ICA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ICA Bundle
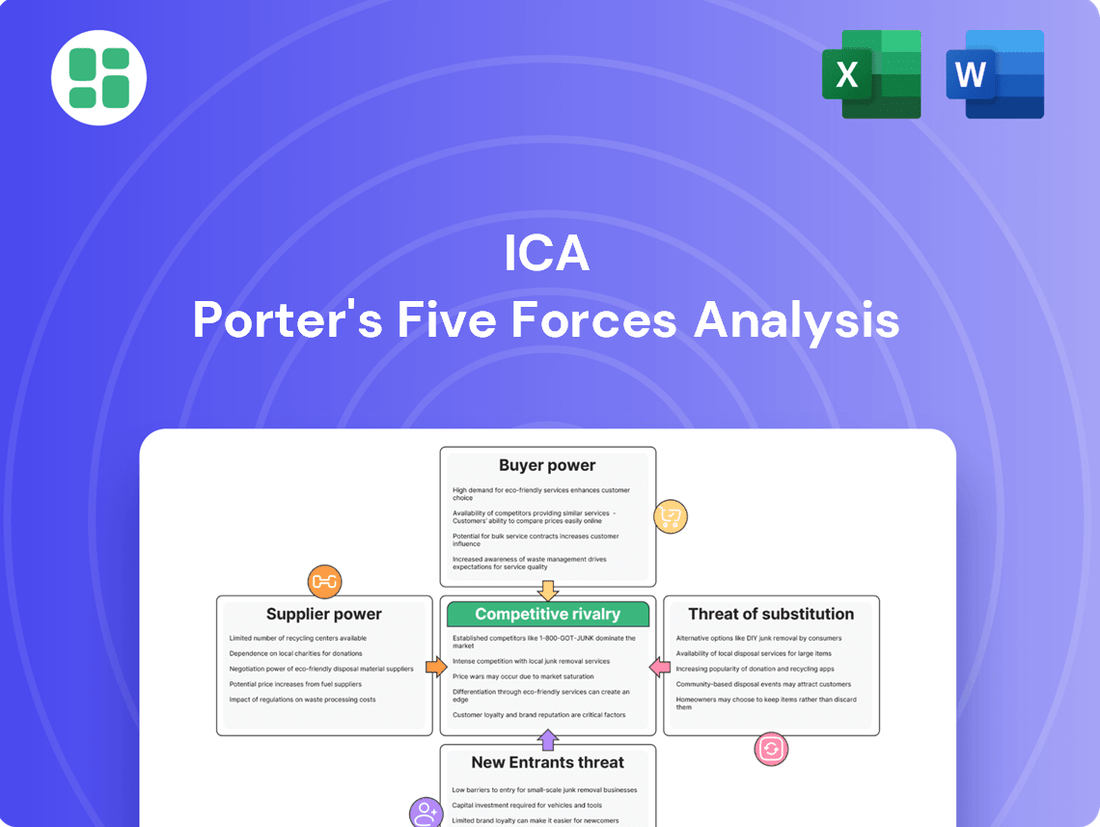
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the competitive landscape ICA operates within, highlighting the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for ICA to identify its strategic advantages and potential vulnerabilities.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore ICA’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Empresas ICA's dependence on a concentrated group of key material suppliers, such as those providing cement, steel, and aggregates, presents a significant challenge. When a few dominant players control the supply of these essential construction inputs, they gain considerable leverage to dictate prices, directly impacting ICA's cost of goods sold.
The Mexican construction materials market is projected for continued growth, with forecasts indicating a steady upward trend through 2024 and beyond. This sustained demand, while positive for the industry overall, can further embolden suppliers, allowing them to command higher prices due to the consistent need for their products.
Suppliers of highly specialized construction machinery, advanced technologies like BIM software, drones, and IoT devices, or unique construction methods such as 3D printing and prefabrication can wield significant bargaining power. For instance, the global construction technology market was valued at approximately $11.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a rising demand for these specialized inputs.
As the construction industry increasingly embraces digital transformation and advanced technologies, securing access to these crucial, specialized inputs becomes paramount. This reliance can amplify supplier leverage, as firms may find it difficult to substitute these unique offerings, potentially leading to higher costs or longer project timelines if suppliers dictate terms.
The availability and cost of skilled labor are critical factors impacting supplier power within the construction industry, directly affecting companies like Empresas ICA. A scarcity of specialized workers can drive up wages and project expenses, giving labor providers greater leverage.
In 2024, continued demand for skilled trades in Mexico, coupled with ongoing emigration of some skilled workers, has exacerbated existing shortages. This dynamic places significant bargaining power in the hands of available skilled labor, potentially increasing ICA's operational costs and impacting project timelines if not managed strategically.
Switching Costs for Inputs
High switching costs for inputs significantly bolster supplier bargaining power for Empresas ICA. These costs can manifest as substantial investments in retooling existing machinery, redesigning production processes, or undertaking extensive personnel retraining to accommodate new materials or components. For instance, if ICA's construction projects require highly specialized concrete mixes or unique steel alloys, changing suppliers necessitates costly adjustments to their pouring equipment or welding procedures. This financial and operational inertia makes it difficult for ICA to readily shift to alternative suppliers, even if they offer slightly lower prices.
Long-term relationships and specific project demands further entrench suppliers, limiting ICA's flexibility. If a particular supplier has been integral to a series of successful projects, or if a current project has unique, bespoke material requirements that only one supplier can meet, ICA becomes more dependent. This dependency, especially in the construction sector where project timelines are critical, means ICA may have to accept less favorable terms from these key suppliers. For example, a major infrastructure project might require a specific type of advanced composite material with a limited number of manufacturers, effectively locking ICA into a single supplier for that critical input.
- High switching costs: Retooling machinery and redesigning processes can represent significant capital expenditures for Empresas ICA when changing suppliers.
- Operational disruption: Retraining personnel to work with new materials or equipment adds to the cost and potential delay in project execution.
- Supplier lock-in: Long-term contracts or unique project specifications can tie ICA to specific suppliers, reducing its leverage in negotiations.
- Impact on project timelines: The inability to quickly switch suppliers can jeopardize project completion dates, a critical factor in the construction industry.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
A supplier's credible threat to integrate forward into the construction industry, perhaps by a large cement manufacturer establishing its own building division, would significantly amplify its leverage in negotiations. This potential action would directly challenge existing construction firms, forcing them to consider the supplier's competitive capabilities.
While this scenario is not a daily occurrence for most major construction projects, the mere possibility can subtly but effectively influence pricing and contract terms. For instance, if a major material supplier like a steel producer were to consider developing its own pre-fabricated building solutions, it could compel general contractors to offer more favorable terms to secure their supply chain.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: A supplier's ability to enter the buyer's industry increases its bargaining power.
- Impact on Negotiations: This threat can lead to more favorable terms for the supplier, such as better pricing or contract conditions.
- Industry Example: A large building materials provider considering developing its own construction services could pressure existing contractors.
- Market Influence: While less common in large-scale projects, the potential for forward integration remains a factor in supplier-buyer dynamics.
Suppliers hold significant bargaining power when they provide critical inputs that are difficult to substitute, especially when the number of suppliers is limited. For Empresas ICA, this means that providers of specialized cement, unique steel alloys, or advanced construction machinery can dictate terms due to high switching costs and the potential for operational disruption if ICA changes suppliers. In 2024, the continued demand for specialized construction technology, valued in the billions, further strengthens the hand of these specialized providers.
The scarcity of skilled labor in Mexico in 2024, exacerbated by emigration, directly translates to increased bargaining power for labor providers. This situation can drive up operational costs for ICA and affect project timelines. Furthermore, suppliers who can credibly threaten to integrate forward into construction services, such as a major material producer offering pre-fabricated solutions, gain considerable leverage, potentially forcing ICA to accept less favorable contract terms.
| Factor | Impact on ICA's Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Context |
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for few dominant suppliers | Mexican construction materials market experiencing steady growth. |
| Switching Costs | Limits ICA's ability to change suppliers | Retooling machinery and process redesign are capital intensive. |
| Labor Scarcity | Increases power of skilled labor providers | Shortages of skilled trades in Mexico in 2024. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers to enter ICA's market | Global construction technology market growth indicates potential for new entrants. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting ICA, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all to inform strategic decision-making.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each force with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Empresas ICA's reliance on massive civil and industrial projects inherently concentrates its customer base, often involving governments or large corporations. These significant clients wield considerable bargaining power, especially given the immense financial commitment and strategic weight of these undertakings, frequently resulting in intense competitive bidding processes.
When construction services are seen as largely the same, customers can readily shop around and choose contractors based on cost alone. This makes it easier for them to switch providers if they find a better deal, increasing their bargaining power.
For Empresas ICA, this means that in segments where their offerings are perceived as commoditized, they face greater pressure from customers to lower prices. For instance, if a client is looking for a standard residential build, they can easily get quotes from multiple firms and pick the cheapest option, putting ICA in a weaker position.
However, for large, intricate projects like major infrastructure developments, ICA’s specialized knowledge and proven history provide a degree of uniqueness. This expertise allows them to command better terms, as clients recognize the value and reduced risk associated with their capabilities, thereby lessening customer bargaining power in these specific instances.
Government budget cuts and fiscal consolidation, as observed in Mexico's infrastructure spending plans for 2025, can amplify customer power. When public investment in physical projects decreases, it directly impacts demand, leading customers to seek more favorable terms or postpone their commitments.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers can significantly impact an industry. For instance, large government entities or major industrial clients might possess the resources and expertise to develop their own construction capabilities for specific projects, especially those that are less complex. This potential, even if not fully realized, acts as a powerful bargaining chip during price negotiations with existing construction firms.
Consider the infrastructure sector. While building entire complex projects in-house is often impractical, a large client might opt to manage certain aspects, like prefabrication or specific engineering tasks, internally. This strategic move can reduce their reliance on external contractors and provide leverage. For example, in 2024, several large-scale public works projects saw increased client involvement in material sourcing and component manufacturing, directly influencing contract terms with primary builders.
- Customer Leverage: Large clients can threaten to build capabilities in-house, reducing their dependence on suppliers.
- Negotiation Power: This threat gives customers more power to negotiate lower prices or better terms.
- Industry Impact: High potential for backward integration can suppress profit margins for suppliers.
- Strategic Consideration: Companies must monitor customer capabilities and potential integration strategies.
Transparency in Bidding and Procurement Processes
Transparency in bidding and procurement significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, particularly within the public sector where Empresas ICA often operates. This openness allows clients to gather and compare numerous bids, fostering a competitive environment that pressures suppliers like ICA to offer more favorable pricing and terms.
For instance, in 2024, many government infrastructure projects mandated detailed public disclosures of bid submissions and evaluation criteria. This level of transparency directly empowers contracting authorities to negotiate more effectively, as they can clearly see the pricing structures and proposed efficiencies from multiple entities.
- Increased Competition: Transparent processes encourage a wider pool of bidders, intensifying competition and giving customers more choices.
- Price Discovery: Open bidding allows customers to benchmark prices, leading to better-negotiated contracts and cost savings.
- Demand for Efficiency: When bids are evaluated transparently, customers can favor proposals demonstrating superior operational efficiency and value.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Transparency levels the playing field by providing customers with the information needed to make informed decisions, diminishing the supplier's informational advantage.
Customers, especially large government entities and corporations that frequently engage Empresas ICA, possess significant bargaining power. This is amplified when construction services are perceived as standardized, allowing clients to easily switch providers based on price. For example, in 2024, a substantial portion of infrastructure projects saw intense price competition, with clients leveraging multiple bids to secure lower costs.
The threat of backward integration, where clients might handle certain project aspects internally, also grants them leverage. In 2025, government entities are increasingly exploring in-house management of material sourcing and component manufacturing for public works, directly impacting negotiation terms with primary contractors like ICA.
| Factor | Impact on ICA | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Commoditization of Services | Increased price pressure | High, especially for standard construction |
| Backward Integration Threat | Leverage for clients | Growing, with clients managing more project components |
| Transparency in Bidding | Enhanced client negotiation power | Significant in public sector projects |
What You See Is What You Get
ICA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete ICA Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within a specific industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring you get precisely what you need for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Mexican construction market is quite busy, with many companies vying for projects. You have a few big domestic and international companies, and then a whole lot of smaller ones too. This means that for the really significant projects, the competition is pretty fierce for a company like Empresas ICA.
For instance, in 2023, the Mexican construction sector saw a significant number of bids for large infrastructure contracts, with major players like Cemex and Promotora y Operadora de Infraestructura (PINFRA) actively participating alongside ICA. This indicates a concentrated effort by key entities to capture market share.
The Mexican construction market saw expansion in 2024, but projections for 2025 suggest a potential slowdown, especially in civil works, driven by decreased government spending. This shift towards a more constrained growth environment naturally fuels heightened competition among industry players vying for fewer available projects.
The construction industry is characterized by substantial fixed costs. Companies often invest heavily in specialized equipment like cranes and excavators, alongside maintaining a skilled workforce and managing significant project-related overheads. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a small construction company to acquire essential heavy machinery could easily run into hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars.
These high fixed costs create significant exit barriers. Once a company has committed to these investments, especially with ongoing long-term projects and the presence of highly specialized, non-transferable assets, it becomes very difficult and costly to simply cease operations. This pressure forces construction firms to aggressively pursue new contracts and projects, even at lower profit margins, simply to cover their fixed expenses and avoid substantial losses from idle capacity.
Differentiation Among Competitors
For many standard construction services, distinguishing one company from another can be tough, often pushing competition into a price war. Empresas ICA, however, leverages its extensive history and proven track record in handling massive, intricate infrastructure projects. This deep experience and established reputation allow ICA to offer a level of differentiation that goes beyond mere cost, appealing to clients who prioritize reliability and technical prowess on complex undertakings.
Empresas ICA's ability to differentiate itself is particularly evident in its specialization in large-scale, complex infrastructure projects. This focus allows them to command a premium and build stronger client relationships based on trust and proven capability, rather than solely competing on price for more commoditized construction tasks. For instance, in 2023, ICA reported significant progress on major infrastructure developments, showcasing their capacity for high-value, differentiated work.
- Specialization in Complex Infrastructure: ICA's focus on large-scale, intricate projects provides a distinct advantage over competitors offering more general construction services.
- Reputation and Experience: A long history of successful project execution builds client confidence and allows for differentiation beyond price.
- Technical Expertise: The ability to manage complex engineering challenges differentiates ICA in a market often driven by cost alone.
Government Policies and Project Allocation
Government policies and how public infrastructure projects are distributed are major forces influencing competition. When governments spend more on infrastructure, it can open up more opportunities, potentially easing some competitive pressures. However, changes in these spending plans can quickly alter the game.
For instance, a projected decrease in federal infrastructure spending for 2025, as indicated by early budget discussions, means fewer projects will be available. This scarcity directly fuels more intense rivalry among companies vying for the remaining contracts. Businesses must adapt their strategies to secure these limited opportunities.
The allocation process itself also plays a role. Transparent and merit-based allocation can foster fair competition, while less predictable or politically influenced distribution can create an uneven playing field. Companies that can effectively navigate these policy landscapes and demonstrate alignment with government priorities are better positioned.
- Government Spending Trends: Anticipated reductions in federal infrastructure outlays for 2025 could lead to a more competitive bidding environment for public works.
- Policy Shifts: Changes in government priorities, such as a renewed focus on green energy infrastructure, can redirect project opportunities and alter competitive dynamics.
- Allocation Mechanisms: The fairness and transparency of how projects are awarded significantly impact the intensity of rivalry among firms.
- Budgetary Constraints: Fiscal pressures on government budgets can lead to project delays or cancellations, forcing companies to re-evaluate their project pipelines and competitive strategies.
The Mexican construction market is intensely competitive, with numerous domestic and international players, including large entities like Cemex and PINFRA, alongside many smaller firms. This high level of rivalry is exacerbated by substantial fixed costs associated with heavy machinery and skilled labor, creating significant exit barriers that compel companies to pursue contracts aggressively, even at lower margins, to cover operational expenses.
Empresas ICA differentiates itself through its specialization in large-scale, complex infrastructure projects, leveraging its extensive experience and reputation to move beyond price-based competition. Government spending patterns, particularly a projected decrease in federal infrastructure outlays for 2025, are expected to intensify this rivalry by reducing the number of available projects, making strategic navigation of policy and transparent allocation mechanisms crucial for success.
| Factor | Impact on ICA | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High rivalry, especially for large projects | Significant presence of major domestic and international firms in 2023 bids. |
| Fixed Costs & Exit Barriers | Pressure to maintain project flow to cover costs | High investment in specialized equipment drives need for continuous contract acquisition. |
| Differentiation Strategy | Leverages specialization and reputation | ICA's focus on complex infrastructure projects noted in 2023 project progress reports. |
| Government Spending | Potential for reduced opportunities if spending declines | Projected decrease in federal infrastructure spending for 2025 impacting project availability. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Clients are increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional large-scale infrastructure projects. For instance, instead of building entirely new facilities, organizations might invest in upgrading existing assets, a trend gaining traction as companies seek cost-efficiency. In 2024, the global infrastructure upgrade and maintenance market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a significant shift in spending priorities.
Modular and prefabricated construction techniques offer another compelling substitute. These methods allow for faster deployment and often lower upfront costs compared to conventional building. The modular construction market, valued at over $100 billion globally in 2023, is expected to see continued robust growth, driven by demand for quicker project completion and reduced site disruption.
Furthermore, the adoption of digital solutions to optimize current infrastructure presents a substantial threat. Predictive maintenance software, IoT sensors for asset monitoring, and advanced analytics can extend the lifespan and improve the performance of existing infrastructure, thereby reducing the perceived need for new construction. This digital transformation in asset management is a key factor influencing capital allocation decisions for many organizations.
Technological advancements are significantly reshaping the construction landscape, presenting a potent threat of substitutes. Innovations such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) are streamlining project management and design, while 3D printing offers rapid, on-site fabrication of building components, potentially reducing reliance on traditional labor and materials. The global construction 3D printing market, valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023, is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift towards alternative construction methodologies.
The threat of substitutes is heightened as clients increasingly favor renovating and maintaining existing structures over new builds. This trend is particularly pronounced during economic downturns or when urban planning policies shift focus. For instance, in 2024, the construction industry saw a significant allocation of resources towards retrofitting and upgrades, driven by sustainability initiatives and cost-saving measures.
Changes in Societal Needs or Urban Planning
Broader societal shifts are significantly impacting the construction industry. For instance, the widespread adoption of remote work, accelerated by events in 2020 and continuing through 2024, has reduced the demand for traditional new office spaces. This trend directly affects the need for certain types of construction materials and services, potentially making older building designs or materials less desirable substitutes for more flexible, adaptable spaces.
Urban planning also plays a crucial role. A growing emphasis on public transportation, evident in many cities' infrastructure investments in 2024, can decrease the demand for new road networks and associated construction. This shift could lead to a greater need for construction solutions focused on transit hubs, pedestrian zones, and sustainable urban development, thereby altering the competitive landscape for substitute construction methods and materials.
Consider these specific impacts:
- Reduced Demand for Traditional Office Construction: As of late 2023 and into 2024, vacancy rates in many major office markets remained elevated, signaling a potential long-term decrease in demand for new office builds. For example, the U.S. office vacancy rate hovered around 13% in Q4 2023, according to commercial real estate data firms.
- Increased Investment in Public Transit: Many municipalities globally are allocating substantial funds to public transport upgrades. In 2024, cities like London and New York continued major rail and bus network expansions, potentially diverting construction resources and demand away from road infrastructure projects.
- Rise of Green Building and Retrofitting: Societal focus on sustainability is driving demand for retrofitting existing structures and constructing new, energy-efficient buildings. This creates opportunities for alternative building materials and methods that offer better environmental performance than conventional ones.
Policy-Driven Alternatives
Government policies increasingly steer development towards sustainability and climate resilience, directly influencing the viability of traditional large-scale construction projects. For instance, in 2024, many municipalities are prioritizing retrofitting existing infrastructure and implementing smart city technologies over new builds, making these policy-driven alternatives a significant threat. This shift favors integrated, technologically advanced, and environmentally friendly solutions that offer long-term efficiency and reduced ecological impact.
These policy shifts can create substitutes by making alternative approaches more economically attractive or even mandatory. Examples include incentives for energy-efficient building materials or regulations favoring renewable energy integration over fossil-fuel-dependent systems. In 2024, the global green building market is projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, demonstrating a clear market preference for sustainable alternatives driven by policy. This trend impacts project types by de-emphasizing purely physical expansion and emphasizing smart, adaptable, and eco-conscious solutions.
- Policy-Driven Alternatives: Government mandates and incentives for sustainability, smart city development, and climate resilience are creating a strong market for alternative solutions.
- Impact on Project Types: These policies favor integrated, technologically advanced, and environmentally friendly solutions over traditional large-scale physical construction.
- Market Trends (2024): The global green building market's projected growth to over $1.5 trillion in 2024 highlights a significant shift towards sustainable alternatives, influenced by policy.
- Economic Attractiveness: Incentives for energy efficiency and renewable energy integration make these alternatives more economically viable and sometimes mandatory.
The threat of substitutes in the construction sector is significant, as clients increasingly opt for upgrading existing infrastructure rather than embarking on entirely new projects. This trend is amplified by modular construction, which offers faster deployment and lower initial costs. Digital solutions, like predictive maintenance software, also extend the life of current assets, reducing the need for new builds.
Technological advancements, such as BIM and 3D printing, are further reshaping construction by offering more efficient and potentially cheaper alternatives to traditional methods. For instance, the global construction 3D printing market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023, indicating a growing adoption of these substitutes.
Broader societal and urban planning shifts also contribute to this threat. The rise of remote work has decreased demand for new office spaces, while increased investment in public transit in cities like London and New York in 2024 diverts resources from road construction. Furthermore, government policies promoting sustainability and climate resilience, with the green building market projected to exceed $1.5 trillion in 2024, favor retrofitting and eco-conscious solutions over traditional construction.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Data/Trend (2023-2024) | Impact on Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Upgrades & Maintenance | Cost-efficiency, extending asset life | Global market projected in hundreds of billions (2024) | Reduces demand for new builds |
| Modular & Prefabricated Construction | Faster deployment, lower upfront costs | Global market over $100 billion (2023) | Offers quicker, often cheaper alternatives |
| Digital Solutions (Predictive Maintenance, IoT) | Optimizing existing assets, extending lifespan | Growing adoption in asset management | Decreases perceived need for new construction |
| 3D Printing in Construction | Rapid on-site fabrication, reduced labor | Global market ~$1.5 billion (2023), significant growth | Potential to disrupt traditional material and labor reliance |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the large-scale construction and infrastructure development sector demands immense capital. Think about the cost of heavy machinery, specialized equipment, and the sheer amount of money needed to keep large, multi-year projects running. For instance, a major infrastructure project in 2024 could easily require billions in upfront investment, making it incredibly difficult for smaller or newer companies to even get a foot in the door.
The Mexican construction industry, particularly for large infrastructure projects, faces a formidable barrier to entry due to extensive regulatory hurdles and protracted permitting processes. New companies must navigate a complex web of approvals, including rigorous environmental impact assessments and a multitude of specific permits, which can significantly delay project commencement and increase upfront costs.
Clients, especially government agencies and major corporations, place a high value on contractors with a demonstrable history of successfully executing large, intricate projects. Empresas ICA's extensive operational history and accumulated expertise offer a significant competitive edge that emerging competitors simply cannot match.
For instance, in 2024, ICA secured contracts for significant infrastructure developments, reinforcing its established reputation. New entrants would struggle to replicate this level of trust and proven capability, making it a substantial barrier to entry.
Access to Distribution Channels and Client Relationships
New companies face significant hurdles in accessing crucial distribution channels and cultivating deep-seated client relationships. For instance, securing contracts for major infrastructure and industrial projects frequently hinges on pre-existing connections with government bodies, private developers, and established access to competitive bidding platforms. These networks are not easily replicated.
Building these essential relationships takes considerable time and effort, creating a substantial barrier for any newcomers attempting to enter the market. Consider the construction sector: in 2024, the average lead time to secure a significant infrastructure contract, from initial contact to project award, often exceeded 18 months, highlighting the entrenched nature of established players' access.
This difficulty in establishing trust and proven track records with key stakeholders means that new entrants often find themselves excluded from lucrative opportunities. For example, in the highly specialized field of aerospace manufacturing, a sector where safety and reliability are paramount, new suppliers in 2024 found it nearly impossible to break into the supply chains of major players like Boeing or Airbus without years of proven performance and extensive vetting, often requiring partnerships with established firms.
- Established Networks: New entrants struggle to replicate the extensive networks and relationships that incumbent firms have built over years with government agencies and private developers.
- Access to Bidding Processes: Gaining entry into competitive bidding processes for major projects is often contingent on a company's history and reputation, which new firms lack.
- Client Trust: Building the necessary trust and demonstrating a track record of successful project delivery is a time-consuming process that deters rapid market entry.
- Industry-Specific Barriers: In sectors like heavy industry or defense, where long-term contracts and security clearances are involved, the barriers to entry are particularly high for new participants.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Benefits
Empresas ICA, as an established player, leverages significant economies of scale in its operations. This scale advantage translates into lower per-unit costs for materials, equipment, and labor, enabling ICA to submit more competitive bids on large infrastructure projects. For instance, in 2023, ICA's substantial project pipeline allowed for bulk purchasing of construction materials, securing favorable pricing that new, smaller entrants cannot easily match.
New entrants into the construction and infrastructure sector face a considerable hurdle in achieving the same cost efficiencies. They must first invest heavily to reach a scale comparable to established firms like ICA, a process that takes time and significant capital outlay. This initial cost disadvantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete directly on price for major contracts, thereby limiting the immediate threat of new entrants.
- Economies of Scale: ICA's large operational footprint allows for cost reductions in procurement and project execution.
- Experience Curve: Years of project experience have honed ICA's management and operational efficiencies, further lowering costs.
- Cost Disadvantage for Newcomers: Entrants must overcome initial high costs to achieve competitive pricing.
- Bidding Competitiveness: ICA's scale and experience enable more aggressive bidding strategies.
The threat of new entrants for Empresas ICA is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital requirements and complex regulatory landscape in large-scale construction. For example, major infrastructure projects in 2024 often demand billions in investment, a barrier that deters many potential competitors from entering the market.
Established relationships and client trust also present a formidable challenge for newcomers. ICA's proven track record, reinforced by securing significant contracts in 2024, builds a level of confidence that new firms cannot easily replicate, making it difficult to gain access to lucrative opportunities.
Furthermore, economies of scale enjoyed by ICA, such as bulk purchasing power demonstrated in 2023, create a cost advantage that new entrants struggle to match initially. This cost disadvantage, coupled with the time and capital needed to build scale, limits the immediate threat from new market participants.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment needed for machinery, equipment, and project financing. | Billions required for major infrastructure projects. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex permitting, environmental assessments, and approvals cause delays and increase costs. | Protracted processes in Mexican construction sector. |
| Client Trust & Track Record | Difficulty in establishing credibility and proven success with clients. | ICA secured major infrastructure contracts in 2024, reinforcing reputation. |
| Access to Networks | Limited pre-existing relationships with government agencies and developers. | Securing contracts often hinges on established connections. |
| Economies of Scale | New entrants face higher per-unit costs due to smaller operational size. | ICA's 2023 bulk purchasing secured favorable material pricing. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.