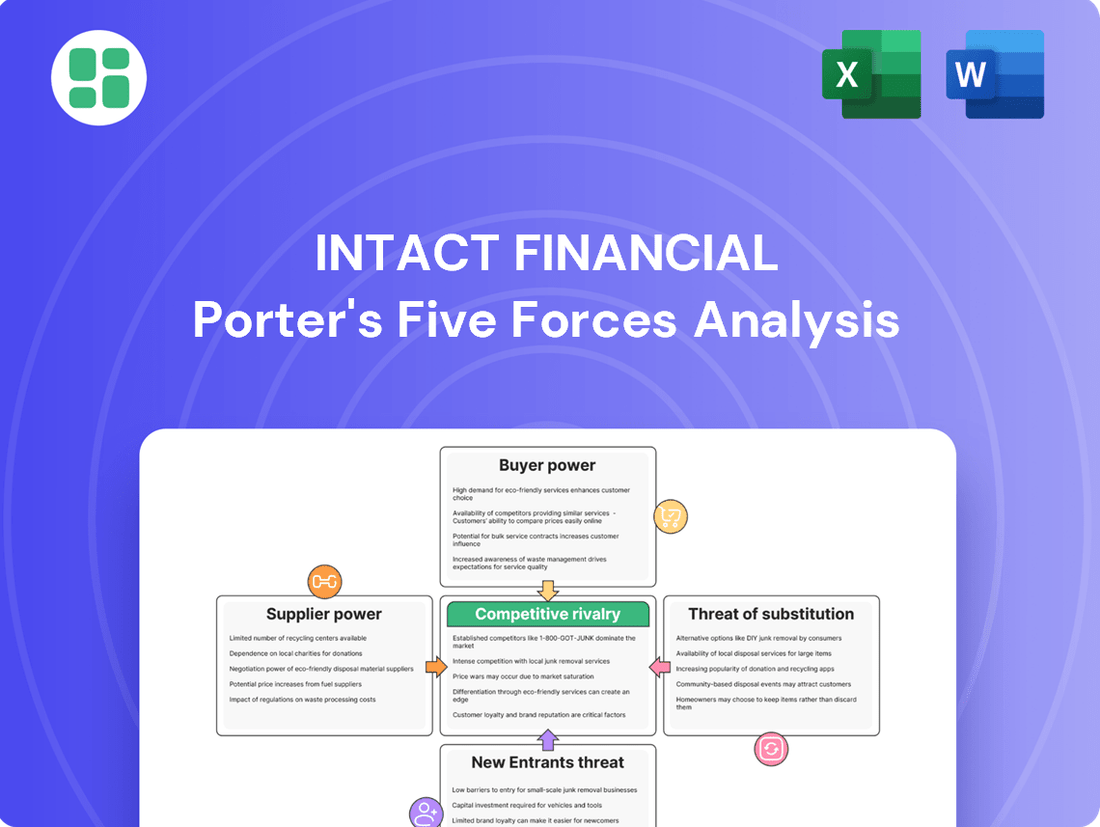
Intact Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Intact Financial Bundle
Intact Financial navigates a complex insurance landscape, where the bargaining power of buyers and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its market. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the true competitive dynamics.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Intact Financial offers a deep dive into these pressures, revealing the intensity of rivalry and the influence of suppliers and new entrants. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making and gain a strategic edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The global reinsurance market, which is essential for property and casualty insurers like Intact Financial, shows a degree of concentration. A few major companies hold a significant share, which can translate into greater influence over pricing and contract terms, particularly for intricate risks or during periods of market hardening.
While reinsurers have seen improved profitability in 2024 and a positive outlook for 2025, this hasn't spurred new entrants to challenge the existing market discipline. Strong capital growth within the sector is also a factor that can help to temper the bargaining power of these established reinsurers.
As the insurance sector increasingly leans on sophisticated analytics, artificial intelligence, and digital infrastructure, the sway of specialized technology and data providers is growing. The surge in insurtech funding, with billions invested globally, underscores this trend. For instance, generative AI solutions are revolutionizing underwriting and claims, making these tech suppliers indispensable for insurers aiming to maintain a competitive edge.
Actuarial, legal, and claims adjusting services are critical for Intact Financial, a major insurer. The specialized knowledge needed in these areas can give providers leverage, as there are fewer qualified experts. For example, the cost of specialized actuarial consulting can represent a significant portion of an insurer's operating expenses, with fees for top-tier firms potentially running into millions annually.
Claims Services and Repair Networks
For property and casualty (P&C) insurers like Intact Financial, a robust network of claims adjusters and repair services is foundational to smooth operations and customer contentment. While many local repair shops exist, the demand for consistent quality and swift action, particularly after widespread disasters, can grant preferred repair partners a degree of leverage.
Intact's strategic emphasis on customer-centric service centers underscores the critical role these networks play. In 2023, Intact reported that its claims satisfaction scores remained high, a testament to the efficiency of its repair networks. The company actively manages these relationships to ensure service standards are met, thereby mitigating potential supplier power.
- Network Dependency: Insurers rely heavily on qualified repair networks to manage claims efficiently.
- Quality and Speed: The need for consistent quality and rapid response, especially post-catastrophe, can increase supplier influence.
- Intact's Strategy: Intact's focus on service centers aims to control and optimize these relationships.
- Supplier Power Mitigation: By fostering strong partnerships and setting clear performance standards, Intact can limit supplier bargaining power.
Capital and Financial Markets
While not typical suppliers, capital and financial markets are crucial for insurers like Intact. These markets provide the essential funding for operations and growth, particularly to meet stringent regulatory capital requirements. The cost of this capital, heavily influenced by prevailing interest rates and overall investor sentiment, directly affects an insurer's financial stability and its capacity to underwrite new business.
Intact Financial's robust financial standing is evident in its strong capital margins and a history of consistent dividend increases. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Intact reported a strong solvency ratio, well above regulatory minimums, showcasing its ability to access and manage capital effectively. This financial strength allows them to navigate market fluctuations and pursue strategic growth initiatives.
- Cost of Capital: Fluctuations in interest rates and investor confidence directly impact Intact's cost of capital, influencing profitability and underwriting capacity.
- Regulatory Capital: Financial markets are vital for meeting and exceeding regulatory capital requirements, ensuring solvency and operational resilience.
- Financial Strength Indicators: Intact's consistent dividend increases and strong capital margins, as observed in early 2024 data, highlight its favorable position within capital markets.
- Access to Funding: The ability to access capital markets efficiently is critical for Intact's growth strategies, acquisitions, and overall market competitiveness.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Intact Financial is generally moderate, influenced by the diverse nature of its operational inputs. While specialized services like actuarial consulting and advanced technology providers can exert considerable influence due to unique expertise and high switching costs, the broader market for many inputs, such as general administrative services, remains competitive.
In 2024, the reinsurance market, a key supplier of risk transfer for Intact, demonstrated resilience with improved profitability, yet this hasn't significantly altered the power dynamic due to strong capital growth within the sector. Similarly, while insurtech providers are becoming more critical, the increasing number of AI and data analytics firms entering the market helps to balance their leverage.
Intact's strategic management of its repair networks, focusing on quality and speed, also plays a role in mitigating supplier power. By cultivating strong relationships and setting clear performance metrics, Intact can maintain a degree of control over these essential service providers.
The cost of capital, influenced by financial markets, remains a significant factor. Intact's strong solvency ratios, as reported in early 2024, indicate a favorable position, allowing them to manage this supplier relationship effectively.
| Supplier Category | Key Considerations | Intact's Mitigation Strategies | Estimated Impact on Intact (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Market concentration, capital growth | Diversification of reinsurance partners, strong internal capital | Moderate |
| Technology & Data Providers | Specialized AI/analytics, high switching costs | Long-term partnerships, internal development | Moderate to High |
| Actuarial, Legal, Claims Services | Specialized expertise, limited qualified providers | In-house capabilities, preferred provider networks | Moderate |
| Capital Markets | Interest rates, investor sentiment, regulatory capital | Strong financial health, consistent dividend growth | Low to Moderate |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping Intact Financial's industry, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing players.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive pressures, allowing Intact Financial to proactively address potential threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers for standard insurance lines, especially in Canada, are quite sensitive to price. This means they actively look for the best deals available. For example, in the Canadian auto insurance market, price is a significant factor for many consumers when choosing a provider.
The proliferation of comparison websites and insurance brokers makes it incredibly easy for consumers to shop around. This ease of access fuels competition, forcing insurers to compete more aggressively on price for products like auto and home insurance. This increased competition directly impacts insurers like Intact Financial.
This price sensitivity in commoditized segments can put considerable pressure on Intact's profit margins. When customers can easily switch providers based on a lower premium, Intact may have to lower its prices to retain market share, potentially squeezing profitability in these standard product lines.
The Canadian property and casualty (P&C) insurance market is quite competitive. Many national and regional companies offer comparable products, giving customers plenty of choices. This means if a customer finds a better deal or terms elsewhere, they can easily switch providers.
Intact Financial operates within this environment, facing direct competition across its main product lines. For instance, in 2023, Intact held a significant market share in Canada, but this also highlights the presence of other substantial players vying for the same customer base. The ease with which customers can compare and move between insurers directly impacts Intact's ability to command premium prices or retain customers without offering competitive advantages.
The proliferation of digital platforms and insurtech innovations significantly boosts customer bargaining power by offering unprecedented transparency and ease of access to information. Customers can now readily compare policies and pricing across multiple providers, a stark contrast to previous eras. For instance, in 2024, the global insurtech market was valued at over $100 billion, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these customer-empowering technologies.
Switching Costs Vary
Switching costs for Intact Financial's customers vary significantly. For individual consumers, the effort to compare and switch auto or home insurance policies is generally minimal, often involving just a few hours of research and paperwork. This low barrier empowers them to shop around for the best rates and coverage, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
However, for Intact's commercial clients, particularly those with complex, integrated, or bundled insurance solutions, switching costs can be considerably higher. These can include the time and resources needed to re-underwrite policies, integrate new systems, and retrain staff. This increased complexity can somewhat temper the bargaining power of these larger customers.
For instance, in 2023, the average customer retention rate for major property and casualty insurers in Canada remained strong, often exceeding 85%, indicating that while switching is possible, inertia and satisfaction levels play a role. Yet, the competitive landscape means that even small increases in switching costs can be a significant deterrent for businesses seeking to change providers.
- Individual Policyholders: Low switching costs mean easy comparison shopping for better rates, increasing their bargaining power.
- Commercial Clients: Higher switching costs associated with complex, integrated, or bundled policies can reduce their bargaining power.
- Customer Retention Data: In 2023, Canadian P&C insurers generally saw retention rates above 85%, suggesting factors beyond just switching costs influence customer loyalty.
Demand for Value-Added Services
Customers are increasingly seeking more than just basic insurance coverage. They expect value-added services that simplify their lives and offer greater peace of mind. This includes seamless digital platforms for policy management, proactive risk assessment, and swift, hassle-free claims handling.
Insurers that excel in delivering these enhanced experiences can significantly influence customer loyalty. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers prioritize digital convenience when choosing an insurance provider, even over slightly lower premiums.
This shift in customer expectations means that insurers like Intact Financial must innovate beyond traditional product offerings. By focusing on customer-centric solutions, they can build stronger relationships and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
- Digital Engagement: Customers expect intuitive apps and online portals for policy access and service requests.
- Personalized Advice: Tailored risk management strategies and financial planning assistance are highly valued.
- Efficient Claims: Streamlined and transparent claims processes are critical for customer satisfaction.
- Proactive Communication: Keeping customers informed about potential risks and policy updates builds trust.
Customers for standard insurance lines, especially in Canada, are quite sensitive to price, actively seeking the best deals. The ease of comparison via digital platforms, with the insurtech market valued at over $100 billion in 2024, amplifies this. For individual policyholders, low switching costs empower them to easily shop around, increasing their bargaining power.
Conversely, commercial clients with complex, integrated insurance solutions face higher switching costs, involving significant time and resources to re-underwrite and integrate new systems, which can temper their bargaining power. While customer retention rates for Canadian P&C insurers exceeded 85% in 2023, indicating factors beyond just switching costs influence loyalty, the competitive landscape means even small increases in switching costs can deter businesses.
Customers now expect value-added services, prioritizing digital convenience, with over 60% of consumers in a 2024 survey indicating this preference. Insurers must innovate beyond traditional offerings, focusing on customer-centric solutions like seamless digital platforms and efficient claims handling to build stronger relationships and differentiate themselves.
| Customer Segment | Switching Costs | Bargaining Power Impact | Key Expectations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Policyholders | Low | High | Price, Digital Convenience |
| Commercial Clients | High (for complex policies) | Moderate to Low | Integrated Solutions, Risk Management |
Same Document Delivered
Intact Financial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Intact Financial, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the insurance industry. This in-depth analysis is crucial for understanding Intact Financial's competitive landscape and strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Intact Financial, while the dominant Property and Casualty (P&C) insurer in Canada, operates within a landscape marked by significant competitive rivalry. The market is fragmented, featuring a substantial number of national and regional players, all vying for market share.
This intense competition is further amplified by the industry's exposure to climate-related catastrophes, demanding constant adaptation and innovation from insurers. For instance, in 2023, Canada experienced a record year for insured losses from natural disasters, exceeding $3.1 billion, a figure that underscores the pressure on all insurers, including Intact, to manage risk and maintain competitive pricing.
Furthermore, evolving consumer expectations necessitate a proactive approach to product development and service delivery. Insurers must continually invest in technology and customer experience to remain relevant and capture market opportunities.
The Canadian property and casualty (P&C) insurance market is mature, meaning growth is generally slower than in developing economies or specialized areas. This maturity often fuels intense rivalry as companies vie for market share, particularly in personal insurance lines where expansion relies heavily on rate adjustments and acquiring new policyholders. Intact Financial's performance in Q1 2025 reflected this, with premium growth of 3%, largely propelled by its personal lines business.
In the property and casualty insurance sector, core offerings like auto and home insurance often become commoditized, meaning price becomes a key differentiator for customers. This intense price competition can pressure profit margins for insurers.
To combat this, Intact Financial and its competitors focus on differentiating themselves through strong brand recognition, superior customer service, and innovative digital platforms. For instance, in 2024, the Canadian P&C insurance industry saw continued investment in digital tools to enhance customer experience, aiming to build loyalty beyond just price.
High Fixed Costs and Capital Requirements
The insurance sector, including companies like Intact Financial, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These stem from essential investments in robust IT systems for claims processing and data management, ongoing expenses for stringent regulatory compliance, and the necessity of maintaining significant capital reserves to cover potential payouts. These high upfront and ongoing expenses create a significant barrier to entry.
These substantial fixed costs mean that achieving economies of scale is crucial for profitability. Larger, established insurers such as Intact Financial can spread these costs over a wider revenue base, giving them a competitive advantage. For new entrants or smaller players, this necessitates a substantial volume of business to simply cover their operational overheads and remain competitive.
- IT Infrastructure: Investments in advanced analytics, AI for risk assessment, and cybersecurity are ongoing and substantial.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to Solvency II or similar capital adequacy regulations requires significant financial resources and dedicated personnel.
- Capital Reserves: Insurers must hold substantial capital to meet their obligations, directly impacting their financial structure and operational flexibility.
- Economies of Scale: In 2023, the global insurance market generated over $6.9 trillion in premiums, highlighting the scale required to be a major player.
Technological Investment and Innovation
Competitive rivalry in the insurance sector is intensifying, largely fueled by significant technological investments. Insurers are pouring capital into areas like artificial intelligence, advanced data analytics, and modern digital platforms. The goal is to refine core operations such as underwriting, claims processing, and ultimately, enhancing the customer experience. This technological arms race means companies that don't keep pace risk falling behind.
Intact Financial, for instance, is actively demonstrating this trend. They are deploying generative AI within their commercial lines of business, aiming to streamline processes and gain a competitive edge. Furthermore, Intact's strategic emphasis on developing and expanding its digital sales channels highlights a commitment to meeting evolving customer expectations and capturing market share through accessible technology.
The impact of these technological advancements is substantial:
- Increased Efficiency: AI and data analytics are automating tasks, leading to faster claims handling and more accurate risk assessment. For example, many insurers reported significant improvements in processing times for certain types of claims in 2024 due to AI integration.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Digital platforms and personalized offerings are becoming crucial for customer acquisition and retention. Companies with robust digital interfaces saw higher customer satisfaction scores in recent surveys.
- New Entrants and Disruption: Insurtech startups, often built on cutting-edge technology, are challenging traditional players by offering innovative products and streamlined digital experiences. Some of these startups have secured substantial venture capital funding in late 2023 and early 2024, indicating strong market interest.
- Data as a Competitive Differentiator: The ability to collect, analyze, and leverage vast amounts of data effectively is becoming a key differentiator, allowing insurers to price risk more accurately and tailor products to specific customer needs.
Competitive rivalry within the Canadian P&C insurance sector is fierce, driven by a mature market and the commoditization of core products like auto and home insurance. Intact Financial, despite its dominant position, faces pressure from numerous national and regional players, all vying for market share. This intense competition is further exacerbated by the need for continuous technological investment to meet evolving customer expectations and differentiate offerings beyond price.
In 2024, the industry saw sustained investment in digital tools to improve customer experience, a trend Intact Financial actively participates in through its focus on digital sales channels. This technological race is crucial, as insurers that fail to adapt risk losing ground to more agile competitors or disruptive insurtech startups, which have attracted significant venture capital funding in recent periods.
The high fixed costs associated with IT infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and capital reserves create substantial barriers to entry, favoring larger players like Intact Financial that can leverage economies of scale. For instance, the global insurance market's sheer size, generating over $6.9 trillion in premiums in 2023, underscores the scale necessary to compete effectively.
| Metric | Intact Financial (Q1 2025) | Canadian P&C Market Trend | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premium Growth | 3% | Mature market, slower growth | Intensifies competition for market share |
| Digital Investment | High focus on digital sales channels | Industry-wide investment in digital tools | Drives differentiation and customer acquisition |
| Technological Adoption (AI) | Generative AI in commercial lines | Increased use for efficiency and risk assessment | Creates a competitive advantage for early adopters |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For large corporations, self-insurance and the establishment of captive insurance companies present a significant substitute for conventional property and casualty (P&C) insurance. This strategy is particularly effective for managing predictable or substantial risks, offering businesses greater autonomy over their risk management processes and the potential for substantial cost savings compared to traditional premiums.
This trend is notably less impactful for individual consumers or smaller businesses, who typically lack the scale and financial capacity to effectively implement self-insurance or captive strategies. For instance, the global captive insurance market has seen consistent growth, with premiums written by captives reaching an estimated $70 billion in 2023, highlighting its appeal to larger entities seeking tailored risk solutions.
Improvements in risk management and loss prevention technologies are increasingly acting as substitutes for traditional insurance. For instance, the widespread adoption of smart home sensors and advanced telematics in vehicles can significantly reduce the likelihood and severity of insurable events like property damage or car accidents. This proactive approach by individuals and businesses diminishes the perceived need for comprehensive insurance coverage.
Government programs and catastrophe bonds can indeed act as substitutes or supplements to traditional property and casualty (P&C) insurance, particularly for large-scale, systemic risks. For example, following major natural disasters, government disaster relief funds, like those administered by FEMA in the United States, can provide financial assistance to affected individuals and communities, offsetting some of the losses that would otherwise be borne by insurers. In 2023, FEMA allocated billions in disaster relief funding, demonstrating the significant role government programs play in risk absorption.
Catastrophe bonds, a form of insurance-linked security, also offer an alternative risk transfer mechanism. These bonds allow insurers and reinsurers to transfer specific risks, such as those from hurricanes or earthquakes, to capital market investors. While they don't replace the day-to-day insurance needs of individuals and businesses, they can absorb significant portions of aggregate losses from catastrophic events. The global catastrophe bond market saw substantial growth, with issuance reaching approximately $15 billion in 2023, indicating their increasing importance in the risk management landscape.
Non-Insurance Risk Transfer Mechanisms
Beyond traditional insurance policies, businesses increasingly utilize non-insurance risk transfer mechanisms. These financial instruments and contractual agreements offer alternative ways to manage potential losses, impacting the demand for conventional insurance. For instance, the global market for financial derivatives, a key substitute, saw significant activity in 2024, with over $600 trillion notional value outstanding in over-the-counter derivatives alone by the end of Q3 2024, as reported by the Bank for International Settlements.
These substitutes can include:
- Derivatives: Financial contracts like futures, options, and swaps used to hedge against market volatility, interest rate fluctuations, or currency exchange risks.
- Indemnification Clauses: Contractual provisions where one party agrees to compensate the other for specific losses or damages, shifting liability.
- Securitization: Packaging financial assets and selling them as securities to investors, transferring the underlying risks.
- Captive Insurance Companies: Wholly owned subsidiaries that provide insurance coverage for their parent company's risks, acting as an internal risk financing mechanism.
Emerging Technologies and Embedded Insurance
New technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are paving the way for embedded insurance. This means coverage is now seamlessly woven into the purchase of products or services, like extended warranties on electronics or travel insurance at flight booking. While traditional insurers often still handle the underwriting, this shift fundamentally alters how insurance is distributed and perceived by consumers.
This trend could make traditional, standalone insurance policies feel less essential for certain needs. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of consumers are open to purchasing insurance directly through the platform where they buy a product. This suggests a growing comfort with integrated solutions, potentially reducing the perceived need for separate insurance shopping.
- Embedded insurance growth: The global embedded insurance market is projected to reach $3.5 trillion in premiums by 2030, according to some industry estimates.
- Consumer adoption: A 2024 survey found that 70% of consumers who purchased embedded insurance reported a positive experience.
- Impact on traditional channels: This can reduce direct customer interaction with insurers, potentially weakening brand loyalty for standalone products.
The threat of substitutes for Intact Financial is amplified by the rise of self-insurance and captive insurance companies, particularly for large corporations. These alternatives offer greater control and potential cost savings, as evidenced by the captive insurance market, which wrote an estimated $70 billion in premiums in 2023. This trend, however, is less relevant for smaller entities lacking the necessary scale.
Advancements in risk management technologies and government programs also serve as substitutes. For instance, smart home sensors can reduce property damage claims, while government disaster relief funds, like those from FEMA in 2023, absorb significant losses. Catastrophe bonds, with $15 billion in issuance in 2023, further transfer risk to capital markets, lessening reliance on traditional insurance for extreme events.
Non-insurance risk transfer mechanisms, such as derivatives, are also significant substitutes. The over-the-counter derivatives market had over $600 trillion in notional value outstanding by Q3 2024. Embedded insurance, seamlessly integrated into product purchases, is another growing substitute, with over 60% of consumers open to such solutions in 2024, potentially reducing the need for standalone policies.
| Substitute Category | Examples | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on Traditional Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance/Captives | Large Corporation Risk Management | Captive premiums: $70 billion (2023) | Reduces demand for P&C insurance from large entities. |
| Risk Management Tech | Smart Home Sensors, Telematics | Widespread adoption | Lowers frequency/severity of insurable events. |
| Government Programs | FEMA Disaster Relief | Billions allocated in 2023 | Absorbs losses from catastrophic events. |
| Capital Markets | Catastrophe Bonds | $15 billion issuance (2023) | Transfers catastrophic risk to investors. |
| Non-Insurance Transfer | Derivatives, Indemnification | OTC Derivatives: >$600 trillion notional (Q3 2024) | Offers alternative risk hedging and liability shifting. |
| Embedded Insurance | Product-integrated coverage | 60%+ consumer openness (2024) | Integrates insurance, potentially reducing standalone policy needs. |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector demands immense capital, with companies needing significant financial reserves to comply with regulations and handle potential claims. For instance, in 2024, property and casualty insurers in the U.S. maintained approximately $1.1 trillion in capital and surplus, a figure that underscores the substantial financial commitment required.
These high capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, deterring new entrants from establishing a significant presence. Launching an insurance operation necessitates not only underwriting expertise but also the financial wherewithal to back policyholder obligations, making market entry particularly challenging for smaller or less-funded entities.
The property and casualty (P&C) insurance sector, especially in Canada, operates under a stringent regulatory framework. This includes intricate licensing procedures, ongoing compliance mandates, and rigorous solvency standards designed to protect policyholders. For instance, in 2023, Canadian insurers faced evolving capital requirements under the new OSFI Guideline E-23, which emphasizes robust risk management and capital adequacy.
Successfully navigating these complex regulatory landscapes requires substantial investment in legal counsel, compliance officers, and specialized operational expertise. This high barrier to entry significantly deters potential new entrants who may lack the necessary resources or knowledge to meet these demanding requirements, thereby protecting established players like Intact Financial.
In the insurance sector, trust is paramount, and established companies like Intact Financial have cultivated significant brand recognition and customer loyalty over decades. Newcomers must overcome the substantial hurdle of building credibility and a solid reputation to draw in a meaningful customer base.
For instance, in 2023, Intact Financial reported a direct premium written of $23.4 billion, demonstrating the scale and market penetration that new entrants would need to match to even begin competing effectively on brand recognition alone.
Economies of Scale and Distribution Networks
Existing insurers leverage significant economies of scale in underwriting, claims handling, and overall operations, which lower their per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major players continued to invest heavily in technology to streamline these processes, further enhancing their cost advantages. New entrants face a steep challenge in matching these operational efficiencies and achieving comparable cost structures without substantial initial capital outlay.
Furthermore, established insurers command extensive distribution networks, built over years through relationships with brokers, agents, and direct customer channels. This widespread reach is crucial for acquiring a diverse customer base and offering a comprehensive product suite. A new entrant would require considerable time and resources to build a comparable network, making it difficult to compete effectively for market share in 2024.
- Economies of scale in underwriting and claims processing reduce costs for established insurers.
- Extensive distribution networks provide a significant advantage in customer acquisition.
- New entrants face high barriers to entry due to the need for substantial investment to replicate these advantages.
- In 2024, the insurance industry saw continued consolidation and technological investment, further solidifying the advantages of scale for incumbents.
Access to Data and Advanced Analytics
New entrants into the insurance market face a significant hurdle in accessing the vast historical claims data that incumbents like Intact Financial possess. This data is essential for developing sophisticated risk assessment models and setting competitive pricing. Without this foundational dataset, new players struggle to match the underwriting accuracy of established insurers.
Leveraging advanced analytics and artificial intelligence further amplifies this advantage. Intact Financial, for instance, can utilize AI to analyze complex patterns in claims data, leading to more precise pricing and product development. New entrants often lack the resources and established data infrastructure to implement similar cutting-edge analytical capabilities, putting them at a distinct disadvantage.
- Data Advantage: Incumbents hold extensive historical claims data, critical for accurate risk assessment.
- Analytical Sophistication: Advanced analytics and AI, powered by proprietary data, enable superior underwriting.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants find it difficult to replicate the data-driven competitive edge of established insurers.
The threat of new entrants for Intact Financial remains relatively low, primarily due to the industry's substantial capital requirements and stringent regulatory environment. For example, in 2024, the U.S. property and casualty insurance sector held approximately $1.1 trillion in capital and surplus, a clear indicator of the financial muscle needed to operate. This high financial barrier, coupled with the complex licensing and compliance mandates, makes it exceedingly difficult for new companies to establish a foothold and compete effectively.
Furthermore, established players like Intact benefit from significant economies of scale and deeply entrenched distribution networks, advantages that are costly and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate. In 2024, continued industry consolidation and technological investments by incumbents further solidified these competitive moats. New entrants also struggle to match the data advantage and analytical sophistication of established insurers, who leverage vast historical claims data and advanced AI for superior risk assessment and pricing.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Intact Financial Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from Intact Financial's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We supplement this with industry-specific research from reputable sources like AM Best and S&P Global Market Intelligence, alongside macroeconomic data to capture broader market influences.