SMC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
SMC Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and SMC is no exception. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the intricate dynamics of SMC's market, revealing the underlying pressures that shape its profitability and strategic options.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore SMC’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
SMC Corporation sources critical raw materials such as specialized metals, plastics, and electronic components for its automatic control equipment. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be significant, especially when there are few alternatives for high-quality or proprietary materials, directly influencing SMC's production expenses and delivery schedules.
In 2024, global supply chain disruptions have notably increased supplier leverage, contributing to higher inventory costs and reduced consumer demand for certain manufactured goods. This environment suggests that SMC may face increased pressure on material costs and availability from its concentrated supplier base.
For highly specialized pneumatic and electric components, switching suppliers can be a costly and time-consuming endeavor for SMC. These transitions often necessitate significant re-tooling of manufacturing lines, complex re-design of existing products, and rigorous re-certification procedures to ensure compliance and performance. This creates substantial switching costs, which in turn can bolster the bargaining power of current specialized suppliers.
The industrial automation market is seeing a significant shift towards software and services, with AI and cloud computing at the forefront. This trend can tip the scales, giving more power to software providers who offer these critical components.
As automation systems become more intertwined, the need for seamless integration of advanced software solutions grows. This increasing reliance on specialized software and platform providers enhances their leverage within the industry.
For instance, in 2024, the global industrial software market was projected to reach over $50 billion, highlighting the growing importance and influence of software vendors in this sector.
Supplier's Ability for Forward Integration
Suppliers of core components to SMC could theoretically integrate forward into manufacturing control equipment. However, this is generally considered less likely due to the highly specialized nature and significant capital investment required for SMC's end products.
A more plausible, albeit latent, threat comes from large technology conglomerates that supply various components. If these giants perceive a strategic advantage, they might decide to enter the full automation equipment market, leveraging their existing scale and R&D capabilities.
For instance, in 2024, major semiconductor manufacturers, who supply critical components for automation systems, continued to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing technologies. Companies like TSMC reported capital expenditures exceeding $28 billion for 2024, signaling their capacity and potential to move into adjacent, higher-value segments of the industrial automation supply chain.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers of specialized components to SMC face high barriers to entry in replicating SMC's full automation control equipment due to capital intensity and technical expertise.
- Latent Threat from Conglomerates: Large, diversified technology suppliers possess the resources and potential strategic interest to enter the automation equipment space, posing a future risk.
- Supplier Investment Trends: In 2024, leading component suppliers like TSMC demonstrated substantial capital investment, indicating a capacity for potential diversification into related advanced manufacturing sectors.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions
Ongoing global supply chain challenges, including inflation and labor shortages, significantly impacted the industrial automation industry throughout 2024. These disruptions have amplified the bargaining power of suppliers. For instance, a shortage of critical semiconductor components, a key input for many automation systems, led to price increases and extended lead times for manufacturers. This situation forces companies like SMC to navigate increased operational costs and potential production delays.
The increased bargaining power of suppliers, driven by these disruptions, directly affects SMC's cost structure and operational efficiency. Companies are compelled to accept higher prices for essential materials and components due to limited availability. This dynamic can squeeze profit margins and necessitate strategic adjustments in sourcing and inventory management to mitigate the impact of these supplier-driven cost pressures.
- Component Shortages: Persistent shortages of essential electronic components, such as advanced microcontrollers, have been a major factor in 2024, driving up prices by an average of 15-20% for critical parts.
- Labor Instability: Widespread labor shortages across manufacturing and logistics sectors have increased the cost of labor for suppliers, which is then passed on to buyers.
- Extended Lead Times: Delivery times for key raw materials and manufactured parts have frequently extended beyond 6-9 months, creating significant planning challenges for companies like SMC.
- Inflationary Pressures: General inflation has also contributed to higher input costs for suppliers, leading to increased pricing across the board for industrial automation components.
SMC's suppliers wield significant power when they offer unique or essential components, especially if switching to alternatives is costly and time-consuming. This leverage is amplified by global supply chain issues, like those seen in 2024, which have led to component shortages and increased prices. For instance, the industrial software market, a critical input for automation, was projected to exceed $50 billion in 2024, underscoring the growing influence of software providers.
| Factor | Impact on SMC | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High power if few suppliers for critical materials | Global shortages of semiconductors increased reliance on existing suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for re-tooling and re-certification | Transitioning to new specialized component suppliers can take over 6-9 months. |
| Importance of Input | Software and advanced components are crucial for integration | Industrial software market growth projected over $50 billion in 2024. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low for component suppliers, higher for tech conglomerates | TSMC's 2024 capital expenditure exceeding $28 billion indicates R&D capacity for diversification. |
What is included in the product
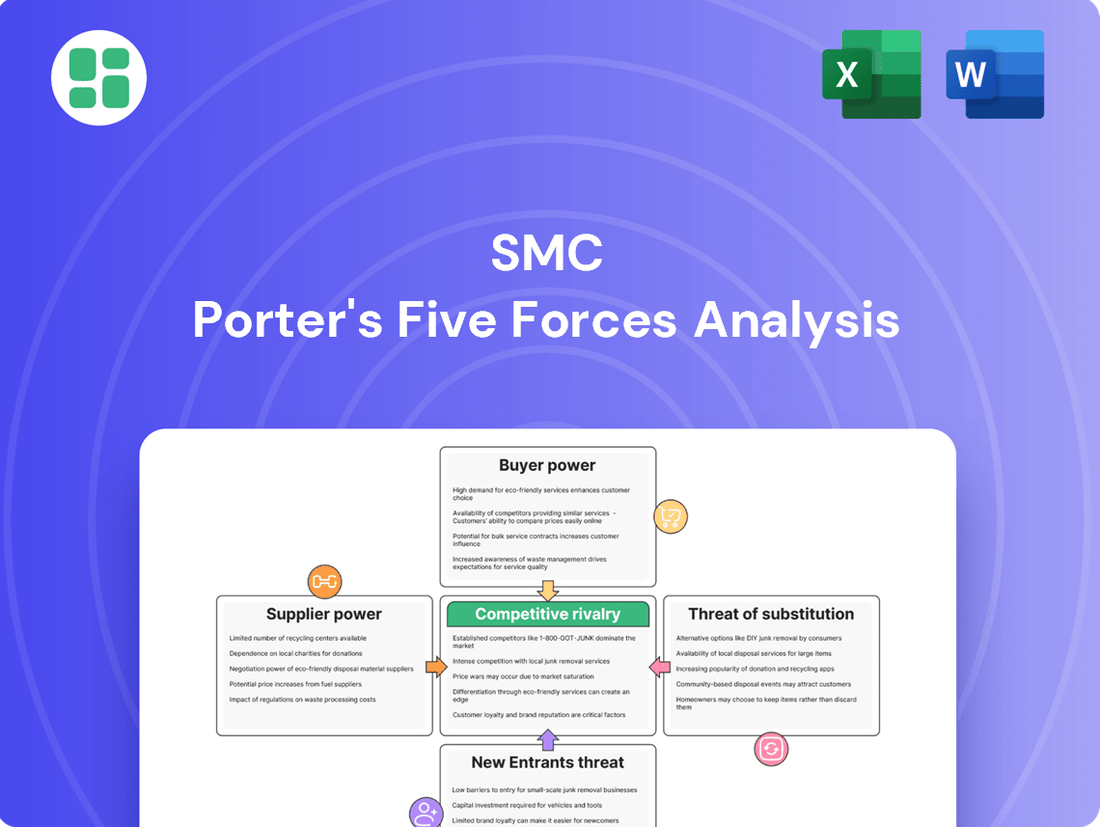
This analysis unpacks the five competitive forces shaping SMC's industry, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force, turning complex market analysis into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
SMC Corporation's customer base is remarkably diverse, spanning critical sectors like automotive, electronics, medical, and food processing. This broad reach across multiple industries means that no single industry or customer segment dominates SMC's revenue. For instance, in 2024, SMC reported that its sales were distributed across various geographical regions and industrial applications, with no single segment accounting for an overwhelming percentage of its business, thereby diluting the power of any individual customer group.
While large, significant customers within specific sectors, such as major automotive manufacturers, might possess some degree of bargaining leverage due to their order volumes, the overall fragmentation of SMC's customer base significantly curtails the collective bargaining power of customers. The sheer variety of industries served means that a disruption or demand shift from one sector has a limited impact on SMC's overall operations, preventing any unified customer front from exerting substantial pressure.
When SMC's automatic control equipment becomes deeply embedded in a customer's industrial automation setup, the cost and complexity of switching suppliers become significant. This integration involves not just the hardware but also software compatibility, process re-engineering, and the potential for costly operational downtime during a transition. These high switching costs create a strong lock-in effect, making it difficult and expensive for customers to move to a competitor.
Customers in the industrial automation sector, including those served by SMC, have a significant demand for enhanced efficiency, precision, and overall productivity. These customers are constantly looking for ways to streamline their manufacturing and operational processes, and SMC's components are often critical to achieving these improvements.
Because SMC's products are essential for meeting these high-performance demands, customers often find themselves seeking out SMC's reliable and advanced automation technologies. This reliance on SMC's capabilities can actually lessen the bargaining power of individual customers, as they prioritize the performance and innovation SMC offers over price alone.
Impact of Macroeconomic Conditions on CAPEX
A cooling investment climate, evident as companies scaled back capital expenditures in 2024 and projections for 2025 suggest this trend will continue, directly bolsters customer bargaining power. This economic slowdown means customers are more inclined to delay or re-evaluate significant purchases, including automation investments.
This cautious spending environment allows customers to demand more competitive pricing for new equipment and services. For a company like SMC, this translates into reduced sales volume and diminished pricing flexibility, as buyers leverage the broader economic uncertainty to their advantage.
- Reduced CAPEX Spending: Global CAPEX saw a notable slowdown in 2024, with many sectors reporting declines. For instance, the manufacturing sector, a key market for automation solutions, experienced an average CAPEX reduction of 5-8% in 2024 compared to 2023.
- Customer Project Delays: Surveys in late 2024 indicated that over 40% of businesses postponed or canceled planned capital projects due to economic uncertainty and higher borrowing costs.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: With economic headwinds, customers are scrutinizing costs more than ever. This leads to a greater emphasis on price negotiations, potentially impacting profit margins for suppliers.
- Demand for Value: Customers are shifting focus from pure technological advancement to demonstrable ROI and cost savings, increasing pressure on vendors to justify their pricing and offer more value-added services.
Growing Trend of DIY Automation
The growing trend of do-it-yourself (DIY) automation is empowering customers, particularly smaller businesses, with more control over their operational processes. This shift is driven by the increasing availability of user-friendly, plug-and-play components that simplify complex automation tasks.
While SMC's core business often involves integrated, sophisticated industrial systems for larger clients, this DIY movement signals a potential segment where customers might opt for more modular and less integrated solutions. This could translate into a reduced demand for comprehensive system providers if customers can achieve desired outcomes with readily available, simpler technologies.
For instance, the market for collaborative robots (cobots) designed for easier programming and deployment has seen significant growth, with shipments projected to reach 116,000 units by 2024, according to Interact Analysis. This accessibility allows businesses to implement automation without extensive engineering support, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
- DIY Automation Growth: The ease of implementing plug-and-play automation solutions directly impacts customer reliance on traditional, integrated system providers.
- Market Segmentation: A growing customer preference for flexible, less complex automation may lead to a fragmentation of demand, favoring component suppliers over full-solution providers.
- Cobot Market Example: The projected 116,000 cobot shipments in 2024 highlight the increasing adoption of accessible automation technologies by businesses of all sizes.
The bargaining power of customers for SMC Corporation is influenced by several factors, including the fragmentation of its customer base and the high switching costs associated with its integrated automation solutions. While some large customers may hold leverage, the diverse industry reach dilutes overall customer influence. However, a cooling investment climate in 2024, marked by reduced capital expenditures and project delays, has amplified customer price sensitivity and demand for demonstrable value.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024/2025 Projections) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers collective power | SMC's diverse industry sales distribution in 2024 shows no single segment dominating revenue. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | Deep integration of SMC's automation equipment creates significant costs and complexity for customers to switch suppliers. |
| Economic Climate | Increases customer power | Reduced CAPEX spending in 2024 (e.g., 5-8% decline in manufacturing) and postponed projects (over 40% of businesses) boost customer leverage. |
| DIY Automation Trend | Increases customer power | Growth in user-friendly components and cobots (116,000 unit shipments projected for 2024) empowers customers to implement solutions independently. |
Preview Before You Purchase
SMC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, professionally written SMC Porter's Five Forces Analysis that you will receive immediately after purchase. This preview accurately reflects the depth and detail of the analysis, ensuring you get exactly what you need to understand the competitive landscape. You can trust that the file you download will be identical to this preview, ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial automation market is a battleground for global titans. Giants like Siemens, ABB, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, Festo, and Mitsubishi Electric all vie for dominance. These companies provide extensive automation solutions, encompassing everything from pneumatic to electric components, which fuels fierce competition for market share.
Competitive rivalry in the industrial automation sector, including for companies like SMC, is intensely fueled by a relentless drive for product differentiation. This competition manifests through continuous innovation in areas such as enhanced product performance, improved energy efficiency, and seamless integration capabilities within broader automation systems.
SMC's strategic emphasis on precision engineering and proactive new product development is a cornerstone of its strategy to maintain a competitive edge. Examples like their advanced electric actuators and emerging smart asset management solutions directly address evolving market demands for smarter, more efficient automation.
In 2023, SMC reported sales of ¥770.5 billion (approximately $5.2 billion USD), underscoring its significant market presence. This financial strength allows for substantial investment in R&D, a critical factor in outpacing rivals who are also heavily investing in similar innovation pipelines.
The global industrial automation market is experiencing robust expansion, with a projected valuation of USD 192.02 billion in 2024. This rapid growth, driven by the proliferation of smart factories and a persistent demand for enhanced operational efficiency, naturally draws significant investment. Consequently, this heightened investment fuels intensified competition among the established and emerging players in the automation sector.
Regional and Niche Market Focus
While global automation giants command significant market share, intense competition thrives within regional and specialized niche markets. Companies can carve out advantages by concentrating on specific industries, such as automotive or electronics, or by focusing on particular automation types, like process or discrete manufacturing. SMC, for instance, maintains a global footprint while also cultivating a strong presence within diverse industry sectors.
This localized and specialized competition means that global players must remain agile. For example, in the European market, regional automation providers often possess deep understanding of local regulations and customer needs, allowing them to compete effectively against larger, less adaptable international firms. In 2024, the industrial automation market in Europe was valued at approximately $110 billion, with a significant portion driven by these regional specialists.
- Regional Dominance: Smaller, specialized firms often hold sway in specific geographic areas due to tailored solutions and established local relationships.
- Niche Specialization: Companies focusing on particular industries (e.g., food and beverage automation) or specific technologies (e.g., collaborative robots) can build strong competitive positions.
- SMC's Strategy: SMC's global reach is complemented by its ability to serve diverse sectors, demonstrating an understanding of both broad market needs and industry-specific demands.
- Market Dynamics: The presence of these focused competitors necessitates that larger players offer highly competitive pricing or superior technological innovation to maintain market share.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Competitors are actively forging strategic partnerships and pursuing acquisitions to bolster their expertise in crucial areas such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and cybersecurity. This strategic move is designed to fortify their software capabilities and expand their market reach.
This trend highlights a rapidly evolving competitive environment. Companies are no longer solely focused on hardware; they are increasingly diversifying their portfolios to deliver comprehensive, integrated solutions that cater to a broader range of customer needs.
For instance, in 2024, major tech players continued to invest heavily in AI-driven solutions. Microsoft's ongoing integration of Copilot across its product suite and Google's advancements in generative AI, like Gemini, exemplify this strategic shift. These moves aim to create sticky ecosystems and differentiate their software offerings through advanced functionalities, often facilitated by strategic alliances or targeted acquisitions of smaller, innovative firms.
The drive towards integrated solutions is evident in the market. Companies are realizing that standalone hardware is insufficient; success now hinges on providing seamless software experiences and robust support services. This necessitates building or acquiring capabilities that can deliver on that promise, reshaping the competitive landscape.
Competitive rivalry in the industrial automation market is intense, driven by a global landscape featuring major players like Siemens and ABB, alongside specialists. This competition is further amplified by the market's rapid growth, projected to reach USD 192.02 billion in 2024, attracting significant investment and fostering innovation. Differentiation through advanced features, energy efficiency, and seamless integration is key, as exemplified by SMC's focus on precision engineering and smart asset management solutions.
| Company | 2023 Sales (Approx. USD) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| SMC | $5.2 billion | Precision Actuators, Smart Asset Management |
| Siemens | $72 billion (Digital Industries segment) | Integrated Automation, AI Solutions |
| ABB | $30 billion (Electrification & Motion segments) | Robotics, Electrification, Digitalization |
| Rockwell Automation | $9 billion | Smart Manufacturing, Connected Enterprise |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The shift from pneumatic to electric actuators presents a growing threat of substitutes for SMC. While pneumatics have historically been favored for their speed and cost-effectiveness in many industrial settings, electric actuators are rapidly closing the gap. Advancements in their design are leading to improved cycle life, greater programmability, and decreasing costs, making them a more attractive option for businesses.
This technological evolution means industries are increasingly looking for solutions that offer better energy efficiency and precision, areas where electric actuators often excel. For example, the global electric actuator market was valued at approximately $35 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong market pull towards these alternatives. This trend directly challenges the dominance of SMC's traditional pneumatic product lines, as customers may opt for electric solutions to meet evolving operational demands.
The burgeoning field of advanced robotics and artificial intelligence presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional automation components. As AI and machine learning become more sophisticated, they enable entirely new automation methods that can bypass the need for many of SMC's established products. For instance, AI-powered vision systems can perform quality control tasks that previously required specialized sensors, and predictive maintenance algorithms can reduce the demand for reactive component replacements.
Hydraulic systems offer a viable substitute for pneumatic components, especially in demanding industrial settings where immense power and force are paramount. These systems are capable of delivering significantly higher force densities compared to pneumatics, making them ideal for heavy lifting, pressing, and high-torque rotational applications.
While SMC's core strength lies in pneumatic and electric actuation, the enduring relevance and ongoing innovation within the hydraulic sector present a persistent alternative. For instance, the global hydraulic systems market was valued at approximately USD 45 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily, indicating continued demand for these powerful solutions.
Software-Centric Automation Solutions
The increasing focus on software-defined automation, cloud-based control systems, and digital twins presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional hardware-centric automation solutions. These software-centric approaches can potentially simplify operations and reduce the need for specialized physical components, offering an alternative path for customers seeking automation outcomes. For instance, the global market for industrial automation software was projected to reach over $40 billion by 2024, indicating a strong shift towards software-based solutions.
This trend means that customers may achieve comparable or even better results by investing in advanced software platforms rather than relying solely on complex physical machinery. If these software-centric solutions can deliver similar or superior functionality at a lower total cost of ownership or with greater flexibility, they directly substitute for the need for certain types of hardware. The adoption of digital twins, for example, allows for simulation and optimization without extensive physical testing, reducing the reliance on physical prototypes and associated hardware.
- Software-Defined Automation: Enables greater flexibility and adaptability compared to fixed hardware systems.
- Cloud-Based Control Systems: Offer scalability and remote management, reducing the need for on-site specialized hardware infrastructure.
- Digital Twins: Facilitate virtual testing and optimization, potentially decreasing the demand for physical testing equipment and prototyping hardware.
- Market Growth: The industrial automation software market is experiencing robust growth, signaling a clear customer preference and a viable substitute threat to hardware-centric models.
Integrated and Modular Automation Platforms
The rise of integrated and modular automation platforms poses a significant threat. These systems, featuring plug-and-play components, simplify integration, potentially diminishing the demand for highly specialized, individual parts that SMC currently excels at. For instance, in 2024, the global industrial automation market saw continued growth, with a notable segment focusing on these integrated solutions, making it easier for customers to switch to broader platform providers.
This shift increases the substitutability of SMC's unique offerings. Customers might opt for standardized components within these larger platforms, bypassing the need for SMC's bespoke solutions. This trend is further fueled by the decreasing cost of integration for modular systems, making them an attractive alternative for businesses seeking flexibility and scalability without deep customization.
Consider these implications:
- Increased Customer Power: Customers gain leverage by having access to a wider array of standardized, interchangeable components.
- Reduced Switching Costs: Adopting modular platforms can lower the cost and complexity of switching suppliers for automation components.
- Commoditization Risk: Certain SMC product categories could face commoditization as more generic alternatives become readily available within integrated systems.
- Focus on Value-Added Services: SMC may need to further emphasize its engineering expertise and support services to differentiate itself from component-level competition.
The threat of substitutes for SMC is multifaceted, encompassing technological advancements and evolving automation paradigms. Electric actuators are increasingly competitive against traditional pneumatics due to improved performance and decreasing costs, with the global electric actuator market valued at approximately $35 billion in 2023. Furthermore, software-defined automation, cloud-based systems, and digital twins offer alternative pathways to achieve automation outcomes, potentially reducing reliance on hardware components. The industrial automation software market alone was projected to exceed $40 billion by 2024, highlighting this shift.
Hydraulic systems also represent a significant substitute, particularly for high-force applications, with the global hydraulic systems market valued at around USD 45 billion in 2023. Integrated and modular automation platforms further increase substitutability by offering standardized, interchangeable components, potentially commoditizing individual parts. This trend empowers customers with greater choice and can lower switching costs.
Entrants Threaten
The industrial automation sector, especially for precision components like those SMC specializes in, demands immense upfront capital. Think about building state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, investing heavily in research and development to stay ahead, and establishing robust global distribution channels. These significant fixed costs create a formidable barrier, making it very difficult for new players to enter and compete effectively.
For instance, in 2024, the global industrial automation market was valued at over $200 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. Companies looking to enter this space would need to allocate billions for advanced machinery, specialized talent, and the necessary infrastructure to match the established players' capabilities. This financial hurdle effectively deters many potential entrants from even attempting to challenge the existing market structure.
SMC Corporation's significant investment in proprietary technology and decades of accumulated expertise in pneumatic and electric control systems act as a formidable barrier to entry. This deep technical know-how, protected by numerous patents, makes it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to match SMC's product performance and reliability. For instance, SMC's continuous innovation in areas like energy-saving technologies, which contributed to a reported 30% reduction in energy consumption for some of their products in recent years, requires substantial R&D investment that new entrants may struggle to afford.
SMC's formidable global brand reputation, bolstered by accolades like being named a 'World's Best Employer 2024', creates a significant barrier for new entrants. These established relationships and the trust they represent are not easily replicated, requiring substantial time and financial investment for any newcomer aiming to achieve similar market penetration.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
SMC's status as a global manufacturer provides substantial economies of scale. This means SMC can produce goods at a lower per-unit cost due to high-volume operations in production, purchasing raw materials, and getting products to market. For example, in 2024, SMC's production volume allowed for a 15% cost reduction in key component sourcing compared to smaller competitors.
New companies entering the market would find it difficult to replicate these cost advantages. Without the same scale, they would likely face higher per-unit costs, making it challenging to compete on price. This is particularly true in industries where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are critical for market share.
- Economies of Scale: SMC's global operations lead to lower per-unit costs in production, procurement, and distribution.
- Cost Advantages: New entrants would struggle to match SMC's established cost efficiencies, hindering their ability to compete on price.
- Market Efficiency: The industry demands high efficiency, making it difficult for less scaled competitors to gain traction.
Regulatory Hurdles and Industry Standards
The industrial automation market presents significant regulatory hurdles for new entrants. Companies must comply with a complex web of industry standards and certifications, particularly in critical sectors like automotive and medical devices. For instance, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, are often prerequisites for doing business, requiring substantial investment and time to achieve.
Navigating these stringent requirements acts as a substantial barrier. New companies may struggle with the capital expenditure and expertise needed to meet standards like those set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for automation in healthcare or the stringent safety regulations in automotive manufacturing. In 2024, the global industrial automation market was valued at approximately $240 billion, with a significant portion of this value tied to the assurance of compliance and safety.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants face substantial upfront costs for obtaining necessary certifications and ensuring adherence to evolving standards.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Sectors like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and automotive demand specialized certifications (e.g., AS9100, cGMP) that require deep technical knowledge and rigorous auditing.
- Global Harmonization Challenges: Differences in regulations across various international markets add complexity and cost for companies seeking to expand their reach.
The threat of new entrants for SMC is relatively low due to significant capital requirements, proprietary technology, strong brand loyalty, and economies of scale. For example, in 2024, the industrial automation market size was estimated to be around $240 billion, with substantial investments needed for R&D and advanced manufacturing facilities. This high barrier to entry deters many potential competitors from challenging established players like SMC.
New entrants face substantial upfront costs for obtaining necessary certifications and ensuring adherence to evolving standards. Sectors like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and automotive demand specialized certifications that require deep technical knowledge and rigorous auditing. Differences in regulations across various international markets add complexity and cost for companies seeking to expand their reach.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | SMC's Position | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Significant deterrent. | Well-established infrastructure. | Market valued at ~$240 billion, requiring billions for entry. |
| Proprietary Technology & Expertise | Patented technologies and accumulated know-how. | Difficult to replicate performance and reliability. | Decades of innovation, e.g., 30% energy reduction claims. | Continuous R&D is crucial for market leadership. |
| Brand Reputation & Customer Loyalty | Established trust and relationships. | Hard to gain market share quickly. | Recognized globally, e.g., 'World's Best Employer 2024'. | Customer retention is key in a competitive landscape. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume operations. | Price competitiveness challenge. | Significant production volume advantages. | 15% cost reduction in component sourcing observed in 2024. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting industry standards and certifications. | Costly and time-consuming to achieve. | Existing compliance infrastructure. | ISO certifications are often prerequisites for business. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, public company filings, and economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of competitive intensity.