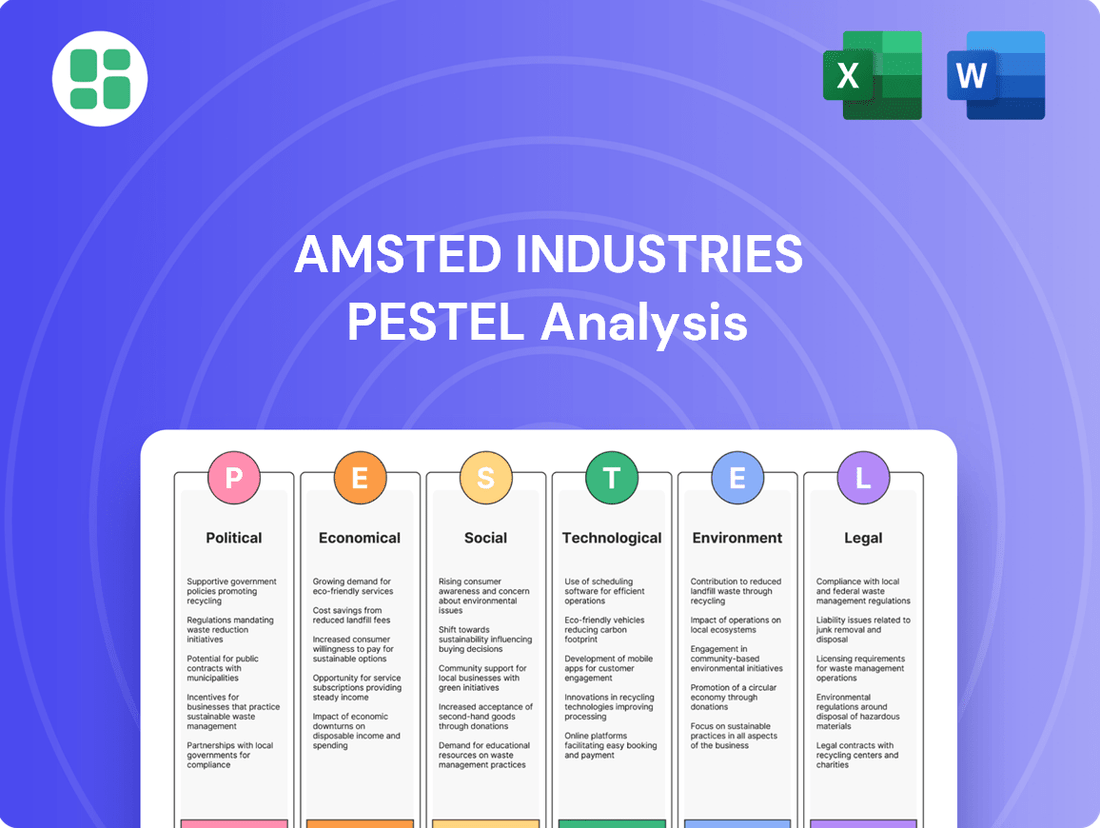
Amsted Industries PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amsted Industries Bundle
Uncover the intricate web of external forces shaping Amsted Industries's path forward. From evolving political landscapes to shifting economic tides and rapid technological advancements, understanding these PESTLE factors is crucial for strategic success. Download our comprehensive analysis to gain actionable intelligence and anticipate future challenges and opportunities.
Political factors
Government investment in large-scale infrastructure projects, especially in rail and road networks, directly impacts Amsted Industries' demand for heavy-duty components. Political budgeting decisions and national infrastructure plans, such as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law enacted in 2021, which allocates over $1 trillion to infrastructure improvements, create significant opportunities for Amsted's core markets.
Amsted Industries, with its global manufacturing footprint, is significantly influenced by evolving trade policies. The imposition or removal of tariffs on steel, a key raw material, directly impacts production costs. For instance, in 2024, ongoing discussions around global steel tariffs and trade agreements, such as potential adjustments to the Section 232 tariffs on steel imports into the United States, could lead to increased material expenses or create opportunities for more favorable sourcing.
Changes in international trade agreements can also affect Amsted's market access for its diverse product lines, ranging from rail components to industrial flow control solutions. Trade disputes or the renegotiation of existing pacts can introduce uncertainty, potentially disrupting supply chains and altering competitive dynamics in key markets. For example, shifts in trade relationships between major economies in 2024 could necessitate adjustments in Amsted's sourcing strategies and export market focus.
Evolving government regulations for the railroad and vehicular sectors directly shape Amsted Industries' product development. For instance, stricter emissions standards, like those being implemented in many regions by 2024-2025, necessitate advanced materials and designs for exhaust systems and engine components. Compliance ensures market access, while non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and lost business opportunities, impacting manufacturing costs and operational efficiency.
Geopolitical Stability
Geopolitical stability is a significant consideration for Amsted Industries, given its global manufacturing footprint and supply chain dependencies. Political instability in key regions can directly impact operations, as seen in the potential for trade disputes or disruptions in countries where Amsted sources raw materials or sells its products. For instance, heightened tensions in Eastern Europe in 2024 continued to pose risks to global energy prices and supply chains, indirectly affecting manufacturing costs and demand for Amsted's components in sectors like transportation and infrastructure.
Shifts in international relations and trade policies can also create uncertainty. Amsted’s reliance on international trade means that changes in tariffs or import/export regulations, potentially influenced by political realignments, could affect profitability. The ongoing geopolitical landscape in 2024 and into 2025 presents a complex environment where companies must remain agile to navigate potential disruptions.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Political unrest in regions critical for raw material sourcing, such as rare earth minerals or specialized alloys, could lead to price volatility and availability issues for Amsted's manufacturing processes.
- Market Access and Demand: Instability in major customer markets, like the automotive or rail industries, due to political factors can reduce demand for Amsted's specialized components.
- Investment Risk: Geopolitical tensions can increase the perceived risk of foreign direct investment, potentially impacting Amsted's strategic expansion plans or the stability of its existing international assets.
Industrial Policy Shifts
Government shifts in industrial policy, such as incentives for domestic manufacturing or reshoring initiatives, can significantly impact Amsted Industries. For instance, policies promoting the resurgence of American manufacturing could offer Amsted a competitive edge by reducing reliance on overseas production and potentially lowering logistical costs.
Conversely, a strong focus on specific sectors, like green transportation, might present Amsted with opportunities to align its product development and market strategy. The US government's Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, with its substantial investments in clean energy and manufacturing, exemplifies this, potentially benefiting Amsted's rail sector through increased demand for components in modernized freight and passenger transport systems.
- Reshoring Incentives: Policies encouraging companies to bring production back to the US could reduce Amsted's supply chain risks and costs.
- Green Transportation Support: Government funding for electric vehicles and sustainable infrastructure may boost demand for Amsted's specialized components in these growing markets.
- Domestic Content Requirements: Mandates for using domestically sourced materials in government-funded projects could favor Amsted's manufacturing capabilities.
Government investment in infrastructure, like the over $1 trillion allocated by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, directly fuels demand for Amsted's rail and heavy-duty components. Evolving trade policies and tariffs, particularly on steel, impact Amsted's raw material costs, with ongoing discussions in 2024 potentially altering sourcing dynamics. Stricter emissions standards for transportation sectors by 2024-2025 necessitate advanced product designs, influencing manufacturing costs and market access.
Geopolitical stability remains a concern for Amsted's global operations, as tensions in 2024 can disrupt supply chains and affect energy prices, indirectly impacting manufacturing costs. Government industrial policies, such as reshoring incentives and support for green transportation, as seen with the US Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, can create competitive advantages and drive demand in specific Amsted markets.
| Political Factor | Impact on Amsted Industries | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Spending | Increased demand for rail and heavy components | Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocating >$1 trillion |
| Trade Policies/Tariffs | Impacts raw material costs (e.g., steel) | Ongoing 2024 discussions on Section 232 tariffs |
| Environmental Regulations | Drives product innovation (e.g., emissions standards) | Stricter standards being implemented by 2024-2025 |
| Industrial Policy (Reshoring) | Potential cost reduction and supply chain stability | US government initiatives promoting domestic manufacturing |
| Green Transportation Support | Boosts demand for specialized components | Inflation Reduction Act (2022) investing in clean energy |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors influencing Amsted Industries, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
A concise PESTLE analysis for Amsted Industries provides a clear overview of external factors, acting as a pain point reliever by simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
Global economic growth is a significant driver for Amsted Industries, as its industrial components are integral to construction, transportation, and manufacturing sectors. A robust global economy, marked by expansions in these key areas, directly correlates with increased demand for Amsted's products, boosting sales volumes and revenue. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a slight deceleration from 3.1% in 2023, but still indicating a stable, albeit moderate, expansion.
Conversely, economic contractions or slowdowns in major markets can negatively impact Amsted's performance. A downturn in construction activity, for example, due to rising interest rates or reduced infrastructure spending, would likely lead to lower demand for Amsted's building components. Similarly, a slowdown in global trade or manufacturing output, perhaps influenced by geopolitical tensions or supply chain disruptions, can directly reduce the need for transportation and industrial machinery parts.
Amsted Industries, a major player in the manufacturing sector, is significantly exposed to the volatility of raw material prices, particularly steel, iron, and other metals. Fluctuations in these essential inputs directly impact production costs, creating either significant cost pressures or potential opportunities. For instance, the average price of hot-rolled coil steel, a key component for Amsted's products, saw considerable swings. In early 2024, prices remained relatively stable compared to the peaks of 2022, but market analysts projected potential increases later in the year due to anticipated demand shifts and geopolitical factors influencing global supply chains.
The dynamics of global commodity markets, driven by supply-demand imbalances and geopolitical events, directly influence Amsted's profitability. For example, disruptions in mining operations or trade disputes can lead to sudden price spikes, squeezing Amsted's margins if these costs cannot be passed on to customers. Conversely, periods of lower commodity prices can offer a competitive advantage by reducing manufacturing expenses, thereby enhancing profitability and potentially allowing for more aggressive pricing strategies.
Rising interest rates, such as the Federal Reserve's benchmark rate hovering around 5.25%-5.50% in early 2024, can significantly dampen capital expenditure by Amsted's customers. Higher borrowing costs make large investments in new railcars, construction equipment, or vehicle fleets less attractive, potentially slowing demand for Amsted's manufactured components.
The broader investment climate directly impacts Amsted's financing capabilities. A robust market may allow Amsted to secure favorable terms for debt or equity financing, supporting its expansion and R&D initiatives. Conversely, a volatile or uncertain investment climate, perhaps influenced by global economic slowdown fears, could increase borrowing costs and make capital more scarce for Amsted's own growth plans.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions continue to pose significant economic challenges, impacting Amsted Industries through increased logistics costs and production delays. Port congestion and labor shortages, prevalent throughout 2024, have escalated shipping expenses and extended lead times, directly affecting Amsted's operational efficiency and its capacity to fulfill customer orders promptly. Geopolitical events further exacerbate these issues, creating uncertainty and driving up the cost of raw materials.
The economic fallout from these disruptions is substantial. For instance, global shipping costs saw significant volatility in late 2024 and early 2025, with certain routes experiencing price surges of over 50% compared to pre-pandemic levels. This directly translates to higher input costs for Amsted and can pressure profit margins if these costs cannot be fully passed on to customers. The ongoing strain on global logistics networks means that reliable and timely delivery of components remains a critical concern for manufacturers like Amsted.
- Increased Costs: Higher freight rates and raw material prices due to supply chain bottlenecks.
- Production Delays: Extended lead times for critical components impacting manufacturing schedules.
- Reduced Availability: Difficulty in securing necessary materials and parts, potentially leading to stockouts.
- Lowered Demand Fulfillment: Inability to meet customer orders on time, risking lost sales and market share.
Inflationary Pressures
Rising inflation in 2024 and 2025 directly impacts Amsted Industries by increasing its operating expenses. Costs for raw materials, energy, and labor are expected to climb, potentially squeezing profit margins if not effectively managed. For instance, the U.S. Producer Price Index (PPI) for manufactured goods saw significant increases throughout 2024, indicating upstream cost pressures for industrial companies like Amsted.
Furthermore, inflation erodes customer purchasing power. This could lead to delayed or reduced capital expenditure plans for Amsted’s clients in sectors like transportation, construction, and manufacturing. Companies facing their own inflationary challenges may also reduce orders or seek more cost-effective alternatives, impacting Amsted's sales volumes and revenue streams.
- Increased Input Costs: Higher prices for steel, aluminum, and energy directly affect Amsted's manufacturing expenses.
- Labor Cost Escalation: Wage inflation, driven by a tight labor market, adds to Amsted's operational overhead.
- Pricing Strategy Adaptation: Amsted must balance passing on higher costs to customers with maintaining competitive pricing to preserve market share.
- Customer Demand Sensitivity: Inflationary pressures on Amsted's customers can lead to reduced demand for its products and services.
Inflationary pressures in 2024 and 2025 are directly increasing Amsted Industries' operating costs, particularly for raw materials like steel and energy, as well as labor. This rise in expenses, reflected in a notable increase in the U.S. Producer Price Index for manufactured goods throughout 2024, challenges Amsted's profit margins unless costs are effectively passed on to customers. Additionally, inflation can diminish customer purchasing power, potentially leading to reduced capital expenditures and lower demand for Amsted's components.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Amsted Industries | 2024/2025 Data Point |
| Global Economic Growth | Drives demand for industrial components in construction, transportation, and manufacturing. | IMF projected global growth of 3.2% in 2024. |
| Raw Material Prices | Directly affects production costs and profitability. | Hot-rolled coil steel prices saw considerable swings, with projections for increases in late 2024. |
| Interest Rates | Influences customer capital expenditure and Amsted's financing costs. | Federal Reserve benchmark rate around 5.25%-5.50% in early 2024. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increases logistics costs, causes production delays, and impacts material availability. | Global shipping costs experienced surges over 50% on certain routes in late 2024/early 2025 compared to pre-pandemic levels. |
| Inflation | Raises operating expenses and can reduce customer demand. | U.S. PPI for manufactured goods showed significant increases throughout 2024. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Amsted Industries PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This Amsted Industries PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company's operations and strategic direction.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the external forces shaping Amsted Industries, from regulatory changes to market trends.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same document you’ll download after payment. This detailed PESTLE analysis will equip you with the insights needed to navigate the complex business landscape Amsted Industries operates within.
Sociological factors
Demographic shifts are presenting challenges for Amsted Industries in securing a consistent pool of skilled manufacturing and engineering talent. The aging workforce in traditional industrial sectors, coupled with a declining interest in vocational trades among younger generations, contributes to a widening skills gap. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a shortage of over 500,000 skilled manufacturing workers by 2030, a trend directly impacting companies like Amsted that rely on specialized expertise.
This skills gap can significantly hinder Amsted's production efficiency, as a lack of qualified personnel in areas like advanced machining or industrial automation can lead to production bottlenecks and slower adoption of new technologies. Furthermore, it poses a risk to innovation, as a shortage of engineers and technicians with cutting-edge skills may limit the company's ability to develop and implement new product designs and manufacturing processes.
Growing public awareness and demand for environmentally responsible products are increasingly shaping Amsted's end-markets. Consumers and businesses alike are prioritizing sustainability, which translates into a need for components that are energy-efficient, built for longevity, and designed with recyclability in mind. For instance, the rail industry is seeing a push for lighter, more fuel-efficient rolling stock, and the automotive sector is heavily invested in electric vehicle technology, both areas where Amsted's innovative material solutions can offer a competitive edge.
Public expectations for safety in transportation and infrastructure are constantly rising, directly impacting regulatory frameworks and the demand for dependable components. Amsted Industries, with its deep roots in these sectors, must navigate this evolving landscape where a strong reputation for safety and compliance is paramount for market success.
For instance, the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) continues to emphasize safety improvements, with initiatives aimed at reducing derailments. In 2023, the FRA reported a slight decrease in overall train accidents compared to previous years, but the focus on preventing catastrophic failures remains intense. This heightened scrutiny means Amsted's commitment to rigorous testing and adherence to standards like AAR (Association of American Railroads) specifications is not just a compliance issue but a critical differentiator, influencing customer purchasing decisions and investor confidence.
Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Global urbanization continues to fuel a consistent demand for Amsted Industries' diverse product portfolio. As more people move to cities, there's a growing need for improved public transportation systems, commercial spaces, and efficient freight movement, all areas where Amsted's components play a crucial role. For instance, the United Nations projects that by 2050, 68% of the world's population will reside in urban areas, a trend that directly translates into increased investment in the infrastructure supporting these growing metropolises.
This urban shift necessitates substantial infrastructure development, creating significant market opportunities for Amsted. Investments in new and upgraded rail lines, bridges, and logistics networks are essential to accommodate population growth and economic activity. In 2024, global infrastructure spending was estimated to reach trillions of dollars, with a significant portion allocated to urban development projects, directly benefiting companies like Amsted that supply critical components for these initiatives.
- Urban Population Growth: The UN estimates 68% global urbanization by 2050, driving demand for transit and construction.
- Infrastructure Investment: Trillions are invested globally in infrastructure annually, with urban projects a major focus.
- Amsted's Role: The company's products are vital for rail, transit, and logistics infrastructure, supporting these growth trends.
- Market Opportunity: Expanding urban centers directly correlate with increased demand for Amsted's specialized manufacturing solutions.
Labor Relations and Unionization
Labor relations significantly impact Amsted Industries' operational stability and cost structure. Unionization levels and the nature of collective bargaining agreements directly influence wage rates, benefits, and work rules, which are critical components of the company's cost base. For instance, the manufacturing sector, where Amsted operates, often sees robust union presence, necessitating careful negotiation to maintain competitive labor costs.
The potential for labor disputes, including strikes or slowdowns, poses a direct threat to production schedules and overall business performance. Amsted must actively manage these relationships to mitigate disruptions. As of recent data, union membership rates in the U.S. manufacturing sector have seen fluctuations, but remain a key consideration for companies like Amsted, with specific industry agreements dictating terms. For example, in 2023, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that approximately 8.7% of all wage and salary workers in manufacturing were represented by unions.
- Unionized Workforce Impact: The proportion of Amsted's workforce that is unionized directly affects its flexibility in implementing operational changes and managing labor costs.
- Collective Bargaining Agreements: The terms of existing and upcoming collective bargaining agreements are crucial for forecasting labor expenses and potential operational disruptions.
- Labor Law Changes: Shifts in labor legislation, such as those concerning union organizing or worker rights, could alter the landscape of labor relations and Amsted's engagement with its workforce.
- Industry Benchmarks: Comparing Amsted's labor practices and costs against industry averages, particularly those in heavy manufacturing and metal fabrication, provides context for its competitive positioning.
Societal attitudes towards manufacturing careers are evolving, with a growing emphasis on safety, work-life balance, and technological advancement influencing recruitment. Companies like Amsted must adapt their employer branding and training programs to attract and retain talent in a competitive labor market.
Public perception of corporate social responsibility also plays a role, with stakeholders increasingly scrutinizing companies' ethical practices, environmental impact, and community engagement. Amsted's commitment to sustainability and responsible operations can enhance its brand reputation and appeal to a broader customer and investor base.
The increasing demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products influences consumer choices and B2B purchasing decisions. Amsted's focus on durable, long-lasting components and efficient manufacturing processes aligns with these societal trends, potentially driving market share.
Changing consumer preferences toward personalized and customized products can create opportunities for Amsted to leverage its engineering capabilities and flexible manufacturing to meet niche market demands.
Technological factors
Amsted Industries is navigating the significant impact of automation and Industry 4.0 adoption on its manufacturing operations. The increasing integration of robotics and smart technologies directly influences production efficiency and Amsted's competitive edge in the market. For instance, by 2024, the global manufacturing automation market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the scale of this technological shift.
This trend necessitates substantial investments in advanced machinery and the digital integration of Amsted's facilities. Such upgrades are crucial for optimizing workflows, reducing operational costs, and maintaining product quality. Companies embracing Industry 4.0 principles often report significant gains in productivity, with some seeing improvements upwards of 20% in specific automated processes.
Breakthroughs in material science, like the development of advanced high-strength steels and lightweight composites, directly impact Amsted Industries' product design and performance. For instance, the automotive sector, a key market for Amsted, is increasingly adopting lighter materials to improve fuel efficiency, pushing component manufacturers to innovate. Amsted's continued investment in research and development is crucial for integrating these next-generation materials into its railcar, vehicle, and industrial components, ensuring competitive advantage and enhanced product capabilities.
Amsted Industries' operational capabilities are significantly enhanced by the ongoing digitalization of its manufacturing processes. Technologies like Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) allow for greater precision in component design and production, directly impacting the quality of their railcar, engine, and other industrial components.
The integration of simulation tools and digital twins enables Amsted to virtually test and optimize production lines before physical implementation. This not only reduces material waste but also accelerates the product development cycle, ensuring Amsted can respond more quickly to market demands and technological advancements in sectors like advanced rail technology and industrial equipment.
Predictive Maintenance and IoT Integration
Amsted Industries can leverage the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and predictive maintenance technologies to transform its industrial components. By embedding sensors, components can continuously transmit data on their performance and wear, enabling Amsted to offer proactive maintenance services. This shift from reactive repairs to predictive upkeep creates new revenue streams and enhances customer value.
The data collected through IoT integration can also inform product design. For instance, insights into component failure patterns can guide Amsted in developing more robust and efficient designs for future product generations. This data-driven approach to innovation is crucial in the evolving industrial landscape, where uptime and reliability are paramount.
- New Service Opportunities: Predictive maintenance services based on real-time component data.
- Product Design Influence: Data-driven improvements in component durability and performance.
- Enhanced Customer Value: Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime for clients.
- Market Trend Alignment: Responding to the growing demand for smart, connected industrial solutions.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, presents a significant technological shift for Amsted Industries. This technology offers the potential to streamline the production of specialized or low-volume components, reducing lead times and tooling costs. For instance, Amsted could leverage 3D printing for rapid prototyping of new railcar parts, accelerating product development cycles. The global 3D printing market was valued at approximately $17.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $60 billion by 2030, indicating substantial growth and adoption potential.
Furthermore, 3D printing can fundamentally alter Amsted's supply chain dynamics. By enabling on-demand production closer to the point of need, it could minimize inventory holding and logistics expenses. This also opens doors for greater customization of industrial components, catering to specific client requirements more efficiently than traditional mass production methods. The aerospace sector, a key industrial market, saw significant adoption with companies reporting up to 70% cost reductions for certain parts through additive manufacturing in recent years.
- Component Customization: 3D printing allows for tailored production of unique or low-volume parts, ideal for specialized industrial applications.
- Supply Chain Disruption: On-demand manufacturing closer to the customer can reduce reliance on extended supply chains and inventory.
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerates design and testing phases for new products, leading to faster market entry.
- Cost Efficiency: Potential for reduced tooling costs and material waste, especially for complex geometries.
Technological advancements are reshaping manufacturing, driving Amsted Industries to embrace automation and Industry 4.0. The global market for industrial automation was expected to exceed $200 billion by 2024, underscoring the scale of this transformation and Amsted's need to invest in smart technologies to maintain competitiveness and efficiency.
Innovations in material science are also critical. As industries like automotive push for lighter, stronger materials to enhance fuel efficiency, Amsted must integrate advanced steels and composites into its product lines. This focus on R&D ensures its components meet evolving performance demands.
Digitalization, including CAD/CAM and simulation tools, allows for greater precision and faster product development cycles, reducing waste and improving quality. The integration of IoT sensors and predictive maintenance offers new service revenue streams and data-driven product design improvements, enhancing customer value and market alignment.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, presents opportunities for streamlined production of specialized parts, reducing lead times and costs. The global 3D printing market, projected to reach $60 billion by 2030, highlights the potential for on-demand production and supply chain optimization.
| Technology Area | Market Growth Projection (2023-2030) | Impact on Amsted Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Automation | Exceeding $200 billion by 2024 | Increased efficiency, need for investment in smart factories |
| Advanced Materials | Growing demand in automotive and aerospace | Product innovation, improved performance and fuel efficiency |
| Digitalization (IoT, AI) | Rapid adoption across industries | Predictive maintenance, data-driven design, new service models |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Projected to reach $60 billion by 2030 | On-demand production, supply chain optimization, rapid prototyping |
Legal factors
Amsted Industries operates within a rigorous legal framework for product liability, especially concerning its industrial components used in critical sectors like rail, vehicular, and construction. Stringent safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) for rail components, directly impact design, manufacturing, and quality control to mitigate risks. The potential for significant lawsuits stemming from product failures, which could lead to substantial financial penalties and reputational damage, necessitates an unwavering commitment to safety and compliance.
Amsted Industries navigates a complex web of legal obligations concerning environmental protection. This includes stringent regulations on air and water emissions, hazardous waste disposal, and the management of chemicals used in its manufacturing processes, particularly in sectors like rail and vehicle components. Failure to comply can result in significant fines; for instance, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) collected over $11.5 billion in fines and penalties in fiscal year 2023 for environmental violations.
The company must ensure adherence to these environmental laws across its diverse global footprint, which involves understanding and implementing varying national and regional standards. Amsted's commitment to sustainability likely includes robust internal compliance programs and audits to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance, which could otherwise lead to operational disruptions and reputational damage.
Amsted Industries must navigate a complex web of labor and employment laws, impacting everything from compensation to workplace safety. For instance, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) dictates minimum wage and overtime pay, directly influencing Amsted's operational costs. In 2024, the federal minimum wage remained at $7.25 per hour, though many states and cities have higher rates, potentially increasing labor expenses for Amsted's facilities in those locations.
Workplace safety regulations, primarily enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), are critical for Amsted, given its manufacturing operations. OSHA's general industry standards aim to prevent accidents and injuries, requiring significant investment in safety protocols and equipment. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines; in 2024, willful violations could result in penalties up to $15,625 per violation, with repeat or willful violations reaching as high as $156,259.
Anti-discrimination laws, such as Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, prohibit unfair treatment based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin, shaping Amsted's hiring and HR practices. Furthermore, if Amsted engages in collective bargaining, the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) governs union relations and contract negotiations, potentially affecting labor costs and operational flexibility.
Antitrust and Competition Laws
Antitrust and competition laws are crucial for Amsted Industries, as they dictate fair play in the industrial components market. These regulations prevent monopolies and anti-competitive behavior, ensuring a level playing field for all players. Amsted must carefully navigate these legal frameworks when formulating its market strategies and considering any acquisitions to avoid penalties and maintain its competitive edge.
The company's approach to mergers and acquisitions is heavily scrutinized under these laws. For instance, in 2023, global antitrust regulators reviewed a significant number of M&A deals, with a particular focus on industries with concentrated market power. Amsted's compliance ensures its growth strategies align with legal boundaries, safeguarding against potential legal challenges that could disrupt operations or impact its financial standing.
- Compliance with antitrust regulations is paramount for Amsted's market strategies and acquisition plans.
- These laws aim to prevent monopolies and ensure fair competition within the industrial components sector.
- Regulatory bodies actively monitor M&A activity, impacting how companies like Amsted pursue growth.
- Adherence to competition laws is vital for maintaining operational integrity and avoiding legal repercussions.
International Trade Laws and Sanctions
Amsted Industries navigates a complex web of international trade laws and sanctions, which directly impact its global operations. Compliance with import/export controls and customs regulations is paramount for maintaining smooth supply chains and market access. For instance, the United States, a key market for Amsted, actively enforces trade restrictions on certain countries, necessitating rigorous due diligence in sourcing and sales activities.
Economic sanctions, such as those imposed by the US and the European Union, can significantly disrupt international business. These sanctions may restrict trade with specific entities or nations, affecting Amsted's ability to sell products or procure materials globally. In 2024, the evolving geopolitical landscape continues to introduce new sanctions regimes, requiring constant monitoring and adaptation of Amsted's international trade strategies to avoid penalties and ensure business continuity.
- Compliance Burden: Amsted must invest in robust compliance programs to adhere to diverse international trade regulations, including those from the US Department of Commerce and the EU's Directorate-General for Trade.
- Sanctions Impact: The company faces potential disruptions to its global sales and sourcing networks due to sanctions targeting countries like Russia or Iran, impacting its ability to conduct business in those regions.
- Customs Duties & Tariffs: Fluctuations in customs duties and tariffs, driven by trade policies and agreements, directly influence the cost of imported components and the competitiveness of Amsted's exported products.
- Geopolitical Risk: Increased geopolitical tensions in 2024 and 2025 necessitate proactive risk management to mitigate the impact of sudden regulatory changes or trade disputes on Amsted's international operations.
Amsted Industries must navigate a complex landscape of intellectual property laws, safeguarding its innovations in areas like advanced manufacturing and material science. Patent protection is crucial for its proprietary technologies, particularly in the rail and vehicle component sectors, where innovation drives competitive advantage. Failure to protect intellectual property can lead to loss of market share and revenue, underscoring the need for robust legal strategies.
Contract law significantly shapes Amsted's relationships with suppliers, customers, and partners. Clear, enforceable contracts are essential for managing supply chain agreements, sales contracts, and joint ventures, ensuring operational stability and mitigating disputes. In 2024, the importance of well-defined contractual terms remains high, especially in volatile global markets where supply chain disruptions are frequent.
Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations are increasingly critical, given the digital nature of modern business operations and customer interactions. Amsted must comply with laws like the GDPR and CCPA to protect sensitive company and customer data. The escalating threat of cyberattacks in 2024 and 2025 means significant investment in cybersecurity measures is a legal and operational imperative.
Environmental factors
Amsted Industries faces increasing pressure from global initiatives and regulatory bodies to reduce its carbon footprint, directly impacting its manufacturing operations and energy usage. The company is actively exploring and implementing cleaner energy sources and more efficient production methods to meet evolving carbon emission reduction targets. For example, many industrial manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient machinery and exploring renewable energy procurement options to align with sustainability goals.
Amsted Industries faces increasing pressure to manage industrial waste generated from its manufacturing processes, with a growing global focus on circular economy principles. The company is actively exploring strategies for waste reduction and enhanced recycling programs across its operations. For instance, in 2024, the manufacturing sector globally saw a 7% increase in investments towards sustainable waste management solutions, a trend Amsted is likely aligning with.
Designing components for recyclability and reuse is becoming a key strategic imperative. This approach not only minimizes environmental impact but also presents opportunities for resource efficiency and potential cost savings. By 2025, it's projected that companies integrating circular design principles into their product lifecycles could see up to a 15% reduction in raw material costs.
Amsted Industries, like many industrial manufacturers, faces increasing pressure from resource scarcity. The global demand for key metals and minerals, crucial for their casting and manufacturing processes, continues to rise, impacting availability and price. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in 2024 that demand for critical minerals like copper and nickel, essential for many industrial applications, is projected to more than double by 2040.
To mitigate these environmental challenges, Amsted actively manages its supply chain with a focus on responsible and sustainable sourcing. This involves rigorous supplier assessments to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and ethical labor practices. The company's commitment to reducing its environmental footprint is demonstrated through initiatives aimed at optimizing material usage and exploring alternative, more sustainable inputs where feasible.
Climate Change Impact on Infrastructure
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as floods, hurricanes, and heatwaves, directly challenge the durability and performance of critical infrastructure. Amsted Industries, through its various segments, designs components for sectors like transportation and energy, which are particularly vulnerable. For instance, railway track components must maintain integrity under more extreme temperature fluctuations, and bridge bearings need to withstand higher wind loads and increased moisture exposure. In 2024, the global cost of natural disasters exceeded $100 billion, highlighting the growing need for resilient infrastructure solutions.
Amsted's commitment to material science and engineering aims to address these evolving demands. Their products are developed with an eye toward longevity and reduced maintenance in increasingly harsh environments. This includes advancements in corrosion resistance for components exposed to saltwater during coastal storms or increased de-icing salts in winter. The company's focus on robust design ensures that their solutions continue to function reliably, even as climate patterns shift, mitigating potential disruptions for their end-users.
Key considerations for Amsted's infrastructure components in the face of climate change include:
- Enhanced material resilience: Developing alloys and coatings that resist extreme temperatures, moisture, and corrosive elements.
- Structural integrity under stress: Designing components to withstand increased physical forces from high winds, flooding, and seismic activity.
- Adaptability to changing conditions: Ensuring products can perform consistently across a wider range of environmental parameters than previously anticipated.
Energy Efficiency Mandates
Amsted Industries is navigating an increasingly stringent regulatory landscape driven by energy efficiency mandates. These regulations are pushing industrial operations and product development towards lower energy consumption. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy's Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) office continues to set ambitious targets for industrial energy productivity, aiming for significant reductions in energy intensity across manufacturing sectors by 2030. Amsted's commitment to optimizing its manufacturing processes directly addresses this by seeking to reduce energy usage per unit of output.
The company's product portfolio also reflects this environmental push. Amsted develops components that enhance energy efficiency within the railroad, vehicular, and construction industries. For example, advancements in wheelset technology for railcars can lead to reduced rolling resistance, thereby lowering fuel consumption for trains. Similarly, components designed for commercial vehicles and construction equipment are increasingly engineered to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and meet evolving environmental standards.
Key areas of focus for Amsted related to energy efficiency mandates include:
- Manufacturing Process Optimization: Implementing technologies and practices to lower energy consumption in Amsted's foundries and manufacturing plants.
- Product Innovation: Developing components that contribute to fuel efficiency and reduced environmental impact in end-use applications.
- Regulatory Compliance: Staying ahead of and adhering to evolving energy efficiency standards and environmental regulations across its operating regions.
- Supply Chain Engagement: Collaborating with suppliers to ensure materials and processes also meet energy efficiency goals.
Amsted Industries is increasingly focused on reducing its environmental footprint, particularly concerning carbon emissions and waste management, driven by global sustainability initiatives and regulatory pressures. The company is investing in cleaner energy and more efficient production methods, mirroring a broader trend in manufacturing where investments in sustainable waste management solutions saw a 7% increase globally in 2024.
Designing for recyclability and reuse is a growing priority, with projections suggesting that companies adopting circular design principles could achieve up to a 15% reduction in raw material costs by 2025. Resource scarcity, especially for critical minerals like copper and nickel, presents a challenge, as demand is expected to more than double by 2040 according to the IEA, prompting Amsted to focus on responsible sourcing and material efficiency.
Extreme weather events are also impacting infrastructure, necessitating components with enhanced resilience and adaptability to harsher conditions. Amsted's material science advancements aim to meet these needs, ensuring product longevity and reliable performance in the face of climate change, a factor underscored by the over $100 billion cost of natural disasters globally in 2024.
Energy efficiency mandates are shaping Amsted's operations and product development, encouraging lower energy consumption in manufacturing and the creation of components that improve fuel economy in end-use applications. This aligns with ambitious energy productivity targets set by bodies like the U.S. Department of Energy's EERE office.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Amsted Industries | Industry Trend / Data Point (2024-2025) |
| Carbon Emissions Reduction | Pressure to lower operational carbon footprint | Global manufacturing investment in sustainable waste management up 7% (2024) |
| Waste Management & Circularity | Focus on waste reduction and recycling programs | Circular design adoption could reduce raw material costs by 15% by 2025 |
| Resource Scarcity | Rising demand and price for critical minerals | Critical mineral demand projected to more than double by 2040 (IEA) |
| Climate Change & Extreme Weather | Need for resilient infrastructure components | Natural disaster costs exceeded $100 billion globally (2024) |
| Energy Efficiency Mandates | Drive for lower energy consumption in manufacturing and products | Ambitious energy productivity targets set by EERE |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Amsted Industries is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from official government publications, reputable financial news outlets, and industry-specific market research reports. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company.