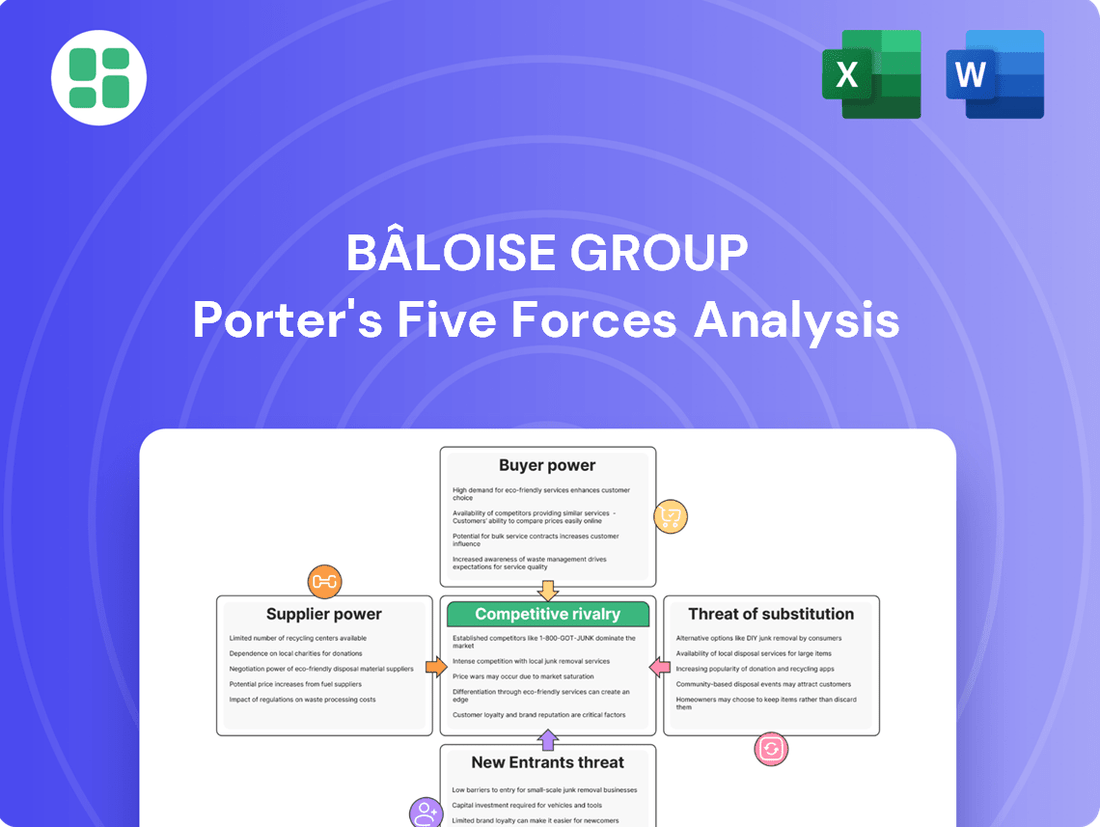
Bâloise Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bâloise Group Bundle
Bâloise Group navigates a complex insurance landscape, where intense rivalry and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its strategic decisions. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the company's competitive position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bâloise Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The global reinsurance market, essential for Bâloise to offload significant risks, is anticipated to stay steady through 2025. This stability is underpinned by healthy operating profits and strong financial reserves within the reinsurance sector.
In mid-2024, property reinsurance rates were moderate, a result of ample available capacity. However, casualty reinsurance prices saw continued increases. This rise is driven by factors like social inflation and escalating litigation expenses, directly impacting Bâloise's costs for transferring risk.
Reinsurers are projected to achieve earnings that meet their cost of capital in the 2024-2025 period. This positive outlook is attributed to favorable pricing environments and a commitment to disciplined underwriting practices across the industry.
The European insurtech market saw substantial growth, with investment in the sector reaching approximately $10 billion in 2023. This expansion, fueled by digital advancements like AI, means specialized technology providers offering critical solutions for claims processing, risk assessment, and operational streamlining can exert considerable bargaining power over insurers like Bâloise.
Bâloise's strategic push into digital transformation and 'insurbanking' models necessitates deeper collaboration with these tech innovators. Consequently, providers of advanced, niche technology solutions, crucial for Bâloise's competitive edge, can command more favorable terms, potentially impacting the group's cost structure and operational agility.
The bargaining power of data and analytics providers for Bâloise Group is substantial, as access to high-quality, comprehensive data is fundamental to their operations. This data is critical for accurate underwriting, effective loss prediction, and crafting personalized insurance products.
Suppliers offering unique or superior datasets, particularly those leveraging advancements in AI and IoT, can significantly influence pricing and impact insurers' operational capabilities. For instance, in 2024, the global data analytics market was projected to reach over $300 billion, highlighting the value and demand for such services.
InsurTech platforms, which often facilitate advanced data and risk management, play a key role. Their ability to enhance underwriting accuracy and loss prediction directly translates into a stronger negotiating position with insurers like Bâloise.
Specialized Professional Services
Providers of specialized professional services, such as actuarial consultants and expert legal counsel, wield significant bargaining power over Bâloise Group. Their niche expertise is often indispensable, especially given the complex regulatory landscape governing the insurance industry, which mandates the involvement of such specialists. For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized actuarial services remained robust, driven by evolving risk models and capital requirements.
The inherent complexity of insurance products and claims, particularly those involving intricate scenarios like natural catastrophe assessments, ensures a consistent and high demand for these specialized services. This sustained need reinforces the suppliers' ability to dictate terms, impacting Bâloise's operational costs and efficiency.
- Niche Expertise: Actuarial consultants and specialized legal teams possess unique skill sets that are difficult for insurers to replicate internally.
- Regulatory Mandates: Compliance with insurance regulations often necessitates the engagement of external, certified professionals.
- Complexity of Claims: Assessing damages from events like major floods or cyberattacks requires specialized knowledge, making these service providers critical.
- Limited Substitutes: For highly specific tasks, the pool of qualified providers is often limited, enhancing their bargaining position.
Financial Market Providers for Investment Solutions
For Bâloise Group's investment and banking services, particularly its pension solutions, the bargaining power of financial market providers such as investment banks and asset managers is a key consideration. These providers dictate terms and conditions that directly influence Bâloise's operational costs and the ultimate profitability of its product offerings. The cost of capital and the investment performance achieved by these external partners are critical factors in determining the attractiveness and competitiveness of Bâloise's financial products for its clientele.
In 2024, the landscape for asset management fees remained competitive, with institutional investors often negotiating for lower management expense ratios (MERs). For instance, average MERs for broad-market equity ETFs in Europe hovered around 0.20% to 0.30%, a benchmark that influences pricing expectations for Bâloise's pooled investment vehicles. Similarly, investment banks' pricing for underwriting or advisory services can fluctuate based on market demand and the perceived risk of transactions, impacting Bâloise's capital raising and strategic investment costs.
- Impact of Asset Manager Fees: Higher fees charged by asset managers directly reduce the net returns available to Bâloise's pension clients, potentially diminishing product appeal.
- Cost of Capital Influence: The interest rates and financing terms offered by investment banks for Bâloise's capital needs or structured products significantly affect its cost structure.
- Performance-Linked Fees: Some providers may charge performance-based fees, creating a direct link between their success and Bâloise's profitability, thereby increasing supplier power when performance is strong.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Bâloise Group is significant, particularly for specialized services and data providers. In 2024, the global data analytics market was projected to exceed $300 billion, underscoring the value and demand for high-quality data crucial for underwriting and risk assessment.
Niche providers, such as actuarial consultants and legal experts, possess indispensable skills, especially given the complex regulatory environment. The demand for these specialized services remained robust in 2024, driven by evolving risk models and capital requirements.
Insurtech platforms offering advanced data and risk management solutions also hold considerable sway, enhancing underwriting accuracy and loss prediction. This leverage impacts Bâloise's operational costs and strategic agility.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factor | Example Impact on Bâloise |
|---|---|---|
| Data & Analytics Providers | Uniqueness/Superiority of Data, AI/IoT Integration | Influences pricing of data services, impacts operational capabilities |
| Insurtech Platforms | Enhancement of Underwriting & Loss Prediction | Strengthens negotiating position, influences cost structure |
| Specialized Professional Services (Actuarial, Legal) | Niche Expertise, Regulatory Mandates, Complexity of Claims | Dictates terms, impacts operational costs and efficiency |
| Financial Market Providers (Asset Managers, Investment Banks) | Market Competitiveness (MERs), Transaction Risk | Affects Bâloise's cost of capital and product profitability |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to the Bâloise Group's insurance and financial services operations.
Instantly identify and prioritize competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, allowing for focused strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, particularly for straightforward property and casualty insurance, are very sensitive to price. This is made worse by how easy it is to compare different insurance deals online, often through comparison websites or directly on insurer's digital platforms. For example, in 2024, data suggests that over 60% of consumers used online comparison tools when shopping for insurance, highlighting a significant shift in buyer behavior.
This ease of comparison puts pressure on companies like Bâloise to keep their prices competitive. If Bâloise's prices are perceived as too high compared to rivals, customers can quickly switch, impacting sales volume and potentially reducing profit margins. This dynamic means Bâloise must carefully balance offering attractive pricing with maintaining profitability in a crowded market.
For Bâloise Group, low switching costs for many private and business clients, especially for standard insurance policies, mean customers can more readily explore alternative providers. This ease of transition amplifies their ability to negotiate better terms or service levels, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The digital age has dramatically shifted the balance of power towards customers. With readily available information through price comparison sites and online reviews, consumers in 2024 can easily compare offerings, understand market pricing, and identify the best value. This enhanced transparency directly diminishes Bâloise Group's ability to dictate terms, as customers are now better equipped to negotiate favorable prices and terms, weakening the company's bargaining power.
Large Corporate Clients' Leverage
Bâloise Group's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by its large corporate clients. These major business customers, due to the sheer volume of premiums they represent, wield considerable negotiation leverage. For instance, in 2024, large corporate accounts often constitute a substantial portion of an insurer's revenue, giving them the ability to demand tailored policies, preferential pricing, and more flexible contract terms. This can directly affect Bâloise's profitability on these key relationships.
The demands from these sophisticated clients are multifaceted. They frequently seek customized insurance solutions that precisely match their unique risk profiles and operational needs. This often translates into requests for specialized coverage, claims handling processes, and risk management services. Meeting these bespoke requirements can increase operational costs for Bâloise, further amplifying the customer's bargaining position.
- Volume of Premiums: Large corporate clients represent a significant portion of Bâloise's premium income, granting them substantial negotiation power.
- Demand for Customization: These clients often require tailored insurance products and services, increasing complexity and potential costs for Bâloise.
- Price Sensitivity: Corporate buyers are typically price-conscious and can leverage competitive market offerings to secure more favorable rates.
- Switching Costs: While potentially high for complex programs, the ability to switch providers can still be a factor in negotiations, especially for large accounts.
Demand for Value-Added Services and Personalization
Customers are increasingly seeking more than just standard insurance policies. They expect tailored products that fit their specific needs, along with user-friendly digital interfaces and services that add extra value, like tools for risk reduction or health management.
This growing demand for customization and enhanced services significantly empowers customers. They can now readily switch to insurers who offer these advanced features, putting pressure on companies like Bâloise Group to innovate and meet these evolving expectations.
- Digital Engagement: In 2024, a significant portion of insurance customers, estimated to be over 70% in many European markets, prefer digital channels for policy management and claims.
- Value-Added Services: Insurers offering integrated health and wellness platforms saw a 15% higher customer retention rate in early 2025 compared to those without.
- Personalization Trends: The market for personalized insurance products, including usage-based insurance and modular policies, is projected to grow by 10-12% annually through 2026.
The bargaining power of customers within the Bâloise Group's operating environment is considerable, driven by price sensitivity and the ease of comparing offerings. In 2024, online comparison tools were used by over 60% of insurance shoppers, a trend that significantly empowers consumers to seek out the most competitive prices. This ease of switching between providers, particularly for standard insurance products, means Bâloise must remain highly competitive to retain its customer base and maintain healthy profit margins.
| Factor | Impact on Bâloise | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on profit margins | Ability to switch for lower premiums |
| Ease of Comparison | Need for competitive pricing | Quickly identifying better deals |
| Digital Engagement | Demand for user-friendly platforms | Preference for insurers with advanced digital services |
| Demand for Customization | Increased operational complexity | Seeking tailored policies and value-added services |
What You See Is What You Get
Bâloise Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the Bâloise Group's Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a deep dive into the competitive landscape of the insurance sector. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, comprehensive file, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The European insurance market, where Bâloise Group primarily operates in Switzerland, Germany, Belgium, and Luxembourg, is a mature landscape. This maturity means there are many established companies, both local and global, all vying for customers. For example, in 2023, the German insurance market alone saw premiums of over €200 billion, indicating a large but highly contested space.
Competition is fierce in specific insurance sectors, notably motor insurance in Germany. Insurers there are actively working to regain profitability following prior losses, which naturally intensifies rivalry and can lead to downward pressure on premium rates.
Across the broader Continental European market, a strong drive for growth among insurers is also fueling aggressive competition. This pursuit of market share can manifest as reduced pricing, directly impacting underwriting margins and profitability for companies like Bâloise Group.
The insurance market, especially for non-life products like auto and home insurance, sees many offerings becoming very similar. This means companies like Bâloise often find themselves competing mainly on price. For example, in 2023, the average premium for comprehensive car insurance in Switzerland saw a slight increase, but the core product features remained largely consistent across providers, highlighting the price-sensitive nature of this segment.
This product commoditization forces Bâloise to look beyond just the policy itself for differentiation. Strong customer service, a trusted brand reputation, and operational efficiency become crucial levers. Companies that can deliver a superior customer experience or operate more cost-effectively can gain an edge even when product features are nearly identical.
High Exit Barriers Sustaining Rivalry
The insurance sector, including companies like Bâloise Group, faces intense competitive rivalry largely due to high exit barriers. These barriers, stemming from extensive regulatory compliance, the long-term nature of insurance liabilities, and significant investments in fixed assets like IT infrastructure and property, make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market. This persistence of even weaker players intensifies competition as they strive to maintain market presence or capture share, rather than ceasing operations.
In 2024, the persistent nature of these barriers means that companies struggling financially are less likely to exit, leading to a crowded competitive landscape. For instance, the Solvency II directive in Europe imposes stringent capital requirements, making it financially prohibitive for many insurers to wind down operations gracefully. This regulatory environment, coupled with the need to manage long-term claims, effectively traps capital within the industry, ensuring that rivalry remains a constant factor for established players like Bâloise.
- Regulatory Obligations: Insurers must meet capital adequacy ratios and adhere to consumer protection laws, which are costly to unwind.
- Long-Term Liabilities: The nature of insurance policies means companies are committed to payouts over many years, preventing swift exits.
- Substantial Fixed Assets: Investments in technology, branch networks, and administrative systems represent significant sunk costs.
Digital Transformation and Insurtech Impact
While Bâloise is actively investing in digital transformation and its 'insurbanking' initiatives, the broader insurtech revolution is intensifying competitive rivalry. New, agile firms are leveraging advanced technology to offer innovative products and services, creating significant disruption for established players.
These insurtech companies can often operate with lower overheads and a more customer-centric approach, forcing traditional insurers like Bâloise to accelerate their own digital innovation to retain market share and relevance. For instance, in 2024, the global insurtech market continued its robust growth, with significant venture capital funding flowing into startups focused on AI-driven underwriting and personalized customer experiences.
- Increased Pressure to Innovate: Insurtechs are setting new benchmarks for digital engagement and product customization, compelling Bâloise to invest heavily in its own digital capabilities.
- Potential for Disruption: Agile new entrants can quickly capture market segments by offering niche products or superior digital experiences, challenging incumbent business models.
- Investment in Digitalization: Bâloise's own digital transformation efforts, including its 'insurbanking' strategy, are a direct response to this heightened competitive pressure, aiming to integrate insurance and banking services more seamlessly.
- Evolving Customer Expectations: The rise of insurtech has also shifted customer expectations towards more convenient, transparent, and personalized insurance solutions, requiring traditional insurers to adapt their offerings and service delivery.
The competitive rivalry within Bâloise Group's operating markets is intense, driven by a mature European insurance landscape with numerous established players. This maturity, evidenced by the over €200 billion in premiums generated in the German insurance market in 2023, means companies frequently compete on price, particularly in segments like German motor insurance where profitability pressures are high. The commoditization of non-life products further exacerbates this, pushing Bâloise to differentiate through customer service and operational efficiency.
High exit barriers, including regulatory capital requirements and long-term liabilities, keep even struggling insurers in the market, intensifying competition. For instance, the Solvency II directive mandates robust capital buffers, making market exit costly and difficult. This environment, coupled with the rise of agile insurtechs leveraging advanced technology and lower overheads, compels Bâloise to continuously innovate its digital offerings and customer experience to maintain its competitive standing.
| Market Characteristic | Impact on Bâloise | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Market Maturity | High competition, price sensitivity | German insurance premiums > €200 billion |
| Product Commoditization | Price-based competition | Consistent core product features in Swiss car insurance |
| Insurtech Disruption | Need for digital innovation | Robust global insurtech market growth |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large corporations increasingly opt for self-insurance or establish captive insurers as a direct substitute for traditional insurance products offered by companies like Bâloise Group. This strategy allows them to retain risk internally, potentially lowering premiums and gaining granular control over their risk management processes.
In 2024, the trend of companies exploring self-insurance and captives continued, driven by a desire for cost efficiency and customized coverage. For instance, many large enterprises found that by pooling their risks within a captive, they could achieve significant savings compared to paying market-rate premiums, especially for predictable loss exposures.
Government social security and welfare systems present a significant threat of substitutes for Bâloise Group. In many European nations where Bâloise operates, comprehensive state-provided healthcare, unemployment benefits, and pension schemes can diminish the demand for private life, health, and supplementary retirement products. For instance, in Switzerland, the mandatory three-pillar pension system, combining state, occupational, and private provisions, means that a substantial portion of retirement income is already covered by public and employer-sponsored plans, potentially reducing the reliance on purely private pension solutions offered by insurers like Bâloise.
Sophisticated financial instruments like catastrophe bonds and derivatives represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional insurance. These Alternative Risk Transfer (ART) mechanisms allow companies to offload specific, often large-scale, risks away from conventional insurance and reinsurance markets. For instance, the catastrophe bond market saw substantial issuance in 2023, with total issuance reaching approximately $15 billion, demonstrating a growing appetite for these ART solutions.
Preventative Technologies and Risk Mitigation Services
The rise of preventative technologies presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional insurance. For instance, smart home sensors can detect water leaks or fires early, potentially preventing substantial damage that would otherwise be claimed. In the automotive sector, telematics devices in vehicles monitor driving behavior, which can lead to lower premiums and encourage safer driving, reducing the need for collision coverage. Cybersecurity solutions are also becoming more sophisticated, offering businesses protection against data breaches and cyberattacks, thereby lessening their reliance on cyber insurance.
Bâloise Group, like other insurers, faces this threat as clients increasingly invest in risk mitigation services. This shift means that the core function of insurance – indemnifying against loss – is being partially replaced by proactive measures that prevent losses from occurring. For example, a company investing heavily in advanced cybersecurity might opt for a lower level of cyber insurance, viewing the technology as a more effective substitute for comprehensive coverage. This trend directly impacts the demand for certain insurance products.
The impact of these substitutes is quantifiable. By 2024, the global market for smart home devices, which includes many preventative technologies, was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars. Similarly, the telematics insurance market has seen significant growth, with a substantial percentage of new vehicle sales incorporating such technology. This growing adoption signifies a tangible reduction in the potential pool of insured events, directly challenging the traditional insurance model.
- Preventative Technologies: Smart home sensors, vehicle telematics, and advanced cybersecurity solutions are increasingly reducing the likelihood and severity of insured events.
- Risk Mitigation Services: Clients are investing more in proactive risk management, which can decrease their dependence on comprehensive insurance policies.
- Market Impact: The growing adoption of these technologies and services directly challenges the traditional role of insurance by preventing losses rather than just covering them.
- Financial Implications: This trend can lead to a reduction in premium volumes for insurers as clients opt for preventative measures over extensive coverage.
Direct Investment and Fintech Platforms
The threat of substitutes for Bâloise Group's investment and pension solutions is significant, primarily from direct investment platforms and a growing array of fintech alternatives. These platforms provide individuals and businesses with direct access to financial markets, often bypassing traditional insurer-managed products.
These substitutes frequently compete on cost, offering lower management fees or transaction charges compared to what Bâloise might charge. For instance, many robo-advisors, which leverage algorithms to manage portfolios, have significantly lower expense ratios than actively managed funds often found in insurance products. As of early 2024, the average expense ratio for robo-advisor portfolios can be as low as 0.25%, whereas traditional managed funds can range from 0.50% to over 1.50%.
Furthermore, fintech solutions often cater to specific investment philosophies or niche markets that Bâloise might not directly address. This includes platforms focused on socially responsible investing (SRI), cryptocurrency, or alternative assets, attracting segments of the market seeking specialized offerings. The ease of use and digital-first experience offered by many fintechs also presents a strong substitute, appealing particularly to younger demographics.
- Lower Fees: Robo-advisors and direct investment platforms often boast lower expense ratios, with some charging as little as 0.25% annually compared to traditional managed funds.
- Direct Market Access: These substitutes allow investors to directly engage with stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments without the wrapper of an insurance product.
- Specialized Offerings: Fintech solutions cater to diverse investment preferences, including ESG investing and alternative assets, broadening investor choice beyond insurer-provided options.
- Digital User Experience: The intuitive and accessible digital interfaces of many fintech platforms appeal to a broad range of investors, especially younger generations.
The increasing availability of direct investment platforms and fintech solutions poses a significant threat of substitutes for Bâloise Group's investment and pension offerings. These alternatives often provide lower fees and direct market access, appealing to a broad investor base. For instance, by early 2024, robo-advisor expense ratios were frequently below 0.25%, a stark contrast to traditional managed funds.
Entrants Threaten
Establishing an insurance company, especially one with broad European reach like Bâloise, demands considerable capital to satisfy rigorous solvency regulations. Bâloise, for example, consistently demonstrates a robust solvency ratio exceeding 200%, a figure that presents a formidable hurdle for aspiring new competitors.
The insurance industry presents significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory requirements. New companies must navigate complex licensing procedures and adhere to a multitude of national and EU-level compliance standards, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a full insurance license in a major European market could extend over 18 months, involving substantial legal and administrative costs.
Incumbent insurers like Bâloise Group benefit from decades of established brand recognition and customer trust, a critical asset in the insurance sector. For instance, Bâloise reported a strong solvency ratio of 224% at the end of 2023, reflecting its financial stability and the trust it has cultivated. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating this level of deeply ingrained customer confidence, which is built over many years of reliable service and consistent performance.
Extensive Distribution Network Development
Building an extensive distribution network, whether through agents, brokers, or direct online channels, requires substantial upfront investment and considerable time. For instance, establishing a comprehensive agency force in the insurance sector can take years and millions in marketing and training. This high barrier makes it difficult for new companies to compete with established players who already possess these vital connections and customer access points.
Existing insurers like Bâloise Group benefit from their long-standing relationships and deep penetration within their markets. In 2024, the insurance industry continues to see consolidation, with larger entities leveraging their scale and established networks to acquire smaller competitors, further solidifying their market position and making entry even more challenging.
- High Capital Investment: Significant funds are needed for marketing, agent recruitment, training, and technology to build a comparable distribution infrastructure.
- Time and Experience: Developing trust and relationships with brokers and agents takes years of consistent performance and support.
- Brand Recognition: Established players often have strong brand loyalty, which new entrants struggle to overcome without a compelling value proposition.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating licensing and compliance across various distribution channels adds complexity and cost for newcomers.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Advantages
Established insurers like Bâloise Group leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to spread the high fixed costs of underwriting, claims processing, and sophisticated IT infrastructure over a larger volume of business, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major European insurers reported operating expense ratios below 20%, a level difficult for newcomers to match immediately.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in replicating these efficiencies. Achieving comparable cost advantages requires substantial upfront investment in technology, personnel, and market penetration, making it challenging to compete on price from the outset. Without the benefit of an established experience curve, new players often start with higher operational costs.
- Economies of Scale: Bâloise Group’s large operational footprint in 2024 allows for cost efficiencies in areas like IT and claims management that new entrants cannot easily replicate.
- Experience Curve: Years of operation have allowed Bâloise to refine processes, reducing costs and improving service quality, a learning curve new entrants must climb.
- Investment Barrier: Reaching the scale necessary to compete on cost requires significant capital, acting as a deterrent for potential new entrants in the insurance market.
The threat of new entrants for Bâloise Group is generally considered low, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscape inherent in the insurance sector. For example, in 2024, the capital needed to establish an insurance operation compliant with Solvency II directives across multiple European markets can easily run into hundreds of millions of euros.
Furthermore, the established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks of incumbents like Bâloise present a significant challenge for newcomers. Bâloise's strong solvency ratio, reported at 224% at the close of 2023, underscores its financial stability and the trust it has built, making it difficult for new entities to gain immediate traction.
The industry's reliance on an experience curve, where operational efficiency and risk assessment improve with time, also acts as a barrier. New entrants must overcome this learning curve, which can take years and significant investment, to achieve cost structures comparable to established players like Bâloise, who in 2024 benefit from operating expense ratios often below 20%.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for licensing, solvency capital, and infrastructure. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the pool of potential entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex and evolving insurance regulations across jurisdictions. | Time-consuming and costly, requiring specialized legal and compliance expertise. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established customer loyalty and perceived reliability of incumbents. | Difficult for new entrants to build credibility and attract customers without a strong value proposition. |
| Distribution Networks | Access to and development of agent, broker, and direct sales channels. | Requires substantial investment in building relationships and market presence over time. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages derived from large operational volumes in underwriting, claims, and IT. | New entrants start with higher per-unit costs, impacting pricing competitiveness. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bâloise Group is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Bâloise's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports from reputable firms and macroeconomic data to capture the broader competitive landscape.