Ascom Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ascom Bundle
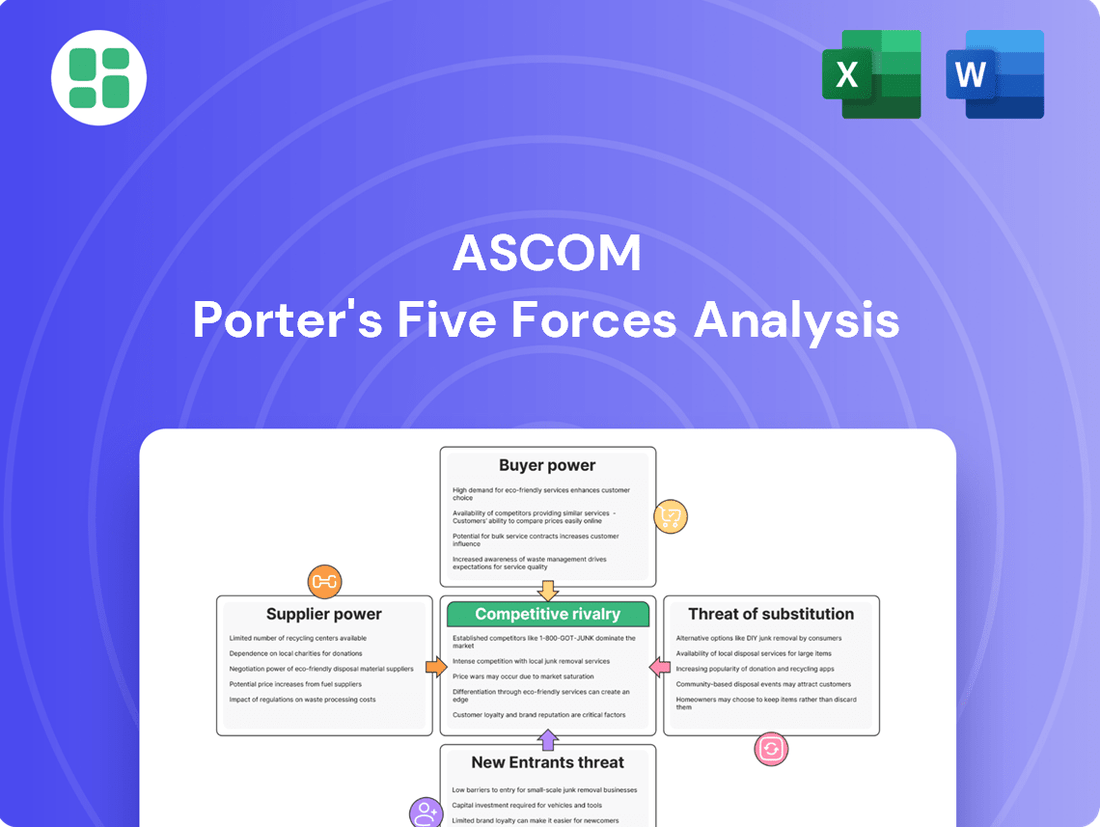
Ascom's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces: the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate Ascom's market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Ascom’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ascom's reliance on specialized hardware and software components for its wireless communication systems and mobile devices means that suppliers of these critical inputs hold considerable bargaining power. A concentrated supplier market, particularly for proprietary technologies, can dictate pricing and supply terms, directly impacting Ascom's manufacturing costs and operational efficiency.
The bargaining power of software and OS vendors is a significant consideration for Ascom. Dominant providers of underlying platforms, such as Microsoft or Google, can exert considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, major cloud service providers saw substantial revenue growth, indicating their increasing market control, which translates to potential leverage over their clients through pricing and service terms.
Ascom operates in a niche technology space, demanding a highly skilled workforce proficient in healthcare IT, software engineering, and advanced development. The intense competition for these specialized professionals significantly impacts labor costs and complicates recruitment efforts, giving these skilled workers considerable bargaining power.
Supplier Switching Costs
Supplier switching costs represent a significant factor in Ascom's bargaining power. Transitioning from one supplier to another for essential components or software can involve substantial expenses for Ascom. These costs often include the need for redesigning products, conducting extensive testing to ensure compatibility and performance, and retraining staff on new systems or materials.
These high switching costs effectively reduce Ascom's negotiating power and flexibility. When it is costly and time-consuming to change suppliers, Ascom finds it more challenging to secure more favorable terms or pricing from its existing suppliers. This can lead to higher input costs, impacting profitability.
- High Switching Costs: Ascom faces significant expenses when changing suppliers, including redesign, testing, and retraining.
- Reduced Negotiating Power: High switching costs limit Ascom's ability to negotiate better terms with current suppliers.
- Impact on Flexibility: The difficulty in switching suppliers curtails Ascom's strategic flexibility in sourcing.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers with proprietary technology or integrated systems can command higher prices due to these switching barriers.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Suppliers holding exclusive proprietary technology or patents vital for Ascom's product lines can dictate higher prices or enforce stringent contract terms. This intellectual property advantage significantly strengthens their position, potentially hindering Ascom's innovation capacity and escalating its operational expenses.
- Intellectual Property as a Barrier: Suppliers with patented components or unique manufacturing processes create a significant barrier to entry for competitors, thereby consolidating their market power.
- Impact on Input Costs: For instance, if a key component for Ascom's healthcare communication systems is protected by a patent held by a single supplier, Ascom's cost of goods sold could be disproportionately affected.
- Strategic Dependence: Ascom's reliance on such specialized suppliers means that any disruption or price increase from these entities can have a direct and substantial impact on Ascom's profitability and competitive pricing strategies.
- Innovation and Cost Trade-offs: Ascom must balance the benefits of cutting-edge technology from these suppliers against the potential for increased costs and reduced flexibility in its supply chain.
Suppliers of critical, specialized components and software for Ascom's communication systems wield significant power. This is amplified when these suppliers possess proprietary technology or operate in concentrated markets, allowing them to influence pricing and terms. Ascom's ability to switch suppliers is often hindered by high switching costs, including redesign and retraining, which further solidifies supplier leverage and can impact operational expenses.
What is included in the product
Ascom's Porter's Five Forces analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within its industry, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive framework that visualizes each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Healthcare organizations, Ascom's main clients, are often under severe budget constraints. In 2024, many public healthcare systems globally continued to grapple with funding shortfalls, forcing them to scrutinize every expenditure. This financial pressure directly translates into heightened bargaining power for these customers.
The need for cost containment means healthcare providers are more likely to demand lower prices and more favorable contract terms from suppliers like Ascom. For instance, a hospital seeking to upgrade its communication systems might leverage competitive bids from multiple vendors, using the lowest offers to negotiate down Ascom's pricing.
Ascom's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by large healthcare providers. Major hospital chains and integrated healthcare systems represent substantial purchasing volumes for Ascom's communication and information solutions. For instance, in 2023, a significant portion of Ascom's revenue was derived from a relatively concentrated customer base within the healthcare sector, underscoring the importance of these major clients.
These large customers leverage their scale to negotiate favorable terms, often demanding tailored solutions and robust support services. Their ability to procure in bulk empowers them to exert considerable pressure on pricing and product specifications, directly impacting Ascom's profit margins and product development roadmap. This concentrated demand means Ascom must carefully manage relationships with these key accounts to maintain market share and profitability.
Healthcare providers are increasingly demanding that new technology solutions work smoothly with their current IT systems, especially Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This need for interoperability means customers have more leverage.
Ascom's ability to offer solutions that integrate well with existing hospital infrastructure, like Epic or Cerner EHRs, is a significant advantage. For instance, in 2024, the global healthcare interoperability market was valued at approximately $3.1 billion, highlighting the strong demand for such capabilities.
Customers can use this demand for seamless integration to negotiate better pricing and contract terms, particularly when implementing complex, system-wide solutions. This bargaining power is amplified for providers who have invested heavily in established EHR platforms.
Availability of Multiple Vendors
The availability of multiple vendors in the market significantly influences the bargaining power of Ascom's customers. While Ascom provides specialized solutions, customers often have the flexibility to source different components of their communication and workflow infrastructure from various providers. This ability to mix and match or even substitute solutions from competing firms directly translates to increased customer leverage.
For instance, in the broader healthcare technology landscape, while Ascom is a key player in nurse call systems and mobile communication, hospitals might also consider solutions from companies like Hillrom for patient monitoring or Stryker for integrated operating room technology. This ecosystem of alternative providers means customers aren't solely reliant on Ascom for all their needs, thereby enhancing their negotiating position.
- Increased Vendor Options: Customers can choose from a wider array of specialized communication and workflow solution providers, not just Ascom.
- Reduced Switching Costs: The ability to integrate solutions from different vendors can lower the perceived cost and complexity of switching away from Ascom.
- Price Sensitivity: With multiple alternatives available, customers are more likely to compare pricing, putting downward pressure on Ascom's pricing power. For example, in 2024, many healthcare IT procurement departments reported actively seeking competitive bids for communication hardware, often finding 15-20% cost savings by comparing multiple vendors for similar functionalities.
Customer's Impact on Reputation
In the specialized healthcare technology sector, Ascom's reputation hinges significantly on customer satisfaction. Large, satisfied clients can act as invaluable references, bolstering the company's market standing. Conversely, a single dissatisfied major customer can quickly damage Ascom's brand image, especially in a niche market where word-of-mouth and industry perception are critical.
This dynamic grants key customers substantial bargaining power. Their ability to influence Ascom's reputation means they can exert considerable leverage during negotiations, demanding high service quality and favorable terms. Customer retention is therefore not just a goal, but a strategic imperative for Ascom, directly impacting its ability to attract new business and maintain its market position.
- Reputation Influence: Satisfied large customers in the niche healthcare market serve as powerful references for Ascom.
- Risk of Dissatisfaction: Dissatisfied key customers can significantly harm Ascom's reputation, impacting future sales.
- Customer Leverage: This reputation impact gives major clients considerable bargaining power in negotiations.
- Service Demands: Customers can leverage their influence to demand high service quality and favorable terms from Ascom.
Healthcare organizations, Ascom's primary customers, often face significant budget constraints. In 2024, many global public healthcare systems continued to experience funding challenges, leading to increased scrutiny of all expenditures. This financial pressure directly amplifies the bargaining power of these clients.
The imperative for cost containment compels healthcare providers to seek lower prices and more advantageous contract terms from suppliers like Ascom. For instance, a hospital looking to upgrade its communication systems might solicit bids from multiple vendors, using the most competitive offers to negotiate down Ascom's pricing.
The bargaining power of Ascom's customers is notably influenced by large healthcare providers. Major hospital networks and integrated healthcare systems represent substantial purchasing volumes for Ascom's communication and information solutions. For example, in 2023, a significant portion of Ascom's revenue was derived from a relatively concentrated customer base within the healthcare sector, highlighting the critical importance of these major clients.
These large customers leverage their scale to negotiate favorable terms, often demanding customized solutions and robust support services. Their capacity for bulk procurement allows them to exert considerable pressure on pricing and product specifications, directly affecting Ascom's profit margins and product development strategies. This concentrated demand necessitates careful management of relationships with these key accounts to sustain market share and profitability.
Healthcare providers increasingly require new technology solutions to integrate seamlessly with their existing IT infrastructure, particularly Electronic Health Records (EHRs). This demand for interoperability enhances customer leverage. Ascom's ability to offer solutions that integrate well with established hospital EHR systems, such as Epic or Cerner, provides a competitive edge. The global healthcare interoperability market was valued at approximately $3.1 billion in 2024, underscoring the strong demand for such capabilities.
Customers can utilize this demand for seamless integration to negotiate better pricing and contract terms, especially when implementing complex, system-wide solutions. This bargaining power is amplified for providers who have made substantial investments in established EHR platforms.
The availability of multiple vendors in the market significantly impacts the bargaining power of Ascom's customers. While Ascom offers specialized solutions, customers often have the flexibility to source different components of their communication and workflow infrastructure from various providers. This ability to mix and match or even substitute solutions from competing firms directly translates to increased customer leverage.
In the broader healthcare technology landscape, while Ascom is a key player in nurse call systems and mobile communication, hospitals may also consider solutions from companies like Hillrom for patient monitoring or Stryker for integrated operating room technology. This ecosystem of alternative providers means customers are not solely dependent on Ascom for all their needs, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Ascom | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Budget Constraints | Healthcare organizations often operate under tight financial limitations. | Increased pressure for lower prices and favorable terms. | Many public healthcare systems globally faced funding shortfalls. |
| Customer Concentration | A few large healthcare providers account for a significant portion of Ascom's revenue. | These large clients have substantial negotiation power due to their volume. | Significant portion of Ascom's 2023 revenue from a concentrated customer base. |
| Interoperability Needs | Demand for seamless integration with existing systems like EHRs. | Customers can leverage integration capabilities to negotiate terms. | Global healthcare interoperability market valued at ~$3.1 billion in 2024. |
| Vendor Availability | Presence of alternative providers for communication and workflow solutions. | Customers can switch or combine solutions, increasing their leverage. | Healthcare IT procurement departments reported 15-20% cost savings by comparing multiple vendors. |
| Reputation Influence | Satisfied clients act as references; dissatisfied clients can damage Ascom's brand. | Key customers can demand high service quality and favorable terms due to their influence. | Word-of-mouth and industry perception are critical in the niche healthcare market. |
Full Version Awaits
Ascom Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ascom Porter's Five Forces Analysis, identical to the document you will receive immediately upon purchase. You are viewing the final, professionally formatted report, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. This detailed analysis is ready for your immediate use the moment your transaction is complete.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ascom navigates a competitive landscape populated by both broad-reaching global technology giants with dedicated healthcare segments and agile, niche players concentrating on specialized healthcare communication solutions. This dynamic rivalry means Ascom must constantly innovate to maintain its edge.
The intensity of this competition isn't uniform; it shifts depending on the specific product category and the geographic region. For instance, in areas like nurse call systems, Ascom might face different competitors than in its workflow solutions segment. This fragmentation requires a tailored strategic approach for each market.
For example, in 2023, the global healthcare IT market, which encompasses communication solutions, was valued at approximately $37.7 billion and is projected to grow significantly. Ascom competes within this expanding market against players like Philips Healthcare, Siemens Healthineers, and various regional specialists, all vying for a share of healthcare providers' technology budgets.
The healthcare ICT sector is a hotbed of innovation, with competitors constantly rolling out new features and better integration. This means Ascom must keep pace, pushing its own product differentiation and innovation at a rapid clip to stay ahead. For instance, in 2023, the global healthcare IT market was valued at approximately $350 billion, and it’s projected to grow significantly, underscoring the intense competitive pressure to innovate.
Intense competition within the healthcare communication and mobility solutions sector inevitably translates into significant pricing pressures for companies like Ascom. Competitors actively vie for market share, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies that can erode profit margins if not managed carefully. For instance, in 2024, the global healthcare IT market, which encompasses Ascom's operating environment, saw continued price sensitivity as providers sought cost-effective solutions.
To counter these pressures, Ascom must continuously articulate and reinforce its distinct value proposition. This involves clearly communicating how its solutions, such as its IntelliSite platform or Unite middleware, deliver tangible benefits like enhanced patient safety through faster response times, streamlined workflows that boost operational efficiency, and ultimately, improved clinical outcomes. Demonstrating this superior value is crucial for justifying its pricing relative to competitors who may offer lower upfront costs but lack comparable depth in functionality or integration.
Market Growth and Saturation
While the broader healthcare digitalization market continues to expand, certain niches within it are showing signs of maturity and potential saturation. This is particularly true for established areas like electronic health records (EHRs) in developed markets. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 90% of office-based physicians in the United States had adopted some form of EHR system, indicating a high level of penetration.
In these more saturated segments, competitive rivalry among vendors intensifies significantly. Companies are forced to differentiate through enhanced features, superior customer support, or aggressive pricing strategies to capture or retain market share. This can manifest as increased spending on sales and marketing, with some reports indicating that marketing budgets for established software providers in healthcare have grown by as much as 15% year-over-year in 2023 as they battle for the remaining market opportunities.
- Market Penetration: Over 90% of US office-based physicians utilized EHRs by the close of 2023.
- Rivalry Tactics: Increased marketing spend, feature differentiation, and price competition are common.
- Growth Variance: While overall healthcare digitalization grows, specific segments like basic EHR adoption are nearing saturation.
- Vendor Strategies: Focus shifts from broad adoption to specialized solutions and customer retention in mature markets.
Strategic Partnerships and Alliances
Competitors in the healthcare technology sector often team up with other companies to deliver more complete packages or reach more customers. For instance, they might partner with medical device makers or healthcare consultants. This strategy allows them to combine expertise and offerings, creating a stronger value proposition for clients.
Ascom itself actively pursues such alliances to bolster its position. A notable example is its collaboration with SEC-COM in Germany, which aims to strengthen Ascom's competitive edge and expand its network within the healthcare ecosystem. These partnerships are crucial for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
- Increased Solution Breadth: Partnerships allow companies to offer integrated solutions, combining hardware, software, and services from multiple providers.
- Market Expansion: Alliances can open doors to new geographical regions or customer segments that a single company might struggle to access alone.
- Innovation Acceleration: Collaborating with complementary businesses can speed up the development of new technologies and services.
- Shared Risk and Resources: Strategic partnerships can distribute the costs and risks associated with large-scale projects or market entry.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Ascom, as it operates in a market with both large, established technology firms and specialized, agile players. This intense competition, particularly in areas like nurse call systems and workflow solutions, drives a constant need for innovation and differentiation. For example, in 2023, the global healthcare IT market, where Ascom competes, was valued at approximately $37.7 billion, highlighting the substantial market share at stake.
The pressure from rivals often leads to pricing challenges, compelling Ascom to clearly demonstrate the superior value of its offerings, such as its IntelliSite platform. Furthermore, in mature segments like EHR adoption, where market penetration in the US reached over 90% by the end of 2023, competition intensifies, leading to increased marketing spend and a focus on feature enhancement.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Ascom |
| Global Tech Giants | Broad portfolios, significant R&D budgets | Pressure on pricing and innovation pace |
| Niche Specialists | Deep expertise in specific areas, agility | Challenge for specialized product segments |
| Established Healthcare IT Vendors | Existing customer relationships, integrated solutions | Competition for market share in mature segments |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Healthcare providers might turn to generic communication tools like standard smartphones with consumer messaging apps or even pagers instead of specialized, integrated healthcare communication systems. This is a real concern, especially for smaller clinics or those facing budget constraints. For instance, the adoption of secure messaging apps in healthcare saw significant growth, with the global market size estimated to reach over $3.5 billion by 2024, indicating a strong existing preference for readily available solutions.
These less specialized alternatives, while not as efficient, represent a viable substitute threat. Their widespread availability and often lower initial cost can make them attractive, particularly when compared to the investment required for dedicated healthcare communication platforms. The continued reliance on these generic tools can limit the market penetration of more advanced, integrated solutions.
The threat of substitutes for Ascom's digital workflow solutions, particularly in healthcare, comes from the persistence of manual or traditional workflows. Some healthcare facilities might opt to stick with or return to paper-based systems, verbal communication, or less integrated manual processes instead of adopting advanced digital solutions. These older methods, while less efficient, can act as a substitute, especially where there's resistance to technological upgrades.
For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that nearly 30% of smaller clinics still primarily use paper records for patient management, representing a direct substitute for digital workflow software. This reliance on established, albeit slower, methods can limit the adoption rate of Ascom's offerings, as these facilities may not see the immediate ROI or have the infrastructure to support a full digital transition.
Hospitals often face a critical decision when allocating limited IT budgets, and investments in alternative infrastructure can act as a potent substitute for specialized communication platforms. For instance, a significant portion of healthcare IT spending in 2024 is directed towards enhancing Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, with many hospitals prioritizing patient data management and interoperability. This focus means that funds that might otherwise be available for advanced communication solutions could be diverted to complete EHR implementations or upgrades, effectively substituting Ascom's offerings with more foundational digital health infrastructure.
In-house Developed Solutions
Large healthcare organizations, particularly those with significant IT resources, may opt to build their own communication and workflow systems. This approach, while demanding in terms of investment, allows for solutions that are meticulously designed to meet specific operational needs, thereby directly competing with Ascom's existing product lines.
For instance, a major hospital network might allocate substantial capital to develop proprietary software that integrates patient monitoring, staff communication, and administrative tasks. This internal development bypasses the need for third-party vendors like Ascom.
- Healthcare IT Spending: Global healthcare IT spending was projected to reach over $400 billion in 2024, indicating significant internal investment capacity within large systems.
- Customization Advantage: In-house solutions offer unparalleled customization, directly addressing unique workflows that off-the-shelf products might not fully support.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: While initial development costs are high, long-term operational savings and greater control can make in-house solutions an attractive alternative for substantial healthcare entities.
Cloud-based Communication Platforms
The growing availability of general-purpose cloud communication tools presents a threat. Platforms like Microsoft Teams and Google Workspace are increasingly incorporating features that can mimic some of Ascom's specialized healthcare communication functionalities. While not as tailored, these broad solutions can meet certain communication requirements in healthcare environments, potentially diverting demand.
For instance, the widespread adoption of Microsoft Teams in enterprise settings means many healthcare organizations already have access to its communication and collaboration features. In 2024, Microsoft reported over 320 million monthly active users for Teams, highlighting its significant market penetration. This broad user base means the barrier to entry for utilizing Teams for internal communications, even in healthcare, is relatively low.
These general platforms can offer a cost-effective alternative for basic messaging, video conferencing, and file sharing. While they may lack the specific clinical workflow integration and advanced alerting capabilities of Ascom's dedicated solutions, their ubiquity and lower incremental cost make them a viable substitute for less critical communication needs within a hospital or clinic. This could lead to a gradual erosion of market share for specialized providers if they do not continually innovate and demonstrate clear value differentiation.
- Market Penetration: Microsoft Teams boasts over 320 million monthly active users as of 2024.
- Functionality Overlap: General platforms offer messaging, video conferencing, and file sharing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Ubiquity and lower incremental costs make them attractive for basic needs.
- Differentiation Challenge: Specialized providers must emphasize unique clinical workflow integration and advanced alerting.
The threat of substitutes for Ascom's digital workflow solutions is significant, stemming from readily available and often lower-cost alternatives. Healthcare providers, especially smaller ones, may opt for generic communication tools like standard smartphones with messaging apps or even older technologies like pagers. These substitutes, while less efficient, are attractive due to their widespread availability and lower initial investment compared to specialized healthcare platforms.
Furthermore, the persistence of manual or traditional workflows poses a threat. Some facilities might continue using paper-based systems or verbal communication rather than adopting advanced digital solutions. This reliance on established, albeit slower, methods can hinder the adoption of new technologies, particularly where resistance to change or a lack of infrastructure exists. For instance, a 2024 survey revealed that nearly 30% of smaller clinics still primarily use paper records for patient management.
Large healthcare organizations might also choose to build their own proprietary communication and workflow systems. This in-house development, though costly initially, offers unparalleled customization to meet specific operational needs. For example, a major hospital network could invest in custom software for patient monitoring and staff communication, thereby bypassing third-party vendors like Ascom. This trend is supported by significant healthcare IT spending, with global projections exceeding $400 billion in 2024, indicating substantial internal investment capacity.
The increasing capability of general-purpose cloud communication tools like Microsoft Teams and Google Workspace also presents a substitute threat. These platforms are incorporating features that can mimic some of Ascom's specialized functionalities. With Microsoft Teams alone boasting over 320 million monthly active users in 2024, their broad market penetration makes them a cost-effective alternative for basic communication needs, potentially eroding market share for specialized providers if differentiation is not maintained.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Penetration/Adoption Data (2024) | Impact on Ascom |
| Generic Communication Tools (Smartphones, Pagers) | Low cost, widespread availability, ease of use | Significant adoption in smaller clinics; pagers still in use | Limits adoption of specialized systems, especially in cost-sensitive segments |
| Manual/Traditional Workflows (Paper-based) | Familiarity, perceived simplicity, low initial tech investment | Nearly 30% of smaller clinics still primarily use paper records | Slows digital transformation, reduces demand for workflow solutions |
| In-house Developed Systems | High customization, full control, potential long-term savings | Global healthcare IT spending projected >$400 billion | Direct competition for large organizations with IT resources |
| General Cloud Communication Platforms (e.g., Microsoft Teams) | Broad functionality (messaging, video), existing user base, cost-effective | Microsoft Teams: >320 million monthly active users | Captures basic communication needs, requires specialized providers to emphasize unique clinical value |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the healthcare ICT market, especially with sophisticated integrated hardware and software solutions, demands a substantial financial commitment. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development to innovate, in manufacturing facilities to produce reliable devices, and in building robust sales and support infrastructure to serve a global clientele.
This high capital requirement acts as a significant barrier, effectively deterring many potential new competitors from entering the space. For instance, developing and launching a new medical-grade communication system can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, a sum that many smaller firms simply cannot afford, thereby safeguarding established players like Ascom.
The healthcare sector presents significant regulatory hurdles, acting as a formidable barrier to new entrants. Strict adherence to data privacy laws like HIPAA and GDPR, alongside medical device regulations and robust cybersecurity standards, demands substantial investment and expertise. For instance, the cost of ensuring compliance with HIPAA alone can run into tens of thousands of dollars for new businesses, deterring many from entering the market.
In the healthcare sector, where patient safety is paramount, brand reputation and trust are significant barriers to entry. Established companies like Ascom have cultivated deep-seated trust through decades of reliable service and successful implementations in critical hospital environments. For instance, Ascom's commitment to quality has been recognized through various industry certifications, underscoring their dependable performance.
New entrants struggle to replicate this level of trust quickly. Hospitals, inherently risk-averse, are hesitant to switch to unproven communication systems that could jeopardize patient care or operational efficiency. This reluctance to adopt new, untested solutions means that a new competitor must not only offer superior technology but also demonstrate an equivalent or greater level of reliability and security, a feat that typically takes considerable time and investment.
Deep Industry Knowledge and Niche Expertise
Ascom's strength in deep industry knowledge and niche expertise significantly deters new entrants. Developing solutions for healthcare communication and workflow requires a profound understanding of intricate clinical processes, regulatory environments, and the specific integration needs of hospital IT systems. New players often struggle to replicate this accumulated expertise, which is crucial for creating viable and competitive offerings in this specialized market.
For instance, Ascom's experience in areas like patient monitoring integration and nurse call systems means they understand the nuances of real-time data delivery and critical event management. This specialized knowledge, built over years, is not easily acquired by newcomers. In 2024, the healthcare technology sector continued to see significant investment, but many startups focused on broader AI or data analytics, often overlooking the deep operational and clinical integration challenges that Ascom has mastered.
- Specialized Healthcare Workflows: Ascom's solutions are tailored to complex, often life-critical, healthcare environments.
- Integration Challenges: Successfully integrating with diverse hospital IT infrastructures (EHRs, PACS) requires deep technical and domain knowledge.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating healthcare regulations (e.g., HIPAA) adds another layer of complexity that new entrants may not fully grasp.
- Accumulated Expertise: Ascom's long history in the sector provides a significant barrier due to its deep understanding of evolving clinical needs and technological requirements.
Existing Customer Relationships and Lock-in
Ascom has built strong, long-standing relationships with its healthcare clients. These partnerships often involve integrating Ascom's solutions deeply into existing hospital IT infrastructures, making it complex and costly for clients to switch to a competitor. This deep integration and established trust create a significant barrier for new companies looking to enter the market.
The high switching costs associated with Ascom's integrated systems are a major deterrent for potential new entrants. For instance, a hospital might face substantial expenses for data migration, retraining staff, and ensuring interoperability with new systems. This customer lock-in means new players must offer exceptionally compelling value propositions to overcome the inertia and expense of switching.
In 2024, the healthcare technology sector continued to see significant investment, yet the entrenched nature of existing vendor relationships, like those Ascom fosters, remains a critical factor limiting new entrants' market penetration. Companies that can demonstrate seamless integration and a clear return on investment are more likely to disrupt this dynamic, but the initial hurdle is substantial.
- Deep System Integration: Ascom's solutions are often embedded within a healthcare provider's core IT architecture, increasing operational reliance and switching difficulty.
- High Switching Costs: Transitioning away from Ascom involves significant financial outlays for data migration, new hardware, software, and extensive staff training.
- Customer Loyalty and Trust: Years of reliable service and support have cultivated strong loyalty, making existing customers less receptive to unfamiliar vendors.
- Market Penetration Challenges: New entrants face the daunting task of convincing clients to undertake costly and disruptive system changes, thereby limiting their ability to gain market share quickly.
The threat of new entrants in Ascom's market is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital required for research, development, manufacturing, and establishing a robust sales and support network. For example, developing advanced healthcare communication systems can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, a barrier that deters many smaller firms.
Regulatory compliance, including data privacy laws like HIPAA and GDPR, adds another formidable layer of complexity and cost. Ensuring adherence to these standards can cost new businesses tens of thousands of dollars, further limiting the appeal for potential entrants.
Established trust and brand reputation are critical deterrents, as hospitals prioritize reliability in patient care. Ascom's long history of dependable service, evidenced by industry certifications, makes it difficult for newcomers to gain the necessary trust quickly.
New entrants also face challenges in replicating Ascom's deep industry knowledge and expertise in specialized healthcare workflows, such as patient monitoring and nurse call systems. In 2024, while tech investment remained high, many startups overlooked the deep operational integration complexities that Ascom has mastered.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ascom leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from regulatory filings and trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.