Preformed Line Products Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Preformed Line Products Bundle
Preformed Line Products operates in a market characterized by moderate buyer power and significant supplier influence, impacting their pricing strategies. The threat of new entrants is tempered by high capital requirements and established brand loyalty within the utility sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Preformed Line Products’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical raw materials like metals, including copper and aluminum, significantly impacts Preformed Line Products (PLP). If there are only a few dominant suppliers for these essential components, their ability to dictate terms and prices to PLP increases. This consolidation can lead to higher input costs for PLP, squeezing profit margins.
Recent market dynamics underscore this vulnerability. For instance, global aluminum prices experienced significant fluctuations throughout 2024, driven by factors such as energy costs and geopolitical events. Similarly, copper prices remained elevated due to robust demand from the electric vehicle sector and infrastructure projects. This environment inherently strengthens the bargaining position of suppliers in these concentrated markets.
Preformed Line Products (PLP) faces significant challenges due to the volatile nature of raw material costs, particularly for copper and aluminum. These metals are critical for PLP's product manufacturing, and their prices have been on an upward trend. For instance, in early 2025, copper prices surged by approximately 15% compared to the previous year, driven by robust demand from the expanding renewable energy sector and the automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles. Similarly, aluminum prices saw an increase of around 10% during the same period, exacerbated by persistent global supply chain disruptions.
Switching suppliers for Preformed Line Products (PLP) could involve substantial financial and operational hurdles. These might include the costs associated with retooling manufacturing lines to accommodate new materials or designs, the expense and time required to requalify new components to meet stringent industry standards, and the potential disruption to established supply chain relationships that have been carefully cultivated over time. These factors collectively increase the difficulty and cost of changing suppliers, thus bolstering the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
Uniqueness and Differentiation of Supplier Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is significantly influenced by the uniqueness and differentiation of their inputs. If suppliers provide highly specialized or proprietary materials and technologies that are crucial for PLP's advanced and innovative product designs, their leverage increases. PLP's commitment to precision engineering in its solutions often necessitates inputs that are not readily available as standardized commodities.
Consider the following:
- Specialized Materials: Suppliers offering unique alloys, advanced polymers, or specific coatings critical for PLP's product performance and durability hold greater bargaining power.
- Proprietary Technologies: If suppliers possess patented manufacturing processes or unique material science expertise that PLP relies on, this enhances their position.
- Critical Components: Inputs that are essential for the functional integrity and competitive advantage of PLP's products, such as specific types of protective coatings or high-strength conductors, give suppliers more sway.
- Limited Alternatives: The absence of readily available substitutes for these specialized inputs further strengthens the suppliers' bargaining power, potentially leading to higher input costs for PLP.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration, meaning they start producing the same products as Preformed Line Products (PLP), is a critical consideration. If a supplier has the technical expertise and financial resources to manufacture cable anchoring and control hardware, they could enter PLP's market directly, thereby increasing their leverage.
While this risk is generally lower for suppliers of basic raw materials, it becomes more pronounced with specialized component manufacturers. For instance, a key supplier of a proprietary connector or a specialized alloy could potentially leverage their existing manufacturing capabilities to compete with PLP. This scenario would shift the power dynamic significantly, as PLP would then face competition from its own supply chain.
- Supplier Capability: Assess if key suppliers possess the manufacturing infrastructure and technical know-how to produce PLP's finished goods.
- Market Incentive: Evaluate if suppliers see a profitable opportunity in entering PLP's market, potentially by capturing existing customer relationships.
- Industry Trends: Monitor for instances in the broader utility and telecommunications hardware sector where suppliers have successfully integrated forward.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is amplified by the limited availability of crucial, specialized materials and technologies. When suppliers offer unique alloys or proprietary manufacturing processes essential for PLP's high-performance products, their leverage increases significantly. This reliance on specialized inputs, coupled with the difficulty and cost of switching, strengthens the suppliers' position, potentially driving up input costs for PLP.
The concentration of suppliers for critical raw materials like copper and aluminum significantly impacts PLP. If only a few dominant suppliers exist for these essential components, their ability to dictate terms and prices to PLP increases, potentially squeezing profit margins. For example, global aluminum prices saw an approximate 10% increase in early 2025 due to persistent supply chain disruptions, while copper prices surged by about 15% driven by demand from the renewable energy and automotive sectors, underscoring supplier leverage in these consolidated markets.
| Factor | Impact on PLP | Supplier Leverage | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Copper, Aluminum) | Higher input costs, potential margin squeeze | High | Aluminum prices +10% (early 2025); Copper prices +15% (early 2025) |
| Specialized/Proprietary Inputs | Reliance on unique materials/technologies | High | PLP's need for advanced polymers and specific coatings |
| Switching Costs | Financial and operational hurdles to change suppliers | High | Costs of retooling, requalification, and supply chain disruption |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers to become competitors | Moderate (for specialized component suppliers) | Monitoring for suppliers entering the utility hardware market |
What is included in the product
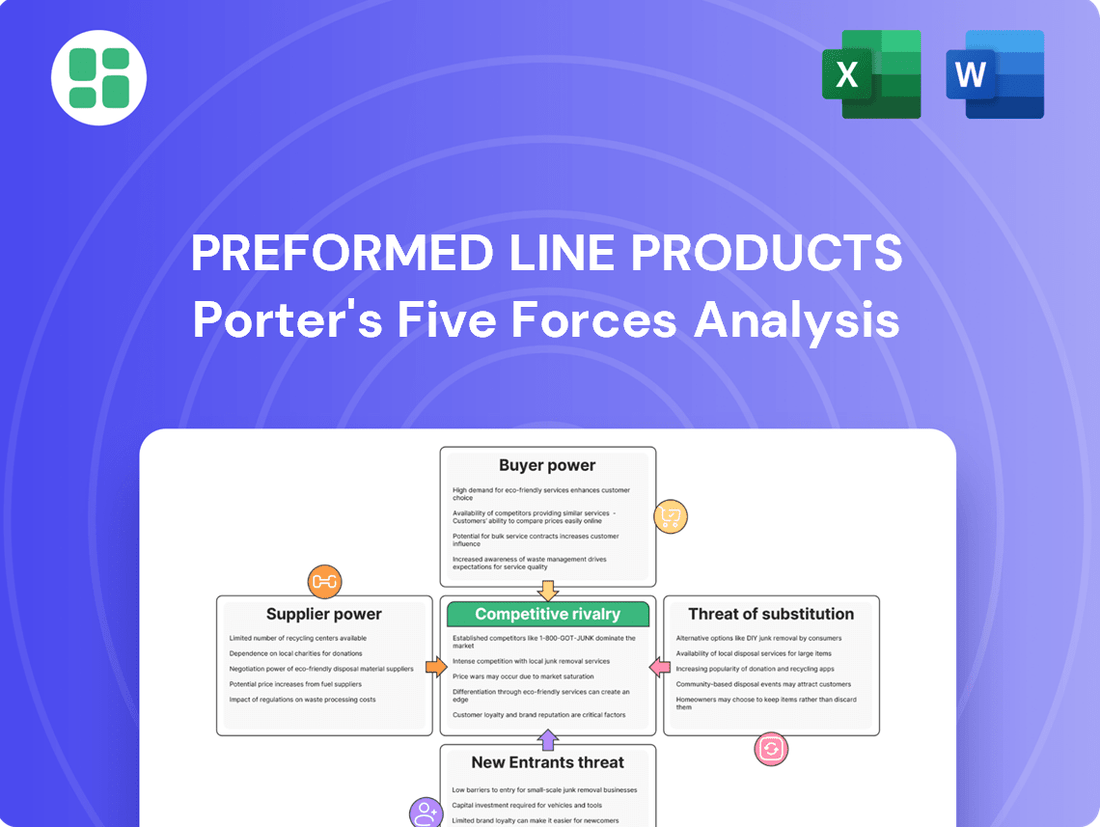
This analysis examines the competitive forces impacting Preformed Line Products, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the power line hardware industry.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape for Preformed Line Products with a dynamic, interactive model that highlights key pressures and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Preformed Line Products' (PLP) bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the concentration and size of its key clients. Major energy utilities, telecommunication network operators, and broadband service providers represent a substantial portion of PLP's revenue base.
When a few large customers make up a significant percentage of PLP's sales, they gain considerable leverage to negotiate pricing, dictate terms, and set service expectations. This is particularly relevant as PLP operates within critical infrastructure sectors where customer consolidation is a common trend.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in Preformed Line Products' (PLP) market position. For customers in critical infrastructure sectors like utilities, changing suppliers can be challenging. This is often due to the need for products to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, meet stringent regulatory requirements, and provide the long-term reliability essential for power transmission and distribution. For example, a utility company might have invested heavily in training its crews on specific PLP installation techniques or have existing contracts that mandate the use of PLP components for warranty or compatibility reasons.
However, the power of customers to switch does increase if competitors can offer genuinely compelling alternatives. If a rival product provides a clear cost advantage without sacrificing performance or introduces innovative features that significantly improve efficiency or safety, customers may be incentivized to explore those options. For instance, a new material composite offering a 15% weight reduction could lead to lower installation labor costs, making it an attractive alternative to PLP's current offerings, potentially shifting customer loyalty.
Customers' sensitivity to price significantly impacts Preformed Line Products (PLP). In the competitive energy and telecom sectors, where PLP operates, price often serves as a primary differentiator. This means that even small price increases can lead customers to seek alternatives.
Many of PLP's customers, particularly those in infrastructure projects, are subject to tight budgets and cost-containment measures. For instance, government funding initiatives like the BEAD program, while boosting demand, also come with strict cost controls, amplifying customer price sensitivity. This financial pressure makes them highly receptive to lower-priced offerings.
Importance of PLP's Products to Customer Operations
The criticality of Preformed Line Products' (PLP) cable anchoring and control hardware to customer operations significantly influences their bargaining power. PLP's offerings are indispensable for the construction and maintenance of essential overhead, underground, and underwater infrastructure. This inherent necessity can diminish a customer's leverage, particularly when viable alternatives are limited.
- Essential Infrastructure Reliance: PLP's products are fundamental components in maintaining critical power and communication networks, making them difficult for customers to substitute without significant operational disruption.
- Limited Availability of Alternatives: The specialized nature of PLP's solutions means that customers often face few, if any, equally effective alternatives, thereby reducing their ability to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms.
- Impact on Operational Continuity: For utilities and telecommunications companies, the reliable performance of PLP hardware is directly tied to service continuity, a factor that often outweighs price considerations in procurement decisions.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers for Preformed Line Products (PLP) centers on the possibility of major clients, such as large utilities or telecom companies, choosing to produce their own cable hardware and systems. This strategic shift could occur if PLP's pricing becomes uncompetitive or if these customers prioritize enhanced control over their supply chains.
While the highly specialized nature of many PLP components makes full in-house manufacturing challenging, significant cost savings or critical supply chain vulnerabilities could incentivize some larger customers to explore this avenue. For instance, a major utility facing rising costs for specialized connectors might assess the feasibility of internal production, especially if their volume justifies the investment.
- Customer Integration Risk: Large utility and telecom companies possess the potential to manufacture PLP's products in-house, particularly if cost pressures mount or supply chain control becomes paramount.
- Component Specialization: The highly specialized nature of many PLP products acts as a natural barrier to complete backward integration for most customers.
- Cost and Control Drivers: Significant price increases from PLP or a strategic imperative for greater supply chain autonomy are the primary motivators for customer backward integration.
The bargaining power of customers for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is moderate, primarily due to the critical nature of their products and the specialized manufacturing involved. While large utility and telecom clients represent significant revenue streams, their reliance on PLP's proven reliability and adherence to industry standards limits their ability to switch easily or exert extreme price pressure.
Customer concentration is a key factor; a few major utility companies and telecommunication providers account for a substantial portion of PLP's sales. This concentration grants these large buyers leverage to negotiate pricing and terms, especially given the ongoing consolidation within these infrastructure sectors. For example, if a single utility accounts for over 10% of PLP's annual revenue, their negotiating position is considerably strengthened.
Switching costs for customers are generally high. Integrating new suppliers requires rigorous testing, qualification, and potential retraining of installation crews, which can be costly and time-consuming for critical infrastructure projects. This inertia favors existing suppliers like PLP, particularly when their products meet stringent performance and safety regulations.
| Customer Segment | Concentration Level | Switching Costs | Price Sensitivity | Overall Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Utilities | High | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Telecom Network Operators | Moderate | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Broadband Service Providers | Moderate | Moderate | High | Moderate |
Preview Before You Purchase
Preformed Line Products Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. Our comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the competitive landscape for Preformed Line Products, meticulously detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This in-depth examination provides actionable insights to inform your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Preformed Line Products (PLP) operates in a market characterized by a significant number of competitors, ranging from large, diversified electrical component manufacturers to smaller, specialized firms. This diverse competitive landscape means rivalry can be intense across various product segments and geographic regions.
For instance, in the global overhead conductor accessories market, PLP competes with giants like CommScope and Nexans, which offer a broad portfolio of utility solutions. Simultaneously, it faces specialized players focusing on specific product niches, such as anchor grips or protective hardware, potentially driving up competition for market share in those particular areas.
The energy, telecommunications, and broadband infrastructure markets are experiencing significant growth, which generally tempers competitive rivalry. However, this dynamic can shift. For instance, while the global cable accessories market is expected to see a healthy 5.14% CAGR from 2025 to 2033, driven by infrastructure upgrades and renewable energy projects, certain segments might face slower expansion.
In 2024, the U.S. communications market, for example, might exhibit more moderate growth compared to other regions or sectors. This slower pace in specific areas can intensify competition as companies vie more aggressively for existing market share, potentially leading to price pressures and increased marketing efforts.
Preformed Line Products (PLP) strives to differentiate its offerings through precision engineering and a focus on innovative, reliable solutions. This approach aims to build higher switching costs for customers, as transitioning to a competitor might involve retooling, retraining, or accepting potentially less robust performance. For instance, in the utility sector, the integration of specialized hardware can make a switch costly and time-consuming.
However, the degree of product differentiation is crucial. If PLP's products are perceived as increasingly similar to those of competitors, they risk becoming commoditized. In 2024, the infrastructure market continues to see advancements, and while PLP's commitment to quality remains, the competitive landscape necessitates ongoing innovation to maintain this differentiation and prevent a slide into price-based competition.
Exit Barriers in the Industry
Companies in the cable hardware manufacturing sector often face significant obstacles when attempting to exit the market. These exit barriers are substantial, influencing the intensity of competition.
High fixed costs are a primary driver of these barriers. Specialized manufacturing facilities, advanced machinery, and established global distribution networks represent considerable investments. For instance, the capital expenditure for setting up a state-of-the-art production line for preformed line products can easily run into tens of millions of dollars. These sunk costs make it financially unviable for many firms to simply shut down operations, even when facing declining revenues or profitability.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized equipment for manufacturing preformed line products can cost upwards of $5 million per production line.
- Global Distribution Networks: Establishing and maintaining a worldwide logistics and distribution system involves significant ongoing operational costs.
- Asset Specificity: Manufacturing equipment is often highly specialized and has limited resale value outside the industry, increasing the cost of exit.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply agreements and customer contracts can also tie companies to the industry, further complicating an exit strategy.
Competitive Strategies and Price Pressure
Competitive rivalry is a significant factor for Preformed Line Products (PLP). Competitors frequently employ strategies centered on pricing, product performance, and customer service to gain market share. In PLP's industry, aggressive pricing by rivals or substantial investments in research and development for enhanced product performance can escalate the intensity of this rivalry.
PLP's own financial reporting for 2024 explicitly highlighted the presence of competitive and customer price pressure within the market. This indicates that PLP is actively contending with rivals who are either undercutting prices or offering superior value propositions that compel customers to seek better terms.
- Pricing Strategies: Competitors may engage in price wars to attract customers, forcing PLP to consider matching or adjusting its own pricing.
- Performance Differentiation: Investments in R&D by rivals to offer enhanced product durability, efficiency, or ease of installation can create a performance gap that PLP must address.
- Service Levels: Superior customer support, faster delivery times, or more comprehensive technical assistance from competitors can also be a key differentiator.
- Market Share Dynamics: The overall market structure, including the number and size of competitors, directly influences the degree of rivalry and the pressure on PLP.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Preformed Line Products (PLP), with numerous competitors vying for market share through pricing, performance, and service. In 2024, PLP's financial reports indicated ongoing price pressures from customers and competitors, underscoring the need for continuous innovation and value enhancement.
The intensity of this rivalry is further shaped by substantial exit barriers, such as high capital investment in specialized manufacturing equipment, which can exceed $5 million per production line. These barriers discourage companies from leaving the market, ensuring a consistently competitive landscape.
PLP differentiates itself through precision engineering and reliable solutions, aiming to increase customer switching costs. However, if products become too similar, commoditization and price-based competition become greater risks, especially in segments with slower growth, like certain areas of the U.S. communications market in 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on PLP |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | Large number of diversified and specialized firms. | Intensifies competition across product segments. |
| Product Differentiation | PLP focuses on engineering and reliability. | Aims to create switching costs, but risk of commoditization exists. |
| Exit Barriers | High capital investment, specialized assets, global networks. | Keeps competitors in the market, sustaining rivalry. |
| Pricing Pressure | Evident in 2024 financial reports. | Requires PLP to manage costs and value proposition effectively. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is intensifying with the rapid advancement of alternative technologies offering connectivity. These substitutes fulfill the fundamental customer need for communication and data transfer, often bypassing the need for traditional wired or overhead infrastructure that PLP's products support.
Emerging wireless solutions, such as 5G and the anticipated 6G networks, are expanding coverage and capacity, presenting a direct alternative to wired connections. Furthermore, satellite broadband is increasingly viable, especially for reaching remote or underserved regions, directly challenging the market for traditional connectivity deployment.
The increasing sophistication and widespread adoption of wireless technologies, such as private 5G networks, present a growing threat to traditional wired infrastructure. While Preformed Line Products (PLP) serves the wired sector, the migration of certain communication services to wireless could dampen demand for some of their cable-related products.
However, it's crucial to note that many advanced wireless deployments, including private 5G, still heavily depend on robust wired backhaul for reliable data transmission. In 2024, the global private 5G market was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, underscoring the significant investment in this area, which in turn can drive demand for the very wired infrastructure PLP specializes in.
Advancements in fiber optic technology pose a significant threat of substitution for traditional copper or coaxial cable systems, particularly in high-speed data transmission. Projects like NTT's IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network) aim to push optical networks further into computing infrastructure, potentially displacing copper even within systems. This trend impacts Preformed Line Products (PLP) as they serve the fiber optic market, but also face competition from these evolving technologies.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is significantly influenced by the price-performance trade-off. Customers will switch to alternatives if they offer a more attractive balance of cost and functionality. For example, while advancements in fiber optics provide superior bandwidth and speed, their higher initial installation costs can make traditional coaxial cables a more appealing substitute in certain scenarios where cost is the primary driver and the performance demands are less stringent. As of 2024, the global fiber optic cable market is projected to reach over $10 billion, yet coaxial cable still holds a substantial market share due to its established infrastructure and lower per-unit cost for certain deployments.
This dynamic means that PLP must continuously assess the evolving cost structures and performance capabilities of competing technologies. If substitute solutions, such as advanced polymer composites or alternative metallic conductors, begin to offer comparable or superior performance at a notably lower price point, PLP's market position could be challenged. For instance, the cost of fiber optic installation, while decreasing, still presents a barrier compared to the readily available and understood coaxial infrastructure in many regions.
Key considerations in this price-performance evaluation include:
- Cost of Installation: The upfront expense associated with deploying a substitute technology versus PLP's solutions.
- Performance Metrics: How substitutes measure up in terms of bandwidth, signal integrity, durability, and latency.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Including maintenance, upgrade, and operational costs over the lifespan of the product.
- Application Suitability: Whether a substitute meets the specific technical requirements of a given use case, even if at a different price point.
Innovation in Cable Management and Installation Methods
Innovations in cable management and installation methods pose a significant threat by potentially reducing the demand for traditional anchoring and control hardware. For instance, the increasing adoption of underground cabling, a trend expected to continue growing, bypasses the need for many overhead line accessories. In 2024, the global market for underground power cables was valued at approximately USD 45 billion, with projections indicating steady growth driven by infrastructure upgrades and aesthetic preferences.
Smart grid technologies also contribute to this threat. As grids become more intelligent and integrated, the complexity of required physical infrastructure may decrease, leading to simpler, more streamlined systems. This shift could mean fewer specialized components are needed for cable support and management. For example, advancements in self-supporting insulated cables require less extensive pole hardware compared to older conductor types.
- Underground cabling adoption: Expected to reduce demand for overhead line hardware.
- Smart grid integration: Simplifies infrastructure needs, potentially decreasing accessory requirements.
- Advanced cable types: Self-supporting cables reduce the need for extensive pole accessories.
The threat of substitutes for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is amplified by the growing availability and decreasing cost of wireless communication solutions. While PLP traditionally serves wired infrastructure, the increasing capability and reach of technologies like 5G and satellite broadband offer alternative ways to deliver connectivity, potentially reducing the need for new or upgraded physical cable networks. For example, in 2024, the global 5G infrastructure market was valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating significant investment in wireless alternatives.
Furthermore, innovations in materials and installation techniques for competing cable types can also act as substitutes. Advancements in fiber optic technology, while often complementary, can also replace older copper infrastructure, impacting the demand for specific PLP products. The price-performance ratio remains a critical factor; if substitute solutions offer comparable or better functionality at a lower total cost of ownership, PLP's market share could be affected.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | Potential Impact on PLP |
|---|---|---|
| 5G/6G Wireless | Ubiquitous coverage, mobility | Reduced demand for new wired backhaul in some applications |
| Satellite Broadband | Remote area access | Alternative to ground-based infrastructure in underserved regions |
| Advanced Fiber Optics | Higher bandwidth, lower latency | Displacement of older copper/coaxial infrastructure |
| Underground Cabling | Aesthetics, protection | Reduced need for overhead line accessories |
Entrants Threaten
The capital requirements for entering the Preformed Line Products (PLP) market are substantial. Establishing global manufacturing facilities, acquiring specialized machinery for precision engineering, and funding ongoing research and development for advanced cable anchoring and control hardware demand significant financial outlays. For example, setting up a new, state-of-the-art manufacturing plant can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, creating a formidable barrier.
New entrants face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels and cultivating crucial customer relationships within the utility and telecommunications sectors. These markets are characterized by long-standing partnerships built on trust and proven performance, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold. For instance, major energy utilities and telecom providers often have deeply embedded supply chains and contractual agreements that new companies struggle to penetrate.
The threat of new entrants for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is significantly influenced by its robust intellectual property and proprietary technology. PLP's commitment to innovative and precision-engineered solutions, often protected by patents and specialized manufacturing processes, creates a substantial barrier to entry. For instance, the company’s investment in research and development, which fuels these proprietary technologies, requires considerable upfront capital and expertise that potential competitors must overcome.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
The threat of new entrants for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is significantly moderated by substantial economies of scale and the experience curve. Established players like PLP benefit from lower per-unit production costs due to their high-volume manufacturing, a factor that is difficult for newcomers to replicate immediately. For instance, in 2024, the global electrical transmission and distribution equipment market, where PLP operates, was valued at approximately $180 billion, with significant consolidation among major players.
New entrants would face the challenge of achieving comparable production efficiencies and cost structures. This learning curve, often referred to as the experience curve, allows incumbent firms to continuously refine their processes, reduce waste, and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
- Economies of Scale: PLP's large-scale production facilities allow for lower per-unit manufacturing costs compared to potential new entrants.
- Experience Curve Advantages: Decades of operational experience have enabled PLP to optimize its processes, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings.
- Capital Investment: Establishing production capabilities to rival PLP's scale requires substantial upfront capital investment, creating a barrier for new companies.
- Supply Chain Optimization: PLP has likely developed highly efficient and cost-effective supply chains over time, which new entrants would struggle to match quickly.
Regulatory Hurdles and Industry Standards
The threat of new entrants into the Preformed Line Products (PLP) market is significantly influenced by substantial regulatory hurdles and stringent industry standards. For products essential to critical infrastructure, such as those used in energy grids and telecommunications, compliance with rigorous safety, performance, and compatibility requirements is paramount. These standards, often established by bodies like the IEEE or national regulatory agencies, can be complex and costly for new companies to navigate and implement.
Achieving certification and meeting these demanding specifications can require significant investment in research, development, testing, and quality control. For instance, products designed for high-voltage power transmission lines must undergo extensive testing to ensure reliability and safety under extreme conditions. This high barrier to entry means that only well-capitalized and technically proficient companies can realistically consider entering the market. In 2024, the ongoing upgrades to 5G infrastructure and the expansion of renewable energy grids continue to drive the need for highly specialized and compliant components, further solidifying the advantage of established players like PLP who have already invested in meeting these exacting standards.
- Stringent Safety and Performance Standards: PLP's products for critical infrastructure must adhere to demanding safety and performance benchmarks, increasing the cost and complexity for new entrants.
- High Compliance Costs: Meeting regulatory requirements and industry-specific standards involves substantial investment in R&D, testing, and quality assurance, creating a financial barrier.
- Complex Certification Processes: New companies face lengthy and intricate processes to obtain necessary certifications, delaying market entry and adding to initial expenses.
- Technological Expertise Required: The specialized nature of products for energy and telecom sectors necessitates advanced technical knowledge and manufacturing capabilities, which are difficult for new entrants to quickly acquire.
The threat of new entrants for Preformed Line Products (PLP) is considerably low due to the substantial capital investment required to establish manufacturing facilities and acquire specialized equipment. For instance, the global market for electrical transmission and distribution equipment, a sector PLP operates within, saw significant investment in new technologies and infrastructure upgrades throughout 2024, indicating high entry costs.
Furthermore, PLP benefits from strong brand recognition and established relationships with key customers in the utility and telecommunications industries, built over decades of reliable performance. Penetrating these established supply chains, which often involve long-term contracts and rigorous vetting processes, presents a significant challenge for any new competitor seeking to enter the market.
Proprietary technology and intellectual property also serve as a formidable barrier; PLP's investment in research and development for advanced cable anchoring and control hardware, often protected by patents, requires considerable expertise and upfront capital that new entrants must overcome. In 2024, the demand for innovative solutions in grid modernization and 5G deployment further emphasized the importance of advanced, proprietary product offerings.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point (2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for manufacturing, machinery, and R&D | Setting up a new, state-of-the-art manufacturing plant can cost tens of millions of dollars. |
| Distribution Channels & Customer Relationships | Difficulty in accessing established utility/telecom supply chains | Major energy utilities and telecom providers have deeply embedded supply chains and long-standing partnerships. |
| Intellectual Property & Technology | Patented and proprietary manufacturing processes | PLP's investment in R&D fuels proprietary technologies that require significant capital and expertise to replicate. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience Curve | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production and optimized processes | The global electrical transmission and distribution equipment market, valued around $180 billion in 2024, shows consolidation among players with scale advantages. |
| Regulatory Hurdles & Industry Standards | Compliance with stringent safety, performance, and compatibility requirements | Products for high-voltage transmission lines require extensive testing and certification, adding to entry costs and complexity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Preformed Line Products is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from publicly traded competitors, and trade association data. We also incorporate insights from company investor relations websites and relevant news archives to capture current market dynamics and strategic positioning.