Integer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Integer Bundle
Integer's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Integer’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Integer's reliance on a limited number of specialized third-party suppliers for critical raw materials and components grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. For instance, if only a few companies can produce a unique, high-purity polymer essential for certain medical devices, those suppliers can dictate terms. This concentration is a key factor in assessing supplier leverage.
The limited supplier base for specialized inputs means Integer has fewer alternatives, increasing the power of those who can provide these unique or high-quality materials. This is particularly true for components requiring advanced manufacturing processes or specific certifications vital for the medical device industry, where quality and compliance are paramount.
Geopolitical tensions and rising inflation in 2024 have already demonstrated the impact of supply chain disruptions on manufacturers. For Integer, these external factors can exacerbate the bargaining power of concentrated suppliers, potentially leading to increased input costs and operational challenges, directly affecting profitability and production schedules.
Suppliers of critical medical device components face increasingly stringent regulatory landscapes, with major shifts expected in 2025 under frameworks like the EU MDR and FDA QMSR. These evolving global quality and safety requirements necessitate significant investment from suppliers.
The substantial costs incurred by suppliers to achieve and maintain compliance with these complex regulations, such as those for device traceability and cybersecurity, can be directly passed on to manufacturers like Integer. This creates a leverage point for suppliers, enhancing their bargaining power.
Integer must actively ensure its supply chain partners not only meet but also adapt to these dynamic global quality and safety mandates. Failure to do so could lead to disruptions or increased component costs, impacting Integer's own product development and market competitiveness.
Integer faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers in the medical device sector. These costs stem from rigorous re-qualification and validation processes, essential for regulatory compliance and product integrity. For instance, in 2023, the medical device industry saw continued investment in quality assurance and regulatory affairs, highlighting the importance of these validation steps.
These substantial switching barriers empower Integer's existing suppliers. The potential for production disruptions and the lengthy, costly process of onboarding new suppliers make Integer hesitant to switch, even if current terms are less attractive. This dynamic solidifies supplier leverage.
The highly specialized nature of components used in critical medical devices, such as those for cardiac, neuromodulation, and vascular applications, further intensifies these supplier relationships. These specialized components often require unique manufacturing processes and materials, making it difficult and time-consuming to find and qualify alternative sources.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
A supplier's ability to forward integrate, meaning they start producing finished products that compete with their customers, poses a potential threat. For Integer, this could involve a component supplier moving into manufacturing complete medical devices.
However, the high capital expenditure, extensive research and development, and stringent regulatory knowledge needed to enter the medical device outsource (MDO) market create substantial barriers. For instance, the global medical device market was valued at approximately $567 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, but the MDO segment demands specialized expertise and significant upfront investment, making it difficult for most suppliers to transition.
- High Barrier to Entry: The medical device industry requires substantial R&D investment and adherence to complex regulations like FDA approvals.
- Capital Intensive: Establishing manufacturing capabilities for finished medical devices demands significant financial resources.
- Regulatory Expertise: Navigating the regulatory landscape for medical devices is a complex and costly undertaking.
- Mitigated Threat: These factors significantly reduce the likelihood of suppliers effectively forward integrating into Integer's core market.
Uniqueness of Inputs
Integer's reliance on unique and specialized inputs for its innovative medical devices significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. For example, the company often needs advanced materials such as high-purity Nitinol, a shape memory alloy crucial for many of its guidewires and catheters. When only a limited number of suppliers can produce these high-specification materials, their leverage over Integer naturally grows.
The uniqueness of these inputs means Integer may face higher costs or less favorable terms if these suppliers have few other customers. This situation can arise with specialized coatings or proprietary manufacturing processes that are essential for the performance and regulatory approval of Integer's products. For instance, a unique biocompatible coating might only be available from one or two specialized chemical companies.
Integer's strategic approach, including acquisitions like Precision Coating, aims to mitigate this dependency. By bringing specialized capabilities in-house, Integer can reduce its reliance on external suppliers for critical components, thereby strengthening its own bargaining position. This vertical integration helps secure supply chains and potentially control input costs for these unique materials.
- Nitinol: A key input for guidewires and catheters, its specialized production limits supplier options.
- Specialized Coatings: Essential for biocompatibility and device performance, these often come from niche suppliers.
- Acquisition Strategy: Integer's move to acquire companies like Precision Coating aims to internalize unique manufacturing capabilities and reduce supplier reliance.
Suppliers of critical components for Integer, particularly those with unique or specialized inputs, wield significant bargaining power. This is amplified by the high switching costs Integer faces due to rigorous validation processes, which can take months and cost millions. For example, in 2024, the medical device industry saw continued emphasis on supply chain resilience, underscoring the importance of supplier relationships and the difficulty of changing them.
The increasing complexity of global regulations, such as the EU MDR and FDA QMSR, places a greater burden on suppliers to invest in compliance. Suppliers who successfully navigate these evolving quality and safety mandates can leverage their expertise and investment to command higher prices from their customers, including Integer.
Integer's strategy to mitigate supplier power includes vertical integration, exemplified by acquisitions like Precision Coating. This move helps secure the supply of specialized materials and reduces reliance on external entities, thereby strengthening Integer's position in negotiations.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Integer's Mitigation Strategy |
| Limited Supplier Base for Specialized Inputs | High | Vertical Integration (e.g., Precision Coating acquisition) |
| High Switching Costs | High | Long-term supplier relationships, rigorous validation processes |
| Supplier Investment in Regulatory Compliance | Moderate to High | Partnering with compliant suppliers, proactive engagement |
| Uniqueness of Inputs (e.g., Nitinol) | High | Exploring alternative material science, R&D for in-house capabilities |
What is included in the product
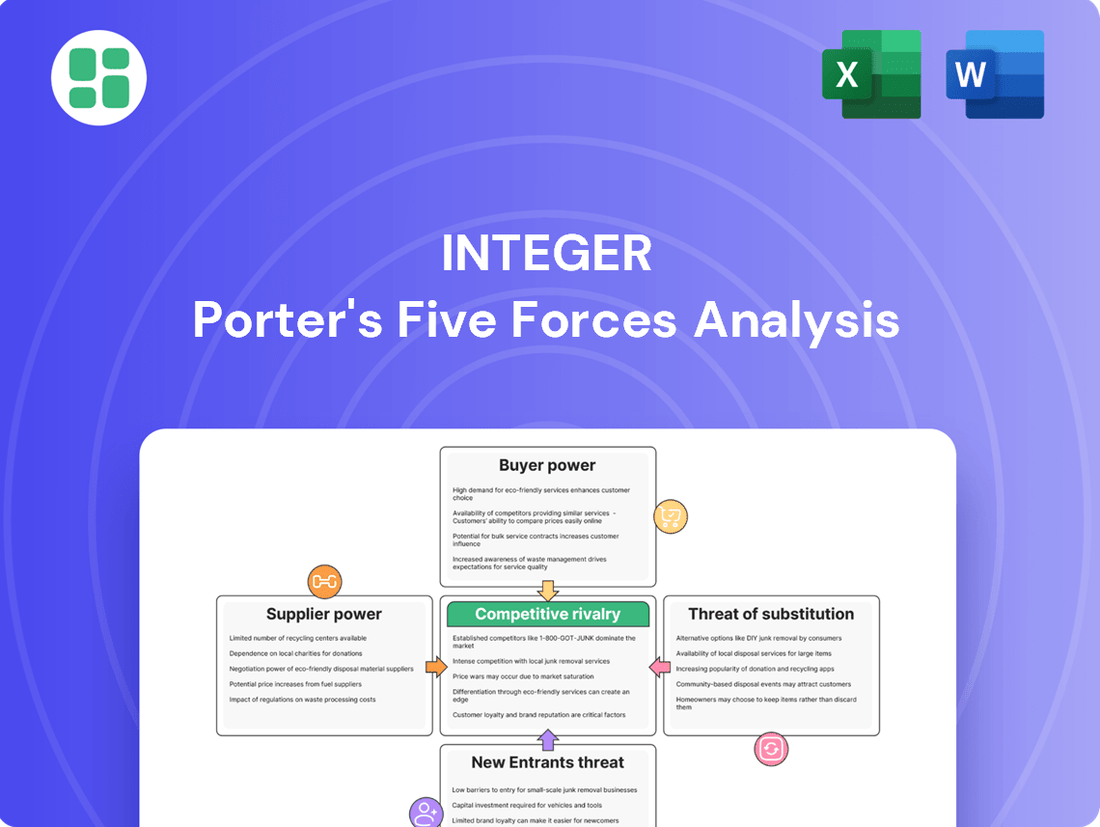
This analysis assesses the competitive intensity and attractiveness of the markets Integer operates within by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures with a visual dashboard, transforming complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Integer's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by high customer concentration. In 2024, the company's top three customers represented a substantial 47% of its total sales. This reliance on a few major clients, typically large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), grants these customers considerable leverage.
This concentration means that the loss or even a reduction in orders from a single key customer can have a disproportionately large impact on Integer's overall revenue and profitability. Such a scenario empowers these major clients to effectively negotiate pricing, demand more favorable contract terms, and potentially dictate product specifications.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in the bargaining power of customers for companies like Integer, especially within the medical device outsourcing (MDO) sector. While a concentrated customer base might suggest strong leverage, the practicalities of changing MDO partners are often complex and expensive. These costs can include substantial investments in re-tooling manufacturing lines, rigorous re-validation processes for regulatory compliance, and the potential for significant delays in bringing new or updated medical devices to market.
Integer's strategic positioning as a provider of innovative and high-quality solutions means its products are frequently deeply embedded within the customer's product development and manufacturing workflows. This high degree of integration, coupled with Integer's specialized technical expertise and proprietary processes, can create a strong incentive for customers to remain with their existing partner. For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry continued to emphasize product reliability and speed to market, making the disruption associated with switching suppliers a considerable deterrent.
Integer's diverse product range, encompassing cardiac rhythm management, neuromodulation, and vascular delivery systems, forms the backbone of its Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) customers' advanced medical devices.
These specialized components are not mere additions; they are critical inputs whose quality directly impacts the functionality and safety of the final medical products. For instance, a failure in a cardiac rhythm management component could lead to severe patient health outcomes and significant regulatory penalties for the OEM.
This deep integration and the critical nature of Integer's offerings mean that customers face substantial risks if they switch suppliers, thereby reducing their bargaining power. Integer's role as a provider of essential, high-quality inputs grants it a degree of pricing leverage.
Customers' Price Sensitivity
Customers in the medical device industry, particularly Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is driven by the constant need to manage costs, even for critical components and manufacturing services. For instance, in 2024, many OEMs reported that component costs represented a substantial portion of their overall product cost, leading them to actively seek competitive bids for even specialized parts.
While the life-saving nature of medical devices is paramount, customers will still prioritize cost-effectiveness, especially when dealing with more standardized or commoditized elements of production. This means that even for essential inputs, the pursuit of better pricing remains a key consideration. This pressure is amplified as the market for certain medical components becomes more saturated.
Integer's strategic advantage lies in its capacity to deliver manufacturing solutions that are not only cost-effective but also accelerate the time-to-market for new devices. By offering competitive pricing structures and streamlining the production process, Integer can effectively counter the intense price pressure exerted by its customer base. This dual focus on cost and speed is crucial for maintaining strong customer relationships in this demanding sector.
- OEMs' Cost Containment Efforts: Many medical device manufacturers aim to reduce their bill of materials by at least 5-10% annually, impacting component sourcing decisions.
- Component Commoditization: For less complex or more widely available medical device components, price can become a primary differentiator among suppliers.
- Integer's Value Proposition: The company's ability to offer integrated manufacturing services, including design for manufacturability and efficient production, helps customers achieve their cost reduction targets.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, reports indicated that supply chain disruptions, while easing, still encouraged OEMs to diversify suppliers and negotiate harder on price for non-critical components.
Customers' Threat of Backward Integration
Customers' threat of backward integration at Integer is influenced by the capabilities of large medical device Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). These OEMs often have the financial muscle and technical expertise to bring component manufacturing in-house, potentially reducing their reliance on suppliers like Integer. However, the strategic decision to backward integrate is complex.
Outsourcing to specialized manufacturers such as Integer allows OEMs to concentrate on their core strengths, such as research, development, and marketing. This division of labor also helps OEMs avoid significant capital investments in manufacturing facilities and can expedite the launch of new products. For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry continued to see a trend of OEMs focusing on innovation rather than vertical integration for component production.
The escalating complexity of modern medical devices further diminishes the attractiveness of full backward integration for many OEMs. Managing the intricate manufacturing processes for specialized components requires distinct skill sets and infrastructure. Integer’s expertise in areas like advanced catheter manufacturing, which saw significant demand in 2024, provides a compelling reason for OEMs to continue outsourcing these critical functions.
- OEMs often prioritize core competencies over vertical integration for component manufacturing.
- Outsourcing to specialists like Integer can reduce capital expenditure and accelerate time-to-market for OEMs.
- The increasing technical complexity of medical devices favors specialized outsourcing partners.
Integer's customers, primarily large Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in the medical device sector, possess significant bargaining power. This is amplified by customer concentration, with Integer's top three customers accounting for 47% of sales in 2024, giving them considerable negotiation leverage on pricing and terms. Despite the high switching costs associated with re-tooling and regulatory re-validation, which typically limit customer power, the intense price sensitivity within the medical device industry means OEMs actively seek cost reductions. For example, many OEMs targeted 5-10% annual reductions in their bill of materials in 2024.
| Customer Factor | Impact on Integer | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for top clients | Top 3 customers = 47% of sales |
| Switching Costs | Generally high for OEMs | Complex re-validation, delays deter switching |
| Price Sensitivity | Strong pressure on component costs | OEMs target 5-10% annual BOM reduction |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Limited by OEM focus on core competencies | OEMs prioritize innovation over in-house component manufacturing |
What You See Is What You Get
Integer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Integer Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the integer market. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase. It meticulously breaks down the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector. You're looking at the actual document, ready for your strategic planning the moment you complete your purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The medical device outsource (MDO) market, where Integer operates, features a mix of large, established medical technology giants and niche, specialized contract manufacturers. This creates a dynamic and often intense competitive environment.
Key players such as Medtronic, Abbott Laboratories, Boston Scientific, Stryker, Smith & Nephew, and Enovis are significant forces, often competing across a broad range of device categories. However, the market also includes specialized players like LISI Group, focusing on specific technologies or market segments.
For instance, in 2024, the global medical device outsourcing market was valued at approximately USD 35 billion and is projected to grow, underscoring the substantial investment and interest from numerous companies, both large and small, vying for market share.
The global medical device market is expanding at a healthy clip, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 9.7% and 15.6% from 2024 through 2029 and even further to 2034. This strong industry growth generally eases competitive pressures by creating ample room for all companies to grow without directly impacting their rivals' market share.
However, this doesn't mean competition isn't fierce. Within specific, rapidly expanding niches of the medical device sector, the battle for market leadership remains intense. Companies are still vying for dominance in these high-demand areas, even with the overall market expanding.
Integer differentiates itself through its innovative, high-quality products and end-to-end development capabilities, particularly in cardiac rhythm management, neuromodulation, and vascular systems. Recent acquisitions, like those for specialized coating services, further bolster this differentiation. For example, in 2023, the medical device industry saw significant investment in R&D, with major players allocating billions to bring novel solutions to market, underscoring the importance of continuous innovation to maintain a competitive edge.
High Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry in the medical device manufacturing sector. Companies often face substantial costs when attempting to leave the market, stemming from massive capital investments in specialized facilities, advanced equipment, and a highly trained workforce. For instance, the development and regulatory approval process for a new medical device can cost tens of millions of dollars, making it difficult to recoup these investments if a company decides to exit.
These substantial sunk costs, coupled with stringent regulatory requirements for product disposal and data management, mean that firms are often compelled to remain operational even when facing diminished profitability. This persistence intensifies competition as companies fight to maintain market share rather than withdrawing. The cost of winding down operations or repurposing specialized assets can be prohibitively expensive, effectively trapping companies in the industry.
Consider the implications:
- Significant Capital Investments: The average R&D expenditure for a new medical device can range from $30 million to over $100 million, creating a substantial barrier to exit.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Complying with FDA regulations, for example, involves extensive documentation and post-market surveillance, adding to the cost and complexity of exiting.
- Specialized Assets: Medical device manufacturing often requires highly specialized, non-transferable equipment, limiting options for asset liquidation.
- Sustained Competitive Pressure: Companies unable to exit continue to compete, potentially leading to price wars or increased marketing efforts to maintain sales volumes.
Strategic Acquisitions and Consolidation
Integer and its rivals are actively pursuing strategic acquisitions to bolster their capabilities, diversify product offerings, and capture greater market share. A prime example is Integer's acquisition of Precision Coating and VSi Parylene in 2025, a move that clearly signals this industry-wide trend.
This ongoing consolidation can significantly ramp up competitive rivalry. As larger, more integrated companies emerge, they often wield broader service portfolios and benefit from enhanced economies of scale, putting pressure on smaller players.
Consequently, competitors are compelled to consider similar strategic maneuvers to avoid falling behind. This pursuit of strategic acquisitions is a key driver in shaping the competitive landscape.
- Integer's 2025 acquisitions of Precision Coating and VSi Parylene
- Consolidation leads to larger entities with broader service portfolios
- Increased economies of scale for acquiring companies
- Competitors must engage in similar strategies to maintain market position
Competitive rivalry within the medical device outsource market is robust, driven by a mix of large corporations and specialized firms. The market's projected growth, with a CAGR between 9.7% and 15.6% from 2024 onward, fuels this competition by creating opportunities for all participants. However, intense battles for leadership persist in specific high-growth niches, pushing companies to innovate and differentiate.
High exit barriers, including substantial capital investments and stringent regulatory requirements, trap companies in the market, intensifying rivalry. For instance, the average R&D expenditure for a new medical device can range from $30 million to over $100 million, making market withdrawal costly. This persistence from companies, even with diminished profitability, leads to sustained competitive pressure and potential price wars.
Strategic acquisitions are a key trend, with Integer's 2025 acquisitions of Precision Coating and VSi Parylene exemplifying this. This consolidation creates larger, more integrated competitors with economies of scale, compelling others to pursue similar strategies to remain competitive.
| Metric | 2024 Value/Projection | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Global MDO Market Value | ~USD 35 billion | Attracts significant competition due to market size. |
| Projected CAGR (2024-2029) | 9.7% - 15.6% | Growth eases some pressure but fuels competition for market share. |
| Average R&D for New Device | $30M - $100M+ | High exit barriers intensify rivalry by keeping firms invested. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) might consider bringing medical device production in-house, a potential substitute for outsourcing to companies like Integer. However, the growing intricacy of medical devices and the demand for specialized knowledge often make outsourcing a more practical choice. For instance, the global medical device market was valued at approximately $520 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale and specialization required.
Establishing in-house manufacturing would necessitate substantial capital outlay and extensive regulatory compliance, making it a significant hurdle for OEMs. Integer, on the other hand, offers established expertise and streamlined processes, which can lead to greater cost efficiency and a quicker path to market for new products.
Alternative therapeutic approaches, while not directly replacing manufacturing services, can indirectly threaten Integer's business. For example, the development of new drug therapies or less invasive procedures might reduce the demand for specific medical devices Integer produces. In 2023, the global pharmaceuticals market was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion, showcasing the significant investment and innovation in this sector, which could lead to such substitutions.
Integer actively manages this threat by maintaining a diverse product portfolio across multiple therapeutic areas, including cardiology, neuromodulation, and vascular systems. This diversification strategy aims to buffer the impact of potential declines in any single product category due to emerging alternative treatments.
Technological advancements, particularly in areas like AI and 3D printing, are rapidly changing how medical devices are designed and produced. These innovations offer new ways to create highly customized and complex devices, potentially serving as alternatives to traditional manufacturing methods.
For Integer, these emerging technologies aren't necessarily a threat of substitution. Instead, the company is actively integrating AI and 3D printing into its operations. This strategic adoption allows Integer to improve its existing product lines and develop novel solutions, ensuring it remains competitive in a dynamic market.
By leveraging these advanced manufacturing techniques, Integer can produce patient-specific implants and instruments, a capability that was previously difficult or impossible. This focus on innovation, rather than being replaced by it, positions Integer to capitalize on the growing demand for personalized medical solutions.
Lower-Cost, Less Complex Devices
The threat of substitutes for Integer's products, particularly in the medical device sector, can arise from simpler, lower-cost alternatives. While Integer excels in advanced, complex medical technologies, a market trend favoring more basic, less resource-intensive devices could pose a challenge. For instance, the growing demand for point-of-care diagnostics that are easier to use and manufacture, potentially bypassing the need for highly specialized components, illustrates this substitution risk.
Integer's strategic decisions reflect an awareness of these market dynamics. The company's planned exit from the Portable Medical market by 2025 signals a deliberate pivot towards segments perceived as having higher growth potential and requiring more sophisticated manufacturing capabilities. This move suggests a focus on areas where its core competencies in complex device manufacturing offer a stronger competitive advantage, away from markets where simpler substitutes might gain traction.
The broader medical device market in 2024 continues to see innovation across the spectrum, from high-end implantables to accessible diagnostic tools. While Integer focuses on areas like advanced cardiovascular and orthopedic technologies, the overall market value for medical devices is substantial, estimated to reach over $600 billion globally by 2024. This vastness means that even if simpler devices capture a portion of the market, Integer's specialized segments remain significant. However, the accessibility of off-the-shelf or less technologically demanding components for certain applications can still represent a viable substitute for some of Integer's offerings, especially in less critical care areas.
- Market Segmentation: The medical device market is diverse, with significant demand for both highly complex and simpler, cost-effective solutions.
- Substitution Risk: A shift in consumer or healthcare provider preference towards less complex, lower-cost devices that require less advanced manufacturing represents a potential substitute.
- Integer's Strategic Focus: Integer's exit from the Portable Medical market by 2025 highlights a strategic move away from potentially more commoditized segments towards higher-growth, complex device areas.
- Market Dynamics: While Integer targets specialized, high-value segments, the overall market's breadth means simpler alternatives can still emerge for certain applications, impacting specific product lines.
Regulatory Shifts Favoring Simpler Solutions
While shifts towards simpler solutions could theoretically be a threat, the reality for medical device outsourcing (MDO) often points elsewhere. Changes in regulatory frameworks that might favor less complex devices could indeed impact demand for highly specialized manufacturing. However, the overarching trend in medical device regulation, particularly as of 2024 and looking towards July 2025, shows an escalation, not a simplification, of scrutiny.
This intensified regulatory environment, especially concerning advanced and AI-driven medical technologies, actually benefits established and compliant MDOs like Integer. Companies that can navigate these complex and evolving compliance landscapes are better positioned. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continues to emphasize robust quality management systems and post-market surveillance for all device classes.
The threat of substitutes, in this context, is more about alternative manufacturing approaches or in-house capabilities rather than regulatory simplification. However, the significant capital investment and specialized expertise required for compliant medical device manufacturing often make outsourcing to experienced partners like Integer a more attractive and less risky option for many medical device companies. In 2023, the global medical device contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $60 billion, with projections indicating continued growth driven by the need for specialized capabilities and regulatory adherence.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Increasing, not decreasing, oversight for medical devices, especially advanced ones.
- Compliance Advantage: Favors established MDOs like Integer with proven compliance frameworks.
- Market Dynamics: High capital and expertise needs for compliance make outsourcing appealing.
- Market Size: Global medical device contract manufacturing market valued around $60 billion in 2023.
The threat of substitutes for Integer's manufacturing services primarily stems from OEMs considering in-house production or alternative therapeutic approaches that reduce demand for specific devices. However, the high capital investment, specialized knowledge, and stringent regulatory compliance required for medical device manufacturing often make outsourcing to experienced partners like Integer a more practical and cost-effective choice for OEMs.
While technological advancements like AI and 3D printing could be seen as substitutes for traditional manufacturing methods, Integer actively integrates these technologies to enhance its offerings and develop personalized solutions, thereby mitigating this threat.
The medical device market is vast, with an estimated global value exceeding $600 billion in 2024. Within this market, simpler, lower-cost devices can emerge as substitutes for highly specialized ones, prompting Integer's strategic exit from less complex segments like Portable Medical by 2025 to focus on high-growth, complex device areas.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | Impact on Integer | Mitigation Strategy | Relevant Data (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Manufacturing by OEMs | OEMs bringing production in-house. | Reduces demand for outsourced manufacturing. | Highlighting cost efficiency, expertise, and regulatory compliance of outsourcing. | Global medical device market: ~$520 billion (2023). |
| Alternative Therapeutic Approaches | New drug therapies or less invasive procedures. | Decreases demand for specific medical devices. | Diversifying product portfolio across multiple therapeutic areas. | Global pharmaceuticals market: ~$1.5 trillion (2023). |
| Simpler, Lower-Cost Devices | Market shift towards less complex, cheaper alternatives. | Potential erosion of market share in less specialized segments. | Strategic exit from markets with simpler substitutes (e.g., Portable Medical by 2025). | Global medical device contract manufacturing market: ~$60 billion (2023). |
| Emerging Manufacturing Technologies | AI, 3D printing offering new production methods. | Potential to replace traditional manufacturing. | Active integration of these technologies into operations. | N/A (Focus on adoption, not replacement). |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the medical device outsource (MDO) manufacturing sector demands a significant capital outlay. Companies need to invest heavily in specialized, often FDA-compliant, facilities, cutting-edge manufacturing equipment, and a workforce possessing advanced technical skills. For instance, setting up a cleanroom facility alone can cost millions of dollars, depending on its classification and size.
Beyond the initial setup, continuous investment in research and development (R&D) is crucial. The medical device industry is characterized by rapid technological evolution and stringent regulatory requirements, necessitating ongoing R&D to innovate and meet evolving customer demands. Companies in this space might allocate 5-10% of their revenue to R&D, a substantial figure that acts as a deterrent for newcomers.
These substantial upfront and ongoing financial commitments create a formidable barrier to entry. Potential new players must be prepared to absorb considerable risk and secure significant funding before even beginning operations, effectively limiting the number of credible new entrants into the MDO market.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the medical device sector. Agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) impose rigorous approval processes. These pathways demand extensive clinical trials, comprehensive documentation, and adherence to robust quality management systems, creating substantial time and financial barriers.
Integer, a prominent manufacturer of medical device components, has cultivated deep-rooted relationships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). This loyalty stems from a well-earned reputation for delivering high-quality, innovative products, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Securing contracts with major medical device companies requires demonstrating a history of reliability, a significant hurdle for any new entrant.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise
Integer's significant barrier to new entrants stems from its proprietary technologies and deep, specialized expertise. The company has cultivated advanced capabilities in cardiac rhythm management, neuromodulation, and vascular systems, further bolstered by strategic acquisitions that enhance its specialized coating technologies. For instance, in 2023, Integer invested heavily in research and development, with R&D expenses reaching approximately $1.7 billion, underscoring the continuous innovation required to compete in its high-tech medical device sectors.
Developing or acquiring comparable advanced manufacturing processes and specialized knowledge is an exceptionally difficult and costly undertaking for potential competitors. This technological moat acts as a significant deterrent, making it challenging for new players to enter and compete effectively. The sheer scale of investment and time required to replicate Integer's established technological infrastructure and intellectual property presents a formidable hurdle.
- Proprietary Technology: Integer holds numerous patents in its core medical device areas.
- Specialized Expertise: Decades of experience in complex medical fields like cardiac rhythm management.
- Acquisition Synergies: Integration of new coating technologies from recent acquisitions enhances competitive advantage.
- High R&D Investment: Continued significant investment in innovation to maintain technological leadership, with R&D spending around $1.7 billion in 2023.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established medical device original equipment manufacturers (MDOs) like Integer Holdings Corporation leverage significant economies of scale. In 2024, Integer's robust supply chain and high-volume production capabilities allow them to negotiate better pricing for raw materials and components, directly reducing their cost of goods sold. This scale advantage means new entrants would struggle to match Integer's per-unit cost efficiency from the outset.
Furthermore, Integer benefits from a well-established experience curve. Through years of refining manufacturing processes and product development, they have achieved higher operational efficiencies and improved product quality. For instance, their expertise in complex catheter manufacturing has led to optimized production cycles and reduced waste, a level of proficiency new competitors would take considerable time and investment to replicate, hindering their ability to compete on price or performance in 2024.
- Economies of Scale: Integer's large-scale operations in 2024 enable lower per-unit manufacturing, procurement, and R&D costs compared to potential new entrants.
- Experience Curve Benefits: Integer's accumulated knowledge and process improvements contribute to higher efficiency and quality, a significant barrier for newcomers.
- Competitive Disadvantage for Entrants: New companies entering the market would face initial cost disadvantages and lower operational efficiency, making it challenging to compete with established players like Integer.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements and high R&D investment. Setting up compliant manufacturing facilities and continuously innovating in the fast-paced medical device sector demands millions in upfront and ongoing costs, acting as a strong deterrent.
Regulatory hurdles, including FDA and EU MDR/IVDR approvals, create formidable barriers. These require extensive clinical trials and robust quality systems, adding significant time and financial burdens for any aspiring competitor.
Integer's proprietary technologies and specialized expertise, particularly in areas like cardiac rhythm management, are difficult and costly to replicate. Their substantial R&D investment, around $1.7 billion in 2023, further solidifies this technological moat.
Economies of scale and experience curve benefits also protect Integer. In 2024, their high-volume production and refined processes lead to cost efficiencies and operational improvements that new entrants would struggle to match initially.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in specialized facilities and equipment (e.g., cleanrooms costing millions). | Significant financial hurdle, requiring substantial funding and risk tolerance. |
| R&D Investment | Continuous innovation and compliance with evolving tech and regulations (5-10% of revenue). | Demands ongoing financial commitment, challenging for new players to keep pace. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Rigorous approval processes (FDA, EU MDR/IVDR) requiring extensive trials and documentation. | Creates substantial time and financial barriers, slowing market entry. |
| Proprietary Technology & Expertise | Unique processes, patents, and deep knowledge in specialized medical fields. | Difficult and expensive for competitors to develop or acquire comparable capabilities. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience Curve | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production and optimized processes. | New entrants face initial cost disadvantages and lower operational efficiency. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Integer Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data, including financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings. This ensures a robust understanding of competitive pressures.