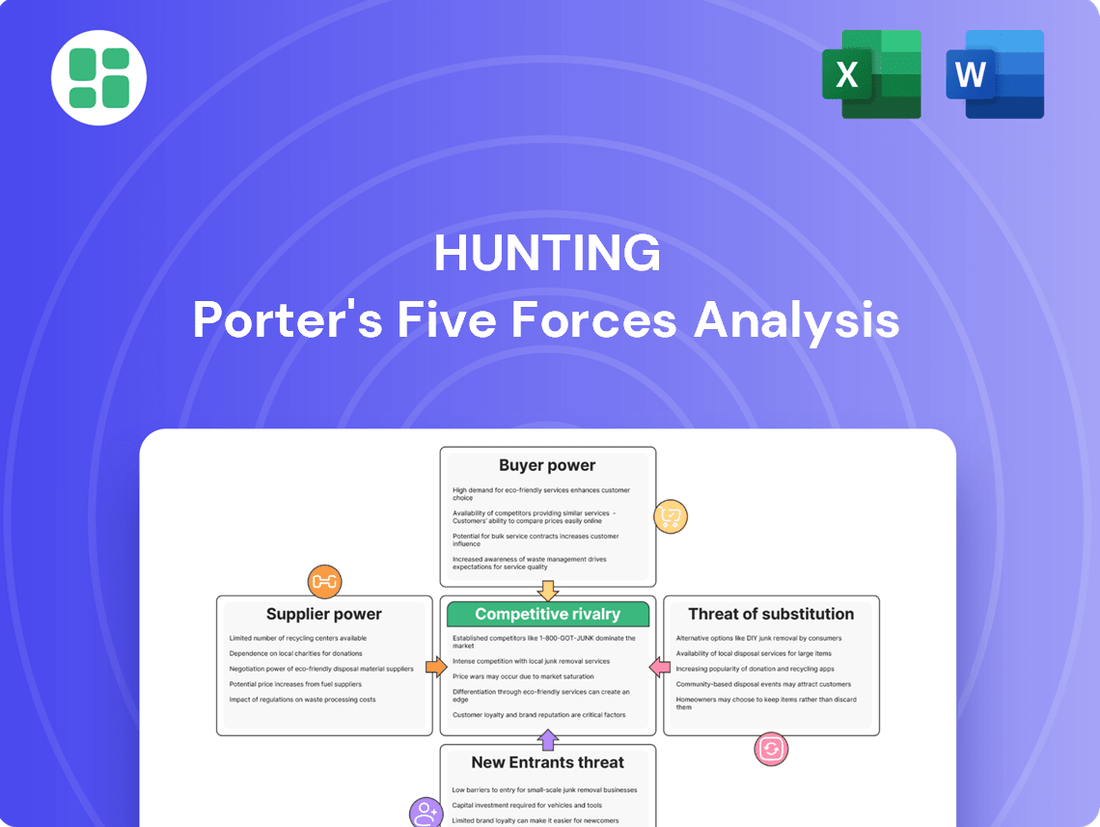
Hunting Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hunting Bundle
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intense competitive landscape Hunting operates within, highlighting the power of buyers and the threat of substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business aiming to thrive.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hunting’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hunting PLC's reliance on highly specialized raw materials and advanced technologies for its precision-engineered equipment means there are often only a limited number of qualified suppliers. This scarcity of specialized input providers grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power, allowing them to influence pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the global market for certain advanced alloys crucial for Hunting's oil and gas sector components saw price increases averaging 8-12% due to supply chain constraints and high demand from multiple industries.
For Hunting PLC, the bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by high switching costs associated with critical inputs. Changing suppliers for essential components or proprietary technologies often entails substantial expenses. These can include the costs of re-qualifying new suppliers, re-tooling manufacturing equipment, and the potential for production disruptions during the transition period. For instance, in the energy sector, specialized components for exploration or production equipment can have very long lead times and require rigorous testing, making a switch costly and time-consuming.
Hunting PLC's reliance on a specialized workforce, encompassing engineers, machinists, and field technicians with deep oil and gas industry expertise, significantly influences supplier power. The availability and cost of this skilled labor directly impact Hunting's operational efficiency and profitability.
In 2024, the global shortage of skilled energy sector professionals continued to be a significant challenge. For instance, reports indicated a growing deficit in experienced petroleum engineers and specialized rig personnel, potentially driving up wages and recruitment costs for companies like Hunting.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or intellectual property crucial for Hunting's operations can leverage this advantage to demand premium pricing and impose stricter terms. This reliance can significantly inflate Hunting's cost structure and diminish its bargaining leverage.
For instance, if a key component for Hunting's advanced drilling equipment relies on a patented micro-filtration system, the supplier of this system holds substantial power. In 2024, companies specializing in such niche, high-tech components often see margins exceeding 30%, allowing them to dictate terms to buyers like Hunting.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique, hard-to-replicate technologies have a significant edge.
- Intellectual Property: Patents and exclusive licensing rights grant suppliers considerable pricing power.
- Increased Costs: Reliance on such suppliers can escalate Hunting's production expenses.
- Reduced Negotiation Power: Hunting's ability to negotiate favorable terms is weakened when essential inputs are controlled by a few powerful suppliers.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics and Disruptions
Geopolitical events, trade policies, and global economic fluctuations significantly impact supply chains, creating scarcity and price volatility for raw materials and components. For instance, the ongoing tensions and trade disputes in 2024 have led to increased lead times and higher costs for critical electronic components, directly benefiting suppliers who can dictate terms.
These external pressures can temporarily or permanently shift the balance of power towards suppliers. When resources become constrained, suppliers gain leverage, often leading to increased prices and less favorable contract terms for buyers. This was evident in the semiconductor industry throughout 2023 and into early 2024, where persistent shortages allowed chip manufacturers to command premium pricing and exert greater control over allocation.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Geopolitical instability and protectionist trade policies in 2024 have exposed the fragility of global supply chains, particularly for industries reliant on specific regions for raw materials.
- Price Volatility: Disruptions have caused significant price swings; for example, certain rare earth minerals, crucial for electronics and defense, saw price increases of up to 15% in the first half of 2024 due to export restrictions and demand surges.
- Supplier Leverage: In sectors facing component shortages, such as automotive manufacturing in 2024, suppliers have been able to enforce stricter payment terms and limit order volumes, increasing their bargaining power.
- Resource Scarcity: The scarcity of key inputs, exacerbated by events like the Red Sea shipping disruptions impacting maritime trade routes in early 2024, empowers suppliers who control access to these vital resources.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hunting PLC is substantial when they offer unique or highly specialized products, as seen with advanced alloys in 2024 where prices rose 8-12% due to limited availability and high demand. High switching costs, including re-qualification and potential production halts, further solidify supplier leverage. Proprietary technology, like patented filtration systems, allows suppliers to command premium pricing, with specialized component providers in 2024 achieving margins over 30%. Geopolitical events and trade policies in 2024 also contribute, causing price volatility and scarcity for critical components, thereby increasing supplier control.
| Factor | Impact on Hunting PLC | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Specialization | Limited qualified suppliers grant significant pricing power. | 8-12% price increase for advanced alloys due to supply constraints. |
| Switching Costs | High expenses for re-qualification and potential disruption reduce buyer flexibility. | Long lead times and rigorous testing for specialized energy sector components. |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers with unique tech can dictate premium pricing. | Niche component suppliers achieving 30%+ margins. |
| Geopolitical/Trade Policies | Disruptions create scarcity and price volatility, empowering suppliers. | 15% price surge in rare earth minerals due to export restrictions. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Hunting's position in the oilfield services sector.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hunting PLC's primary customers are major international oil and gas companies. These entities are typically large, consolidated, and wield significant purchasing power, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, major oil producers continued to consolidate, increasing their collective bargaining leverage.
The oil and gas sector is inherently cyclical, meaning its fortunes rise and fall with global economic activity and commodity prices. During industry downturns, customers, such as refiners or energy producers, experience significant pressure to reduce their own operational costs. This cost-cutting imperative directly translates into a heightened demand for lower prices from their suppliers, including companies like Hunting.
This cyclicality significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers when market conditions turn unfavorable for service providers. For instance, in 2023, global oil prices experienced volatility, with Brent crude averaging around $82 per barrel, down from higher levels in previous years. Such price fluctuations often force upstream and midstream companies to scrutinize their expenditures, making them more sensitive to supplier pricing and more inclined to negotiate aggressively.
The bargaining power of customers in the hunting industry is influenced by the degree of product standardization and associated switching costs. While many hunting products are specialized, some equipment or services might be more commoditized, enabling customers to move between providers with less friction. This flexibility grants customers greater leverage, pushing companies like Hunting to maintain competitive pricing and service levels to retain their business.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers is a significant factor in assessing the bargaining power of customers for companies like Hunting. Large customers, particularly in the oil and gas sector, may have the financial resources and technical expertise to develop their own manufacturing capabilities or service divisions. This potential allows them to produce critical components or provide essential services in-house, thereby reducing their dependence on external suppliers.
For instance, major oil and gas exploration companies could invest in specialized manufacturing facilities or acquire existing service providers to handle the production of certain equipment, such as specialized valves or drilling components, that Hunting currently supplies. This strategic move would directly diminish Hunting's customer base for those specific products or services. In 2024, the energy sector saw continued emphasis on cost optimization and supply chain resilience, which could accelerate such integration efforts by large players seeking greater control and cost savings.
- Reduced Dependence: Customers integrating backward can source inputs internally, lessening their reliance on suppliers like Hunting.
- Cost Control: In-house production can offer greater cost predictability and potentially lower unit costs for large buyers.
- Supply Chain Security: Backward integration enhances a customer's control over the availability and quality of critical components.
- Market Power Shift: The ability of customers to produce their own inputs significantly strengthens their bargaining power against suppliers.
Demand Fluctuation and Project Discretion
Customers' ability to delay or cancel exploration and production projects, often due to shifting market prices or internal strategic realignments, directly influences the demand for Hunting's offerings. This flexibility in managing project timelines and capital expenditures grants them considerable leverage during price and contract negotiations.
For example, during periods of oil price volatility, such as the fluctuations seen in 2024, customers may postpone non-essential projects. This can lead to a significant reduction in orders for specialized equipment and services, thereby increasing the bargaining power of these customers as they seek more favorable terms.
- Demand Sensitivity: Customers can easily postpone or cancel projects, directly impacting Hunting's order book.
- Market Conditions Impact: Fluctuations in commodity prices or economic downturns amplify customers' ability to defer investments.
- Negotiating Leverage: This discretion over project timing and spending empowers customers to demand better pricing and terms.
The bargaining power of Hunting PLC's customers, primarily major oil and gas companies, is substantial due to their concentrated market position and significant purchasing volume. In 2024, these large entities continued to consolidate, amplifying their collective ability to negotiate favorable terms and pricing from suppliers.
The cyclical nature of the oil and gas industry further empowers customers. During downturns, when oil prices are volatile, such as the average Brent crude price of approximately $82 per barrel in 2023, customers face intense pressure to reduce costs. This economic reality makes them more aggressive in negotiating prices with service providers like Hunting.
Customers' ability to switch suppliers is also a key factor. While some of Hunting's products are specialized, commoditized offerings allow customers to move between providers with relative ease. This flexibility grants them leverage, compelling Hunting to maintain competitive pricing and service standards to retain business.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High | Major international oil and gas companies are consolidated entities. |
| Purchasing Volume | High | Large order sizes allow for significant negotiation leverage. |
| Industry Cyclicality | Increases during downturns | Brent crude averaged ~$82/barrel in 2023, increasing customer cost pressure. |
| Switching Costs | Varies (Lower for commoditized products) | Customers can more easily change suppliers for standardized equipment. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Significant | Energy sector's 2024 focus on cost optimization may drive integration efforts. |
| Project Deferral Ability | High | Customers can postpone projects due to market volatility, impacting demand. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hunting Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing a thorough examination of the competitive landscape for hunting. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted document immediately after purchase, ensuring you have all the insights needed to understand industry attractiveness and strategic positioning. No placeholders or sample content, just the ready-to-use analysis you see here.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The upstream oil and gas services sector, where Hunting PLC operates, is decidedly mature. This maturity translates into a highly competitive environment, populated by a significant number of global giants and niche specialists vying for business. In 2024, the industry saw continued pressure on margins due to this intense rivalry, forcing companies to focus on operational efficiency and technological advancement to stand out.
Hunting PLC faces intense competition from larger, integrated oilfield service giants like Schlumberger, Halliburton, and Baker Hughes. These behemoths possess extensive global networks, comprehensive service offerings, and significantly deeper financial reserves, allowing them to aggressively pursue and often win large-scale projects, thereby intensifying rivalry for Hunting.
For instance, in 2023, Schlumberger reported revenues of approximately $30.4 billion, Halliburton around $23.9 billion, and Baker Hughes roughly $21.4 billion, dwarfing Hunting's reported revenue of $1.1 billion for the same period. This stark financial disparity highlights the competitive disadvantage Hunting faces in bidding for major contracts where scale and extensive capital are crucial differentiators.
Competitive rivalry in the hunting sector is intensely fueled by a relentless technological race and the constant pursuit of product differentiation. Companies are pouring significant resources into research and development, aiming to deliver hunting solutions that are not only more efficient but also safer and kinder to the environment. Hunting's continued success hinges directly on its capacity to either match or surpass these ongoing innovations, ensuring its offerings remain at the cutting edge.
Market Consolidation and Pricing Pressures
Industry consolidation, often driven by mergers and acquisitions, can significantly alter the competitive landscape. When fewer, larger players emerge, the rivalry intensifies as these entities battle more fiercely for market share. This often translates into aggressive pricing strategies as companies vie for dominance.
The oilfield services sector, for instance, has experienced notable consolidation. In 2023, major players continued to integrate operations, leading to a more concentrated market. This trend has demonstrably impacted pricing power and the intensity of competition among the remaining service providers.
- Increased Market Concentration: Consolidation reduces the number of independent competitors, potentially leading to oligopolistic or even monopolistic tendencies.
- Pricing Power Dynamics: Fewer, larger competitors can exert greater influence over pricing, potentially leading to price wars or, conversely, tacit price collusion.
- Impact on Smaller Players: Consolidation can squeeze out smaller, less efficient competitors, further concentrating market power among the survivors.
High Exit Barriers
The oil and gas equipment and services sector is characterized by substantial exit barriers, primarily due to the specialized nature of its assets and significant fixed costs. These high upfront investments mean companies often find it difficult to divest or repurpose their assets, even when market conditions deteriorate.
This situation can force companies to continue operating at a loss during downturns simply to try and recover their initial investments. For example, in 2023, many oilfield service providers maintained operations despite reduced demand, hoping to avoid complete write-offs of their specialized drilling rigs and processing equipment. This persistence in the face of adversity directly contributes to overcapacity within the industry.
The resulting overcapacity intensifies competitive rivalry, as more players vie for a smaller pool of available projects. Companies are compelled to compete more aggressively on price to secure contracts, further squeezing profit margins. This dynamic is a hallmark of industries with high exit barriers, where the cost of leaving the market is prohibitive.
- Specialized Assets: High investment in unique, industry-specific equipment.
- Significant Fixed Costs: Large outlays for manufacturing, infrastructure, and technology.
- Continued Operation: Companies may operate at a loss to avoid asset write-downs.
- Overcapacity: Excess supply of services and equipment relative to demand.
- Intensified Rivalry: Increased competition, often price-driven, due to companies staying in the market.
The competitive rivalry within the upstream oil and gas services sector is fierce, driven by a mature market and the presence of large, well-capitalized competitors. This intense competition, particularly evident in 2024, forces companies like Hunting to prioritize operational efficiency and innovation to maintain market position.
The disparity in financial strength between Hunting and industry giants like Schlumberger (approx. $30.4 billion revenue in 2023) and Halliburton (approx. $23.9 billion revenue in 2023) underscores the challenge smaller players face in securing large contracts.
Consolidation within the sector further exacerbates rivalry, leading to fewer, more dominant players who can engage in aggressive pricing strategies. This trend, observed throughout 2023, reshapes market dynamics and pressures profit margins for all participants.
| Company | Approx. 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Competitor Status |
|---|---|---|
| Schlumberger | 30.4 | Industry Giant |
| Halliburton | 23.9 | Industry Giant |
| Baker Hughes | 21.4 | Industry Giant |
| Hunting PLC | 1.1 | Specialized Player |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The accelerating global shift towards renewable energy sources, driven by decarbonization efforts, presents a substantial threat to traditional fossil fuel demand. This transition directly impacts the upstream oil and gas sector, potentially shrinking the market for products like those supplied by Hunting. By 2024, renewable energy capacity additions continued to grow, with solar photovoltaic (PV) alone accounting for a significant portion of new global electricity generation capacity.
Technological advancements are significantly impacting the oil and gas sector, acting as a potent force of substitution. Improvements in drilling efficiency, for instance, allow companies to extract more hydrocarbons from existing wells. In 2024, innovations in hydraulic fracturing and directional drilling continue to boost recovery rates, potentially reducing the need for new exploration and, consequently, the demand for services and equipment that Hunting plc provides.
Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques, such as chemical injection and thermal methods, are also becoming more sophisticated and cost-effective. These advancements enable operators to access previously uneconomical reserves, thereby extending the life of existing fields and substituting the need for new production assets. This directly impacts the market for specialized equipment and services, a core offering for companies like Hunting.
Furthermore, digital optimization, including the use of AI and advanced analytics in reservoir management and production operations, allows for more precise and efficient extraction. By minimizing downtime and maximizing output from existing infrastructure, these digital tools can diminish the demand for certain upstream products and services. For example, predictive maintenance software can reduce the need for routine equipment replacements, a segment where Hunting operates.
The development of alternative hydrocarbon production methods presents a significant threat. While not directly substituting Hunting's core equipment, innovations like enhanced oil recovery (EOR) techniques or more efficient fracking technologies could reduce the overall demand for traditional drilling services and equipment. For instance, advancements in AI-driven reservoir analysis, which saw significant investment in 2024, aim to maximize output from existing wells, potentially slowing the need for new well construction.
Customer In-house Capabilities
Large oil and gas operators possess the financial muscle to develop or enhance their in-house capabilities for critical functions like equipment maintenance, manufacturing, and specialized services. This internal development can directly substitute the need for external providers such as Hunting. For instance, a major operator might invest millions in establishing its own repair facilities or fabricating certain components, thereby shrinking the market available to companies like Hunting.
The trend towards vertical integration by major players directly impacts Hunting's addressable market. As these operators bring more services in-house, the demand for Hunting's offerings in those specific areas diminishes. This strategic shift by customers represents a significant threat, as it removes potential revenue streams and forces Hunting to adapt its service portfolio to remain competitive.
- Customer In-house Capabilities Threat: Major oil and gas companies can develop internal expertise and infrastructure for equipment maintenance and specialized services, reducing reliance on external suppliers.
- Market Reduction: This trend directly shrinks the addressable market for companies like Hunting, as operators bring previously outsourced functions in-house.
- Financial Capacity: Large operators often have the substantial capital required to invest in these internal capabilities, making them a credible threat.
- Strategic Integration: The drive for greater control and cost efficiency encourages vertical integration, posing a persistent challenge to service providers.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Efforts
The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and conservation presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional oil and gas. As economies worldwide prioritize reducing energy consumption, the overall demand for fossil fuels could decline. This trend is already visible, with many nations setting ambitious energy reduction targets.
For instance, in 2024, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that advancements in energy efficiency measures could save the equivalent of several million barrels of oil per day globally. This directly impacts the long-term demand outlook for oil and gas, making new exploration and production projects less attractive.
- Reduced Demand: Increased efficiency lowers the overall need for energy, directly impacting oil and gas consumption.
- Policy Support: Government initiatives and international agreements in 2024 continue to promote energy conservation.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in areas like building insulation and efficient appliances are making energy savings more accessible.
- Shifting Consumer Behavior: A growing awareness of climate change is encouraging consumers to adopt more energy-conscious lifestyles.
The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) represents a direct substitute for internal combustion engine vehicles, thereby reducing demand for refined petroleum products. This shift, gaining significant momentum in 2024, directly impacts the demand for crude oil, a key commodity Hunting's products support. Global EV sales continued their upward trajectory, with projections for 2025 indicating further substantial growth, underscoring this substitution threat.
The development and widespread availability of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen and advanced biofuels, also pose a threat. These alternatives can power transportation and industrial processes, directly competing with fossil fuels. By 2024, investments in green hydrogen production and sustainable aviation fuels were on the rise, signaling a move away from traditional hydrocarbon reliance.
The threat of substitutes for Hunting's products is amplified by the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and conservation across industries. As businesses and consumers strive to reduce their energy footprint, the overall demand for oil and gas can contract. For example, in 2024, numerous countries implemented stricter energy efficiency standards for buildings and industrial equipment, further dampening the need for energy inputs that Hunting's offerings facilitate.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the specialized upstream oil and gas equipment and services sector presents a formidable challenge due to exceptionally high capital requirements. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development, advanced manufacturing facilities, precision machinery, and substantial inventory. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art fabrication plant for offshore drilling components can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant hurdle for potential new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the oil and gas services sector, particularly for specialized technology like advanced drilling equipment, is significantly dampened by the immense need for specialized technology and expertise. Established companies, such as Hunting PLC, have invested decades and substantial capital in developing proprietary designs and advanced engineering capabilities. For instance, Hunting's focus on precision manufacturing for downhole tools requires a deep understanding of materials science and operational environments that new entrants would find exceedingly difficult and costly to replicate quickly.
The oil and gas sector is characterized by exceptionally stringent regulatory and safety standards. New companies entering this arena must navigate a complex web of compliance requirements, which often involve substantial upfront investment in safety protocols and environmental protection measures. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for obtaining environmental permits and safety certifications in the upstream oil and gas sector can run into millions of dollars, significantly raising the barrier to entry.
Established Customer Relationships and Brand Loyalty
Major oil and gas companies have cultivated deep-seated relationships with their suppliers, built on years of trust and reliability in a high-stakes industry. This makes it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to establish similar rapport and gain access to essential resources.
Brand loyalty is another significant barrier. Customers in this sector often prioritize proven performance and safety records, which established players have meticulously built over decades. For instance, in 2024, the average contract duration for critical equipment in the upstream oil and gas sector often exceeds five years, reflecting this loyalty.
- Established relationships foster trust, making it hard for new entrants to secure supply chains.
- Brand loyalty is a significant hurdle, as customers favor proven reliability and safety.
- The lengthy process of building trust and loyalty acts as a deterrent to new competition.
Economies of Scale and Global Distribution Networks
Existing players, such as Hunting PLC, leverage significant economies of scale in their manufacturing processes and procurement of raw materials. This allows them to produce goods at a lower per-unit cost than a new entrant could initially manage. For example, in 2023, Hunting PLC reported revenue of $1.1 billion, indicating a substantial operational footprint that generates cost advantages.
Furthermore, Hunting PLC benefits from a deeply entrenched global distribution and service network, built over years of operation. New companies entering the market would face immense difficulty in replicating this extensive reach and the associated logistical efficiencies. Establishing such a network requires considerable capital investment and time, creating a substantial barrier for potential competitors.
- Economies of Scale: Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale production.
- Global Reach: Established distribution and service networks provide market access.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing leads to better pricing on raw materials.
- Brand Loyalty: Existing customer relationships built on reliability and service.
The threat of new entrants in the specialized oil and gas equipment sector is considerably low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements, specialized technology, and stringent regulations create significant hurdles. Established companies also benefit from strong customer loyalty and existing distribution networks, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data Point (2024/2023) |
| Capital Requirements | Extremely high investment needed for R&D, facilities, and machinery. | Deters new entrants due to massive upfront costs. | Hundreds of millions for a single advanced fabrication plant. |
| Technology & Expertise | Proprietary designs and advanced engineering are difficult to replicate. | Requires significant time and investment to develop comparable capabilities. | Decades of investment in proprietary downhole tool technology. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex safety and environmental standards necessitate costly adherence. | Adds millions in upfront costs for permits and certifications. | Average millions for environmental permits and safety certifications. |
| Customer Relationships | Established trust and reliability make it hard for newcomers to secure business. | New entrants struggle to build the necessary rapport. | Average contract duration for critical equipment exceeds five years. |
| Economies of Scale | Existing players achieve lower per-unit costs through large-scale operations. | New entrants face higher initial production costs. | Hunting PLC's 2023 revenue of $1.1 billion indicates significant scale advantages. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of diverse data, including industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from key players, and publicly available government data to capture the competitive landscape.