Beijing BDStar Navigation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Beijing BDStar Navigation Bundle
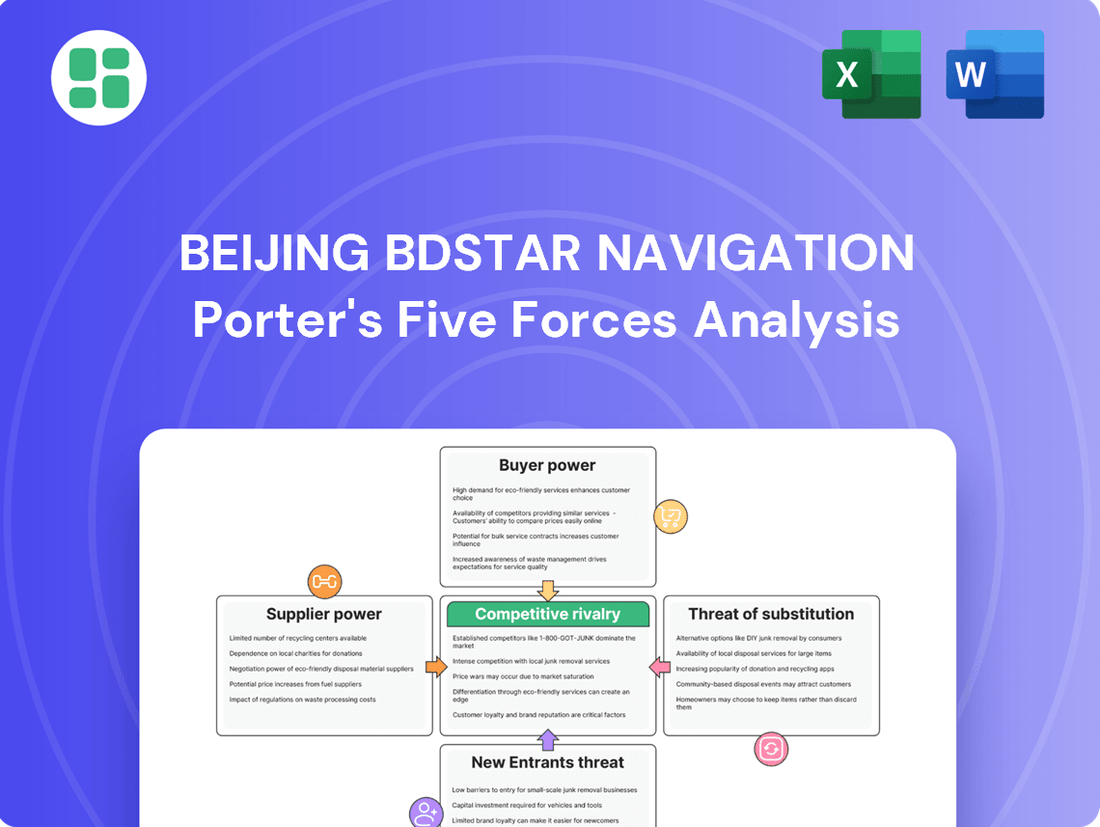
Beijing BDStar Navigation operates within a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry and evolving technological landscapes. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this competitive arena.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Beijing BDStar Navigation’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BDStar Navigation's reliance on specialized component suppliers, particularly for advanced GNSS chips and modules, grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. This is amplified when alternative suppliers for these critical technologies are limited, as is the case in the global GNSS chip market.
The global GNSS chip market, projected to reach over $10 billion by 2026, is dominated by a few key players, including companies based in the United States, Russia, and China. This concentration means that BDStar may face limited options for sourcing essential components, potentially leading to higher costs or supply chain disruptions if these dominant suppliers exert their influence.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or patents for essential components, like specialized semiconductor designs or advanced navigation algorithms, can wield significant bargaining power over BDStar Navigation. This leverage stems from the unique nature of their offerings, making them difficult to replace.
The competitive landscape for intellectual property in China's supply chain is robust, evidenced by over 129,000 cumulative patent applications for satellite navigation filed by the end of 2024. This high volume of innovation suggests that BDStar may face suppliers with strong IP protection, potentially increasing their ability to dictate terms.
The cost and complexity of switching suppliers for highly integrated components, such as the GNSS chips BDStar relies on, can be substantial. This raises the bargaining power of these suppliers. For instance, if BDStar needs to change its primary chip provider, the process could involve significant redesign efforts for its navigation modules and extensive re-certification procedures to meet industry standards, potentially costing millions.
These switching costs extend beyond just the component price. BDStar would need to invest in new tooling, retrain engineers on different chip architectures, and potentially face lengthy delays in product development and market entry. For specialized ceramic materials crucial for antenna performance, finding and qualifying new suppliers with equivalent quality and reliability can also be a complex and time-consuming undertaking, further solidifying existing supplier leverage.
Supplier Concentration
Supplier concentration is a critical factor influencing BDStar Navigation's bargaining power. If BDStar relies on a limited number of suppliers for essential raw materials or advanced manufacturing services, those suppliers gain significant leverage. This is particularly relevant in specialized industries like global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), where a few dominant nations control the underlying infrastructure, indirectly shaping the supply chain for chip manufacturers and related components.
The GNSS market is a prime example. With only a handful of countries operating their own satellite navigation systems, the ecosystem for GNSS chips and related technologies is inherently concentrated. This concentration means that suppliers of these specialized components, often tied to these national systems, can command higher prices and dictate terms, potentially impacting BDStar's cost structure and operational flexibility.
- Concentrated Supplier Base: A small number of suppliers for critical components can dictate terms and prices.
- GNSS Ecosystem Dependence: The global GNSS chip industry is influenced by a few major nations controlling satellite navigation systems.
- Impact on BDStar: High supplier concentration can lead to increased costs and reduced negotiation power for BDStar.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of forward integration by suppliers presents a significant challenge to Beijing BDStar Navigation. If key component providers, such as advanced semiconductor manufacturers, decide to move into developing and selling complete end-user navigation solutions themselves, they could bypass BDStar entirely. This would directly increase their leverage over BDStar, as they would control both the components and the final product, potentially dictating terms and pricing.
Consider the scenario where a leading chip manufacturer, already supplying BDStar with critical processing units, develops its own integrated navigation system. This new offering could be marketed directly to BDStar's existing customer base, such as automotive manufacturers or defense contractors. Such a move would not only cannibalize BDStar's market share but also diminish BDStar's value proposition as an integrator.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into BDStar's core business of end-user product development.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Increases supplier leverage by controlling both components and final solutions.
- Example Scenario: Chip manufacturers offering integrated navigation systems directly to BDStar's customers.
- Market Implications: Potential for market share erosion and diminished value proposition for BDStar.
BDStar Navigation faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the concentrated nature of the global GNSS chip market, where a few dominant players control essential technologies. This reliance on specialized components, often protected by intellectual property, limits BDStar's options and can lead to increased costs and supply chain vulnerabilities.
The high cost and complexity associated with switching suppliers for integrated components, such as GNSS chips, further empower these suppliers. BDStar's potential need for extensive redesigns, re-certifications, and investments in new tooling underscores the leverage held by its current component providers.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, where they might develop and sell complete navigation solutions directly to BDStar's customers, poses a substantial risk. This could erode BDStar's market share and diminish its value proposition, amplifying supplier leverage.
| Factor | Description | Impact on BDStar | Supporting Data (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited number of suppliers for critical GNSS chips and modules. | Increased costs, reduced negotiation power. | Global GNSS chip market dominated by a few key international players. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | Suppliers possess unique designs and patents for essential components. | Difficulty in finding substitutes, higher pricing power. | Over 129,000 cumulative patent applications for satellite navigation in China by end of 2024. |
| Switching Costs | High expense and complexity in changing component providers. | Entrenches existing supplier relationships, strengthens their leverage. | Potential for millions in costs for redesign and re-certification for new chips. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers potentially entering BDStar's end-user product market. | Market share erosion, diminished value proposition. | Chip manufacturers could offer integrated navigation systems directly to BDStar's clients. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Beijing BDStar Navigation dissects the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within the satellite navigation industry.
Navigate the competitive landscape with ease, as Beijing BDStar Navigation's Porter's Five Forces analysis offers a clear, actionable framework to identify and mitigate strategic threats.
Gain a competitive edge by proactively addressing market pressures, allowing for informed strategic adjustments and a more resilient business model.
Customers Bargaining Power
BDStar Navigation's diverse customer base, spanning high-precision positioning, autonomous driving, and IoT sectors, significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer. This fragmentation means that no individual client can exert undue pressure on pricing or terms, as BDStar's revenue is not overly reliant on any one entity.
The broad adoption of BeiDou technology across numerous industries, from consumer electronics to critical industrial infrastructure, further solidifies this advantage. For instance, the growth in the automotive sector, where BDStar is a key player, saw a substantial increase in vehicle production in 2024, underscoring the wide market penetration and reduced dependence on specific automotive manufacturers.
Customers in mass markets, such as those buying smartphones or wearables, are very sensitive to price. This means they have significant power to negotiate lower prices. BDStar's presence in consumer chips and data services puts it in direct contact with these price-conscious buyers.
Customers' ability to switch to alternative GNSS providers or competing positioning technologies significantly impacts their bargaining power. For instance, the continued global presence and widespread adoption of systems like GPS and Galileo provide users with readily available alternatives, potentially reducing their reliance on any single provider.
While China's domestic satellite navigation industry, including Beidou, is rapidly expanding, competition from established international systems means customers still have choices. This competitive landscape, especially in sectors where interoperability is key, empowers customers to negotiate better terms or seek out the most cost-effective and feature-rich solutions available in 2024.
Volume of Purchases
The volume of purchases significantly influences the bargaining power of customers for Beijing BDStar Navigation. Large-volume customers, like major automotive manufacturers or substantial IoT solution providers, can leverage their purchasing power to negotiate more favorable pricing, demand customized product features, and secure advantageous contract terms. This dynamic is evident in BDStar's strategic moves, such as acquiring a stake in Shenzhen Tianli Automotive Electronics Technology, indicating a deliberate effort to solidify relationships with key high-volume clients within critical market segments.
BDStar's ability to manage relationships with these large buyers is crucial. For instance, if a major automotive OEM represents a substantial portion of BDStar's revenue, that OEM's purchasing volume grants them considerable leverage. This can translate into pressure on BDStar to offer volume discounts or invest in specialized R&D to meet specific needs, potentially impacting BDStar's profit margins.
- High-volume customers can dictate terms: Large buyers can demand lower prices, extended payment terms, or exclusive product variations due to their significant order sizes.
- Strategic partnerships are key: BDStar's focus on acquiring stakes in companies like Shenzhen Tianli Automotive Electronics Technology highlights the importance of securing and deepening relationships with major clients to mitigate their bargaining power.
- Impact on profitability: The ability of large customers to negotiate better terms can directly affect BDStar's revenue and profit margins, especially if these customers represent a significant percentage of total sales.
Customer's Importance to BDStar
The bargaining power of customers for BDStar is significantly influenced by how essential its solutions are to a client's core operations and the degree of proprietary technology the customer possesses. When BDStar's products are critical for a customer's success, and the customer lacks comparable in-house capabilities, their ability to negotiate lower prices or demand more favorable terms diminishes.
For instance, in the burgeoning field of autonomous driving, where centimeter-level positioning accuracy is non-negotiable, BDStar's specialized positioning solutions are not merely beneficial but absolutely vital. This indispensability directly translates to a reduced bargaining power for these customers, as finding viable alternatives is difficult and the cost of failure is exceptionally high. In 2024, the demand for high-precision GNSS modules, a key BDStar offering, saw robust growth, with the global market expected to reach over $6 billion, underscoring the critical nature of these components for advanced applications.
- Criticality of Solution: BDStar's positioning technology is indispensable for applications like autonomous vehicles, where precision is paramount.
- Customer's Proprietary Technology: Customers with less proprietary technology are more reliant on BDStar's specialized offerings, thus reducing their bargaining power.
- Market Dependence: The growing reliance on advanced positioning systems in sectors like automotive and industrial automation strengthens BDStar's position.
BDStar Navigation faces moderate customer bargaining power, primarily driven by the availability of alternatives and customer price sensitivity in certain segments. However, the critical nature of its high-precision positioning solutions in sectors like autonomous driving significantly reduces this power for key clients.
The extensive adoption of BeiDou across various industries, including the robust growth in the automotive sector in 2024, demonstrates BDStar's wide market reach. This broad customer base, coupled with the indispensable nature of its advanced positioning technology for applications such as autonomous vehicles, limits the leverage individual customers can exert.
While mass-market consumers are price-sensitive, BDStar's strategic focus on high-value industrial and automotive clients, where precision is paramount, shifts the balance. The company's efforts to solidify relationships with high-volume clients, like through investments in automotive electronics, further mitigate customer power by creating strategic dependencies.
| Factor | BDStar Navigation's Position | Impact on Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Diverse customer base across multiple sectors. | Lowers power; revenue not dependent on single clients. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Global presence of GPS, Galileo alongside Beidou. | Moderate power; customers have choices. |
| Switching Costs | High for critical applications like autonomous driving. | Lowers power; difficult and costly to switch. |
| Price Sensitivity | High in mass-market consumer segments. | Increases power for consumer-focused products. |
| Criticality of Product | Essential for high-precision applications (e.g., autonomous driving). | Significantly lowers power for these key clients. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Beijing BDStar Navigation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Beijing BDStar Navigation, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full immediate utility.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese satellite navigation market is a dynamic arena, marked by substantial growth and a crowded field of domestic contenders. BDStar operates within this environment, facing robust competition from established entities.
Key rivals such as Space Star Technology, Hunan Bynav Technology, NavInfo, and Shanghai Huace Navigation Technology are actively vying for market share. This fragmentation fuels intense rivalry, as these companies continuously innovate and refine their offerings to capture a larger portion of the expanding Chinese market.
The high industry growth rate fuels competitive rivalry as companies aggressively pursue market share. In 2024, China's satellite navigation and positioning service industry saw its output value climb to 575.8 billion yuan, marking a robust 7.39% year-on-year increase. This expansion, largely propelled by BeiDou system advancements and its broad adoption, creates fertile ground for intense competition among industry players.
Competitive rivalry in the GNSS sector is intense, driven by relentless innovation in chips, modules, and high-precision solutions. Companies are constantly pushing for better accuracy, enhanced reliability, and seamless integration to stand out. BDStar is actively pursuing this differentiation through its 'Cloud + Chip' strategy and its intelligent location digital base (iLDB®) platform, aiming to offer unique value to its customers.
Government Support and BeiDou Integration
The Chinese government's robust backing of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System significantly shapes the competitive landscape, offering a distinct advantage to domestic players like BDStar. This support translates into preferential policies and direct investment, fostering an environment where companies deeply integrated with BeiDou can thrive.
Government mandates and incentives actively promote the adoption of BeiDou across a wide array of sectors. This integration is crucial for industries ranging from automotive and transportation to agriculture and public safety, creating substantial market opportunities for BDStar and its peers.
- Government Investment: China's commitment to BeiDou development is substantial, with significant state funding allocated to its expansion and technological advancement.
- Policy Support: Favorable regulations and national strategies prioritize BeiDou integration, creating a protected domestic market and encouraging its adoption in critical national projects.
- BDStar's Role: As a key player in BeiDou's ecosystem, BDStar benefits directly from this national infrastructure, gaining a competitive edge through early access and deep integration capabilities.
- Market Penetration: By 2024, BeiDou has achieved widespread adoption, with its chipsets integrated into millions of devices, underscoring the success of government-led integration efforts.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
The landscape of competitive rivalry for companies like Beijing BDStar Navigation is intensifying as strategic partnerships and acquisitions become key differentiators. These moves are not just about growth; they are about consolidating market position and acquiring crucial technological advancements. For instance, BDStar has strategically invested in and acquired stakes in related technology firms, such as Shenzhen Tianli Automotive Electronics Technology, demonstrating a clear intent to bolster its capabilities and expand its market footprint.
This consolidation trend means that rivals are also actively pursuing similar strategies. Companies are merging or forming alliances to gain access to new markets, share research and development costs, and offer more comprehensive solutions to customers. This dynamic creates a more formidable competitive environment where scale and integrated offerings are increasingly important.
- Strategic Investments: BDStar's acquisition of a stake in Shenzhen Tianli Automotive Electronics Technology highlights a trend of investing in complementary technologies.
- Market Expansion: Such partnerships and acquisitions are often driven by the desire to reach new customer segments or geographical regions.
- Capability Enhancement: Companies are buying or partnering to gain access to specialized expertise, such as advanced AI or data analytics, crucial for navigation and positioning systems.
- Competitive Pressure: The aggressive M&A activity by competitors forces other players to either join the consolidation wave or risk being left behind with less integrated offerings.
Competitive rivalry in China's satellite navigation sector is fierce, with numerous domestic players vying for market share. The industry's rapid growth, evidenced by a 7.39% increase in output value to 575.8 billion yuan in 2024, intensifies this competition. Companies like Space Star Technology, Hunan Bynav Technology, NavInfo, and Shanghai Huace Navigation Technology are key rivals, constantly innovating to capture this expanding market.
BDStar navigates this intense competition by focusing on technological differentiation, such as its 'Cloud + Chip' strategy and iLDB® platform. The strong government backing for the BeiDou system provides a significant advantage to domestic firms like BDStar, fostering an environment where deep integration with BeiDou is rewarded. This support is crucial as BeiDou chipsets are increasingly embedded in millions of devices, a trend that accelerated through 2024.
| Key Competitors | 2024 Market Focus | Competitive Strategy Example |
|---|---|---|
| Space Star Technology | BeiDou integration, high-precision services | Expanding application areas in smart cities |
| Hunan Bynav Technology | Automotive and IoT solutions | Developing advanced sensor fusion for autonomous driving |
| NavInfo | Mapping and navigation data services | Investing in HD map technologies for ADAS |
| Shanghai Huace Navigation Technology | GNSS receivers and solutions | Enhancing accuracy and reliability for industrial applications |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While satellite navigation systems like BeiDou are dominant, alternative positioning technologies present a significant threat of substitutes. Inertial Navigation Systems (INS), which rely on accelerometers and gyroscopes, are particularly effective in environments where satellite signals are weak or unavailable, such as tunnels or dense urban canyons. In 2024, the market for INS is projected to reach over $7 billion globally, indicating strong adoption.
Furthermore, Wi-Fi-based positioning and Bluetooth beacons are increasingly used for indoor navigation, offering a cost-effective alternative to GNSS in retail spaces and large buildings. Lidar and radar-based systems are also gaining traction, especially in autonomous vehicle applications where precise, short-range positioning is critical. These technologies are often integrated into hybrid solutions, enhancing overall positioning accuracy and reliability.
The rise of lightweight mapping solutions in autonomous driving presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like BDStar, which may focus on traditional high-definition (HD) mapping. These new approaches leverage real-time vehicle perception and advanced algorithms, diminishing the necessity for highly detailed, pre-existing map data. For instance, by 2024, many automotive manufacturers are investing heavily in on-board sensor fusion and AI to interpret their surroundings dynamically, potentially bypassing the need for extensive outsourced mapping services.
The increasing availability of 5G networks and sophisticated terrestrial positioning systems presents a significant threat to traditional Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) services, particularly in densely populated urban environments. These technologies can deliver highly accurate location data, potentially replacing GNSS for a range of applications.
The rollout of 5G RedCap (Reduced Capability) technology, especially within China's industrial IoT sector, is a prime example of this shift. This deployment offers alternative connectivity and positioning solutions, directly impacting the market share of established GNSS providers like BDStar Navigation.
Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)
The threat of substitutes for Beijing BDStar Navigation's core technologies, particularly in the realm of positioning, is influenced by advancements in Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs). For scenarios where Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals are unreliable, such as within tunnels or dense urban environments, IMUs offer a viable alternative or a complementary solution. Enhanced IMU precision can significantly lessen the reliance on continuous GNSS availability.
The market for IMUs is experiencing substantial growth, driven by their increasing integration across various industries. For instance, the global IMU market was valued at approximately $4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $7.8 billion by 2028, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of around 11.5%. This expansion underscores their growing importance as substitutes or enhancers to GNSS-dependent systems.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing improvements in IMU sensor technology, including MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) and optical gyroscopes, are leading to higher accuracy and lower costs, making them more competitive with GNSS solutions.
- Application Diversification: IMUs are finding broader applications beyond traditional navigation, including in consumer electronics, automotive safety systems, and industrial automation, further increasing their accessibility and potential as substitutes.
- Hybrid Systems: The most significant impact may come from the integration of IMUs with GNSS in hybrid systems, where IMUs compensate for GNSS signal outages, thereby reducing the overall vulnerability to signal loss and potentially diminishing the sole reliance on GNSS.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs
The threat of substitutes for Beijing BDStar Navigation's offerings is influenced by cost-performance trade-offs. Customers may choose less precise, lower-cost positioning solutions if their specific applications don't demand high accuracy, or if the expense of high-precision GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) solutions is not justified by the perceived benefits. This dynamic creates a market segment where simpler, more affordable alternatives can readily substitute BDStar's advanced technologies.
For instance, in 2024, while advanced GNSS modules offering centimeter-level accuracy can command premium pricing, basic GPS modules suitable for general location tracking might be available at a fraction of the cost. This price disparity allows for substitution, particularly in consumer electronics or less critical industrial applications where sub-meter accuracy is sufficient. The market for inertial navigation systems (INS) also presents a substitute threat, especially in environments where GNSS signals are unreliable, though these systems often come with their own cost and complexity considerations.
- Cost Sensitivity: Applications with lower accuracy requirements, such as basic asset tracking or non-critical navigation, are more susceptible to substitution by cheaper alternatives.
- Performance Thresholds: If the performance gap between BDStar's high-precision solutions and available substitutes does not meet a critical threshold for a given application, customers will likely opt for the lower-cost option.
- Technological Maturity of Substitutes: As alternative positioning technologies mature and become more cost-effective, their threat as substitutes increases, potentially eroding market share for high-cost, high-performance solutions.
Alternative positioning technologies pose a significant threat to Beijing BDStar Navigation. Inertial Navigation Systems (INS), crucial for signal-denied environments, saw their global market exceed $7 billion in 2024. Indoor navigation increasingly relies on Wi-Fi and Bluetooth beacons, offering cost-effective solutions where GNSS is less viable.
The automotive sector's shift towards on-board sensor fusion and AI for dynamic environmental interpretation, bypassing traditional HD mapping, further exemplifies this threat. By 2024, many manufacturers were heavily investing in these on-board capabilities.
Furthermore, the expansion of 5G networks, including China's 5G RedCap for industrial IoT, provides alternative positioning solutions that can directly compete with or supplement GNSS services, especially in urban areas.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | 2024 Market Relevance/Impact |
| Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) | Operation in GNSS-denied areas | Global market projected over $7 billion |
| Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Beacons | Cost-effective indoor positioning | Increasing adoption in retail and large buildings |
| On-board Sensor Fusion/AI | Dynamic environmental interpretation | Bypassing traditional HD mapping in automotive |
| 5G Networks (incl. RedCap) | Alternative terrestrial positioning | Direct competition/supplementation to GNSS in urban/IoT sectors |
Entrants Threaten
The satellite navigation and high-precision positioning industry demands significant upfront capital for research and development, infrastructure build-out, and advanced manufacturing. For instance, developing cutting-edge GNSS chips and modules, a core competency for companies like BDStar, requires immense financial commitment, acting as a substantial barrier for newcomers.
The highly technical nature of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) chip design, signal processing, and precision algorithms creates a significant barrier to entry. Developing this level of expertise requires substantial investment in research and development, along with a considerable amount of time.
China's intellectual property landscape in satellite navigation, evidenced by its numerous patent applications, further solidifies this barrier. New entrants would struggle to replicate or innovate upon this existing technological foundation without significant resources and specialized knowledge.
The satellite navigation sector, particularly for high-stakes uses like autonomous vehicles and defense, faces substantial regulatory scrutiny and demands numerous certifications. These requirements act as a considerable deterrent for newcomers aiming to enter the market.
China has established specific performance standards for Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) within its automotive sector. For instance, the national standard GB/T 38757.1-2020 outlines requirements for intelligent connected vehicles, including aspects of PNT, which new entrants must adhere to.
Established Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships
Established brand reputation and customer relationships present a significant barrier to new entrants in the satellite navigation market. Companies like BDStar Navigation have cultivated strong ties with industrial and governmental clients over many years. These long-standing relationships are built on trust and a proven track record, making it difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market. For instance, BDStar's involvement in major national projects, such as the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, underscores its deep integration and reliability within critical sectors.
Newcomers face the daunting task of not only matching existing technological capabilities but also replicating the loyalty and trust that BDStar and its peers have earned. This is especially true in high-stakes applications where precision and dependability are paramount. The cost and time required to build such credibility are substantial, acting as a powerful deterrent.
- Established Loyalty: BDStar's long-term partnerships with key players in defense, transportation, and surveying sectors are a significant hurdle for new competitors.
- High Stakes Applications: The critical nature of satellite navigation in areas like national defense and autonomous systems demands proven reliability, which is hard for new entrants to demonstrate quickly.
- Brand Recognition: BDStar's brand is synonymous with robust navigation solutions in China, built through consistent performance and strategic government backing.
Access to BeiDou System and Related Ecosystem
New entrants face a significant hurdle in accessing and integrating with China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS). Established companies like BDStar possess deep integration and privileged access to this critical ecosystem, which is fundamental for operating in the Chinese market.
Developing comparable capabilities or navigating the complexities of BeiDou integration requires substantial investment and time. For instance, in 2024, the global GNSS market, which includes BeiDou, was valued at approximately $11.5 billion, highlighting the scale of investment needed to compete.
- Proprietary Access: BDStar benefits from established relationships and technical integration with the BeiDou system, creating a barrier for newcomers.
- Ecosystem Lock-in: The extensive network of BeiDou-dependent applications and services makes it difficult for new entrants to gain traction without seamless integration.
- Development Costs: Replicating or integrating with BeiDou's advanced features, such as its high-precision services, demands significant R&D expenditure.
The threat of new entrants in the satellite navigation sector, particularly for BDStar Navigation, is considerably low due to immense capital requirements for R&D and infrastructure. For instance, the global GNSS market, valued at approximately $11.5 billion in 2024, necessitates substantial investment to compete effectively.
Technical expertise in GNSS chip design and signal processing is a significant barrier, as is navigating China's stringent regulatory environment and certification processes. BDStar's established brand reputation and deep integration with the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System further solidify these entry barriers, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Beijing BDStar Navigation leverages data from official company filings, industry-specific market research reports, and reputable financial news outlets to capture the competitive landscape.