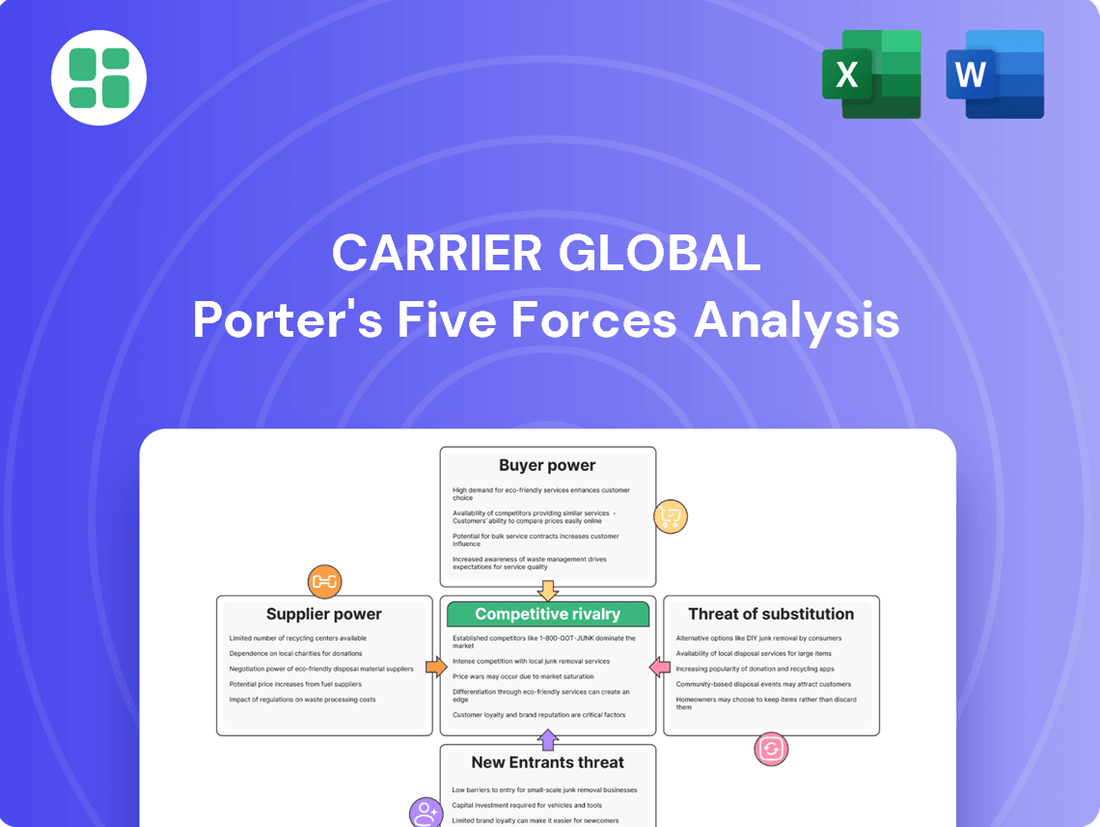
Carrier Global Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Carrier Global Bundle
Carrier Global navigates a complex landscape where intense rivalry and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its market. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Carrier Global’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Carrier Global's reliance on a global supply chain for its diverse product portfolio, from HVAC systems to fire and security solutions, means that supplier concentration is a key factor. If a significant portion of critical components or specialized technologies comes from a limited number of suppliers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage.
This leverage is amplified when Carrier Global finds it difficult to substitute these unique or patented technologies, as this limits their options and strengthens the supplier's position. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor shortage highlighted how a few key chip manufacturers could exert significant pricing power over industries like HVAC and building automation, impacting production timelines and costs for companies like Carrier.
The cost and complexity for Carrier Global to switch suppliers for its HVAC, refrigeration, and fire and security solutions can be substantial. This is particularly true for integrated systems or highly specialized components, where significant investment in research, development, and testing is required for new suppliers.
High switching costs, encompassing potential redesign efforts, re-tooling manufacturing processes, and the rigorous re-qualification of new suppliers, directly bolster the bargaining power of Carrier's existing suppliers. These factors make it economically and operationally challenging for Carrier to change its supply base frequently.
Carrier's strategic approach, including its Carrier Alliance program, aims to cultivate long-term relationships with preferred suppliers. This initiative is designed to foster collaboration, ensure quality, and potentially mitigate the inherent power of suppliers by creating a more stable and committed supply chain ecosystem.
Suppliers offering unique or proprietary inputs, like specialized refrigerants or advanced sensors for building automation systems, can command greater leverage. Carrier's commitment to cutting-edge, sustainable technologies often necessitates these specialized components, potentially sourced from a concentrated supplier base.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is generally low for Carrier Global. The significant capital investment and technical expertise required to manufacture HVAC units or security systems act as substantial barriers to entry for most component suppliers. This complexity limits their ability to credibly threaten to produce Carrier's end products themselves, thereby reducing their bargaining power.
For instance, establishing a manufacturing facility comparable to Carrier's global footprint would necessitate billions of dollars in investment and years of development. This high barrier means few suppliers possess the resources or capabilities to effectively integrate forward into Carrier's core markets.
- Low Threat of Forward Integration: Component suppliers face high capital requirements and technical hurdles to enter Carrier's manufacturing space.
- Barriers to Entry: The complexity and scale of producing HVAC and security systems deter most suppliers from attempting forward integration.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: This low threat preserves Carrier's bargaining power by limiting suppliers' ability to dictate terms or capture value by entering Carrier's industry.
Importance of Carrier to Suppliers
Carrier Global's substantial size makes it a critical customer for numerous suppliers. For instance, in 2023, Carrier reported revenues of $22.1 billion, illustrating the significant volume of business it generates. This scale inherently shifts leverage towards Carrier.
When a supplier derives a large portion of its income from Carrier, its ability to negotiate favorable terms is diminished. This dependency can force suppliers to accept lower prices or less favorable payment schedules to retain Carrier's business.
Carrier's purchasing power, amplified by its global operations and high demand, enables it to secure advantageous pricing and contract conditions. This is a common dynamic where large buyers can dictate terms, thereby reducing the bargaining power of their suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers heavily reliant on Carrier's orders face reduced bargaining power.
- Carrier's Scale Advantage: Carrier's significant revenue, $22.1 billion in 2023, allows it to negotiate better terms.
- Price Negotiation: The company's size enables it to command lower prices and more favorable conditions from its suppliers.
Carrier Global's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by several factors, including supplier concentration, the uniqueness of inputs, and switching costs. While Carrier's substantial scale, evidenced by its $22.1 billion in revenue for 2023, generally provides leverage, the reliance on specialized components can shift power back to suppliers.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Carrier's business is minimal due to the immense capital and technical expertise required. This dynamic helps maintain Carrier's ability to negotiate favorable terms, though the specific nature of its supply chain, particularly for advanced technologies, requires careful management of supplier relationships.
| Factor | Impact on Carrier's Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration & Uniqueness of Inputs | Can increase supplier power if critical components are sourced from few providers or are highly specialized. | Semiconductor shortages in 2024 demonstrated how limited chip manufacturers could exert pricing power. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs for integrated systems or specialized components strengthen existing supplier leverage. | Significant investment in R&D, re-tooling, and re-qualification is needed for new suppliers. |
| Carrier's Purchasing Power | Carrier's large scale and demand generally provide significant leverage, enabling favorable pricing. | Carrier's 2023 revenue of $22.1 billion signifies substantial purchasing volume. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low, as suppliers face high barriers to enter Carrier's complex manufacturing operations. | Billions in investment and years of development are required to match Carrier's global footprint. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Carrier Global, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing Carrier Global's bargaining power of suppliers and buyers.
Customers Bargaining Power
Carrier Global interacts with a broad spectrum of customers, from individual homeowners to large industrial enterprises, utilizing direct sales, a network of distributors, and service centers. While single residential buyers possess minimal leverage, substantial commercial and industrial clients, particularly those involved in large construction projects or bulk purchases, can significantly influence pricing and contract conditions.
The bargaining power of these larger customers is amplified by their volume. For instance, major construction projects often involve substantial HVAC system orders, giving these clients considerable sway. Carrier's strategic emphasis on securing large commercial HVAC backlogs, as highlighted by their 2025 projections, underscores the critical importance of these high-volume customers and their potential to negotiate favorable terms.
Customer switching costs for Carrier Global’s HVAC, fire, and security systems can be substantial for large commercial and industrial clients. These costs stem from the complexity of installation, the need to integrate new systems with existing infrastructure, and the potential for operational disruptions during a transition. For instance, a major data center upgrading its cooling systems faces significant expenses beyond the hardware itself, including labor, recalibration, and testing, which can easily run into hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Once a Carrier system is installed and operational, these high switching costs generally diminish the bargaining power of these large customers. They are less likely to switch to a competitor for minor price differences due to the significant upfront investment and ongoing commitment required. This sticky customer base provides Carrier with a degree of pricing stability and reduces the pressure from competitors seeking to poach existing clients.
However, the landscape shifts when customers are considering new installations or full system replacements. In these scenarios, switching costs can be considerably lower, allowing customers more flexibility to compare offerings and negotiate terms between different manufacturers. This means that while Carrier benefits from high switching costs for its installed base, it must remain competitive on initial pricing and performance to win new business.
Customers in the HVAC and building technology sectors are showing a heightened sensitivity to pricing. This trend is amplified by increased competition and the wider availability of energy-efficient options, pushing buyers to scrutinize costs more closely.
The industry's move towards SEER2-compliant systems and sustainable technologies means customers are increasingly focused on total cost of ownership. They are evaluating not just the upfront price but also long-term operational expenses and potential energy savings, making value a critical purchasing factor.
Availability of Information
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, with easy access to details about product performance, pricing, and what rivals offer. This transparency, fueled by online reviews and industry comparisons, allows them to make smarter buying choices and negotiate better deals. For instance, in 2024, consumer electronics reviews on platforms like Consumer Reports and Wirecutter significantly influenced purchasing decisions, with over 70% of consumers consulting online reviews before buying. This heightened awareness directly impacts Carrier's ability to command premium pricing, as customers can readily compare features and costs across the HVAC market.
The widespread availability of information directly translates into stronger bargaining power for customers. They can easily identify alternative suppliers and understand the true value of Carrier's offerings. This makes it harder for Carrier to differentiate solely on product features without also competing on price, potentially squeezing profit margins. In the B2B sector, procurement platforms in 2024 have also increased transparency, allowing large industrial clients to benchmark pricing for HVAC systems more effectively, further intensifying this dynamic.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can readily access data on energy efficiency ratings, installation costs, and long-term maintenance expenses for HVAC systems.
- Price Benchmarking: Online comparison tools and industry reports allow buyers to easily benchmark Carrier's pricing against competitors like Daikin or Trane.
- Influence on Sales: Positive online reviews and readily available product comparisons in 2024 have shown to increase conversion rates by up to 40% for companies with transparent pricing and performance data.
- Negotiation Leverage: Armed with comprehensive market intelligence, customers can negotiate more aggressively on price and service terms with Carrier.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers backward integrating to produce their own HVAC, refrigeration, or security systems is generally low for Carrier Global. This is primarily due to the highly specialized manufacturing processes, substantial research and development investments, and significant capital expenditures inherent in these industries. For instance, developing and producing advanced variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems or sophisticated building automation controls requires deep technical expertise and dedicated facilities that most customers lack.
This low threat of backward integration directly contributes to a reduced bargaining power for Carrier's customers. They are less likely to possess the capabilities or resources to effectively manufacture these complex systems themselves, making them more reliant on Carrier's offerings. In 2023, Carrier's revenue reached $22.1 billion, underscoring the scale and complexity of its operations that are difficult for typical customers to replicate.
However, the situation can differ for very large corporate clients or major real estate developers. These entities might exert influence by specifying particular components or even dictating design elements for their projects. While this doesn't equate to full backward integration, it represents an indirect form of market influence, allowing them to negotiate terms or push for customization that aligns with their strategic objectives.
- Low Likelihood of Full Backward Integration: Customers typically lack the specialized manufacturing, R&D, and capital required to produce Carrier's complex HVAC, refrigeration, and security systems.
- Reduced Customer Bargaining Power: The inability of most customers to produce these systems in-house limits their leverage in negotiations with Carrier.
- Indirect Influence from Large Clients: Major corporations and developers can exert influence through component specification and design input, rather than direct integration.
- Carrier's Market Scale: Carrier's substantial 2023 revenue of $22.1 billion highlights the operational complexity that deters customer integration.
The bargaining power of Carrier Global's customers is a mixed bag, leaning towards moderate but with significant variation based on customer type. While individual homeowners have little sway, large commercial and industrial clients can exert considerable pressure on pricing and contract terms due to the sheer volume of their purchases. This is particularly true for major construction projects where HVAC system orders are substantial, giving these clients significant leverage, as evidenced by Carrier's focus on securing large commercial backlogs for 2025.
Customer switching costs are a key factor in mitigating this power. For large clients with integrated Carrier systems, the expense and complexity of switching to a competitor are often prohibitive, creating a sticky customer base. However, for new installations or full system replacements, switching costs are lower, enabling customers to shop around and negotiate more effectively. The increasing customer focus on total cost of ownership and readily available market information further empowers buyers to benchmark prices and demand better value.
The threat of backward integration by customers is generally low, given the specialized nature and high capital investment required for Carrier's advanced systems. This inability for most customers to produce their own equipment in-house limits their direct bargaining power. Nevertheless, large clients can still influence outcomes by specifying components or dictating design elements, representing an indirect form of leverage.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Carrier |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Homeowners | Low volume, limited negotiation expertise | Minimal impact on pricing or terms |
| Small Commercial Businesses | Moderate volume, some price sensitivity | Slight pressure on pricing, especially for standard systems |
| Large Commercial & Industrial Clients | High volume, significant project scope, potential for specification influence | Substantial leverage on pricing, contract terms, and customization; high switching costs for installed base, but lower for new projects |
| Government & Institutional Buyers | Bulk purchasing, competitive bidding processes | Can exert significant price pressure through formal procurement procedures |
Same Document Delivered
Carrier Global Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Carrier Global, providing an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the HVAC and refrigeration industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate utility. You'll gain access to a detailed breakdown of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry, all presented in a ready-to-use format.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Carrier Global operates in mature markets like HVAC, refrigeration, fire, security, and building automation, which are populated by a significant number of both global and regional players. This maturity means the playing field is crowded, with many companies vying for the same customers.
Key rivals that directly challenge Carrier Global include Daikin, a major Japanese competitor known for its innovation in HVAC, Trane Technologies, a significant player in building efficiency solutions, and Johnson Controls, a diversified industrial company with a strong presence in building technologies. Other notable competitors are Lennox International and Midea Group, a Chinese conglomerate with a vast manufacturing base and expanding global reach.
The sheer volume and diversity of these competitors create a highly competitive environment. For instance, in the HVAC sector alone, the global market was valued at approximately $130 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, but this growth is shared among many established and emerging companies, intensifying the battle for market share and profitability.
The HVAC market is expected to expand at a robust compound annual growth rate of 6.7% between 2024 and 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing global temperatures, a rise in new building projects, and stricter energy efficiency standards.
While this expansion presents significant opportunities, it also naturally escalates competitive rivalry. As the market matures and the pie gets bigger, companies like Carrier are intensely focused on capturing a greater market share, leading to more aggressive competition for customers and contracts.
Carrier Global itself has experienced impressive HVAC sales growth throughout 2024. Looking ahead, the company anticipates this positive momentum to continue, projecting double-digit growth specifically within its commercial HVAC segment for 2025, underscoring the dynamic and competitive nature of this expanding industry.
Carrier Global actively combats commoditization in the HVAC sector by emphasizing product differentiation through innovation. Their offerings extend beyond basic climate control to include smart, sustainable, and digitally integrated solutions. This includes advancements like AI-powered climate management and energy recovery technologies, setting them apart from competitors offering more standard equipment.
The company's strategic emphasis on electrification, system integration, and building resilience is a key differentiator. Carrier’s commitment to these areas, supported by substantial research and development investments, is designed to foster a competitive edge. For instance, their focus on connected systems allows for enhanced efficiency and user control, a feature not universally present in the industry.
Carrier's dedication to innovation is evident in their significant R&D spending. In 2023, the company reported $650 million in R&D expenses, a clear signal of their commitment to developing advanced climate solutions. This investment fuels the creation of products that offer superior energy efficiency and advanced features, directly addressing evolving market demands for sustainability and intelligent building management.
Exit Barriers
Carrier Global faces significant exit barriers in the HVAC and building technology markets. High fixed costs associated with manufacturing facilities and extensive distribution networks make it financially challenging for companies to cease operations. For instance, in 2023, Carrier Global reported capital expenditures of $1.2 billion, reflecting ongoing investments in its operational infrastructure.
The specialized nature of HVAC equipment and the need for highly trained technicians further increase exit barriers. Companies cannot easily repurpose these specialized assets for other industries. Furthermore, long-term customer contracts, common in service and maintenance agreements, lock companies into the market, even when profitability declines. This contractual commitment ensures a degree of sustained competition.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investments in manufacturing, R&D, and distribution create substantial financial commitments.
- Specialized Assets: HVAC equipment and related infrastructure are not easily transferable to other industries.
- Long-Term Contracts: Customer agreements for installation, maintenance, and service create ongoing obligations.
- Steady Demand: The essential nature of HVAC services provides a baseline of business, discouraging rapid exits.
Strategic Stakes and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry in the HVAC sector is intense, with companies frequently making strategic acquisitions to bolster market share and product offerings. Carrier's acquisition of Viessmann Climate Solutions in 2024 for €12 billion exemplifies this trend, significantly altering the competitive dynamics and strengthening Carrier's position in the European market.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Competitors actively pursue mergers and acquisitions to consolidate market presence and broaden their product portfolios.
- Carrier's Portfolio Moves: Carrier Global's 2024 acquisition of Viessmann Climate Solutions for €12 billion is a prime example of strategic portfolio enhancement.
- Reshaping the Landscape: Such significant M&A activity directly influences industry structure and intensifies rivalry among key players.
- High Stakes: The continuous pursuit of strategic acquisitions underscores the substantial stakes involved in maintaining or gaining competitive advantage within this sector.
Competitive rivalry within Carrier Global's operating sectors, particularly HVAC, is fierce due to a crowded market with numerous global and regional players. Companies like Daikin, Trane Technologies, and Johnson Controls are significant competitors, constantly innovating and vying for market share. The HVAC market's projected growth, estimated at 6.7% CAGR from 2024-2029, intensifies this competition as firms aim to capture a larger portion of the expanding pie.
Carrier Global actively differentiates itself through innovation, focusing on smart, sustainable, and digitally integrated solutions, as evidenced by its substantial R&D investments, reaching $650 million in 2023. This strategy aims to counter market commoditization and maintain a competitive edge. The company's strategic moves, such as the €12 billion acquisition of Viessmann Climate Solutions in 2024, highlight the aggressive pursuit of market consolidation and enhanced capabilities among key industry players.
| Key Competitors | Primary Focus Areas | 2023 R&D Investment (Approximate) |
| Daikin | HVAC, Refrigeration | Not Publicly Disclosed (Significant) |
| Trane Technologies | Building Efficiency, HVAC | Not Publicly Disclosed (Significant) |
| Johnson Controls | Building Technologies, HVAC | Not Publicly Disclosed (Significant) |
| Lennox International | HVAC | Not Publicly Disclosed (Significant) |
| Midea Group | Appliances, HVAC | Not Publicly Disclosed (Significant) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While direct substitutes for Carrier Global's integrated HVAC, refrigeration, and security systems are scarce, alternative methods can address similar needs. For example, advancements in passive design and natural ventilation offer ways to manage building climate control, potentially reducing the demand for traditional HVAC, especially in new builds or specific regions. In 2023, the global green building market was valued at approximately $1.14 trillion, indicating a growing interest in energy-efficient and alternative building solutions.
The threat of substitutes for Carrier Global's HVAC solutions intensifies when alternatives offer similar performance at a lower price point or boast superior advantages. For instance, geothermal heat pumps are increasingly viable, presenting enhanced energy efficiency and environmental benefits. This trend is further propelled by government incentives, such as tax credits, and growing consumer demand for sustainable options.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives for Carrier Global's HVAC and refrigeration products hinges on several factors. Awareness of competing technologies, the perceived advantages of these alternatives, and how simple it is to make the change all play a significant role. For instance, if a competitor offers a slightly more energy-efficient unit with a comparable price point and straightforward installation, customers might be more inclined to consider it.
The increasing focus on sustainability and green building initiatives is a key driver here. Regulatory incentives, like tax credits for energy-efficient upgrades or stricter emissions standards, are making alternative solutions more attractive. As customers become more environmentally conscious, they are more likely to explore and adopt substitutes that offer demonstrable sustainability benefits, potentially impacting demand for traditional offerings.
Switching Costs for Customers
For customers already invested in Carrier's HVAC systems, the cost of switching to a substitute like a passive building design or an entirely new climate control approach can be significant. This involves expenses related to redesigning infrastructure, the physical installation of new equipment, and the necessary operational adjustments to integrate a different system. These switching costs can act as a barrier, making it less likely for existing customers to defect to competitors or alternative solutions.
However, the threat of substitutes intensifies considerably in the context of new construction projects. For builders starting from scratch, the upfront costs and complexities associated with integrating a Carrier system versus a substitute are much lower. This allows for greater flexibility in choosing alternative climate control methods, thereby increasing the competitive pressure on Carrier from substitute products and services.
In 2024, the building sector saw a continued emphasis on energy efficiency and integrated building management systems. For instance, the growth in smart building technology and demand for net-zero energy buildings means that alternative solutions offering comprehensive environmental control, beyond traditional HVAC, present a more viable and attractive option for new developments. This trend directly impacts the perceived switching costs for new projects, potentially eroding Carrier's market share if substitute offerings provide a more compelling value proposition.
- High Switching Costs for Existing Customers: Redesign, installation, and operational adjustments deter customers from switching away from established Carrier systems.
- Lower Switching Costs for New Construction: Builders have greater freedom to adopt alternative climate control methods without the legacy costs associated with retrofitting.
- Impact of Energy Efficiency Trends: The growing demand for integrated and passive building designs in 2024 makes substitutes more appealing for new projects, increasing competitive threat.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are continuously reshaping industries, and for Carrier Global, this presents a significant threat from substitutes. Innovations in smart building materials, such as self-healing concrete or advanced insulation, can reduce the reliance on traditional HVAC systems. For instance, by 2024, the global smart building market is projected to reach over $100 billion, indicating a growing demand for integrated solutions that might bypass the need for separate climate control units.
Furthermore, the development of passive environmental controls, like advanced natural ventilation systems or building designs that optimize solar gain, could further diminish the market for Carrier's core heating and cooling products. As energy efficiency becomes paramount, technologies that drastically cut down the need for active climate management pose a direct challenge. The increasing integration of smart building technologies, aimed at boosting productivity and safety, also creates a landscape where holistic building management systems could supplant the need for individual, specialized equipment.
- Smart Building Market Growth: The global smart building market is expected to exceed $100 billion by 2024, highlighting a trend towards integrated solutions.
- Passive Design Impact: Innovations in passive design and advanced insulation materials can reduce the demand for active heating and cooling systems.
- Integrated Technology Threat: The rise of comprehensive smart building technologies that enhance productivity and safety could reduce the need for Carrier's standalone climate and security products.
The threat of substitutes for Carrier Global's offerings is moderate but growing, primarily driven by advancements in energy efficiency and integrated building solutions. While direct substitutes for complex HVAC and refrigeration systems are limited, alternative approaches to climate control and building management are gaining traction. The increasing adoption of passive design principles and natural ventilation, particularly in new construction, presents a viable alternative for managing building environments, potentially reducing reliance on traditional active systems.
The competitive landscape is also shaped by the evolving definition of building efficiency. As the global green building market continues its upward trajectory, projected to reach over $1.14 trillion in 2023, there's a clear market pull towards solutions that minimize energy consumption. This trend is amplified by government incentives and a growing consumer preference for sustainable technologies, making alternatives like geothermal heat pumps more appealing due to their enhanced energy efficiency and environmental benefits.
For new construction projects in 2024, the cost and complexity of integrating alternative climate control methods are significantly lower compared to retrofitting existing buildings. This flexibility allows builders to readily adopt solutions that offer integrated environmental control, potentially bypassing the need for separate, specialized Carrier systems. The burgeoning smart building market, anticipated to exceed $100 billion by 2024, further underscores this shift towards holistic building management systems.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Carrier | Key Drivers | Market Trend Example (2023-2024) |
| Passive Building Design & Natural Ventilation | Moderate, increasing in new builds | Energy efficiency focus, reduced operational costs | Growing interest in green building solutions (>$1.14T market in 2023) |
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | Moderate, growing | Higher energy efficiency, environmental benefits, government incentives | Increased consumer demand for sustainable options |
| Integrated Smart Building Systems | Moderate, increasing | Holistic building management, enhanced productivity/safety | Smart building market projected to exceed $100B by 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering Carrier Global's diverse markets, including HVAC, refrigeration, and fire and security, demands significant capital. Think about the cost of building advanced manufacturing plants, funding ongoing research and development, establishing robust distribution channels, and creating a widespread service network. These upfront expenses create a substantial hurdle for potential new players.
For instance, the global HVAC market alone was valued at approximately $130 billion in 2023, with projections showing continued growth. To even begin competing, a new entrant would need to invest hundreds of millions, if not billions, to establish the necessary infrastructure and product lines to match Carrier's established global presence and comprehensive offerings.
Established players like Carrier Global benefit from substantial economies of scale. For instance, in 2023, Carrier reported net sales of $22.1 billion, reflecting their vast operational capacity. This scale allows for lower per-unit manufacturing costs and more efficient procurement of raw materials, creating a significant hurdle for newcomers aiming to compete on price.
Furthermore, Carrier's decades of accumulated experience in product development, engineering, and market penetration translate into invaluable know-how. This expertise leads to optimized designs, more reliable products, and a deeper understanding of customer needs, all of which contribute to a cost and efficiency advantage that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
Carrier Global benefits from decades of brand building, fostering deep customer loyalty and a reputation for dependable, high-quality products. This established trust is a substantial barrier for newcomers aiming to capture market share in the HVAC and refrigeration sectors.
New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and product development to even begin to rival Carrier's recognized reliability and innovation, a challenge underscored by Carrier's 2023 revenue of $22.1 billion, reflecting its significant market presence and customer base.
Access to Distribution Channels
Carrier Global's established access to distribution channels presents a significant barrier for new entrants. The company utilizes a multi-faceted approach, including direct sales teams, a robust network of independent distributors, and a global infrastructure of service centers. This comprehensive network is vital for reaching a broad customer spectrum and offering crucial after-sales support.
New companies would struggle to replicate Carrier's extensive reach and established relationships within these distribution and service networks. Building a comparable system requires substantial investment and time, creating a hurdle that deters potential competitors. For instance, in 2023, Carrier's HVAC segment alone generated over $19 billion in revenue, underscoring the scale of its market penetration facilitated by these channels.
- Established Distribution Network: Carrier Global operates through direct sales, independent distributors, and global service centers, providing broad market access.
- High Setup Costs: New entrants face significant capital investment and time to build equivalent distribution and service capabilities.
- Customer Reach and Support: Carrier's channels are critical for reaching diverse customers and delivering essential aftermarket services, a challenge for newcomers.
- Market Penetration: The scale of Carrier's operations, exemplified by its 2023 revenue, highlights the difficulty in matching its market presence through existing channels.
Regulatory and Certification Hurdles
The HVAC, refrigeration, fire, and security sectors are heavily regulated, demanding adherence to rigorous energy efficiency standards, such as the updated SEER2 (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio 2) requirements implemented in the US in 2023, and various safety certifications.
New companies face significant challenges in understanding and meeting these complex compliance obligations, which directly translate into increased costs and extended timelines for market entry. For instance, obtaining UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification for fire safety equipment can take months and involve substantial testing fees.
These regulatory and certification barriers act as a formidable deterrent to potential new entrants, thereby strengthening Carrier Global's position by limiting the influx of new competition.
- Stringent Regulations: HVAC, refrigeration, fire, and security industries are subject to extensive government regulations.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Compliance with standards like SEER2 (effective 2023 in the US) is mandatory.
- Safety Certifications: Obtaining necessary certifications (e.g., UL, CE) is a costly and time-consuming process for new players.
- Market Entry Barriers: These hurdles increase the cost and complexity of entering the market, protecting incumbents like Carrier.
The threat of new entrants for Carrier Global is generally low due to several significant barriers. High capital requirements for manufacturing, R&D, and distribution, coupled with established economies of scale, make it difficult for newcomers to compete. Carrier's substantial 2023 net sales of $22.1 billion highlight its operational capacity and cost advantages.
Brand loyalty and established distribution networks, built over decades, further deter new players. Replicating Carrier's extensive market reach and customer trust, as evidenced by its strong 2023 revenue across segments like HVAC (over $19 billion), requires immense investment and time.
Additionally, stringent industry regulations and the need for costly certifications, such as SEER2 standards effective in the US from 2023, add complexity and expense for potential entrants, solidifying Carrier's market position.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Carrier's Advantage (2023 Data) |
| Capital Requirements | High cost for manufacturing, R&D, distribution | Significant hurdle | Net Sales: $22.1 billion |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large production volumes | Price competition difficulty | Vast operational capacity |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Established trust and recognition | Difficult to gain market share | Strong customer base |
| Distribution & Service Networks | Extensive global reach and established relationships | Challenging to replicate | HVAC segment revenue: >$19 billion |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to energy efficiency (SEER2) and safety standards | Increased costs and time to market | Expertise in navigating regulations |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Carrier Global is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, and regulatory filings to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.