Xiamen Tungsten Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Xiamen Tungsten Bundle
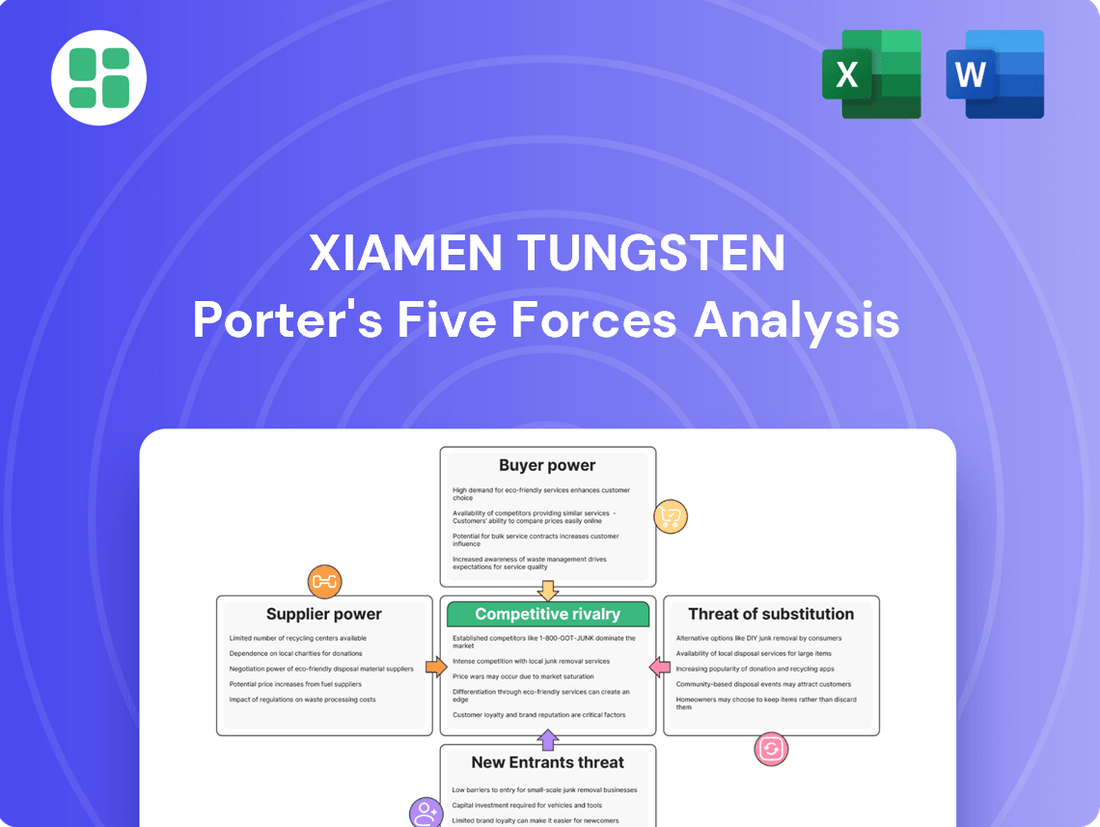
Xiamen Tungsten faces significant competitive pressures, with the threat of substitutes and the bargaining power of buyers posing notable challenges. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the complex tungsten market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Xiamen Tungsten’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Xiamen Tungsten's reliance on tungsten ore, with China controlling over 80% of global supply, grants immense power to its few suppliers. This concentration, often involving state-owned enterprises and large private mining operations, means these entities can significantly influence pricing and availability.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is further amplified by recent developments. For instance, China's export restrictions on critical materials like tungsten, implemented starting December 1, 2024, directly impact global supply chains. This tightening of availability inherently strengthens the position of Chinese suppliers, potentially leading to higher costs for companies like Xiamen Tungsten.
Tungsten's unique properties, including its highest melting point of 3,422°C and exceptional hardness, make it indispensable for high-temperature industrial processes and demanding defense applications. This inherent value grants suppliers significant leverage, as finding comparable materials for these critical uses is exceptionally difficult.
The scarcity of readily available and economically viable substitutes for tungsten in sectors like cemented carbides and advanced military hardware significantly strengthens the bargaining power of its suppliers. For companies like Xiamen Tungsten, this limited substitutability translates into fewer options for sourcing primary raw materials, increasing supplier influence.
Tungsten's classification as a strategic mineral by the US and NATO countries, essential for military and advanced technology, underscores its critical nature. China's historical dominance and past export restrictions highlight its significant leverage in the global tungsten market, directly impacting supply chain stability.
This geopolitical dimension amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly those in nations with substantial tungsten reserves. For instance, in 2023, China accounted for approximately 70% of global tungsten mine production, solidifying its position as a key influencer on pricing and availability.
High Switching Costs for Alternative Sources
Developing new, non-Chinese tungsten mines and processing facilities is a capital-intensive and time-consuming endeavor, requiring substantial investment and advanced technology. The global tungsten market, heavily reliant on China, saw Chinese exports of unwrought tungsten and tungsten products reach approximately 70,000 metric tons in 2023, underscoring the concentration of supply.
While efforts are underway to diversify global supply, such as the Sangdong Mine in South Korea and projects in Australia and the US, these new sources are still ramping up and represent only a fraction of global demand. For instance, the Sangdong mine aims to produce around 3,000 metric tons of tungsten concentrate annually once fully operational, a relatively small amount compared to China's output.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing new tungsten mines and processing plants globally requires billions of dollars in upfront capital and advanced technological expertise, creating significant barriers to entry.
- Long Development Timelines: Bringing new tungsten projects from exploration to full production can take a decade or more, making rapid shifts in supply extremely challenging.
- Limited Alternative Scale: Current alternative sources outside China are not yet at a scale to fully substitute Chinese supply, forcing buyers like Xiamen Tungsten to rely on existing, concentrated sources.
Supplier Integration and Vertical Control
Major tungsten suppliers, particularly in China, exhibit significant vertical integration, encompassing mining, smelting, and downstream processing. This control over the entire value chain grants them substantial leverage in setting prices and dictating supply conditions, thereby diminishing Xiamen Tungsten's bargaining power for essential raw materials and intermediate goods.
For instance, China's dominance in tungsten production means that a few large, integrated players can significantly influence global supply. In 2023, China accounted for approximately 70% of global tungsten mine production, underscoring the concentrated nature of the supplier landscape.
Xiamen Tungsten's own extensive vertical integration, spanning from mining to the production of finished tungsten products, serves to partially offset this external supplier power by securing its own internal supply needs. However, this does not entirely eliminate the influence of upstream suppliers, especially for specialized or high-purity materials.
- Supplier Integration: Key tungsten suppliers, especially in China, control mining, smelting, and processing, increasing their pricing power.
- Market Concentration: China's substantial share of global tungsten output (around 70% in 2023) concentrates power among a few integrated suppliers.
- Xiamen Tungsten's Mitigation: The company's own vertical integration helps secure internal supply but doesn't fully negate external supplier influence.
- Negotiation Disadvantage: This integration limits Xiamen Tungsten's ability to negotiate favorable terms for critical inputs, impacting cost structures.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Xiamen Tungsten is substantial, largely due to China's overwhelming control over global tungsten production. In 2023, China accounted for approximately 70% of global tungsten mine output, concentrating significant leverage in the hands of a few large, integrated suppliers.
These suppliers often control the entire value chain, from mining to processing, allowing them to dictate terms and prices for essential raw materials. Recent export restrictions, such as those implemented by China starting December 1, 2024, further bolster supplier influence by tightening global availability.
The critical nature of tungsten, with few viable substitutes in high-tech and defense sectors, means companies like Xiamen Tungsten have limited options, intensifying supplier leverage.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Xiamen Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | China's ~70% global mine production share (2023) | High leverage for a few key suppliers. |
| Export Restrictions | China's implemented controls (e.g., Dec 1, 2024) | Reduced availability strengthens supplier pricing power. |
| Lack of Substitutes | Indispensable for high-temp and defense uses | Limits Xiamen Tungsten's sourcing options. |
| Supplier Vertical Integration | Control over mining, smelting, and processing | Enables suppliers to set prices and conditions. |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Xiamen Tungsten, this analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting the tungsten industry, revealing strengths, weaknesses, and strategic opportunities.
Xiamen Tungsten's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, actionable framework to identify and mitigate competitive threats, transforming market uncertainty into strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Xiamen Tungsten's broad reach across sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics inherently limits the sway of any single customer group. This wide industrial application base means the company isn't beholden to the demands of just one market, reducing the risk of concentrated customer pressure.
The company's strategic expansion into burgeoning fields such as new energy materials, including battery components and photovoltaic tungsten wires, further diversifies its customer portfolio. This move is crucial as it taps into high-growth markets, potentially offsetting any concentrated bargaining power from more established, mature industries.
Tungsten products like cemented carbides, tungsten powder, and tungsten wires are absolutely critical for many of Xiamen Tungsten's customers. These materials are often the backbone of high-performance applications where their unique properties, such as extreme hardness and heat resistance, are simply irreplaceable.
For example, in the manufacturing of cutting tools and wear-resistant components, tungsten's role is paramount, ensuring durability and precision. Similarly, in defense applications, tungsten's density and strength make it a vital material, leading to a high degree of customer dependence on a consistent and reliable supply chain from Xiamen Tungsten.
Customers' bargaining power is a mixed bag for Xiamen Tungsten. While many are indeed price-sensitive, especially in crowded markets, the demanding nature of tungsten applications often means quality and consistent performance trump the absolute cheapest option. This is great news for Xiamen Tungsten if they can reliably deliver top-notch products, as it limits how much customers can push prices down.
Customer Concentration in Specific Segments
While Xiamen Tungsten operates across a diversified product portfolio, customer concentration can emerge in specific, high-volume segments. For instance, a few major automotive manufacturers or significant players in the defense sector might account for a substantial portion of demand for particular tungsten products. This concentration allows these large customers to wield considerable bargaining power, often demanding favorable pricing or customized specifications due to their significant purchase volumes.
- Concentrated Demand: Key end-user industries like automotive and aerospace can represent concentrated customer bases for Xiamen Tungsten's high-purity or specialized tungsten products.
- Volume Leverage: Large customers, by virtue of their scale, can negotiate better terms, potentially impacting Xiamen Tungsten's profit margins on specific product lines.
- Niche Market Power: In niche applications where Xiamen Tungsten is a primary supplier, even a single significant customer can exert substantial influence.
Availability of Substitutes for End Products
While direct substitutes for tungsten itself are scarce, customers can often find alternative materials or product designs that lessen their dependence on tungsten. For instance, in applications demanding high density, materials like depleted uranium or lead might serve as replacements. Similarly, advancements in battery technology could lead to chemistries that do not require tungsten.
The availability of these substitutes directly impacts Xiamen Tungsten's bargaining power. If customers can easily switch to alternative materials or designs, they gain leverage to negotiate lower prices or better terms. This is particularly relevant in sectors where tungsten's unique properties are not absolutely indispensable.
- Limited Direct Substitutes: Tungsten's unique properties, such as its high melting point and density, make direct substitution challenging in many core applications like filaments or high-speed cutting tools.
- Indirect Substitution through Design/Technology: Customers can reduce tungsten usage by redesigning products or adopting new technologies. For example, lighter materials in automotive or aerospace could reduce the need for tungsten alloys.
- Alternative Material Examples: In certain high-density applications, depleted uranium or lead are potential substitutes. For battery applications, the shift towards lithium-ion or solid-state batteries may reduce reliance on tungsten components.
- Impact on Pricing Power: The greater the ease and cost-effectiveness of adopting these alternatives, the stronger the customer's bargaining power, potentially pressuring Xiamen Tungsten's pricing and profit margins.
Xiamen Tungsten's customers possess moderate bargaining power. While tungsten is critical in many applications, limiting direct substitution, large volume buyers in sectors like automotive and defense can negotiate favorable terms. The company's diversification into new energy materials in 2024, targeting high-growth markets, helps mitigate this power by broadening its customer base and reducing reliance on any single segment.
| Customer Segment | Key Applications | Estimated Bargaining Power Influence | 2024 Market Share Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Cutting tools, wear parts, lighting | Moderate to High (due to volume) | Significant demand for high-performance components. |
| Aerospace | High-temperature alloys, specialized components | Moderate (due to specialized needs and quality focus) | Consistent demand for critical, high-specification materials. |
| Electronics | Filaments, specialized coatings | Low to Moderate (due to niche requirements) | Growing demand driven by technological advancements. |
| New Energy | Battery materials, photovoltaic components | Emerging Moderate (potential for concentrated demand in specific battery chemistries) | Rapid growth area, with Xiamen Tungsten investing heavily in 2024. |
Same Document Delivered
Xiamen Tungsten Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Xiamen Tungsten, offering a detailed examination of industry competition. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted analysis. This means no surprises or placeholder content, just the comprehensive strategic insights you need.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The tungsten industry is fiercely competitive, largely due to China's overwhelming production dominance, supplying over 80% of the world's annual output. This concentration naturally fuels intense rivalry among numerous domestic producers, both large and small.
Xiamen Tungsten, a key player, navigates this highly competitive Chinese market. In 2024, China's tungsten concentrate production remained robust, solidifying its position as the primary global supplier, which intensifies the competitive pressures faced by all domestic entities, including Xiamen Tungsten.
The tungsten market is seeing significant consolidation, with larger companies buying out smaller competitors. This trend aims to boost efficiency and leverage economies of scale. For instance, Sandvik Group's acquisition of Buffalo Tungsten, Inc. in December 2023 highlights this move, directly increasing competitive pressure in North America.
Major tungsten producers are also actively expanding their production capabilities. This expansion occurs through both building new facilities and acquiring existing operations. Such capacity increases, coupled with consolidation, mean fewer, but stronger, players are shaping the competitive landscape.
Companies like Xiamen Tungsten are actively diversifying beyond basic tungsten into higher-value areas like cemented carbides and battery materials. This strategy aims to lessen direct competition in the commodity tungsten market and secure greater value throughout their entire supply chain.
In 2023, Xiamen Tungsten reported revenue from its new energy materials segment, which includes battery materials, reached RMB 10.2 billion, a significant increase from RMB 7.5 billion in 2022, showcasing the impact of this diversification on reducing reliance on traditional tungsten products.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Technological advancements significantly fuel competitive rivalry in the tungsten industry. Companies actively invest in research and development to innovate tungsten processing, leading to new product categories like PV tungsten wires crucial for the burgeoning solar energy sector. For instance, in 2023, global investment in renewable energy, including solar, reached over $570 billion, highlighting the demand for such specialized materials.
Companies demonstrating a commitment to R&D, focusing on creating more efficient, durable, or specialized tungsten products, are positioned to secure a substantial competitive advantage. This innovation drive means that firms that can leverage material science breakthroughs to enhance tungsten's properties, such as its high melting point or density, will likely outperform rivals.
- Innovation in processing techniques: Companies are developing novel methods to refine and shape tungsten, improving yield and reducing costs.
- New product development: The demand for specialized tungsten products, like those used in advanced electronics and renewable energy components, is a key driver of innovation.
- Material science advancements: Breakthroughs in understanding and manipulating tungsten alloys and composites allow for the creation of materials with enhanced performance characteristics.
- R&D investment: Leading tungsten producers are allocating significant resources to R&D, with some reporting R&D expenditure as a percentage of revenue in the range of 3-5% in 2023, aiming to stay ahead of technological curves.
Geopolitical Factors and Trade Policies
Geopolitical tensions and evolving trade policies are major players in shaping the competitive landscape for companies like Xiamen Tungsten. For instance, China's past export restrictions on critical minerals, including rare earths and tungsten itself, have historically caused significant price volatility and supply chain disruptions globally. These actions directly impact the cost of raw materials for manufacturers and can create uneven playing fields, favoring domestic producers or those with secured alternative supply chains.
The global push for supply chain resilience, particularly evident in 2024, sees various nations implementing policies aimed at securing domestic sources of critical minerals. This includes incentives for exploration and production, as well as tariffs or import restrictions on materials from certain regions. Such measures can lead to regional competitive advantages or disadvantages, as companies must navigate a complex web of international regulations and potential trade barriers.
- Global Tungsten Market Dynamics: In 2023, global tungsten mine production was estimated to be around 80,000 metric tons, with China being the dominant producer.
- Impact of Trade Policies: Tariffs and export quotas can increase the cost of imported tungsten products, potentially benefiting local suppliers.
- Supply Chain Security Efforts: Countries are actively seeking to diversify their tungsten sources, reducing reliance on single suppliers and fostering new competitive relationships.
- Price Volatility: Geopolitical events and policy changes have historically led to significant fluctuations in tungsten prices, impacting profitability and investment decisions.
The tungsten industry is characterized by intense competition, primarily driven by China's significant market share, accounting for over 80% of global production. This dominance creates a highly competitive environment for domestic producers like Xiamen Tungsten.
Consolidation is a notable trend, with larger entities acquiring smaller ones to gain efficiency and scale. For example, Sandvik's acquisition of Buffalo Tungsten in late 2023 exemplifies this, intensifying competition in specific markets.
Companies are also expanding production capacity through new builds and acquisitions, leading to fewer, but stronger, competitors. Xiamen Tungsten is actively diversifying into higher-value segments like battery materials, as evidenced by its new energy materials revenue reaching RMB 10.2 billion in 2023, up from RMB 7.5 billion in 2022.
Technological innovation is a key differentiator, with companies investing in R&D for advanced tungsten products, such as PV tungsten wires for solar energy. Global renewable energy investment exceeded $570 billion in 2023, underscoring the demand for such innovations.
SSubstitutes Threaten
For many of tungsten's core uses, like in cutting tools or defense applications where extreme hardness and heat resistance are crucial, there are few direct substitutes that can match its performance. This significantly lowers the threat of substitution in these vital sectors.
While widespread substitution for tungsten is challenging due to its unique properties, certain niche applications do face alternative materials. For example, in cemented carbide production, molybdenum carbide, niobium carbide, or titanium carbide can partially or fully replace tungsten carbide in specific wear-resistant components, potentially impacting demand in those segments.
Furthermore, in high-density applications, such as radiation shielding or counterweights, depleted uranium and lead emerge as viable substitutes. For instance, lead's lower cost and established use in applications like radiation shielding present a direct competitive threat to tungsten in these particular markets.
Ongoing advancements in material science present a significant threat of substitutes for tungsten. For instance, research into high-performance ceramics and novel alloy compositions is steadily improving their capabilities, potentially making them viable alternatives in applications where tungsten has traditionally dominated, such as in cutting tools and electronics.
Innovations in composite materials, particularly those incorporating advanced polymers or carbon-based structures, are also gaining traction. These materials offer unique combinations of strength, lightness, and thermal resistance, which could challenge tungsten's market share in sectors like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where performance and weight are critical factors.
Recycling and Circular Economy Initiatives
The growing emphasis on recycling tungsten scrap and implementing circular economy principles presents a significant threat of substitution for primary tungsten mining. As these initiatives mature, they can directly displace demand for newly extracted tungsten.
The efficiency and cost-effectiveness of tungsten recycling are key drivers of this substitution. For instance, advancements in recycling technology could make recovered tungsten competitive with primary sources, potentially lowering overall market prices and impacting the profitability of mining operations. By 2024, global efforts to boost metal recycling rates are intensifying, with many countries setting ambitious targets to reduce reliance on virgin materials.
This shift towards a circular economy for tungsten could fundamentally alter the competitive landscape for companies heavily invested in primary extraction and processing. It necessitates a strategic re-evaluation of business models to incorporate or compete with recycled tungsten supply chains.
- Reduced Demand for Primary Mining: Efficient recycling can directly substitute the need for newly mined tungsten, impacting companies focused on extraction.
- Cost Competitiveness: Advancements in recycling technology can make recovered tungsten a more cost-effective alternative, pressuring primary producers.
- Circular Economy Goals: Global initiatives promoting circular economies aim to increase the use of recycled materials, creating a structural shift away from virgin resources.
- Market Price Impact: A substantial increase in recycled tungsten supply could lead to downward pressure on tungsten prices.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs of Substitutes
Potential substitutes for tungsten often present a clear cost-performance trade-off. While some materials might be cheaper upfront, they frequently fall short in critical areas like hardness, heat resistance, or durability, which are paramount for Xiamen Tungsten's core markets.
For instance, substituting tungsten carbide in high-wear industrial applications with ceramics or hardened steels can result in significantly higher maintenance costs and reduced operational efficiency due to their lower lifespan. This performance gap makes substitutes less appealing for demanding sectors such as aerospace and heavy manufacturing.
Xiamen Tungsten's strategic focus on producing high-performance tungsten products directly counters the attractiveness of these substitutes. By offering superior material properties, the company ensures its customers experience better long-term value, even if the initial cost is higher.
The global market for cemented carbide, a primary application for tungsten, was valued at approximately $15.5 billion in 2023, with projections indicating continued growth. This demonstrates a strong market preference for tungsten's performance characteristics over potentially cheaper alternatives.
While tungsten boasts unique properties, certain substitutes offer a cost advantage in less demanding applications, presenting a threat. For example, in some wear-resistant parts, molybdenum carbide or titanium carbide can be used, though they may not match tungsten's hardness. Similarly, for radiation shielding, lead is a more economical option than tungsten, despite offering lower performance in extreme scenarios. These material trade-offs mean that for applications where peak performance isn't the absolute priority, cheaper substitutes can chip away at tungsten's market share.
Advancements in material science are continuously improving the capabilities of substitute materials. High-performance ceramics and novel alloys are becoming more competitive, potentially encroaching on tungsten's traditional strongholds like cutting tools and electronics. Furthermore, innovations in composite materials, such as advanced polymers and carbon-based structures, offer unique benefits like lighter weight and thermal resistance, which could displace tungsten in sectors like aerospace and automotive.
The growing emphasis on tungsten recycling poses a significant threat of substitution for primary tungsten. As recycling technologies improve, recovered tungsten becomes a more cost-effective alternative to newly mined material. By 2024, global recycling rates are increasing, with many nations setting targets to reduce reliance on virgin resources, directly impacting the demand for primary tungsten extraction.
| Substitute Material | Application Area | Key Advantage | Xiamen Tungsten's Core Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Carbide | Wear-resistant components | Lower cost | Superior hardness and heat resistance |
| Lead | Radiation shielding | Significantly lower cost | High density and durability |
| High-performance Ceramics | Cutting tools, electronics | Improving performance, potentially lower cost | Exceptional hardness, thermal stability |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight, specific thermal properties | Durability, high-temperature performance |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the tungsten industry, especially in mining and advanced processing, demands substantial capital. For instance, establishing a new tungsten mine can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars for exploration, extraction equipment, and processing facilities.
This high capital intensity acts as a significant deterrent for potential new players. The sheer scale of investment needed for state-of-the-art smelting and refining technologies, which are crucial for producing high-purity tungsten products, further raises the barrier to entry.
New entrants face significant hurdles in accessing raw materials, particularly high-quality tungsten ore reserves. China dominates global reserves, holding approximately 70% as of recent estimates, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to secure a reliable and cost-effective supply outside of this dominant region.
The challenge is compounded by the scarcity of economically viable tungsten deposits elsewhere. Developing new mines requires substantial capital investment and extensive geological surveying, a barrier that can deter potential new players looking to enter the tungsten market.
Xiamen Tungsten's strategic advantage lies in its integrated operations, spanning from mining and ore processing to the production of downstream tungsten products. This vertical integration provides them with a secure and controlled supply chain, a significant competitive edge that new entrants would struggle to replicate.
The tungsten mining and processing sector faces significant barriers to entry due to rigorous environmental regulations and licensing processes. Navigating these complex requirements, which often demand specialized expertise and substantial investment in compliance, deters potential new competitors.
Established Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships
Established brand reputation and customer relationships present a significant barrier for new entrants into the tungsten market, particularly for companies like Xiamen Tungsten. These existing players have cultivated deep trust and loyalty within specialized industrial sectors, built over years of consistent quality and reliable supply. For instance, Xiamen Tungsten's long-standing relationships with major players in the automotive and aerospace industries mean new competitors must overcome substantial hurdles in establishing credibility and securing initial contracts.
Newcomers face the daunting task of replicating the established trust and quality assurance that Xiamen Tungsten has meticulously built. This involves not only matching product specifications but also demonstrating a robust and dependable supply chain, which can take years and significant investment to develop. In 2024, the global demand for tungsten remained strong, driven by industrial applications, yet the barriers to entry for new suppliers were amplified by the need to prove reliability against established, trusted brands.
- Brand Loyalty: Xiamen Tungsten benefits from established brand recognition, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share.
- Customer Relationships: Long-term partnerships with key industrial clients create switching costs and loyalty.
- Supply Chain Integration: Existing players have optimized their supply chains, offering efficiency and reliability that new entrants struggle to match.
- Quality Assurance: A proven track record of quality is paramount in specialized sectors, posing a challenge for unproven new suppliers.
Technological Expertise and Intellectual Property
The production of high-value tungsten products, like cemented carbides and specialized tungsten wires for photovoltaic applications and battery materials, demands significant technological expertise. This advanced know-how, coupled with proprietary processes and robust intellectual property, forms a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants. For instance, companies investing in R&D for next-generation battery materials, a rapidly growing sector, face considerable upfront costs and long development cycles.
New players would need to either undertake costly and time-consuming research and development or acquire existing technologies, further intensifying the barrier to entry. In 2024, the global market for advanced materials, including those utilizing tungsten, continued to see substantial investment in innovation, with leading firms protecting their advancements through patents. This focus on intellectual property means that replicating the quality and efficiency of established players is a complex and expensive undertaking.
- High R&D Investment: Developing advanced tungsten products requires significant capital outlay for research and development, often in the tens of millions of dollars annually for leading firms.
- Proprietary Processes: Established companies possess unique manufacturing techniques and formulations that are difficult and costly to replicate, providing a competitive edge.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Extensive patent portfolios protect key technologies, making it challenging for new entrants to operate without infringing on existing intellectual property rights.
- Acquisition Costs: The alternative to R&D is acquiring existing companies with the necessary expertise and IP, which can involve multi-million dollar transactions.
The threat of new entrants in the tungsten industry is considerably low, largely due to the immense capital required to establish operations. Building a new tungsten mine, for example, can cost upwards of hundreds of millions of dollars for exploration, equipment, and processing.
Furthermore, China's dominance in tungsten reserves, holding approximately 70% as of recent estimates, makes securing a reliable raw material supply a significant challenge for newcomers. This scarcity, coupled with stringent environmental regulations and complex licensing processes, adds further layers of difficulty.
Established players like Xiamen Tungsten also benefit from strong brand loyalty and deep customer relationships built over years, creating high switching costs for clients. Replicating the quality assurance and technological expertise in advanced tungsten products, which often involves proprietary processes and extensive R&D, presents another substantial barrier.
In 2024, the global tungsten market continued to be characterized by these high barriers. The need for substantial investment in technology and the protection of intellectual property through patents by existing firms means that new entrants face a complex and costly undertaking to compete effectively.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing mining and processing facilities | Hundreds of millions USD for a new mine |
| Raw Material Access | Securing reliable tungsten ore supply | Challenging due to China's 70% reserve dominance |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Environmental compliance and licensing | Requires specialized expertise and investment |
| Technology & IP | Advanced processing and proprietary methods | High R&D costs, patent protection by incumbents |
| Brand & Relationships | Building trust and customer loyalty | Years of consistent quality and supply needed |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Xiamen Tungsten Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like CRU and Roskill, and global trade statistics.
We leverage insights from financial filings, expert interviews with industry analysts, and recent news from major players in the tungsten market to accurately assess competitive pressures.