Hornbeck Offshore Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hornbeck Offshore Services Bundle
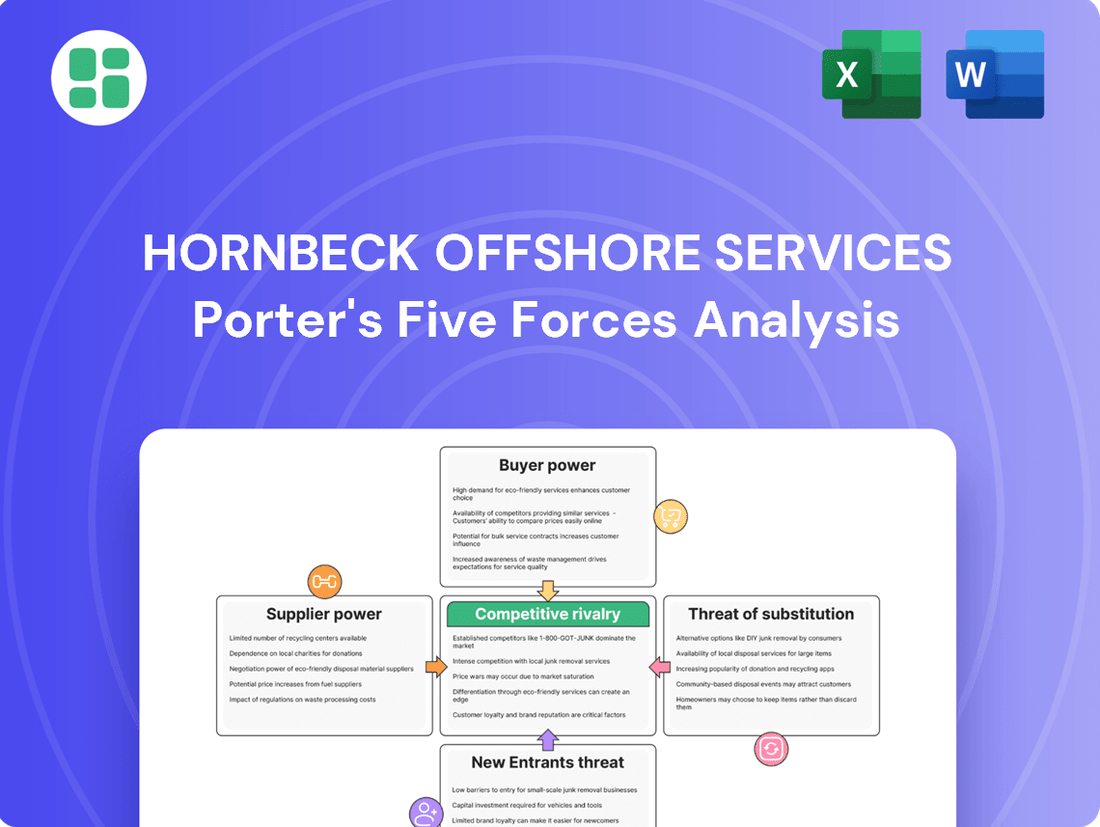
Hornbeck Offshore Services operates in a sector characterized by significant capital requirements, influencing the threat of new entrants. Buyer power can be substantial due to the specialized nature of their services and the concentration of major oil and gas clients. The intensity of rivalry among existing players is a key factor, impacting pricing and service offerings.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hornbeck Offshore Services’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of specialized marine equipment, like dynamic positioning systems and advanced subsea technologies, wield considerable influence. Hornbeck Offshore Services' dependence on these high-cost, niche components means fewer providers can dictate terms and pricing. For instance, the global market for advanced offshore crane systems, crucial for deepwater operations, is dominated by a handful of manufacturers, giving them substantial bargaining power.
The market for specialized offshore vessel construction and significant repair or retrofitting services is often concentrated, granting shipyards substantial leverage. This concentration means fewer options for companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services when seeking these critical capabilities.
Recent legal proceedings involving Hornbeck and Eastern Shipbuilding Group concerning the completion and conversion of MPSVs underscore the critical role and potential bargaining power of these specialized shipyards. These partnerships are essential for fleet modernization and expansion.
The scarcity of shipyards equipped to build or extensively modify complex offshore vessels, especially those meeting Jones Act requirements, can lead to inflated costs and extended project timelines. This limited supply chain directly impacts Hornbeck's operational efficiency and capital expenditure planning.
Fuel represents a significant expense for offshore vessel operators like Hornbeck Offshore Services, with global oil price shifts directly affecting their bottom line. For instance, in early 2024, crude oil prices, like West Texas Intermediate (WTI), experienced volatility, trading in a range that could significantly impact operational budgets.
While fuel is a standardized commodity, the specialized logistics required to deliver it to remote offshore locations, coupled with the substantial volumes Hornbeck requires, can grant fuel suppliers considerable leverage. This can be exacerbated in regions where only a limited number of providers can effectively serve the market.
Consequently, Hornbeck Offshore Services faces direct exposure to the inherent volatility of energy markets, a risk that suppliers can readily pass on through pricing adjustments, impacting the company's cost structure and profitability.
Highly Skilled Crew and Specialized Labor
The demand for experienced and highly trained offshore personnel, especially those proficient in operating advanced vessels and subsea equipment, can grant significant bargaining power to specialized crew agencies and individual mariners. A shortage of qualified personnel, particularly for complex deepwater and multi-purpose support vessels (MPSVs), can lead to higher labor costs and competition for talent.
This specialized labor is crucial for safety and operational efficiency in the offshore oil and gas sector. For instance, in 2024, the demand for certified welders and divers with experience in deepwater operations remained robust, with reports indicating a 15% increase in average daily rates for these specialized roles compared to 2023.
- High demand for specialized skills: Offshore operations increasingly rely on personnel with expertise in advanced vessel navigation, subsea technology, and safety protocols.
- Talent shortages: A persistent gap exists for qualified mariners, particularly those experienced with complex deepwater and multi-purpose support vessels (MPSVs).
- Impact on labor costs: Scarcity of skilled crew can drive up wages and benefits, increasing operational expenses for companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services.
- Operational necessity: The proficiency of the crew directly impacts the safety and efficiency of critical offshore activities, making them indispensable.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
Providers of regulatory and compliance services wield significant bargaining power over companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services. The offshore industry is heavily regulated, with stringent rules concerning maritime safety, environmental protection, and operational standards. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continually updates its safety and environmental regulations, requiring ongoing compliance efforts. In 2024, the focus on decarbonization and emissions reduction, driven by initiatives like the IMO's Greenhouse Gas Strategy, further increased the demand for specialized compliance expertise.
These specialized firms offer critical services such as certification, audits, and safety training, which are essential for Hornbeck to operate legally and safely. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and operational shutdowns. The cost of non-compliance is so high that it makes these service providers indispensable, granting them considerable leverage in negotiations. For example, a single environmental violation could lead to millions in fines and reputational damage, far exceeding the cost of proactive compliance services.
- Essential Expertise: Specialized firms possess knowledge of complex maritime, environmental, and safety regulations.
- High Cost of Non-Compliance: Penalties for failing to meet standards can be financially crippling for offshore operators.
- Indispensable Services: Certifications, audits, and training are critical for legal and safe operation.
- Market Leverage: The necessity of these services gives providers strong negotiating power.
Suppliers of highly specialized offshore equipment, such as advanced subsea technologies and dynamic positioning systems, hold significant bargaining power due to the limited number of manufacturers and the high cost of these niche components. For instance, the market for critical deepwater offshore crane systems is concentrated among a few key global players, allowing them to dictate terms.
The scarcity of shipyards capable of constructing or extensively modifying complex offshore vessels, particularly those adhering to Jones Act requirements, translates to inflated costs and longer project timelines for companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services. This limited supply chain directly impacts capital expenditure planning and operational efficiency.
The bargaining power of fuel suppliers is amplified by the specialized logistics required for delivery to remote offshore locations and the substantial volumes consumed by operators like Hornbeck. Fluctuations in global oil prices, such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI) in early 2024, directly impact operational budgets, and suppliers can pass these costs on.
A shortage of qualified and experienced offshore personnel, especially for complex deepwater and multi-purpose support vessels (MPSVs), grants specialized crew agencies and individual mariners considerable leverage. In 2024, demand for certified welders and divers with deepwater experience remained strong, with average daily rates for these roles reportedly increasing by 15% compared to 2023.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Hornbeck Offshore Services | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment Manufacturers | Limited number of suppliers for niche, high-cost components; high switching costs. | Dictated pricing, potential for extended lead times. | Concentrated market for advanced offshore crane systems. |
| Shipyards (Specialized Construction/Repair) | Concentrated market; limited capacity for complex vessels; Jones Act compliance needs. | Inflated costs, longer project timelines for fleet upgrades. | Legal disputes highlight reliance on specific shipyards. |
| Fuel Suppliers | Specialized logistics for remote delivery; high volume demand; commodity price volatility. | Direct exposure to energy market price swings; increased operational costs. | WTI oil price volatility impacted budgets in early 2024. |
| Skilled Labor Providers/Mariners | Shortage of qualified personnel for advanced vessels; high demand for specific expertise. | Increased labor costs, competition for talent, potential operational delays. | 15% increase in average daily rates for certified deepwater welders/divers (vs. 2023). |
What is included in the product
This analysis details the competitive landscape for Hornbeck Offshore Services, examining the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Hornbeck Offshore's Porter's Five Forces, simplifying strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hornbeck Offshore Services' customers, primarily major oil and gas companies, wield substantial bargaining power. These giants, like ExxonMobil or Shell, often procure services in large volumes, giving them leverage to negotiate favorable pricing. For instance, in 2024, major oil producers continued to consolidate their supplier bases, seeking economies of scale and predictable cost structures, which directly impacts service providers like Hornbeck.
The sophisticated nature of these clients means they are well-informed about market rates and can easily switch between providers. Competitive bidding is a common practice, and their ability to award or withhold contracts based on price and performance puts significant pressure on margins for vessel operators. This dynamic is amplified by the project-based demand in the offshore sector, allowing customers to adjust their commitments as market conditions fluctuate.
The bargaining power of Hornbeck Offshore's customers is significantly influenced by the specifics of each project and the length of the contracts involved. For instance, in the spot market or for shorter-term projects, customers often hold more sway, especially if there's ample vessel availability.
Conversely, long-term contracts for highly specialized vessels or crucial offshore operations can shift the power dynamic, providing Hornbeck with greater stability and pricing control. This is particularly true when projects demand unique capabilities that few competitors can offer.
The inherent cyclicality of the offshore oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) sector also plays a critical role. During periods of high E&P activity, customer demand intensifies, potentially limiting their negotiating leverage. Conversely, downturns can empower customers, as they seek to reduce costs amidst lower activity levels. For example, in 2023, a significant portion of the offshore drilling market saw increased demand for specialized vessels, which could have strengthened Hornbeck's position on new, longer-term contracts.
Switching costs for customers in the offshore support vessel (OSV) market, particularly for Hornbeck Offshore Services, can be a significant factor in their bargaining power. While customers have choices among OSV providers, the cost and complexity of changing suppliers mid-project can be moderate.
For instance, once a vessel is deployed for a complex deepwater or subsea project, switching to another provider can lead to substantial delays and unexpected expenses. This disruption can erode the customer's leverage. In 2024, the oil and gas industry continued to emphasize project continuity, making mid-project OSV changes less desirable.
However, for new projects or less integrated operations, the barriers to switching are considerably lower. This allows customers greater flexibility and increases competition among OSV providers, thereby enhancing their bargaining power in initial contract negotiations.
Diversification of Hornbeck's Customer Base
Hornbeck Offshore Services' strategic move to diversify its customer base beyond traditional oil and gas operations significantly dilutes the bargaining power of its core clients. By actively pursuing opportunities in sectors like offshore wind and supporting military contracts, Hornbeck reduces its reliance on any single industry segment. This expansion is crucial for balancing the leverage that large oil and gas companies might otherwise exert.
This diversification strategy directly addresses the concentrated power of oil and gas customers. For instance, in 2024, the offshore wind sector saw substantial investment growth, with projects across the globe requiring specialized marine support vessels, a service Hornbeck is increasingly offering. This expansion into new markets means Hornbeck is less susceptible to price pressures from a limited pool of traditional clients.
- Reduced Dependence: By serving offshore wind developers and military entities, Hornbeck lessens its reliance on the oil and gas sector, a key factor in mitigating customer bargaining power.
- Market Expansion: Growth in the offshore wind market, with projected global investments in the tens of billions of dollars annually through 2025, provides alternative revenue streams and strengthens Hornbeck's market position.
- Balanced Power Dynamics: A broader customer portfolio allows Hornbeck to negotiate from a stronger position, as the loss of any single oil and gas client becomes less impactful on overall business operations.
Economic Sensitivity to Oil and Gas Prices
The bargaining power of customers for Hornbeck Offshore Services is significantly shaped by their economic sensitivity to oil and gas prices. When oil and gas prices are low, customers, often exploration and production companies, tend to scale back their investment in offshore projects. This reduction in activity directly impacts demand for Hornbeck's specialized vessels.
In 2024, for instance, fluctuations in crude oil prices, such as Brent crude averaging around $80 per barrel in the first half of the year, directly influenced the capital expenditure budgets of these E&P companies. Lower prices generally translate to reduced project commitments, thereby increasing the leverage of these customers.
- Reduced Demand: Lower commodity prices lead customers to decrease their offshore drilling and production activities, resulting in fewer vessel charter requirements.
- Oversupply of Vessels: When customer demand falls, Hornbeck's fleet can become underutilized, creating an oversupply of offshore support vessels in the market.
- Price Negotiation: An oversupplied market empowers customers to negotiate lower charter rates and more favorable contract terms, directly impacting Hornbeck's revenue and profitability.
- Shift to Lower-Cost Services: Customers may also seek out less specialized or lower-cost vessel options if their project economics are squeezed by low commodity prices.
Hornbeck Offshore Services' customers, primarily major oil and gas companies, possess significant bargaining power due to their large-scale operations and market influence. These clients, often global energy giants, can leverage their purchasing volume and industry knowledge to negotiate favorable terms. For example, in 2024, continued consolidation among oil and gas producers meant fewer, larger buyers, intensifying their ability to dictate pricing and contract conditions.
The sophisticated nature of these customers means they are well-informed about market rates and can readily switch between service providers if better terms are offered. This competitive bidding environment, coupled with the project-based demand in the offshore sector, allows clients to adjust their commitments based on market fluctuations, directly pressuring Hornbeck's margins.
The bargaining power of Hornbeck's customers is also tied to the cyclicality of the oil and gas industry. During periods of low oil prices, such as when Brent crude averaged around $80 per barrel in early 2024, exploration and production companies often reduce capital expenditures. This reduced activity leads to lower demand for offshore support vessels, empowering customers to negotiate lower charter rates and more favorable contract terms.
| Customer Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Volume of Procurement | High | Major oil companies charter multiple vessels for large-scale projects. |
| Market Information Access | High | Clients possess detailed knowledge of prevailing charter rates and competitor offerings. |
| Switching Costs (for new projects) | Low to Moderate | Easier to switch providers for new contracts; mid-project changes can be costly. |
| Sensitivity to Oil Prices | High | Reduced E&P spending when oil prices are low (e.g., Brent around $80/barrel in H1 2024) increases customer leverage. |
Same Document Delivered
Hornbeck Offshore Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Hornbeck Offshore Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the offshore support vessel industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, featuring a thorough breakdown of each force and its implications for Hornbeck Offshore. You can be confident that the insights and formatting presented in this preview are identical to the final, ready-to-use document you'll download.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The offshore support vessel market, especially in regions like the U.S. Gulf of Mexico and Latin America, features a dynamic competitive landscape. It's a mix of well-established, larger companies and numerous smaller, regional operators, all vying for contracts, which naturally fuels intense rivalry.
Across the broader offshore sector, there's a noticeable trend towards consolidation. We've seen significant merger and acquisition (M&A) activity, suggesting that companies are looking to gain scale and market share. This ongoing consolidation has the potential to significantly alter the competitive dynamics in the coming years.
Hornbeck Offshore Services itself has been an active participant in this environment. The company has made strategic acquisitions of vessels, a clear indicator of the competitive pressures. These moves highlight a strategy focused on building a larger, more modern fleet to better compete for business.
The offshore vessel industry, including companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services, is inherently capital-intensive. This means significant upfront investment in acquiring and maintaining a fleet of vessels, plus ongoing costs for crewing and operations. These high fixed costs create a powerful incentive for companies to keep their vessels busy, or highly utilized, to spread those costs and turn a profit.
For instance, the average cost to build a modern offshore support vessel can range from tens of millions to over a hundred million dollars, depending on its size and capabilities. This substantial investment means that even when demand is lower, these fixed costs continue to accrue, pressuring companies to secure contracts at almost any price to avoid substantial losses.
This drive for utilization often leads to intense rivalry. When there are more vessels available than needed for the work, companies often engage in aggressive bidding to win contracts. This can drive down day rates, making it harder for everyone to cover their costs and achieve healthy margins, especially during downturns in the oil and gas sector.
The offshore vessel market experiences significant swings, directly tied to global energy needs and oil and gas investment. When too many vessels are available or activity slows, competition heats up, pushing down daily charter rates as companies fight for limited work.
Conversely, when demand surges and vessel availability tightens, as anticipated for 2025 with increased offshore activity, day rates and company profits tend to rise. For instance, in early 2024, the offshore support vessel (OSV) market saw day rates for certain vessel classes, like Platform Supply Vessels (PSVs), climb by 15-20% compared to the previous year, reflecting a tightening supply-demand balance.
Differentiation and Specialization
Hornbeck Offshore Services (HOS) differentiates itself by focusing on technologically advanced, high-specification Offshore Support Vessels (OSVs) and Multi-Purpose Support Vessels (MPSVs). This specialization targets complex deepwater and subsea projects, allowing HOS to command premium rates and reduce direct price competition with operators of standard OSVs. For instance, HOS's fleet includes vessels designed for dynamic positioning and complex subsea construction, capabilities not found in all OSV offerings.
While HOS aims for differentiation, the broader OSV market still faces intense rivalry. Competitors like Tidewater and Edison Chouest Offshore also invest heavily in modernizing their fleets, acquiring new, technologically advanced vessels. This ongoing fleet renewal creates continuous pressure for HOS to innovate and maintain its competitive edge in specialized services. In 2024, the OSV market saw continued demand for high-specification vessels supporting offshore wind and deepwater oil and gas exploration, but also faced challenges from overcapacity in certain vessel classes.
- Fleet Specialization: HOS emphasizes its high-spec OSVs and MPSVs for deepwater and subsea projects.
- Differentiation Strategy: This focus aims to reduce direct price competition compared to standard OSV services.
- Competitive Landscape: Competitors are also modernizing fleets, intensifying the need for innovation.
- Market Dynamics: 2024 showed demand for specialized vessels but also highlighted overcapacity in some segments.
Regional Market Dynamics
Competitive rivalry for Hornbeck Offshore Services is significantly shaped by its regional market focus. The company's strong presence in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico and Latin America means its primary competitors are other offshore service providers with established operations in these particular basins. This localized competition intensifies rivalry, as companies vie for contracts and market share within these specific geographic areas.
The intensity of this rivalry is further influenced by several regional factors. For instance, the U.S. Gulf of Mexico operates under the Jones Act, a cabotage law that mandates the use of U.S.-built, U.S.-owned, and U.S.-crewed vessels for certain maritime activities. This regulation creates a distinct competitive landscape for U.S.-flagged vessels, impacting cost structures and market access for both domestic and international players. In 2024, the U.S. offshore oil and gas sector continued to see robust activity, particularly in the Gulf of Mexico, driving demand for offshore support vessels.
- Regional Focus: Hornbeck Offshore Services primarily competes in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico and Latin America, leading to concentrated rivalry with regional specialists.
- Jones Act Impact: In the U.S., the Jones Act influences competition by favoring U.S.-flagged vessels, affecting cost and market entry for all participants.
- Market Dynamics: Regional supply-demand balances for offshore services and the presence of major oil and gas operators directly shape the competitive intensity in these specific basins.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for Hornbeck Offshore Services, driven by a market characterized by numerous players and fluctuating demand tied to oil and gas activity. The high capital intensity of owning and operating vessels means companies are constantly pressured to maximize vessel utilization, often leading to aggressive bidding and downward pressure on day rates, particularly during market downturns.
Hornbeck Offshore Services strategically differentiates itself by focusing on high-specification vessels for complex deepwater and subsea projects, aiming to avoid direct price competition with operators of standard offshore support vessels. However, competitors are also investing in fleet modernization, necessitating continuous innovation from HOS to maintain its competitive edge.
The company's regional concentration in areas like the U.S. Gulf of Mexico intensifies rivalry, as it directly competes with other established regional operators. Regulations like the Jones Act in the U.S. further shape this landscape, impacting cost structures and market access for all participants, with robust activity in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico in 2024 driving demand for these specialized services.
The offshore vessel market experienced a tightening supply-demand balance in early 2024, with day rates for certain vessel classes, such as Platform Supply Vessels (PSVs), increasing by 15-20% year-over-year. This trend is expected to continue into 2025 as offshore activity ramps up, potentially improving profitability for well-positioned companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services.
| Metric | Hornbeck Offshore Services (HOS) | Key Competitors (Examples) | Market Trend (Early 2024) |
| Fleet Specialization | High-spec OSVs, MPSVs for deepwater/subsea | Tidewater, Edison Chouest Offshore (Fleet Modernization) | Demand for specialized vessels strong |
| Competitive Intensity | High, driven by regional focus (US GoM, LatAm) | Concentrated rivalry with regional specialists | Intensified by Jones Act in U.S. |
| Day Rate Trend | Aims for premium rates | Varies by vessel class and utilization | PSV rates up 15-20% YoY |
| Capital Intensity Impact | High fixed costs drive utilization focus | Significant investment in fleet renewal | Pressure to maintain high vessel utilization |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for offshore logistics, particularly for specialized services like transporting supplies and personnel to offshore oil and gas platforms and supporting subsea construction, is remarkably low. There simply aren't direct alternatives that can replicate the unique capabilities of offshore support vessels (OSVs) and multipurpose supply vessels (MPSVs) in such demanding environments.
The inherent nature of offshore operations, requiring robust marine transportation designed for harsh conditions and remote locations, makes direct substitution highly improbable for current needs. This fundamental requirement solidifies the demand for OSV and MPSV services, as alternative modes of transport cannot effectively or safely fulfill these critical roles.
While direct vessel substitution for Hornbeck Offshore Services is generally low, technological advancements in offshore operations pose an indirect threat by potentially reducing the demand for certain vessel services. Innovations like sophisticated subsea robotics (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are increasingly capable of performing tasks previously requiring extensive surface support or personnel transfers. Hornbeck's own provision of ROVs highlights their engagement with these technologies, suggesting an understanding of this evolving landscape.
A significant long-term threat to Hornbeck Offshore Services stems from a global pivot away from offshore oil and gas towards onshore unconventional sources and renewable energy. This transition could shrink the primary market for their offshore support vessels.
While Hornbeck is strategically expanding into the offshore wind sector, a swift global energy transition might still impact its core oil and gas business. However, current energy forecasts indicate robust demand for offshore oil and gas, suggesting the substitution effect is not an immediate crisis.
For instance, in 2024, the International Energy Agency projected that offshore wind capacity could more than double by 2030, highlighting the growing renewable energy landscape. Despite this, global oil demand was still anticipated to rise in 2024, reaching approximately 103.2 million barrels per day, demonstrating the continued relevance of offshore oil and gas operations.
Efficiency Improvements Reducing Vessel Needs
Improvements in drilling efficiency, platform self-sufficiency, or optimized logistics by oil and gas operators can reduce the need for offshore support vessels (OSVs). For instance, advancements in subsea technology might allow for fewer trips for equipment deployment and maintenance. This trend directly impacts demand for services like those provided by Hornbeck Offshore Services, pushing them to innovate.
While not a direct replacement for the vessel itself, increased operational efficiency by customers can lead to a lower overall demand for OSV services. This means fewer vessel days are required to achieve the same operational output. For example, if a client can complete a project with 10% fewer vessel days due to better planning, Hornbeck's revenue from that project would decrease.
This potential reduction in demand pressures companies like Hornbeck to offer more integrated and higher-value services. They might focus on specialized services, enhanced data analytics during transit, or more comprehensive onboard support to differentiate themselves and maintain profitability. In 2024, the industry saw a continued focus on cost optimization by operators, making efficiency gains a priority.
- Reduced Vessel Utilization: Enhanced drilling techniques and platform autonomy can decrease the number of OSV trips needed for operations.
- Lowered Demand for Services: Greater customer operational efficiency directly translates to less overall demand for charter days.
- Strategic Shift: Hornbeck must adapt by providing value-added services beyond basic vessel transport to counter this threat.
Alternative Methods for Data Acquisition/Inspection
While Hornbeck Offshore Services' Marine Production Support Vessels (MPSVs) are essential for intricate subsea work, the threat of substitutes is emerging. For routine data acquisition and initial inspections, advancements in drone technology, both aerial and underwater, present a viable alternative. These unmanned systems can capture crucial visual and sensor data, potentially reducing the reliance on larger, more costly vessels for less complex tasks.
Satellite monitoring also offers a substitute for certain observational needs. For example, tracking vessel movements or monitoring surface conditions can be achieved through satellite imagery, lessening the demand for dedicated offshore support for these specific functions. This shift could impact the utilization rates of MPSVs for preliminary surveys or continuous monitoring operations.
However, it's important to note that these substitutes are not a complete replacement. For complex subsea construction, intervention, and maintenance requiring direct manipulation or heavy lifting, specialized marine support vessels like Hornbeck's MPSVs remain indispensable. The effectiveness of drones and satellites is largely confined to data gathering and preliminary assessments, not the intricate physical interventions that define a significant portion of the offshore support market.
Consider these points regarding substitutes:
- Drone Technology: Aerial and underwater drones can perform visual inspections and basic data collection, offering a cost-effective alternative for routine tasks.
- Satellite Monitoring: Satellites can provide surface-level data, vessel tracking, and environmental monitoring, substituting for some vessel-based observation needs.
- Limited Scope of Substitutes: These alternatives are primarily for data acquisition and preliminary inspection, not for complex subsea construction or intervention work.
- Continued Demand for Specialized Vessels: The need for MPSVs for critical subsea operations remains strong, as drones and satellites cannot replicate the capabilities of specialized marine support.
The threat of substitutes for Hornbeck Offshore Services' core offerings is generally low, as specialized offshore vessels like OSVs and MPSVs are crucial for operations in harsh environments. However, technological advancements are introducing indirect substitutes for certain tasks. For instance, drones and satellite monitoring can replace some observational and data-gathering functions, potentially reducing the need for vessel days in preliminary surveys or routine inspections.
These substitutes are not a direct replacement for complex subsea construction or intervention work, where Hornbeck's specialized vessels remain indispensable. The global energy transition also presents a long-term substitution threat as the market shifts away from offshore oil and gas. Despite this, current demand for offshore oil and gas, projected to rise in 2024, indicates that the substitution effect is not an immediate crisis for Hornbeck's primary business.
| Substitute Technology | Application in Offshore Sector | Impact on Hornbeck Offshore Services |
|---|---|---|
| Drones (Aerial & Underwater) | Visual inspections, data acquisition, basic surveys | Reduces demand for OSVs/MPSVs on less complex tasks |
| Satellite Monitoring | Surface condition tracking, vessel movement monitoring | Decreases need for vessel-based observation for certain functions |
| Renewable Energy Transition | Shift from fossil fuels to wind, solar, etc. | Shrinks the core oil and gas market, impacting demand for traditional offshore support |
Entrants Threaten
The offshore support vessel industry demands immense capital for fleet acquisition, construction, and upkeep. For instance, a single, advanced offshore vessel can cost tens of millions of dollars, creating a substantial financial hurdle for newcomers aiming to compete with established players like Hornbeck Offshore Services.
Operating sophisticated offshore supply and multi-purpose support vessels, particularly in challenging deepwater and complex subsea settings, requires a significant depth of specialized technical knowledge, highly skilled and experienced crews, and substantial operational infrastructure. Newcomers face a steep climb in acquiring this intricate expertise and establishing a track record for safety and dependability, a process that demands considerable time and financial investment.
The offshore services sector is deeply entrenched in a web of stringent regulations. For instance, the Jones Act in the U.S. mandates that vessels operating between U.S. ports must be built, flagged, owned, and crewed by Americans. This alone presents a substantial barrier for foreign or new domestic entrants lacking the requisite capital and infrastructure.
Navigating these complex maritime laws, environmental protection standards, and safety certifications demands significant upfront investment and ongoing operational expenses. Newcomers must secure numerous licenses and approvals, a process that can be both time-consuming and costly, effectively deterring many potential competitors from entering the market.
The financial burden of maintaining compliance is a perpetual challenge. Companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services must continuously invest in adhering to evolving safety protocols and environmental mandates, a cost that new entrants must also be prepared to absorb from day one, adding to the threat's potency.
Established Customer Relationships and Contracts
Hornbeck Offshore Services (HOS) benefits significantly from deeply entrenched relationships with major oil and gas corporations and government agencies. These aren't casual connections; they are often built over years through consistent performance and trust, making it difficult for new players to penetrate these vital client networks, particularly for large-scale, critical projects. For instance, HOS has historically secured significant contracts with companies like Shell and ExxonMobil, underscoring the value of these established partnerships.
The challenge for new entrants is amplified by the existing contractual landscape and the industry's inherent preference for operators with a proven track record of reliability and safety. Securing these initial, often long-term, contracts is a substantial hurdle, as clients typically prioritize established providers for their offshore support needs. This preference, coupled with the capital-intensive nature of the offshore vessel market, creates a robust barrier to entry.
- Long-Term Contracts: HOS's existing contracts provide a stable revenue stream and a competitive advantage, making it harder for new entrants to secure immediate business.
- Customer Loyalty: Established relationships foster customer loyalty, as clients often prefer to work with known and trusted service providers.
- High Switching Costs: For clients, switching from a proven provider like HOS to a new entrant can involve significant costs related to vetting, onboarding, and potential project disruptions.
Industry Oversupply and Cyclicality
The historical cyclicality of the offshore vessel market, often characterized by periods of oversupply, naturally discourages new entrants. Significant capital investment in new vessels during an upswing carries the substantial risk of encountering an immediate market downturn and heightened competition, making such ventures precarious.
While the offshore vessel market might appear to have tight supply in 2024-2025, the extremely long investment horizon required for new vessel construction means that any new entrant must contend with inherent market volatility over many years. This extended commitment amplifies the risk associated with anticipating future demand and pricing.
- Historical Oversupply: The offshore vessel industry has a well-documented history of boom and bust cycles, where periods of high demand and new vessel construction are often followed by oversupply and depressed rates.
- Capital Intensity: Building offshore vessels requires immense capital, often hundreds of millions of dollars per vessel, making it a significant barrier to entry for companies without substantial financial backing.
- Market Volatility: The offshore oil and gas sector, a primary driver of demand for these vessels, is subject to fluctuating commodity prices and geopolitical events, creating an unpredictable operating environment.
- Long Lead Times: The construction of specialized offshore vessels can take several years, meaning that orders placed during a perceived market upturn may arrive when the market has already softened, exacerbating the impact of oversupply.
The threat of new entrants in the offshore support vessel industry, impacting companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements for fleet acquisition and construction. For instance, building a single, modern offshore vessel can easily cost upwards of $50 million, a substantial financial barrier that deters many potential competitors. This high cost of entry, coupled with the need for specialized technical expertise and navigating stringent regulations like the Jones Act, creates a formidable challenge for newcomers aiming to compete in this capital-intensive sector.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of acquiring and constructing specialized offshore vessels. | Significant financial hurdle, requiring substantial upfront investment. |
| Technical Expertise & Experience | Need for specialized knowledge in operating complex vessels and deepwater operations. | Steep learning curve and time investment to build a track record. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to maritime laws, safety certifications, and environmental standards. | Complex and costly process requiring numerous licenses and approvals. |
| Established Relationships | Deeply entrenched ties with major oil and gas companies and government agencies. | Difficulty in penetrating client networks and securing initial contracts. |
| Market Cyclicality & Volatility | History of boom-and-bust cycles and unpredictable demand. | Increased risk for new entrants investing heavily during perceived market upturns. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hornbeck Offshore Services is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including their SEC filings, investor presentations, and annual reports. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry analysis firms and market research databases to provide a robust understanding of the offshore oil and gas services sector.