Amyris Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amyris Bundle
Amyris operates in a dynamic biotech landscape, facing intense competition and significant buyer power from its diverse customer base. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The full analysis reveals the real forces shaping Amyris’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amyris's proprietary strain engineering and fermentation platforms significantly diminish supplier bargaining power. By developing unique biological pathways internally, they reduce reliance on external, highly specialized biotechnology components. This internal innovation is key to their cost structure and competitive advantage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Amyris, particularly concerning plant-based sugars, is generally moderate. These sugars, the core feedstock, are typically commoditized agricultural products, meaning there are often multiple sources available. For instance, in 2024, global sugar production remained robust, with major producing regions like Brazil and India contributing significantly to the supply.
While disruptions like adverse weather in key growing areas or the emergence of regional monopolies for specific sugar types could temporarily elevate supplier power, the broad availability of diverse plant-based sugar sources globally tends to mitigate this. Amyris's strategic approach, which includes vertical integration and a degree of control over its fermentation processes, likely provides it with considerable flexibility in managing its sugar sourcing and therefore limits the leverage of individual suppliers.
Suppliers of highly specialized enzymes and reagents crucial for Amyris's precision fermentation processes can wield significant bargaining power. This is due to the niche nature and proprietary intellectual property often tied to these biological inputs. For instance, a unique enzyme with patent protection could command higher prices, directly impacting Amyris's cost of goods sold.
However, Amyris's robust research and development infrastructure, particularly its focus on organism engineering, provides a counterbalancing force. By developing proprietary strains and potentially producing some key components in-house, Amyris can reduce its reliance on external suppliers. This internal capability allows for greater control over supply chain costs and innovation, mitigating the suppliers' leverage.
Skilled Labor and Scientific Talent
The synthetic biotechnology field, where Amyris operates, is heavily reliant on specialized scientific and engineering expertise. This scarcity of highly skilled professionals, particularly in areas like strain engineering, fermentation science, and synthetic chemistry, grants these individuals significant bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the demand for bioengineers and synthetic biologists continued to outstrip supply, leading to competitive salary offers and retention bonuses across the industry.
Amyris's ability to innovate and maintain efficient operations hinges on its capacity to attract and retain this elite talent. The intense competition for these individuals can directly impact labor costs, potentially increasing operational expenses and influencing the pace of research and development projects. Companies often compete not just on salary but also on challenging projects and opportunities for scientific advancement.
- High Demand for Specialized Skills: Fields like synthetic biology, metabolic engineering, and bioprocess development require advanced degrees and practical experience, creating a tight labor market.
- Impact on R&D Costs: The competitive nature of hiring top scientific minds can drive up R&D budgets as companies offer attractive compensation packages.
- Retention Challenges: Retaining key scientific personnel is critical, as their departure can disrupt ongoing projects and knowledge transfer.
Manufacturing Equipment and Infrastructure
Suppliers of advanced fermentation equipment and specialized bioreactors can exert considerable bargaining power, particularly for companies like Amyris aiming for large-scale manufacturing. The cost and technical complexity of such infrastructure mean that few suppliers can meet demand, giving them leverage in pricing and terms. For instance, the capital expenditure for a state-of-the-art fermentation facility can run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, making the choice of equipment supplier a critical decision with long-term implications.
Amyris's strategic decision to take full control of its precision fermentation plant in Brazil, as reported in late 2023, highlights a move to mitigate supplier power. By owning and operating its manufacturing assets, Amyris aims to gain greater control over production processes, costs, and the supply chain for essential equipment and maintenance. This vertical integration can reduce dependency on external service providers and potentially negotiate better terms for future equipment needs or upgrades.
- Specialized Equipment: High-tech bioreactors and fermentation vessels are often proprietary and require specialized manufacturing, limiting the number of capable suppliers.
- Capital Intensity: The significant upfront investment in manufacturing infrastructure means companies are locked into their equipment choices for extended periods.
- Amyris's Brazil Facility: Amyris's acquisition of full ownership of its Brazilian plant in late 2023 is a strategic play to enhance control over its manufacturing capabilities.
- Supplier Dependence: For companies not pursuing full ownership, reliance on a few key equipment suppliers can lead to higher costs and potential production disruptions if supplier relationships sour.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Amyris is generally moderate, influenced by the commoditized nature of its primary feedstock, plant-based sugars. While global sugar production remained strong in 2024, with significant contributions from Brazil and India, localized disruptions could temporarily shift power. Amyris's internal innovation and control over fermentation processes help mitigate reliance on any single sugar supplier.
However, suppliers of highly specialized enzymes and reagents critical for Amyris's precision fermentation can wield significant power due to the niche nature and intellectual property involved. The scarcity of top talent in synthetic biology also grants individuals in this field considerable bargaining power, impacting R&D costs. Furthermore, specialized fermentation equipment suppliers hold leverage due to the capital intensity and technical complexity of their offerings, though Amyris's move to fully own its Brazil plant in late 2023 aims to reduce this dependency.
| Supplier Category | Bargaining Power Level | Key Influencing Factors | Amyris's Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-based Sugars (Feedstock) | Moderate | Global production volume, availability of diverse sources, weather impacts. | Internal innovation, control over fermentation processes, diverse sourcing. |
| Specialized Enzymes & Reagents | Significant | Niche nature, proprietary intellectual property, patent protection. | Robust R&D, organism engineering, potential in-house component production. |
| Highly Skilled Scientific Talent | Significant | Scarcity of expertise in synthetic biology, metabolic engineering, bioprocess development. | Competitive compensation, challenging projects, opportunities for advancement. |
| Advanced Fermentation Equipment | Significant | Technical complexity, capital intensity, limited number of capable suppliers. | Vertical integration (e.g., Brazil plant ownership), strategic sourcing. |
What is included in the product
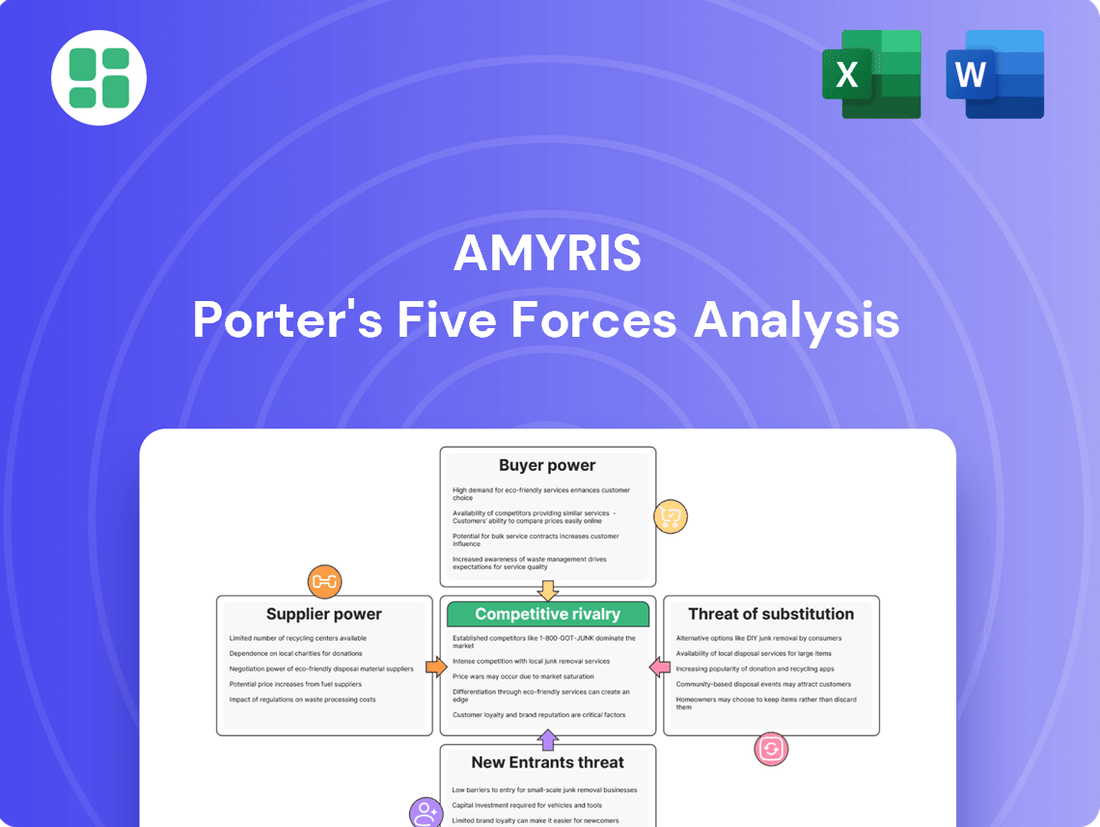
This analysis dissects Amyris's competitive environment by examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, streamlining strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Amyris's diverse end markets, including flavors, fragrances, cosmetics, nutraceuticals, and pharmaceuticals, significantly dilute the bargaining power of individual customers. This broad market reach means that no single industry or large client holds disproportionate sway over the company's pricing or terms. For example, in 2024, Amyris continued to see growth in its consumer ingredient sales, which helped balance any potential pressures from its industrial biotechnology segment.
Amyris's commitment to sustainable, bio-based ingredients offers a compelling value proposition, particularly as consumer and business demand for eco-friendly products continues to surge. This focus on environmental responsibility can lessen customers' inclination to haggle over price, as they value the unique benefits provided. For instance, in 2024, the global market for sustainable chemicals was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting a significant willingness to pay a premium for greener alternatives.
For customers in sectors like cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, integrating a new ingredient is a complex process. It typically involves extensive research and development, reformulation efforts, navigating regulatory approvals, and rigorous retesting. These steps collectively create substantial hurdles and costs for businesses looking to switch ingredient suppliers.
When Amyris's ingredients become part of a customer's established product lines, the investment in R&D, regulatory compliance, and manufacturing processes makes changing suppliers a costly and time-consuming undertaking. For instance, a successful cosmetic formulation using Amyris's squalane might require months of testing and regulatory submissions before it can be launched. This significant investment in time and resources inherently limits the bargaining power of these customers.
Customer Concentration in Specific Segments
Customer concentration in specific market segments can indeed grant significant bargaining power to a few large buyers. If Amyris relies heavily on a handful of major clients for a substantial portion of its revenue, these clients could leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate more favorable pricing or terms. This is a common dynamic, particularly in specialized B2B markets.
For instance, if a significant percentage of Amyris's 2024 revenue came from a few key partners in the cosmetics or industrial biotech sectors, those partners would have a stronger hand in negotiations. While specific customer concentration data for Amyris isn't publicly detailed in a way that allows for precise percentage breakdowns of individual customer sales, the general principle holds true.
However, it is important to note that strategic partnerships and co-development agreements can mitigate this risk. When Amyris engages in such collaborations, it fosters a more symbiotic relationship, aligning interests and reducing the potential for purely adversarial price discussions. These partnerships can lead to more stable demand and shared innovation, thereby balancing the bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers is influenced by several factors, including:
- Customer Concentration: The degree to which sales are concentrated among a few large customers.
- Availability of Substitutes: The easier it is for customers to switch to alternative suppliers or technologies.
- Switching Costs: The expenses or difficulties customers face when changing suppliers.
- Customer's Importance to the Supplier: How critical a particular customer's business is to the supplier's overall revenue.
Importance of Amyris's Ingredients to End Products
Amyris's ingredients are often the linchpin in their customers' end products, providing crucial performance attributes or enabling compelling sustainability narratives. For instance, their squalane is a key emollient in premium skincare, directly impacting product feel and efficacy. This makes Amyris a vital supplier, as substituting these specialized components can be challenging and costly for their clients.
The difficulty in replicating Amyris's proprietary ingredients significantly strengthens their hand when negotiating with customers. This is particularly true for ingredients developed through their fermentation technology, which offers a unique value proposition. In 2024, Amyris continued to emphasize these differentiated offerings in their market approach.
- Criticality of Ingredients: Amyris's specialized ingredients are often non-substitutable, forming the core of a customer's product formulation and value proposition.
- Performance and Sustainability Claims: These ingredients directly contribute to unique performance benefits and environmental credentials that customers market to their own consumers.
- Replication Difficulty: The proprietary nature and complex production processes for Amyris's ingredients make them hard for competitors to replicate, reducing customer options.
- Enhanced Bargaining Position: The combination of criticality and replication difficulty grants Amyris greater leverage in pricing and contract negotiations.
Amyris's diverse customer base across multiple industries, from cosmetics to pharmaceuticals, limits the bargaining power of any single buyer. This broad market reach, exemplified by continued growth in consumer ingredients in 2024, prevents any one segment from dictating terms. The unique, sustainable nature of Amyris's bio-based ingredients also commands a premium, as customers increasingly value eco-friendly attributes, a trend supported by the projected multi-billion dollar market for sustainable chemicals in 2024.
High switching costs for customers, stemming from the extensive R&D, reformulation, and regulatory hurdles involved in integrating new ingredients, significantly reduce their ability to negotiate aggressively. For example, a cosmetic product incorporating Amyris's squalane might require months of testing and approval processes, locking in the supplier. The critical role and difficult-to-replicate nature of Amyris's proprietary ingredients, such as those derived from their fermentation technology, further bolster their bargaining position by making substitution challenging and costly for clients.
Preview Before You Purchase
Amyris Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Amyris Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape for the company. You are viewing the exact document you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and no hidden surprises. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing valuable insights into industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Amyris operates in a competitive landscape with formidable established synthetic biology players like Ginkgo Bioworks, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Twist Bioscience. These companies are actively vying for market share by excelling in technological advancements, achieving economies of scale, and offering a diverse portfolio of engineered molecules and specialized services.
The synthetic biology market is booming, with forecasts suggesting it could reach tens of billions of dollars by 2030. This rapid expansion is fueled by a growing desire for sustainable products and breakthroughs in technologies like gene editing and AI. For instance, the global synthetic biology market was valued at approximately USD 11.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly in the coming years.
Competitive rivalry in the biotechnology sector, particularly for companies like Amyris, often hinges on the distinctiveness and effectiveness of their proprietary strain engineering and fermentation platforms. This focus on technological uniqueness allows companies to stand out based on their innovation capabilities rather than simply competing on price.
Amyris's 'Lab-to-Market' operating system, honed over two decades, is a prime example of this differentiation. It facilitates the rapid co-creation and scaling of novel ingredients, giving Amyris a significant edge over rivals who may not possess such integrated and experienced development infrastructure.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Companies in the synthetic biology sector, including Amyris, often forge strategic partnerships and collaborations. These alliances are crucial for speeding up research and development, broadening market access, and distributing the inherent risks of innovation.
Amyris itself has a history of working with various entities. A notable recent development is a significant agreement to develop critical medicines, underscoring a strategic approach that complements direct competition with collaborative efforts.
- Accelerated R&D: Partnerships allow companies to pool resources and expertise, leading to faster development cycles for new products and technologies.
- Market Expansion: Collaborations can open doors to new geographic regions or customer segments that a single company might struggle to penetrate alone.
- Risk Sharing: By jointly investing in and developing new ventures, companies can mitigate the financial and technological risks associated with pioneering new fields like synthetic biology.
- Amyris's Strategy: Amyris's recent agreement to develop critical medicines highlights its use of partnerships to achieve strategic goals beyond its core fermentation-based production.
Impact of Amyris's Restructuring
Amyris's emergence from Chapter 11 bankruptcy in May 2024 marks a significant pivot, sharpening its competitive stance by concentrating on its research and development capabilities and the scaling of sustainable ingredients. This strategic realignment, which includes divesting consumer brands, is designed to streamline its operations and bolster its financial health.
The restructuring is expected to enhance Amyris's cost efficiency and liquidity. This focus on core competencies could position the company as a more potent player within the specialized sustainable ingredients market, potentially intensifying rivalry for businesses reliant on similar biotechnological advancements and ingredient sourcing.
- Focus on Core: Amyris is now concentrating on its R&D and sustainable ingredient production, moving away from consumer-facing brands.
- Financial Health Improvement: The restructuring aims to improve cost structure and liquidity, making the company more financially agile.
- Competitive Impact: A more focused Amyris could increase competitive pressure on other players in the sustainable ingredients sector.
- Market Position: By divesting consumer brands, Amyris signals a strategic intent to be a stronger competitor in its B2B ingredient offerings.
Amyris faces intense competition from established players like Ginkgo Bioworks and emerging biotech firms, all vying for market share through innovation and scale. The synthetic biology market, projected to reach tens of billions by 2030, is characterized by rapid technological advancements and a growing demand for sustainable solutions, intensifying rivalry.
Amyris's competitive edge lies in its proprietary strain engineering and fermentation platforms, allowing differentiation through technological uniqueness rather than price. Its integrated 'Lab-to-Market' system accelerates the development and scaling of novel ingredients, providing an advantage over less experienced competitors.
Following its Chapter 11 emergence in May 2024, Amyris has strategically refocused on its R&D and sustainable ingredient scaling, divesting consumer brands to improve efficiency and liquidity. This streamlined approach is poised to intensify competition within the specialized sustainable ingredients market.
| Competitor | Key Strengths | Amyris's Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Ginkgo Bioworks | Extensive organism library, broad platform capabilities | Integrated 'Lab-to-Market' system, rapid co-creation |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | Broad life sciences portfolio, established supply chains | Specialized fermentation expertise, sustainable ingredient focus |
| Twist Bioscience | Leading DNA synthesis platform | Proprietary strain engineering, scaling experience |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitutes for Amyris's bio-based ingredients are conventional petroleum-derived chemicals. These have historically offered a cost advantage and widespread availability.
However, the landscape is shifting. Growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations are making petroleum-based options less attractive. For instance, in 2024, the global chemical industry faced increasing scrutiny over its carbon footprint, with many regions implementing or strengthening carbon pricing mechanisms.
Consumer preference for sustainable products is a powerful driver, pushing manufacturers to seek greener alternatives like those Amyris provides. This trend is reflected in market research indicating a growing premium consumers are willing to pay for eco-friendly goods, directly impacting the perceived value of bio-based ingredients over their petrochemical counterparts.
Naturally sourced ingredients, like those extracted directly from plants, can indeed pose a threat of substitution for products made using Amyris's precision fermentation. For example, if consumers strongly prefer traditional botanical extracts, this could reduce demand for fermented alternatives.
However, Amyris's approach often creates molecules that are difficult or impossible to obtain sustainably from nature in sufficient quantities or purity. In 2024, the demand for high-purity, bio-identical ingredients in cosmetics and flavors remained strong, a segment where precision fermentation excels by offering consistency and scalability that natural extraction struggles to match, thereby mitigating this substitution threat.
The threat of substitutes for Amyris's products is closely tied to the cost-performance trade-offs available in the market. While traditional petroleum-based chemicals can sometimes present a lower upfront cost, Amyris's bio-based alternatives frequently showcase a more compelling sustainability story. This environmental advantage, coupled with often equivalent or even improved performance characteristics such as higher purity and greater consistency, allows Amyris to command a premium price from environmentally conscious customers.
Regulatory and Consumer Preference Shifts
The increasing regulatory landscape favoring sustainable and bio-based products directly diminishes the appeal of conventional chemical substitutes. For instance, as of early 2024, several major markets are implementing stricter regulations on petrochemical-derived ingredients, pushing manufacturers towards alternatives like those Amyris produces.
Consumer demand for 'clean' and 'natural' ingredients is a powerful force, making traditional, less sustainable options less attractive. By mid-2024, surveys indicated that over 60% of consumers in key Western markets are willing to pay a premium for products with transparent, natural ingredient lists, directly benefiting companies aligned with these preferences.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Emerging regulations in the EU and North America are increasingly penalizing or restricting the use of certain synthetic chemicals, thereby increasing the cost and reducing the availability of traditional substitutes.
- Consumer Preference: A significant portion of consumers, estimated at over 70% in developed economies by Q2 2024, actively seek out products labeled as natural, organic, or sustainably sourced, directly impacting purchasing decisions away from conventional alternatives.
- Amyris's Position: This societal and regulatory shift creates a favorable market environment for Amyris, as its bio-based ingredients directly meet these growing demands, making them a more attractive and viable alternative to traditional substitutes.
Innovation in Alternative Production Methods
Innovation in alternative production methods, particularly in green chemistry and bio-based material extraction, presents an ongoing threat of substitution for Amyris. As new, potentially more efficient or cost-effective techniques emerge, they could offer comparable or superior products to those Amyris currently produces through its synthetic biology platform. For instance, advancements in enzymatic synthesis or fermentation processes developed by competitors could disrupt market share if they achieve significant cost advantages or performance improvements.
Amyris's strategy to mitigate this threat centers on its robust research and development pipeline and its established leadership in synthetic biology. By continuously innovating and bringing novel, cost-effective bio-based solutions to market, Amyris aims to maintain a competitive edge and preempt the adoption of substitute technologies. The company's focus on proprietary strain development and process optimization is key to staying ahead of evolving production methodologies.
- Ongoing advancements in green chemistry could yield alternative bio-based ingredients.
- Emerging extraction techniques might offer more economical routes to similar compounds.
- Amyris's R&D investment, a significant portion of its operational expenses, aims to counter these threats through continuous innovation.
- The company's leadership in synthetic biology provides a strong foundation for developing superior and cost-competitive bio-based products.
The threat of substitutes for Amyris's bio-based ingredients is multifaceted, primarily stemming from conventional petroleum-derived chemicals and, to a lesser extent, naturally extracted ingredients. While petrochemicals have historically held a cost advantage, increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products are leveling the playing field. For example, by mid-2024, over 60% of consumers in key Western markets expressed a willingness to pay a premium for eco-friendly goods, directly impacting the perceived value of bio-based alternatives.
Amyris's precision fermentation technology often produces molecules that are difficult to source sustainably from nature in the required purity and scale. This technological advantage, coupled with a strong R&D focus on proprietary strain development, helps mitigate the threat from natural extraction. The company's investment in innovation, a significant part of its operational budget, aims to maintain its leadership in synthetic biology and preempt the adoption of competing bio-based production methods.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantage | Amyris's Mitigation Strategy | Market Trend Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum-based Chemicals | Historically lower cost, widespread availability | Superior sustainability profile, higher purity, consistency | Increasing regulatory pressure on petrochemicals, growing consumer preference for bio-based |
| Naturally Extracted Ingredients | Perceived "naturalness" | Scalability, purity, and consistency difficult to achieve through natural means; proprietary molecule production | Demand for high-purity, bio-identical ingredients favors fermentation; natural extraction limitations in scale and purity |
| Emerging Green Chemistry/Bio-based Methods | Potential for cost efficiency, alternative production routes | Continuous R&D investment, leadership in synthetic biology, process optimization | Ongoing advancements could challenge market share if cost or performance advantages emerge |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a synthetic biology company like Amyris demands immense upfront capital for research, development, and advanced manufacturing facilities. Amyris, for instance, has invested heavily in its fermentation technology and global production network, creating a high barrier for newcomers.
The significant R&D expenditure required to develop novel bio-based molecules and optimize production processes deters potential entrants. In 2023, the synthetic biology market saw substantial venture capital funding, but the sheer scale of investment needed for commercial viability remains a key deterrent.
The synthetic biology sector is built upon intricate proprietary strain engineering, genetic constructs, and specialized fermentation processes. This creates a highly complex intellectual property (IP) landscape that can be a significant barrier for newcomers.
New entrants must either invest heavily in developing their own novel IP or navigate the costly and time-consuming process of licensing existing technologies. For instance, the cost of patent filing and maintenance can run into tens of thousands of dollars annually per patent family.
The synthetic biology sector, where companies like Amyris operate, requires a very specific and advanced skill set. Success hinges on deep knowledge in areas like molecular biology, metabolic engineering, and fermentation processes. This specialized scientific expertise is not easily acquired, creating a substantial hurdle for any new player looking to enter the market.
Building a team with this level of scientific proficiency is a considerable challenge. The scarcity of talent in these niche fields means that new entrants face a lengthy and costly process to assemble an experienced group. For instance, recruiting top-tier synthetic biologists can take months, and the competition for these individuals is fierce, driving up compensation costs.
This talent gap acts as a significant barrier to entry. Companies that can attract and retain this specialized workforce, much like established players, possess a distinct advantage. The time and resources needed to cultivate such expertise mean that new companies often struggle to match the innovation and operational efficiency of incumbents.
Regulatory Hurdles and Market Access
The threat of new entrants in the bio-based ingredients sector is significantly shaped by substantial regulatory hurdles and the complexities of market access. Launching novel bio-based ingredients, especially for sensitive applications like food, cosmetics, or pharmaceuticals, necessitates rigorous and often lengthy approval processes across multiple jurisdictions. These can include extensive testing for safety, efficacy, and environmental impact, adding considerable time and cost to market entry.
For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for novel food ingredients can take years and involve substantial investment in scientific data generation. Similarly, cosmetic ingredient regulations, like those in the European Union under REACH, require comprehensive dossiers detailing chemical properties and safety assessments. These barriers effectively deter many potential new players who lack the financial resources and regulatory expertise to navigate such demanding landscapes.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating diverse and evolving regulations across industries like food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals presents a significant barrier.
- Lengthy Approval Processes: Gaining necessary approvals for novel bio-based ingredients can span several years, demanding substantial investment.
- High Cost of Compliance: Meeting safety, efficacy, and environmental standards requires significant financial outlay for testing and documentation.
- Market Access Challenges: Securing shelf space and distribution channels in established markets can be difficult for new, unproven entrants.
Economies of Scale and Established Supply Chains
Established players like Amyris leverage significant economies of scale in their fermentation and downstream processing, making it difficult for newcomers to achieve comparable cost efficiencies. For instance, Amyris's large-scale manufacturing capabilities allow them to spread fixed costs over a greater volume of product, driving down per-unit production expenses.
Furthermore, Amyris has cultivated robust and often exclusive supply chain relationships for critical raw materials, such as specific sugars and nutrients required for their fermentation processes. These established networks provide a reliable and cost-effective source of inputs, a significant hurdle for new entrants attempting to secure similar quality and quantity of materials at competitive prices.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the substantial capital investment and time required to replicate Amyris's integrated production and distribution infrastructure. Building out comparable manufacturing capacity and securing reliable, large-volume supply chains would necessitate multi-million dollar investments, creating a high barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Amyris's large-scale fermentation facilities enable lower per-unit production costs, a benchmark difficult for new entrants to meet.
- Supply Chain Integration: Established relationships for raw materials and distribution networks provide Amyris with cost and reliability advantages.
- Capital Investment: Replicating Amyris's operational scale and supply chain security requires substantial upfront capital, deterring many potential competitors.
The threat of new entrants into the synthetic biology sector, where Amyris operates, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required for research, development, and advanced manufacturing. Amyris's substantial investments in proprietary fermentation technology and global production infrastructure create high barriers, deterring many potential competitors. For instance, establishing a commercial-scale fermentation facility can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
The intricate intellectual property landscape and the need for specialized scientific talent further complicate market entry. Developing novel bio-based molecules and optimizing production processes demand deep expertise in areas like metabolic engineering and fermentation science. In 2023, the synthetic biology market saw significant venture capital activity, but the sheer scale of investment needed for commercial viability remains a key deterrent for newcomers.
Regulatory complexities and market access challenges also act as formidable barriers. Gaining approvals for novel bio-based ingredients, particularly for food and cosmetic applications, involves lengthy and costly processes across multiple jurisdictions. The U.S. FDA approval for novel food ingredients, for example, can take years and require substantial investment in scientific data generation, effectively deterring new players without the necessary resources and expertise.
Economies of scale in production and integrated supply chains further solidify the position of established players like Amyris. Their large-scale manufacturing capabilities allow for lower per-unit costs, and established relationships for raw materials provide reliability and cost advantages. Replicating this operational scale and supply chain security necessitates substantial upfront capital, creating a high barrier to entry.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Amyris Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable sources.
We leverage data from regulatory filings, patent databases, and scientific publications to understand the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers in the biotechnology sector.