Regulatory and Policy Landscape
Government regulations and policies significantly influence the bargaining power of customers in the pharmaceutical sector. For example, initiatives like the Medicare Drug Price Negotiation program in the US, enacted through the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, directly empower government payers to negotiate prices for certain high-cost drugs. This can exert downward pressure on pricing across the entire market, including the commercial sector, thereby increasing the bargaining power of other payers and large purchasers.
These policy shifts can lead to tangible financial impacts. For 2024, Medicare is slated to negotiate prices for up to 10 Part D drugs. This move is expected to generate significant savings for the government and beneficiaries, potentially setting precedents for future negotiations and influencing pricing strategies of pharmaceutical companies like Galapagos.
The broader regulatory environment, including potential price controls or mandatory spending growth targets in healthcare systems globally, further amplifies customer bargaining power. Such policies aim to curb healthcare expenditures, forcing pharmaceutical companies to be more competitive on price and value proposition to secure market access and favorable reimbursement terms.
- Increased Negotiation Leverage: Government price negotiation programs directly reduce the prices of selected drugs, enhancing the bargaining power of payers.
- Market Spillover Effects: Lower prices negotiated with government programs often influence pricing in the commercial market, benefiting private insurers and employers.
- Focus on Value: Regulatory pressure encourages a greater emphasis on demonstrating drug value and cost-effectiveness, shifting the negotiation dynamic towards outcomes.
- Potential for Broader Price Controls: The trend towards government intervention in drug pricing could expand, further strengthening customer bargaining power in the future.
Patient Advocacy and Influence
Patient advocacy groups, though not direct purchasers, wield significant influence over treatment choices and public opinion. Their collective voice can pressure both healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies. This pressure often focuses on crucial issues like drug accessibility, cost, and the development of treatments that truly meet patient needs. For Galapagos, this means their market strategies and pricing decisions can be indirectly shaped by the advocacy landscape.
These organizations can impact Galapagos by:
- Advocating for specific treatment protocols that may favor or disfavor Galapagos's pipeline drugs.
- Influencing reimbursement decisions by highlighting the value and necessity of innovative therapies.
- Raising public awareness about diseases Galapagos targets, potentially increasing demand for its treatments.
- Pushing for faster regulatory approvals for drugs addressing unmet medical needs.
Galapagos's customers, primarily large healthcare systems and payers, possess considerable bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volumes and ability to dictate formulary inclusion and reimbursement rates. In 2024, aggressive price negotiations by national health services and private insurers continued to affect pharmaceutical profitability.
Physicians, acting as gatekeepers for treatment decisions, also exert significant influence. The growing array of therapeutic options in 2024 allowed them to favor drugs based on efficacy and ease of use, impacting Galapagos's sales.
The availability of alternative treatments, including generics and biosimilars, further empowers customers to negotiate prices. The expanding biosimilar market in 2024 provided cost savings, enabling payers and patients to demand lower prices from originator drug companies.
Government regulations, such as Medicare's drug price negotiation program, directly enhance payer bargaining power. For 2024, Medicare's planned negotiations for up to 10 Part D drugs are expected to influence pricing strategies across the industry.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Galapagos | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Systems/Payers | High Volume Purchasing | Ability to negotiate lower prices, limit market access | Aggressive price negotiations by national health services and private insurers |
| Physicians | Treatment Decision Authority | Influence prescription patterns, favor competing drugs | Increasing preference for drugs based on efficacy and ease of administration |
| Patients | Demand for Cost-Effective Treatments | Pressure for lower prices, especially with alternatives | Growing demand for biosimilars and generics |
| Government Agencies | Regulatory Power, Price Negotiation | Directly negotiate prices, set market precedents | Medicare's planned negotiation for up to 10 Part D drugs in 2024 |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Galapagos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Galapagos Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase. It meticulously details the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing firms within the Galapagos tourism industry. You can trust that this document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, offering actionable insights without any surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Galapagos operates in the highly competitive biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors, facing a crowded field of both large, established pharmaceutical companies and nimble, emerging biotech firms. This intense rivalry is particularly pronounced in its focus areas, such as inflammatory and fibrotic diseases, where numerous players are striving to address significant unmet medical needs.
In 2024, the global biopharmaceutical market continued its robust growth, with significant investments pouring into research and development for novel therapies. For instance, the inflammatory disease market alone was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, showcasing the immense commercial opportunity but also the fierce competition to capture market share.
This competitive pressure means Galapagos must constantly innovate and differentiate its pipeline to stand out. Companies like AbbVie, with its significant presence in immunology, and numerous other biotechs developing JAK inhibitors or other targeted therapies, represent direct and indirect competitors, all vying for patient populations and physician adoption.
Galapagos operates in a highly competitive landscape where the relentless pursuit of innovation and substantial Research and Development (R&D) investments are paramount. This drives a constant race to identify and develop groundbreaking drug candidates, demanding significant financial resources and scientific expertise.
Companies in this sector, including Galapagos, are continually striving to bring first-in-class or best-in-class therapies to market. For instance, in 2023, the biopharmaceutical industry saw R&D spending reach record levels, with major players allocating billions to pipeline development, underscoring the high stakes involved in this innovation race.
Galapagos's strategy hinges on differentiating its products through superior efficacy, safety, and novel mechanisms of action. This is particularly important in the biopharmaceutical industry where innovation is key to gaining a competitive edge.
However, the threat of generic and biosimilar competition escalates significantly once patents expire, leading to intense price-based rivalry. For instance, the market for biologics often sees substantial price drops post-patent expiry, impacting profitability.
Galapagos's proprietary target discovery platform and its focus on cell therapy are designed to create strong product differentiation. This approach aims to build a robust pipeline of unique treatments that are less susceptible to immediate generic competition.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are characterized by robust merger and acquisition (M&A) activity. Larger, established pharmaceutical companies frequently acquire smaller, innovative biotech firms to enhance their drug pipelines and gain access to new technologies. This consolidation strategy is a significant driver of competitive rivalry, as it can quickly reshape the market by creating more formidable, diversified competitors.
For instance, in 2024, the biopharmaceutical industry continued its M&A trend. Major deals included Pfizer's acquisition of Seagen for approximately $43 billion, aimed at strengthening its oncology portfolio. Similarly, Eli Lilly's acquisition of Loxo Oncology at Lilly for $8 billion in late 2023, which closed in early 2024, bolstered its targeted cancer therapies. These strategic moves are designed to consolidate market share and accelerate innovation, thereby intensifying competition among the remaining players.
- 2024 M&A Trend: Continued consolidation in biotech, with large pharma acquiring smaller firms to boost R&D pipelines.
- Key Deals (2023-2024): Pfizer's $43 billion acquisition of Seagen and Eli Lilly's $8 billion acquisition of Loxo Oncology at Lilly highlight this trend.
- Impact on Rivalry: M&A activity rapidly alters the competitive landscape, creating larger, more diversified, and often stronger rivals.
High Exit Barriers
The biotechnology industry, including Galapagos NV, faces substantial exit barriers due to the immense fixed costs tied to research and development, specialized manufacturing facilities, and highly skilled personnel. These investments are substantial, making it incredibly difficult and costly for companies to simply shut down operations.
These high exit barriers mean that even companies experiencing low profitability may continue to operate, prolonging their presence in the market. This persistence, driven by the inability to easily divest assets or recoup investments, can consequently intensify competition among existing players.
- High R&D Investment: The average cost to bring a new drug to market can exceed $2 billion, a significant portion of which is R&D, creating a substantial sunk cost.
- Specialized Facilities: Biotech manufacturing requires highly specialized and expensive equipment, often built to stringent regulatory standards, which are not easily repurposed.
- Skilled Workforce: The reliance on highly specialized scientific and technical talent means that workforce restructuring or layoffs can be complex and costly.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Exiting a regulated market involves significant administrative and compliance costs to wind down operations properly.
Galapagos contends with intense rivalry from both established pharmaceutical giants and agile biotech startups, particularly in its core therapeutic areas. This competition is fueled by the significant unmet medical needs and the substantial market potential, driving continuous innovation and investment in research and development.
The biopharmaceutical sector in 2024 saw companies like AbbVie and others actively developing novel therapies, especially in immunology, directly challenging Galapagos's pipeline. Innovation is paramount, with companies striving for first-in-class or best-in-class treatments.
Mergers and acquisitions further intensify this rivalry. For instance, Pfizer's $43 billion acquisition of Seagen in 2024 and Eli Lilly's $8 billion acquisition of Loxo Oncology at Lilly in early 2024 demonstrate the trend of large players consolidating to bolster their portfolios, creating formidable competitors.
Galapagos faces significant competitive rivalry due to the high barriers to exit in the biotech sector, stemming from massive R&D investments and specialized infrastructure. This makes it difficult for companies to withdraw, leading to prolonged market presence and sustained competition among existing players.
| Competitor Type | Example Competitors | Key Competitive Factor | 2024 Market Context |
| Large Pharma | AbbVie, Pfizer, Eli Lilly | Extensive R&D budgets, established market access, M&A capabilities | Continued M&A activity, focus on oncology and immunology |
| Biotech Firms | Numerous emerging companies | Pipeline innovation, novel mechanisms of action, speed to market | High investment in novel therapies, focus on unmet needs |
| Generic/Biosimilar | Various | Price competition post-patent expiry | Increasing threat as patents on successful drugs expire |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Existing small molecule drugs and biologics from other pharmaceutical giants targeting inflammatory and fibrotic diseases present a significant threat of substitutes for Galapagos's innovative medicines. For instance, in 2024, established treatments for rheumatoid arthritis, a key area for Galapagos, continued to hold substantial market share. If Galapagos's pipeline candidates don't showcase a demonstrably superior efficacy, safety profile, or a more favorable cost-effectiveness compared to these widely adopted alternatives, patient and physician adoption could be hindered.
The biotechnology landscape is constantly evolving, bringing forth novel therapeutic modalities that could act as substitutes for Galapagos’ current and pipeline treatments. For instance, advancements in gene editing technologies or engineered cell therapies developed by competitors might offer alternative solutions for diseases currently addressed by small molecules or antibody-based drugs. These emerging therapies, if proven effective and safe, could directly compete by providing superior patient outcomes or more convenient administration.
Non-pharmacological interventions, like physical therapy and lifestyle changes, can act as substitutes for certain Galapagos drugs, potentially limiting their market reach. For instance, in areas like inflammatory diseases, robust physical rehabilitation programs can sometimes reduce the reliance on biologic therapies.
While not always a direct replacement, these alternatives can influence the overall demand for pharmaceutical solutions. Consider the market for osteoarthritis; while drugs exist, the growing emphasis on exercise and weight management as primary treatments presents a significant competitive force.
The impact of these substitutes is evident in market dynamics. For example, the increasing adoption of minimally invasive surgical techniques in some orthopedic conditions could reduce the long-term patient pool for pain management medications, a segment where pharmaceutical companies often compete.
Biosimilars and Generics
The increasing availability of biosimilars and generics poses a significant threat, especially as patents on established drugs expire. These lower-cost alternatives directly compete with originator products, forcing price reductions across the pharmaceutical market. For instance, by early 2024, the U.S. market had seen numerous biosimilars approved for blockbuster biologics, with some biosimilars capturing substantial market share within months of launch, indicating a clear pricing pressure.
While Galapagos is dedicated to developing novel, first-in-class medicines, the broader industry trend of biosimilar and generic penetration cannot be ignored. This dynamic can indirectly impact Galapagos by influencing overall pricing expectations and reimbursement strategies for all pharmaceutical products, including innovative ones. The competitive landscape is shifting as more biosimilars enter the market, with analysts projecting continued growth in the biosimilar sector throughout 2024 and beyond, further intensifying this threat.
- Biosimilar Market Growth: The global biosimilar market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $100 billion by 2030, indicating a substantial increase in competitive alternatives.
- Impact on Pricing: Biosimilar entry has been shown to reduce the prices of originator biologics by an average of 20-30% within the first year of market entry.
- Galapagos' Focus: Galapagos' strategy centers on innovative therapies, aiming to differentiate through novel mechanisms of action, which may offer some insulation from direct generic competition but not from broader market pricing pressures.
Off-label Use of Existing Drugs
Physicians may prescribe existing drugs for 'off-label' uses, meaning for conditions not officially approved by regulatory bodies. This can happen if they believe a drug might effectively treat symptoms or underlying mechanisms of inflammatory or fibrotic diseases, even without specific approval for those indications.
This practice presents an unexpected source of substitution for Galapagos' pipeline drugs. For instance, in 2024, a significant percentage of prescriptions for certain autoimmune therapies were off-label, highlighting the prevalence of this phenomenon.
- Off-label prescriptions can divert patients from novel treatments.
- Physician confidence in existing drug efficacy drives this substitution.
- This trend poses a competitive threat to drugs in development.
Existing treatments, including small molecules and biologics from competitors, pose a significant threat of substitution for Galapagos's pipeline. In 2024, established drugs for inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis maintained strong market positions, meaning Galapagos's new candidates must demonstrate clear advantages in efficacy, safety, or cost to gain traction.
The rise of biosimilars and generics is another substantial threat, especially with patent expirations. By early 2024, numerous biosimilars for major biologics had entered the U.S. market, quickly capturing share and exerting pricing pressure. This trend is expected to continue, impacting overall market pricing expectations for all pharmaceuticals.
Emerging therapeutic modalities such as gene editing or engineered cell therapies could also serve as substitutes, offering potentially superior outcomes or administration convenience compared to current or pipeline treatments. Furthermore, non-pharmacological interventions like physical therapy and lifestyle changes can reduce reliance on certain medications, particularly in areas like inflammatory or orthopedic conditions.
| Threat Category | Nature of Threat | 2024 Impact/Observation | Galapagos Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Established Therapies | Existing small molecule and biologic drugs | Continued strong market share for competitors in inflammatory diseases. | Need for superior efficacy/safety/cost-effectiveness. |
| Biosimilars & Generics | Lower-cost alternatives to originator drugs | Rapid market share gain by biosimilars, driving price reductions. | Indirect pressure on pricing and reimbursement strategies. |
| Novel Modalities | Gene editing, cell therapies | Advancements offering potential for better patient outcomes. | Potential direct competition with pipeline candidates. |
| Non-Pharmacological | Physical therapy, lifestyle changes | Reduced reliance on medications in certain disease areas. | Can limit market reach for specific drug classes. |
Entrants Threaten
The biotechnology sector, particularly drug discovery and development, presents a substantial threat of new entrants due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Establishing the necessary research and development capabilities, navigating complex and lengthy clinical trials, and building out manufacturing infrastructure demands billions of dollars. For instance, Galapagos, a prominent player, reported R&D expenses of €485.8 million in 2023, illustrating the scale of investment needed to compete effectively.
Extensive regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process for new drugs is notoriously rigorous, often involving multiple phases of clinical trials that can span several years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars. In 2023, the FDA approved 55 novel drugs, a decrease from 50 in 2022, highlighting the demanding nature of market entry.
Galapagos's robust intellectual property, particularly its extensive patent portfolio covering drug targets, compounds, and manufacturing methods, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. For instance, as of early 2024, Galapagos had a pipeline with numerous compounds in various stages of development, each likely protected by multiple patents. This legal shield makes it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to innovate without infringing on existing IP, necessitating either costly licensing or the development of entirely distinct, and often less proven, therapeutic approaches.
Need for Specialized Expertise and Talent
The biotechnology industry, including companies like Galapagos, requires exceptionally specialized knowledge in science, medicine, and regulatory affairs. New entrants face significant hurdles in acquiring and keeping hold of top-tier talent crucial for areas such as identifying therapeutic targets, developing new drugs, managing clinical trials, and manufacturing advanced therapies like cell therapies.
This talent scarcity directly impacts the threat of new entrants. For example, in 2024, the demand for skilled biopharmaceutical professionals continued to outstrip supply, driving up compensation and making it difficult for startups to compete with established players for experienced personnel. Companies like Galapagos, with their existing research infrastructure and established reputation, have a distinct advantage in attracting and retaining this critical human capital.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: The biotech sector consistently needs experts in genomics, proteomics, bioinformatics, and regulatory compliance.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: New companies struggle to attract experienced scientists and regulatory affairs specialists who are often drawn to larger, more established organizations.
- Cost of Expertise: The high salaries and benefits required to attract leading talent represent a significant barrier to entry for potential competitors.
- Galapagos' Advantage: As an established player, Galapagos benefits from its existing talent pool and employer brand, mitigating this specific threat.
Brand Loyalty and Established Relationships
The threat of new entrants in the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors is significantly mitigated by strong brand loyalty and deeply entrenched customer relationships. Established companies, like those operating in Galapagos' space, have cultivated trust over years with healthcare providers, payers, and patient advocacy groups. This makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
Building this level of trust and securing market share in a sector characterized by stringent regulations and complex approval processes is a formidable hurdle. For instance, the average time to bring a new drug to market can exceed 10 years, with costs often running into billions of dollars. This lengthy and expensive process acts as a powerful deterrent to potential new competitors.
- Established Relationships: Existing pharmaceutical and biotech firms benefit from long-standing ties with doctors, hospitals, insurance companies, and patient communities, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
- High Barriers to Entry: The substantial capital investment required for research, development, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals, often exceeding $2 billion per successful drug, presents a significant challenge for new players.
- Brand Reputation: A proven track record of efficacy, safety, and patient support builds strong brand equity, making it difficult for new entrants to attract customers away from trusted names.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex and evolving regulatory landscapes, such as those governed by the FDA and EMA, demands extensive expertise and resources, which new companies may lack.
The threat of new entrants in the biotechnology sector, where Galapagos operates, is generally considered low due to immense capital requirements, stringent regulatory pathways, and the need for specialized expertise. For instance, bringing a new drug to market can cost upwards of $2 billion, a significant hurdle for any newcomer.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Galapagos Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and economic indicators to capture the competitive landscape.