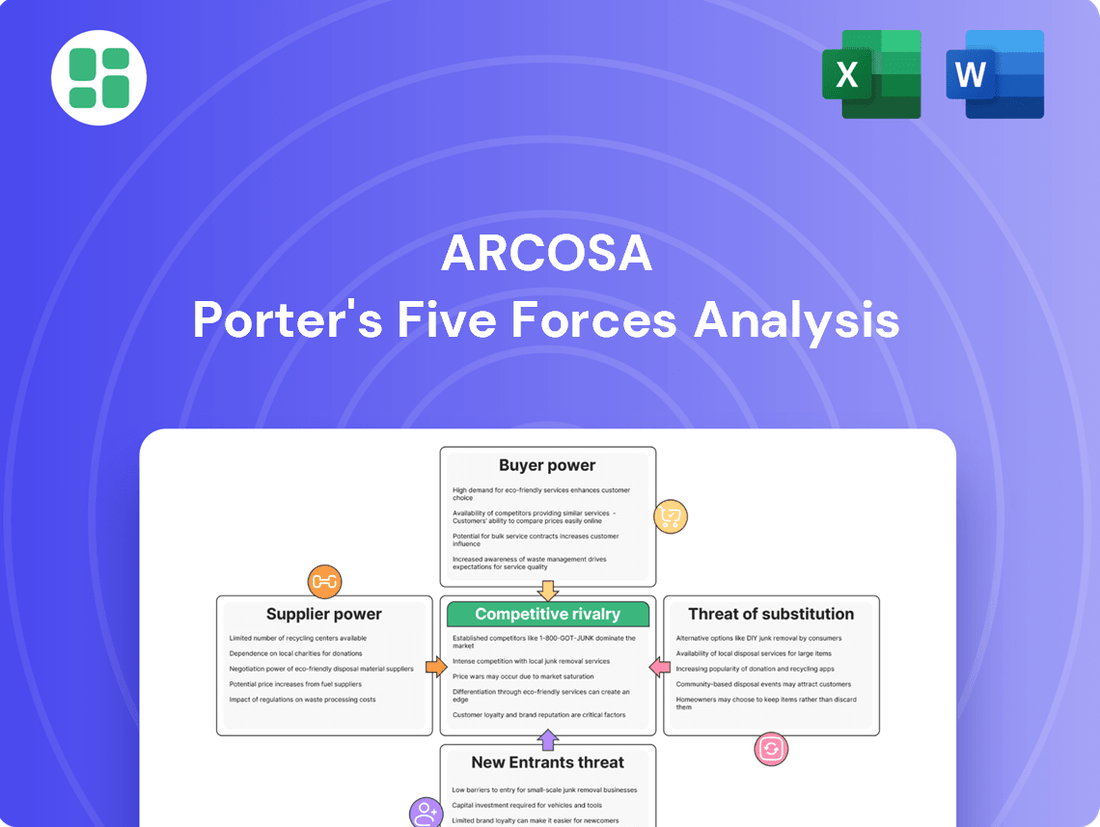
Arcosa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Arcosa Bundle
Arcosa's competitive landscape is shaped by significant buyer power and the constant threat of substitutes, impacting its pricing and market share. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Arcosa’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Arcosa relies heavily on raw materials like steel, energy, and fuel for its manufacturing operations. The concentration of suppliers in these sectors can grant them significant bargaining power, potentially impacting Arcosa's input costs. However, Arcosa's diversified sourcing strategy is designed to lessen the influence of any one supplier.
Arcosa might face moderate to high switching costs for specialized components or large-volume raw materials, which could give suppliers more leverage. However, Arcosa's long history and strong supplier relationships likely mitigate some of these costs, reducing supplier power.
The company's strategic partnerships and long-term contracts are key to stabilizing supply chains and pricing. This proactive approach helps Arcosa manage supplier relationships effectively, lessening the impact of potential price hikes or supply disruptions.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Arcosa's business is generally low. Suppliers in the infrastructure materials industry typically don't possess the capital, technical know-how, or established distribution channels needed to manufacture Arcosa's specialized products like engineered structures or barges.
The substantial investment required for Arcosa's varied product lines, coupled with the need for deep technical expertise and broad market reach, serves as a significant barrier. This makes it unlikely for suppliers to effectively compete by moving into Arcosa's manufacturing space.
Uniqueness of Supplier Inputs
While many of Arcosa's raw materials, like steel and aggregates, are readily available commodities, the company's reliance on specialized components or proprietary technologies for certain segments can amplify supplier leverage. For instance, the Engineered Structures division, which produces wind towers and utility structures, may depend on suppliers providing advanced materials or unique manufacturing processes. This dependence on specialized inputs grants those suppliers increased bargaining power.
Arcosa's strategic acquisitions, such as the purchase of Stavola, are designed to mitigate this risk by vertically integrating and gaining greater control over crucial material sources. This move aims to secure supply chains and potentially reduce the bargaining power of external suppliers for those specific materials.
- Specialized Inputs: Arcosa's Engineered Structures segment might require unique materials or technologies, giving those suppliers more influence.
- Proprietary Technologies: Reliance on suppliers with exclusive or patented components can strengthen their bargaining position.
- Acquisition Strategy: Acquisitions like Stavola aim to internalize key material sourcing, reducing dependence on external suppliers.
- Commodity vs. Specialty: While commodity inputs offer less supplier power, specialty items are a key area of focus for Arcosa's supplier management.
Supplier Compliance and Standards
Arcosa's commitment to rigorous compliance for its global suppliers, encompassing ethical conduct, human rights, and responsible material sourcing such as 3TGs, shapes its supplier relationships. This framework necessitates that suppliers meet Arcosa's exacting standards, ensuring product integrity and ethical supply chains.
While this stringent adherence benefits Arcosa by guaranteeing quality and ethical sourcing, it also positions suppliers who consistently meet these demanding criteria with a degree of bargaining power. These compliant, high-quality suppliers are crucial for Arcosa's operations.
- Supplier Compliance: Arcosa mandates strict adherence to ethical practices, human rights, and material sourcing standards (e.g., 3TGs) from its global supply base.
- Quality Assurance: This compliance ensures Arcosa receives high-quality materials and maintains ethical sourcing throughout its operations.
- Supplier Leverage: Suppliers capable of consistently meeting Arcosa's rigorous standards can gain leverage due to their critical role in the supply chain.
Arcosa's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the availability of specialized components and proprietary technologies, particularly in its Engineered Structures segment. For instance, the need for advanced materials for wind towers can empower specific suppliers. Arcosa's strategy to mitigate this includes vertical integration through acquisitions like Stavola, aiming to secure critical material sources and reduce external supplier dependence.
| Segment | Key Inputs | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineered Structures | Advanced materials, proprietary manufacturing processes | High (for specialized inputs) | Vertical integration (e.g., Stavola acquisition) |
| Transportation Products | Steel, aggregates | Moderate (commodity-based) | Diversified sourcing, long-term contracts |
| Energy Infrastructure Products | Steel, specialized coatings | Moderate to High | Strategic partnerships, supplier compliance standards |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Arcosa, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its diverse markets.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Arcosa's market pressures.
Streamline strategic planning by quickly assessing the impact of each force on Arcosa's profitability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Arcosa's customer base spans diverse infrastructure sectors like construction, energy, and transportation. While this diversification generally mitigates risk, Arcosa experienced some customer concentration in 2021, with its largest customer representing about 15% of its total revenue. This level of reliance on a single major client could give that customer considerable bargaining power, potentially influencing pricing and contract terms.
Customers in infrastructure and construction markets, particularly for products like aggregates, exhibit significant price sensitivity. Arcosa's challenge lies in differentiating its offerings in segments where price becomes a primary comparison point for buyers, potentially limiting its pricing power.
Despite this, Arcosa has demonstrated an ability to pass through costs and enhance margins. For instance, in Q1 2024, Arcosa reported a 7.1% increase in revenue to $636.5 million, with segment profit up 14.6% year-over-year, indicating some success in managing pricing pressures.
Customer switching costs are a key factor in Arcosa's market. For major infrastructure builds, changing suppliers for essential materials or engineered parts isn't simple. It often means dealing with complicated logistics, potential project delays, and unexpected cost increases, which can be quite substantial.
These complexities translate into moderate to high switching costs for Arcosa's customers. Once a project is in motion or a supplier relationship is cemented, these costs can significantly limit a customer's ability to bargain for better terms, thereby strengthening Arcosa's position.
Arcosa's substantial backlog in areas like utility structures and barges further reinforces this. These long-term commitments effectively lock in customers, reducing their flexibility and bargaining power over time.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
Arcosa's customers, such as construction firms and utility providers, generally lack the capacity for backward integration into manufacturing. The immense capital outlay, specialized technical knowledge, and significant operational scale necessary to produce aggregates, engineered structures, or barges make this an impractical endeavor for most clients.
This inability of customers to vertically integrate backward serves to limit their bargaining power. For instance, Arcosa's engineered structures segment, which supplies critical components for infrastructure projects, benefits from this dynamic as customers typically do not possess the facilities or expertise to fabricate these complex items themselves.
In 2023, Arcosa reported net sales of $2.3 billion, with its infrastructure products segment contributing significantly. The specialized nature of many of these products, like wind towers and utility structures, inherently restricts a customer's ability to replicate Arcosa's manufacturing processes, thereby reinforcing Arcosa's pricing power.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing manufacturing facilities for Arcosa's product lines, such as aggregates or specialized steel structures, would necessitate investments in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Technical Expertise Gap: Customers would need to acquire highly specialized engineering and manufacturing skills, which are not core competencies for most construction or utility companies.
- Operational Scale Disadvantage: Arcosa benefits from economies of scale in its production processes, a level of output that individual customers would struggle to match economically.
- Limited Backward Integration: The vast majority of Arcosa's customer base relies on Arcosa for these manufactured components, indicating a low propensity or capability for backward integration.
Information Availability and Purchasing Volume
Large customers, such as government agencies or major construction companies, often wield significant bargaining power due to their deep market knowledge and procurement experience. This allows them to push for more competitive pricing. Their substantial purchasing volumes also amplify this leverage.
Arcosa's financial performance in 2024, with a reported backlog of approximately $2.3 billion as of the first quarter, indicates robust demand. This strong demand can serve as a counterweight to the bargaining power of individual large customers, providing Arcosa with more flexibility in its pricing and contract negotiations.
- Customer Information: Large buyers possess extensive market data, enabling them to negotiate effectively.
- Purchasing Volume: High order volumes grant customers greater influence.
- Arcosa's Backlog: A strong backlog of around $2.3 billion in early 2024 demonstrates healthy demand, mitigating some customer power.
Arcosa's customers generally face high switching costs when dealing with specialized infrastructure components, as changing suppliers can lead to project delays and increased expenses. This inherent stickiness in customer relationships limits their ability to bargain for better terms. For instance, the complexity of fabricating items like wind towers means most clients cannot easily find or integrate alternative suppliers, thus reducing their bargaining leverage.
The inability of Arcosa's customers to effectively integrate backward into manufacturing also significantly curbs their bargaining power. The immense capital, technical expertise, and operational scale required to produce items like aggregates or engineered structures are typically beyond the reach of their client base. This reliance on Arcosa's specialized production capabilities strengthens the company's position.
While large customers can exert influence through volume and market knowledge, Arcosa's robust backlog, standing at approximately $2.3 billion in early 2024, provides a strong counter-balance. This healthy demand allows Arcosa more flexibility in negotiations, effectively mitigating some of the individual bargaining power of its larger clients.
| Factor | Impact on Arcosa's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High | Complex logistics, project delays, and cost increases associated with changing suppliers for specialized infrastructure components. |
| Backward Integration Capability | Low | High capital requirements, technical expertise gap, and operational scale disadvantage prevent most customers from producing Arcosa's products internally. |
| Customer Concentration | Potential Risk | In 2021, the largest customer represented about 15% of revenue, indicating potential leverage for that specific client. |
| Price Sensitivity | Significant in some segments | Customers in construction markets, especially for aggregates, are highly price-sensitive, potentially limiting Arcosa's pricing power. |
| Arcosa's Backlog | Mitigating Factor | A backlog of approximately $2.3 billion in Q1 2024 demonstrates strong demand, reducing customer leverage. |
Same Document Delivered
Arcosa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Arcosa Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring you get the full, professionally formatted analysis without any alterations or placeholders. This ensures you have all the insights needed to understand Arcosa's market position and strategic implications.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Arcosa navigates a competitive terrain with a varied field of rivals across its business segments. These range from large, diversified industrial conglomerates to smaller, specialized regional operators, creating a dynamic market environment.
Key competitors include established players like Eagle Materials, Cemex, and James Hardie Industries. However, Arcosa also contends with numerous niche firms focusing on specific product lines within its served markets, such as infrastructure, energy, and construction materials.
For instance, in the construction materials sector, Arcosa competes with companies that have significant market share and broad product portfolios. This diverse competitive structure demands Arcosa to maintain a sharp focus on operational excellence and ongoing strategic adjustments to stay ahead.
The infrastructure, energy transition, and transportation sectors are seeing robust demand and growth, largely fueled by significant federal funding initiatives and the ongoing need to upgrade aging infrastructure. This expansionary environment is a key factor in moderating competitive rivalry.
When industries are growing healthily, companies like Arcosa can increase their revenues by simply participating in the expanding market, rather than needing to aggressively steal market share from rivals. This dynamic reduces the pressure for price wars or costly market-share battles. For instance, Arcosa reported strong revenue growth in 2024 and anticipates a positive outlook for 2025, demonstrating its ability to capitalize on these favorable market conditions.
Arcosa navigates competitive rivalry by differentiating its offerings, particularly in Engineered Structures and Transportation Products. While segments like aggregates are more standardized, Arcosa's custom wind towers and specialized barges provide unique value, lessening direct price competition. In 2023, Arcosa's revenue from its Engineered Structures segment was approximately $1.1 billion, showcasing the strength of its specialized products.
High switching costs for intricate projects further insulate Arcosa from intense rivalry. Customers investing in Arcosa's complex solutions face considerable expense and disruption if they were to change suppliers. This stickiness is a key factor in maintaining market position.
Furthermore, Arcosa strategically employs acquisitions to bolster its product portfolio and expand its market presence, thereby reducing the impact of direct competition. For instance, the acquisition of Chicago Bridge & Iron Company's steel plate structures business in 2021 significantly enhanced its capabilities in engineered structures.
Exit Barriers
The capital-intensive nature of manufacturing infrastructure-related products, such as large facilities and specialized equipment, presents significant exit barriers for companies operating within Arcosa's market segments. This high cost to leave the industry means that even underperforming competitors might persist, prolonging competitive rivalry, especially during economic slowdowns. For instance, the infrastructure sector often requires substantial upfront investment in plants and machinery, making it difficult for firms to recoup their capital if they decide to exit.
Arcosa has actively managed its business mix by divesting non-strategic assets, a move that highlights the importance of portfolio optimization in industries with high exit barriers. This strategic approach allows Arcosa to focus resources on more profitable and synergistic areas, mitigating the impact of prolonged rivalry from entrenched, less efficient competitors. Such divestitures can also free up capital for reinvestment or debt reduction, strengthening the company's competitive position.
- High Capital Investment: Manufacturing infrastructure products necessitates substantial investment in specialized facilities and equipment, creating a significant financial hurdle for companies wishing to exit the market.
- Persistence of Struggling Competitors: Due to high exit barriers, less successful companies may remain operational longer than they otherwise would, intensifying competitive pressure.
- Arcosa's Portfolio Management: Arcosa's strategic divestitures of non-core assets demonstrate proactive management to enhance its competitive standing in the face of these industry dynamics.
- Impact on Rivalry: The presence of deeply invested, potentially less agile competitors due to exit barriers can lead to sustained and sometimes aggressive pricing or market share battles.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
Competitors in Arcosa's markets likely pursue diverse strategic objectives, including gaining market share, expanding geographically, achieving cost leadership, or specializing in niche segments. This suggests a dynamic competitive landscape where Arcosa must continually adapt.
Arcosa’s own strategy centers on optimizing its business portfolio, growing its expansion-focused segments, and mitigating the impact of economic cycles. For example, in 2024, Arcosa continued to refine its segment mix, aiming for more stable revenue streams.
The acquisition of Stavola in 2023 for $185 million exemplifies Arcosa's strategic intent to move into higher value-added construction products, a clear indicator of repositioning for competitive advantage and enhanced profitability.
- Market Share Growth: Competitors may prioritize increasing their footprint in key segments like infrastructure or energy transition markets.
- Cost Efficiency: Some rivals might focus on operational streamlining to offer competitive pricing, particularly in commodity-driven product lines.
- Product Innovation: Investment in new technologies and product development is a common strategy to differentiate and capture emerging demand.
- Geographic Expansion: Companies could be looking to enter new regional markets or strengthen their presence in existing ones to diversify revenue.
Arcosa faces a competitive environment populated by a mix of large, diversified players and specialized niche operators across its various business segments. While growth in sectors like infrastructure and energy transition, fueled by substantial federal funding, moderates direct rivalry by allowing companies to grow organically, Arcosa still contends with established firms like Eagle Materials and Cemex. The company's strategy of product differentiation, particularly in Engineered Structures, and high customer switching costs help mitigate intense price competition.
| Competitor | Primary Segments | 2024 Estimated Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Competitive Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eagle Materials | Aggregates, Cement, Concrete | ~2.5 | Cost leadership, regional strength |
| Cemex | Cement, Ready-Mix Concrete, Aggregates | ~17.5 | Global scale, diversified products |
| James Hardie Industries | Fiber Cement Siding & Building Products | ~4.0 | Product innovation, brand building |
SSubstitutes Threaten
In the construction products sector, while traditional aggregates remain dominant, the threat of substitutes is present. For instance, the increasing use of recycled concrete aggregate, which can offer cost savings and environmental benefits, presents a potential substitute for virgin materials. In 2023, the global recycled aggregate market was valued at approximately $30 billion and is projected to grow, indicating a growing acceptance of these alternatives.
For Arcosa's engineered structures, direct material substitutes for products like utility poles or wind towers are scarce. However, indirect substitutes can emerge from shifts in technology. For example, advancements in distributed energy generation or changes in grid modernization strategies could influence the demand for traditional infrastructure components. Arcosa's strategic positioning in essential infrastructure, such as its significant backlog in utility structures, helps to buffer against a high threat from direct material substitutions.
The performance and cost-effectiveness of potential substitutes are critical. For example, while rail and truck transport can substitute for barge services, barges maintain a significant cost advantage for bulk freight over waterways, making them a difficult substitute to fully displace.
For a substitute to pose a substantial threat to Arcosa's barge segment, it would need to offer comparable performance in terms of capacity and reliability, coupled with a competitive price point. In 2024, the cost per ton-mile for barge transport remains notably lower than trucking or rail for bulk commodities, reinforcing its competitive position.
Customer propensity to substitute for Arcosa's products, particularly in large-scale infrastructure, is generally low. This is because the stakes are incredibly high – project integrity, safety, and long-term performance are paramount. Think about a bridge or a wind turbine; you can't afford to experiment with unproven materials when lives and massive investments are on the line. Arcosa's customers prioritize reliability and a history of success, making them hesitant to switch to alternatives that lack this established track record.
Regulatory and Standards Impact
Many of Arcosa's key products, particularly those in Engineered Structures and Transportation Products segments, are subject to rigorous industry standards and regulatory compliance. For instance, Arcosa's wind towers must adhere to American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards, and its utility structures often need to meet specific American National Standards Institute (ANSI) guidelines. New substitute materials or technologies entering these markets must navigate these same demanding specifications. This compliance journey is often lengthy and expensive, creating a significant barrier to entry for potential substitutes.
The substantial investment required to gain regulatory approval for alternative materials or designs can deter their development and adoption. This regulatory hurdle effectively limits the threat of substitutes by making it difficult and costly for them to meet the established performance and safety benchmarks that Arcosa's products already satisfy. For example, the Federal Highway Administration's (FHWA) approval process for new bridge materials can take years, showcasing the inherent challenge for substitutes in gaining traction.
- Stringent Compliance: Arcosa's products, like wind towers and utility poles, must meet demanding industry standards (e.g., ASME, ANSI).
- Costly Qualification: New substitute materials face significant time and financial investment to achieve regulatory approval.
- Barrier to Adoption: The rigorous specifications and approval processes act as a strong deterrent to the widespread use of substitutes.
Evolution of Infrastructure Needs
The fundamental need for robust infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utility grids, creates a persistent demand for Arcosa's core products, making direct substitution challenging.
While technological advancements like smart grids might alter specific component designs, the essential physical materials and structures Arcosa provides remain critical for infrastructure functionality.
For instance, the U.S. Department of Transportation's 2024 infrastructure report highlighted ongoing investments in bridge repair and replacement, underscoring the enduring need for components like steel beams and concrete structures that Arcosa manufactures.
The sheer scale and foundational nature of these infrastructure projects mean that entirely new, non-physical solutions are unlikely to replace the tangible elements Arcosa supplies in the foreseeable future.
- Sustained Demand: The ongoing need for physical infrastructure ensures a stable market for Arcosa's products.
- Technological Adaptation, Not Substitution: While technology evolves, the core physical needs of infrastructure remain.
- Critical Role of Physical Components: Arcosa's products are integral to the very existence of essential infrastructure.
- Limited Viability of Alternatives: The scale and nature of infrastructure projects make complete substitution by non-physical means impractical.
The threat of substitutes for Arcosa's products is generally low due to the specialized nature and stringent requirements of the infrastructure sector. For Arcosa's core offerings in engineered structures and transportation products, direct material substitutes are scarce, and any potential alternatives face significant hurdles in meeting performance, safety, and regulatory standards. The cost-effectiveness and customer acceptance of substitutes are also key factors limiting their impact.
For example, in the construction aggregates market, recycled concrete aggregate is emerging as a substitute for virgin materials, with the global market valued at around $30 billion in 2023. However, for Arcosa's engineered structures like utility poles and wind towers, the threat of direct material substitutes is minimal. Instead, indirect substitutes might arise from technological shifts in energy generation or grid modernization, which could influence demand for traditional infrastructure components.
The barge segment faces limited substitution threats, as barges maintain a significant cost advantage for bulk freight over waterways compared to rail or truck transport. In 2024, the cost per ton-mile for barge transport remains substantially lower for bulk commodities, reinforcing its competitive position against these alternatives.
Furthermore, Arcosa's customers prioritize reliability and a proven track record, making them hesitant to adopt unproven substitutes, especially given the high stakes involved in infrastructure projects. The rigorous industry standards and lengthy, expensive qualification processes for new materials, such as adherence to ASME or ANSI guidelines, create substantial barriers to entry for potential substitutes.
| Product Segment | Potential Substitute | Key Limiting Factor for Substitute | Arcosa's Advantage | 2024 Market Insight |
| Aggregates | Recycled Concrete Aggregate | Performance consistency, customer perception | Established supply chain, proven quality | Recycled aggregate market growing, but virgin materials still dominant |
| Engineered Structures (Utility Poles, Wind Towers) | Advanced Composite Materials | High upfront cost, regulatory approval time | Existing certifications, economies of scale | Infrastructure spending remains robust, demand for traditional components steady |
| Transportation Products (Railcars) | Alternative Shipping Methods (e.g., enhanced trucking) | Capacity limitations for bulk, cost per ton-mile | Cost efficiency for bulk, established infrastructure | Barge transport cost per ton-mile remains lower than truck/rail for bulk in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering Arcosa's core markets, like heavy manufacturing for construction, engineered structures, and transportation products, demands massive upfront capital. Think of the cost for state-of-the-art factories, specialized equipment, and building out robust distribution channels. This substantial financial hurdle naturally discourages many potential new players from even attempting to compete.
For instance, establishing a new steel fabrication plant comparable to Arcosa's facilities could easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. This high barrier to entry is a significant protective factor for Arcosa, limiting the number of viable new competitors.
Furthermore, Arcosa's strategic approach of acquiring existing players, as seen in their recent market consolidations, effectively raises the capital bar even higher. These acquisitions not only expand Arcosa's capacity but also solidify their market presence, making it even more challenging for newcomers to gain traction without comparable resources.
Established players like Arcosa leverage significant economies of scale in production, procurement, and distribution, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, Arcosa's substantial manufacturing footprint allows for bulk purchasing of raw materials, driving down input expenses compared to a new entrant attempting to establish similar supply chain relationships. This cost advantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price without substantial initial investment and volume.
Arcosa's decades of operational experience translate into refined processes, optimized resource allocation, and enhanced product quality. This accumulated knowledge, often referred to as the experience curve, allows Arcosa to operate more efficiently and with fewer errors than a nascent competitor. New entrants would face a steep learning curve, incurring higher initial costs and potentially lower quality as they build their operational expertise.
Arcosa's established brand identity and deeply ingrained customer relationships present a formidable barrier to new entrants. Decades of consistent quality, reliable service, and operational efficiency have cultivated a strong reputation and significant customer loyalty across its various business segments. For instance, Arcosa's infrastructure products, like utility structures and wind towers, benefit from long-standing relationships with major utility companies and renewable energy developers who prioritize proven performance and dependability.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Arcosa benefits from deeply entrenched distribution channels and supply chain integrations, especially in core markets like aggregates and specialized structures. For instance, Arcosa's extensive network of ready-mix concrete plants and aggregate quarries across the United States provides significant logistical advantages.
Newcomers face substantial hurdles in establishing comparable networks, requiring immense capital investment and time to secure reliable access to raw materials and efficient transportation routes. This established infrastructure acts as a formidable barrier, limiting the ease with which new competitors can enter and operate effectively.
The difficulty in replicating Arcosa's existing infrastructure network is a key competitive advantage, directly impacting the threat of new entrants.
- Arcosa's established distribution network provides efficient delivery of products, a critical factor in industries like construction materials.
- New entrants would need to invest heavily in logistics and supplier relationships to match Arcosa's existing supply chain capabilities.
- Securing access to essential raw materials, such as aggregates, at competitive prices is a significant challenge for potential new players.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
The infrastructure, construction, and transportation sectors are characterized by significant regulatory hurdles. New companies must secure numerous licenses and permits, and rigorously adhere to demanding safety and environmental regulations. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain a major construction permit in the US can extend from several months to over a year, depending on the jurisdiction and project complexity, significantly increasing initial capital outlay and delaying market entry for potential competitors.
Compliance with these intricate regulatory frameworks represents a substantial barrier. New entrants face considerable costs associated with legal counsel, compliance officers, and the implementation of necessary safety and environmental protocols. This complexity and expense can deter smaller or less-resourced companies from entering the market, thereby protecting established players like Arcosa.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating a web of federal, state, and local regulations.
- Licensing and Permitting: Acquiring necessary approvals for operations and projects.
- Safety and Environmental Standards: Meeting stringent requirements that demand significant investment in compliance.
- Increased Costs and Time-to-Market: The financial and temporal burden of regulatory adherence acts as a deterrent for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Arcosa is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for manufacturing and infrastructure. For example, building a new, modern manufacturing facility can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant barrier. Arcosa's existing economies of scale in purchasing and production also create a cost advantage that newcomers would struggle to match without massive initial investment.
Arcosa's established brand reputation and long-standing customer relationships, particularly in sectors like utility structures, foster loyalty that new entrants find difficult to penetrate. Furthermore, the company's extensive distribution networks and supply chain integrations, such as its numerous aggregate quarries and ready-mix concrete plants, require immense capital and time to replicate, effectively locking out many potential competitors.
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape, including obtaining licenses and adhering to safety and environmental standards, adds significant costs and delays for new companies. In 2024, the average time to secure major construction permits can extend over a year, increasing the financial and temporal burden for potential entrants.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Arcosa's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost for facilities and equipment | Existing, large-scale manufacturing base |
| Economies of Scale | Higher per-unit costs for smaller volumes | Lower input costs through bulk purchasing |
| Brand Reputation & Customer Loyalty | Difficulty in building trust and market share | Decades of proven performance and reliability |
| Distribution & Supply Chain | Challenges in securing raw materials and logistics | Extensive network of quarries and plants |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Significant time and cost for compliance | Established expertise in navigating regulations |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Arcosa is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Arcosa's own investor relations materials, publicly available financial statements, and industry-specific market research reports. We also integrate insights from trade publications and economic data to provide a robust assessment of the competitive landscape.