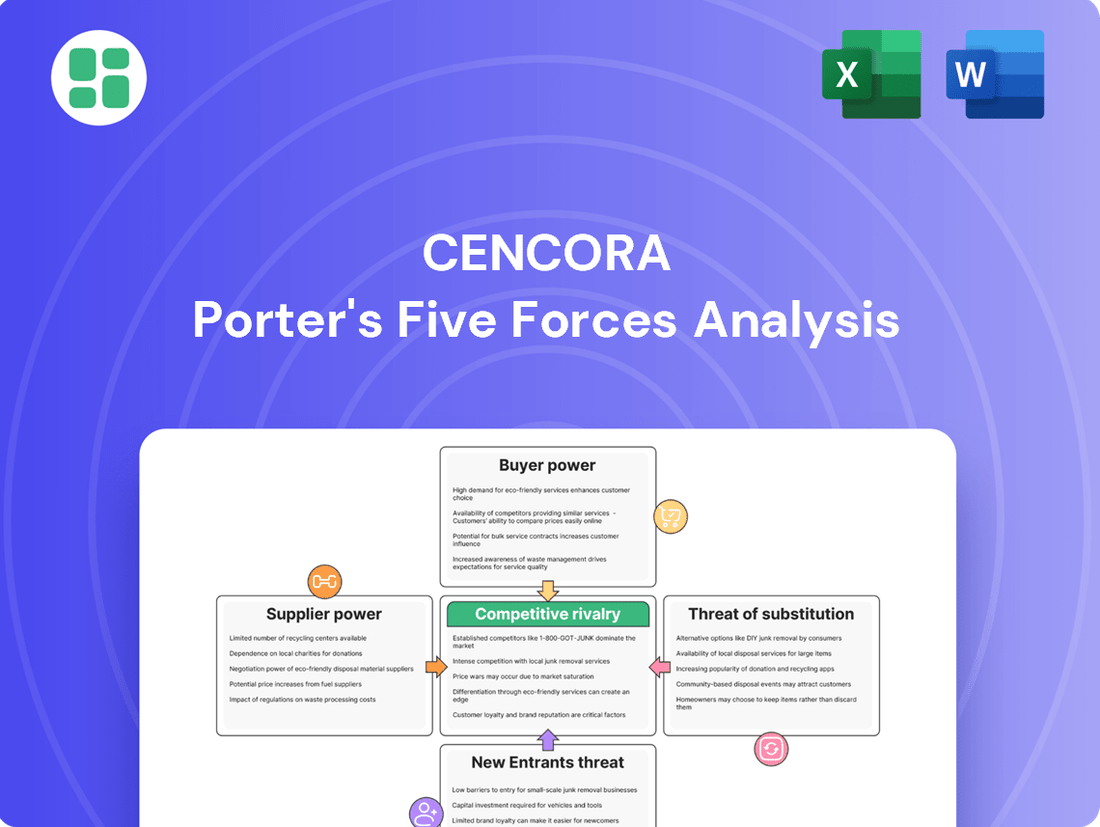
Cencora Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cencora Bundle
Cencora operates in a dynamic healthcare landscape, facing significant competitive pressures from rivals and the constant threat of new market entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of both its suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating this complex environment.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Cencora’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cencora's core suppliers are pharmaceutical manufacturers, and the industry's structure significantly impacts their bargaining power. In 2024, the pharmaceutical sector, particularly for high-value branded and specialty drugs, remains characterized by a notable concentration of major players. For instance, a handful of companies often dominate the market for specific therapeutic areas due to extensive patent protection and the immense cost and complexity of research and development.
This concentration means Cencora often faces a limited number of viable sourcing options for critical medications. When a few large manufacturers control a significant portion of the supply for essential drugs, their ability to dictate terms, including pricing and volume, increases substantially. This dynamic directly translates to higher supplier bargaining power, potentially impacting Cencora's cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the pharmaceutical sector is significantly influenced by product differentiation. For Cencora, suppliers offering highly differentiated, patented, or specialty drugs wield considerable power. This is because these unique products are essential to meet specific patient and provider demands, leaving Cencora with fewer alternatives.
Conversely, for generic drugs, Cencora faces a different dynamic. The presence of multiple manufacturers for these commoditized products means Cencora has greater leverage. This increased leverage stems from the intense competition among generic producers, allowing Cencora to negotiate more favorable terms.
Switching pharmaceutical suppliers presents considerable hurdles for Cencora. These include the expense and intricate processes of renegotiating contracts, adapting established logistics, and ensuring ongoing regulatory compliance across various markets. For instance, a shift in a major supplier could necessitate extensive validation of new supply chains, a process that can take months and incur substantial upfront costs.
These high switching costs inherently bolster the bargaining power of established pharmaceutical manufacturers. When it is difficult and costly for Cencora to change suppliers, these manufacturers can often command more favorable terms, potentially impacting Cencora's profitability and operational flexibility.
Threat of Forward Integration by Manufacturers
The threat of forward integration by manufacturers can impact Cencora's bargaining power. Some large pharmaceutical manufacturers, particularly those with high-value specialty drugs, may explore distributing their products directly to healthcare providers or patients. This bypasses the need for intermediaries like Cencora, potentially reducing Cencora's revenue streams.
- Direct Distribution for Specialty Drugs: Manufacturers might find it more profitable to manage the complex logistics of specialty drug distribution themselves, especially for products requiring specific handling or patient support.
- Reduced Reliance on Distributors: If successful, this strategy could lessen the reliance of manufacturers on traditional distributors, thereby diminishing Cencora's leverage in negotiations.
- Market Share Impact: While broad distribution remains complex, even a small shift towards direct sales for niche products could chip away at Cencora's market share and influence.
Importance of Cencora to Suppliers
Cencora's position as one of the top three pharmaceutical distributors in the U.S. grants it considerable sway with its suppliers. By handling approximately one-third of the domestic drug distribution market, Cencora represents a vital conduit for pharmaceutical manufacturers seeking to reach a vast array of healthcare providers across the nation.
This extensive market penetration translates into significant bargaining power for Cencora. Manufacturers rely on Cencora's established network and logistical capabilities to ensure their products reach pharmacies, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities efficiently. In 2024, Cencora's scale of operations means that securing favorable terms from such a dominant player is paramount for supplier profitability.
- Market Share: Cencora distributes roughly one-third of all pharmaceuticals in the U.S.
- Network Access: Provides manufacturers with access to a broad base of healthcare providers.
- Negotiating Leverage: This widespread reach allows Cencora to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers.
Cencora's suppliers, primarily pharmaceutical manufacturers, hold significant bargaining power, especially for patented and specialty drugs. The concentration within these segments, where a few companies dominate specific therapeutic areas due to R&D costs and patents, limits Cencora's sourcing options. This allows manufacturers to dictate terms, impacting Cencora's cost of goods sold.
Conversely, for generic drugs, Cencora benefits from a more competitive supplier landscape, enabling it to negotiate more favorable terms. The high switching costs associated with changing pharmaceutical suppliers further strengthen the position of established manufacturers, as Cencora faces substantial expense and logistical challenges in renegotiating contracts and adapting supply chains.
The threat of forward integration by manufacturers, particularly for high-value specialty drugs, could reduce Cencora's reliance on distribution services. While Cencora's substantial market share in the U.S. distribution market provides some leverage, the inherent power of key pharmaceutical suppliers remains a critical factor in its operational environment.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Cencora | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Specialty/Branded Drugs) | Increases supplier bargaining power | High due to patent protection and R&D investment |
| Product Differentiation | High for unique/patented drugs, low for generics | Critical for specialty drug sourcing negotiations |
| Switching Costs for Cencora | High, bolstering supplier leverage | Significant due to contract renegotiations and logistics |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential to reduce Cencora's role | Manufacturers may explore direct distribution for niche products |
| Cencora's Market Share | Provides some counter-leverage | Distributes ~1/3 of US pharmaceuticals, offering access to providers |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cencora dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and overall industry attractiveness within its market.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, built to highlight Cencora's strategic vulnerabilities and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cencora's customer base is heavily concentrated among large healthcare systems, hospital networks, and major pharmacy chains. Giants like Walgreens, Cigna, and Kaiser Permanente represent a substantial portion of Cencora's revenue. This concentration means these major players wield significant influence.
Their immense purchasing volume grants them considerable bargaining power. They can negotiate favorable terms, pricing, and service level agreements, directly impacting Cencora's profit margins. For instance, in 2023, Cencora's top ten customers accounted for approximately 40% of its total revenue, highlighting the leverage these entities possess.
The standardization of distribution services, particularly for common pharmaceuticals, can empower customers. If Cencora's core delivery function is viewed as a commodity, buyers may exert more pressure on pricing, seeking the best available rates. This is a key consideration in their bargaining power.
While Cencora provides a comprehensive suite of services, the fundamental act of moving drugs can appear similar across providers. This perception of standardization, even if Cencora offers more, can lead customers to treat the service as interchangeable, thus increasing their leverage in negotiations.
Healthcare providers encounter significant switching costs when moving from one primary pharmaceutical distributor to another. These costs include potential disruptions to their crucial supply chain, the expense and effort of integrating new inventory management and ordering systems, and the time required to build new relationships and trust with a different supplier. For instance, a hospital might need to retrain staff on new ordering platforms and reconfigure their entire pharmaceutical receiving and storage processes.
Despite these inherent switching costs, the competitive landscape for pharmaceutical distribution in 2024 means that these barriers are not insurmountable. Rival distributors are often willing to offer aggressive pricing, extended credit terms, or dedicated support services to entice providers to switch. Cencora, as a major player, must consider how its pricing and service levels compare to competitors who are actively seeking to attract new business by minimizing the perceived cost of switching for customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, such as large hospital networks or integrated delivery systems, can significantly impact Cencora's bargaining power. These entities might explore setting up their own in-house distribution channels, especially for high-demand or specialized pharmaceuticals.
While requiring substantial initial investment, this potential move by customers directly enhances their leverage. For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical distribution market continues to see consolidation among large healthcare providers, making such integration more feasible.
- Customer Integration: Major hospital systems and integrated delivery networks (IDNs) possess the scale to consider developing their own pharmaceutical distribution infrastructure.
- Cost and Efficiency Drivers: The primary motivators for backward integration are often cost reduction and greater control over the supply chain for essential or high-volume medications.
- Market Dynamics: As of mid-2024, the increasing complexity of drug sourcing and the desire for predictable supply chains are fueling interest in vertical integration among large healthcare purchasers.
- Impact on Distribution Margins: Successful backward integration by a significant customer segment would directly reduce the volume of business available to distributors like Cencora, potentially squeezing profit margins.
Price Sensitivity of Customers and Reimbursement Pressures
Healthcare providers, such as pharmacies and hospitals, are increasingly feeling the squeeze from reimbursement pressures and the need to control costs. This makes them very sensitive to the prices they pay for the products and services they receive.
For Cencora, this translates directly into strong demands for lower distribution costs. For instance, in 2024, many healthcare systems reported significant increases in their operating expenses, driven by factors like labor shortages and inflation, which intensifies their focus on supplier pricing.
- Price Sensitivity: Healthcare providers are actively seeking ways to reduce their overall drug acquisition costs to meet budget targets.
- Reimbursement Pressures: Declining reimbursement rates from government payers and private insurers force providers to negotiate harder with their suppliers.
- Impact on Cencora: Cencora's customers, driven by these pressures, will likely push for more favorable pricing terms, potentially impacting Cencora's gross margins on distribution services.
Cencora's customers, particularly large healthcare systems and pharmacy chains, possess substantial bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volume and the relative standardization of distribution services. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly influencing Cencora's profitability. The threat of backward integration and the customers' own cost pressures further amplify this leverage.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Cencora |
|---|---|---|
| Large Hospital Networks | High purchase volume, potential for backward integration | Increased price negotiation, potential loss of business |
| Major Pharmacy Chains (e.g., Walgreens) | Significant market share, price sensitivity | Pressure for lower distribution fees, impact on margins |
| Integrated Delivery Networks (IDNs) | Scale for self-distribution, cost control focus | Leverage for customized terms, risk of disintermediation |
Same Document Delivered
Cencora Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cencora Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase. No alterations or placeholders exist; you get the full, ready-to-use report instantly.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. pharmaceutical wholesale and distribution sector is a tight-knit arena, largely controlled by just three giants: Cencora, McKesson, and Cardinal Health. Together, these titans command an overwhelming share, supplying more than 90% of all pharmaceuticals distributed within the United States. This oligopolistic structure means competition is fierce, with each of these large, deeply entrenched players constantly vying for market position and advantage.
The pharmaceutical wholesale and distribution market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a significant expansion driven by rising global drug sales, a growing elderly population, and the continuous launch of new and advanced medications. This upward trend in the industry creates fertile ground for competition.
As the market expands, particularly in high-value segments such as specialty pharmaceuticals, existing players and new entrants are intensifying their efforts to capture a larger share. This dynamic fuels a competitive rivalry as companies strive for efficiency, strategic partnerships, and broader market reach to stand out.
While many distributors offer similar core services, Cencora stands out by providing specialized solutions. These include a strong focus on oncology, complex specialty logistics, strategic market access for manufacturers, and advanced data analytics. This differentiation is key in a sector where basic distribution margins are often thin.
These higher-margin, value-added services are critical for Cencora to gain and maintain a competitive edge. For instance, their specialty pharmacy services, which are a significant part of their differentiation, saw substantial growth. In 2023, Cencora's specialty segment revenue continued to be a strong performer, reflecting the demand for these specialized capabilities.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The pharmaceutical distribution sector, where Cencora operates, is characterized by significant fixed costs. These include the substantial investments required for sophisticated warehousing facilities, extensive logistics networks, and advanced IT systems necessary for efficient and compliant drug handling. For instance, building and maintaining a national distribution center can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
These high fixed costs create formidable barriers to entry for new competitors. More importantly, they also act as significant exit barriers for established players. Companies are compelled to continue operating and competing intensely to spread these fixed costs over a larger volume of sales, rather than shutting down and incurring substantial losses from underutilized assets.
- High Capital Investment: Pharmaceutical distributors require massive upfront capital for specialized, temperature-controlled warehouses and a complex, nationwide delivery infrastructure.
- Operational Scale is Key: To achieve profitability, distributors must operate at a very large scale to cover their extensive fixed costs, leading to intense competition for market share.
- Exit is Costly: The specialized nature of the assets and the integrated supply chain make it difficult and expensive for companies to divest or repurpose their infrastructure, locking them into continued competition.
Strategic Partnerships and Customer Loyalty
Cencora cultivates deeply entrenched relationships with its major clients, including prominent names like Walgreens, Cigna, and Kaiser Permanente. These enduring partnerships, even with annual renewal processes, underscore a significant level of customer loyalty and create a sticky business environment. This stickiness is a crucial factor in managing competitive rivalry within the sector.
The stability of these long-term contracts directly impacts competitive dynamics. For instance, Cencora's ability to retain major clients like Walgreens, a Fortune 50 company, demonstrates a competitive advantage. This loyalty reduces the likelihood of these large customers switching to competitors, thereby lowering the intensity of rivalry for Cencora's core business.
- Customer Retention: Cencora's strong relationships with key clients like Walgreens and Cigna translate into high customer retention rates, a vital component in mitigating competitive rivalry.
- Partnership Stability: Despite annual renewals, the consistent re-engagement with major partners highlights the "stickiness" of Cencora's services, making it harder for rivals to poach these accounts.
- Market Concentration: In a concentrated market, the loyalty of a few large customers significantly influences the overall competitive landscape, as gaining or losing such accounts has a substantial impact.
Competitive rivalry in pharmaceutical distribution is intense, primarily due to the market's oligopolistic nature, dominated by Cencora, McKesson, and Cardinal Health, which collectively hold over 90% of the U.S. market. This concentration forces these giants into aggressive competition for market share, driven by the industry's substantial growth and the increasing demand for specialized pharmaceuticals.
The high fixed costs associated with sophisticated logistics and warehousing create significant barriers to entry and exit, compelling existing players to compete fiercely to spread these costs. Cencora differentiates itself through value-added services like oncology and specialty logistics, which command higher margins and are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a sector where basic distribution yields thin profits.
Furthermore, deeply entrenched relationships with major clients, such as Walgreens and Cigna, contribute to customer stickiness and reduce the likelihood of account switching, thereby moderating rivalry for core business. However, the pursuit of new clients and expansion into high-growth segments ensures that competitive pressures remain elevated.
| Competitor | Market Share (Approx. U.S.) | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Cencora | ~30-35% | Specialty pharma, oncology, data analytics, market access |
| McKesson | ~30-35% | Broad portfolio, technology solutions, patient services |
| Cardinal Health | ~25-30% | Medical products, pharmaceutical distribution, performance management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large healthcare providers, such as major hospital networks, possess the purchasing power to bypass traditional distributors like Cencora and negotiate directly with drug manufacturers. This can lead to lower acquisition costs for them. For instance, in 2024, many large health systems continued to explore direct-to-physician or direct-to-hospital purchasing models for certain high-volume or specialty medications.
The rise of direct-to-patient (DTP) models, particularly for complex or specialty pharmaceuticals, presents another substitute channel. Patients, often guided by their physicians, may receive medications directly from the manufacturer or a specialized pharmacy, circumventing the need for wholesale distribution services. This trend is expected to grow, especially as personalized medicine advances.
The growing presence of specialty pharmacies and integrated healthcare models presents a significant threat of substitution for Cencora's core distribution business. These entities, which manage complex and high-cost medications from end-to-end, can bypass traditional distribution channels. For instance, by 2024, the specialty pharmacy market continued its robust expansion, with some estimates projecting it to reach hundreds of billions of dollars globally, directly competing for patient access and manufacturer partnerships.
Cencora is proactively addressing this by strengthening its own leadership in the specialty pharmaceutical space. This strategy aims to capture value within these evolving models rather than being displaced by them. Their investments and acquisitions in specialty capabilities demonstrate a clear understanding of this competitive dynamic.
Technological advancements, particularly in digital health and AI, pose a significant threat of substitutes for Cencora. These technologies can streamline pharmaceutical supply chains, potentially creating new distribution models that bypass traditional intermediaries. For instance, AI-powered platforms could facilitate direct-to-patient delivery or virtual distribution networks, reducing the need for Cencora's existing infrastructure and services.
Generic and Biosimilar Adoption
The increasing adoption of generic and biosimilar drugs presents a significant threat of substitutes for Cencora. These alternatives, often priced lower, can erode the market share of branded pharmaceuticals, impacting Cencora's distribution volumes and potentially its revenue mix. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. generic drug market continued its robust growth, with generics accounting for approximately 90% of all prescriptions filled, a trend that directly pressures the demand for higher-margin branded products.
While Cencora benefits from the distribution of generics, a substantial shift towards biosimilars, in particular, could alter overall revenue streams and necessitate adjustments in distribution strategies. Biosimilars, while complex, offer cost savings similar to generics. By 2024, the U.S. biosimilar market was projected to reach over $20 billion, indicating a growing competitive landscape that Cencora must navigate.
- Generic Drug Market Share: Generics captured around 90% of U.S. prescriptions in 2024, highlighting their widespread adoption.
- Biosimilar Market Growth: The U.S. biosimilar market was expected to exceed $20 billion by 2024, signaling a significant competitive force.
- Price Sensitivity: Lower pricing of generics and biosimilars directly challenges the profitability of branded drug distribution.
- Distribution Dynamics: Evolving market share between branded and generic/biosimilar drugs can alter Cencora's distribution needs and revenue models.
In-house Logistics and Supply Chain Management by Large Entities
Large healthcare entities, such as major hospital networks or national pharmacy chains, possess the financial clout and operational scale to develop their own in-house logistics and supply chain capabilities. This allows them to potentially bypass third-party distributors for specific product lines or volumes, directly impacting Cencora's market share.
For instance, a significant portion of pharmaceutical distribution relies on specialized cold chain management. Organizations capable of investing in and maintaining these advanced temperature-controlled infrastructure and tracking systems can view Cencora's distribution services as a less essential component for those specific, high-value products.
- In-house Logistics as a Substitute: Large healthcare organizations may build their own distribution networks, particularly for high-volume or specialized (e.g., cold chain) pharmaceuticals, reducing reliance on external distributors like Cencora.
- Cost and Efficiency Drivers: The decision to insource logistics is often driven by potential cost savings and greater control over efficiency, especially for entities with substantial purchasing power and complex supply chain needs.
- Impact on Cencora: This trend represents a threat as it directly siphons off potential revenue streams and reduces the overall market volume available to Cencora, particularly from its largest clients.
The threat of substitutes for Cencora stems from various alternative channels and models that bypass traditional wholesale distribution. Large healthcare providers are increasingly exploring direct purchasing from manufacturers, driven by a desire for cost savings and greater control over their supply chains. This trend was particularly noticeable in 2024, with many major health systems actively investigating direct-to-physician or direct-to-hospital procurement for key medications.
Direct-to-patient (DTP) models and the expansion of specialty pharmacies also represent significant substitutes. These entities manage complex pharmaceuticals from origin to administration, often circumventing wholesale distributors. The specialty pharmacy market continued its robust growth in 2024, with global market size projections reaching hundreds of billions, directly competing for patient access and manufacturer relationships.
| Substitute Channel | Key Characteristics | Impact on Cencora |
| Direct Purchasing by Large Providers | Bypasses intermediaries, potential for lower acquisition costs. | Reduces Cencora's sales volume and client base. |
| Direct-to-Patient (DTP) Models | Manufacturer or specialized pharmacy delivery to patients. | Circumvents wholesale distribution services. |
| Specialty Pharmacies | End-to-end management of complex, high-cost drugs. | Competes for high-margin product distribution. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the pharmaceutical wholesale and distribution sector, where Cencora operates, demands significant financial muscle. New players must invest heavily in building and maintaining vast warehousing networks, a modern fleet of temperature-controlled vehicles for secure transport, and sophisticated IT systems for inventory management and order fulfillment. These substantial upfront capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, deterring many potential competitors from entering the market.
The pharmaceutical supply chain is a heavily regulated industry, demanding strict adherence to complex licensing, safety, and security protocols, exemplified by the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA). For instance, compliance with DSCSA serialization requirements, which became fully effective in November 2023, necessitates significant investment in technology and processes, creating a substantial barrier for new entrants seeking to operate within this space.
Existing players like Cencora leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in bulk purchasing and sophisticated logistics networks, which are crucial in the pharmaceutical distribution sector. For instance, in 2023, Cencora reported revenues exceeding $250 billion, a scale that allows for substantial cost reductions per unit distributed. New entrants would find it incredibly challenging to match these operational efficiencies and cost advantages, as building a comparable infrastructure from scratch requires immense capital investment and time.
Established Relationships and Networks
The established relationships and networks within the pharmaceutical distribution sector pose a significant threat to new entrants. The dominant players, often referred to as the 'Big Three' distributors, have cultivated decades-long, deeply entrenched connections with both the manufacturers of life-saving medications and a sprawling network of healthcare providers, including hospitals, pharmacies, and clinics.
These strong, trust-based relationships are not easily replicated. They are built on consistent reliability, efficient logistics, and a proven track record of service, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2023, the top three pharmaceutical distributors in the US collectively handled over 90% of the prescription drug market, a testament to their market dominance and the strength of their existing networks.
- Deeply Entrenched Partnerships: Long-standing ties with pharmaceutical manufacturers ensure consistent supply agreements and favorable terms.
- Extensive Healthcare Provider Networks: Vast reach across hospitals, pharmacies, and clinics facilitates efficient product delivery and market penetration.
- High Switching Costs for Customers: Healthcare providers are reluctant to disrupt established, reliable supply chains, creating a barrier for new distributors.
- Trust and Reliability: Years of dependable service have fostered significant trust, a crucial element in a sector dealing with critical medicines.
Specialized Expertise and Technology
New companies entering the pharmaceutical distribution market face significant hurdles due to the specialized knowledge and technology required. Distributing pharmaceuticals, particularly those needing precise temperature control or those classified as specialty drugs, demands sophisticated cold chain infrastructure and deep operational expertise. For instance, maintaining the integrity of biologics, which often require temperatures between 2°C and 8°C, necessitates substantial investment in refrigerated warehousing and specialized transportation networks.
Developing these advanced capabilities, including the integration of robust data analytics platforms for supply chain visibility and efficiency, presents a considerable barrier. New entrants must also navigate complex regulatory landscapes and establish reliable relationships with manufacturers and healthcare providers, further increasing the difficulty of market entry. In 2024, the global pharmaceutical cold chain market was valued at over $19 billion, highlighting the scale of investment needed to compete effectively.
- Specialized Infrastructure: Cold chain logistics require significant capital investment in temperature-controlled vehicles, warehouses, and monitoring systems.
- Technological Integration: Advanced data analytics and supply chain management software are crucial for efficiency and compliance, posing a steep learning curve and investment requirement.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating stringent pharmaceutical regulations, including Good Distribution Practices (GDP), demands specialized knowledge and robust quality management systems.
- Industry Relationships: Building trust and securing contracts with pharmaceutical manufacturers and healthcare providers is a lengthy and complex process for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants into Cencora's pharmaceutical distribution market is relatively low. Significant capital investment is required for warehousing, logistics, and IT infrastructure, deterring many potential competitors. For example, the global pharmaceutical cold chain market, crucial for specialty drugs, was valued at over $19 billion in 2024, underscoring the scale of initial investment needed.
Strict regulatory compliance, such as the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA), which mandates serialization and traceability, adds another layer of complexity and cost. New entrants must navigate these stringent requirements, which can be a substantial barrier. Furthermore, established players benefit from immense economies of scale, with companies like Cencora achieving revenues exceeding $250 billion in 2023, allowing for significant cost advantages that are difficult for newcomers to match.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in infrastructure (warehousing, fleet, IT). | Significant deterrent due to substantial financial outlay. | Global pharmaceutical cold chain market valued at over $19 billion (2024). |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, safety, and security protocols (e.g., DSCSA). | Requires specialized knowledge and investment in compliance systems. | DSCSA serialization requirements fully effective November 2023. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations (purchasing, logistics). | New entrants struggle to compete on cost due to lack of scale. | Cencora's 2023 revenues exceeded $250 billion. |
| Established Relationships | Deeply entrenched ties with manufacturers and healthcare providers. | Difficult for newcomers to build trust and secure contracts. | Top three US distributors handled over 90% of prescriptions in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cencora Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Cencora's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports from firms like IQVIA and McKinsey. We also incorporate data from pharmaceutical and healthcare trade publications, and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.