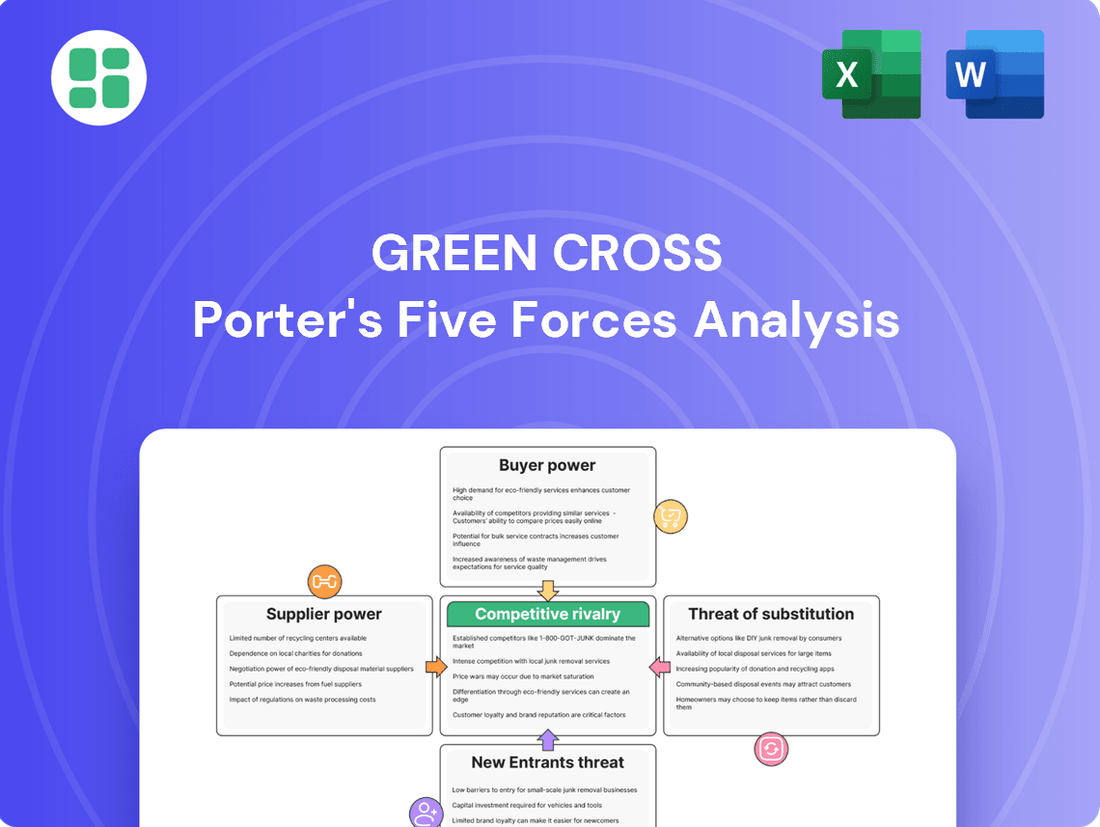
Green Cross Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Green Cross Bundle
Green Cross operates within a dynamic market, influenced by factors like the bargaining power of buyers and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape and identifying strategic opportunities.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Green Cross’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of plasma collection centers is considerable because plasma is a vital, strictly regulated raw material for GC Pharma's plasma-derived medicines. Global demand for these life-saving therapies is on the rise, requiring a consistent, high-quality plasma supply, which inherently grants these specialized suppliers significant influence. GC Pharma's dependence on a strong network of these centers to secure this crucial input directly impacts production expenses and output capabilities.
Suppliers of specialized manufacturing equipment, especially for intricate processes like advanced fractionation and purification, wield significant bargaining power. These technologies are often unique and demand substantial upfront capital, making it costly for biopharmaceutical firms, including GC Pharma, to switch suppliers. This reliance on a select group of equipment makers can affect how efficiently production runs and how smoothly technological advancements are integrated.
The biopharmaceutical sector, including companies like GC Pharma, depends critically on a workforce possessing advanced scientific and medical expertise. This includes specialized roles such as researchers, clinical trial managers, and highly trained manufacturing engineers.
A scarcity of these skilled professionals directly translates into higher recruitment expenses and increased salary demands. For GC Pharma, this means a potential escalation in operational costs, impacting profitability and the ability to scale operations efficiently.
This specialized talent pool effectively acts as a powerful supplier, as their unique skills and knowledge are essential for innovation and production within the industry. In 2024, the demand for biopharmaceutical talent remained robust, with reports indicating a persistent shortage in key areas, driving up compensation packages.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
Companies offering regulatory and compliance services, particularly those specializing in navigating complex frameworks like FDA and EU Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), hold significant bargaining power. Their specialized knowledge is crucial for securing product approvals and maintaining market access, making their services non-negotiable for many businesses.
The increasing global complexity and stringency of regulations mean that the need for expert compliance services is only growing. For instance, the pharmaceutical and medical device industries, heavily reliant on such services, saw global regulatory filings increase significantly in 2024, underscoring the demand for these specialized providers.
- High Switching Costs: Businesses often invest heavily in establishing compliance protocols with specific service providers, making it costly and time-consuming to switch.
- Limited Number of Experts: The niche expertise required means there are often fewer qualified providers, concentrating power in their hands.
- Criticality of Service: Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, product recalls, or market exclusion, highlighting the indispensable nature of these suppliers.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers hold considerable sway in the biopharmaceutical sector due to the critical need for specialized handling of high-value, temperature-sensitive products. Their expertise in maintaining cold chains and managing intricate global distribution networks is indispensable. For instance, the global cold chain logistics market was valued at approximately $17.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, underscoring the demand for these specialized services.
The increasing complexity of international regulations and the growing emphasis on supply chain resilience further bolster the bargaining power of these 3PL providers. Companies like DHL, Kuehne+Nagel, and UPS Healthcare are key players, offering integrated solutions that are difficult for biopharmaceutical firms to replicate internally. The rising costs associated with maintaining these specialized operations mean that 3PLs can command premium pricing.
- Specialized Expertise: Biopharma requires strict temperature control, often between 2-8°C or even ultra-low temperatures for certain biologics, a capability not all logistics providers possess.
- Global Reach & Compliance: Navigating diverse international shipping regulations, customs, and import/export laws for pharmaceuticals is a complex task that experienced 3PLs manage.
- Supply Chain Resilience: In an era of potential disruptions, companies rely on 3PLs with robust contingency plans and diversified networks to ensure product availability.
- Cost of Switching: The significant investment in specialized equipment, training, and established relationships makes switching 3PL providers a costly and time-consuming endeavor for biopharmaceutical companies.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the biopharmaceutical industry, including those for plasma collection, specialized equipment, skilled labor, regulatory services, and logistics, is significant. This power stems from high switching costs, the limited availability of specialized expertise or resources, and the critical nature of the goods or services provided. For GC Pharma, these factors can lead to increased operational costs and potential disruptions if not managed strategically.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on GC Pharma |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Collection Centers | Vital raw material, rising global demand, strict regulations | Higher procurement costs, potential supply volatility |
| Specialized Equipment Manufacturers | Unique technology, high capital investment, costly to switch | Dependency on specific vendors, potential delays in tech adoption |
| Skilled Workforce (e.g., researchers, engineers) | Scarcity of specialized talent, high demand in 2024 | Increased recruitment and salary expenses, operational cost escalation |
| Regulatory & Compliance Service Providers | Complex global regulations, critical for market access | Essential service costs, risk of non-compliance penalties |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Providers | Specialized handling (cold chain), global reach, regulatory navigation | Premium pricing for specialized services, reliance on external networks |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the five competitive forces impacting Green Cross, offering insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, new entrant threats, and the influence of substitute products.
Effortlessly pinpoint and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hospitals and large healthcare systems are major buyers of GC Pharma's plasma-derived therapies and vaccines. These institutional customers, due to their significant purchasing volume, can negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting GC Pharma's revenue. Their decisions are heavily influenced by budget limitations and the presence of competing treatment options.
Government health agencies and national immunization programs are significant customers for pharmaceutical companies, especially for vaccines and essential medicines. Their large-scale procurement, driven by public health mandates, makes them powerful players in the market.
These entities wield substantial bargaining power through their immense purchasing volumes and their ability to influence pricing via reimbursement rates and competitive tenders. For instance, in 2024, many national health services continued to negotiate aggressively on drug prices, impacting manufacturer revenues.
Insurance companies and Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) wield considerable influence over Green Cross (GC) Pharma's success. They dictate which of GC Pharma's drugs are included on formularies and at what reimbursement rates, directly impacting patient access and sales, particularly for high-cost specialty treatments. For instance, in 2024, PBMs continued to consolidate, with the top three PBMs managing prescriptions for over 200 million Americans, giving them immense leverage in price negotiations.
This payer power is amplified as they increasingly scrutinize the value proposition of specialty drugs. Payers are demanding robust evidence of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, putting pressure on GC Pharma to justify the pricing of its therapies. The trend of value-based contracting, where reimbursement is tied to patient outcomes, is also gaining traction, further empowering payers to negotiate terms that reflect demonstrated value.
Pharmaceutical Distributors and Wholesalers
Pharmaceutical distributors and wholesalers hold considerable bargaining power due to their essential role in connecting manufacturers like Green Cross (GC) Pharma with a fragmented customer base of hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. Their established logistical networks and deep market penetration capabilities allow them to negotiate favorable terms, impacting GC Pharma's pricing and sales volumes. For instance, in 2023, the global pharmaceutical distribution market was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion, highlighting the scale and influence of these intermediaries.
Their ability to consolidate demand from numerous smaller buyers presents a unified front, increasing their leverage. Distributors also manage inventory, reduce the complexity of reaching diverse healthcare providers, and often offer value-added services, further strengthening their position. This intermediary function is critical for efficient market access, particularly for specialized or niche pharmaceutical products.
- Established Networks: Distributors possess extensive relationships with healthcare providers, making it difficult for manufacturers to bypass them.
- Logistical Expertise: Their efficient supply chain management and warehousing capabilities are crucial for timely drug delivery.
- Market Access: They provide manufacturers with access to a broad and often geographically dispersed customer base.
- Consolidated Demand: Distributors aggregate purchasing power from multiple smaller customers, enhancing their negotiating strength.
Patient Advocacy Groups (Indirect Influence)
Patient advocacy groups, though not direct price negotiators, wield significant indirect power. For conditions like rare diseases, these organizations can amplify public awareness and lobby for policy shifts, effectively increasing demand for particular treatments. This can influence market acceptance and access to therapies, impacting pharmaceutical companies.
In 2024, the influence of patient advocacy groups continues to grow, particularly in areas with unmet medical needs. For instance, groups advocating for cystic fibrosis treatments have been instrumental in driving access and reimbursement discussions, indirectly shaping the market landscape for companies developing therapies for this condition. Their sustained efforts in raising awareness and advocating for policy changes can translate into substantial market demand and regulatory support.
- Indirect Influence: Patient advocacy groups shape demand and market access for treatments, especially for rare diseases.
- Awareness and Lobbying: These groups raise public awareness and lobby for policy changes impacting therapy adoption.
- Market Impact: Their efforts can influence public perception and regulatory support, crucial for market success.
Customers, particularly large institutional buyers like hospitals and government health agencies, possess significant bargaining power. Their substantial purchasing volumes allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting GC Pharma's revenue streams.
Insurance companies and Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) also exert considerable influence by determining drug formulary placement and reimbursement rates, affecting patient access and sales. In 2024, the consolidation of PBMs, with the top three managing prescriptions for over 200 million Americans, amplified their negotiation leverage.
Distributors and wholesalers, due to their essential role in market access and logistics, can negotiate beneficial terms, impacting GC Pharma's pricing and sales volumes, as seen in the approximately $1.5 trillion global pharmaceutical distribution market in 2023.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitals/Healthcare Systems | High Purchase Volume, Budget Constraints | Negotiate aggressive pricing for plasma-derived therapies. |
| Government Agencies | Large-Scale Procurement, Public Health Mandates | Influence vaccine pricing through tenders and reimbursement rates. |
| Payers (Insurers/PBMs) | Formulary Control, Value-Based Scrutiny | Dictate drug access and reimbursement, demanding cost-effectiveness data. |
| Distributors/Wholesalers | Logistical Networks, Market Access | Negotiate terms based on consolidated demand and supply chain efficiency. |
Full Version Awaits
Green Cross Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Green Cross Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the competitive landscape. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, offering no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The biopharmaceutical sector, especially in plasma-derived therapies and vaccines, is a battleground for major global competitors. Companies like CSL Behring, Grifols, Takeda, Pfizer, and Merck are giants in this space, boasting significant research and development budgets and established worldwide distribution channels.
These established players create a highly competitive environment, constantly vying for market dominance and pushing the boundaries of innovation. For instance, in 2023, the global vaccine market alone was valued at approximately $60 billion, with these major companies holding substantial shares.
Their deep pockets and extensive experience allow them to invest heavily in new drug discovery and manufacturing, making it challenging for smaller or newer entrants to gain traction. This intense rivalry often translates to pressure on pricing and a continuous need for product differentiation.
The biopharmaceutical sector, where Green Cross Porter operates, is characterized by intense competition driven by exceptionally high research and development (R&D) costs and lengthy product development timelines. Companies must commit significant capital to innovation, often billions of dollars, to discover and bring new therapies to market. For instance, the average cost to develop a new drug was estimated to be around $2.6 billion in 2023, a figure that underscores the financial burden.
This necessitates continuous investment in R&D to stay competitive and develop differentiated products. Companies face pressure to secure market leadership and achieve substantial sales to recoup these massive upfront investments. Failure to innovate or a delay in bringing a successful drug to market can severely impact a company's financial health and competitive standing.
The pharmaceutical industry, including companies like Green Cross, is acutely aware of the impending 'patent cliff.' This refers to the period when patents on blockbuster drugs expire, leading to a significant drop in revenue. For instance, in 2024, several major pharmaceutical companies continued to grapple with the loss of exclusivity for key medications, impacting billions in sales globally.
This expiration of patent protection directly fuels competitive rivalry. As soon as patents lapse, generic and biosimilar manufacturers can introduce lower-cost alternatives. These more affordable versions directly compete with the originator products, forcing established players to either lower prices or risk losing substantial market share, a challenge GC Pharma actively navigates.
Consequently, the threat of patent expirations necessitates a relentless focus on innovation and robust product lifecycle management. Companies must invest heavily in research and development to bring new, patent-protected drugs to market before their existing revenue streams are eroded by generic competition. This dynamic is a constant pressure point in the industry.
Competition in Niche and Rare Disease Markets
While regulatory incentives like market exclusivity for orphan drugs exist, the limited patient pools in rare disease markets often concentrate competition among a few specialized players. This intense rivalry necessitates highly focused research, development, and commercialization efforts to secure a dominant position within a specific therapeutic niche.
- Intense Rivalry: Companies aggressively compete for leadership in treating specific rare diseases, often with only a handful of competitors.
- Targeted Strategies: Success hinges on precise development and commercialization plans tailored to small, specific patient populations.
- Market Share Focus: Capturing a significant portion of a niche market is crucial for profitability due to the limited overall patient numbers.
For instance, in 2024, the cystic fibrosis market, a rare disease area, saw continued intense competition among companies like Vertex Pharmaceuticals, which reported over $10 billion in revenue from its CF franchise in 2023, demonstrating the high stakes in even small patient populations.
Global Market Expansion and Strategic Partnerships
Biopharmaceutical companies are aggressively pursuing global expansion, with a particular focus on high-growth regions like Asia-Pacific. This outward push is often facilitated by strategic partnerships, allowing companies to share R&D costs and gain access to new distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, numerous collaborations were announced targeting the burgeoning markets in Southeast Asia and India, aiming to leverage local expertise and patient populations.
These international ventures and increasing alliances directly escalate competitive rivalry. As more companies establish a presence in diverse geographical areas and pool resources for innovation, the market becomes more saturated with advanced therapies and novel approaches. This dynamic intensifies the pressure to differentiate and secure market share, as evidenced by the growing number of patent filings and new drug approvals originating from these expanded operations.
- Increased Market Penetration: Global expansion means more companies vying for customers in formerly less contested territories.
- Accelerated Innovation Cycles: Partnerships often lead to faster development and commercialization of new biopharmaceutical products.
- Heightened Competition for Talent: As companies grow globally, competition for skilled researchers and sales professionals intensifies across all regions.
- Diversification of Competitive Strategies: Companies must now compete not only on product efficacy but also on global supply chain management and localized market access.
Competitive rivalry in the biopharmaceutical sector, where Green Cross operates, is fierce due to enormous R&D costs and long development cycles, often exceeding $2 billion per drug as of 2023. This necessitates continuous innovation to recoup massive investments and avoid being outpaced by competitors. The threat of patent cliffs, where blockbuster drug patents expire, further intensifies this rivalry, as generic and biosimilar alternatives emerge, forcing price adjustments and a constant drive for new, patent-protected products.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (approx. USD billions) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| CSL Behring | 14.5 | Plasma-derived therapies, vaccines |
| Grifols | 6.1 | Plasma-derived therapies, diagnostics |
| Takeda | 30.3 | Oncology, rare diseases, plasma-derived therapies |
| Pfizer | 58.5 | Vaccines, oncology, internal medicine |
| Merck | 60.1 | Oncology, vaccines, animal health |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of advanced therapies like gene and cell therapies presents a substantial threat to Green Cross Porter's traditional protein and plasma-derived products. These cutting-edge treatments, especially for conditions like rare genetic disorders and certain cancers, offer the potential for one-time cures or highly durable responses, directly challenging the long-term market for existing therapies. By mid-2025, the market for cell and gene therapies is projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, indicating a significant shift in treatment preferences and a growing competitive landscape.
The emergence of new vaccine technologies like mRNA and recombinant subunit platforms poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional vaccine manufacturing methods. These innovative approaches allow for much faster development cycles; for instance, mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 were developed and deployed within a year, a stark contrast to the multi-year timelines for many conventional vaccines. This speed, coupled with potential improvements in efficacy and manufacturing adaptability, directly challenges the market position of established vaccine producers.
Small molecule drugs can present a significant threat of substitution for certain therapeutic areas, particularly where oral administration or cost-effectiveness is paramount. For instance, in managing chronic inflammatory conditions or specific infectious diseases, patients and healthcare systems might opt for orally administered small molecules over more complex and expensive biologic or plasma-derived treatments, even if the latter offer highly targeted mechanisms. This preference for convenience and affordability can erode the market share of more intricate therapies.
Improved Diagnostics and Preventive Measures
Advances in diagnostic tools and public health initiatives focused on prevention can significantly reduce the incidence or severity of diseases, thereby indirectly lessening the demand for pharmaceutical interventions. For instance, the global market for in-vitro diagnostics was valued at approximately $90 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong trend toward early detection and proactive health management.
Enhanced health awareness, coupled with improved hygiene practices and the widespread availability of targeted preventive vaccines, can serve as effective substitutes for treating established diseases. The success of vaccination programs, such as those against HPV or influenza, demonstrates how prevention can directly impact the need for later-stage medical treatments. In 2024, global spending on vaccines is expected to continue its upward trajectory, reflecting this shift towards preventative healthcare.
- Diagnostic Market Growth: The in-vitro diagnostics market reached around $90 billion in 2023, highlighting the increasing reliance on early detection.
- Preventive Healthcare Impact: Successful vaccination campaigns reduce the prevalence of diseases, lessening the demand for subsequent treatments.
- Public Health Initiatives: Investments in public health and hygiene education contribute to disease prevention, acting as substitutes for pharmaceutical solutions.
- Shifting Healthcare Focus: The growing emphasis on wellness and preventative measures indicates a long-term trend that could impact traditional treatment markets.
Biosimilars and Generics for Biologics
Biosimilars and generics represent a significant threat to originator biologic and pharmaceutical products once their patents expire. These lower-cost alternatives can rapidly capture market share, directly impacting pricing power and revenue streams for established companies. For instance, the U.S. biosimilar market, while still developing, saw significant growth. By early 2024, over 40 biosimilar products had been approved by the FDA, with many more in the pipeline, indicating a growing competitive landscape.
The economic advantage offered by biosimilars and generics is substantial. For example, studies have shown that biosimilar adoption can lead to savings in the billions. A 2023 report projected that U.S. healthcare could save between $100 billion and $250 billion over the next decade due to biosimilar uptake, directly illustrating the pricing pressure they exert. This forces originator companies to focus on continuous innovation and differentiation to maintain their competitive edge.
- Biosimilar Market Growth: Over 40 biosimilar products approved by the FDA in the U.S. by early 2024.
- Projected Savings: U.S. healthcare could save $100-$250 billion over the next decade due to biosimilar adoption.
- Impact on Originators: Significant erosion of market share and pricing power for branded biologic and pharmaceutical products post-patent expiry.
- Strategic Imperative: Originator companies must prioritize innovation to mitigate revenue loss from biosimilar and generic competition.
The threat of substitutes for Green Cross is multifaceted, encompassing advanced therapies, new vaccine technologies, small molecule drugs, and preventive healthcare measures. These alternatives challenge traditional protein and plasma-derived products by offering cures, faster development, greater convenience, or reduced disease incidence.
Biosimilars and generics represent a significant substitution threat, especially after patent expiry, by offering lower-cost alternatives that erode market share and pricing power. The U.S. biosimilar market, with over 40 FDA-approved products by early 2024, exemplifies this trend, projecting substantial healthcare savings and forcing originator companies to innovate.
| Substitution Threat | Impact on Green Cross | Key Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Therapies (Gene/Cell) | Challenges traditional protein/plasma products; potential for cures | Market projected tens of billions by mid-2025 |
| New Vaccine Technologies (mRNA) | Faster development, adaptability vs. traditional methods | COVID-19 mRNA vaccines developed within a year |
| Small Molecule Drugs | Preference for oral administration/cost-effectiveness | Potential erosion of market share for complex therapies |
| Preventive Healthcare/Diagnostics | Reduces demand for treatments; focus on early detection | In-vitro diagnostics market ~$90 billion in 2023 |
| Biosimilars & Generics | Erodes market share and pricing power post-patent expiry | Over 40 biosimilar products approved by FDA (early 2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical sector presents a significant hurdle for newcomers due to its exceptionally high capital investment requirements. Developing a new drug can cost upwards of $2.6 billion, a figure that encompasses extensive research, rigorous clinical trials across multiple phases, and the establishment of highly specialized, compliant manufacturing facilities.
These substantial upfront costs, coupled with the long development timelines, create a formidable barrier to entry. For instance, bringing a new drug to market typically takes 10-15 years, during which time significant capital must be continuously deployed without any guarantee of return.
This financial barrier effectively deters many potential new entrants, allowing established players with deep pockets and existing infrastructure to maintain a strong market position. The need for specialized equipment, regulatory compliance, and a highly skilled workforce further inflates these initial investment demands.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly impede new entrants. Companies like Green Cross Porter must navigate complex approval pathways, often involving lengthy clinical trials and rigorous compliance with bodies such as the FDA and EMA. For instance, the average time for a new drug to get FDA approval can extend to over a decade, with costs easily reaching hundreds of millions of dollars.
Established biopharmaceutical companies, like Green Cross Porter, boast extensive intellectual property and patent portfolios. These patents protect their innovative drugs and manufacturing methods, creating significant hurdles for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical industry saw continued heavy investment in R&D, with major players securing new patents to maintain market exclusivity.
The sheer breadth of these patent portfolios means new entrants must either discover entirely new therapeutic approaches or navigate expensive licensing deals and potential legal battles. This effectively raises the cost and complexity of entering the market, deterring many potential competitors who lack the resources to challenge existing IP rights.
Need for Established Brand Reputation and Trust
The healthcare industry, particularly pharmaceuticals like Green Cross, demands a high degree of trust and a well-established brand reputation. For new entrants, building this credibility with healthcare providers, patients, and payers is an arduous and time-consuming process. Incumbent companies often possess decades of proven track records and deep-rooted relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold, especially in sensitive areas such as treatments for rare diseases or the development and distribution of vaccines.
Consider the pharmaceutical sector's reliance on clinical trial data and regulatory approvals; these processes inherently favor established players with a history of successful navigation. For instance, in 2024, the average time for a new drug to go from discovery to market approval remained substantial, often exceeding 10 years, a period during which established companies can further solidify their market position and brand loyalty. New entrants face significant hurdles in replicating this level of trust and market access.
- Brand Loyalty: Established pharmaceutical companies benefit from strong brand loyalty among prescribers and patients, built over years of consistent performance and effective treatments.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex regulatory pathways, such as those managed by the FDA or EMA, requires expertise and resources that new entrants may lack, further favoring established entities.
- R&D Investment: Companies with a long history have made significant investments in research and development, creating a portfolio of products and a pipeline that deters new competitors.
- Distribution Networks: Existing players have established and efficient distribution networks, crucial for timely delivery of medicines, a logistical challenge for newcomers.
Complex and Specialized Supply Chain Networks
The intricate and specialized nature of supply chain networks presents a formidable barrier for potential new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector. Developing and managing a resilient, global, and temperature-controlled supply chain for high-value biopharmaceuticals, such as plasma-derived products and vaccines, is a substantial logistical and financial undertaking. For instance, the global cold chain logistics market was valued at approximately $16.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, underscoring the investment required.
New players often lack the established infrastructure and deep expertise necessary to efficiently distribute these sensitive products, creating a significant hurdle to market entry. Companies like Green Cross, with decades of experience, have built robust distribution networks capable of maintaining stringent temperature requirements, a capability that is difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate quickly.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a compliant cold chain infrastructure requires substantial upfront capital, including specialized refrigerated vehicles, storage facilities, and monitoring technology.
- Operational Complexity: Managing a global, temperature-sensitive supply chain involves intricate planning, risk mitigation for product spoilage, and adherence to diverse regulatory standards across different regions.
- Lack of Established Relationships: New entrants may struggle to secure reliable logistics partners experienced in handling biopharmaceuticals, whereas established firms have long-standing relationships built on trust and performance.
The threat of new entrants in the biopharmaceutical industry is generally low due to exceptionally high barriers. These include massive capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, lengthy development cycles, and stringent regulatory approvals, often taking over a decade and costing billions. Established companies benefit from strong brand loyalty, extensive patent portfolios, and complex, specialized supply chains, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Extensive investment needed for R&D, clinical trials, and manufacturing facilities. | Deters entry due to high upfront costs and long payback periods. | Drug development cost: ~$2.6 billion. FDA approval time: often >10 years. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and lengthy approval processes by bodies like FDA/EMA. | Requires significant expertise and resources to navigate, favoring incumbents. | Average time for new drug approval: 10-15 years. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents protect innovations, creating exclusivity. | New entrants must innovate entirely new approaches or face costly legal challenges. | Continued heavy R&D investment and patent acquisition by major pharma in 2024. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established players have built credibility with healthcare providers and patients. | Difficult for newcomers to gain market access and patient/physician confidence. | Years of proven track records and deep-rooted relationships are key differentiators. |
| Supply Chain Complexity | Specialized, temperature-controlled logistics for biopharmaceuticals. | Requires substantial infrastructure investment and operational expertise, a challenge for new players. | Global cold chain logistics market valued at ~$16.1 billion in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Green Cross Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports from reputable firms, and regulatory filings from relevant government agencies.