Deere Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Deere Bundle
Deere's position in the agricultural and construction equipment market is shaped by powerful forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the presence of substitutes is crucial for any stakeholder.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Deere’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Deere & Company’s dependence on specialized components, such as advanced electronics crucial for precision agriculture and complex hydraulic systems, significantly shapes supplier power. In 2024, the agricultural technology sector saw continued innovation, meaning suppliers of these high-tech parts often possess unique, proprietary technology or patents.
This limited supplier base for critical, cutting-edge components grants these suppliers considerable leverage. If a supplier holds exclusive rights to a technology vital for Deere's product differentiation, their ability to dictate terms, including price and delivery schedules, is amplified. For instance, a key supplier of GPS guidance systems for John Deere tractors, holding a patent on a particularly accurate algorithm, could command higher prices.
Consequently, Deere must cultivate robust, strategic relationships with these specialized suppliers. Such partnerships are essential not only for securing a consistent supply of these indispensable parts but also for collaboratively managing costs and fostering innovation. Failure to do so could lead to production delays or increased manufacturing expenses, impacting Deere's overall profitability and market competitiveness.
Deere's reliance on substantial volumes of raw materials like steel, rubber, and various metals for its complex manufacturing operations makes it susceptible to supplier power. Recent volatility in commodity markets, with steel prices experiencing significant swings throughout 2023 and into early 2024, directly impacts Deere's cost structure.
Disruptions within global supply chains, a persistent issue since 2021, further enhance the bargaining leverage of raw material suppliers. These events can limit availability and drive up prices, directly affecting Deere's production costs and profitability.
To counter this, Deere actively manages its supply chain by holding higher inventory levels of key raw materials and strategically diversifying its supplier base across different geographical regions, aiming to reduce dependence on any single source.
Deere's extensive global supply chain, a network spanning numerous countries, inherently introduces complexities. This intricate web means that disruptions in one region, whether due to geopolitical shifts or localized events, can significantly impact operations and, in turn, empower suppliers in those affected areas. For instance, in 2024, ongoing trade tensions and regional conflicts highlighted the fragility of certain supply lines, giving suppliers of critical components in those zones greater bargaining power.
To mitigate these risks and bolster resilience, Deere has strategically pursued dual-sourcing for many components, ensuring that no single supplier holds undue influence. Furthermore, the company actively invests in expanding supplier capacity, a move that not only secures future supply but also helps to balance the power dynamic by reducing supplier reliance on Deere's immediate demand. These proactive measures are vital in navigating the increasingly unpredictable global sourcing landscape.
Supplier Switching Costs
Supplier switching costs are a significant factor in Deere's bargaining power of suppliers. For highly integrated or custom-designed components, switching suppliers can involve substantial costs for Deere, including retooling, re-engineering, and rigorous qualification processes. This inherent difficulty in changing suppliers strengthens the position of existing suppliers.
Deere's strategic approach includes establishing long-term agreements with critical suppliers. These agreements help to foster stable, predictable relationships, mitigating some of the risks associated with supplier dependency. For instance, in 2023, Deere reported that its cost of goods sold was approximately $30.5 billion, highlighting the substantial value of its supplier relationships.
- High Switching Costs: For specialized parts and integrated systems, Deere faces considerable expenses and time delays when attempting to switch suppliers, reinforcing supplier leverage.
- Supplier Dependency: The need for custom-fit components creates a natural dependency, giving suppliers more power in negotiations.
- Long-Term Agreements: Deere's use of long-term contracts aims to secure supply and stabilize pricing, though these can also lock Deere into relationships that might become less favorable over time.
- Impact on Margins: High switching costs can translate into less favorable pricing for Deere, potentially impacting profit margins on its machinery.
Technological Partnership Influence
As Deere & Company integrates advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things into its agricultural and construction equipment, its reliance on specialized technology suppliers grows. These suppliers, possessing unique expertise and intellectual property in areas like autonomous driving systems and precision agriculture software, gain significant bargaining power. For instance, Deere's investment in AI and machine learning for its autonomous tractors, a key part of its 2024 strategy, directly increases its dependence on providers of these sophisticated solutions.
The bargaining power of these technology suppliers stems from several factors:
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers offering patented algorithms or exclusive software essential for Deere's innovation pipeline hold considerable sway.
- Limited Alternatives: The scarcity of providers with comparable advanced technological capabilities for specialized agricultural applications means fewer viable options for Deere.
- Supplier Concentration: In niche technology sectors, a few dominant players can dictate terms, impacting Deere's procurement costs and contract negotiations.
- Switching Costs: The significant investment required for Deere to integrate and validate new technology platforms from different suppliers can deter easy transitions, strengthening the position of incumbent tech partners.
The bargaining power of Deere's suppliers is significant, particularly for specialized components and raw materials. In 2024, the agricultural technology sector’s rapid innovation means suppliers of advanced electronics and software often possess proprietary technology, limiting Deere's alternatives and increasing their leverage. For example, a key supplier of GPS guidance systems with patented algorithms can command higher prices, impacting Deere's cost structure.
Deere's reliance on substantial volumes of raw materials like steel and rubber, coupled with persistent global supply chain disruptions observed since 2021, further empowers suppliers. Volatility in commodity markets, such as steel price swings in early 2024, directly affects Deere's production expenses. To mitigate this, Deere diversifies its supplier base and increases inventory levels of critical materials.
Supplier switching costs are a major factor; retooling and re-engineering for custom-designed components can be substantial, reinforcing existing supplier leverage. Deere’s use of long-term agreements aims to stabilize relationships and pricing, though these can also limit flexibility. In 2023, Deere's cost of goods sold was approximately $30.5 billion, underscoring the critical nature of its supplier relationships.
| Key Factor | Impact on Deere | 2024 Context |
| Proprietary Technology | Increases supplier pricing power | High demand for AI/IoT in precision agriculture |
| Limited Alternatives | Reduces Deere's negotiation options | Niche technology sectors dominated by few players |
| High Switching Costs | Locks Deere into existing relationships | Significant investment needed for component integration |
| Commodity Price Volatility | Affects Deere's cost of goods sold | Steel prices saw significant swings in early 2024 |
What is included in the product
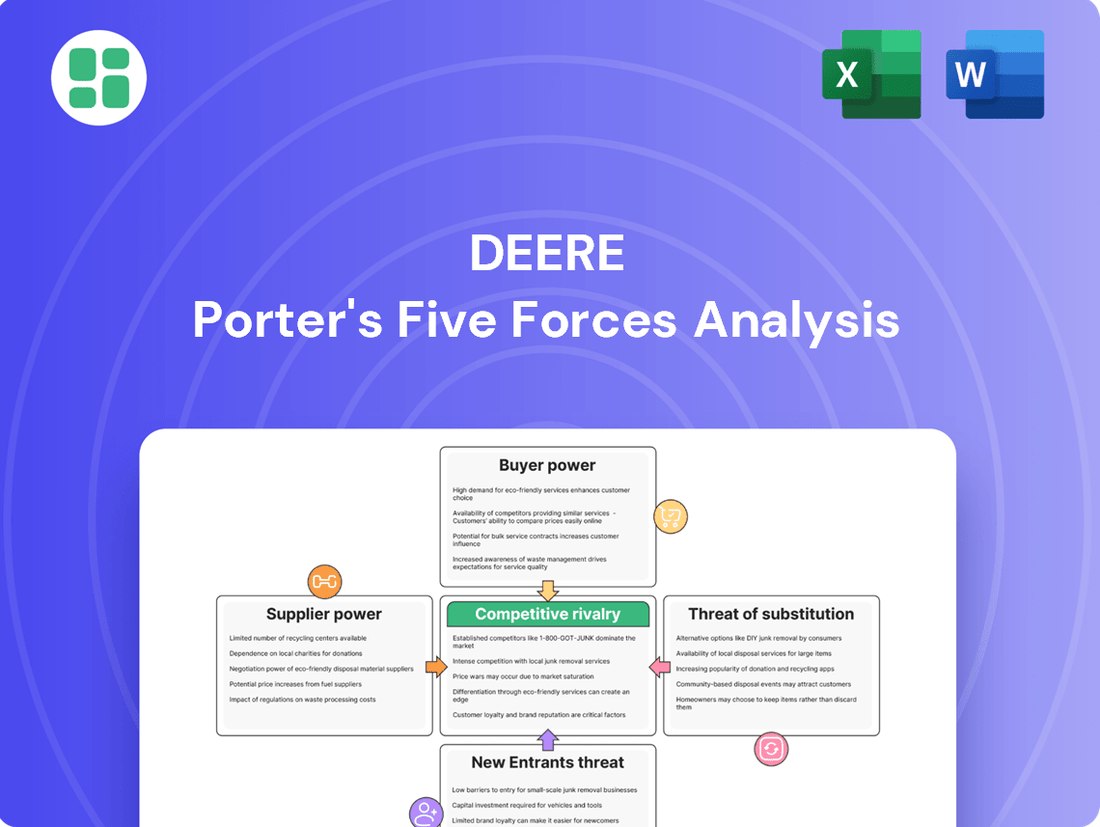
Deere's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity of the agricultural and construction machinery markets, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry dynamics, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, particularly large-scale agricultural operations and major construction companies, often invest heavily in Deere's machinery. For instance, a single large tractor can cost upwards of $500,000, and a fleet of specialized construction equipment can run into millions. This significant capital outlay means that once a customer commits to Deere's product line and integrated support systems, the cost and complexity of switching to a competitor become substantial, thereby limiting their immediate bargaining power on future purchases.
The availability of used agricultural and construction equipment significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. A strong secondary market offers a cost-effective alternative to new machinery, directly impacting pricing negotiations. In 2024, a notable surplus in the used equipment market was observed, which consequently exerted downward pressure on the prices of new equipment and amplified customer leverage.
Recent economic conditions, characterized by declining farm income due to lower commodity prices and elevated interest rates, have significantly impacted the agricultural sector. For instance, in 2023, many farmers faced squeezed margins, which naturally leads to a more cautious approach when considering large capital expenditures like new machinery.
This financial pressure directly translates into increased bargaining power for Deere's customers. With reduced disposable income and higher borrowing costs, farmers are more likely to delay purchases, negotiate harder on price, or seek out used equipment, all of which can diminish Deere's pricing flexibility and profitability.
Deere itself has acknowledged these market challenges. In its fiscal year 2023 earnings calls, the company highlighted the impact of these economic headwinds on order activity and customer sentiment, underscoring the heightened price sensitivity among its agricultural clientele.
Strong Brand Loyalty and Dealer Network
Deere's enduring brand reputation and its vast global dealer network are significant assets that foster strong customer loyalty, acting as a counterweight to customer bargaining power. This loyalty is built on trust and consistent performance, making customers less inclined to switch. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Deere reported net income of $10.17 billion, underscoring the strength of its market position and customer relationships.
The extensive support, readily available parts, and accessible financial services provided through Deere's dealers add substantial value for customers. This integrated ecosystem creates a high switching cost, as customers benefit from a seamless experience and reliable service. This comprehensive offering makes it less attractive for many customers to consider competitors.
- Brand Loyalty: Deere's strong brand recognition reduces price sensitivity among customers.
- Dealer Network: Over 1,000 dealers globally ensure widespread availability and support.
- Integrated Services: Parts, service, and financing options enhance customer retention.
- Switching Costs: The comprehensive support system makes it costly and inconvenient for customers to move to other brands.
Demand for Precision Agriculture and Technology
Customers are increasingly seeking advanced precision agriculture and smart construction technologies. This demand for tools that boost efficiency and profitability gives them significant leverage. For instance, in 2023, John Deere reported a 16% increase in revenue for its Smart Industrial segment, driven by strong demand for these advanced solutions.
This trend empowers customers to negotiate for specific features and tightly integrated systems. They are less likely to accept one-size-fits-all solutions, pushing manufacturers like Deere to customize offerings. Deere's strategic focus on its Smart Industrial operating model directly addresses this by aiming to deliver connected, intelligent solutions tailored to evolving customer requirements.
- Increased Customer Leverage: Demand for precision agriculture and smart construction tech grants customers more power in feature and integration negotiations.
- Deere's Strategic Response: The Smart Industrial operating model is designed to meet these sophisticated customer needs.
- Market Trend: Customers prioritize efficiency and profitability gains offered by advanced technologies, influencing product development.
While Deere's strong brand and dealer network create loyalty, customer bargaining power is amplified by the significant investment required for their machinery, making switching costly. The robust used equipment market in 2024 offered a tangible alternative, pressuring new equipment prices.
Economic pressures on farmers, like squeezed margins in 2023, further enhance their negotiation leverage. Customers demanding advanced technologies also gain power, pushing Deere to customize offerings to meet specific efficiency needs.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Deere's Counterbalance |
|---|---|---|
| High Capital Investment | Limits immediate switching, reducing short-term power. | Integrated support and financing foster loyalty. |
| Used Equipment Market (2024 Surplus) | Provides cost-effective alternatives, increasing negotiation leverage. | Focus on new technology and integrated solutions. |
| Economic Headwinds (e.g., 2023 Farm Income) | Increases price sensitivity and demand for better terms. | Strong brand reputation and customer relationships. |
| Demand for Advanced Technology | Empowers customers to negotiate for specific features and customization. | Smart Industrial operating model to meet evolving needs. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Deere Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Deere Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the agricultural machinery industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately after purchase, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The agricultural and construction equipment sectors are characterized by a handful of dominant global companies. Key players like CNH Industrial, which owns brands such as Case IH and New Holland, alongside AGCO and Kubota, fiercely contest market share.
This concentrated market structure fuels intense rivalry, with these established giants competing vigorously across their entire product portfolios and geographical footprints. For instance, in 2024, the global agricultural machinery market was valued at approximately $140 billion, with these major players holding significant portions of that value.
Competitive rivalry in the agricultural equipment sector is intensely fueled by a race for innovation, especially in areas like precision agriculture, autonomous machinery, and the growing adoption of electrification. Companies are pouring substantial resources into research and development, aiming to deliver advanced solutions that boost farmer productivity and significantly lower operating expenses. Deere's strategic focus on digital transformation underscores its commitment to leading these technological advancements.
The agricultural equipment industry frequently experiences intense pricing pressure. This is often driven by volatile commodity prices, which directly impact farmer purchasing power, and by elevated interest rates that increase the cost of financing new machinery. For instance, in early 2024, the lingering effects of supply chain disruptions and fluctuating demand led to periods where dealers offered significant discounts on new equipment, particularly in segments experiencing oversupply.
These market dynamics in 2024 and projected into 2025 have amplified competitive rivalry among major players like John Deere, CNH Industrial, and AGCO. Companies are compelled to meticulously manage their inventory levels and production schedules to avoid being caught with excess stock, which can further erode pricing power. This careful balancing act is crucial for maintaining profitability in a market where price concessions can quickly become the norm.
Extensive Dealer Networks and Aftermarket Services
Competitive rivalry in the agricultural equipment sector is intensified by the critical role of extensive dealer networks and comprehensive aftermarket services. This goes beyond just selling machinery; it encompasses the availability of financing, parts, and skilled repair technicians. Companies like John Deere, with their deeply entrenched dealer infrastructure, leverage this to foster strong customer loyalty and maximize the lifetime value of their equipment.
These established networks represent a substantial barrier to entry for new competitors, requiring significant capital investment and time to replicate. In 2024, John Deere's commitment to its dealer network was evident in its ongoing investments in technology and training to support advanced equipment and precision agriculture solutions. This focus on service and support differentiates them, making switching costs high for existing customers who rely on reliable uptime and readily available parts.
- Dealer Network Strength: John Deere's extensive network provides crucial local support, parts availability, and service expertise, enhancing customer retention.
- Aftermarket Services: Robust aftermarket support, including parts and maintenance, is a key differentiator that increases customer lifetime value.
- Barrier to Entry: The significant investment required to build comparable dealer and service networks creates a substantial hurdle for new market entrants.
- Customer Retention: Reliable service and parts availability directly contribute to customer loyalty and reduced churn in a competitive market.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The agricultural machinery sector, where Deere operates, demands substantial capital for state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, cutting-edge research and development, and extensive global distribution networks. These significant upfront investments translate into high fixed costs for all players. For instance, establishing a new advanced manufacturing facility can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a figure that Deere regularly invests in its global operations.
These high fixed costs, combined with the specialized nature of machinery and technology, create formidable exit barriers. Companies find it incredibly difficult and costly to divest or shut down operations. This lack of easy exit means that firms are compelled to battle intensely for market share and profitability rather than withdrawing, thereby fueling aggressive competition among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: Deere's commitment to innovation and production capacity is substantial. In fiscal year 2023, the company reported capital expenditures of approximately $2.3 billion, underscoring the significant investment in its operational infrastructure and R&D.
- Specialized Assets: The machinery produced is highly specialized, often requiring dedicated production lines and unique components, making it difficult to repurpose for other industries.
- Intensified Rivalry: Companies are incentivized to fight for market position due to the difficulty of exiting, leading to price competition and increased marketing efforts.
Competitive rivalry within the agricultural equipment sector is fierce, driven by a concentrated market with a few dominant global players. These companies, including Deere, CNH Industrial, and AGCO, actively compete across product lines and geographies, as evidenced by the approximately $140 billion global agricultural machinery market in 2024.
Innovation, particularly in precision agriculture and automation, is a key battleground, with companies investing heavily in R&D to enhance farmer productivity. This intense competition also manifests in pricing pressures, often influenced by volatile commodity markets and financing costs. For instance, in early 2024, discounts were observed due to supply chain effects and fluctuating demand.
The strength of dealer networks and aftermarket services significantly intensifies rivalry, creating high switching costs and barriers to entry. John Deere's substantial investments in its dealer infrastructure in 2024 highlight the importance of this customer retention strategy.
Furthermore, high capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, coupled with specialized assets, result in formidable exit barriers, compelling companies to engage in sustained competitive battles for market share and profitability.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The robust pre-owned equipment market acts as a powerful substitute for new machinery. For instance, in 2024, the global used agricultural machinery market continued to show strong demand, with many farmers prioritizing cost-effectiveness. This readily available secondary market allows buyers to acquire functional equipment at a fraction of the cost of new models, directly impacting Deere's sales volume.
The appeal of used equipment intensifies when new inventory levels are high or during periods of economic uncertainty. In 2024, reports indicated that dealers were actively managing excess new inventory, which often led to more aggressive pricing on used machines to move them, further strengthening the substitute threat.
The threat of substitutes for Deere's equipment is significant, particularly from equipment rental services. For smaller operators or those with project-specific needs, renting offers a compelling alternative to purchasing expensive machinery. This flexibility allows businesses to access the right equipment without the upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs associated with ownership.
The rental market has seen robust growth, with the global equipment rental market size valued at approximately $115 billion in 2023 and projected to reach over $150 billion by 2028. This expansion highlights the increasing adoption of rental models across various industries, including construction, where temporary needs are common. For instance, a small contractor might rent a specialized excavator for a single project rather than buying one, directly impacting potential sales for Deere.
Technological upgrades for existing machinery present a significant threat of substitutes for Deere. The development of advanced retrofit kits and software upgrades allows customers to enhance the capabilities of their current equipment, effectively adding features like precision agriculture. This strategy extends the useful life of older machines, diminishing the immediate pressure to purchase new equipment.
For instance, in 2024, the aftermarket parts and services sector for agricultural machinery continued to grow, offering farmers cost-effective solutions to improve efficiency. These upgrades can cost a fraction of a new machine's price, making them an attractive alternative for those looking to boost productivity without a full capital outlay.
Alternative Farming Practices or Construction Methods
While the direct threat of substitutes for heavy agricultural and construction machinery might seem low, alternative farming practices and construction methods can emerge as long-term substitutes. For instance, a growing interest in smaller-scale, organic, or specialized niche agriculture could reduce the demand for large, high-horsepower tractors and implements. In 2024, the organic food market continued its upward trajectory, with global sales projected to reach over $300 billion, indicating a potential shift in demand for certain types of equipment.
Similarly, in construction, advancements in prefabrication and modular building techniques can lessen the reliance on traditional on-site heavy machinery. Outsourcing specific tasks to specialized service providers who own and operate their equipment also presents a substitute for direct ownership. This model can be attractive to smaller operators or those with intermittent needs, potentially impacting the overall sales volume for manufacturers like Deere.
- Shifting Agricultural Trends: Increased adoption of smaller-scale, organic, and niche farming could decrease demand for large-scale machinery.
- Construction Innovations: Prefabrication and modular building methods may reduce the need for heavy on-site construction equipment.
- Outsourcing Services: The rise of specialized third-party service providers offering equipment operation can substitute for direct machinery ownership.
- Market Data: The global organic food market exceeded $300 billion in sales in 2024, reflecting a growing alternative consumer preference.
Multi-Purpose and Modular Equipment
The rise of multi-purpose and modular equipment presents a significant threat of substitutes for highly specialized machinery. Customers increasingly favor versatile machines that can handle various tasks or modular designs with interchangeable parts, reducing the need for multiple single-purpose units. This trend is driven by a desire to optimize asset utilization and decrease the overall size of equipment fleets.
For instance, by mid-2024, the construction equipment rental market saw a notable uptick in demand for compact track loaders equipped with a wide array of attachments, from buckets to augers and breakers. This single machine, with its modular capabilities, effectively substitutes for separate skid steers, excavators, and specialized trenchers. Companies are looking to consolidate their equipment needs, and in 2023, the global compact equipment market was valued at over $25 billion, with modularity being a key growth driver.
- Increased Versatility: Modular equipment allows a single base unit to perform functions previously requiring multiple specialized machines.
- Cost Efficiency: Customers can achieve broader utility with fewer units, leading to reduced capital expenditure and maintenance costs.
- Optimized Fleet Management: The trend supports a move towards smaller, more adaptable fleets, improving operational efficiency and reducing storage needs.
- Market Demand: Industry reports from 2024 indicate a growing customer preference for adaptable solutions over single-function equipment.
The threat of substitutes for Deere is multifaceted, encompassing everything from used equipment and rentals to alternative technologies and operational methods. The robust pre-owned market, coupled with the growing equipment rental sector, offers cost-effective alternatives for many customers. For instance, the global equipment rental market was valued at around $115 billion in 2023, showcasing the significant adoption of rental models. Furthermore, technological upgrades for existing machinery allow users to enhance capabilities, extending the life of older equipment and delaying new purchases. In 2024, the aftermarket parts and services sector continued its growth, providing farmers with cost-effective efficiency boosts.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Deere | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used Equipment Market | Availability of functional machinery at lower price points. | Reduces demand for new equipment sales. | Strong demand continued in 2024, driven by cost-effectiveness. |
| Equipment Rental Services | Access to machinery without ownership costs. | Limits capital expenditure for customers, impacting sales. | Global market projected to exceed $150 billion by 2028. |
| Retrofit Kits & Upgrades | Enhancing existing machinery capabilities. | Extends equipment lifespan, delaying new purchases. | Aftermarket sector growth in 2024 offered cost-effective solutions. |
| Alternative Practices | Smaller-scale farming, prefabrication in construction. | Shifts demand away from large-scale, specialized machinery. | Organic food market sales exceeded $300 billion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the heavy machinery manufacturing sector, like that dominated by Deere, requires substantial financial backing. We're talking billions of dollars for R&D, setting up massive factories, and creating robust sales and support systems. For instance, a new entrant would need to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing technologies and global supply chains, mirroring the scale of operations already established by industry leaders.
Deere & Company, a leader in agricultural and construction equipment, benefits significantly from strong brand loyalty and deeply established networks. For instance, John Deere's brand recognition is a powerful deterrent, cultivated over decades of consistent quality and customer service. This loyalty means customers are less likely to switch to a new, unproven brand, even with competitive pricing.
The company's extensive dealer network is another formidable barrier. In 2024, John Deere operates thousands of dealerships globally, providing crucial sales, service, and parts support. Replicating this vast infrastructure and the trust associated with it would require massive investment and time, making it extremely difficult for new entrants to gain a foothold in the market.
The technological complexity in modern agricultural and construction equipment acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. Think about the advanced systems involved, like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), GPS navigation, and even autonomous operating capabilities. These aren't simple machines anymore; they are sophisticated technological platforms.
Developing these cutting-edge solutions demands immense investment in research and development, along with a deep pool of specialized engineering talent. Companies like John Deere, for instance, invest billions annually in R&D, with their 2023 R&D spending reaching approximately $2.2 billion. This continuous innovation and the resulting accumulation of intellectual property, including patents and proprietary software, create a formidable hurdle for any new player looking to enter the market.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Costs
The agricultural machinery sector, including companies like Deere & Company, faces significant regulatory barriers. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce strict emissions standards for off-road diesel engines, requiring substantial investment in advanced engine technology. New entrants must dedicate considerable resources to research, development, and testing to meet these evolving global environmental and safety mandates, such as those from the European Union's Stage V emissions regulations.
Navigating these complex and often country-specific regulations presents a substantial cost and time burden for any new company aiming to enter the market. This includes obtaining certifications, ensuring product compliance, and adapting manufacturing processes, all of which can deter potential competitors and protect established players.
The financial implications are considerable. For example, developing new engine technology to meet stringent emissions standards can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. This capital-intensive requirement acts as a significant deterrent, raising the barrier to entry considerably.
- Stringent Emissions Standards: Compliance with regulations like the EPA's Tier 4 Final and upcoming Tier 5 standards necessitates advanced, costly engine technology.
- Global Safety Mandates: Meeting diverse international safety certifications and operational standards requires significant upfront investment and ongoing adaptation.
- Environmental Impact Regulations: Adherence to rules concerning chemical usage, waste disposal, and product lifecycle management adds complexity and cost.
- High Compliance Costs: The combined expenses of R&D, testing, certification, and legal counsel to meet regulatory requirements can easily reach tens to hundreds of millions of dollars for new entrants.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
Established players like Deere leverage substantial economies of scale in manufacturing and supply chains, enabling lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, Deere's extensive global manufacturing footprint and bulk purchasing power for components like engines and hydraulics significantly reduced their production expenses compared to potential newcomers. This cost advantage makes it challenging for new entrants to match pricing and achieve profitability without substantial upfront investment.
New entrants face a steep uphill battle due to Deere's entrenched cost advantages. Without the volume to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers or spread R&D costs across a large production base, startups would likely incur much higher per-unit costs. This disparity in cost structure acts as a powerful barrier, limiting the threat of new competition by making it economically unfeasible for them to enter and compete effectively in the agricultural machinery market.
- Economies of Scale: Deere's vast production volumes in 2024 allow for significant cost reductions per unit.
- Procurement Advantages: Bulk purchasing of raw materials and components grants Deere better pricing power than new entrants.
- R&D Investment: Deere's substantial R&D spending is spread across a larger sales base, lowering the per-unit R&D cost.
- Pricing Flexibility: Lower cost structures provide Deere with greater flexibility to adjust pricing, pressuring new competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the heavy machinery sector, where Deere operates, is generally low due to several formidable barriers. High capital requirements, estimated in the billions for R&D, manufacturing facilities, and distribution networks, make entry extremely difficult. For example, establishing a global supply chain and advanced manufacturing capabilities comparable to Deere's would necessitate immense upfront investment.
Deere's strong brand loyalty, cultivated over decades, and its extensive, trusted dealer network further deter new competitors. In 2024, Deere's thousands of global dealerships provide essential sales, service, and parts support, a network that would take years and vast resources to replicate. This deep integration into customer operations and the associated trust are significant deterrents.
Technological complexity, including AI, IoT, and autonomous capabilities, demands massive R&D investment and specialized talent. Deere's 2023 R&D spending of approximately $2.2 billion underscores the continuous innovation required, creating a substantial hurdle for newcomers lacking such resources and expertise.
Regulatory compliance, particularly stringent emissions standards like EPA's Tier 4 Final and upcoming Tier 5, adds significant cost and complexity. New entrants must invest heavily in meeting these global environmental and safety mandates, a process that can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, further raising the barrier to entry.
Economies of scale provide Deere with a significant cost advantage. In 2024, their large-scale production and bulk purchasing power for components allow for lower per-unit costs, making it challenging for new entrants to compete on price and achieve profitability without matching Deere's operational volume.
| Barrier | Description | Estimated Cost for New Entrant (Illustrative) |
| Capital Requirements | Establishing manufacturing, R&D, and distribution. | Billions of USD |
| Brand Loyalty & Dealer Network | Building trust and replicating global support infrastructure. | Hundreds of millions to billions of USD |
| Technological Expertise | Investing in advanced R&D and specialized talent. | Billions of USD annually |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting emissions and safety standards. | Hundreds of millions of USD |
| Economies of Scale | Achieving cost efficiencies through high production volume. | Requires matching existing scale to overcome |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Deere leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and government agricultural statistics to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.