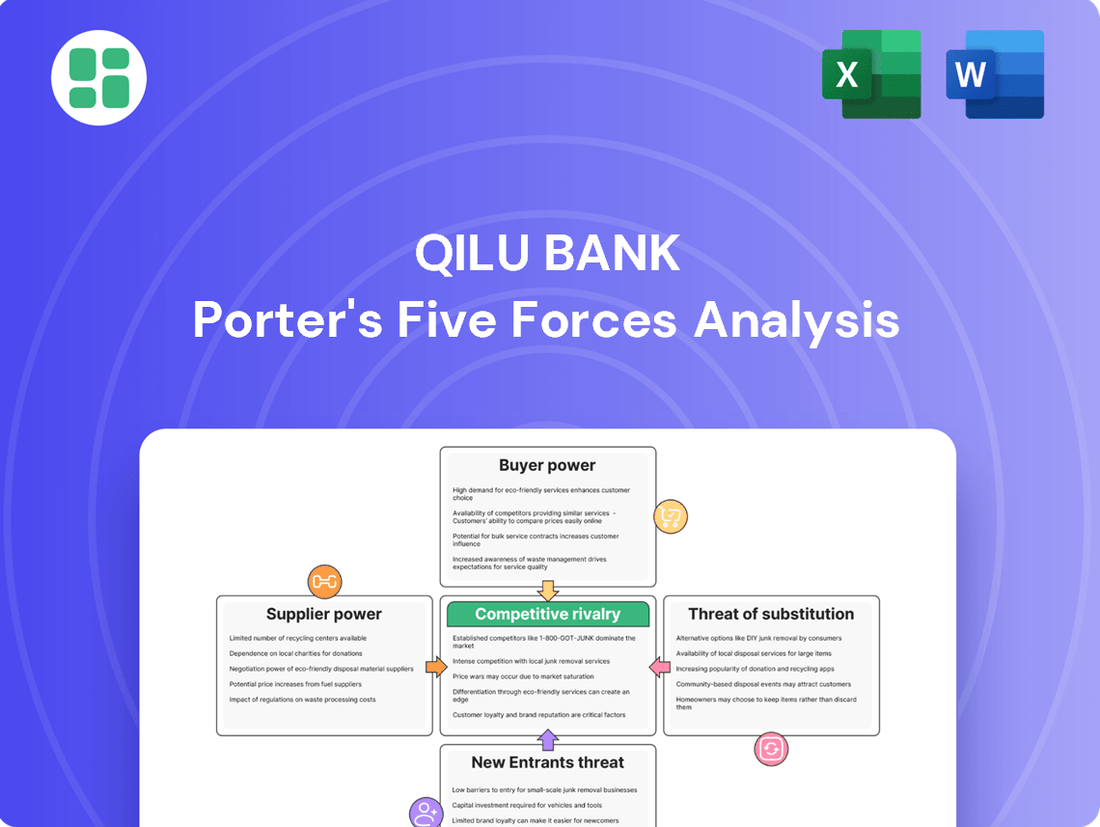
Qilu Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Qilu Bank Bundle
Qilu Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing pressures from intense rivalry, evolving customer demands, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment and identifying strategic opportunities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Qilu Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors, from individuals to corporations, are a crucial source of capital for Qilu Bank, acting as suppliers. Their ability to negotiate for better rates is heightened when other banks offer more attractive deposit products or when moving funds becomes easier. For instance, in 2023, the average deposit growth rate for Chinese banks was around 9.5%, indicating a competitive landscape where Qilu Bank must remain responsive to market rates to attract and retain these vital capital providers.
When interest rates rise, as they did in many global markets throughout 2023 and early 2024, depositors gain more leverage. They can seek out higher yields elsewhere, forcing Qilu Bank to potentially increase its own deposit rates to remain competitive. This directly impacts the bank's cost of funds, a key factor in its profitability. Data from the People's Bank of China in late 2023 showed a slight upward trend in benchmark deposit rates, illustrating this dynamic.
Suppliers of long-term capital, like shareholders and bondholders, hold sway by choosing where to invest based on Qilu Bank's financial health and broader market trends. Qilu Bank's capacity to secure capital on favorable terms is directly tied to its creditworthiness, profitability, and the confidence investors place in it.
For instance, in 2023, Qilu Bank's net profit attributable to parent company shareholders was RMB 20.89 billion, a 3.57% increase year-on-year. This performance influences investor appetite. A higher cost of capital, whether through equity or debt, directly erodes Qilu Bank's profitability and limits its capacity for future expansion and lending activities.
Technology and infrastructure providers, such as those offering core banking systems and cybersecurity, hold significant bargaining power over Qilu Bank. The specialized nature of these services and the high costs associated with switching vendors can make it difficult for the bank to change suppliers. For instance, replacing a core banking system can cost millions of dollars and disrupt operations for months.
The concentration of providers in certain niche areas, like specialized payment processing or advanced AI-driven fraud detection, further amplifies their influence. Qilu Bank's reliance on a limited number of these critical suppliers can lead to increased operational expenses and reduced flexibility in adopting new technologies. In 2024, the global market for banking software and services was valued at over $50 billion, with a few dominant players controlling significant market share.
Skilled Labor and Talent Pool
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly concerning skilled labor, significantly impacts Qilu Bank. The availability and cost of specialized banking professionals, such as IT specialists, risk managers, and financial analysts, directly affect the bank's operational efficiency and the quality of its services. In 2024, a competitive landscape for financial talent means Qilu Bank faces increased wage pressures and challenges in retaining top performers, which can hinder innovation and the development of sophisticated financial products.
Here’s a breakdown of how this affects Qilu Bank:
- Talent Scarcity: A shortage of experienced IT professionals in the banking sector, a trend observed throughout 2024, raises recruitment costs and extends hiring timelines for Qilu Bank.
- Wage Inflation: The demand for specialized skills, like cybersecurity experts and data scientists, has led to upward pressure on salaries, impacting Qilu Bank's personnel expenses.
- Retention Challenges: Competitors offering more attractive compensation or career advancement opportunities can lure away key Qilu Bank employees, necessitating robust retention strategies.
- Impact on Service Delivery: Difficulty in attracting and keeping skilled personnel can compromise the bank's ability to offer cutting-edge digital services and manage complex financial risks effectively.
Regulatory and Central Bank Influence
Regulatory bodies like China's National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC) wield considerable influence over Qilu Bank, akin to suppliers impacting costs. These entities set crucial parameters such as reserve requirements, capital adequacy ratios, and benchmark interest rates, directly affecting the cost of funds and Qilu Bank's operational flexibility. For instance, changes in the PBOC's benchmark lending rates can alter the profitability of Qilu Bank's loan portfolio.
The cost of compliance with evolving regulatory frameworks represents a significant operational expenditure for Qilu Bank. In 2024, financial institutions globally, including those in China, continued to navigate stringent capital requirements and anti-money laundering regulations, which necessitate investments in technology and personnel. These compliance costs can be viewed as an indirect cost imposed by these influential bodies, impacting Qilu Bank's overall cost structure.
- Regulatory Mandates: NFRA and PBOC set reserve requirements and capital adequacy ratios, influencing liquidity and lending capacity.
- Interest Rate Policies: PBOC's benchmark rates directly impact Qilu Bank's cost of borrowing and lending income.
- Compliance Costs: Adherence to evolving regulations in 2024 incurred substantial operational expenses for financial institutions.
Depositors, acting as key suppliers of capital, exert significant bargaining power on Qilu Bank. This power is amplified when alternative financial institutions offer more attractive deposit rates or when the ease of transferring funds increases. In 2023, the competitive landscape for deposits in China saw an average growth rate of about 9.5%, underscoring the need for Qilu Bank to remain competitive with its offerings to attract and retain these essential capital providers.
The bank's ability to secure capital on favorable terms is directly linked to its perceived financial health and investor confidence. Suppliers of long-term capital, such as shareholders and bondholders, can shift their investments based on Qilu Bank's performance and broader market conditions. Qilu Bank's net profit attributable to its parent company shareholders reached RMB 20.89 billion in 2023, a 3.57% year-on-year increase, which influences investor interest and the cost of equity capital.
Technology and infrastructure providers hold considerable sway due to the specialized nature of their services and the high costs associated with switching vendors. The global market for banking software and services, valued at over $50 billion in 2024, is dominated by a few key players, increasing their leverage. Qilu Bank's reliance on these critical suppliers can lead to higher operational expenses and reduced flexibility in adopting new technologies.
Skilled labor also represents a significant supplier group for Qilu Bank, with the availability and cost of specialized banking professionals directly impacting operational efficiency. In 2024, the demand for IT specialists and risk managers has driven wage inflation, making it challenging for Qilu Bank to recruit and retain top talent, thus potentially hindering innovation and the development of sophisticated financial products.
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Qilu Bank dissects the competitive intensity within its operating environment, examining the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing Qilu Bank's market position against rivals and substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
Qilu Bank's customers, encompassing individuals, businesses, and government bodies, wield significant bargaining power. This stems from the wide array of alternative banking and financial service providers readily available in the market.
While certain switching costs are associated with intricate corporate dealings or loan portability, the barriers for routine retail banking services remain relatively low. This ease of transition empowers customers to seek out more favorable terms or superior services.
For instance, in 2024, the digital banking landscape continued to mature, with many fintech companies offering competitive rates on savings accounts and streamlined loan application processes, further amplifying customer choice and the ability to switch.
Customers today have unprecedented access to information about financial products. Online comparison sites and financial news outlets make it easy for consumers to see how Qilu Bank's offerings stack up against competitors. This means customers are more aware of pricing and features than ever before.
This increased transparency directly fuels price sensitivity, especially for straightforward products like savings accounts and standard personal loans. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate for a 1-year fixed deposit across major Chinese banks saw a narrow range, highlighting how easily customers can spot differences and demand better terms. Qilu Bank, like its peers, faces pressure to offer competitive rates to win and keep these customers.
Consequently, Qilu Bank must remain vigilant about its pricing strategies. Failing to offer competitive rates for these standardized products could lead to customer attrition. This competitive pressure can, in turn, squeeze the bank's net interest margins, impacting profitability.
Major corporate clients and government entities, due to the sheer volume and complexity of their financial requirements, wield considerable bargaining power. They can effectively negotiate for customized financial solutions, more competitive interest rates on loans, and advantageous terms for substantial deposits or investment banking engagements. Qilu Bank's dependence on a select group of these large clients for a significant portion of its revenue inherently amplifies their leverage during negotiations.
Digital Sophistication of Customers
The increasing digital sophistication of Qilu Bank's customers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. As consumers become more comfortable with and demanding of online and mobile platforms, they expect seamless, fast, and personalized banking experiences. This heightened expectation forces Qilu Bank to continually upgrade its digital infrastructure and services to remain competitive.
Customers accustomed to the innovative offerings from fintech companies are less loyal to traditional banks if their digital needs aren't met. For instance, a significant portion of Qilu Bank's customer base, particularly younger demographics, actively uses mobile banking apps for most transactions. In 2024, mobile banking penetration in China continued its upward trend, with reports indicating over 80% of urban bank customers utilized mobile channels for daily banking activities.
- Digital Expectations: Customers now demand intuitive interfaces, quick transaction processing, and personalized financial insights, directly impacting Qilu Bank's service delivery standards.
- Fintech Competition: The rise of agile fintech solutions offering superior digital experiences creates an easily accessible alternative for customers, increasing switching likelihood.
- Investment Pressure: Qilu Bank faces ongoing pressure to invest heavily in its digital channels to maintain customer satisfaction and market share against digitally native competitors.
Diversification of Customer Financial Needs
Customers today have increasingly diverse financial needs, often seeking more than just basic banking services. They are looking for wealth management, insurance, and even investment banking solutions. This broadens their options considerably.
Because customers can now source these varied financial products from a multitude of specialized providers, not just traditional banks, their collective bargaining power is significantly amplified. They can easily switch to competitors offering better value or a more integrated experience across their financial needs.
To counter this, Qilu Bank needs to focus on providing a comprehensive and highly competitive range of financial services. This strategy is crucial for retaining customers who manage multiple financial products and services with different institutions.
- Diversified customer needs: Clients now demand wealth management, insurance, and investment banking alongside traditional services.
- Increased provider options: Customers can access specialized financial products from various non-bank entities, enhancing their leverage.
- Qilu Bank's strategic imperative: Offering a broad and competitive suite of services is essential to retain these multi-product customers.
Qilu Bank's customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the abundant availability of alternative financial providers and the ease with which they can switch services, especially for routine banking needs. This power is further amplified by increasing customer financial sophistication and the demand for integrated, digital-first experiences, forcing Qilu Bank to offer competitive rates and superior digital services to retain its client base.
| Factor | Impact on Qilu Bank | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Continued growth of fintech and digital-only banks provides numerous competitor options. |
| Switching Costs (Retail) | Low | Minimal barriers for basic accounts; digital onboarding simplifies transitions. |
| Customer Information Access | High | Online comparison tools and financial media increase price and feature transparency. |
| Digital Expectations | High | Over 80% of urban bank customers in China used mobile channels for daily banking in 2024, demanding seamless digital experiences. |
| Diversified Needs | High | Customers seek integrated wealth management, insurance, and investment services, increasing options beyond traditional banking. |
Full Version Awaits
Qilu Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Qilu Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of industry competition and profitability. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Qilu Bank operates in a fiercely competitive Chinese banking sector. It faces intense rivalry not only from dominant state-owned commercial banks and national joint-stock banks but also from numerous other city and rural commercial banks. This broad competitive base necessitates continuous innovation and a clear differentiation strategy for Qilu Bank to stand out.
The competitive pressure is particularly acute within Qilu Bank's home base of Shandong province. Here, a multitude of local banks are vying for market share, intensifying the struggle for customers and profitability. For instance, as of the first half of 2024, the total assets of commercial banks in Shandong reached over 15 trillion RMB, highlighting the sheer scale of the market and the depth of competition.
Homogeneity in core banking products like savings accounts and personal loans means Qilu Bank faces fierce competition primarily on price. For instance, the average interest rate on personal loans in China hovered around 6.5% in early 2024, a figure many banks struggle to significantly deviate from.
This lack of unique features for many traditional offerings turns them into commodities. Consequently, Qilu Bank must focus intensely on offering competitive interest rates, minimizing fees, and delivering exceptional customer service to attract and retain clients, as seen in the broader Chinese banking sector.
When core products are easily replicated, it puts downward pressure on profit margins. Banks like Qilu Bank often find themselves in a constant battle for market share, which can erode overall profitability if differentiation strategies aren't effectively implemented.
The Chinese banking sector, while large, is characterized by significant market concentration, with dominant state-owned banks like ICBC, CCB, ABC, and BOC holding substantial market share. This creates an intensely competitive environment for regional players like Qilu Bank. For instance, as of the end of 2023, the total assets of the top four state-owned banks exceeded 100 trillion RMB, dwarfing the asset base of many city commercial banks.
Navigating a stringent regulatory landscape further shapes competitive rivalry. Policies such as the implementation of Basel III standards, which dictate capital adequacy ratios, and ongoing interest rate liberalization, directly influence profitability and strategic maneuvering for all banks. These regulations, while aimed at stability, can also amplify competitive pressures as banks adapt to new requirements and market dynamics.
Qilu Bank must therefore differentiate itself and find its niche within this concentrated and regulated market. Success hinges on its ability to adapt to evolving regulatory frameworks, such as the ongoing digital transformation mandates, while simultaneously competing on service quality and product innovation against much larger, state-backed institutions.
Regional and Local Market Dynamics
Qilu Bank's competitive landscape is primarily defined by its operations within Shandong province, where it faces intense rivalry from other city commercial banks and the extensive branch networks of major national banks. This regional focus means that local market saturation and the specific economic health of Shandong are key determinants of competitive intensity.
Success in this environment often depends on a deep understanding of local economic nuances and the cultivation of strong relationships within the community. For instance, as of late 2023, Shandong province’s GDP growth was reported at 6.0%, highlighting a dynamic but also competitive economic environment where local banks like Qilu Bank must differentiate themselves.
- Regional Focus: Qilu Bank's primary competition is within Shandong province, facing numerous local and national banking players.
- Market Saturation: The concentration of financial institutions in Shandong directly impacts Qilu Bank's market share and pricing power.
- Local Economic Influence: The economic conditions and growth trajectory of Shandong province significantly shape the intensity of competition.
- Community Ties: Strong local knowledge and established community relationships are critical competitive advantages for Qilu Bank.
Non-Price Competition and Service Quality
Beyond just offering competitive prices, banks like Qilu Bank face intense rivalry through non-price factors such as service quality, convenience, and the adoption of digital technologies. Customers increasingly expect seamless digital experiences and personalized interactions.
To stay ahead, Qilu Bank needs to prioritize investments in enhancing its customer service, expanding its digital offerings, and developing tailored financial solutions. For instance, in 2023, the banking sector saw a significant push towards digital transformation, with many institutions reporting increased investment in fintech and customer-facing digital platforms.
Failing to match the service advancements and digital innovations of competitors can directly impact customer loyalty. A decline in service quality or a lack of convenient digital channels can lead to customer attrition, eroding Qilu Bank's market share and competitive position.
- Service Quality Focus: Banks are differentiating through customer service, aiming for higher customer satisfaction scores.
- Digital Innovation: Investment in mobile banking apps and online platforms is crucial for attracting and retaining tech-savvy customers.
- Personalized Offerings: Tailoring financial products and advice to individual customer needs is becoming a key competitive advantage.
- Customer Retention: In 2024, many banks are focusing on retention strategies, recognizing that acquiring new customers is more costly than keeping existing ones.
Qilu Bank encounters substantial competitive rivalry within the Chinese banking sector, particularly in its home province of Shandong. This rivalry stems from a crowded market featuring large state-owned banks, national joint-stock banks, and numerous local commercial banks, all vying for customers and market share. For instance, as of the first half of 2024, Shandong province's commercial banking sector held over 15 trillion RMB in total assets, underscoring the intense competition for resources.
The competitive landscape is further intensified by the commoditization of core banking products, forcing banks like Qilu Bank to compete heavily on price, with personal loan interest rates hovering around 6.5% in early 2024. This price-based competition, coupled with the need to invest in digital transformation and superior customer service to differentiate, puts pressure on profit margins. The dominance of major state-owned banks, whose combined assets exceeded 100 trillion RMB by the end of 2023, creates a challenging environment for regional players striving to gain an edge.
| Competitor Type | Market Share Influence | Key Competitive Tactics |
|---|---|---|
| State-Owned Banks | High (Dominant) | Scale, extensive networks, government backing |
| National Joint-Stock Banks | Moderate to High | Brand recognition, diverse product offerings, digital capabilities |
| City/Rural Commercial Banks (Shandong) | High (Regional) | Local market knowledge, community relationships, price competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech payment and lending platforms represents a substantial threat of substitution for Qilu Bank. Companies like Alipay and WeChat Pay offer seamless digital payment solutions, often integrated into daily life, diverting transaction volumes from traditional banking. In 2023, mobile payment transactions in China, dominated by these platforms, reached trillions of yuan, showcasing the scale of this shift.
Furthermore, online lending platforms provide accessible and often faster alternatives for consumers and small businesses seeking credit, directly challenging Qilu Bank's lending business. These platforms leverage data analytics for quicker approvals, potentially eroding the bank's market share in consumer and SME financing.
For Qilu Bank's corporate clients, the ability to raise capital directly through bond issuance or equity markets represents a significant substitute for traditional bank loans. As China's capital markets continue to mature, a growing number of companies, especially larger and more established ones, are likely to bypass bank intermediaries. This shift directly reduces the demand for corporate lending services offered by Qilu Bank.
Customers have a wide array of wealth management and investment alternatives beyond traditional banking. These include specialized mutual funds, brokerage services from securities firms, and increasingly popular online wealth management platforms and robo-advisors. For instance, in 2024, the global robo-advisor market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating strong customer adoption of these digital alternatives.
These substitutes often present diverse investment portfolios and the potential for attractive returns, drawing capital away from bank deposits and proprietary investment products. This competition pressures banks like Qilu Bank to innovate and enhance their own wealth management services to retain clients and assets. Qilu Bank needs to clearly articulate its unique value proposition in this crowded market.
Non-Bank Financial Institutions
Non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) present a significant threat of substitution for Qilu Bank. Entities like trust companies, asset management firms, and micro-lenders offer specialized services that can directly compete with traditional banking products. For instance, asset management firms compete for investment deposits, while micro-lenders offer alternative credit solutions, particularly to small businesses and individuals who might find traditional bank loans restrictive.
These NBFIs often operate with lighter regulatory burdens or a sharper focus on specific market niches. This agility allows them to innovate and cater to underserved customer segments more effectively than larger, more diversified banks. Qilu Bank must contend with this specialized competition across various facets of its operations, from wealth management to lending.
In 2024, the growth of China's asset management sector underscored this threat. The total assets under management in China's public funds industry surpassed 27 trillion yuan by the end of Q1 2024, indicating a substantial pool of capital being directed away from traditional bank deposits and towards specialized investment vehicles. Furthermore, the micro-lending sector continued to expand, providing crucial funding to SMEs, a segment Qilu Bank also serves.
- Specialized Services: NBFIs offer alternatives to savings accounts, loans, and investment products provided by Qilu Bank.
- Regulatory Flexibility: Less stringent regulations allow NBFIs to adapt more quickly and offer competitive pricing or terms.
- Niche Market Focus: These institutions often target specific customer segments or transaction types that traditional banks may overlook.
- Competitive Landscape: Qilu Bank faces direct competition from NBFIs in areas like wealth management, consumer finance, and SME lending.
Emergence of Digital Currencies and CBDCs
The rise of digital currencies, including potential Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. If widely adopted, these digital alternatives could bypass conventional deposit accounts and payment rails, directly challenging Qilu Bank's intermediary function and its ability to attract and retain customer funds.
This shift could diminish the reliance on commercial banks for basic financial transactions and savings. For instance, by mid-2024, several countries, including China with its digital yuan pilot, are actively exploring or implementing CBDCs, indicating a tangible move towards these digital alternatives.
The implications for Qilu Bank are profound:
- Reduced Deposit Base: Customers might shift funds from traditional bank accounts to digital currencies for transactional ease or perceived security, shrinking the bank's core funding source.
- Disintermediation of Payments: Direct peer-to-peer digital currency transactions could bypass Qilu Bank's payment processing systems, eroding fee-based revenue streams.
- Increased Competition: The emergence of new digital payment providers and platforms, potentially leveraging CBDCs, could intensify competition for customer loyalty and transaction volume.
The threat of substitutes for Qilu Bank is significant, primarily driven by the burgeoning fintech sector and evolving customer preferences. Digital payment platforms like Alipay and WeChat Pay have captured substantial transaction volumes, diverting them from traditional banking channels. In 2023, China's mobile payment market alone processed trillions of yuan, highlighting this shift.
Online lending platforms offer a faster, data-driven alternative for credit, directly impacting Qilu Bank's lending business, particularly for SMEs and consumers. Moreover, the increasing maturity of capital markets allows corporations to bypass banks for financing through bond and equity issuance, reducing demand for corporate loans. The global robo-advisor market, projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in 2024, signifies a strong customer migration towards digital wealth management solutions, competing directly with Qilu Bank's investment products.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Qilu Bank | Key Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
| Fintech Payment Platforms | Diverts transaction volumes, reduces fee income | Trillions of yuan in mobile payments (2023) |
| Online Lending Platforms | Erodes market share in consumer and SME credit | Faster approval times, data-driven underwriting |
| Direct Capital Markets Access | Reduces demand for corporate lending | Growing corporate reliance on bond/equity issuance |
| Digital Wealth Management/Robo-advisors | Attracts investment capital away from bank deposits | Global robo-advisor market projected to reach hundreds of billions (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Qilu Bank is significantly low due to the substantial capital and regulatory barriers inherent in the banking sector. Authorities like the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC) mandate rigorous licensing processes and ongoing compliance, requiring immense financial resources and expertise to navigate.
Established brand loyalty and trust are significant barriers for new entrants in the banking sector, particularly for institutions like Qilu Bank. Years of consistent service and positive customer interactions have cultivated deep-seated trust, making customers reluctant to switch to unfamiliar providers. In 2023, Qilu Bank reported a strong customer deposit base, reflecting this loyalty.
Existing banks, like Qilu Bank, leverage significant economies of scale. This means their operational costs per customer are lower due to their vast customer bases and established infrastructure, including extensive branch networks and advanced technology platforms. For instance, in 2023, major Chinese banks reported operating costs that were a fraction of their revenue, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Building a comparable operational scale requires immense capital investment in technology, compliance, and physical presence, making it challenging to compete on price from the outset. This disparity in scale creates a barrier, as startups cannot immediately benefit from the same cost advantages that Qilu Bank enjoys.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role. Qilu Bank's years of operation have honed its risk management, customer service, and product development processes, leading to greater efficiency and reduced costs over time. This accumulated expertise allows them to offer more competitive pricing and absorb unexpected costs more readily than a nascent competitor.
Access to Distribution Channels and Networks
New entrants face significant hurdles in establishing robust distribution channels, a critical factor for customer acquisition and service delivery in the banking sector. Building an extensive network of physical branches, ATMs, and sophisticated digital platforms requires substantial capital investment and considerable time. For instance, traditional banks often have decades of investment in their branch networks, creating a formidable barrier.
While digital-only banks can circumvent the costs associated with physical infrastructure, they still face the challenge of investing heavily in advanced online platforms and aggressive marketing campaigns to gain widespread customer recognition and trust. This is crucial for competing with established players.
Qilu Bank, with its established presence and multi-channel distribution strategy, benefits from a significant advantage in reaching a broad customer base and providing seamless service delivery. As of the first quarter of 2024, Qilu Bank operated over 1,000 outlets and had a substantial digital banking user base, demonstrating its entrenched position.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing a comprehensive branch network and advanced digital infrastructure demands significant upfront investment, deterring many potential new entrants.
- Time and Brand Recognition: Building customer trust and brand loyalty through physical and digital touchpoints takes years, a period new entrants must overcome.
- Qilu Bank's Advantage: Qilu Bank's existing network of over 1,000 outlets and a strong digital presence as of Q1 2024 gives it a considerable edge in market penetration and customer accessibility.
- Digital Investment Needs: Even digital-first competitors must invest heavily in technology and marketing to rival the reach and established reputation of incumbent banks.
Fintech-Driven Disruption from Non-Banks
The threat of new entrants for Qilu Bank is significantly shaped by agile fintech companies and large tech giants. These players aren't necessarily seeking to become full-service banks but rather target lucrative segments like payments, lending, and wealth management with innovative, technology-driven solutions. For instance, by mid-2024, digital payment platforms continued to gain traction, with transaction volumes processed by non-traditional providers showing robust year-over-year growth, directly impacting traditional transaction fee revenues for banks.
These non-bank entities often operate with lower overheads and a more flexible regulatory framework, allowing them to offer competitive pricing and user-friendly experiences. This can lead to a gradual erosion of Qilu Bank's market share in specific, profitable product lines. In 2024, the growth of Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services, often provided by fintechs, demonstrated this trend, capturing a notable portion of consumer credit origination that might have previously gone to traditional banks.
- Fintechs and Big Tech Entering Niche Markets: Companies like Ant Group and Tencent in China, or PayPal and Square globally, are increasingly offering specialized financial services.
- Technological Agility: Their ability to rapidly deploy new technologies and adapt to market changes poses a challenge to established institutions.
- Data Utilization: Leveraging vast amounts of customer data allows them to offer highly personalized and efficient services, often at lower costs.
- Market Share Erosion: While not always direct competitors across the board, their success in specific areas like digital payments or online lending can chip away at traditional bank revenues.
The threat of new entrants for Qilu Bank is generally low, primarily due to the high capital requirements and stringent regulatory environment in China's banking sector. Obtaining the necessary licenses and establishing the required infrastructure demands significant financial investment and adherence to strict compliance standards, which act as substantial deterrents for most potential newcomers.
Qilu Bank benefits from established economies of scale and brand loyalty, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively. The bank's extensive operational infrastructure and years of building customer trust create a significant barrier. For instance, as of Q1 2024, Qilu Bank operated over 1,000 outlets, a physical presence that is costly and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate.
While fintech and big tech firms are entering specific financial service niches, they typically do not pose a direct, full-scale threat to established banks like Qilu Bank. These agile competitors often focus on areas like digital payments or online lending, leveraging technology to gain market share in specific segments. However, their ability to challenge the core banking operations of established institutions remains limited by regulatory scope and the need for comprehensive financial services.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Qilu Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the bank's official annual reports, filings with regulatory bodies like the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), and industry-specific market research reports from reputable sources.