Falabella Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Falabella Bundle
Falabella navigates a dynamic retail landscape, facing significant pressure from powerful buyers and intense rivalry within the industry. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Falabella’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Falabella's vast retail presence, spanning department stores, home improvement, and supermarkets, involves a diverse supplier base. For many standard products, Falabella's significant purchasing power, driven by its scale, allows it to negotiate favorable terms and pricing, thereby reducing supplier leverage.
However, the bargaining power of suppliers can increase for specialized or high-demand items, particularly in sectors like fashion and electronics where certain brands hold considerable sway. This concentration of power among a few key suppliers in these niche areas can impact Falabella's cost structure and product availability.
Switching costs for Falabella's suppliers are not uniform across its diverse product lines. For many everyday retail items, the ease of finding alternative suppliers keeps these costs relatively low.
However, when Falabella sources specialized or proprietary products, or relies on suppliers with deeply integrated technological solutions, the expense and effort to switch become significant. This can involve substantial costs for contract renegotiations, reconfiguring supply chains, and ensuring product quality and consistency remain unchanged, directly impacting the bargaining power of these specific suppliers.
The uniqueness of a supplier's offerings significantly impacts their bargaining power. When suppliers provide highly differentiated products or exclusive brands that are difficult for Falabella to source elsewhere, their leverage increases. This is particularly relevant in the competitive retail landscape where unique merchandise can be a key differentiator for Falabella.
Falabella's strategic push to expand its third-party e-commerce platform and enhance its marketplace capabilities directly addresses this. By onboarding a wider array of sellers and diversifying its product sourcing, Falabella aims to reduce its reliance on any single supplier. This diversification is a key strategy to dilute the bargaining power of individual suppliers by presenting a broader selection of alternatives to its customers and to Falabella itself.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While less common in the broader retail landscape, there's a theoretical possibility for large, established brands or manufacturers to pursue forward integration. This would involve them developing their own direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales channels, effectively bypassing traditional retailers like Falabella.
However, Falabella's robust omnichannel strategy, which includes a significant physical store footprint and a well-developed online presence, presents a substantial barrier. This extensive distribution network is challenging for most suppliers to fully replicate, thus mitigating this specific threat.
- Deterrent Factor: Falabella's established omnichannel capabilities and extensive physical store network act as a significant deterrent to supplier forward integration.
- Supplier Challenge: Replicating Falabella's vast distribution and customer reach is a complex and costly undertaking for most individual suppliers.
- Market Position: Falabella's scale and market penetration make it a critical partner for suppliers, reducing the incentive for them to bypass it.
Importance of Falabella to Suppliers
For many suppliers, especially smaller or regional ones, Falabella acts as a vital gateway to a vast customer base and a significant distribution network. Falabella's expansive reach throughout Latin America, encompassing countries like Chile, Peru, Colombia, and Argentina, makes it an indispensable client for these businesses.
This substantial market access grants Falabella considerable leverage in negotiations. For instance, in 2023, Falabella reported consolidated sales of approximately CLP 11.7 trillion (around USD 13 billion), underscoring the sheer volume of business it represents for its suppliers.
Falabella's ongoing commitment to enhancing its retail infrastructure and expanding its digital presence, including its e-commerce platforms and logistics capabilities, further cements its position as a critical sales channel. This strategic focus ensures that brands partnering with Falabella gain access to an increasingly integrated and growing marketplace.
- Market Access: Falabella provides crucial market access for numerous suppliers, particularly smaller and regional entities.
- Customer Volume: The company's significant market presence across Latin America makes it a key customer, enhancing its bargaining power.
- Sales Channel Importance: Falabella's investments in retail and digital platforms solidify its role as an essential sales channel for brands.
Falabella's significant purchasing volume, particularly for standardized goods, allows it to negotiate favorable terms, thereby limiting supplier power. However, suppliers of unique or high-demand items, such as specific fashion brands or electronics, can exert greater influence due to limited alternatives for Falabella.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also influenced by the switching costs Falabella faces. While sourcing common retail items involves low switching costs due to readily available alternatives, specialized or technologically integrated products present higher costs for renegotiation and supply chain adjustments, thus increasing supplier leverage in those specific instances.
Falabella's expansive market access across Latin America, with consolidated sales reaching approximately CLP 11.7 trillion (around USD 13 billion) in 2023, makes it an indispensable partner for many suppliers, especially smaller ones. This scale and reach grant Falabella considerable leverage in negotiations, as bypassing Falabella would mean losing access to a vast customer base and distribution network.
| Factor | Impact on Falabella | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Scale | Reduces supplier power for standard goods | Low to Moderate |
| Product Uniqueness/Demand | Increases supplier power for specialized items | Moderate to High |
| Switching Costs | Low for common goods, high for specialized/integrated products | Low for common goods, High for specialized |
| Market Access Provided | Crucial for suppliers, increases Falabella's leverage | Low |
What is included in the product
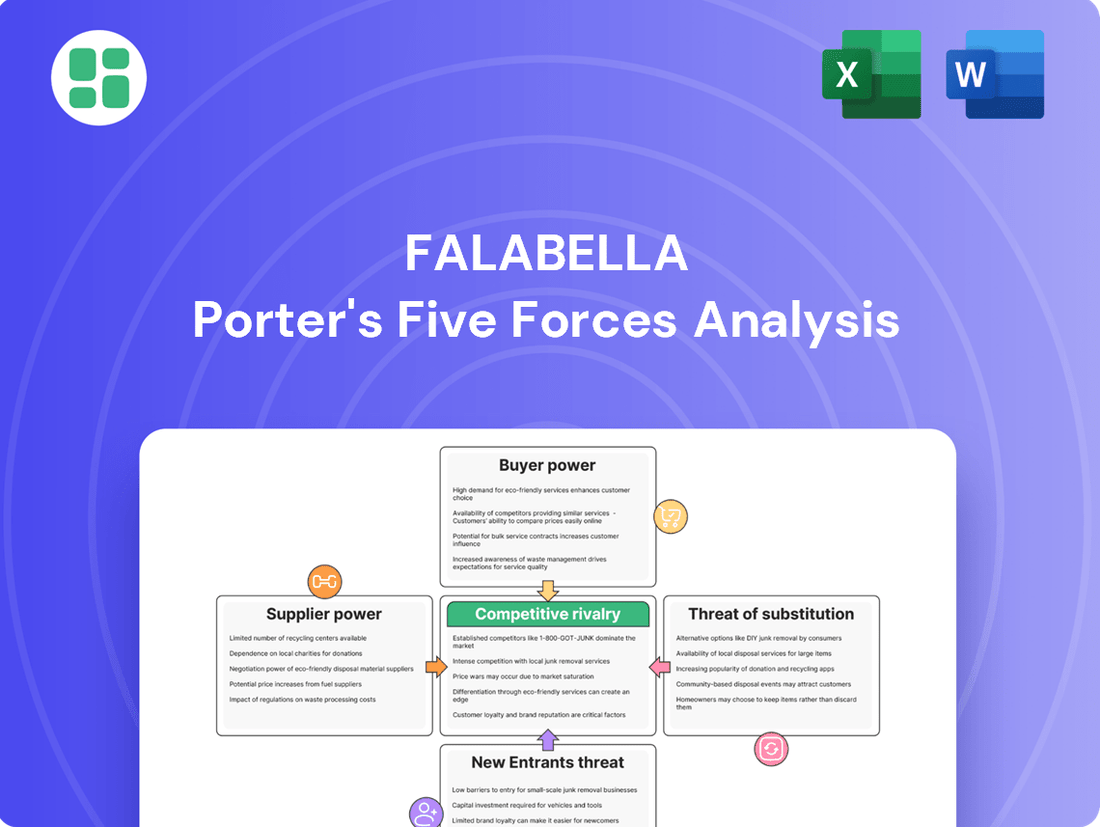
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within Falabella's retail and financial services sectors, evaluating buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the industry's existing competitive rivalry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrants, substitutes, and rivalry.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in Falabella's diverse Latin American markets frequently demonstrate significant price sensitivity, especially for products that are easily substituted or commoditized. This means that a small change in price can lead to a substantial shift in purchasing decisions.
The widespread adoption of digital platforms and readily accessible online price comparison tools in 2024 has dramatically amplified this. Consumers can now effortlessly identify the most competitive prices across various retailers, directly increasing the pressure on Falabella to maintain aggressive pricing strategies and offer compelling value to keep its customer base loyal.
Customers have a vast selection of choices across Falabella's diverse business areas. In retail, this includes other department stores, specialized shops, and a rapidly expanding online marketplace. For financial services, traditional banks and innovative fintech firms present numerous alternatives.
This wide availability of substitutes directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers. For instance, in 2024, the Chilean retail sector saw significant competition, with online sales accounting for approximately 15% of total retail revenue, offering consumers more price-sensitive options outside of traditional department stores.
Customer switching costs for Falabella are strategically managed to foster loyalty. While individual retail transactions might have low switching friction, Falabella's integrated model, which includes Banco Falabella and the CMR Puntos loyalty program, significantly raises the barrier to entry for competitors. This ecosystem approach encourages customers to consolidate their spending and financial activities with Falabella, making a move to a competitor less appealing due to the loss of accumulated benefits and convenience.
Customer Loyalty and Brand Identity
Falabella leverages its extensive brand history and diverse product range to cultivate strong customer loyalty. This is particularly evident in how its integrated financial services complement its retail operations, creating a sticky customer experience.
The CMR Puntos loyalty program is a key driver of this loyalty. As of late 2023, the program boasted over 20.6 million users, incentivizing repeat business and fostering engagement across Falabella's various retail and financial platforms. This extensive user base significantly reduces the bargaining power of customers by making switching less attractive.
- Customer Loyalty: Falabella's established brand and varied offerings foster repeat business.
- Integrated Services: Financial services enhance the retail experience, increasing stickiness.
- CMR Puntos Program: Over 20.6 million users drive engagement and reduce switching.
Customer Sophistication and Demand for Value
Modern customers are increasingly savvy, expecting more than just good prices. They want convenience, tailored experiences, and speedy service. This heightened sophistication directly translates to greater bargaining power.
Falabella is actively addressing these evolving customer expectations. By investing heavily in technology and logistics, they aim to provide a superior customer journey. For instance, their commitment to faster delivery, with 60% of orders reaching customers within 48 hours, is a key strategy to meet this demand for efficiency and satisfaction.
- Customer Sophistication: Growing demand for personalization, convenience, and efficient service.
- Value Proposition: Customers now seek a holistic value proposition beyond just price.
- Falabella's Response: Investments in technology and logistics to improve delivery times and customer experience.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Enhanced customer expectations empower them to demand better terms and service from retailers like Falabella.
Falabella's customers wield considerable bargaining power due to widespread product availability and easy price comparisons, amplified by digital platforms in 2024. The company counters this by fostering loyalty through its integrated ecosystem, including the CMR Puntos program with over 20.6 million users, and by investing in enhanced customer experiences like faster delivery, aiming for 60% of orders within 48 hours.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Falabella | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are highly responsive to price changes, especially for commoditized goods. | Increases pressure for competitive pricing. | Focus on value proposition beyond price, loyalty programs. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Numerous retail and financial alternatives exist across Latin America. | Empowers customers to switch easily. | Integrated services, loyalty program benefits. |
| Switching Costs | Low for individual transactions, but higher within Falabella's ecosystem. | Can reduce customer churn if benefits are perceived. | Enhance benefits of CMR Puntos and integrated financial services. |
| Customer Sophistication | Demand for personalization, convenience, and speed is rising. | Customers expect more, increasing bargaining power. | Investments in technology, logistics, and customer service. |
Same Document Delivered
Falabella Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Falabella Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. You're viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be instantly available for download upon purchase. Rest assured, what you see is precisely what you get—a ready-to-use strategic tool for understanding Falabella's industry dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Falabella operates within intensely competitive retail and financial services sectors across Latin America. Its rivals are varied, encompassing large regional retail groups, global brands, specialized niche providers, and a burgeoning e-commerce market. This diverse competitive environment fuels significant rivalry across all of Falabella's operational segments.
The growth rate in Latin American retail markets presents a mixed picture. While some segments are expanding, others are maturing, which naturally leads to more intense competition. Companies are fighting harder for every customer.
Falabella is actively investing to capitalize on these growth opportunities. For 2025, the company has outlined significant capital expenditures, including plans for new store openings and upgrades to its technological infrastructure. This strategy aims to secure market share and enhance its competitive edge in a dynamic environment.
Falabella stands out by offering an integrated omnichannel experience, blending physical stores, various retail formats like department stores, home improvement centers, and supermarkets, with robust financial services. This unique, synergistic approach creates a significant edge over competitors focused on single segments, nurturing customer loyalty through enhanced convenience and a comprehensive shopping journey.
Exit Barriers
Falabella faces significant competitive rivalry partly due to high exit barriers. These barriers, such as substantial investments in physical stores, extensive distribution networks, and significant real estate holdings, make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market. For instance, in 2024, major retailers like Falabella continue to operate large store footprints across Latin America, representing millions of square feet of retail space that cannot be easily divested.
These entrenched assets, coupled with long-term lease agreements and a considerable number of employees, create a strong incentive for existing players to stay and compete, even when market conditions are unfavorable. This persistence fuels ongoing rivalry, as companies are less likely to exit and more inclined to fight for market share, potentially leading to price wars or intensified promotional activities.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Retailers like Falabella have significant capital tied up in physical infrastructure.
- Long-Term Commitments: Leases and employee contracts create ongoing obligations.
- Sustained Rivalry: Companies are compelled to compete rather than exit, intensifying market competition.
- Impact on Pricing: The inability to easily exit can lead to more aggressive pricing strategies.
Strategic Importance of the Market
Latin America represents a crucial battleground for retailers and financial services, attracting significant ongoing investment and fueling intense competition. Falabella, with its established footprint across key regional economies, faces relentless pressure from both traditional competitors and emerging digital disruptors.
This strategic importance translates into heightened rivalry. For instance, in 2023, e-commerce sales in Latin America saw robust growth, with projections indicating continued expansion, directly impacting traditional retail models and forcing established players like Falabella to innovate and adapt rapidly to maintain market share.
- Sustained Investment: Latin America continues to attract substantial capital from global and local players seeking growth.
- Digital Disruption: The rise of e-commerce and fintech challengers intensifies competition for established brick-and-mortar retailers.
- Falabella's Position: Deep regional presence offers advantages but also exposes it to diverse competitive threats.
- Competitive Intensity: The market's strategic value ensures a high level of ongoing rivalry across all sectors.
The competitive rivalry within Falabella's operating regions is substantial, driven by a diverse array of players including large conglomerates, global brands, and agile e-commerce specialists. This intense competition is further amplified by high exit barriers, such as significant investments in physical retail infrastructure and established distribution networks, which compel existing companies to remain and fight for market share. For example, in 2024, the retail sector in Latin America continued to see major players maintain extensive store portfolios, representing billions in fixed assets that are not easily liquidated, thus perpetuating a highly competitive landscape.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Falabella |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | Numerous regional and global retailers, plus online-only players. | Requires continuous innovation and aggressive marketing. |
| Industry Growth Rate | Mixed, with some segments maturing and others growing rapidly. | Intensifies competition for market share in expanding segments. |
| Exit Barriers | High due to substantial investments in physical stores and logistics. | Encourages existing firms to stay and compete, even in challenging conditions. |
| Product Differentiation | Falabella's omnichannel strategy offers a competitive advantage. | Helps retain customers but requires ongoing investment to maintain differentiation. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Falabella's diverse retail operations is significant, stemming from alternative product categories that satisfy similar consumer desires. For instance, consumers might increasingly prioritize spending on experiences like travel or entertainment rather than purchasing physical goods, or they may turn to niche online retailers offering unique, artisanal products that bypass traditional department store or supermarket channels. This shift in consumer preference directly impacts traditional retail models.
In 2024, the global market for experiences, including travel and leisure, continued its strong growth trajectory, often outpacing the growth of traditional retail sectors. This indicates a tangible diversion of consumer spending. For example, reports from early 2025 highlighted that discretionary spending on experiences saw an average increase of 8% year-over-year in key Latin American markets where Falabella operates, compared to a more modest 3% for general merchandise in physical retail.
The rise of e-commerce and niche online platforms poses a considerable threat of substitution for Falabella. Consumers can readily find a wide selection of goods and services online, often at more attractive prices and with greater variety, diminishing their need for Falabella's traditional retail offerings and even its broader online presence. For instance, the global e-commerce market size was projected to reach over $6.3 trillion in 2023, highlighting the scale of these digital alternatives.
Fintech companies and digital-only banks present a significant threat of substitutes to traditional financial services, including those offered by Banco Falabella. These innovative players often deliver more streamlined, user-friendly, and cost-effective alternatives for banking, payments, and credit. For instance, by mid-2024, the digital banking sector saw substantial growth, with many neobanks reporting double-digit percentage increases in customer acquisition year-over-year.
These agile, technology-first entities can quickly adapt to changing consumer preferences, offering features like instant account opening, personalized financial management tools, and lower transaction fees. This competitive pressure forces established institutions like Falabella to accelerate their own digital transformation strategies to retain market share and customer loyalty. Falabella's ongoing investments in its digital platforms are a direct acknowledgment of this evolving competitive landscape.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Brands
The proliferation of direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands presents a significant substitute threat to established retailers like Falabella. These D2C companies, particularly prominent in sectors such as fashion, home goods, and beauty, effectively circumvent traditional retail intermediaries. This allows them to offer consumers unique products directly from the manufacturer, often at competitive price points and with a more personalized brand experience.
This trend means consumers have readily available alternatives that bypass the physical and online stores of traditional department stores. For instance, the global D2C e-commerce market was projected to reach over $323 billion in 2023, demonstrating substantial consumer adoption. This necessitates that Falabella continually refine its product assortment, emphasizing curated selections and superior customer engagement to retain its appeal against these agile, digitally native competitors.
- D2C Growth: The D2C model bypasses traditional retail, offering direct access to manufacturers' products.
- Sector Impact: Fashion, home goods, and beauty are key sectors experiencing significant D2C brand growth.
- Consumer Benefit: Consumers gain access to unique products and potentially better pricing and personalized experiences.
- Falabella's Challenge: Requires enhanced curation and customer experience to compete with D2C alternatives.
Changing Consumer Lifestyles and Preferences
Shifting consumer lifestyles present a significant threat of substitutes for Falabella. For instance, the burgeoning popularity of minimalist living and a heightened emphasis on sustainability directly challenge traditional consumption patterns. As consumers increasingly embrace the sharing economy or opt for experiences over material possessions, demand for certain retail goods could wane.
To counter this, Falabella needs to proactively adapt its offerings. This means re-evaluating its product assortment to include more sustainable options and exploring business models that align with the sharing economy. For example, by May 2024, reports indicated a 15% year-over-year increase in consumer spending on sustainable products in Latin America, a trend Falabella must address.
- Evolving Lifestyles: Growing preference for minimalism and sustainability reduces demand for traditional retail.
- Sharing Economy Impact: Increased participation in sharing platforms offers alternatives to ownership.
- Adaptation Necessity: Falabella must adjust product mix and business models to meet new consumer values.
- Market Data: Latin American consumer spending on sustainable goods saw a 15% rise by May 2024.
The threat of substitutes for Falabella is substantial, encompassing shifts towards experiences over goods and the rise of niche online players. This diversifies consumer spending away from traditional retail channels.
In 2024, the global experience market continued to outpace general merchandise retail growth, with Latin American markets showing an 8% increase in experience spending versus 3% for retail goods. This highlights a clear diversion of consumer funds.
The increasing adoption of digital-first financial services by fintech and neobanks offers consumers more streamlined and cost-effective alternatives to Banco Falabella's traditional banking and credit offerings. By mid-2024, neobanks were experiencing significant customer acquisition growth, signaling a shift in consumer preference for digital financial solutions.
| Substitute Category | Description | 2024 Impact/Trend |
| Experiences (Travel, Entertainment) | Consumers prioritizing spending on activities over physical goods. | 8% YoY growth in Latin America, outpacing retail. |
| Niche Online Retailers / D2C Brands | Direct access to unique products, often with better pricing and personalization. | Global D2C market projected over $323 billion in 2023; Falabella needs enhanced curation. |
| Fintech and Digital Banks | Streamlined, cost-effective digital alternatives for financial services. | Neobanks reporting double-digit customer acquisition growth by mid-2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter Falabella's diverse retail and financial services markets is a significant barrier. Establishing a nationwide presence necessitates massive investments in physical stores, sophisticated distribution networks, and extensive marketing campaigns. For example, Falabella's planned US$650 million investment for 2025 underscores the sheer financial muscle needed to even approach their scale of operations, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
Falabella's formidable brand recognition and deeply ingrained customer loyalty across Latin America present a substantial barrier to new entrants. Building this level of trust and equity from the ground up is a monumental task, demanding significant investment in marketing and a considerable time commitment. For instance, in 2024, Falabella continued to leverage its established reputation, with its digital platforms reporting millions of active users, a testament to its enduring customer relationships.
Falabella's significant economies of scale in purchasing, logistics, and marketing create a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. These scale advantages, honed through years of regional operation, allow Falabella to secure better terms with suppliers and optimize its supply chain, leading to cost efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in 2023, Falabella's consolidated net revenue reached approximately CLP 12.7 trillion (USD 13.5 billion), a testament to the sheer volume of its operations.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Falabella benefits significantly from its deeply entrenched relationships with suppliers and a highly developed distribution network. This includes a substantial physical store footprint and sophisticated logistics infrastructure, both vital for seamless retail operations. For instance, in 2023, Falabella reported over 300 stores across Latin America, underscoring the scale of its distribution capabilities.
Newcomers face a formidable barrier in replicating this access. Establishing comparable supply chain agreements and distribution channels is not only intricate but also demands substantial capital investment. For example, building a nationwide logistics network similar to Falabella's could easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a prohibitive sum for many nascent businesses.
- Supplier Relationships: Falabella's long-standing partnerships provide preferential terms and reliable inventory, difficult for new entrants to match.
- Logistics Infrastructure: The company's extensive network of warehouses and transportation assets ensures efficient product delivery, a significant hurdle for competitors to overcome.
- Retail Footprint: A vast number of physical stores acts as a direct distribution channel, enhancing market reach and customer accessibility.
- Cost of Entry: Securing similar distribution capabilities would require massive upfront investment, deterring potential new players in the market.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers (especially in Financial Services)
The financial services sector, including operations like Banco Falabella, is heavily protected by a formidable wall of regulatory and legal hurdles. Obtaining the necessary licenses, adhering to strict compliance mandates, and navigating rigorous oversight are substantial deterrents for potential newcomers. For instance, in Chile, where Falabella operates significantly, banking licenses require substantial capital reserves and extensive due diligence, making it a high-cost entry point.
While innovative fintech companies have found ways to enter the market with potentially lighter initial regulatory loads, establishing a comprehensive banking operation comparable to Falabella's requires immense capital and a deep understanding of complex legal frameworks. This complexity significantly limits the threat of new entrants who wish to replicate the full spectrum of services offered by established banks.
- Licensing Requirements: Banks must secure specific operating licenses, often involving lengthy application processes and proof of financial stability.
- Compliance Costs: Ongoing adherence to regulations like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) adds significant operational expenses.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing a bank necessitates substantial initial capital investment to meet regulatory reserve requirements and build infrastructure.
- Supervisory Oversight: Financial institutions are subject to continuous monitoring by central banks and financial regulatory bodies, increasing the burden on new players.
The threat of new entrants for Falabella is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. While the retail and financial sectors demand significant investment, creating substantial barriers, the company's strong regional presence and customer trust in 2024 make it challenging for newcomers to gain immediate traction. For instance, Falabella's ongoing digital transformation efforts, which saw continued growth in online sales throughout 2024, further solidify its market position.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Falabella leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific market research reports and competitor analysis platforms to provide a comprehensive view of the retail landscape.