Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil Bundle
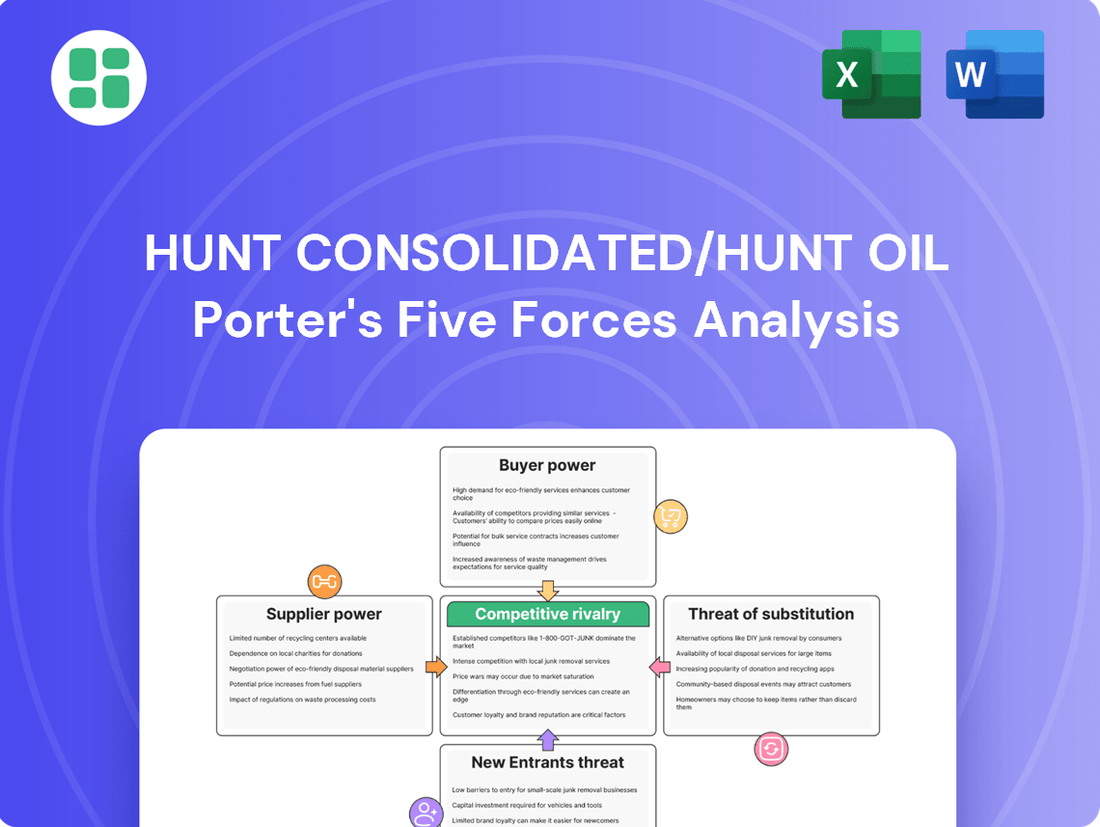
Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil operates within a dynamic energy sector, facing intense competition from established players and emerging ventures. Understanding the forces of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes is crucial for navigating this complex landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized oil and gas drilling equipment, advanced seismic technology, and complex oilfield services wield considerable power. This is due to the niche nature of their products and the substantial costs associated with switching providers, making it difficult for companies like Hunt Oil to find readily available alternatives.
The oilfield services sector is seeing increased concentration as digitalization and automation become more prevalent, consolidating expertise among a limited number of key industry players. For instance, in 2024, the global oilfield services market was projected to reach over $200 billion, with a significant portion of this value driven by specialized technological solutions.
This trend can translate into higher capital expenditures for energy companies. Coupled with factors like rising import duties on essential equipment, which can add 10-15% to procurement costs for certain components, the bargaining power of these specialized suppliers becomes even more pronounced.
The suppliers of critical raw materials, like steel essential for pipelines and drilling equipment, hold significant bargaining power. This power is directly tied to fluctuating global commodity prices and the overall stability of supply chains. For instance, in early 2024, steel prices experienced volatility due to increased industrial demand and ongoing supply chain disruptions, impacting infrastructure project costs.
Geopolitical events and trade disputes, such as tariffs imposed on imported materials, can further amplify supplier leverage. These factors directly influence the cost and availability of necessary components, leading to increased project development expenses for companies like Hunt Consolidated, which operates in the oil and gas and power infrastructure sectors.
Hunt Consolidated's broad operational footprint exposes it to material cost fluctuations across its energy, real estate, and power generation businesses. For example, the cost of lumber, a key real estate input, saw a notable increase in late 2023 and early 2024, driven by strong housing market demand and limited supply, illustrating the widespread impact of raw material availability.
The availability of skilled labor significantly impacts Hunt Consolidated's bargaining power with its "suppliers," which in this context includes its own workforce. A scarcity of specialized engineers, geologists, and experienced construction professionals, particularly in the demanding energy exploration and large-scale real estate sectors, can empower these workers. This tight labor market, a trend observed through 2024, can lead to increased wage demands and higher labor costs for Hunt, directly affecting its operational expenses across its diverse business units.
Technological Advancements and Proprietary Tech
Suppliers possessing unique or cutting-edge technologies, such as those in enhanced oil recovery or digital drilling, can significantly influence pricing. Hunt Oil, like other independent energy firms, depends on these innovations to optimize operations and boost extraction yields, thereby granting these technology providers considerable bargaining power.
The oil and gas sector is experiencing a technological revolution, with advancements in exploration and drilling dramatically increasing production volumes and lowering costs. For instance, by mid-2024, the adoption of AI-driven drilling optimization tools was reported to reduce non-productive time by as much as 15% in some operations, directly impacting the value proposition of technology suppliers.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with patented or exclusive technologies in areas like advanced seismic imaging or specialized drilling fluids hold a strong position.
- Innovation Impact: The continuous development of more efficient extraction methods, such as those utilizing nanotechnology, allows suppliers to charge premium prices.
- Operational Dependence: Hunt Oil's need for these specialized technological solutions to maintain competitiveness and operational efficiency makes it susceptible to supplier price increases.
- Market Trends: The overall trend towards digitalization and automation in the energy sector amplifies the leverage of technology providers who offer these critical capabilities.
Regulatory and Environmental Service Providers
The increasing focus on environmental regulations and sustainability is bolstering the bargaining power of specialized service providers. These companies offer crucial services like environmental compliance, carbon capture, and emissions reduction, which are becoming non-negotiable for energy firms. For instance, global spending on energy transition technologies, including decarbonization, was projected to reach over $2 trillion in 2024, highlighting the critical nature of these services.
Hunt Consolidated, with its diverse operations in energy and real estate, must engage with these environmental service providers. Their commitment to social responsibility and sustainable practices means they rely on these suppliers for essential, often unique, solutions. The demand for decarbonization programs in the oil and gas sector alone is driving significant investment, with some estimates suggesting a need for trillions of dollars globally to meet climate targets by 2030.
- Growing Demand for ESG Services: The market for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) consulting and services is expanding rapidly, giving providers more leverage.
- Specialized Expertise: Providers with niche skills in areas like carbon accounting or circular economy solutions are in high demand.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Companies like Hunt face increasing costs to meet evolving environmental standards, making the services of compliance providers indispensable.
- Investment in Green Technologies: The global push for green technologies means suppliers of these solutions are in a strong position to negotiate terms.
Suppliers of specialized oilfield equipment and advanced seismic technology possess significant bargaining power due to the niche nature of their offerings and high switching costs for companies like Hunt Oil. The increasing concentration within the oilfield services sector, driven by digitalization, further consolidates this power among fewer key players. For instance, the global oilfield services market was projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, with specialized technological solutions forming a substantial portion of this value.
The bargaining power of raw material suppliers, such as steel producers, is directly influenced by volatile global commodity prices and supply chain stability. In early 2024, steel prices saw fluctuations due to robust industrial demand and persistent supply chain disruptions, impacting infrastructure project costs. Geopolitical factors, including tariffs on imported materials, can exacerbate supplier leverage, increasing development expenses for firms like Hunt Consolidated.
Suppliers of proprietary technologies, particularly in areas like enhanced oil recovery and digital drilling, command considerable influence. Hunt Oil's reliance on these innovations to optimize operations and boost yields grants these providers strong negotiating positions. By mid-2024, AI-driven drilling optimization tools were reported to reduce non-productive time by up to 15% in certain operations, underscoring the value and leverage of technology suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Key Bargaining Factors | Impact on Hunt Consolidated |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment & Technology | Niche products, high switching costs, proprietary tech | Increased capital expenditure, operational dependence |
| Raw Materials (e.g., Steel) | Commodity price volatility, supply chain stability, tariffs | Higher project costs, material availability risks |
| Environmental Services | ESG compliance needs, specialized expertise, regulatory pressure | Increased operational costs, reliance on compliance solutions |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil, detailing threats from rivals, new entrants, buyer/supplier power, and substitutes to inform strategic decision-making.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape for Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil, transforming complex industry dynamics into actionable insights for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
For Hunt Oil, the commodity nature of crude oil and natural gas significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Refiners and utility companies view these products as largely undifferentiated, meaning their purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by price. This lack of product differentiation allows customers to easily switch between suppliers, putting pressure on Hunt Oil to remain competitive on cost.
The global oil market in 2025 is projected to be a buyer's market, with increased supply forecasts further strengthening customer leverage. This environment means that customers, such as large refining conglomerates or national power grids, can command more favorable terms. For instance, if a major refinery can secure a slightly lower price from an alternative producer, the cost savings can be substantial, given the sheer volume of oil they purchase annually.
Hunt Oil's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by buyer concentration in key markets. If Hunt's customers are large, integrated energy companies or major industrial consumers, their substantial purchasing volume grants them considerable leverage in price negotiations.
While Hunt Oil has a global presence, the regional concentration of refining and power generation facilities can empower a limited number of large buyers. For example, the increasing demand for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) driven by geographical supply and demand imbalances might tighten the LNG market in the early 2030s, but current market dynamics, as of mid-2025, generally favor buyers, enhancing their bargaining power.
Customers in the energy sector, especially those in competitive downstream markets or regulated power sectors, are keenly aware of input costs. This means their profitability is directly tied to the price of oil and gas, which in turn puts significant pressure on producers like Hunt Consolidated to maintain competitive pricing. For instance, in early 2024, WTI crude oil prices hovered in the low $70s, and Henry Hub natural gas prices remained low, creating a challenging environment for producers.
These commodity price pressures can significantly limit the financial incentives for companies like Hunt Oil to invest in new drilling programs. When the cost of extraction and production approaches or exceeds the market price, the risk-reward calculation for expansion becomes unfavorable, directly impacting the bargaining power of customers who can then demand lower prices or seek alternative, cheaper suppliers.
Demand for Diversified Energy Sources
The growing demand for diversified energy sources significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers. As large industrial users and power utilities actively seek to reduce their dependence on traditional fossil fuels, their leverage over suppliers like Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil increases. This diversification trend is supported by data showing that clean power generation is projected to exceed 40% of the global electricity mix in 2024, a substantial rise from previous years.
This shift empowers customers to negotiate more favorable terms, as they have viable alternatives readily available. They can explore various procurement strategies, including long-term power purchase agreements for renewable energy, which can reduce their reliance on any single fuel source. This dynamic fundamentally alters the buyer-seller relationship in the energy sector.
- Customer Diversification: Industrial and utility customers are actively seeking a broader energy portfolio, moving beyond fossil fuels.
- Renewable Energy Growth: Clean power is expected to constitute over 40% of global electricity generation in 2024, providing customers with alternatives.
- Negotiating Leverage: Increased availability of diverse energy options allows customers to demand better pricing and contract terms.
- Strategic Procurement: Customers can leverage alternative procurement strategies, such as renewable PPAs, to enhance their bargaining position.
Customer Base in Real Estate and Power
In Hunt Consolidated's real estate operations, the bargaining power of customers is generally moderate, leaning higher for large, significant tenants or institutional buyers who can negotiate terms for substantial office or retail spaces. For instance, securing anchor tenants for major developments often involves considerable negotiation.
Within the power sector, particularly in regulated utility markets, individual customers have limited bargaining power due to the essential nature of electricity and regulatory frameworks. However, large industrial consumers or entities with significant power purchase agreements might possess some leverage, though this is often constrained by the non-discretionary demand for electricity.
The burgeoning demand for electricity, fueled by trends like electrification of transportation, the immense power needs of AI data centers, and industrial reshoring initiatives, is a critical factor. This surge in demand, projected to continue significantly through 2024 and beyond, inherently strengthens the position of power generators by reducing the relative impact of any single customer's bargaining power.
- Real Estate: Bargaining power is higher for large tenants and institutional buyers in major projects.
- Power Sector (Regulated): Individual customer power is low due to essential service and regulation.
- Power Sector (Industrial): Large industrial users may have some negotiation ability, but it's limited by demand.
- Demand Surge Impact: Rising electricity demand from AI, electrification, and reshoring is reducing customer leverage in power generation.
Hunt Oil faces substantial customer bargaining power due to the commodity nature of oil and gas, where price is the primary differentiator and switching costs are low for buyers like refiners and utilities. This leverage is amplified by global market conditions favoring buyers, as seen in 2024 with ample supply forecasts. Large, concentrated buyers, such as major energy conglomerates, can exert significant pressure on pricing due to their high-volume purchases, making competitive pricing crucial for Hunt Oil.
The growing demand for diverse energy sources further empowers customers, as they increasingly seek alternatives to fossil fuels. With clean power projected to exceed 40% of the global electricity mix in 2024, customers have more options and can negotiate better terms, often through strategies like renewable power purchase agreements. This shift fundamentally alters the buyer-seller dynamic, reducing reliance on any single fuel supplier.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context (as of mid-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Nature of Oil/Gas | High | Products viewed as undifferentiated, price is key. |
| Buyer Concentration | High (for large buyers) | Large refiners/utilities have significant purchasing volume. |
| Global Supply/Demand | Favorable to buyers | Ample supply forecasts strengthen buyer leverage. |
| Energy Diversification | Increasing | Clean power >40% of global electricity mix (2024 projection). |
| Customer Profitability | High | Input costs directly impact customer margins. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the energy sector. You are looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing actionable insights into the industry's structure and competitive dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) sector is intensely competitive, featuring a mix of supermajors, national oil companies, and a multitude of independent players like Hunt Oil. This fragmentation means Hunt Oil constantly contends with rivals of varying scales and resources, all vying for exploration rights and production dominance.
In 2023, the global oil and gas market saw significant activity, with companies investing heavily in E&P projects. For instance, total upstream capital expenditure was projected to reach approximately $560 billion, highlighting the substantial financial commitments required and the competitive pressure to secure profitable reserves.
This competitive landscape necessitates a strong focus on operational efficiency and cost management. Hunt Oil, like its peers, must leverage technological advancements and strategic partnerships to maintain a competitive edge in an industry where production costs can significantly impact profitability.
The oil and gas sector is known for its dramatic price swings, making competitive rivalry fierce. During periods of low prices, companies often engage in aggressive competition to secure market share and revenue, which can severely impact their bottom lines.
While 2024 saw a degree of stability in oil prices, forecasts for West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude to reach the high $60s by late 2025 indicate that price sensitivity will remain a significant factor influencing competitive dynamics.
The exploration and production (E&P) sector, where Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil operates, is characterized by significant upfront capital investments in exploration, drilling, and essential infrastructure. These substantial initial outlays translate directly into high fixed costs for companies.
These high fixed costs create considerable exit barriers. Companies find themselves compelled to continue production, even when market prices are low, simply to recoup their initial investments and cover ongoing operational expenses. This dynamic naturally intensifies competitive rivalry among players in the sector.
Looking ahead, the capital intensity of upstream operations is projected to increase. Industry estimates suggest a cumulative need of $4.3 trillion in capital expenditures between 2025 and 2030, underscoring the ongoing financial commitment required to maintain and expand operations within the E&P landscape.
Diversification Across Industries
Hunt Consolidated's strategic diversification into sectors like real estate and power significantly broadens its competitive rivalry landscape. In real estate, the company contends with a vast array of regional developers and institutional investors, a dynamic that intensified in 2024 with a notable flight to quality among tenants and investors, leading to varied performance across different property types and geographic locations.
The power generation sector presents another layer of intense competition. Hunt faces established traditional utility providers alongside a rapidly expanding field of renewable energy developers, particularly in solar and wind. This competition is driven by evolving energy policies and a growing demand for sustainable power sources, with significant investment flowing into renewables throughout 2024.
- Real Estate Competition: Hunt competes with numerous developers and investors in regional markets, facing varied performance based on geography and property type in 2024.
- Power Sector Rivalry: Competition in power includes traditional utilities and a growing number of renewable energy developers, with substantial investment in renewables continuing in 2024.
- Market Dynamics: The real estate market in 2024 saw a pronounced flight to quality, impacting rental rates and property valuations differently across sectors.
- Renewable Energy Growth: Significant capital continued to be deployed into renewable energy projects in 2024, increasing competitive pressures for power generation companies.
Geopolitical and Regulatory Landscape
Competitive rivalry within the oil and gas sector, including for Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil, is significantly influenced by the geopolitical and regulatory landscape. Shifting political climates and evolving regulations can create advantages or disadvantages for companies operating in different regions or focusing on specific energy sources. For instance, in 2024, many nations continued to implement or refine policies aimed at energy transition, impacting the operational costs and investment attractiveness of traditional oil and gas projects.
Hunt Oil, with its global footprint, must adeptly manage these varied and often unpredictable political and regulatory environments. This complexity presents a substantial strategic hurdle, as compliance requirements and market access can change rapidly. The ongoing energy transition, coupled with the imposition of tariffs on certain goods or services within the energy supply chain, further complicates the competitive dynamics, potentially altering cost structures and market competitiveness for all players.
Key factors shaping this competitive rivalry include:
- Geopolitical Stability: Regions with greater political stability generally offer more predictable operating conditions, while volatile areas introduce higher risks and potential disruptions to supply chains and operations.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Differing national and international regulations on emissions, exploration, production, and taxation directly impact profitability and strategic planning. For example, the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, which began its transitional phase in October 2023 and fully applies from 2026, affects the competitiveness of energy imports.
- Energy Transition Policies: Government incentives for renewable energy and mandates for reduced fossil fuel consumption alter investment flows and create new competitive pressures from alternative energy providers. By mid-2024, global investment in clean energy was projected to exceed $2 trillion annually, a significant shift from historical energy investments.
- Trade Policies and Tariffs: Tariffs on equipment, materials, or refined products can increase operational costs and influence where companies choose to invest or source their supplies, impacting Hunt Oil’s global competitiveness.
The competitive rivalry for Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil is multifaceted, extending beyond the oil and gas sector into real estate and power generation, each with unique competitive pressures. In 2024, the real estate market saw a significant flight to quality, impacting performance differently across property types and regions. Similarly, the power sector experienced intensified competition due to substantial investments in renewable energy, a trend that continued throughout the year.
The global oil and gas E&P sector remains intensely competitive, with Hunt Oil facing rivals of all sizes. Upstream capital expenditures were projected to reach approximately $560 billion in 2023, underscoring the high financial stakes. This necessitates a relentless focus on operational efficiency and cost management to maintain an edge, especially given the industry's susceptibility to price volatility.
High fixed costs and significant exit barriers in E&P compel companies to continue production even during price downturns, intensifying rivalry. Projections indicate cumulative capital expenditures between 2025 and 2030 could reach $4.3 trillion, highlighting the ongoing financial demands in this capital-intensive industry.
Geopolitical and regulatory shifts further shape competitive dynamics. In 2024, many nations advanced energy transition policies, impacting the cost and investment appeal of traditional oil and gas. Global investment in clean energy was projected to exceed $2 trillion annually by mid-2024, showcasing a significant shift in investment flows and creating new competitive pressures from alternative energy providers.
| Sector | Key Competitive Factors | 2023/2024 Data Points |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas E&P | Operational efficiency, cost management, price volatility, capital intensity | ~ $560 billion projected upstream capex (2023) |
| Real Estate | Regional market dynamics, flight to quality, property type performance | Varied performance across sectors and geographies in 2024 |
| Power Generation | Renewable energy investment, traditional utility competition, energy policies | Projected > $2 trillion annual clean energy investment (mid-2024) |
| Geopolitical/Regulatory | Energy transition policies, regulatory frameworks, trade policies | EU CBAM transitional phase began Oct 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for Hunt Oil's core fossil fuel business stems from the accelerating adoption of renewable energy technologies. Solar, wind, and advancements in battery storage are rapidly closing the cost gap with traditional energy sources.
These alternatives are further bolstered by supportive government policies and regulatory frameworks, especially within the electricity generation sector. By 2024, clean power sources accounted for over 40% of global electricity generation, with solar and wind leading the charge in new capacity additions.
The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the electrification of industrial operations present a significant long-term threat to Hunt Consolidated's core oil and gas business. As sectors traditionally reliant on fossil fuels transition to cleaner energy sources, demand for crude oil, especially for transportation fuels, faces potential stagnation or decline. For instance, by 2023, global EV sales surpassed 13 million units, a substantial increase from previous years, indicating a clear shift in consumer and industrial preferences.
Improvements in energy efficiency across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors are significantly reducing overall energy demand. This trend directly lessens the need for traditional fossil fuels, acting as a powerful substitute for new energy supply and impacting the long-term outlook for companies like Hunt Oil.
The acceleration of energy efficiency is particularly evident with record investments in clean energy technologies. For instance, global investment in the energy transition reached an estimated $1.1 trillion in 2023, a substantial portion of which directly supports efficiency measures and renewable alternatives to oil and gas.
Alternative Power Generation Technologies
Hunt Consolidated, particularly in its power generation operations, faces a growing threat from alternative energy sources. Technologies like small modular reactors (SMRs) and hydrogen fuel are gaining traction, offering lower carbon emissions compared to traditional natural gas. These emerging solutions are attracting significant investment and policy support, positioning them as viable long-term replacements for existing power generation methods.
The push for decarbonization is a major driver behind this substitution threat. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy has committed billions to advancing clean hydrogen production and advanced nuclear technologies. These investments signal a clear direction towards a lower-carbon energy future, directly impacting the long-term viability of natural gas-reliant power generation.
- Advanced Nuclear (SMRs): Offer potential for reliable, low-carbon baseload power, with projects progressing globally.
- Hydrogen Power: Emerging as a clean fuel for power generation, with significant government and private sector investment in infrastructure and technology development.
- Renewable Integration: Enhanced grid capabilities and energy storage solutions are making intermittent renewables more competitive, further pressuring traditional power sources.
Shift in Real Estate Preferences
The real estate sector is experiencing a significant shift, with a growing demand for modernized, energy-efficient, and amenity-rich buildings. This trend presents a threat of substitutes for older, less efficient properties. Hunt's real estate developments need to align with these evolving occupier demands to maintain their competitive edge.
Occupiers are increasingly prioritizing what's known as a 'flight to quality,' favoring newer office buildings equipped with desirable amenities over older, less appealing spaces. For instance, in 2024, the vacancy rate for prime office space in major global cities remained significantly lower than that of older, Class B or C properties, highlighting this preference.
- Flight to Quality: Occupiers are actively seeking upgraded, modern workspaces.
- Energy Efficiency: Buildings with strong sustainability credentials are more attractive.
- Amenity-Rich Environments: Features like fitness centers, collaborative spaces, and advanced technology are key differentiators.
- Market Data: In 2024, markets saw a clear divergence in performance between new, well-appointed properties and older, less desirable stock.
The threat of substitutes for Hunt Oil's core fossil fuel business is substantial, driven by the rapid advancement and adoption of renewable energy technologies like solar and wind power. These alternatives are becoming increasingly cost-competitive, further supported by favorable government policies. By 2024, clean energy sources represented over 40% of global electricity generation, with solar and wind leading new capacity additions, directly challenging fossil fuels.
The electrification of transportation through electric vehicles (EVs) and the broader trend towards industrial process electrification represent significant substitutes for traditional oil and gas demand. Global EV sales surpassed 13 million units by 2023, signaling a clear market shift away from internal combustion engines. This transition directly impacts the long-term demand for crude oil, especially for transportation fuels.
Improvements in energy efficiency across all sectors also act as a powerful substitute, reducing the overall need for new energy supply, including fossil fuels. Global investment in the energy transition reached an estimated $1.1 trillion in 2023, with a significant portion dedicated to efficiency measures. This trend directly lessens the demand for traditional energy sources, impacting Hunt Oil's market outlook.
| Substitute Technology | Key Trend | Impact on Hunt Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind) | Cost competitiveness, policy support, >40% global electricity generation by 2024 | Directly displaces demand for fossil fuels in power generation |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Rapid adoption, >13 million global sales by 2023 | Reduces demand for gasoline and diesel, impacting transportation fuel markets |
| Energy Efficiency | Record investments ($1.1 trillion in energy transition by 2023) | Lowers overall energy consumption, reducing the need for new fossil fuel supply |
Entrants Threaten
The exploration and production sector of oil and gas demands immense capital. This includes costs for land acquisition, seismic testing, drilling operations, and building necessary infrastructure. Such significant financial requirements create a formidable barrier, making it challenging for newcomers to enter the market and compete with established companies like Hunt Oil.
The sheer scale of investment needed deters many potential competitors. In 2024, upstream oil and gas investments are projected to exceed $600 billion, marking a decade high. This substantial financial commitment underscores the difficulty for new entrants to gain a foothold.
The oil and gas sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles, including intricate permitting procedures and rigorous environmental compliance mandates. These requirements necessitate considerable specialized knowledge and substantial financial investment, creating a significant barrier for any new companies looking to enter the market.
For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain permits for new oil and gas exploration projects could extend over 18 months, with compliance costs often representing 15-20% of initial capital expenditure. These stringent government regulations on exploration and production activities act as a notable market restraint for oilfield services, limiting the ease with which new competitors can establish themselves.
Established players like Hunt Oil benefit from deep-rooted access to critical resources and infrastructure. This includes decades of proprietary geological data, proven reserves, and extensive networks of pipelines and processing facilities. For instance, Hunt Oil’s significant involvement in LNG projects, a capital-intensive sector, underscores the advantage of existing, large-scale infrastructure that new entrants would find exceedingly difficult and costly to replicate.
Brand Reputation and Established Relationships
Hunt Consolidated's enduring brand reputation, built over 80 years of global operations, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. This long-standing presence has fostered deep-rooted relationships with key stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and government entities worldwide. These established networks and the trust they represent are difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate, significantly raising the cost and complexity of market entry.
The institutional knowledge accumulated by Hunt Consolidated is another critical factor. This expertise, honed through decades of navigating diverse energy and real estate markets, provides a competitive edge that new companies would struggle to match quickly. For instance, their extensive experience in securing permits and understanding regulatory landscapes in various international jurisdictions acts as a substantial deterrent.
- Established Trust: Hunt's 80+ year operational history has cultivated significant industry respect and trust.
- Global Networks: Deep relationships with suppliers, customers, and governments worldwide create high switching costs for partners.
- Regulatory Navigation: Decades of experience in diverse international markets provide invaluable expertise in securing permits and compliance.
- Brand Equity: Hunt's strong brand recognition in energy and real estate sectors translates into customer loyalty and preferred supplier status.
Technological Expertise and Talent Pool
The sophisticated technologies and specialized talent needed for modern oil and gas extraction, complex real estate development, and advanced power generation present significant barriers for new entrants. Companies like Hunt Consolidated have cultivated decades of accumulated expertise and a deep pool of specialized talent, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their operational efficiency and technical capabilities. For instance, the digitalization and automation transforming the drilling services market, as seen in the increasing adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance, demand highly specialized engineering and data science skills that are not easily acquired.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in matching the operational scale and technical proficiency of established players like Hunt. The capital investment required to acquire cutting-edge exploration and production technology, coupled with the need for highly skilled geoscientists and engineers, creates a substantial entry barrier. In 2024, the average cost for a new offshore oil platform can easily exceed $1 billion, and the specialized workforce to operate it is equally scarce and expensive.
- Technological Sophistication: Modern oil and gas operations rely on advanced seismic imaging, directional drilling, and reservoir simulation software, all requiring significant upfront investment and ongoing technical support.
- Talent Acquisition: The global shortage of experienced petroleum engineers and data scientists in the energy sector, a trend continuing into 2024, makes it challenging and costly for new companies to build a competitive workforce.
- Digitalization Demands: The oilfield services sector is increasingly driven by data analytics and automation, requiring new entrants to invest heavily in IT infrastructure and personnel with expertise in areas like IoT and machine learning.
The threat of new entrants for Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements and economies of scale. The upstream oil and gas sector alone saw global investment projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, a decade high, making it difficult for smaller players to match the financial muscle of established companies. Furthermore, the intricate regulatory landscape, with permit acquisition potentially taking over 18 months and compliance costs reaching 15-20% of initial expenditure in 2024, acts as a formidable barrier.
Existing infrastructure and deep-rooted relationships further deter new competition. Hunt Oil's extensive network of pipelines and processing facilities, exemplified by their substantial LNG project involvement, represents an asset that is prohibitively expensive for newcomers to replicate. Their 80-year operational history has also built an invaluable institutional knowledge and brand equity, fostering trust and loyalty that new entrants struggle to establish quickly.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | Immense investment for exploration, drilling, and infrastructure. | Upstream oil & gas investment projected > $600 billion. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex permitting and environmental compliance. | Permit acquisition can take > 18 months; compliance costs 15-20% of capex. |
| Infrastructure & Scale | Existing networks of pipelines, processing facilities, and proven reserves. | Hunt Oil's significant LNG project infrastructure. |
| Brand & Relationships | 80+ years of operational history, trust, and stakeholder networks. | Deep-rooted relationships with suppliers, customers, and governments. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hunt Consolidated/Hunt Oil Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including publicly available company filings (10-K, annual reports), industry-specific market research from firms like Wood Mackenzie and IHS Markit, and relevant government data from agencies such as the EIA and FERC.