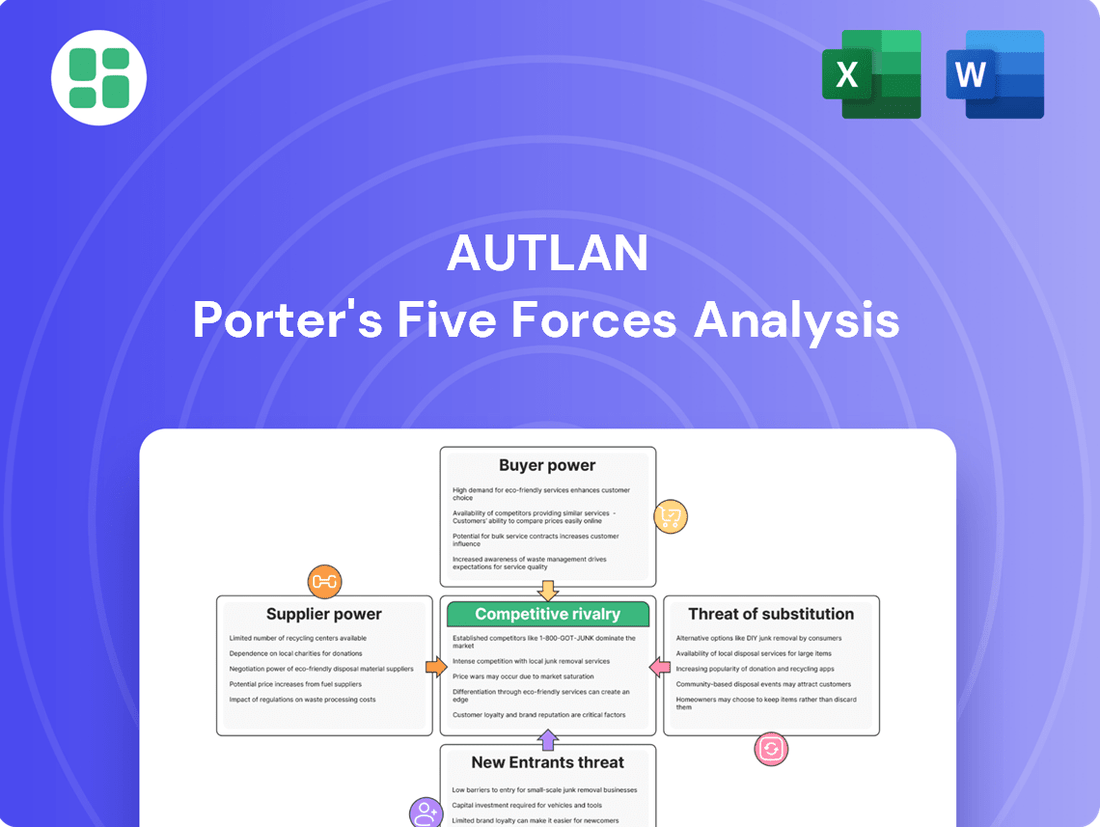
Autlan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Autlan Bundle
Understanding Autlan's competitive landscape requires a deep dive into the five forces that shape its industry. From the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers to the threat of new entrants and substitutes, these forces dictate profitability and strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Autlan’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Autlan, a significant manganese producer in Mexico and the Americas, sources specialized mining equipment and processing chemicals. If the number of suppliers for these critical inputs is limited and they offer unique products, their bargaining power increases considerably. For instance, in 2024, the global market for certain advanced mining extraction technologies saw consolidation, with a few key manufacturers dominating supply.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts the bargaining power of suppliers. For Autlan, a producer of manganese ore and ferroalloys, this means considering alternatives for essential raw materials and processing technologies. If there are multiple readily available sources of manganese or alternative methods for ferroalloy production, suppliers of these inputs would have less leverage.
In 2024, the global manganese market saw fluctuations due to geopolitical events and increased demand from the steel industry, a primary consumer of manganese. While Autlan's self-supply of manganese ore mitigates some supplier risk for its core input, the cost and availability of other critical materials, such as electricity and specialized refractory materials for furnace linings, remain important considerations. For instance, the price of metallurgical coal, a key input in ferroalloy production, saw a notable increase in early 2024, averaging around $120 per tonne, which can affect the cost structure and potentially empower coal suppliers.
Autlan's reliance on ferroalloys and electricity as key inputs for its ferroalloy products significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. The criticality of these inputs means suppliers who can consistently provide high-quality, essential materials have a stronger hand.
For instance, specialized ferroalloy compositions that are vital for achieving specific steel grades or performance characteristics can elevate a supplier's leverage. If Autlan needs unique alloys not readily available from multiple sources, those suppliers gain considerable power.
Conversely, if the raw materials or electricity are commoditized and widely available from numerous providers, Autlan would have more options, thus reducing supplier bargaining power. In 2023, global ferroalloy prices saw fluctuations, impacting input costs and potentially shifting leverage dynamics based on availability and demand.
Switching Costs for Autlan
High switching costs significantly bolster the bargaining power of Autlan's suppliers. If Autlan faces substantial expenses, such as retooling specialized mining equipment, retraining its workforce on new machinery, or re-certifying complex processing systems, it becomes more challenging and costly to change suppliers.
This deep integration with specific supplier technologies or product lines directly translates to increased supplier leverage. For instance, if Autlan relies on highly specialized mining or processing machinery from a particular vendor, the investment required to transition to an alternative could be prohibitive, granting that supplier considerable power in negotiations.
- High Switching Costs: Retooling equipment, retraining staff, and re-certifying processes are significant hurdles for Autlan when considering supplier changes.
- Supplier Dependence: Autlan's investment in specialized technology or products from a particular supplier increases that supplier's leverage.
- Industry Specifics: The mining and processing sectors often involve highly specialized machinery, amplifying the impact of switching costs on supplier power.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into ferroalloy or steel production is a key consideration for Autlan. If suppliers could realistically make these products themselves, their bargaining power would increase substantially. This would allow them to capture more value in the supply chain.
However, the significant capital investment and specialized technical expertise needed for ferroalloy manufacturing and the broader steel industry generally make this a low threat for most of Autlan's non-ore suppliers. For instance, establishing a ferroalloy plant can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier that few raw material providers can overcome.
- Capital Intensity: Ferroalloy production requires substantial upfront investment in furnaces, refining equipment, and infrastructure, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Technical Expertise: Operating these facilities demands specialized knowledge in metallurgy, chemical processes, and quality control, which many raw material suppliers may lack.
- Market Access: Suppliers would need to develop sales channels, logistics, and customer relationships within the competitive steel market, a significant undertaking.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Environmental regulations and permitting processes for manufacturing facilities add further complexity and cost to forward integration.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Autlan is influenced by several factors, notably the concentration of suppliers and the uniqueness of their offerings. Limited suppliers for specialized mining equipment or processing chemicals, especially those with proprietary technology, can exert significant influence. For example, in 2024, consolidation in the advanced mining technology sector meant fewer manufacturers controlled key equipment, increasing their leverage.
Autlan's ability to switch suppliers is also a critical determinant. High switching costs, stemming from investments in specialized machinery, workforce retraining, or process re-certification, empower suppliers. If Autlan is deeply integrated with a specific vendor's technology, the expense of transitioning elsewhere grants that supplier considerable negotiation power.
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration into ferroalloy or steel production is generally low for Autlan's raw material providers due to the immense capital and technical expertise required. However, for suppliers of critical processing inputs, the possibility, however remote, can still influence their stance.
| Factor | Impact on Autlan | 2024 Data/Example |
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers exist for critical inputs. | Consolidation in advanced mining tech increased supplier leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower suppliers. | Specialized machinery and retraining are significant barriers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low for raw materials, higher for specialized inputs. | Establishing ferroalloy plants can cost hundreds of millions. |
What is included in the product
A comprehensive assessment of the competitive forces shaping Autlan's industry, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual, actionable breakdown of each Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Autlan's customer concentration in the steel industry is a key factor in their bargaining power. If a few major steel manufacturers represent a significant portion of Autlan's ferroalloy sales, these large buyers can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms. For instance, if the top three steel producers in Mexico, where Autlan operates, account for over 60% of its ferroalloy revenue, their collective purchasing power becomes substantial.
Ferroalloys are indeed crucial for steelmaking, acting as essential additives to impart desired properties like strength and corrosion resistance. This inherent necessity provides Autlan with a degree of bargaining power, as steel producers rely on these inputs. For instance, manganese alloys, a key product for Autlan, are vital for deoxidation and alloying in steel production, with global demand for manganese ferroalloys showing steady growth, projected to reach over 25 million metric tons by 2024.
However, the bargaining power of Autlan's customers, primarily steel manufacturers, is significantly influenced by the ease of switching suppliers and the proportion of ferroalloy costs within their total production expenses. If steel companies can readily source comparable ferroalloys from multiple producers, or if ferroalloys constitute a minor fraction of their overall manufacturing costs, their ability to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms increases considerably. In 2023, the global steel industry faced fluctuating raw material costs, with ferroalloy prices experiencing volatility due to supply chain disruptions and demand shifts, impacting customer purchasing decisions.
The availability of substitute products for steel, such as aluminum, composites, and carbon fibers, can indirectly impact the bargaining power of customers in the ferroalloys market. For instance, in the automotive sector, the increasing adoption of lightweight materials like aluminum, which saw a significant increase in use in vehicle manufacturing throughout 2024, could lead to a reduced demand for steel. This shift could then translate into lower demand for ferroalloys, thereby strengthening the negotiating position of steel manufacturers who are the primary customers for ferroalloys.
Switching Costs for Customers
The ease with which steel manufacturers can switch between ferroalloy suppliers significantly influences customer bargaining power. When switching costs are low, meaning it's simple and inexpensive to change suppliers, customers gain leverage.
This low switching cost environment allows steel manufacturers to more readily negotiate for better prices or more favorable contract terms. For instance, if ferroalloy product specifications are largely standardized and alternative suppliers are abundant, customers face minimal disruption or expense when making a change.
In 2024, the global ferroalloy market saw continued price volatility, influenced by factors like energy costs and raw material availability. This environment often benefits buyers with low switching costs, as they can capitalize on competitive pricing.
- Low Switching Costs: Steel manufacturers can easily change ferroalloy suppliers if products are standardized and alternatives are readily available.
- Price Negotiation: Customers with low switching costs can effectively negotiate for better prices and terms from ferroalloy producers.
- Market Dynamics (2024): Price volatility in the ferroalloy market in 2024 generally favors buyers who can switch suppliers with ease.
- Supplier Competition: A competitive supplier landscape further amplifies customer power when switching costs are minimal.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, particularly major steel producers, could significantly shift bargaining power. If these large entities could realistically produce their own ferroalloys or even mine manganese, their reliance on external suppliers like Autlan would diminish, granting them greater leverage.
However, the practicalities of such a move are substantial. The capital investment required for establishing mining operations and ferroalloy production facilities is immense, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, developing a new manganese mine can cost upwards of $500 million, a significant hurdle for even large steel companies.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing mining and ferroalloy production facilities requires substantial upfront capital, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Specialized Expertise: The technical knowledge and skilled labor needed for efficient mining and ferroalloy processing are specialized and not readily available.
- Operational Complexity: Managing the entire supply chain, from resource extraction to refined product, introduces significant operational complexities and risks.
The bargaining power of Autlan's customers, primarily steel manufacturers, is influenced by their concentration and the importance of ferroalloys to their production. If a few large steel producers represent a significant portion of Autlan's sales, they can demand better pricing. For example, if the top three steel clients account for over 60% of Autlan's ferroalloy revenue, their collective purchasing power is substantial. The global ferroalloy market in 2024 experienced price volatility, which can empower buyers with more options.
The ease with which steel manufacturers can switch suppliers also plays a crucial role. When switching costs are low, meaning it's simple and inexpensive to change ferroalloy providers, customers gain leverage and can negotiate more favorable terms. This was evident in 2024, where competitive pricing in the ferroalloy market benefited buyers able to switch suppliers easily.
The threat of backward integration by major steel producers, where they might produce their own ferroalloys, could also increase customer bargaining power. However, the immense capital investment, often exceeding $500 million for a new manganese mine, and specialized expertise required for such ventures present significant barriers, limiting this threat for many customers.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context |
| Customer Concentration | High if few large buyers dominate sales | If top 3 clients represent >60% of revenue |
| Switching Costs | High if costs are low | Low switching costs allow for easier price negotiation. 2024 saw competitive pricing favoring buyers. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential to increase power, but costly | Mine development costs can exceed $500 million, requiring specialized expertise. |
What You See Is What You Get
Autlan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Autlan provides a deep dive into the competitive landscape, offering actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Autlan operates in a competitive landscape populated by several significant global players in the manganese mining and ferroalloy sector. Key competitors include Eramet SA, South32 Limited, MOIL Limited, and Ferroglobe, all of which possess substantial operational scale and market reach.
While Autlan distinguishes itself as the leading producer of manganese ferroalloys within the Americas, the industry's globalized nature exposes it to intense competition from these large international entities. This broad competitive base necessitates continuous strategic adaptation and operational efficiency.
The global ferroalloys market, including manganese, is on an upward trajectory, with projections indicating continued growth. This expansion is largely fueled by the robust demand from the steel industry and the emerging applications in battery technology. For instance, the global ferroalloys market was valued at approximately USD 200 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach over USD 260 billion by 2028, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.5%.
A growing market environment typically softens competitive rivalry. When industries are expanding, companies can achieve their growth targets by capturing a share of the new demand rather than engaging in aggressive tactics to steal existing market share from competitors. This dynamic can lead to less intense price wars and a more collaborative, albeit still competitive, market landscape.
Specifically, the manganese market, a key component in steel production, is projected to see a CAGR of approximately 4.8% between 2024 and 2030. This steady growth suggests that established players and new entrants alike have opportunities to expand their operations and sales without necessarily resorting to cutthroat competition. The increasing use of manganese in electric vehicle batteries further bolsters this positive outlook, creating new avenues for growth.
Ferroalloys, including those produced by Autlan, are largely viewed as commodity products, making it tough to stand out. This often means price is the main battleground for competitors. For instance, in 2023, the global ferroalloys market saw intense price competition driven by supply-demand dynamics and raw material costs.
However, Autlan aims to differentiate itself through a strong emphasis on product quality and superior commercial service. The company's production of specialized manganese products, such as Alkaline EMD (Electrolytic Manganese Dioxide), offers a distinct advantage. Alkaline EMD is crucial for battery manufacturing, a rapidly growing sector where specific performance characteristics are highly valued.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The mining and ferroalloy sectors are inherently capital-intensive, demanding substantial upfront investment in equipment and infrastructure. For instance, establishing a new mine can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars.
This high fixed cost structure creates a significant barrier to entry but also fuels intense competition among existing players. During market downturns, companies are compelled to operate at high capacity to spread these fixed costs over a larger production volume, leading to price wars and increased rivalry.
Furthermore, high exit barriers, such as the specialized nature of assets and environmental reclamation obligations, can trap unprofitable companies in the market. This means even struggling firms may continue to operate, adding to the competitive pressure and potentially depressing industry profitability.
- Capital Intensity: Setting up a new mine can cost upwards of $500 million, with significant ongoing investment in machinery and maintenance.
- Operational Pressure: Companies often prioritize covering high fixed costs, leading to increased production and price competition, especially when demand falters.
- Exit Barriers: Specialized equipment and regulatory requirements for mine closure can make it prohibitively expensive for firms to leave the market, prolonging intense rivalry.
Strategic Stakes
The ferroalloy and manganese sector holds significant strategic importance for national economies, particularly in steel production and infrastructure development. This strategic weight often invites government intervention or support, which can reshape competitive dynamics within the industry. For instance, governments might offer subsidies or impose trade barriers to protect domestic producers, thereby influencing the competitive landscape for companies like Autlan.
Autlan's established position within Mexico's industrial framework also plays a crucial role in its competitive rivalry. Its integration into the national supply chains for key industries provides a degree of insulation from global market volatility and can foster strong relationships with domestic customers. This local advantage can be a significant differentiator against international competitors.
The strategic stakes are further elevated by the cyclical nature of commodity prices and global demand for steel and related products. Companies with robust financial health and efficient operations, like Autlan, are better positioned to weather downturns and capitalize on upswings. In 2023, global manganese ore prices experienced fluctuations, influenced by factors such as Chinese steel production levels and supply chain disruptions, highlighting the inherent strategic considerations for market participants.
- Strategic Importance: Ferroalloys are critical inputs for steelmaking, a cornerstone of modern infrastructure and manufacturing.
- Government Influence: National economic strategies can lead to protectionist measures or support for domestic ferroalloy producers.
- Autlan's Mexican Position: A strong domestic presence can offer supply chain advantages and market stability.
- Market Dynamics: Fluctuations in global demand and commodity prices, as seen in 2023 manganese prices, underscore the strategic importance of efficient operations and financial resilience.
Competitive rivalry in the ferroalloy sector is significant, with major global players like Eramet and South32 competing with Autlan. While Autlan leads in the Americas, the industry's commodity nature often centers competition on price, as seen with intense price competition in the global ferroalloys market during 2023.
However, Autlan differentiates through specialized products like Alkaline EMD for batteries, a growing market. The capital-intensive nature of mining, with new mines costing upwards of $500 million, creates high fixed costs and exit barriers, intensifying rivalry, especially during market downturns.
The strategic importance of ferroalloys in steel production and government interventions can also shape competition. Autlan's strong Mexican position offers domestic advantages, while market volatility, such as the 2023 manganese price fluctuations, emphasizes the need for operational efficiency and financial resilience.
| Competitor | Market Position | Key Products |
| Eramet SA | Global Player | Manganese, Nickel, Mineral Sands |
| South32 Limited | Global Player | Aluminium, Coal, Manganese, Nickel |
| MOIL Limited | Indian State-Owned | Manganese Ore |
| Ferroglobe | Global Player | Silicon Metal, Ferroalloys |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitute materials for steel, and by extension Autlan's ferroalloys, is a significant consideration. Alternatives like aluminum, carbon fiber composites, and advanced plastics are gaining traction across industries such as automotive and construction, driven by their favorable lightweighting and strength-to-weight ratios.
For instance, the automotive sector is a key consumer of steel, but the push for fuel efficiency and electric vehicles has accelerated the adoption of aluminum. By 2024, it's estimated that the average vehicle could incorporate a substantial amount of aluminum, directly impacting steel demand.
The attractiveness of substitute products hinges on their price relative to the performance benefits they offer. For instance, while advanced materials like carbon fiber offer significant weight reduction in vehicles, their substantially higher cost compared to traditional steel currently restricts their broad adoption. However, continuous technological progress in manufacturing and material science in 2024 suggests this price-performance balance could shift, potentially increasing the threat of substitution.
Steel manufacturers and their customers are increasingly considering alternatives due to evolving design needs and environmental regulations. For instance, the automotive sector, a major steel consumer, is seeing a push towards lightweighting to meet stricter emissions targets, driving the adoption of materials like aluminum and advanced composites. In 2024, global aluminum demand, particularly for automotive applications, is projected to remain robust, indicating a sustained competitive pressure on steel.
Threat of Alternative Technologies for Steel Production
Beyond direct material substitutions, emerging steelmaking technologies present a significant threat. Innovations in 'green steel' production, for instance, could drastically reduce the need for traditional ferroalloys, thereby impacting demand for Autlan's products. This shift is driven by global decarbonization efforts, with many countries setting ambitious targets for reducing industrial emissions.
New processes that require less or entirely different types of ferroalloys could disrupt the market. For example, advancements in direct reduced iron (DRI) using hydrogen instead of natural gas, a key focus for many steelmakers aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050, might lessen the reliance on traditional blast furnace inputs. The global steel industry is investing heavily in these cleaner technologies; in 2023, investments in green steel initiatives were estimated to be in the tens of billions of dollars worldwide.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in steelmaking, such as hydrogen-based DRI, can decrease reliance on traditional ferroalloys.
- Green Steel Initiatives: Global push for decarbonization is accelerating the adoption of new, less input-intensive steel production methods.
- Investment Trends: Significant global investments in green steel technologies by 2023 indicate a potential shift in demand for conventional raw materials.
- Reduced Ferroalloy Demand: Successful implementation of these new technologies could lead to a substantial reduction in the demand for ferroalloys.
Substitutes for Hydroelectric Power
Autlan's energy segment faces competition from various substitutes for hydroelectric power. Mexico's commitment to renewable energy expansion means solar and wind power are increasingly viable alternatives. For instance, Mexico's National Electric System (SEN) reported that renewable sources, excluding hydro, contributed approximately 29% of the total electricity generation in 2023, a figure expected to grow.
These alternative energy sources, particularly solar and wind, are becoming more cost-competitive due to technological advancements and government incentives. While hydropower is a clean energy source, the upfront capital costs and geographical limitations for new hydroelectric projects can make them less attractive compared to the more distributed and modular nature of solar and wind installations. In 2024, Mexico continued to see substantial investment in solar projects, with new capacity additions expected to further pressure traditional power sources.
- Increased Investment in Solar and Wind: Mexico's energy policy prioritizes the growth of non-hydro renewable sources.
- Cost Competitiveness: Solar and wind technologies are becoming more economically viable, challenging hydroelectric power's market share.
- Geographical Flexibility: Solar and wind can be deployed in a wider range of locations compared to large-scale hydroelectric dams.
- Policy Support: Government incentives and targets for renewable energy deployment favor the expansion of solar and wind capacity.
The threat of substitutes for Autlan's ferroalloys, primarily used in steel production, is intensifying. Materials like aluminum, composites, and advanced plastics are increasingly adopted in sectors like automotive due to their lightweight properties, directly impacting steel demand. By 2024, the automotive industry's growing use of aluminum, driven by fuel efficiency demands, represents a significant substitution pressure.
Furthermore, the rise of 'green steel' technologies poses a substantial threat. Innovations such as hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) aim to reduce reliance on traditional ferroalloys. Global investments in these cleaner steelmaking methods, estimated in the tens of billions of dollars by 2023, underscore a potential market shift away from conventional inputs.
| Substitute Material | Key Industries | 2024 Trend/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, Aerospace, Construction | Increasing adoption for lightweighting; projected robust demand in automotive. |
| Carbon Fiber Composites | Automotive, Aerospace | High performance, but cost remains a barrier for widespread use. |
| Advanced Plastics | Automotive, Consumer Goods | Growing use in non-structural components; cost-effective for specific applications. |
| Green Steel Technologies (e.g., Hydrogen DRI) | Steel Manufacturing | Potential to significantly reduce ferroalloy requirements; driven by decarbonization efforts. |
Entrants Threaten
The manganese mining and ferroalloy production sectors demand immense upfront capital. Establishing a new manganese mine alone can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, covering everything from geological surveys and land acquisition to the construction of shafts, processing facilities, and essential transportation infrastructure. For instance, new large-scale mining operations in 2024 often exceed $500 million in initial investment.
Control over high-quality manganese ore deposits is a significant hurdle for potential new entrants in the ferroalloy market. Companies like Autlan, which already possess established mining operations, hold a distinct advantage in securing these essential raw materials. For instance, in 2023, Autlan's mining segment contributed significantly to its overall revenue, demonstrating the value of integrated resource control.
Autlan, as an established player in the mining sector, leverages significant economies of scale. This means they can produce their copper and other minerals at a lower cost per unit compared to smaller operations. For instance, in 2023, Autlan reported a production of 102,100 tonnes of copper, enabling them to spread fixed costs over a larger output.
New companies entering the copper mining market would face a substantial challenge in matching Autlan's scale. Building mines, processing facilities, and distribution networks requires immense capital investment. Without achieving similar production volumes, new entrants would struggle to achieve competitive unit costs, making it difficult to price their products attractively against Autlan.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The mining and energy sectors in Mexico face significant regulatory hurdles, acting as a substantial barrier to new entrants. These industries require extensive permits, rigorous environmental impact assessments, and unwavering adherence to stringent safety and environmental standards. For instance, the General Law of Ecological Equilibrium and Environmental Protection (LGEEPA) in Mexico mandates detailed environmental studies before any project can commence, a process that can be both time-consuming and financially burdensome for newcomers.
Navigating these complex regulatory frameworks is a major deterrent. New companies must invest heavily in legal expertise and compliance measures to secure the necessary approvals. In 2023, the cost of obtaining environmental permits for large-scale mining projects in Mexico could easily run into millions of dollars, not to mention the ongoing costs of maintaining compliance. This creates a high barrier to entry, favoring established players with existing infrastructure and experience in managing these requirements.
- Permit Acquisition: New entrants must secure numerous permits from federal and state agencies, including SEMARNAT and PROFEPA.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Comprehensive EIAs are mandatory, detailing potential ecological effects and mitigation strategies.
- Safety Standards: Strict adherence to mining safety regulations, overseen by the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare, is critical.
- Land Use and Indigenous Rights: Compliance with regulations regarding land acquisition and consultation with indigenous communities adds another layer of complexity.
Brand Loyalty and Distribution Channels
Even though ferroalloys are largely seen as commodities, established players in the market benefit significantly from deep-rooted relationships with major steel industry clients. These long-standing connections, often built over years, are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in 2024, major steel producers continued to prioritize suppliers with proven track records and integrated supply chains, making it challenging for new entrants to secure initial orders.
Furthermore, the existence of efficient and established distribution channels presents a substantial barrier. Incumbents have optimized logistics and warehousing, allowing for cost-effective delivery of ferroalloys to diverse customer bases. A new entrant would need to invest heavily in building a comparable distribution network, a process that not only requires significant capital but also considerable time to achieve the same level of efficiency and reach.
- Established Customer Relationships: Steel manufacturers often favor suppliers with a history of reliability and quality, creating a hurdle for new ferroalloy producers seeking to break into the market.
- Efficient Distribution Networks: The logistical infrastructure in place for existing ferroalloy suppliers allows for cost-effective and timely delivery, a competitive advantage that new entrants must overcome.
- Commodity Nature: While ferroalloys are commodities, the associated services and supply chain integration provided by incumbents add a layer of differentiation that is hard for new firms to match.
- Capital Investment: Building both customer loyalty and distribution capabilities requires substantial upfront investment, deterring many potential new entrants in the ferroalloy sector.
The threat of new entrants in the manganese mining and ferroalloy sectors is significantly low due to immense capital requirements. Establishing new mining operations in 2024 often necessitates initial investments exceeding $500 million. This high cost, coupled with the need for extensive regulatory compliance and securing critical ore deposits, deters potential new players.
Economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like Autlan, which produced 102,100 tonnes of copper in 2023, further solidify this barrier. New entrants would struggle to match these production volumes and achieve competitive unit costs. Furthermore, established relationships with steel industry clients and optimized distribution networks create additional hurdles that are difficult and costly for newcomers to overcome.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Autlan Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.