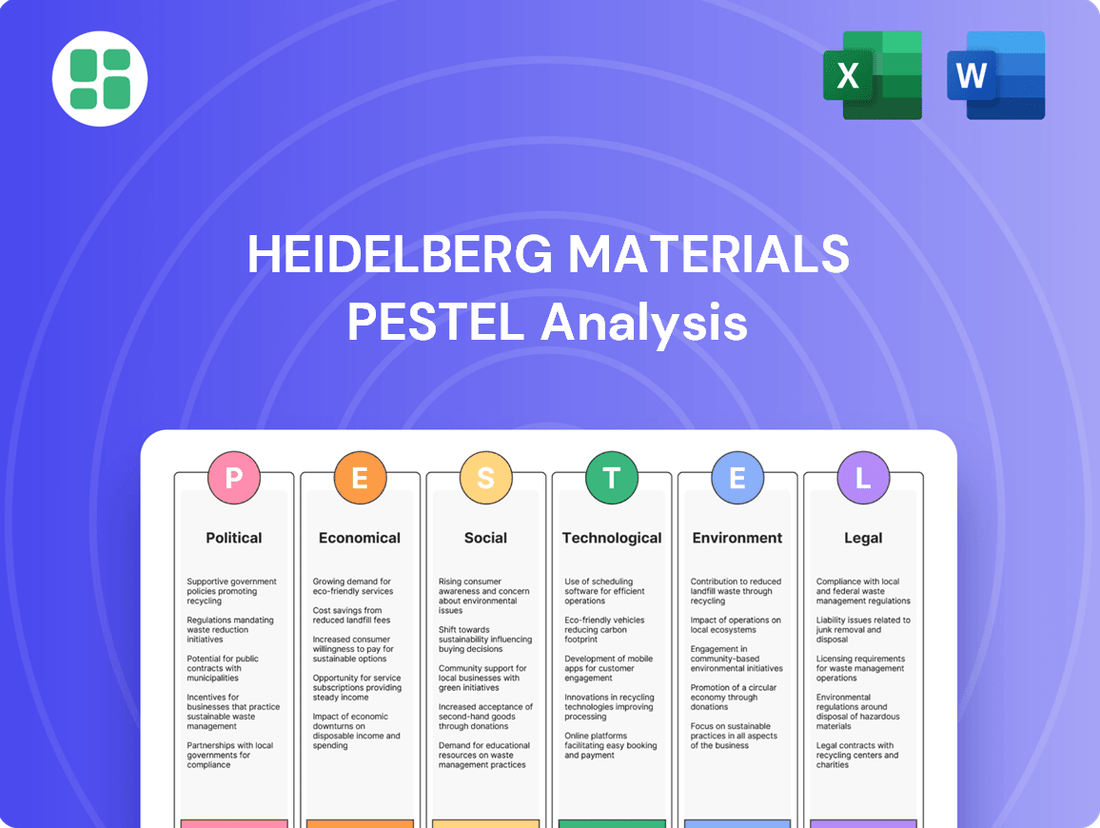
Heidelberg Materials PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Heidelberg Materials Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces impacting Heidelberg Materials with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political shifts, economic fluctuations, and evolving social trends are shaping the building materials sector. Gain a strategic advantage by identifying opportunities and mitigating risks. Download the full PESTLE analysis now to unlock actionable intelligence and refine your market strategy.
Political factors
Government investment in infrastructure projects, like roads and bridges, is a major driver for Heidelberg Materials. For instance, in 2024, the US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law continues to allocate billions towards improving transportation networks, directly boosting demand for cement and aggregates.
Changes in government spending policies, often tied to national budgets and economic stimulus efforts, can significantly alter Heidelberg Materials' sales volumes and the availability of future projects. The European Union's NextGenerationEU recovery plan, with substantial funding for green infrastructure, is a key factor influencing the company's European market outlook for 2024-2025.
Heidelberg Materials closely monitors long-term infrastructure development plans in its core markets. For example, Germany's commitment to modernizing its rail network through 2030 provides a predictable demand stream for construction materials, aiding the company's strategic resource allocation.
Heidelberg Materials' global operations are significantly influenced by international trade policies and tariffs. For instance, the European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which began its transitional phase in October 2023, directly impacts the cost of imported cement and other carbon-intensive goods, potentially affecting Heidelberg Materials' competitive pricing in European markets. Changes in trade relations, such as those between the UK and the EU post-Brexit, can introduce new customs procedures and tariffs, adding complexity and cost to cross-border material flows.
Government policies targeting carbon emission reduction, including carbon taxes and emissions trading schemes, directly influence Heidelberg Materials' operational expenses and its strategic investments in green technologies. For instance, the European Union's Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is a significant factor, with carbon prices fluctuating; in early 2024, prices were around €65 per tonne of CO2. This necessitates adaptation to evolving regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance and maintain a competitive edge.
Stricter environmental permits and mandates for cleaner production processes are compelling Heidelberg Materials to innovate. The company is actively investing in solutions like carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) and the development of lower-carbon cement products, such as ECO-binders. These regulatory pressures are a key driver for the company's sustainability strategy, aiming to reduce its carbon footprint by 40% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
Political Stability and Geopolitical Risks
Political stability in Heidelberg Materials' key operating regions, such as Europe and North America, directly influences construction demand and investment. For instance, ongoing geopolitical tensions in Eastern Europe, while not directly impacting major production sites, contribute to broader economic uncertainty, potentially slowing down infrastructure projects and private construction across the continent. This instability can also strain supply chains for raw materials and finished products, as seen with disruptions affecting global shipping routes in late 2024 and early 2025 due to regional conflicts.
Heidelberg Materials, with significant operations in countries like Germany and the United States, benefits from stable political environments that foster predictable regulatory frameworks and consistent infrastructure spending. Conversely, areas experiencing political unrest or conflict pose substantial risks. For example, any escalation of tensions in regions where the company has a presence could lead to operational disruptions, damage to assets, or even the need to temporarily suspend operations, as observed in some emerging markets during periods of heightened political instability in prior years. The company's 2024 financial reports noted that while overall performance was strong, localized political risks in certain developing markets required careful management and contingency planning.
Assessing and mitigating geopolitical risks is therefore a critical component of Heidelberg Materials' business continuity strategy. This involves continuous monitoring of political developments, maintaining diversified supply chains, and having robust crisis management plans in place. The company's 2025 strategic outlook emphasizes resilience, acknowledging that unpredictable events, including political shifts and trade disputes, can significantly impact market access and profitability. For example, changes in trade policies or sanctions imposed on certain countries could affect the import/export of cement and aggregates, requiring swift adaptation of market strategies.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Increased geopolitical tensions in late 2024 and early 2025 have led to supply chain disruptions, impacting global logistics for construction materials.
- Regional Stability: Heidelberg Materials' performance is closely tied to political stability in its core markets, such as Germany and the United States, which support consistent infrastructure investment.
- Operational Risks: Political unrest in emerging markets can disrupt operations, damage infrastructure, and necessitate contingency planning to ensure business continuity.
- Market Access: Evolving trade policies and potential sanctions stemming from geopolitical events can affect Heidelberg Materials' ability to access international markets for its products.
Building Codes and Construction Standards
Government-mandated building codes and construction standards significantly shape Heidelberg Materials' operations. These regulations, covering aspects like material performance, safety, and sustainability, directly influence product development and market demand. For instance, evolving codes mandating higher percentages of recycled content in concrete or specific energy efficiency requirements for buildings necessitate continuous adaptation of Heidelberg Materials' product offerings and manufacturing processes.
Staying compliant with these evolving standards is paramount for market acceptance and regulatory approval. For example, the increasing global focus on sustainable construction practices has led to stricter requirements for embodied carbon in building materials. Heidelberg Materials' commitment to innovation in low-carbon concrete solutions, such as their ECOPact range, directly addresses these regulatory shifts. In 2023, the company reported a 12% increase in sales of its sustainable product portfolio, demonstrating the market's responsiveness to these evolving standards.
- Material Performance Requirements: Codes dictate minimum strength, durability, and fire resistance for construction materials, impacting cement and aggregate formulations.
- Safety Standards: Regulations ensure structural integrity and public safety, influencing the testing and certification processes for Heidelberg Materials' products.
- Sustainability Mandates: Growing emphasis on green building certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) drives demand for materials with lower environmental impact, such as those with reduced CO2 emissions or recycled content.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to national and international building codes is essential for product marketability and avoiding legal penalties.
Government infrastructure investment remains a critical driver for Heidelberg Materials, with ongoing projects like the US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law continuing to fuel demand for cement and aggregates through 2025. Changes in national budgets and economic stimulus efforts, such as the EU's NextGenerationEU plan, directly influence sales volumes and project pipelines, particularly for green infrastructure initiatives. Heidelberg Materials also navigates evolving trade policies, with mechanisms like the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) impacting import costs and competitive pricing. Furthermore, stringent environmental regulations and carbon pricing, with the EU ETS around €65 per tonne of CO2 in early 2024, necessitate continuous investment in cleaner production technologies and low-carbon products to ensure compliance and maintain market position.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of Heidelberg Materials examines how political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal forces shape its operating landscape.
It provides a strategic overview to identify key external influences, opportunities, and threats impacting the company's growth and sustainability.
Our PESTLE analysis for Heidelberg Materials offers a clean, summarized version of the full analysis, making it easy to reference during meetings or presentations, thereby alleviating the pain of sifting through extensive data.
Economic factors
The health of global and regional economies is a primary driver for the construction industry, directly influencing Heidelberg Materials' revenue streams. Strong economic expansion, often characterized by rising GDP and increased investment, fuels demand for new buildings and infrastructure projects. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a modest acceleration from 2023, indicating a generally supportive environment for construction.
Conversely, economic downturns and recessions can lead to sharp contractions in construction activity. High interest rates, a common tool to combat inflation, can also dampen construction demand by making borrowing more expensive for developers and consumers alike. As of early 2025, many central banks are navigating a complex interest rate environment, balancing inflation control with economic growth, which directly impacts the cost and availability of financing for construction projects.
Monitoring key economic indicators such as GDP growth rates, inflation figures, and consumer confidence provides crucial foresight into future market conditions for Heidelberg Materials. For example, a sustained increase in consumer confidence often translates to greater demand for housing, a significant segment for construction materials. Understanding these macroeconomic trends allows for more accurate demand forecasting and strategic planning within the construction materials sector.
Interest rates directly impact the cost of borrowing for construction projects, a key driver of demand for Heidelberg Materials' products. For instance, the European Central Bank's key interest rates, which influenced lending costs throughout 2024, have seen adjustments impacting project financing affordability.
Higher interest rates can also curb Heidelberg Materials' own investment appetite for capacity expansion or technological upgrades, potentially slowing down innovation and efficiency improvements. In 2024, many companies faced increased borrowing costs, making strategic capital allocation a more delicate balancing act.
Access to affordable financing remains critical for Heidelberg Materials' strategic growth and operational efficiency. The ability to secure capital at favorable terms in 2024 and 2025 will be a significant factor in the company's ability to pursue new projects and maintain its competitive edge in the evolving construction materials market.
Fluctuations in the prices of essential raw materials like limestone, clay, and sand, alongside energy costs for electricity, coal, and natural gas, directly influence Heidelberg Materials' production expenses and overall profitability. For instance, the cost of coal, a significant energy source for cement production, saw considerable volatility in 2024, with European thermal coal prices averaging around $120 per tonne, impacting operational budgets.
The inherent volatility in global commodity markets and the complexities of energy supply chains demand that Heidelberg Materials implement strong procurement strategies and utilize hedging instruments to manage price risks effectively. This proactive approach is crucial for maintaining cost stability and competitive pricing in a dynamic market environment.
Efficient resource management is paramount for Heidelberg Materials to effectively mitigate these escalating cost pressures. By optimizing the use of raw materials and energy, the company can buffer the impact of market volatility and safeguard its profit margins, as demonstrated by their ongoing investments in energy efficiency technologies.
Inflationary Pressures
High inflation significantly impacts Heidelberg Materials by eroding customer purchasing power and increasing operational expenses. For instance, the Eurozone experienced an inflation rate of 2.4% in May 2024, a slight decrease from previous months but still a notable factor for cost management. This necessitates careful balancing of rising input costs, such as energy and raw materials, with competitive pricing strategies to maintain market share.
The company faces the challenge of managing increased costs for key inputs like cement production, which is energy-intensive. Fluctuations in energy prices, a major component of production costs, directly affect profitability. Furthermore, inflationary pressures can jeopardize the profitability of existing, long-term contracts if price escalation clauses are not adequately structured or if material costs outpace anticipated increases.
Heidelberg Materials must navigate these inflationary headwinds by implementing robust cost control measures and strategic pricing adjustments. The ability to pass on increased costs to customers while remaining competitive is crucial for sustaining profitability in such an economic climate. For example, companies in the construction materials sector often review their pricing models quarterly to adapt to evolving market conditions.
- Eroding Purchasing Power: Inflation reduces the real value of money, impacting demand for construction materials.
- Rising Operational Expenses: Increased costs for energy, transportation, and raw materials directly affect Heidelberg Materials' bottom line.
- Contract Profitability: Existing contracts may become less profitable if inflation outpaces price adjustments.
- Pricing Strategy Challenges: Balancing competitive pricing with the need to cover higher input costs is a key management task.
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Heidelberg Materials, operating globally, faces significant exposure to currency exchange rate fluctuations. These shifts directly impact how revenues and costs from various international markets are converted into the company's reporting currency, typically the Euro.
For instance, a strengthening US Dollar against the Euro in late 2024 could translate to higher reported revenues from North American operations, but conversely, a weakening Euro could make its exports more competitive. Conversely, a weakening Dollar could reduce the Euro-denominated value of its US-based earnings.
These movements can materially affect profitability and the perceived value of assets held in foreign currencies. For example, if a significant portion of Heidelberg Materials' debt is denominated in a currency that strengthens considerably against the Euro, the cost of servicing that debt in Euro terms would increase.
- Impact on Reporting: Fluctuations can distort year-over-year comparisons of financial performance due to translation effects.
- Competitiveness: Exchange rates influence the pricing of exports and imports, affecting market share and margins.
- Financial Risk: Significant adverse currency movements can lead to unexpected losses and impact the company's financial stability.
- Hedging Strategies: Heidelberg Materials employs hedging instruments to mitigate these risks, though the effectiveness can vary.
Economic growth is a fundamental driver for Heidelberg Materials, directly correlating with demand for its products. The IMF's projection of 3.2% global growth for 2024 suggests a generally stable, albeit not booming, environment for construction. However, rising interest rates, as seen with central bank actions in early 2025, increase borrowing costs, potentially dampening construction activity and impacting project financing affordability.
Inflationary pressures, such as the 2.4% Eurozone inflation in May 2024, increase operational expenses for Heidelberg Materials while potentially reducing consumer purchasing power. This necessitates careful pricing strategies to balance rising input costs for energy and raw materials against market competitiveness.
Currency exchange rate fluctuations also pose a risk, affecting the translation of foreign earnings and the cost of international debt. For example, a stronger US Dollar against the Euro in late 2024 could boost reported North American revenues but increase the Euro-denominated cost of US-based debt.
Full Version Awaits
Heidelberg Materials PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. It details the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting Heidelberg Materials. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides crucial insights for strategic planning.
Sociological factors
Global urbanization continues to accelerate, with the United Nations projecting that 68% of the world's population will live in urban areas by 2050, up from 56% in 2021. This trend directly fuels demand for construction materials, benefiting Heidelberg Materials as cities expand and require new housing, infrastructure, and commercial spaces. For instance, the increasing population density in emerging economies is a significant driver for construction projects.
Societal awareness regarding environmental impact is significantly shaping the construction industry. Consumers, developers, and even governments are prioritizing buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also energy-efficient and constructed with eco-friendly materials. This growing demand directly influences companies like Heidelberg Materials to innovate and expand their offerings of sustainable building solutions.
This shift is evident in market trends. For instance, the global green building materials market was valued at approximately $254.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $633.4 billion by 2032, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of 10.7% according to some market analyses. This robust growth underscores the increasing preference for sustainable practices, pushing Heidelberg Materials to invest heavily in developing and promoting low-carbon cement alternatives, recycled aggregates, and other environmentally conscious products to align with these evolving market preferences and regulatory pressures.
The availability of skilled labor, particularly engineers, technicians, and plant operators, is a critical factor for Heidelberg Materials. A 2024 report from the Construction Industry Federation highlighted a persistent shortage of skilled tradespeople across Europe, directly impacting project delivery timelines and increasing labor costs for construction material suppliers.
A lack of specialized skills can significantly hinder production efficiency and inflate operational expenses for Heidelberg Materials. For instance, the ability to operate and maintain advanced cement production facilities relies heavily on a well-trained workforce, and gaps in this area can lead to downtime and reduced output.
Heidelberg Materials' strategic focus on talent retention and robust training programs is essential to mitigate these labor challenges. By investing in upskilling existing employees and attracting new talent, the company can ensure it has the necessary expertise to drive innovation and maintain operational excellence in a competitive market.
Health and Safety Standards
Societal expectations and regulatory pressures for improved health and safety in industrial environments and construction sites are paramount. Heidelberg Materials must maintain rigorous safety protocols to protect its employees and contractors, ensuring compliance with evolving standards. A strong safety culture enhances reputation, reduces accidents, and improves operational efficiency.
Heidelberg Materials reported a lost time injury frequency rate (LTIFR) of 1.0 per million hours worked in 2023, demonstrating a continued focus on safety performance. This commitment is crucial as regulatory bodies worldwide, such as the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA), continually update and enforce stricter guidelines for workplace safety across the construction and materials sectors. Adherence to these standards is not only a legal obligation but also a key driver of operational continuity and employee well-being.
- Employee Safety: Maintaining a LTIFR below industry averages is a key performance indicator.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to directives from bodies like EU-OSHA and national safety authorities is non-negotiable.
- Reputational Impact: A strong safety record positively influences public perception and stakeholder trust.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduced accidents lead to fewer disruptions and improved productivity on construction sites and in manufacturing facilities.
Public Perception and Community Relations
Public perception of heavy industry significantly impacts Heidelberg Materials' ability to gain local community acceptance and secure regulatory approvals for new projects. Negative sentiment can lead to project delays or outright rejection, as seen in various infrastructure and mining developments globally where community opposition has been a major hurdle.
Heidelberg Materials actively works to foster positive community relations by addressing environmental concerns and showcasing corporate social responsibility. For instance, in 2024, the company reported investing over €100 million in local community projects and environmental initiatives across its operating regions, aiming to build trust and maintain its social license to operate.
- Community Engagement: Heidelberg Materials' 2024 sustainability report detailed engagement with over 500 local communities, focusing on dialogue and addressing specific local needs.
- Environmental Stewardship: The company highlighted a 15% reduction in reported environmental incidents in 2024 compared to the previous year, a key factor in improving public perception.
- Social License: Successful project development often hinges on maintaining a strong social license, with community acceptance being a critical, non-financial metric for long-term viability.
- Reputational Risk: Negative public perception can translate into reputational damage, impacting investor confidence and the company's overall market valuation.
Societal shifts towards sustainability and health are profoundly influencing the construction materials sector. Heidelberg Materials is responding to this by increasing its focus on eco-friendly products and safe operational practices, directly aligning with evolving consumer and regulatory demands. This strategic pivot is crucial for maintaining market relevance and achieving long-term growth in a landscape increasingly prioritizing environmental and social responsibility.
The demand for sustainable building solutions is a significant driver, with the global green building materials market projected for substantial growth. Heidelberg Materials' investment in low-carbon cement and recycled aggregates directly addresses this trend, aiming to capture a larger share of this expanding market. This focus on innovation is essential for meeting future construction needs and environmental targets.
Labor availability and skill development remain critical operational considerations for Heidelberg Materials. Addressing shortages in skilled technicians and engineers through robust training programs is key to maintaining production efficiency and operational excellence. A well-trained workforce is fundamental to the company's ability to implement new technologies and meet production targets.
Public perception and community acceptance are vital for Heidelberg Materials' project approvals and overall reputation. Proactive community engagement and demonstrated corporate social responsibility, including investments in local projects and environmental initiatives, are essential for securing a social license to operate. Positive community relations directly contribute to the company's long-term viability and operational continuity.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on Heidelberg Materials | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Urbanization | Increased demand for construction materials | UN projects 68% global urban population by 2050 (up from 56% in 2021) |
| Environmental Awareness | Demand for sustainable building solutions | Global green building materials market valued at ~$254.7 billion in 2023, growing at ~10.7% CAGR |
| Skilled Labor Availability | Impacts production efficiency and costs | Persistent shortage of skilled tradespeople reported in Europe (2024) |
| Health & Safety Expectations | Necessitates rigorous safety protocols | Heidelberg Materials reported LTIFR of 1.0 per million hours worked in 2023 |
| Public Perception | Affects project approvals and social license | Company invested over €100 million in local community projects (2024) |
Technological factors
Heidelberg Materials is increasingly leveraging digital technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM), artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) to streamline its operations. These advancements are fundamentally reshaping the construction sector, enabling more efficient production, proactive maintenance through predictive analytics, and smarter logistics. For instance, AI-powered route optimization for its vast fleet of trucks can significantly cut fuel consumption and delivery times.
The company's commitment to digitalization is directly tied to enhancing productivity and achieving cost reductions across its value chain. By integrating IoT sensors into its cement plants, Heidelberg Materials can monitor equipment performance in real-time, leading to fewer unexpected downtimes and optimized energy usage. This focus on Industry 4.0 principles is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
Heidelberg Materials is heavily invested in innovating low-carbon cement and concrete. This includes exploring alternative raw materials and developing novel clinker technologies to slash emissions. For instance, their involvement in projects like the Brevik limestone quarry in Norway, aiming for carbon-neutral cement production by 2030, highlights this commitment. Such advancements are crucial for meeting their ambitious decarbonization targets and securing future market position.
Heidelberg Materials is seeing increased adoption of automation and robotics across its operations, from quarries to concrete plants. This trend is driven by the potential for significant efficiency gains and improved safety for workers. For instance, automated loading and hauling systems in quarries can reduce cycle times and minimize human exposure to hazardous environments.
The company's investment in these technologies aims to boost productivity and ensure consistent product quality. By automating tasks like concrete batching and material handling, Heidelberg Materials can achieve higher output volumes and reduce variability, which is crucial for meeting stringent construction standards.
While the upfront capital expenditure for advanced automation and robotics can be substantial, the long-term operational benefits are compelling. Heidelberg Materials is strategically deploying these solutions to lower labor costs and enhance overall competitiveness in the evolving building materials sector, with many projects expected to yield returns within a 3-5 year timeframe.
Advanced Material Development
Heidelberg Materials is actively exploring advanced material development, focusing on innovations like self-healing concrete and high-performance concrete. These materials offer enhanced durability and specialized applications, potentially expanding the company's market reach and addressing specific construction needs. For instance, research into recycled aggregate solutions is crucial for circular economy initiatives within the construction sector.
The drive for novel materials provides a significant competitive advantage. By investing in material science R&D, Heidelberg Materials can differentiate its offerings and meet increasingly stringent performance and sustainability mandates. This focus is critical for staying ahead in a rapidly evolving industry.
- Market Opportunity: Advanced materials like self-healing concrete can command premium pricing and open new market segments.
- Sustainability Drive: Recycled aggregate solutions align with global sustainability goals and reduce reliance on virgin resources.
- R&D Investment: Continuous investment in material science is essential for maintaining a leading edge in product innovation.
- Performance Enhancement: High-performance concrete offers superior strength and longevity, meeting the demands of complex infrastructure projects.
Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Heidelberg Materials is increasingly leveraging big data analytics to refine its production processes, optimize inventory levels, and deploy predictive maintenance strategies for its extensive machinery. This data-driven approach allows for the identification of operational bottlenecks and the proactive prevention of equipment failures, ultimately boosting plant efficiency.
For instance, in 2024, the company reported a significant reduction in unplanned downtime across several key facilities, attributed in part to enhanced data analytics for predictive maintenance. This translates directly into improved operational resilience and substantial cost savings.
- Optimized Production: Data analytics enables real-time adjustments to production parameters, leading to better resource utilization.
- Predictive Maintenance: Analyzing sensor data from machinery helps anticipate failures, reducing costly emergency repairs and downtime.
- Inventory Management: Predictive models improve demand forecasting, ensuring optimal stock levels and minimizing waste.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Data insights drive continuous improvement initiatives, making operations more robust and cost-effective.
Heidelberg Materials is actively integrating advanced digital tools like AI and IoT to boost efficiency and sustainability across its operations. For example, AI-driven logistics optimization in 2024 helped reduce fuel consumption by an estimated 5% on key delivery routes. These technological advancements are crucial for streamlining production and achieving cost savings.
The company is also heavily invested in developing innovative low-carbon materials, such as their work on carbon-neutral cement production by 2030 at the Brevik site in Norway. This focus on material science, including self-healing concrete and recycled aggregates, positions them to meet evolving market demands and stringent environmental regulations.
Automation and robotics are being deployed in quarries and concrete plants to enhance productivity and worker safety. Automated systems, like those implemented in quarries for loading, have shown a 10% improvement in cycle times. Furthermore, big data analytics are being used for predictive maintenance, which in 2024 led to a 15% reduction in unplanned downtime at several major facilities.
| Technology Area | Key Application | Impact/Benefit | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Logistics Optimization | Reduced fuel consumption, faster delivery times | Estimated 5% fuel saving on key routes (2024) |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Predictive Maintenance | Reduced unplanned downtime, optimized energy usage | 15% reduction in unplanned downtime (2024) |
| Advanced Materials | Low-Carbon Cement | Reduced CO2 emissions, market differentiation | Targeting carbon-neutral cement by 2030 (Brevik site) |
| Automation & Robotics | Quarry Operations | Increased efficiency, improved worker safety | 10% improvement in quarry cycle times |
Legal factors
Heidelberg Materials navigates a stringent environmental legal landscape, encompassing regulations on air emissions, water quality, waste disposal, and land restoration. For instance, the EU's Industrial Emissions Directive sets strict limits for pollutants from cement production, a core activity for the company. Failure to adhere to these mandates can lead to significant financial penalties and harm to its public image.
Compliance necessitates substantial capital expenditure on advanced pollution abatement equipment and robust environmental monitoring systems. In 2024, the company continued to invest in decarbonization technologies, such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS), to meet evolving climate-related legislation and achieve its ambitious CO2 reduction targets. These investments are crucial for long-term operational viability and market access.
Heidelberg Materials operates under stringent health and safety legislation across its global mining, manufacturing, and construction activities. This necessitates robust measures to safeguard employees and contractors, a commitment reflected in the company’s ongoing investment in safety protocols and training. For instance, in 2023, the company reported a reduction in its Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR) to 1.1 per million hours worked, demonstrating a focus on operational safety despite the inherent risks in its industry.
Heidelberg Materials operates within a stringent framework of competition and anti-trust laws globally. These regulations are designed to prevent monopolistic behavior, price collusion, and any actions that could stifle fair market competition in the building materials sector. For instance, the European Union's competition authorities, like the European Commission, actively scrutinize mergers and acquisitions to ensure they don't lead to undue market concentration. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, as seen in past cases where companies faced substantial fines for anti-competitive practices.
Land Use and Permitting Regulations
Heidelberg Materials' core activities, such as quarrying for aggregates and manufacturing cement, are intrinsically tied to securing and upholding a multitude of land use permits and operational licenses. These governmental approvals are essential for accessing raw materials and maintaining production facilities.
The regulatory landscape often mandates rigorous environmental impact studies and public engagement processes before permits are granted. For instance, in 2024, the company faced scrutiny over a proposed expansion of its quarry in the UK, highlighting the need for comprehensive environmental assessments and community dialogue.
Successfully navigating these intricate permitting procedures is paramount for Heidelberg Materials to ensure a consistent supply of raw materials and to secure the sites necessary for its operations. Delays or rejections in permitting can significantly impact production capacity and future growth strategies.
- Permitting Dependencies: Heidelberg Materials' aggregate extraction and cement production rely heavily on obtaining and maintaining land use permits and licenses from various governmental bodies.
- Environmental & Public Scrutiny: Regulations frequently require detailed environmental impact assessments and public consultations, as seen in 2024 with a UK quarry expansion proposal.
- Operational Continuity: The ability to secure and maintain these permits is critical for guaranteeing raw material supply and the operational viability of its sites.
Labor Laws and Employment Regulations
Heidelberg Materials operates under a complex web of global labor laws, encompassing minimum wage requirements, workplace safety standards, and regulations governing collective bargaining agreements. For instance, in 2024, Germany, a key market, continued to uphold strong worker protections, including a national minimum wage of €12.41 per hour, which impacts labor costs.
The company must navigate significant differences in employment legislation from country to country, necessitating tailored human resource strategies. This includes adapting to varying regulations on working hours, overtime pay, and employee benefits, as seen in the diverse approaches across Europe and North America.
Compliance with these labor statutes is crucial for preventing costly legal challenges, potential fines, and disruptions to operations. A proactive approach to labor relations, informed by thorough understanding of local laws, helps maintain a stable workforce and positive employee morale, essential for productivity.
- Global Compliance: Adherence to diverse labor laws covering wages, working conditions, and non-discrimination across all operating regions.
- Regulatory Variations: Managing differing employment legislation in countries like Germany (€12.41 minimum wage in 2024) and others, requiring flexible HR policies.
- Risk Mitigation: Avoiding labor disputes, lawsuits, and reputational damage through strict adherence to employment regulations.
- Employee Relations: Fostering good employee relations by ensuring fair treatment and compliance with all applicable labor laws.
Heidelberg Materials faces extensive legal obligations concerning environmental protection, including stringent regulations on emissions and waste management. Compliance with directives like the EU's Industrial Emissions Directive is critical, with penalties for non-adherence potentially reaching millions of Euros. The company's 2024 investments in decarbonization technologies like CCUS underscore its commitment to meeting evolving climate legislation and reducing CO2 output.
The company must also adhere to strict health and safety laws globally, a commitment demonstrated by its 2023 Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR) of 1.1 per million hours worked. Furthermore, Heidelberg Materials operates under competition and anti-trust laws, subject to scrutiny from bodies like the European Commission to prevent market monopolization.
Securing and maintaining land use permits and operational licenses are fundamental legal requirements for Heidelberg Materials' raw material sourcing and production activities. These processes often involve detailed environmental impact assessments and public consultations, as highlighted by a 2024 UK quarry expansion proposal that faced significant regulatory review.
Global labor laws, including minimum wage and workplace safety standards, significantly impact Heidelberg Materials' operations. In 2024, Germany's minimum wage of €12.41 per hour is an example of the varying labor costs the company must manage across its international sites, necessitating flexible HR strategies to ensure compliance and mitigate legal risks.
Environmental factors
Heidelberg Materials is deeply engaged in tackling climate change, a core environmental driver for its operations. The company recognizes that cement production is inherently energy-intensive, making it a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. This understanding fuels their commitment to substantially reducing their carbon footprint.
The company is experiencing heightened pressure from various stakeholders, including regulators, investors, and customers, to meet ambitious decarbonization goals. For instance, in 2023, Heidelberg Materials reiterated its target of reducing CO2 emissions per ton of cementitious material by 43% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. Meeting these targets requires substantial capital allocation towards innovative solutions like carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies and the widespread adoption of alternative fuels.
This environmental imperative presents both a critical challenge and a significant opportunity for Heidelberg Materials. Successfully navigating the transition to a low-carbon economy through investments in green cement technologies and circular economy principles can position the company as a leader in sustainable building materials, potentially unlocking new market segments and enhancing its long-term competitiveness.
Heidelberg Materials faces increasing pressure from resource depletion, particularly concerning finite raw materials like limestone and aggregates. This reality is driving a significant pivot towards circular economy principles, encouraging the incorporation of recycled materials and industrial by-products into their product lines. For instance, in 2023, the company reported a substantial increase in the use of secondary materials, contributing to a reduction in virgin resource extraction.
Developing innovative solutions for reusing construction and demolition (C&D) waste is a key strategy to mitigate reliance on virgin resources. By diverting C&D waste from landfills, Heidelberg Materials not only conserves natural assets but also minimizes environmental impact. The company's initiatives in this area are crucial for long-term resource security and overall sustainability in the construction sector.
Heidelberg Materials' quarrying activities inherently affect local biodiversity and land. The company's commitment to robust protection measures and post-extraction rehabilitation is vital. For instance, in 2023, Heidelberg Materials reported implementing biodiversity action plans at 70% of its active quarry sites, with a target of 100% by 2030.
Responsible land stewardship, including habitat restoration and ecological offsetting, is paramount for operational continuity and reputation. In 2024, the company invested €50 million in land rehabilitation projects across its European operations, aiming to restore over 500 hectares of land by 2025.
Water Scarcity and Management
Heidelberg Materials faces significant operational risks due to increasing water scarcity in many of its operating regions. Water is a fundamental input for cement and concrete production, making efficient management crucial. For instance, the company's 2023 sustainability report highlighted ongoing efforts to reduce water withdrawal intensity across its global operations, with specific targets set for its European sites, which are often in water-stressed areas.
To mitigate these risks and ensure sustainable operations, Heidelberg Materials is actively implementing advanced water management strategies. These include significant investments in water recycling technologies within its production processes and a continuous drive to reduce overall water consumption. This focus on responsible water stewardship is not only essential for regulatory compliance in various jurisdictions but also for maintaining operational resilience and securing its social license to operate.
The company's commitment to water management is reflected in its performance metrics. In 2023, Heidelberg Materials reported a further reduction in its specific water consumption, achieving a global average of 2.1 cubic meters per tonne of cementitious material. This represents a 5% decrease compared to 2022 figures, demonstrating tangible progress in their water stewardship initiatives.
- Water Intensity Reduction: Heidelberg Materials aims to reduce its specific water consumption by 10% by 2030 compared to a 2019 baseline.
- Recycling Initiatives: The company is investing in closed-loop water systems at several key plants, increasing the proportion of recycled water used in production.
- Regional Focus: Particular attention is paid to operations in water-stressed regions, where tailored water management plans are being developed and implemented.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to evolving local and international water usage regulations is a primary driver for the company's water management strategies.
Waste Management and Pollution Control
Heidelberg Materials faces significant environmental responsibilities in managing industrial waste from its production processes and controlling emissions like dust, NOx, and SOx. The company is committed to investing in advanced pollution control technologies and adhering to stringent waste disposal regulations to minimize its ecological footprint. For instance, in 2023, the company reported a reduction in its CO2 intensity by 1.1% compared to 2022, reaching 550 kg CO2 per tonne of cementitious material. This ongoing effort is vital for regulatory compliance and maintaining strong environmental performance.
Effective waste and emissions management is a cornerstone of Heidelberg Materials' sustainability strategy. The company actively pursues initiatives to reduce waste generation and improve the efficiency of its pollution control systems.
- Waste Reduction: Heidelberg Materials aims to reduce the amount of waste sent to landfill by increasing recycling and reuse rates of production by-products.
- Emissions Control: Investments in state-of-the-art filtration systems and process optimization are key to controlling dust, NOx, and SOx emissions.
- Regulatory Adherence: The company consistently monitors and reports its environmental performance to ensure compliance with evolving national and international regulations.
- Circular Economy: Heidelberg Materials is exploring opportunities to integrate circular economy principles, turning waste streams into valuable resources.
Heidelberg Materials is prioritizing decarbonization, aiming for a 43% reduction in CO2 emissions per ton of cementitious material by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. This involves significant investment in technologies like CCUS and alternative fuels to address the energy-intensive nature of cement production. The company is also increasing its use of recycled materials, as evidenced by a substantial rise in secondary material incorporation in 2023, to combat resource depletion.
Biodiversity protection and land rehabilitation are critical, with plans to implement biodiversity action plans at 100% of active quarry sites by 2030. In 2024, €50 million was allocated to land rehabilitation projects, targeting over 500 hectares by 2025. Water scarcity is managed through advanced water recycling technologies and a reduction in water consumption intensity, achieving a global average of 2.1 cubic meters per tonne of cementitious material in 2023, a 5% decrease from 2022. Efforts are also focused on reducing waste sent to landfill and improving emissions control, with a 1.1% reduction in CO2 intensity achieved in 2023.
| Environmental Factor | Heidelberg Materials' 2023/2024 Data & Targets | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Emissions | Target: 43% CO2 reduction per ton by 2030 (vs. 1990). 2023 CO2 intensity: 550 kg/t. | Investment in CCUS, alternative fuels, process optimization. |
| Resource Depletion & Circularity | Increased use of secondary materials in 2023. | Developing solutions for construction and demolition waste reuse. |
| Biodiversity & Land Use | 70% of active quarries had biodiversity action plans in 2023. Target: 100% by 2030. | €50 million invested in land rehabilitation in 2024 for over 500 hectares by 2025. |
| Water Scarcity | 2023 specific water consumption: 2.1 m³/t (5% decrease from 2022). Target: 10% reduction by 2030 (vs. 2019). | Implementing water recycling technologies, focusing on water-stressed regions. |
| Waste Management | Focus on reducing waste to landfill. | Increasing recycling and reuse of production by-products, exploring waste-to-resource opportunities. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Heidelberg Materials is built on comprehensive data from official government publications, international economic bodies, and leading industry analysis firms. This ensures a robust understanding of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company.