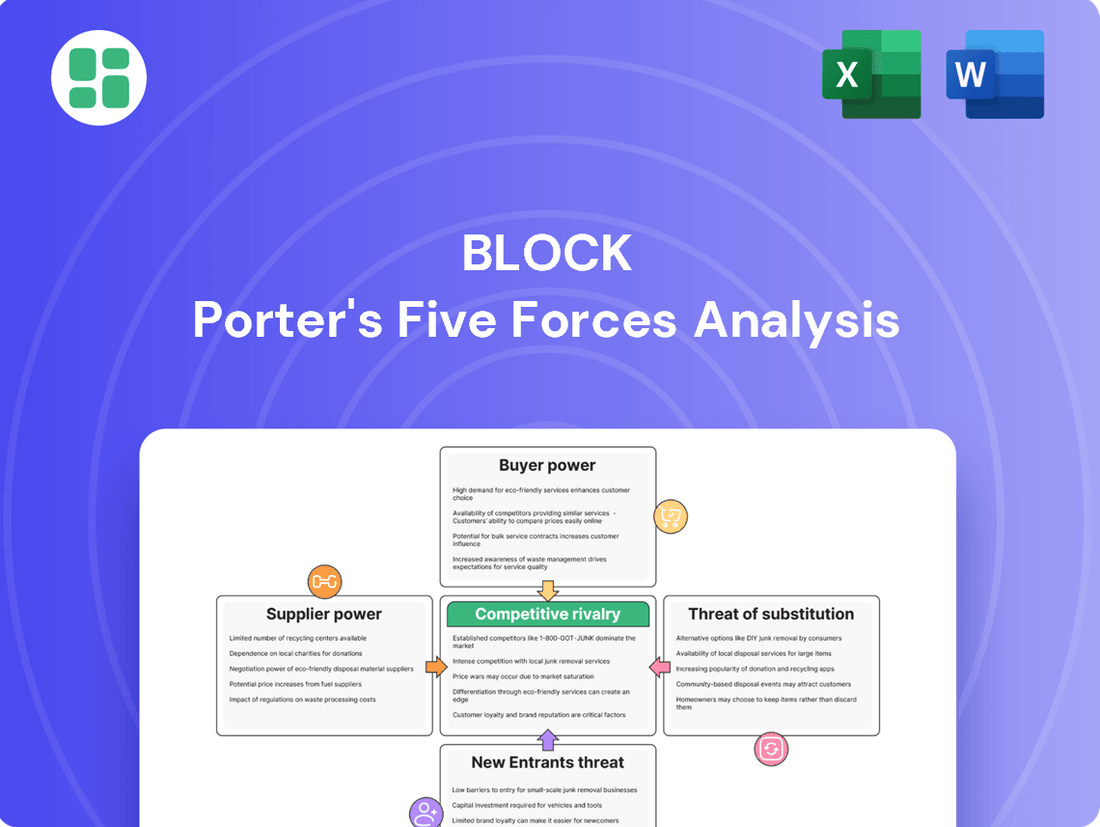
Block Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Block Bundle
Block's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from intense rivalry to the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Block’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Block's reliance on key technology providers for cloud infrastructure, payment networks, and hardware presents a significant factor in supplier bargaining power. The cloud computing market, for instance, is highly concentrated, with major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure holding substantial market share, granting them considerable leverage. In 2023, AWS alone captured an estimated 31% of the global cloud infrastructure services market, highlighting this concentration.
However, Block's considerable scale and its strategic importance as a major customer can mitigate some of this supplier power. The company's ability to negotiate favorable terms is enhanced by its significant transaction volumes and its role in driving adoption of certain technologies. Furthermore, Block actively pursues strategic partnerships and diversifies its supplier relationships to reduce dependence on any single entity, thereby strengthening its negotiating position.
Block's reliance on essential inputs like payment network access, such as Visa and Mastercard, is a significant factor in the bargaining power of its suppliers. These networks are fundamental to Block's Square and Cash App payment processing services, making them indispensable and granting these networks considerable leverage. Without access to these established payment rails, Block's core business would be severely hampered.
Furthermore, the need for highly skilled talent in areas like software development, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology also plays a role. The competition for these specialized skills is fierce, and the availability and cost of such talent directly impact Block's innovation capacity and growth strategies. This demand can translate into higher labor costs or more demanding employment terms for Block.
Switching Block's core technology infrastructure, like its cloud providers or critical payment network relationships, presents significant financial and operational hurdles. These high switching costs effectively bolster the bargaining power of Block's current suppliers, as the expense and complexity of transitioning are substantial deterrents.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers might integrate forward into offering direct financial services, potentially competing with Block. While major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure could theoretically develop more integrated financial tools, their core business models are not centered on directly challenging Block's diverse fintech ecosystem. This specific threat of forward integration from traditional payment network or cloud providers into granular fintech services remains relatively low for Block.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. When numerous suppliers offer similar hardware components or generic software tools, their individual leverage diminishes. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry saw a robust supply of various microprocessors, allowing companies to negotiate favorable terms.
Conversely, specialized inputs create a different dynamic. For unique offerings like advanced AI/ML capabilities or specialized blockchain development expertise, the pool of qualified suppliers is often much smaller. This scarcity grants these niche providers greater bargaining power, as demonstrated by the premium pricing for highly sought-after quantum computing development services in the current market.
Block's strategic approach to internal development, such as its work on proprietary Bitcoin mining chips, directly addresses this by aiming to reduce reliance on external specialized suppliers. This vertical integration can mitigate the bargaining power of those suppliers, especially in critical technology areas.
- Limited Supplier Pool: Specialized inputs like advanced AI/ML or unique blockchain expertise often have fewer providers, increasing their bargaining power.
- Generic Input Availability: For hardware components or common software, a wider range of suppliers typically limits individual supplier leverage.
- Block's Mitigation Strategy: Internal development of key components, like Bitcoin mining chips, aims to reduce dependence on external specialized suppliers.
Block's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the concentration of its input providers and the availability of substitutes. For essential services like cloud computing, a concentrated market with providers like AWS, which held approximately 31% of the global cloud infrastructure market in 2023, can exert significant influence. However, Block's substantial scale as a customer and its efforts to diversify suppliers help to counterbalance this power.
The company's reliance on critical payment networks, such as Visa and Mastercard, represents a key area where supplier bargaining power is high due to the indispensable nature of these rails for Block's operations. Conversely, the availability of generic hardware components in 2024, with ample semiconductor supply, allows Block to negotiate more favorable terms for these inputs.
Block's strategic focus on internal development, such as its proprietary Bitcoin mining chips, is a direct effort to reduce its dependence on specialized external suppliers and thereby enhance its own bargaining position. This approach is crucial for mitigating the leverage held by providers of unique or scarce technological expertise.
| Input Type | Supplier Concentration | Availability of Substitutes | Block's Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure | High (e.g., AWS ~31% market share in 2023) | Moderate | Moderate (mitigated by scale) |
| Payment Networks | High (e.g., Visa, Mastercard) | Low | Low |
| Generic Hardware | Low (e.g., ample semiconductor supply in 2024) | High | High |
| Specialized AI/Blockchain Expertise | High (limited providers) | Low | Low (mitigated by internal development) |
What is included in the product
This analysis examines the five competitive forces impacting Block, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitutes.
Visualize competitive intensity across all five forces on a single, intuitive dashboard, eliminating the guesswork in strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
For individual users of Block's Cash App, moving to other peer-to-peer payment or banking applications such as Venmo, Zelle, PayPal, or Google Pay is quite straightforward. There's very little hassle or expense involved in making this switch. This ease of transition for consumers directly boosts their influence.
This low switching cost for individual consumers means they hold significant bargaining power. Block, therefore, faces the constant need to innovate and introduce attractive new features to keep its Cash App users engaged and loyal. In 2023, the peer-to-peer payment market saw continued growth, with platforms like Cash App and Venmo facilitating billions of transactions, highlighting the competitive landscape where user retention is paramount.
Small businesses have a wealth of payment processing and business management options beyond Square, such as Stripe, PayPal, and QuickBooks Payments. This availability allows them to easily compare pricing, features, and customer service. In 2024, the fintech market continues to see robust competition, with many providers offering competitive rates to attract new users.
Customers in the financial services sector, encompassing both small businesses and individual consumers, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is especially true for elements like transaction fees, interest rates, and various service charges. The sheer volume of competing financial products and services available means customers can readily switch to providers offering more favorable pricing.
For Block, this price sensitivity directly impacts its Square and Cash App platforms. Maintaining competitive pricing structures is crucial for Block to not only attract new users but also to ensure the loyalty of its existing customer base. For instance, in 2023, the average interchange fee for debit card transactions in the US was around 23 cents, a benchmark that providers like Block must consider when structuring their own fee schedules to remain attractive.
Customer Concentration is Low
Block's customer concentration is remarkably low, with millions of small businesses and individual users forming its customer base. This fragmentation means no single customer or small group of customers contributes a substantial percentage to Block's overall revenue, significantly diminishing the bargaining power of any individual customer seeking special terms or pricing.
While individual customers have limited leverage, the sheer volume of users can still exert collective pressure, especially in price-sensitive segments. For instance, Block's Cash App reported over 56 million monthly active users as of Q1 2024, highlighting the potential for widespread customer sentiment to influence market dynamics.
- Low Customer Concentration: Block serves a vast and diverse customer base, preventing any single entity from wielding significant influence.
- Reduced Individual Bargaining Power: The fragmented nature of its users limits the ability of individual customers to negotiate preferential terms.
- Potential for Collective Power: Despite low individual power, the aggregate behavior of millions of users can still impact market conditions, particularly concerning pricing.
- Market Reach: With millions of active users across its various platforms, Block benefits from a broad market presence that dilutes the impact of any single customer's demands.
Impact of Customer Feedback and Reviews
In today's connected world, customer feedback and online reviews wield considerable influence, particularly for consumer-focused digital platforms. For instance, a significant portion of consumers, around 80-90% according to various studies from 2023 and early 2024, report reading online reviews before making a purchase decision or trying a new service. This trend is especially pronounced for mobile applications like Cash App and Tidal, where user experience is paramount.
Negative sentiment shared on social media or review sites can rapidly erode a brand's reputation and deter potential new users. Consider that a single negative review can sometimes lead to a noticeable drop in conversion rates for apps. This transparency essentially amplifies the collective power of customers; their shared experiences can act as a powerful catalyst for adoption or a significant barrier.
- Digital Influence: In 2023, over 75% of consumers reported trusting online reviews as much as personal recommendations.
- App Adoption: For apps like Cash App, a strong positive review average can boost download rates by up to 15-20%.
- Reputation Risk: Negative social media trends can go viral, impacting brand perception for services like Tidal within hours.
Block's customers, both individuals using Cash App and small businesses using Square, generally have high bargaining power. This is largely due to low switching costs; users can easily move to competing payment or business management services. For instance, in 2024, the fintech market continues to offer numerous alternatives with competitive pricing, making it simple for customers to compare and switch providers if Block's offerings become less attractive.
The sheer number of users, such as Cash App's over 56 million monthly active users as of Q1 2024, also means that while individual power is limited, collective sentiment, particularly regarding pricing and fees, can exert significant pressure on Block to maintain competitive rates.
Furthermore, the prevalence of online reviews and social media means customer feedback can rapidly influence brand perception. With studies in 2023 and early 2024 showing that a vast majority of consumers consult online reviews before trying new services, Block must actively manage its reputation to mitigate the impact of negative sentiment.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Block | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
| Switching Costs | Ease of moving to alternative payment/business solutions | High customer bargaining power | Numerous fintech alternatives available; minimal fees to switch between P2P apps. |
| Customer Concentration | Block's user base is highly fragmented | Low individual customer bargaining power | Millions of users across Cash App and Square platforms. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are sensitive to transaction fees and service charges | Pressure on Block to maintain competitive pricing | Interchange fees benchmarked around $0.23 for debit cards (2023); competitive rates are key in fintech. |
| Digital Influence | Impact of online reviews and social media sentiment | Amplifies collective customer power | 80-90% of consumers read reviews; positive app reviews can boost downloads by 15-20%. |
Same Document Delivered
Block Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Block Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing valuable insights without any surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Block operates within a fintech market that is both highly fragmented and incredibly diverse. This means Block isn't just competing with one type of company; it's up against players in payment processing, peer-to-peer payments, digital banking, and even adjacent sectors like music streaming. For example, in the payment processing space alone, Block's Square competes with giants like Stripe and PayPal, alongside many smaller, specialized providers.
The sheer variety of competitors highlights the dynamic nature of this industry. Constant innovation means new threats emerge regularly, and established players must continually adapt. In 2024, the fintech sector continued its rapid expansion, with global fintech revenue projected to reach over $330 billion, indicating the intensity of the competition as more companies fight for a piece of this growing pie.
In the payment processing arena, Block Porter (formerly Square) faces formidable rivals such as Stripe and PayPal, alongside nimble startups and traditional banking institutions. This dynamic landscape demands constant innovation to stand out.
For its Cash App service, Block Porter contends with established digital wallets and P2P payment platforms like Venmo, Apple Cash, Zelle, and Google Pay. These competitors are actively vying for market share in the rapidly expanding digital payments sector.
The sheer intensity of this competition underscores the critical need for Block Porter to continuously differentiate its product offerings and invest heavily in aggressive marketing strategies to capture and retain customers.
Block, Inc. strives to stand out by building an integrated ecosystem. Through Square, it offers businesses a broad range of tools, while Cash App provides various financial services to consumers. This strategy aims to make customers more committed by linking multiple services together.
However, the competitive landscape is robust. Rivals are also developing strong, integrated offerings or focusing on specific market segments, presenting a challenge to Block's differentiation efforts. For instance, PayPal's Venmo and its broader payment services offer a competing ecosystem, and specialized fintech firms often provide highly tailored solutions that can attract specific customer bases.
In 2023, Square's seller ecosystem processed $217.6 billion in gross payment volume, demonstrating the scale of its integrated business solutions. Cash App, meanwhile, saw its user base grow, contributing to Block's overall ecosystem engagement, though direct comparisons of ecosystem lock-in are complex due to varying business models.
Industry Growth and Consolidation
The global fintech market is experiencing robust expansion, with projections indicating continued strong growth. This expansion naturally draws in more players and capital, consequently intensifying competitive rivalry. For instance, the fintech sector's market size was estimated to be around $11.3 trillion in 2023 and is expected to reach over $33.4 trillion by 2030, showcasing a compound annual growth rate of 16.7%. This surge in market value fuels aggressive competition as companies vie for dominance.
As the industry matures and opportunities abound, companies are actively pursuing market share, leading to heightened competition. This often translates into aggressive pricing strategies, innovative product development, and increased marketing efforts. The sheer volume of new entrants and the expansion of existing firms means that the landscape is constantly shifting, with a premium placed on agility and customer acquisition.
Furthermore, the fintech industry is witnessing a trend of consolidation. Larger, established fintech companies are actively acquiring smaller, innovative startups to gain access to new technologies, customer bases, or talent. This M&A activity, such as PayPal's acquisition of Paidy in 2021 for $2.7 billion, reshapes the competitive arena, leaving fewer, but often more formidable, major players. This consolidation can lead to a more concentrated market, where the remaining entities compete fiercely for the remaining market share.
- Fintech Market Growth: Projected to grow from $11.3 trillion in 2023 to over $33.4 trillion by 2030.
- CAGR: The fintech sector is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 16.7%.
- Consolidation Example: PayPal's $2.7 billion acquisition of Paidy in 2021 highlights industry consolidation.
- Impact of Consolidation: Intensifies rivalry among remaining major entities.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Compliance Costs
The financial services sector, including cryptocurrency operations like Block Porter, faces intensifying regulatory scrutiny. This evolving landscape necessitates substantial investments in compliance infrastructure and fraud prevention measures. For instance, in 2024, the global spending on financial crime compliance by financial institutions was projected to reach over $100 billion, highlighting the significant operational costs involved.
These compliance costs act as a considerable barrier to entry for smaller competitors, potentially consolidating the market among well-capitalized firms. Conversely, companies that proactively adapt and excel in regulatory adherence can leverage this as a competitive advantage, building trust and operational resilience.
- Increased Compliance Burden: Regulatory changes in 2024, such as enhanced Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements, demand continuous adaptation.
- Investment in Technology: Firms are investing in RegTech solutions, with the RegTech market expected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated $34.8 billion by 2027, up from $11.7 billion in 2022.
- Barrier to Entry: High compliance costs can deter new entrants and smaller players, favoring established entities with greater financial resources.
- Competitive Differentiator: Effective compliance management can become a key differentiator, enhancing reputation and customer trust.
Block Porter operates in a highly competitive fintech environment, facing rivals across payments, digital banking, and P2P services. Companies like Stripe, PayPal, Venmo, Apple Cash, Zelle, and Google Pay are direct competitors, forcing Block to constantly innovate and differentiate its offerings. This intense rivalry is fueled by the fintech market's rapid growth, projected to exceed $330 billion in revenue in 2024, with the overall market size expected to reach over $33.4 trillion by 2030.
The competitive landscape is characterized by aggressive pricing, product development, and marketing efforts as companies vie for market share. Consolidation is also a trend, with major players acquiring startups, which can further intensify competition among the remaining large entities. For example, PayPal's acquisition of Paidy for $2.7 billion in 2021 illustrates this consolidation trend.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Block's Offerings |
| Payment Processing | Stripe, PayPal | Square |
| P2P Payments/Digital Wallets | Venmo, Apple Cash, Zelle, Google Pay | Cash App |
| Integrated Financial Services | Various Fintechs | Square Ecosystem, Cash App Ecosystem |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Despite the surge in digital payment solutions, traditional methods like cash, physical checks, and Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers continue to serve as viable substitutes. These methods remain prevalent, especially among certain age groups and for specific transaction types, representing a persistent threat to newer payment systems.
While their overall market share may be shrinking, the sheer volume of transactions still processed through these traditional channels cannot be ignored. For instance, in 2023, the Federal Reserve reported that checks, though declining, still accounted for billions of dollars in payments annually, demonstrating their continued relevance.
For Cash App users, the threat of substitutes is significant due to the proliferation of digital wallets and peer-to-peer (P2P) payment services. Platforms like Venmo, PayPal, Google Pay, Apple Pay, Zelle, Wise, and Revolut offer comparable functionalities, allowing for easy money transfers and digital transactions.
These alternatives present a low barrier to entry and low switching costs for consumers. For instance, many users already have accounts with these services for other purposes, making it simple to shift their P2P transactions. This ease of adoption directly challenges Cash App's user base and market share.
In 2024, the P2P payment market continued its robust growth, with Zelle alone reporting over 2.7 billion transactions valued at $1.1 trillion in 2023, showcasing the scale of competition. PayPal, a major player, processed $1.3 trillion in total payment volume in 2023, highlighting the intense competition Block faces in capturing and retaining consumer transaction volume.
The growing trend of embedded finance presents a substantial threat of substitution for traditional financial service providers. Non-financial companies are increasingly integrating financial offerings like payments, lending, and insurance directly into their customer journeys. For instance, e-commerce platforms offering 'Buy Now, Pay Later' (BNPL) at checkout directly compete with standalone lenders.
This integration allows businesses to capture customer transactions and data, potentially reducing the need for customers to engage with specialized fintechs or banks. By offering these services frictionlessly within their own ecosystems, companies can enhance customer loyalty and capture a larger share of the value chain. This shift means that Block, for example, may face competition not just from other fintechs but also from the very platforms it aims to serve.
The market for embedded finance is expanding rapidly. Projections suggest the global embedded finance market could reach $7 trillion by 2030, highlighting the significant potential for this model to disrupt existing financial service delivery. This growth indicates that many businesses are finding value in offering financial products, thereby creating a potent substitute for services traditionally provided by companies like Block.
Traditional Banking and Investment Services
Traditional banks and established brokerage firms represent significant substitutes for Cash App's banking and investing features. These incumbents offer a wide array of financial services, often with long-standing customer relationships and trust. For instance, in 2024, traditional banks continued to hold a substantial share of consumer deposits, indicating their continued relevance.
While Block's strategy focuses on accessibility and serving the unbanked or underbanked, consumers still have the option to utilize conventional financial institutions for their banking, saving, and investment requirements. This accessibility to familiar and widely available services acts as a constant competitive pressure.
- Established Trust: Traditional banks benefit from decades of operation and established brand recognition, fostering customer loyalty.
- Comprehensive Offerings: Incumbent institutions typically provide a broader spectrum of financial products, including complex investment vehicles and lending options.
- Regulatory Familiarity: Consumers are often more comfortable with the regulatory frameworks governing traditional banks, perceiving them as inherently safer.
- Digital Adoption: Many traditional banks have significantly invested in their digital platforms, narrowing the gap in user experience with fintech alternatives.
Diverse Music Streaming Platforms
The music streaming market presents a significant threat of substitutes for Block's Tidal. Competitors like Spotify, Apple Music, Amazon Music, and YouTube Music offer extensive catalogs and often have more established user bases and diverse monetization strategies, including robust free tiers.
These substitutes frequently offer similar or superior value propositions, making customer loyalty a challenge. For instance, Spotify reported over 615 million monthly active users as of Q1 2024, dwarfing Tidal's user base and highlighting the scale of competition.
The ease with which consumers can switch between platforms, often driven by pricing or exclusive content, further intensifies this threat. Many platforms provide comparable audio quality and discovery features, diminishing Tidal's unique selling points.
- Market Saturation: The presence of numerous established streaming services like Spotify and Apple Music creates a highly competitive landscape.
- Competitive Pricing: Many substitutes offer free, ad-supported tiers or comparable subscription prices, reducing the perceived value of Tidal's premium offerings.
- Feature Parity: Competitors often match or exceed Tidal's features, including vast music libraries, curated playlists, and podcast integration.
- User Acquisition: Major players like Spotify and Apple Music leverage massive existing ecosystems and marketing budgets to attract and retain users, posing a significant barrier for Tidal.
The threat of substitutes for Block's various offerings is substantial, stemming from both traditional financial services and emerging digital alternatives. In the digital payments space, while Block's Cash App competes, established players like PayPal and newer entrants offering seamless P2P transactions present a constant challenge. For instance, Zelle processed over 2.7 billion transactions valued at $1.1 trillion in 2023, illustrating the immense scale of alternative payment methods.
Embedded finance is also a growing substitute, with non-financial companies integrating financial services directly into their customer experiences. This trend, projected to reach $7 trillion by 2030, means companies like Block may face competition from platforms they aim to serve, as businesses increasingly offer services like 'Buy Now, Pay Later' at checkout.
Traditional banks and brokerages remain significant substitutes for Block's banking and investing features. These incumbents benefit from established trust and offer comprehensive financial services, with many having significantly enhanced their digital platforms. In 2024, traditional banks continued to hold a large share of consumer deposits, underscoring their ongoing relevance.
In the music streaming sector, Block's Tidal faces intense competition from giants like Spotify, which boasted over 615 million monthly active users as of Q1 2024. These substitutes often offer comparable features, vast libraries, and competitive pricing, making it difficult for Tidal to retain users.
| Service Area | Block's Offering | Key Substitutes | Substitute Market Share/Scale (2023/2024 Data) | Threat Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments | Cash App | Venmo, PayPal, Zelle, Google Pay, Apple Pay | Zelle: 2.7B+ transactions, $1.1T value (2023); PayPal total payment volume: $1.3T (2023) | High |
| Embedded Finance | (Integrated into platforms) | E-commerce BNPL, Banking-as-a-Service | Global market projected to reach $7T by 2030 | High |
| Banking/Investing | Cash App (banking/investing features) | Traditional Banks, Brokerage Firms | Traditional banks hold substantial consumer deposits (2024) | Medium-High |
| Music Streaming | Tidal | Spotify, Apple Music, Amazon Music, YouTube Music | Spotify: 615M+ monthly active users (Q1 2024) | High |
Entrants Threaten
The financial services sector, particularly in fintech and cryptocurrency, faces formidable regulatory hurdles. New companies must contend with intricate licensing processes, robust anti-money laundering (AML) protocols, and stringent know-your-customer (KYC) mandates. These compliance demands necessitate significant upfront investment in legal expertise and operational infrastructure, effectively deterring many potential market entrants.
Building and scaling a robust financial technology infrastructure, including secure payment processing systems, data centers, and customer support networks, demands significant capital investment. For instance, launching a new digital banking platform in 2024 could easily require hundreds of millions of dollars for technology development, regulatory compliance, and marketing.
New entrants need substantial funding to compete with established players like Block, which already possess extensive resources and infrastructure. In 2024, major fintech companies like Block reported billions in revenue, demonstrating the scale of operations that newcomers must overcome.
In the financial services sector, establishing brand trust is a significant barrier to entry. Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and customer service to cultivate the confidence that established players already enjoy. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers cite brand reputation as a primary factor when choosing a financial service provider.
Network effects also present a formidable challenge. Platforms that benefit from a growing user base, such as payment apps or digital exchanges, become more valuable as more people join. This creates a virtuous cycle for incumbents; by 2024, major fintech platforms reported user bases in the tens of millions, making it difficult for new entrants to achieve critical mass and offer comparable utility.
Technological Expertise and Innovation Pace
The fintech landscape is evolving at breakneck speed, driven by advancements in AI, machine learning, and blockchain. Newcomers need substantial technical know-how and ongoing investment in research and development to even compete.
To truly make an impact, these new entrants must not only replicate existing technological capabilities but also out-innovate them. This presents a significant hurdle for those without established R&D infrastructure and a proven track record of innovation.
- Fintech R&D Spend: Global fintech R&D spending is projected to reach over $200 billion by 2025, underscoring the high investment required.
- AI Adoption in Finance: In 2024, approximately 85% of financial institutions reported using AI in some capacity, highlighting the pervasive nature of this technology.
- Blockchain Investment: Venture capital investment in blockchain-based fintech solutions saw a notable increase in early 2024, signaling continued interest in this area.
Access to Payment Networks and Merchant Relationships
Gaining access to major credit card networks like Visa and Mastercard is a significant hurdle for new payment processors. These networks have established partnerships and extensive vetting processes that can take considerable time and resources to navigate. For instance, in 2024, the sheer volume of transactions processed by Visa and Mastercard, totaling trillions globally, underscores their entrenched market position and the difficulty for newcomers to secure comparable access.
Building a widespread merchant acceptance network is equally challenging. Established players, such as Block Porter's competitors, have cultivated long-standing relationships with millions of businesses. These existing ties offer them economies of scale and preferred terms that new entrants would find difficult to match in the short term. In 2023, the merchant services sector saw continued consolidation, with larger players acquiring smaller ones, further concentrating merchant relationships and increasing the barrier to entry.
- Network Access: Securing partnerships with Visa and Mastercard is a lengthy and complex process, limiting new entrants.
- Merchant Relationships: Established firms possess extensive, long-term relationships with merchants, creating a significant competitive advantage.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbents benefit from lower per-transaction costs due to their large processing volumes, a feat difficult for new players to replicate quickly.
The threat of new entrants in the financial services sector, especially fintech, is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements and complex regulatory landscapes. New players must navigate intricate licensing, AML, and KYC protocols, demanding substantial upfront investment in legal and operational infrastructure. For instance, launching a new digital banking platform in 2024 could easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
Building robust technological infrastructure and cultivating brand trust are also major deterrents. Established firms like Block, with billions in revenue in 2024, possess significant resources and customer loyalty that newcomers struggle to match. A 2024 survey found over 60% of consumers prioritize brand reputation when selecting financial services.
Network effects, where platforms become more valuable with more users, create a strong barrier. Major fintech platforms already boast tens of millions of users by 2024, making it difficult for new entrants to achieve critical mass and offer comparable utility.
Access to essential networks like Visa and Mastercard is a significant hurdle, with lengthy vetting processes. Furthermore, securing widespread merchant acceptance is challenging, as incumbents have cultivated long-standing relationships with millions of businesses, benefiting from economies of scale that are hard for new entrants to replicate quickly.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Cost to launch new digital banking platform | ~$100M - $500M+ |
| Regulatory Compliance | Investment in legal and operational infrastructure | Significant upfront costs for licensing, AML/KYC |
| Brand Trust | Consumer preference for established providers | 60%+ cite brand reputation as key factor |
| Network Effects | User base size of incumbent fintech platforms | Tens of millions of users |
| Network Access | Partnership complexity with major card networks | Lengthy and resource-intensive vetting |
| Merchant Relationships | Incumbent advantage in business partnerships | Millions of established merchant relationships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Block Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from blockchain explorer platforms, cryptocurrency exchange reports, and academic research papers to understand industry dynamics. We also incorporate insights from industry news outlets and developer community discussions to capture emerging trends and competitive pressures.