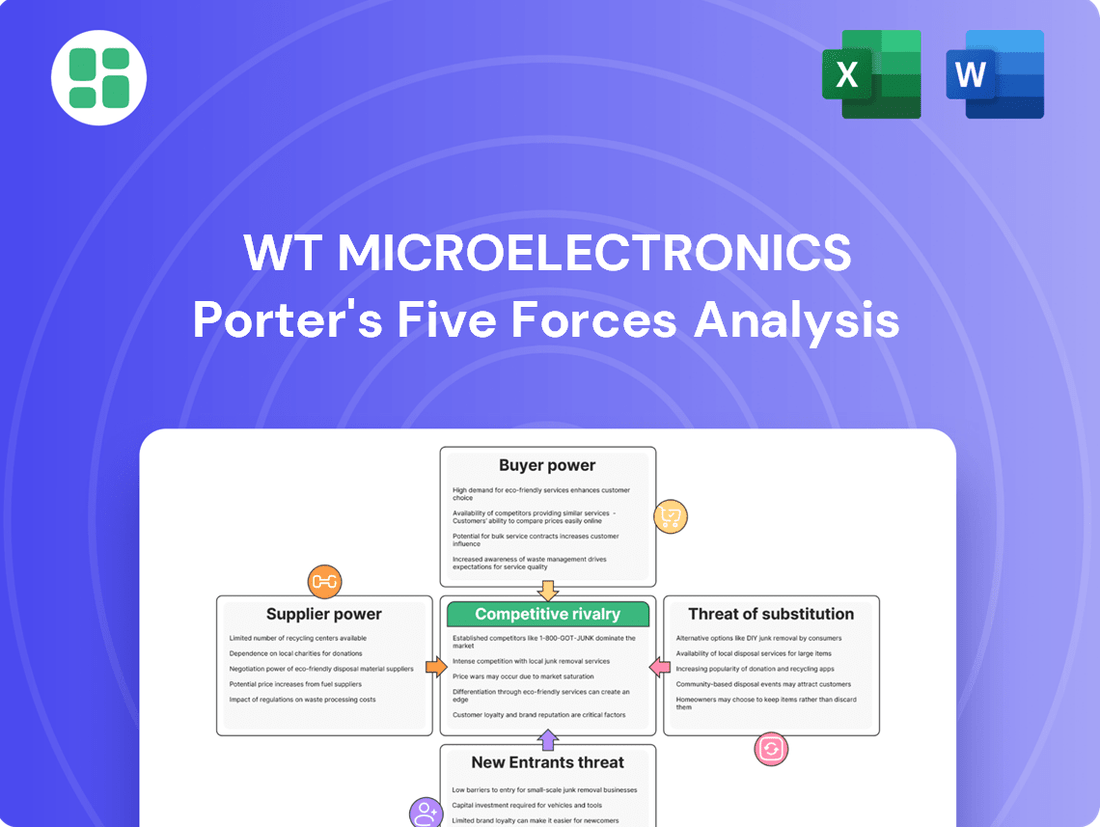
WT Microelectronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
WT Microelectronics Bundle
WT Microelectronics operates in a dynamic semiconductor distribution landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping WT Microelectronics’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The semiconductor supply chain is highly concentrated, with a handful of giants like TSMC, Samsung, Intel, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm holding significant sway. These companies are crucial suppliers for distributors such as WT Microelectronics, and their dominance translates into considerable bargaining power.
This power is amplified for specialized components, particularly those critical for AI acceleration and high-bandwidth memory (HBM). Demand for these advanced chips is so robust that many are already booked through 2025, giving suppliers the upper hand in pricing and allocation decisions.
Furthermore, the proprietary intellectual property and advanced manufacturing processes employed by these leading semiconductor firms create unique offerings that are difficult for distributors to replicate or substitute. This uniqueness further restricts the alternatives available to companies like WT Microelectronics, strengthening the suppliers' bargaining position.
WT Microelectronics likely faces significant switching costs when changing core suppliers, a common challenge in the semiconductor distribution industry. These costs can encompass the rigorous process of qualifying new components, which involves extensive testing and validation to ensure compatibility and performance. Furthermore, re-certifying entire supply chains to meet industry standards and regulatory requirements adds another layer of expense and time.
The potential need to re-design customer solutions, if a new supplier's components differ significantly, represents a substantial investment for WT Microelectronics. This could involve engineering efforts, new product development cycles, and extensive customer collaboration. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to grapple with supply chain complexities, making supplier diversification a strategic, albeit costly, consideration for distributors.
Consequently, building and maintaining robust, long-term relationships with established semiconductor manufacturers is paramount for WT Microelectronics. These partnerships are vital for securing a consistent and reliable supply of critical components, which directly impacts WT Microelectronics' ability to meet customer demand and maintain its market position. Such relationships often translate into more favorable pricing and access to cutting-edge technologies, directly influencing the company's profitability and competitive edge.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while a theoretical concern, is generally low for WT Microelectronics. While large semiconductor manufacturers could potentially bypass distributors by selling directly to Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) or Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), the operational complexity and cost of managing such a broad customer base and intricate logistics make this impractical for most. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor market saw continued demand for specialized distribution services, highlighting the value proposition of intermediaries.
Importance of Volume to Suppliers
WT Microelectronics' substantial purchasing volume makes it a key client for numerous semiconductor suppliers. This scale grants WT Microelectronics a degree of negotiating power, particularly for more common components where supply is ample. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry saw continued strong demand for AI-related chips, but also a stabilization in demand for other segments, potentially shifting leverage for those specific product categories.
However, the bargaining power of suppliers remains a significant factor, especially concerning advanced and in-demand technologies. For cutting-edge products, where demand frequently outstrips production capacity, suppliers can dictate terms more effectively. This dynamic is evident in the ongoing supply chain constraints for high-performance computing processors and specialized memory modules, where WT Microelectronics, despite its volume, faces limited leverage.
The importance of volume to suppliers can be illustrated by these points:
- Key Customer Status: WT Microelectronics' large order quantities solidify its position as a crucial customer for many semiconductor manufacturers, influencing supplier willingness to negotiate.
- Leverage on Standard Components: For widely available chips, WT Microelectronics can leverage its volume to secure more favorable pricing and allocation terms.
- Supplier Dominance in Niche Markets: For highly specialized or new-technology components, suppliers often retain significant power due to limited production and high demand, reducing WT Microelectronics' leverage.
- Market Dynamics Influence: Overall market conditions, such as the semiconductor shortage experienced in recent years and its subsequent easing in certain sectors in 2024, directly impact the balance of power between WT Microelectronics and its suppliers.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. For many semiconductor components, particularly specialized chips, there are few, if any, readily available substitutes. Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) often require very specific integrated circuits (ICs) that are integral to their product designs, making direct substitution difficult or impossible without substantial redesign efforts.
This scarcity of direct substitutes for the core products distributed by WT Microelectronics inherently strengthens the bargaining position of the semiconductor manufacturers themselves. They can command higher prices and more favorable terms when customers have limited alternatives for essential components. For instance, in 2024, the demand for advanced AI chips outstripped supply, allowing leading manufacturers to dictate terms more effectively.
However, WT Microelectronics mitigates this supplier power by curating a diverse portfolio of components from a wide array of semiconductor manufacturers. This strategy reduces its absolute dependence on any single supplier. By offering a broad selection of chips from multiple sources, WT Microelectronics can negotiate more effectively and shift sourcing if one supplier becomes too demanding. For example, if a particular supplier of memory chips raises prices significantly, WT Microelectronics can leverage its relationships with other memory manufacturers to maintain competitive pricing for its clients.
- Limited Substitutes: Many semiconductor components, especially custom or high-performance chips, lack direct substitutes, increasing supplier leverage.
- OEM/ODM Design Dependence: Product designs are often locked into specific chip architectures, reducing flexibility for buyers.
- Supplier Strength: Semiconductor manufacturers with proprietary technology or dominant market share possess considerable bargaining power due to the lack of alternatives.
- WT Microelectronics' Mitigation: Offering a broad product range from multiple suppliers helps WT Microelectronics reduce its reliance on any single entity, thereby lessening supplier bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers to WT Microelectronics is substantial, particularly for advanced components like AI chips and HBM. Leading manufacturers such as TSMC and Samsung, holding critical intellectual property and advanced manufacturing capabilities, face limited direct substitutes for their cutting-edge products. This scarcity, coupled with robust demand, allows them to dictate pricing and allocation, as seen with many advanced chips already booked through 2025. While WT Microelectronics' significant purchasing volume provides some leverage on standard components, the concentration of power among a few key suppliers for specialized technologies remains a dominant factor.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on WT Microelectronics | Example (2024/2025 Outlook) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Market Share | High supplier leverage due to limited competition | TSMC's dominance in advanced foundry services |
| Proprietary Technology/IP | Few or no direct substitutes for specialized chips | NVIDIA's AI GPU architectures |
| High Demand for Advanced Components | Suppliers can dictate terms and pricing | Bookings for HBM and AI accelerators extending into 2025 |
| Switching Costs for Distributors | Difficulty and expense in changing core suppliers | Component qualification and supply chain re-certification |
| WT Microelectronics' Volume | Provides some negotiation power for standard components | Leverage in securing allocation for less in-demand chip types |
What is included in the product
This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the competitive forces impacting WT Microelectronics, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic analysis of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
WT Microelectronics benefits from a diversified customer base, serving numerous Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) across multiple sectors. This broad reach means that while individual large clients might possess considerable purchasing power due to high volumes, the overall customer concentration remains low, mitigating significant risk for WT Microelectronics.
The company’s strategic value proposition, focused on optimizing component sourcing and streamlining production workflows, positions it as an indispensable partner. This value-added approach distinguishes WT Microelectronics from being perceived as a mere supplier of standardized parts, thereby strengthening its position against potential customer leverage.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in WT Microelectronics' competitive landscape. For Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs), the process of changing distributors involves substantial effort. This includes the time and resources needed to re-qualify new supply channels, which can be a lengthy and complex undertaking, especially in the electronics industry where component quality and reliability are paramount.
Furthermore, altering established logistics and supply chain operations presents another hurdle. OEMs and ODMs have finely tuned processes in place, and integrating a new distributor requires adjustments to inventory management, shipping, and receiving protocols. These changes can lead to temporary disruptions in production schedules, impacting output and potentially incurring additional costs due to delays or inefficiencies.
WT Microelectronics actively mitigates these customer switching costs through its robust service offerings. The company provides comprehensive supply chain management solutions, simplifying procurement and logistics for its clients. Coupled with dedicated technical support, which assists customers in overcoming design and production challenges, WT Microelectronics fosters a strong sense of stickiness. This makes it less economically and operationally attractive for customers to switch to a competitor, thereby reinforcing WT Microelectronics' bargaining power.
While semiconductor components themselves can be highly standardized, WT Microelectronics distinguishes itself by offering significant value-added services. These include sophisticated supply chain management, efficient logistics, dedicated warehousing, and crucial technical support. This focus on service delivery mitigates the inherent risk of customers leveraging product standardization to negotiate lower prices.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers for WT Microelectronics is generally low. Most Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) do not possess the necessary scale, specialized expertise, or substantial capital required to replicate WT Microelectronics' comprehensive semiconductor distribution and supply chain management capabilities.
While some larger clients might explore direct sourcing for specific components, undertaking the full backward integration of the intricate global semiconductor supply chain is typically impractical and cost-prohibitive for them. This significantly curtails the risk of customers effectively becoming their own distributors, thereby diminishing their bargaining power in this regard.
- Limited Customer Scale: Few customers can match WT Microelectronics' global reach and operational efficiency in semiconductor logistics.
- High Capital & Expertise Barrier: Establishing a comparable distribution network demands immense investment and specialized knowledge.
- Complexity of Semiconductor Supply Chain: Managing diverse suppliers, inventory, and regulatory compliance globally is a significant undertaking.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most OEMs/ODMs prefer to concentrate on product design and manufacturing rather than distribution.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in the electronic components market, particularly those with slim profit margins, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are highly attuned to the cost of components when making purchasing decisions.
However, WT Microelectronics can effectively counter this by providing value-added services that extend beyond the mere unit price of components. Their expertise in optimizing supply chains, offering robust technical support, and guaranteeing consistent component availability are crucial differentiators.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in sectors like consumer electronics, where margins are often tight, are highly sensitive to component pricing.
- Value Beyond Price: WT Microelectronics mitigates pure price competition by offering optimized supply chain solutions, ensuring component availability and providing essential technical support.
- Mitigating Competition: These services create significant value for customers, reducing the impact of minor price differences and fostering loyalty.
WT Microelectronics faces moderate bargaining power from its customers, largely due to the price sensitivity prevalent in many electronics sectors. However, the company effectively counters this by offering substantial value-added services that extend beyond component pricing, such as optimized supply chains and technical support, thereby fostering customer loyalty and reducing the impact of minor price variations.
In 2023, WT Microelectronics reported net sales of approximately NT$178.7 billion (US$5.8 billion), indicating a broad customer base across various segments of the electronics industry. While specific customer concentration figures are not publicly detailed, the company's diversified revenue streams suggest that no single customer dominates its sales, limiting individual customer leverage.
| Metric | 2023 Value (NT$ billions) | Approximate USD Equivalent (billions) |
|---|---|---|
| Net Sales | 178.7 | 5.8 |
Preview Before You Purchase
WT Microelectronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for WT Microelectronics, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the semiconductor industry. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted analysis, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electronic component distribution landscape is undeniably crowded, featuring formidable global entities such as WPG Holdings, Avnet, and Arrow Electronics. These established players operate on a significant scale, setting a high bar for market entry and competition.
WT Microelectronics' strategic acquisition of Future Electronics in late 2023, a deal valued at approximately $5.9 billion, has significantly reshaped its market position. This move has propelled WT Microelectronics into the upper echelon of global distributors, underscoring a market that, while consolidating, remains intensely contested.
This heightened level of competition inherently exerts downward pressure on profit margins. Consequently, companies like WT Microelectronics are compelled to emphasize and develop value-added services to differentiate themselves and maintain profitability in this dynamic environment.
The semiconductor industry is on a strong growth trajectory, with global sales anticipated to hit record levels in 2024 and 2025. This expansion is largely fueled by surging demand for artificial intelligence, advanced computing, and the automotive sector. A growing market generally eases competitive pressures as there's more business available for everyone.
While the overall outlook is positive, the growth isn't uniform across all segments. For instance, components essential for AI applications are experiencing exceptionally high demand, whereas other areas of the semiconductor market are seeing a more gradual recovery. This unevenness means that while the industry's growth can temper rivalry, intense competition may still persist in specific high-demand niches.
While semiconductor components can appear standardized, distributors like WT Microelectronics distinguish themselves through crucial value-added services. These include expert technical support, efficient logistics, sophisticated supply chain optimization, and tailored inventory management solutions. This focus on service excellence moves competition beyond mere price, fostering customer loyalty.
WT Microelectronics' robust suite of services and its deeply entrenched relationships with both leading semiconductor manufacturers and a broad customer base significantly increase switching costs. Customers who rely on WT's integrated support and supply chain solutions face considerable disruption and potential inefficiency if they were to switch to a competitor, thereby mitigating intense direct price competition.
Exit Barriers
The electronic component distribution industry demands substantial capital for warehousing, sophisticated logistics, and advanced IT systems, alongside a specialized workforce. These considerable fixed costs and unique assets present significant exit barriers for companies operating within this sector.
Consequently, firms facing financial difficulties often find it more practical to remain in the market and continue competing, rather than incurring further losses by exiting. This dynamic intensifies competitive rivalry as these companies strive to survive.
- High Capital Investment: WT Microelectronics, like its peers, invests heavily in its global supply chain and IT infrastructure, estimated in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Specialized Assets: The need for climate-controlled warehouses and advanced tracking systems makes assets difficult to redeploy elsewhere.
- Continued Competition: Companies with substantial sunk costs are incentivized to continue operations even at lower profit margins, leading to persistent rivalry.
Diversity of Competitors
WT Microelectronics operates in a highly fragmented market where competitors often pursue distinct strategies. Some players might concentrate on specific geographic regions, while others specialize in particular types of electronic components or target niche end markets. This strategic divergence means that rivalry can manifest in varied forms, from comprehensive distribution models to highly specialized service offerings, intensifying competition across different market segments.
For example, while WT Microelectronics might have a broad reach, competitors like Arrow Electronics or Avnet often have deep expertise in specific areas, such as industrial automation or aerospace and defense. These specialized competitors can exert significant pressure by offering tailored solutions and dedicated support within their chosen niches. This diversity in approach means that WT Microelectronics must constantly adapt its strategies to counter the unique strengths of various rivals.
- Diverse Competitive Strategies: Competitors may focus on broad-line distribution, niche market specialization, or specific geographic regions.
- Specialized Expertise: Rivals often possess deep knowledge in particular component types or end-user industries, offering tailored solutions.
- Varied Competitive Approaches: Competition ranges from comprehensive service models to highly specialized offerings, intensifying rivalry in different segments.
- Market Fragmentation: The presence of numerous players with differing strategic priorities creates a dynamic and complex competitive landscape.
The competitive rivalry within electronic component distribution is intense, driven by large global players and WT Microelectronics' strategic acquisition of Future Electronics for $5.9 billion in late 2023. This heightened competition, while tempered by a growing semiconductor market projected to reach record sales in 2024-2025, still pressures profit margins, pushing companies to focus on value-added services. The industry's high capital requirements and specialized assets create significant exit barriers, encouraging firms to remain competitive even at lower margins, further intensifying rivalry.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Markets/Specializations | Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| WPG Holdings | ~7.5 | Asia-Pacific, broad product portfolio | Regional strength, comprehensive offerings |
| Avnet | ~24.4 | Global, industrial, aerospace, defense | Integrated solutions, digital transformation |
| Arrow Electronics | ~33.0 | Global, broad product range, IoT, cloud | End-to-end solutions, design support |
| WT Microelectronics (post-acquisition) | ~13.0 (pro forma) | Asia-Pacific, IoT, AI, automotive | Value-added services, supply chain optimization |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) possess the theoretical ability to bypass distributors like WT Microelectronics and procure components directly from semiconductor makers. This approach, however, faces significant practical hurdles.
Managing relationships with a multitude of semiconductor suppliers, coordinating complex logistics for diverse components, and providing essential technical support for a broad product portfolio are substantial challenges that OEMs/ODMs often prefer to avoid. For instance, in 2024, the average semiconductor supply chain involves coordinating with dozens of specialized manufacturers, each with unique ordering processes and lead times.
WT Microelectronics' established proficiency in navigating these complexities, along with its comprehensive supply chain management services and deep supplier relationships, effectively diminishes the threat of direct sourcing by OEMs/ODMs. The company's ability to consolidate procurement and offer integrated solutions provides considerable value, making direct sourcing a less attractive option for most customers.
Customers might consider building their own component management systems, handling procurement, storage, and technical assistance internally. This path demands significant capital for facilities, skilled personnel, and a worldwide supply chain infrastructure.
For original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and original design manufacturers (ODMs), especially those prioritizing product innovation and production, the financial outlay and operational complexity of in-house management are often prohibitive. In 2023, the average cost for a mid-sized electronics manufacturer to establish a dedicated component sourcing and logistics department, including IT systems and personnel, could easily exceed $5 million, a substantial barrier.
Consequently, WT Microelectronics' specialized, integrated services present a far more economical and streamlined alternative. The company's established global network and expertise in managing complex supply chains offer a clear advantage, allowing clients to focus on their core competencies rather than the intricacies of component management.
The threat of substitutes for WT Microelectronics' offerings is present as alternative technologies or design approaches emerge. For instance, the increasing sophistication of chiplet technology and highly integrated Systems-on-Chip (SoCs) could lessen the demand for discrete, traditional semiconductor components that WT Microelectronics distributes. This trend requires WT Microelectronics to continuously adapt its product portfolio to align with these evolving technological landscapes.
Availability of Refurbished or Used Components
The availability of refurbished or used electronic components presents a potential threat of substitutes for WT Microelectronics. For less demanding or cost-conscious applications, these pre-owned parts can fulfill similar functions, impacting the demand for new components. The global market for refurbished electronics is experiencing significant growth, with some estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate of over 10% in recent years.
However, this threat is largely mitigated for WT Microelectronics' core business. High-performance, mission-critical, and cutting-edge applications, which form the bulk of their customer base, necessitate new components. Reliability, performance guarantees, and manufacturer warranties are paramount in these sectors, making refurbished options unsuitable substitutes. For instance, in the automotive or aerospace industries, the stringent safety and performance standards preclude the use of used parts.
The market dynamics show a clear bifurcation:
- Cost-Sensitive Segments: Refurbished components can offer a viable lower-cost alternative.
- High-Performance Applications: New components are essential due to reliability, warranty, and performance requirements.
- Market Growth: The used electronics market is expanding, indicating increasing consumer acceptance for pre-owned goods in certain sectors.
Software-Defined Solutions Reducing Hardware Dependency
The burgeoning trend of software-defined vehicles (SDVs) and similar software-centric systems presents a potential threat by diminishing the reliance on purely hardware-based solutions. This shift could see value migrating from traditional hardware components to sophisticated software and adaptable, programmable hardware architectures.
For WT Microelectronics, this necessitates a strategic alignment with the evolving landscape of hardware-software integration. The company must adapt its product portfolio and service offerings to cater to the increasing demand for flexible and interconnected components that support these software-driven ecosystems.
- Software-Defined Vehicles: The automotive industry is increasingly prioritizing software for vehicle functionality, potentially reducing the need for specialized, fixed-function hardware.
- Programmable Hardware: Demand is growing for flexible hardware that can be reconfigured via software, offering greater adaptability than traditional, purpose-built chips.
- Value Shift: Value creation is moving towards software development, data analytics, and over-the-air updates, which can influence the perceived value of hardware components alone.
- WT Microelectronics' Response: The company must focus on providing components that facilitate seamless hardware-software integration and support the dynamic needs of SDV architectures.
The threat of substitutes for WT Microelectronics is primarily influenced by technological advancements and evolving customer needs. While direct sourcing by OEMs/ODMs and building in-house component management systems are theoretically possible, the significant operational complexities and costs make them impractical for most clients. For instance, establishing a dedicated component sourcing department in 2023 could cost over $5 million.
Emerging technologies like chiplets and highly integrated Systems-on-Chip (SoCs) could reduce demand for discrete components, necessitating WT Microelectronics' adaptation. Similarly, the growing market for refurbished electronics, which saw over 10% CAGR in recent years, presents a substitute for cost-sensitive applications, though high-performance sectors still require new parts due to reliability demands.
The shift towards software-defined vehicles (SDVs) also poses a threat by reducing reliance on fixed-function hardware. This trend requires WT Microelectronics to focus on components that enable seamless hardware-software integration, supporting adaptable, programmable architectures rather than purely traditional chips.
| Threat of Substitute | Description | Impact on WT Microelectronics | Mitigation Strategies | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sourcing by OEMs/ODMs | Customers procuring components directly from manufacturers. | Low; high logistical and relationship management burden. | Value-added services, consolidated procurement, technical support. | Complexity of managing dozens of suppliers remains a deterrent. |
| In-house Component Management | Customers building internal systems for procurement and logistics. | Low; prohibitive capital and operational costs. | Economical and streamlined integrated services. | Significant capital investment ($5M+ in 2023) discourages this. |
| Alternative Technologies (Chiplets, SoCs) | Integrated solutions reducing demand for discrete components. | Moderate; requires portfolio adaptation. | Focus on components supporting advanced architectures. | Continuous evolution of semiconductor integration. |
| Refurbished/Used Components | Pre-owned parts for cost-sensitive applications. | Low for core business; high-performance applications require new parts. | Focus on reliability and warranty for critical sectors. | Market growth in refurbished electronics, but not for mission-critical use. |
| Software-Centric Systems (SDVs) | Shift from hardware to software-driven functionality. | Moderate; requires focus on hardware-software integration. | Offer components enabling flexible, interconnected systems. | Increasing demand for adaptable hardware in evolving industries. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global semiconductor component distribution market demands massive upfront capital. Companies need to build extensive logistics, secure warehousing, implement sophisticated IT, and hold significant inventory. This financial hurdle alone acts as a powerful deterrent for many aspiring competitors.
For instance, establishing a robust global supply chain infrastructure, a core competency for players like WT Microelectronics, can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars. This includes setting up regional distribution hubs and ensuring compliance with international trade regulations, which further escalates initial investment needs.
WT Microelectronics' existing, well-established global infrastructure, built over years, presents a formidable competitive advantage. This substantial capital investment creates a significant barrier to entry, protecting its market position from new, less capitalized challengers.
Established distributors like WT Microelectronics leverage substantial economies of scale in purchasing and logistics, a significant barrier for newcomers. Their sheer volume allows for preferential pricing and optimized supply chains, making it tough for new entrants to match cost efficiencies without massive upfront capital. For instance, in 2024, major electronics distributors reported operating margins that reflect these scale advantages, often in the low to mid-single digits, which would be challenging for a nascent competitor to replicate.
WT Microelectronics has cultivated deep, enduring relationships with leading semiconductor manufacturers and a diverse global customer base of OEMs and ODMs. These established connections are vital for WT Microelectronics to guarantee consistent supply and drive product demand.
New companies entering the market would find it exceptionally difficult to replicate WT Microelectronics' vast and trusted network, which has been developed and strengthened over many years of operation. This significant barrier makes it challenging for potential competitors to gain a foothold.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The semiconductor industry, including companies like WT Microelectronics, faces significant regulatory hurdles that act as a barrier to new entrants. Navigating the intricate web of international trade regulations, tariffs, and export controls, particularly for advanced technologies, requires substantial investment in legal and compliance expertise. For instance, the US Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) export control regulations, updated frequently, can significantly impact supply chains and market access, demanding continuous adaptation and specialized knowledge.
Meeting stringent quality certifications and environmental standards, such as those mandated by the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) or industry-specific ISO standards, adds another layer of complexity and cost. New players must allocate considerable resources to ensure compliance, which can deter smaller or less capitalized entrants from the market.
The geopolitical landscape further complicates entry, with varying national security concerns and trade policies influencing market access and operational requirements. For example, the ongoing US-China trade tensions and the resulting restrictions on technology transfer create a challenging environment for any new company aiming to operate globally within the semiconductor sector.
- Complex International Regulations: Companies must adhere to a multitude of trade laws, tariffs, and export controls across different jurisdictions.
- High Compliance Costs: Significant investment is required in legal, compliance, and quality assurance teams to meet stringent industry standards.
- Geopolitical Influences: National security concerns and trade disputes can lead to sudden policy changes, impacting market entry and operations.
Technical Expertise and Value-Added Services
WT Microelectronics distinguishes itself by offering more than just semiconductor components; it provides essential technical expertise and value-added services, including comprehensive supply chain management. This integrated approach creates a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants.
New players must invest heavily in acquiring or developing deep technical knowledge across a spectrum of semiconductor technologies and establish robust service infrastructures to even begin competing. For instance, the semiconductor industry in 2024 continues to see significant R&D spending, with major players investing billions to stay ahead in technological innovation, a cost new entrants would need to match.
- Technical Depth: New entrants require specialized engineering talent to understand and support complex semiconductor applications.
- Service Infrastructure: Building capabilities for design-in support, logistics, and inventory management is a costly necessity.
- Customer Integration: WT Microelectronics' deep relationships with clients, often involving co-development, are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
The threat of new entrants in the semiconductor distribution market, impacting WT Microelectronics, is significantly mitigated by immense capital requirements for logistics, warehousing, and IT infrastructure. Furthermore, the need to build extensive, trusted relationships with both semiconductor manufacturers and a broad customer base presents a substantial barrier, as does the necessity of navigating complex international regulations and geopolitical influences.
New entrants must also invest heavily in technical expertise and value-added services to compete with established players like WT Microelectronics, making market entry a costly and challenging endeavor. For example, in 2024, the average cost for a new semiconductor distributor to establish a basic global operational footprint, including warehousing and compliance, could easily exceed $50 million.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Effort for New Entrants (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Logistics, warehousing, IT, inventory | $50M+ for basic global presence |
| Supplier Relationships | Securing agreements with major manufacturers | Years of effort and proven track record |
| Customer Base | Establishing trust and supply agreements with OEMs/ODMs | Years of effort and consistent performance |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating trade laws, tariffs, export controls | Significant legal and compliance investment |
| Technical Expertise | Offering design-in support and technical services | High cost for specialized engineering talent |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our WT Microelectronics Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and regulatory filings to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.